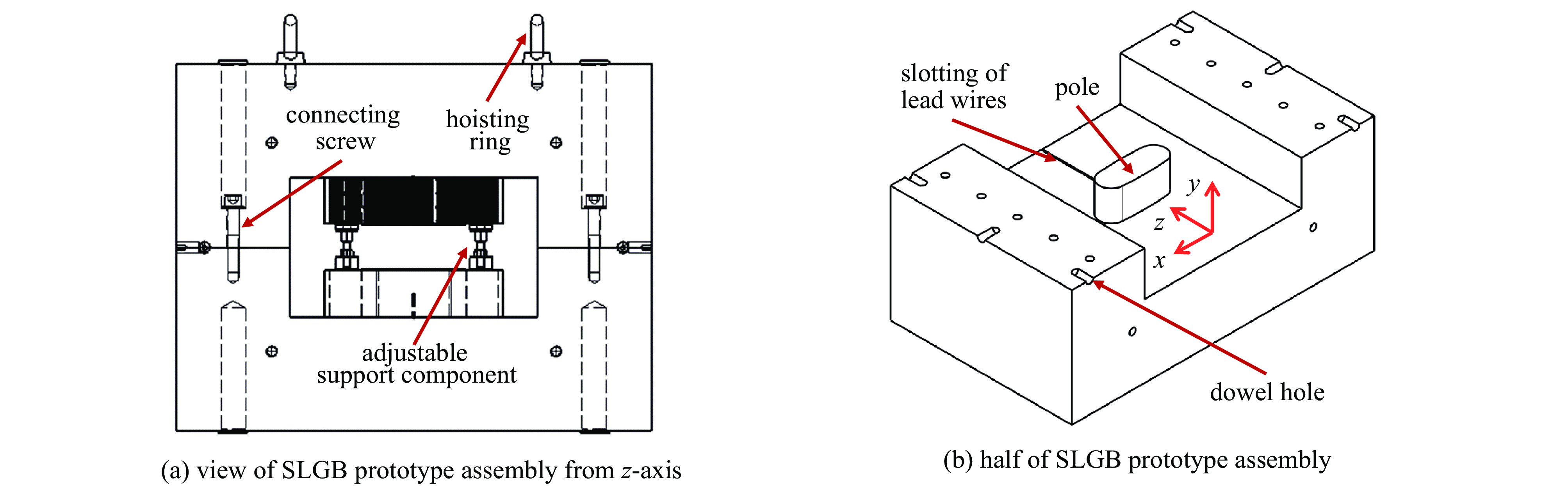
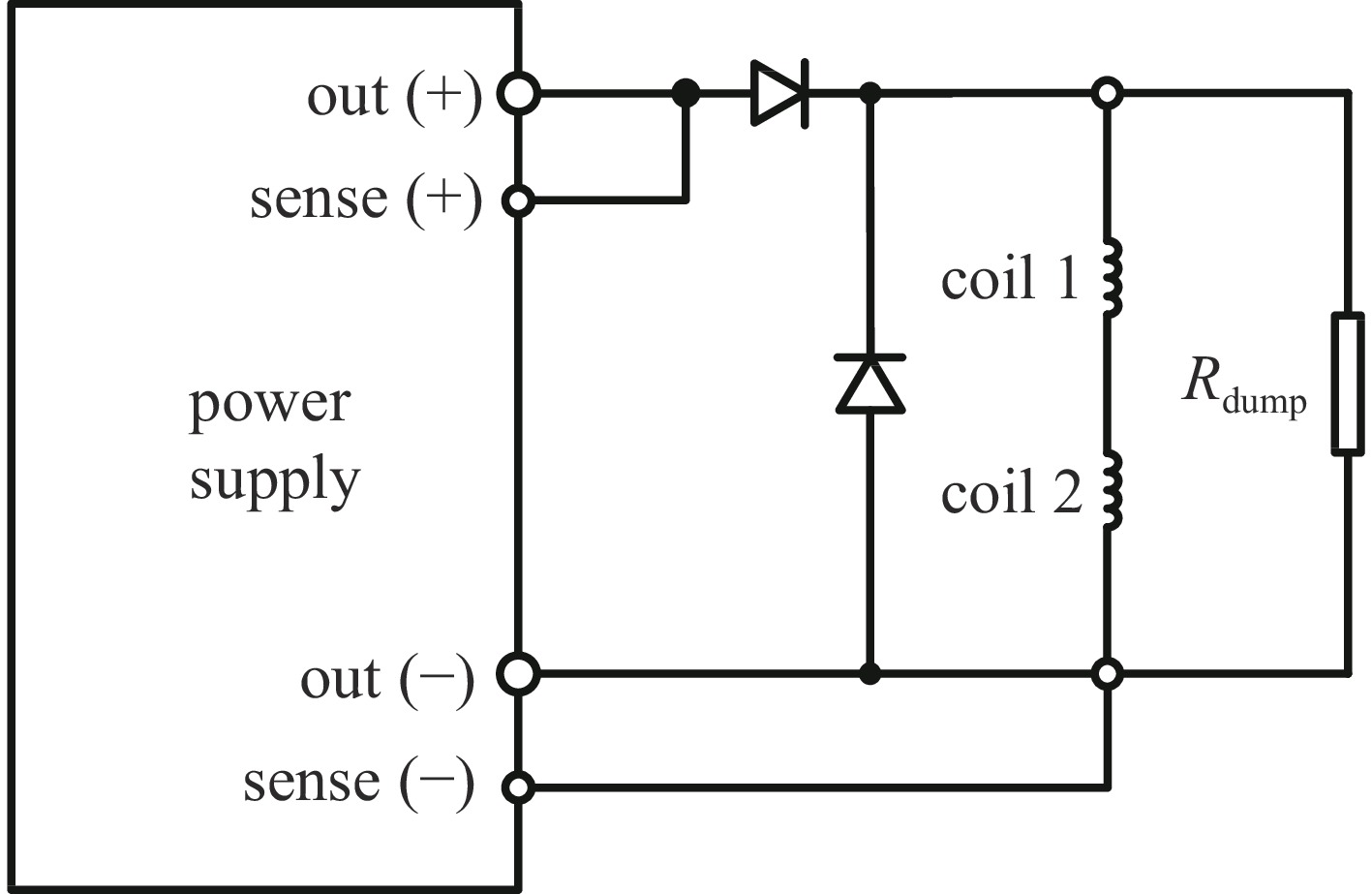
Development of a superconducting longitudinal gradient bend prototype for Hefei Advanced Light Facility storage ring
-
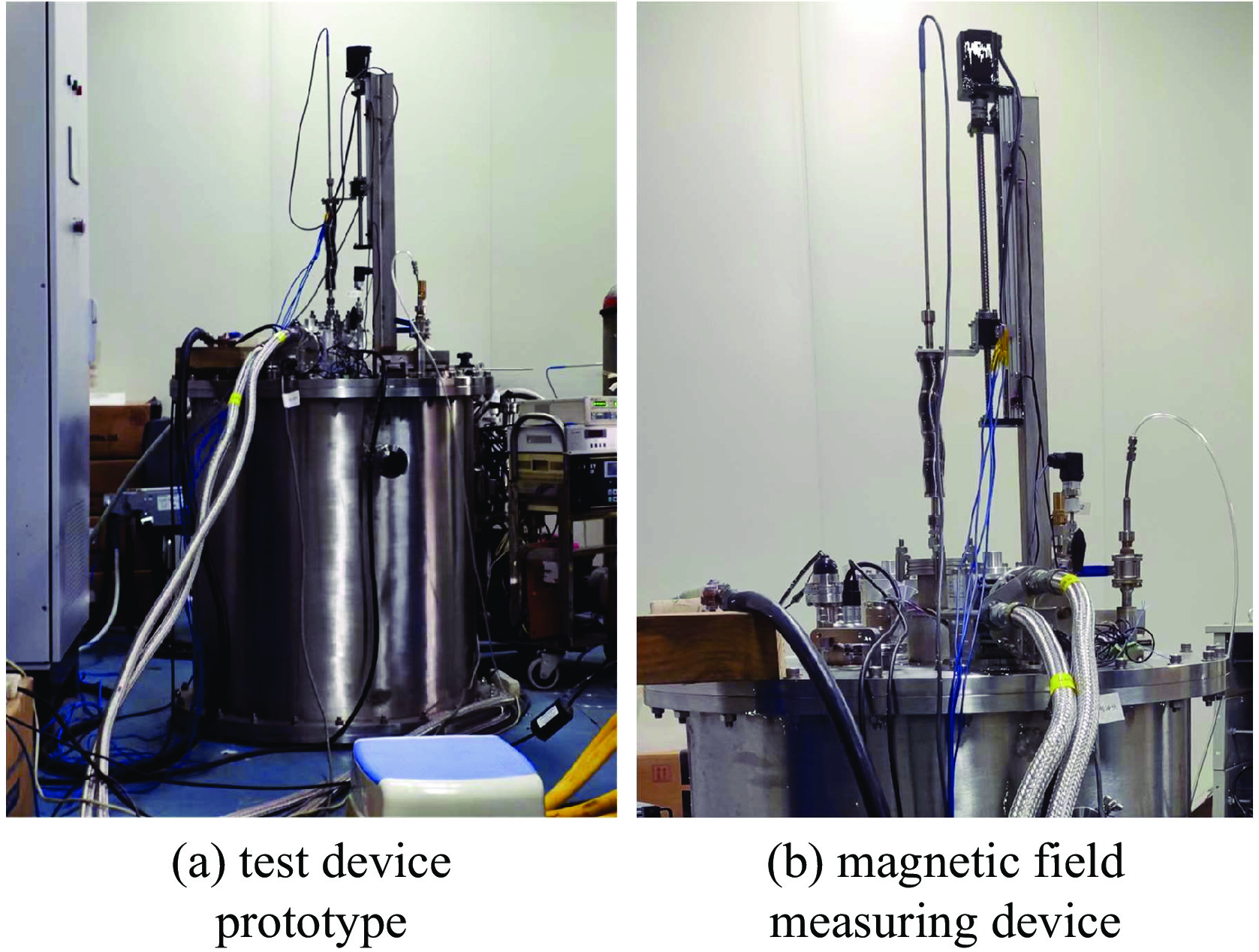
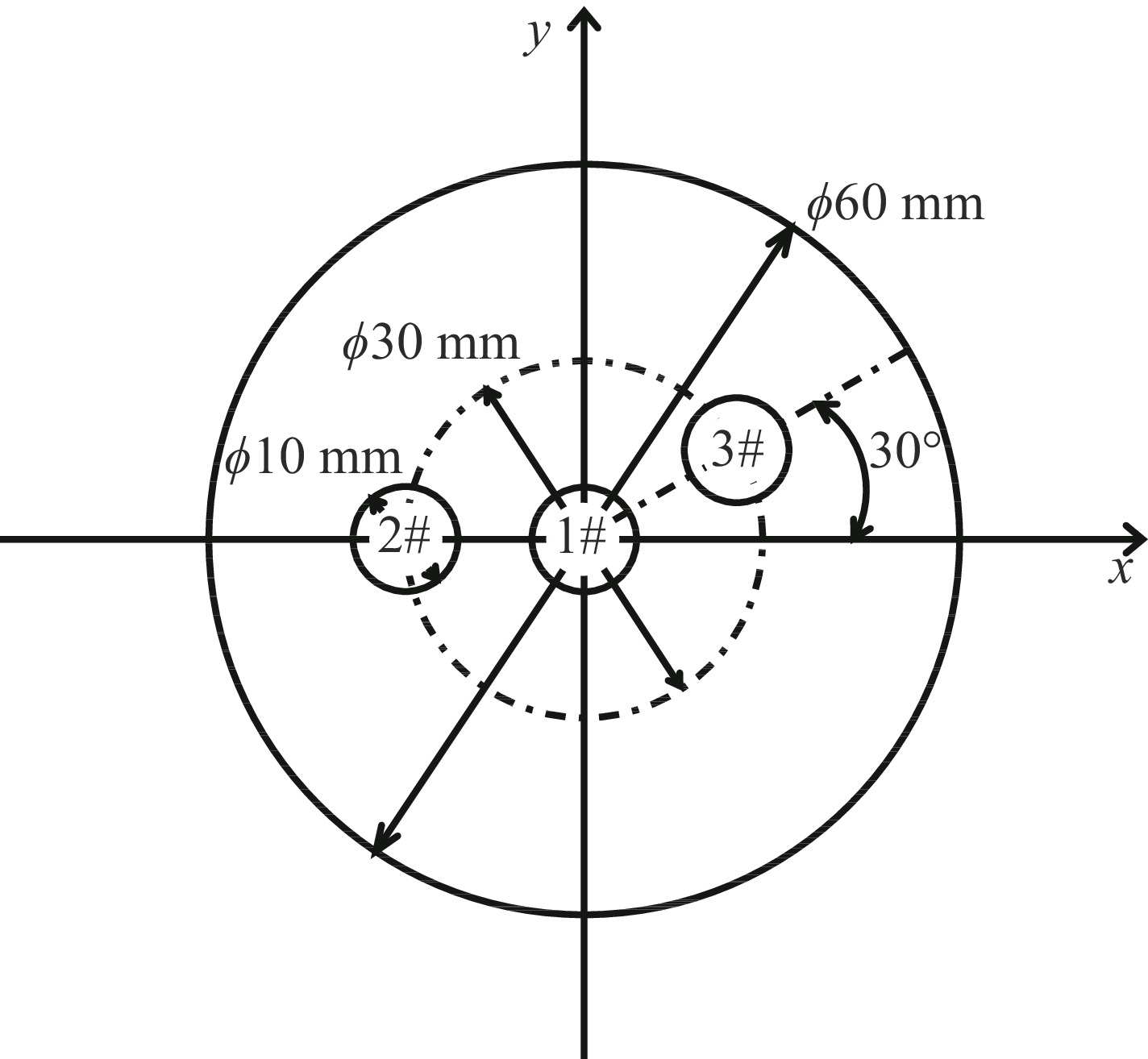
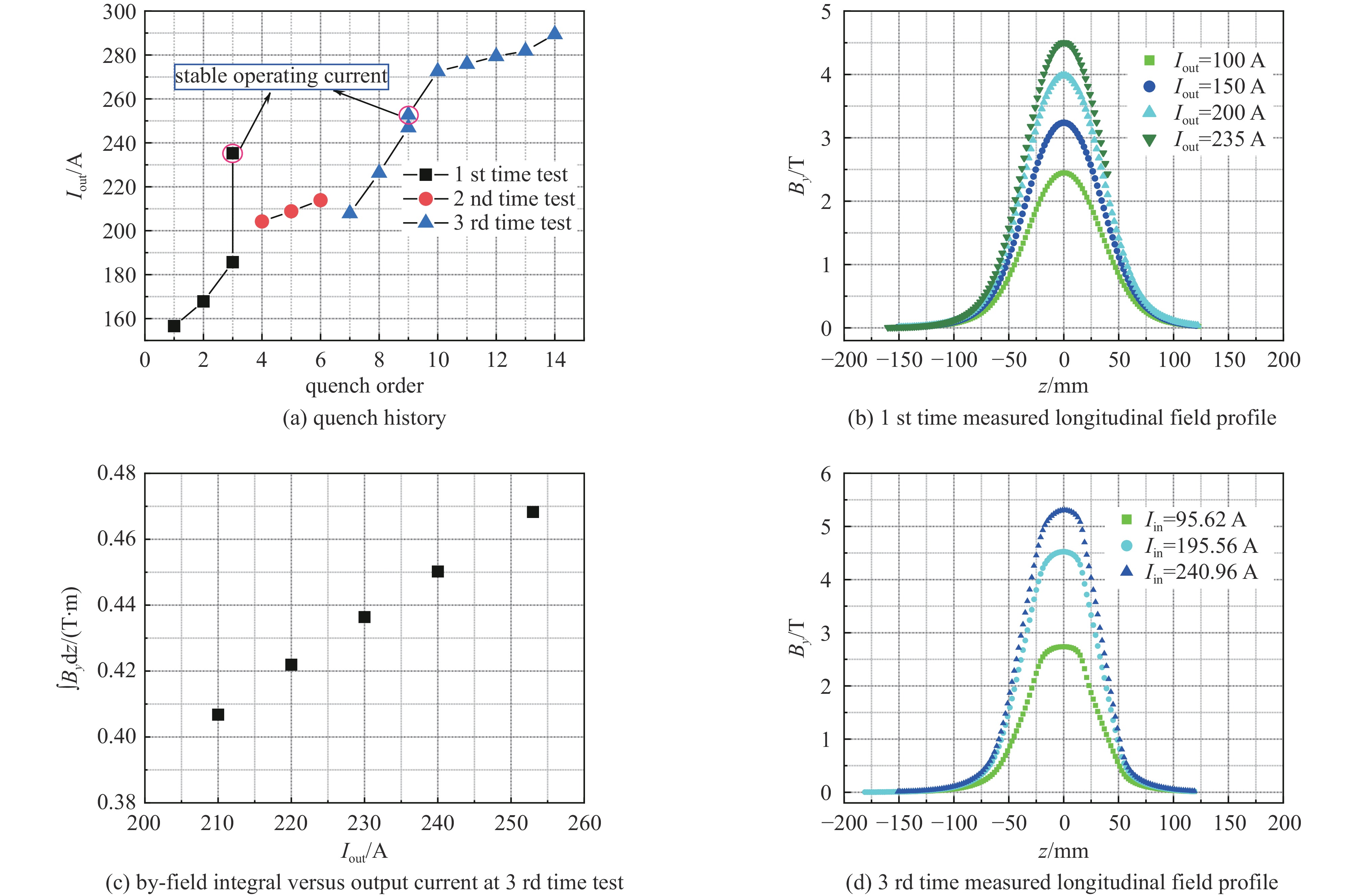
摘要: 介绍了合肥先进光源储存环超导纵向梯度弯铁样机的研制工作,基于已发展的一种磁体结构参数优化方法,综合考虑磁场空间分布需求和超导线圈工作负载,完成了磁铁结构的设计和优化。为了验证磁体设计方案,应用一种矩形铌钛线材和DT4C电工纯铁材料,研制了一台纵向长度0.30 m、磁极间隙46 mm的磁体样机。并搭建了一套简易低温测试装置,对该磁体进行了励磁特性测量,经过10余次失超,测得磁体最大工作电流大于275 A。磁体纵向磁场分布测量结果表明,该磁体在约196 A工作电流下,纵向磁场积分值达到0.4 T·m,峰值磁场约4.5 T。测试结果与理论设计结果基本一致,表明该种超导磁体的设计是可行的。Abstract: This paper presents the development of superconducting longitudinal gradient bend prototype for Hefei Advanced Light Facility storage ring. The magnet structure parameters were optimized using a developed method that considered the requirements of spatial magnetic field distribution and magnet operating load. To verify the magnet design, a prototype magnet with a longitudinal length of 0.30 m and a pole gap of 46 mm was fabricated using a rectangular niobium-titanium wire and DT4C material. A simple low-temperature test device was built to measure the magnetizing characteristics of the magnet, and after more than 10 times of quench, the maximum operating current of the magnet was measured to be more than 275 A. The longitudinal magnetic field distribution of the magnet was measured, revealing an integral field of 0.4 T·m and a peak magnetic field of approximately 4.5 T at an operating current of about 196 A. The test results are basically consistent with the theoretical design, indicating that the design is reliable.
-
表 1 铌钛超导线材主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of the NbTi wire
bare wire size insulated wire size Cu:NbTi
ratiocritical current
at 4.2 K, 7 T/Anumber of
filamentsfilament
diameter/μmRRR
(273 K/10 K)1.20 mm×0.75 mm 1.28 mm×0.83 mm 1.3 ≥566 630 27.6 ≥566 表 2 超导纵向梯度二极磁铁样机主要设计参数
Table 2. Main design parameters of the SLGB prototype
magnet
typeyoke
thickness/mmpole
gap/mmpole length
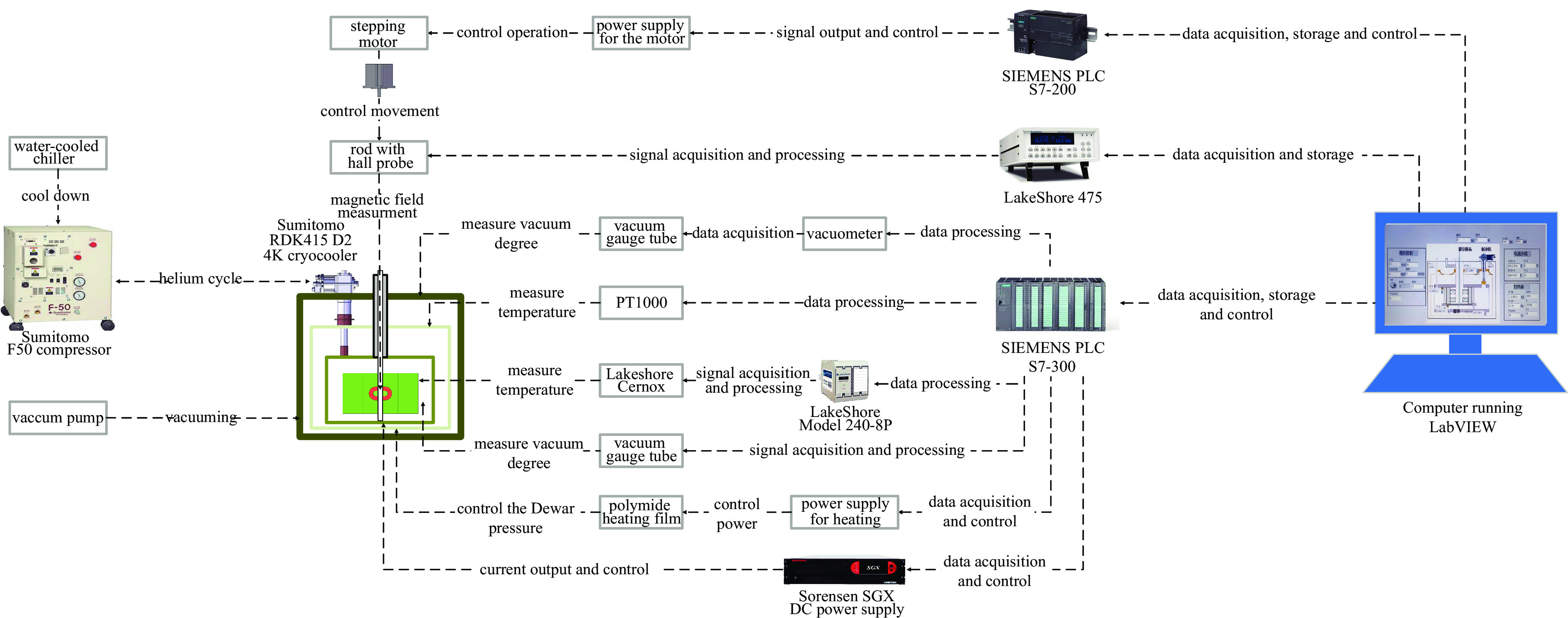
along
beam/mmpole length
transverse to
beam/mmturns
per
layernumber
of
layersconductor
length per
coil/moperating
current/Apeak
field at
conductor/Tstored
energy/kJracetrack coils,
DT4 yoke and pole120 46 39 109 38 36 500 252 6.35 14 表 3 低温装置热负载计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results for the heat load of cryogenic device
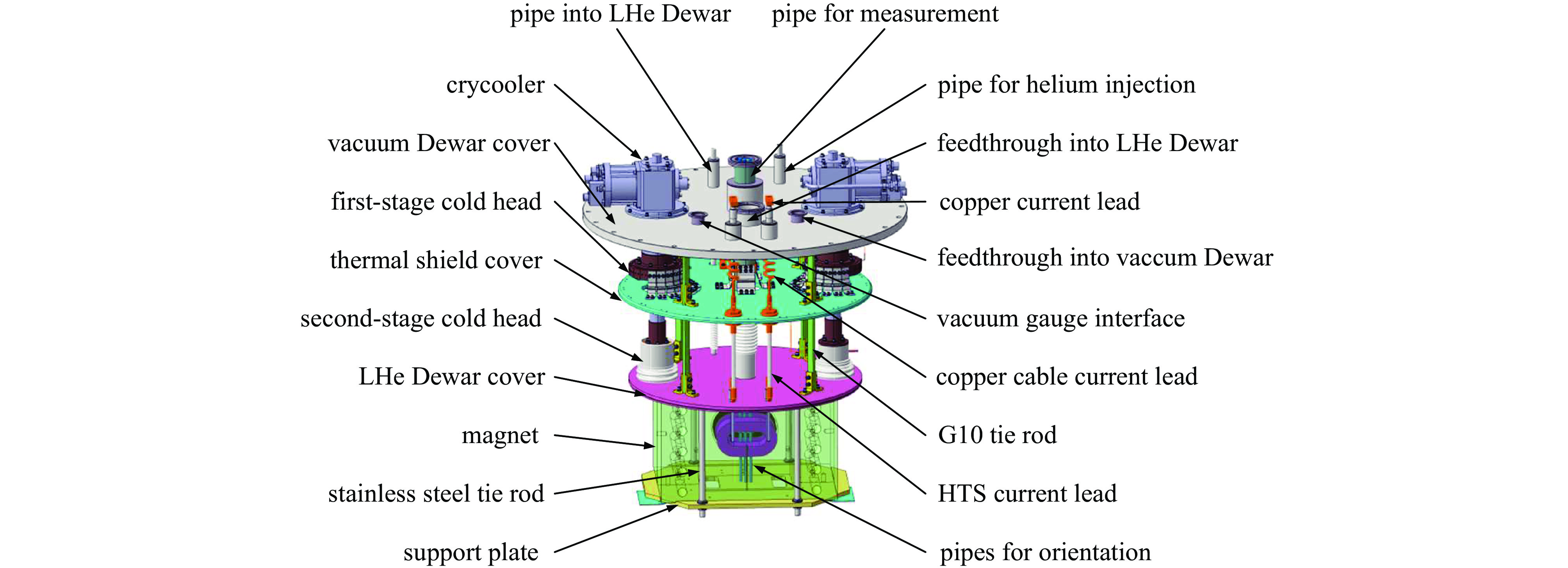
source of thermal load first stage cold head thermal load/W second stage cold head thermal load /W G10 rods 0.15×4 0.07×4 thermal radiation 2.3 0.2 current leads (thermal conduction) 8×2 0.1×2 current leads (joule heat) 10×2 —— pipes 4 0.1 gas 0.4 0.03 else 1 0.1 total 44.3 0.71 表 4 SLGB样机实测结果与仿真结果对比
Table 4. Comparison between measured results and simulation results of the SLGB prototype
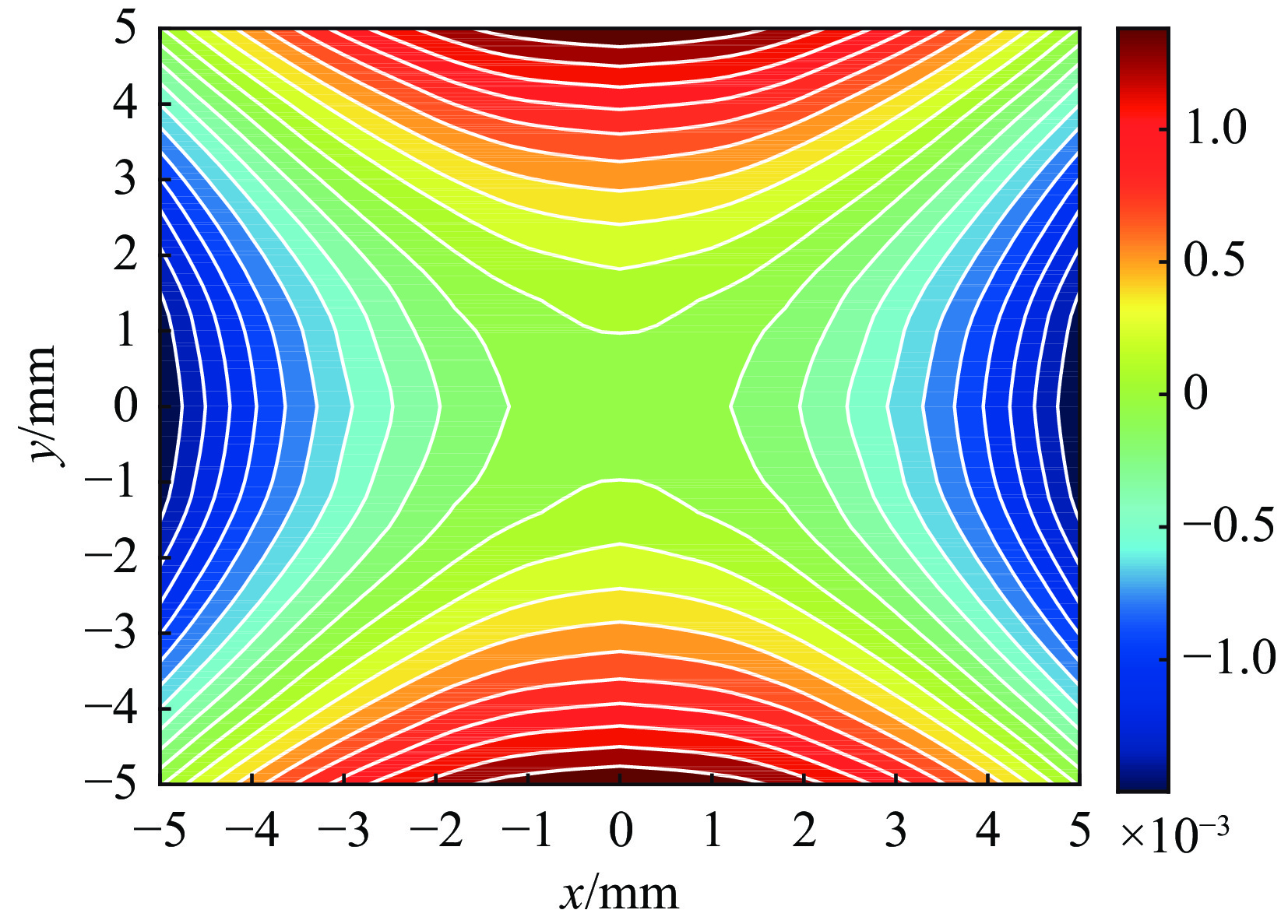
Iin/A Bp/T ∫Bydz/(T·m) measurement 195.56 4.5245 0.4004 original simulation 251.40 4.8985 0.3992 updated simulation 240.41 4.6019 0.4000 -
[1] 焦毅, 白正贺. 第四代同步辐射光源物理设计与优化[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:104004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220136Jiao Yi, Bai Zhenghe. Physics design and optimization of the fourth-generation synchrotron light sources[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 104004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220136 [2] 焦毅, 徐刚, 陈森玉, 等. 衍射极限储存环物理设计研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:045108 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.045108Jiao Yi, Xu Gang, Chen Senyu, et al. Advances in physical design of diffraction-limited storage ring[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 045108 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.045108 [3] Hettel R. DLSR design and plans: an international overview[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2014, 21(5): 843-855. doi: 10.1107/S1600577514011515 [4] Riemann B, Streun A. Low emittance lattice design from first principles: reverse bending and longitudinal gradient bends[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2019, 22: 021601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.22.021601 [5] Kashikhin V S, Borland M, Chlachidze G, et al. Longitudinal gradient dipole magnet prototype for APS at ANL[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26: 4002505. [6] Saeidi F, Pourimani R, Rahighi J, et al. Normal conducting superbend in an ultralow emittance storage ring[J]. Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, 2015, 18: 082401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.18.082401 [7] Le Bec G, Chavanne J, Villar F, et al. Magnets for the ESRF diffraction-limited light source project[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26: 4000107. [8] Citadini J, Vilela L N P, Basilio R, et al. Sirius-details of the new 3.2 T permanent magnet superbend[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2018, 28: 4101104. [9] Calzolaio C, Sanfilippo S, Sidorov S, et al. Design of a superconducting longitudinal gradient bend magnet for the SLS upgrade[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2017, 27: 4000305. [10] Streun A, Wrulich A. Compact low emittance light sources based on longitudinal gradient bending magnets[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2015, 770: 98-112. [11] Juchno M, Venturini M, Virostek S, et al. Conceptual design of superbend and hardbend magnets for Advance Light Source upgrade project[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2020, 30: 4100505. [12] Vianna A A, Seraphim R M, Pereira A G C, et al. Conceptual design of a C-shaped 6.4 T superconducting dipole magnet[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2022, 32: 4002005. [13] Calzolaio C, Gabard A, Lerch P, et al. Longitudinal gradient bend magnets for the upgrade of the Swiss Light Source storage ring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2020, 30: 4100905. [14] Zbanik J, Wang S T, Chen J Y, et al. ALS superbend magnet system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2001, 11(1): 2531-2534. doi: 10.1109/77.920381 [15] Chen C, Wang L, Feng G Y, et al. Electromagnetic design study of a superconducting longitudinal gradient bend magnet based on the HALF storage ring[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2023, 18: P06003. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/18/06/P06003 [16] 白正贺, 刘刚文, 何天龙, 等. 合肥先进光源储存环初步物理设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:104003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220137Bai Zhenghe, Liu Gangwen, He Tianlong, et al. Preliminary physics design of the Hefei Advanced Light Facility storage ring[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 104003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220137 [17] 张骁龙, 申飞, 任亭亭, 等. 基于LabVIEW的超导磁体数据监测与分析系统[J]. 仪表技术, 2021(2):38-42Zhang Xiaolong, Shen Fei, Ren Tingting, et al. LabVIEW-based superconducting magnet data monitor and analysis system[J]. Instrumentation Technology, 2021(2): 38-42 [18] 周安若, 马毅龙, 陈登明, 等. 1J50软磁合金的温度稳定性研究[J]. 功能材料, 2014, 45(16):16030-16032 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2014.16.007Zhou Anruo, Ma Yilong, Chen Dengming, et al. Study on the temperature-magnetic stability of 1J50 alloy[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2014, 45(16): 16030-16032 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2014.16.007 [19] 汪天龙, 邱清泉, 靖立伟, 等. 铁磁材料低温磁性能测量研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2019, 48(3):898-904Wang Tianlong, Qiu Qingquan, Jing Liwei, et al. Measurement of magnetic properties of ferromagnetic materials at low temperature[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019, 48(3): 898-904 [20] 陈敏, 丘明, 肖立业, 等. 铁芯材料在低温下的磁性能的研究[J]. 电工电能新技术, 2003, 22(1):35-38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3076.2003.01.009Chen Min, Qiu Ming, Xiao Liye, et al. Study on magnetic characteristics of the ferromagnetic materials at 77K[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 2003, 22(1): 35-38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3076.2003.01.009 -





 下载:
下载: