Simulation of the thermal effect on high power Bi target for the large-scale 211At production
-
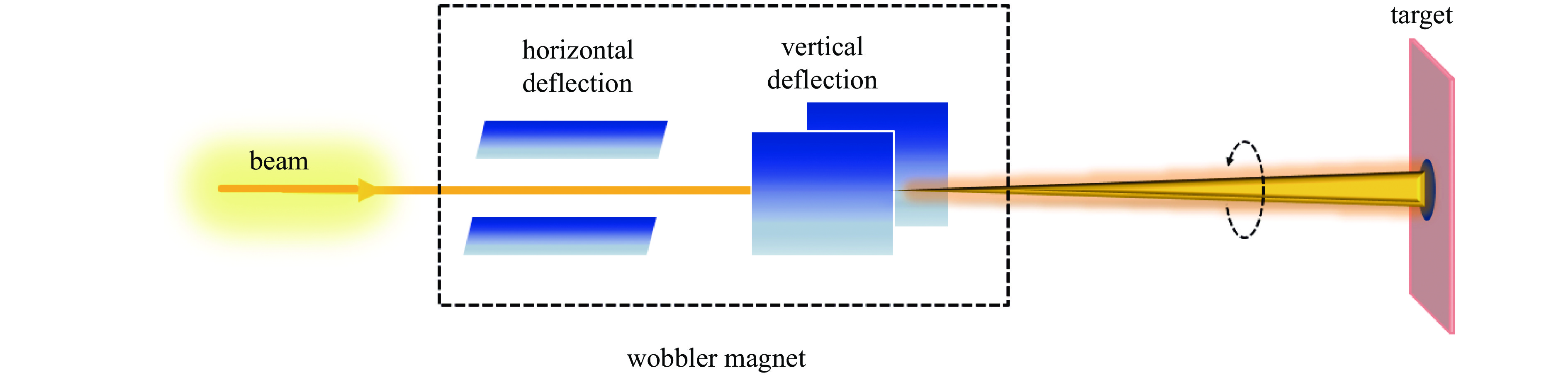
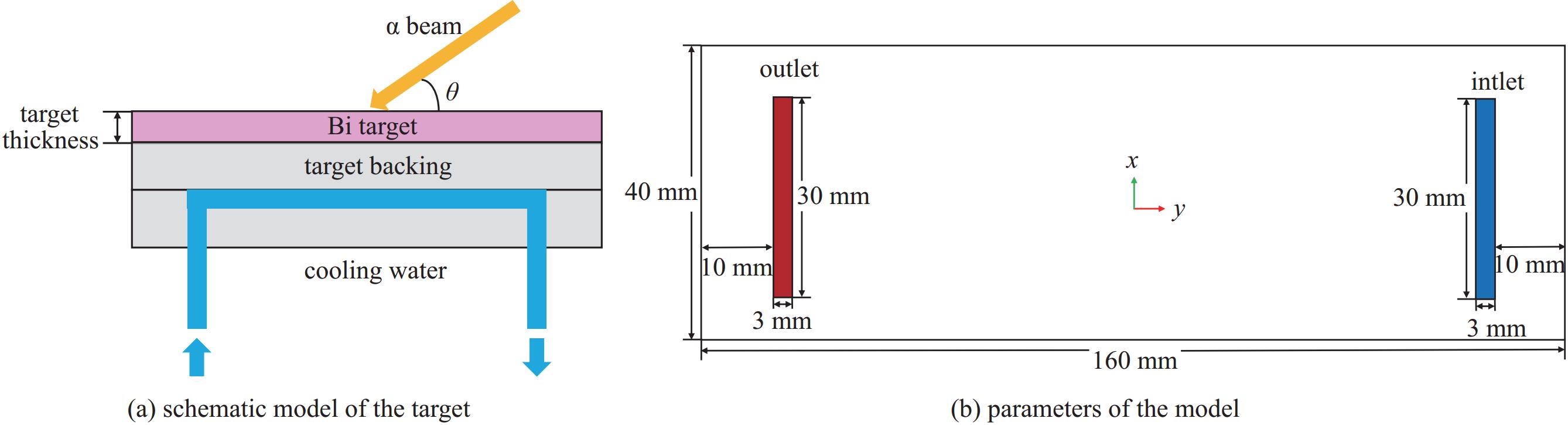
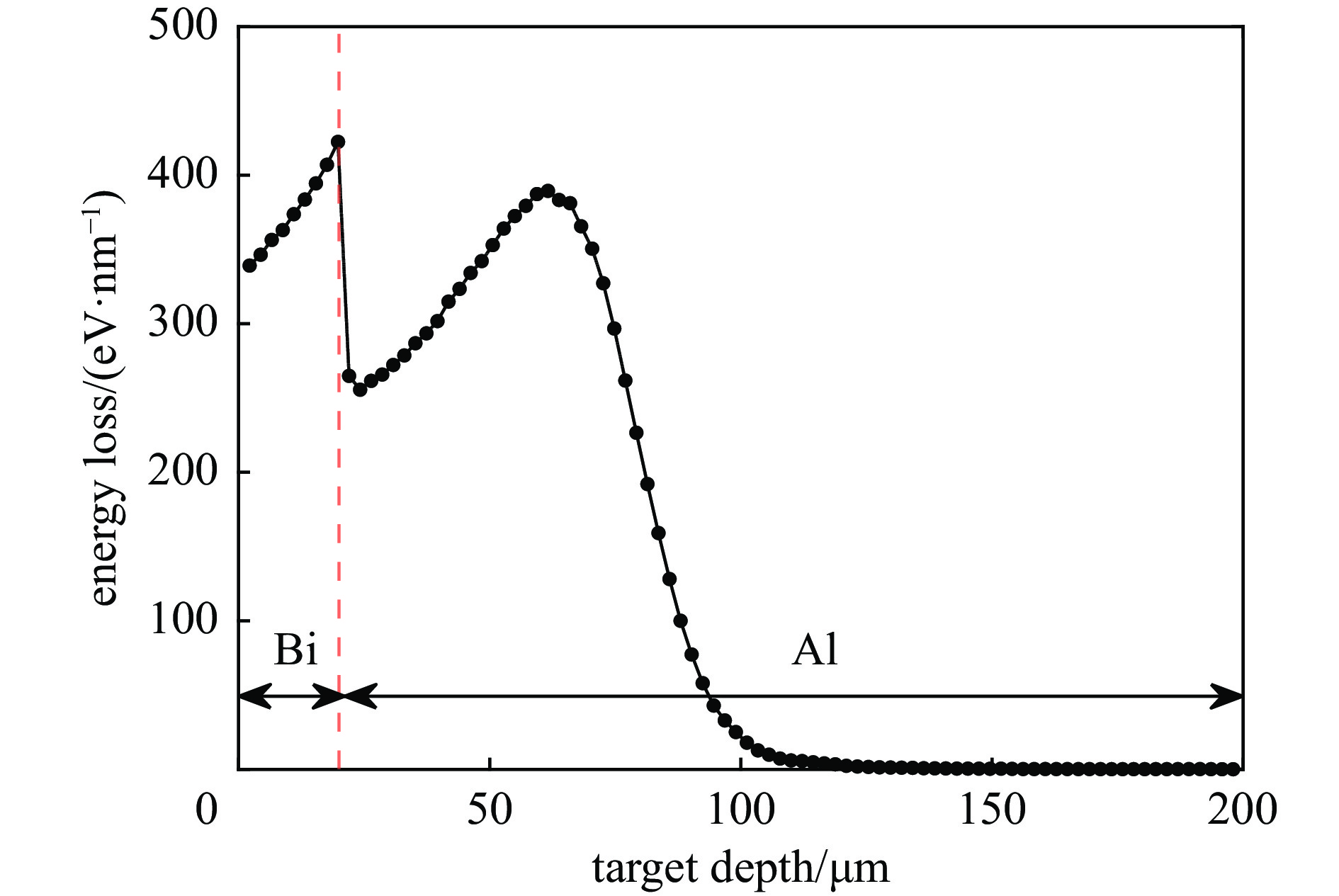
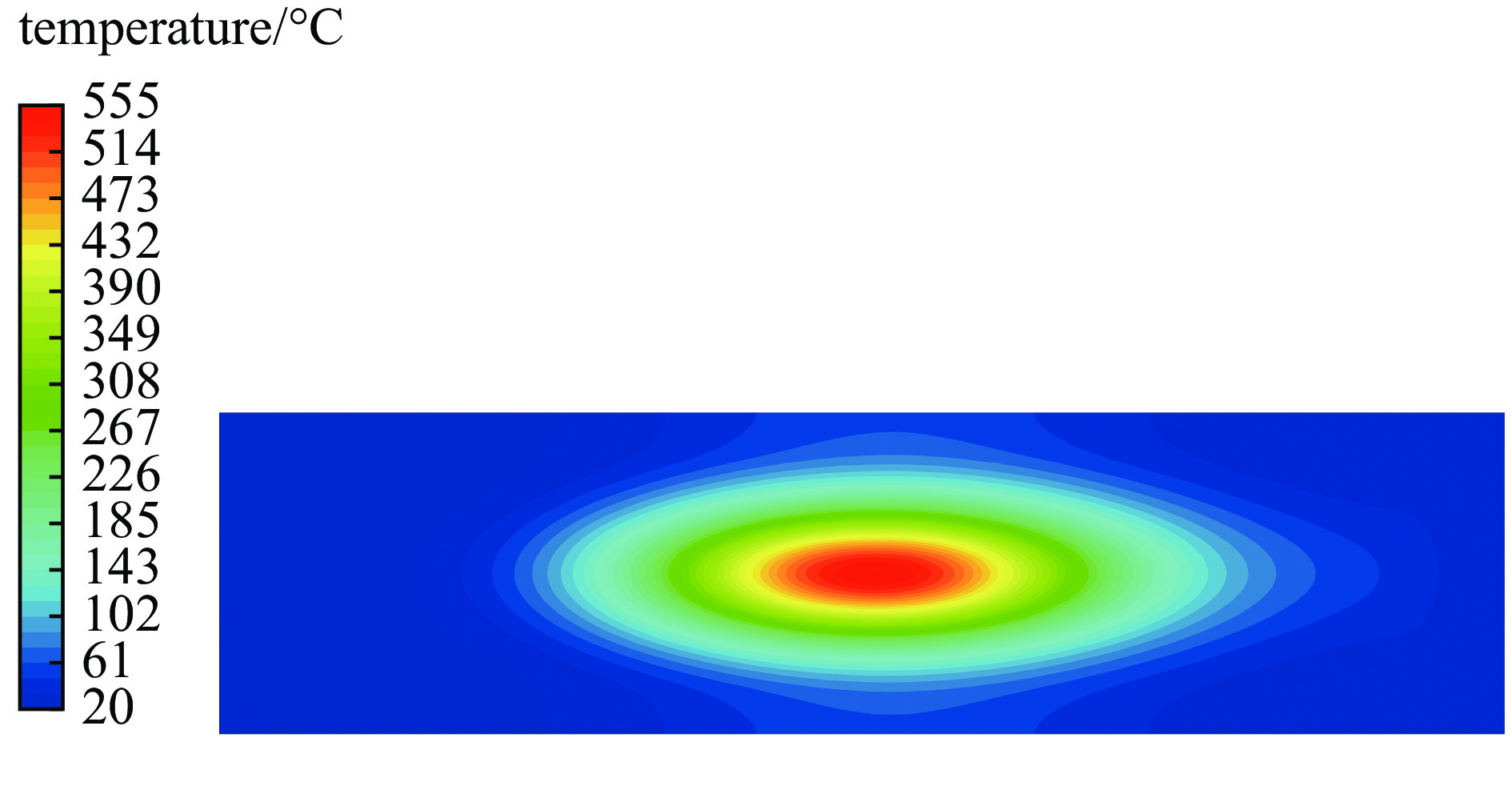
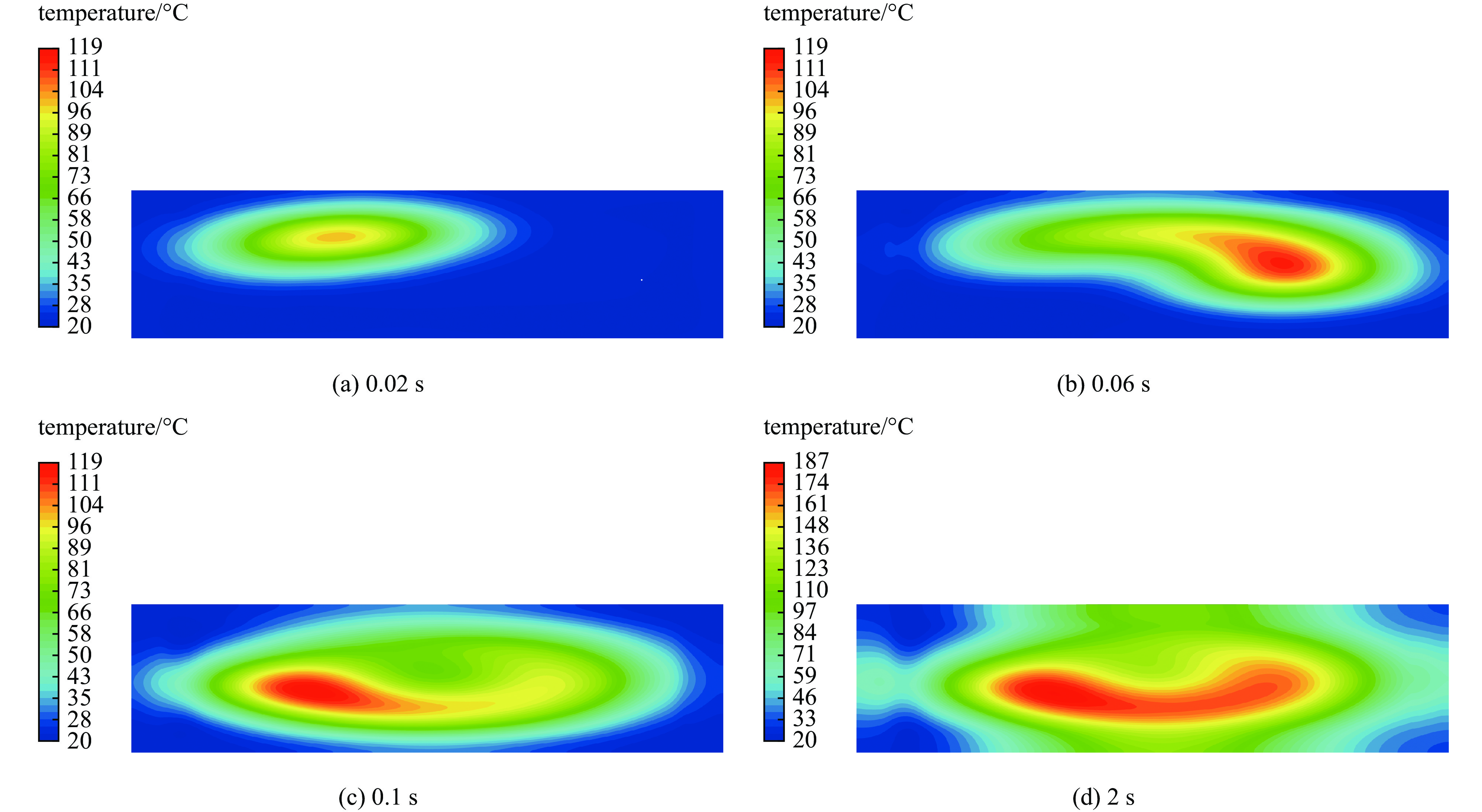
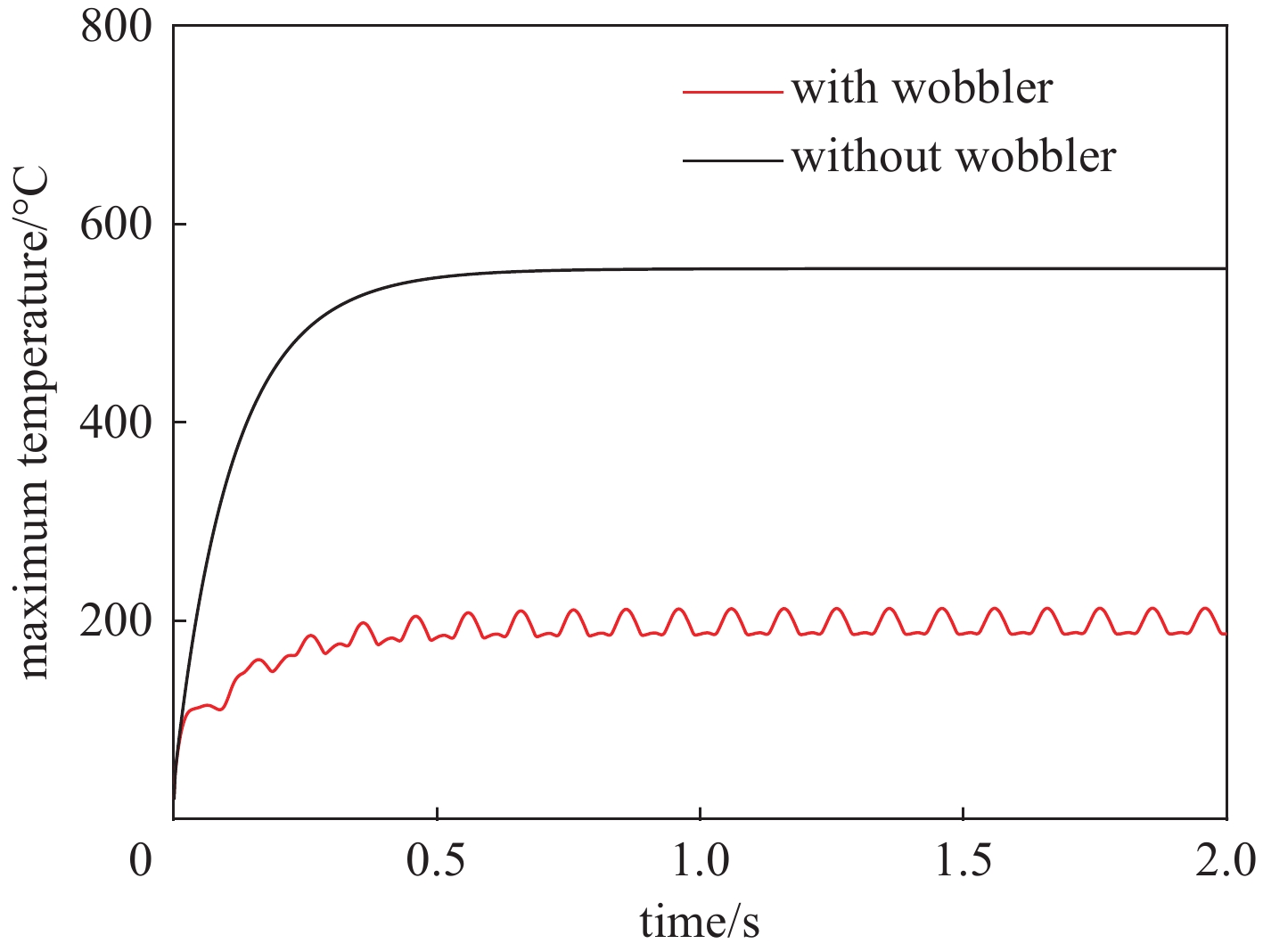
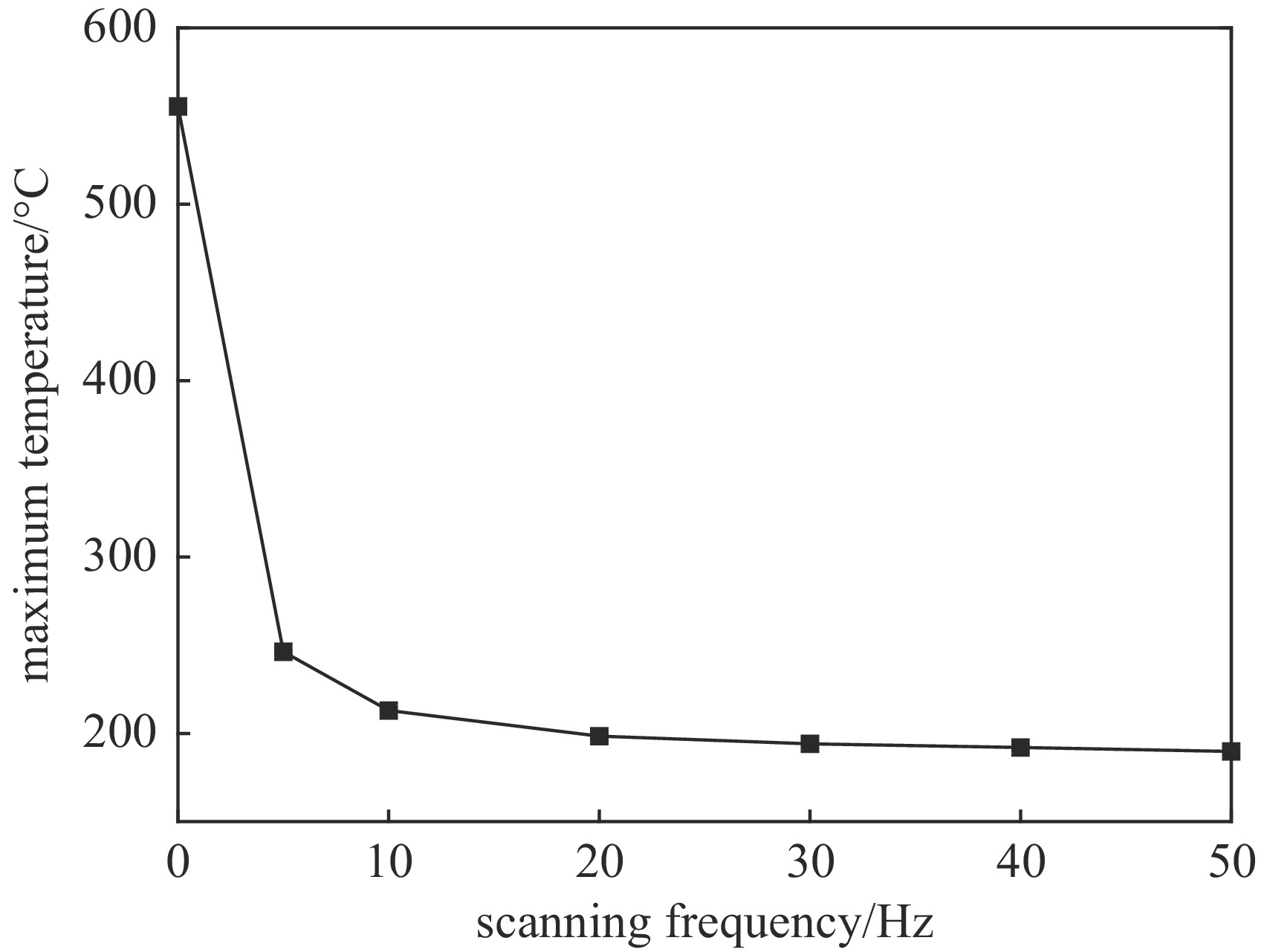
摘要: 为提高用于医用同位素211At生产的金属Bi靶在高束流功率作用下的可靠性与使役寿命,对多种束流均匀化方法进行了模拟与对比,利用计算流体力学(CFD)方法模拟分析了在wobbler磁铁作用下强度为500 eμA的α束流轰击Bi靶产生的热效应,为靶系统的设计和寿命的延长提供了关键技术支撑。结果表明,通过扫描实现束流均匀化可大幅降低靶上的最大热功率密度;在靶前采用wobbler磁铁对束流进行周期性圆扫描可有效降低Bi靶的表面温度。当扫描频率为50 Hz时,Bi靶最高温度为189.8 ℃,低于其熔点(271.3 ℃),能够满足Bi靶在此高功率束流照射下安全运行的温度要求。Abstract: To improve the reliability and operation life of metallic Bi targets for the production of medical isotope 211At using high current α beam, several beam uniformization methods were simulated and compared. The thermal effect of 500 eμA α beam bombarding a Bi target with wobbler magnet was modeled and analyzed by computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method, which provided key technical support for the design of target system and the improvement of target life time. The results showed that the peak beam thermal effect on the target was obviously reduced by applying beam scanning. In front of the target, a wobbler magnet was used to periodically scan the beam, which could effectively reduce the temperature on Bi target surface. With a scanning frequency of 50 Hz, the highest temperature on Bi target was 189.8 ℃, lower than the melting point of Bi metal (271.3 ℃), which could meet the temperature requirement of Bi target under such a high beam power condition.
-
Key words:
- Bi target /
- α beam /
- At-211 /
- isotope production /
- computational fluid dynamics
-
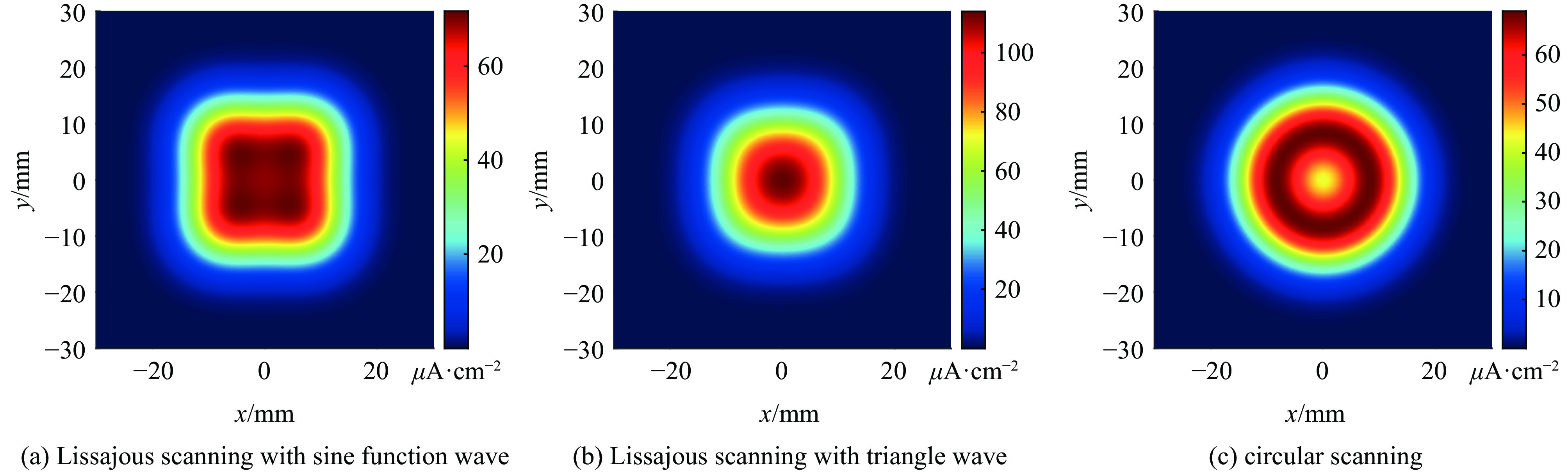
表 1 扫描前后最大流强密度
Table 1. Maximum current density before and after scanning
scanning mode maximum current density/(μA·cm−2) before scanning 318.31 Lissajous scanning(a) 71.16 Lissajous scanning(b) 113.88 circular scanning 68.94 表 3 相关材料物性参数
Table 3. Physical parameters of materials
material density/(kg∙m−3) specific heat capacity/(J∙kg−1∙K−1) thermal conductivity/(W·K−1·m−1) Bi 9800 130 8 Al 2719 871 202.4 water 998.2 4182 0.6 -
[1] Li Feize, Yang Yuanyou, Liao Jiali, et al. Recent progress of astatine-211 in endoradiotherapy: Great advances from fundamental properties to targeted radiopharmaceuticals[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2022, 33(7): 3325-3338. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.03.025 [2] 陈德胜, 刘葳豪, 黄清钢, 等. 加速器生产医用同位素211At及单抗标记[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11):1376-1384,1416 doi: 10.6023/A21060266Chen Desheng, Liu Weihao, Huang Qinggang, et al. Accelerator production of the medical isotope 211At and monoclonal antibody labeling[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(11): 1376-1384,1416 doi: 10.6023/A21060266 [3] Wang Yiwei, Chen Daiyuan, Dos Santos Augusto R, et al. Production review of accelerator-based medical isotopes[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(16): 5294. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165294 [4] 张天爵, 温凯, 刘景源, 等. 中高能回旋加速器及固体靶生产医用放射性核素技术研究[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2022, 42(6):340-346 doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn321828-20220215-00045Zhang Tianjue, Wen Kai, Liu Jingyuan, et al. Research on medical radioisotope production technology by medium and high-energy cyclotron and solid target[J]. Chinese Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 2022, 42(6): 340-346 doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn321828-20220215-00045 [5] Feng Yutian, Zalutsky M R. Production, purification and availability of 211At: Near term steps towards global access[J]. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 2021, 100/101: 12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2021.05.007 [6] Kleeven W, Abs M, Delvaux J L, et al. Recent development and progress of IBA cyclotrons[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2011, 269(24): 2857-2862. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2011.04.031 [7] Ren Jieru, Deng Zhigang, Qi Wei, et al. Observation of a high degree of stopping for laser-accelerated intense proton beams in dense ionized matter[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5157. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18986-5 [8] Zhao Yongtao, Zhang Yanning, Cheng Rui, et al. Benchmark experiment to prove the role of projectile excited states upon the ion stopping in plasmas[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2021, 126: 115001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.115001 [9] Ren Jieru, Ma Bubo, Liu Lirong, et al. Target density effects on charge transfer of laser-accelerated carbon ions in dense plasma[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2023, 130: 095101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.095101 [10] Wei Wenqing, Zhang Shizheng, Deng Zhigang, et al. Proton-boron fusion yield increased by orders of magnitude with foam targets[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2308.10878, 2023. [11] Oliver C, Ibarra A, Gallego A, et al. Phase-space transformation for a uniform target irradiation at DONES[C]//Proceedings of LINAC 2016. 2017: 424-426. [12] Thomsen H D, Møller S P. The beam delivery system of the European Spallation Source[C]//Proceedings of HB2016. 2016: 427-432. [13] Tsoupas N. Uniform beam distributions of charged particle beams[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2011, 1336(1): 11-15. [14] Renner T R, Chu W T. Wobbler facility for biomedical experiments[J]. Medical Physics, 1987, 14(5): 825-834. doi: 10.1118/1.596009 [15] Katagiri K, Hojo S, Nakao M, et al. Wobbled beam irradiation system for radioisotope production in NIRS cyclotron facility[C]//Proceedings of the 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan. 2015: 1380-1383. [16] 贾先禄, 张天爵, 吕银龙, 等. 30MeV医用回旋加速器束流输运线上旋转扫描磁铁的研制[J]. 高能物理与核物理, 2007, 31(3):292-295 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3052.2007.03.014Jia Xianlu, Zhang Tianjue, Lv Yinlong, et al. Wobbling magnet design for beam line of CYCIAE-30 medical cyclotron[J]. High Energy Physics and Nuclear Physics, 2007, 31(3): 292-295 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3052.2007.03.014 [17] Wang Y, Sato N, Komori Y, et al. Present status of 211At production at the RIKEN AVF cyclotron[C]//Radiochemistry & Nuclear Chemistry. 2020: 192. [18] 孙立军. ANSYS Fluent 2020工程案例详解[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2021Sun Lijun. ANSYS Fluent 2020 engineering case[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2021 [19] Ziegler J F, Ziegler M D, Biersack J P. SRIM – The stopping and range of ions in matter (2010)[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2010, 268(11/12): 1818-1823. [20] Yang Yao, Zhai Y H, Jiang P Y, et al. Commissioning progress of LEAF at IMP[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1401: 012019. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1401/1/012019 -




 下载:
下载: