Design of solenoid snake for Super Tau-Charm Facility based on particle swarm optimization algorithm
-
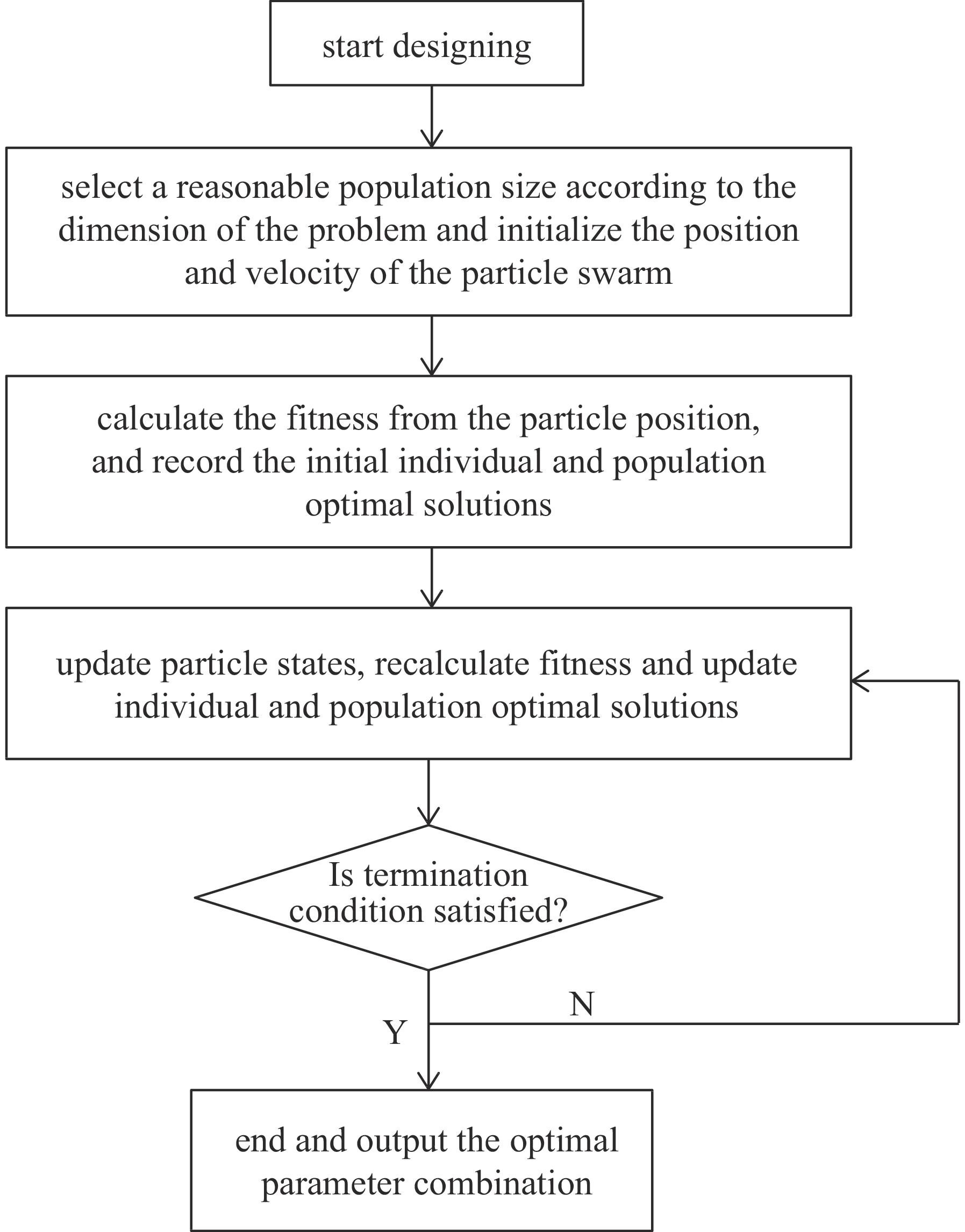
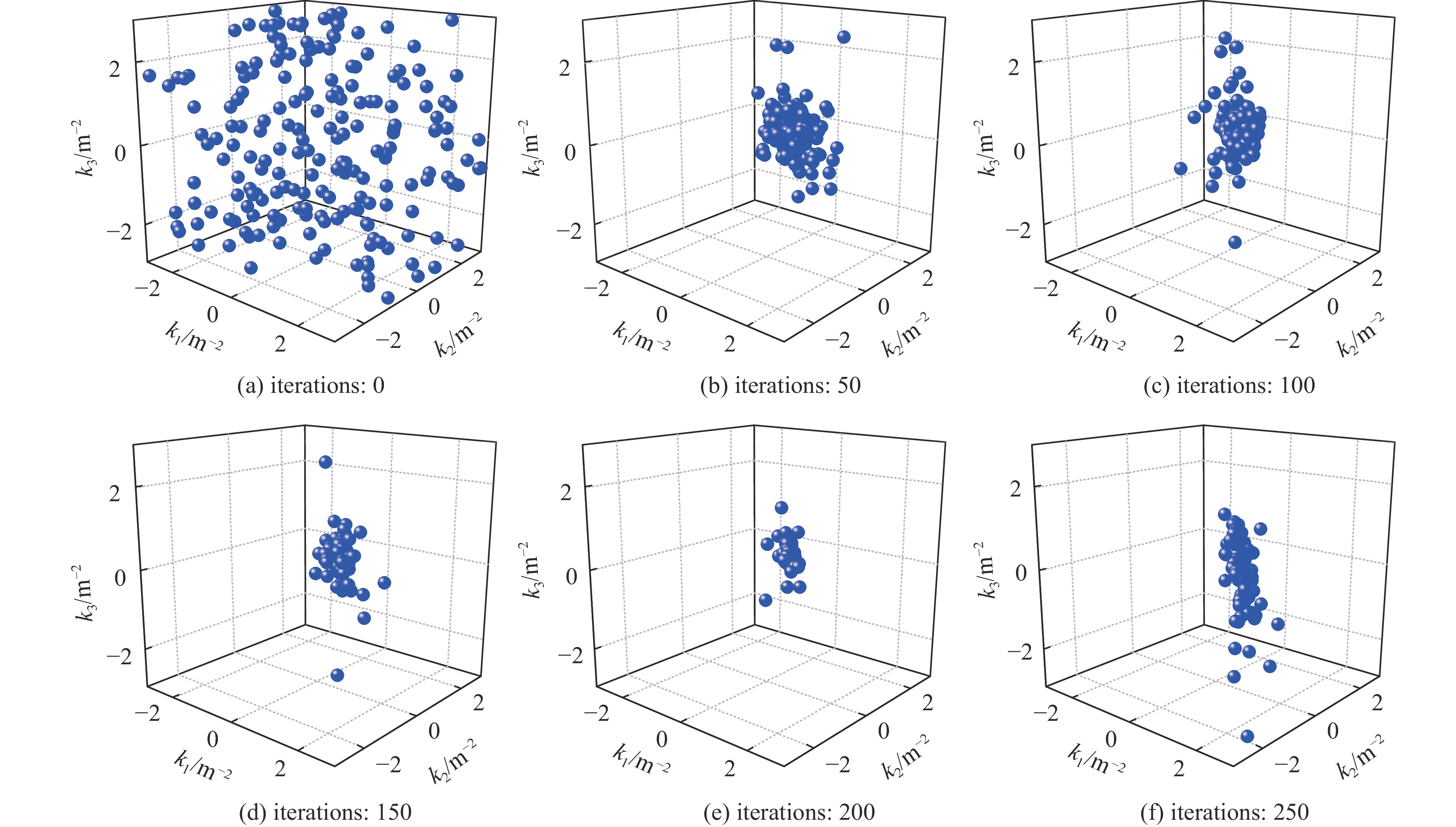
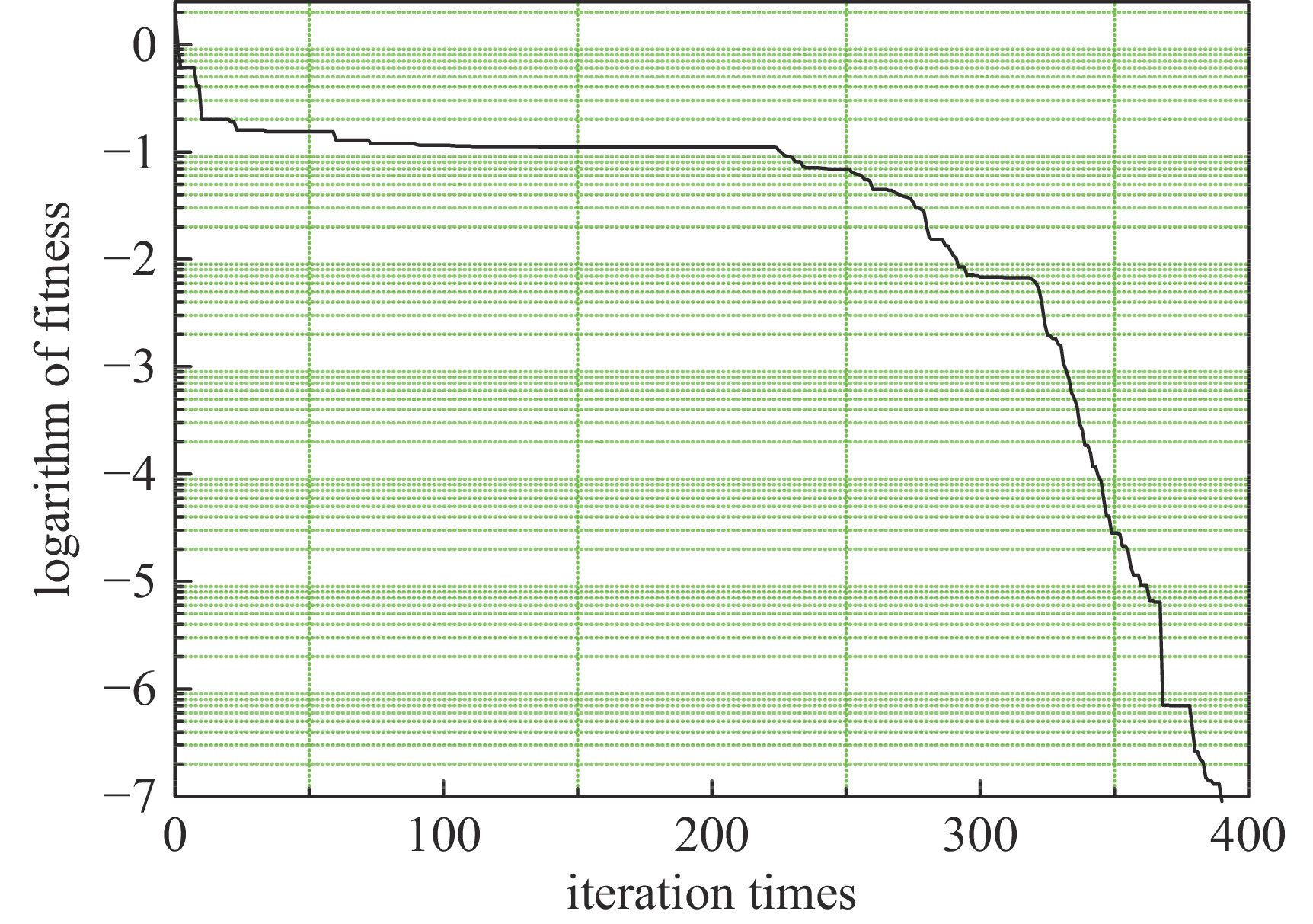
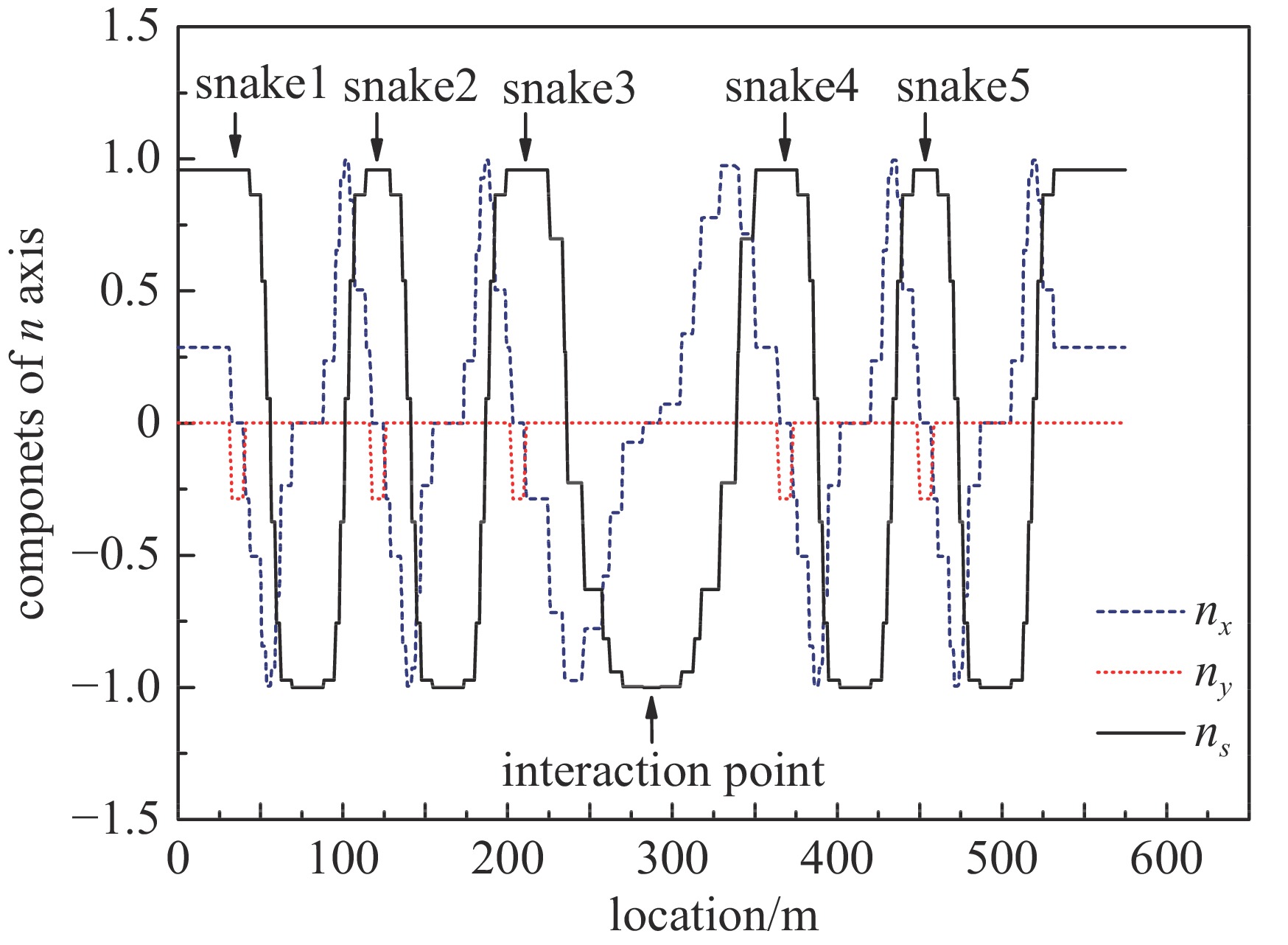
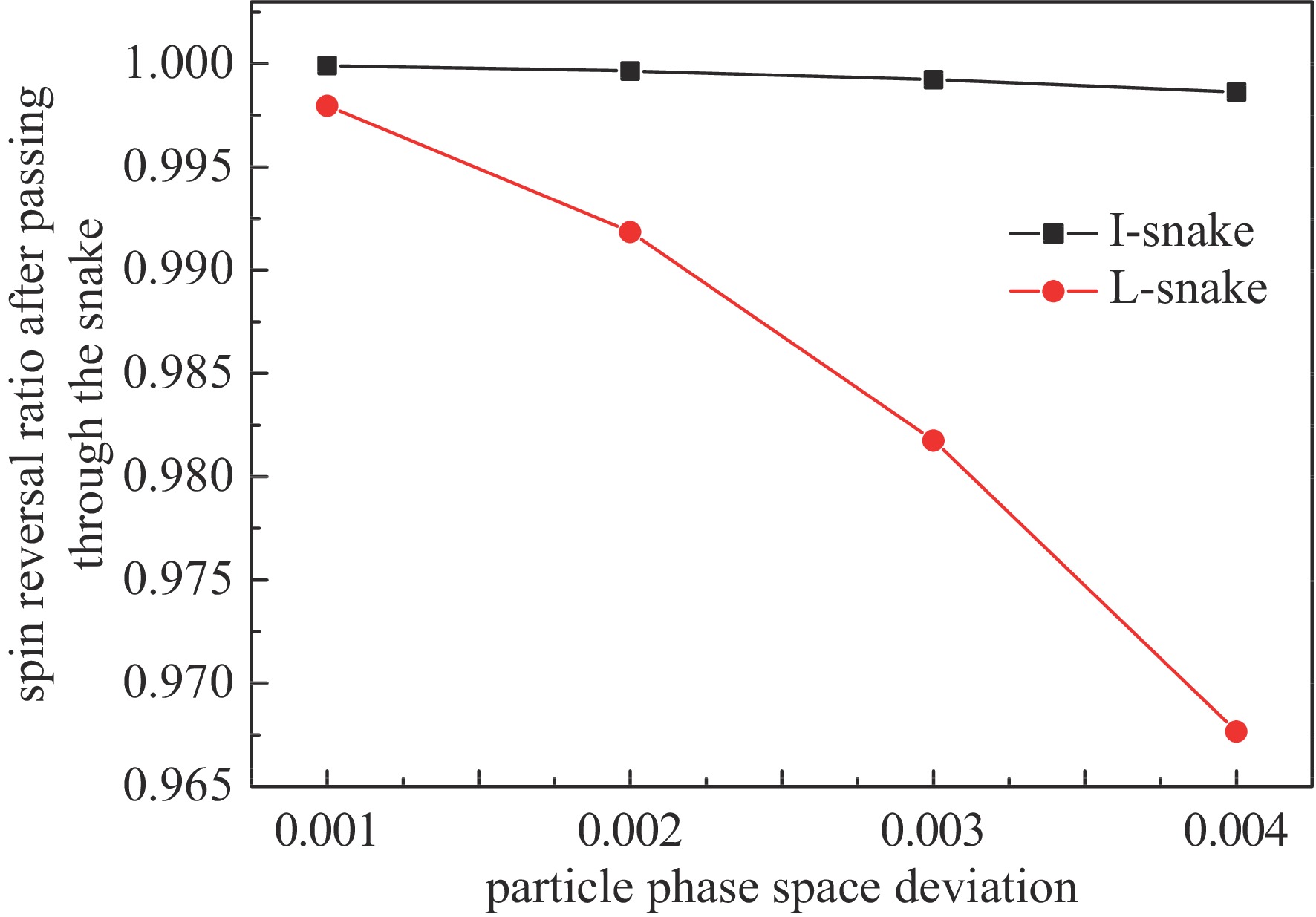
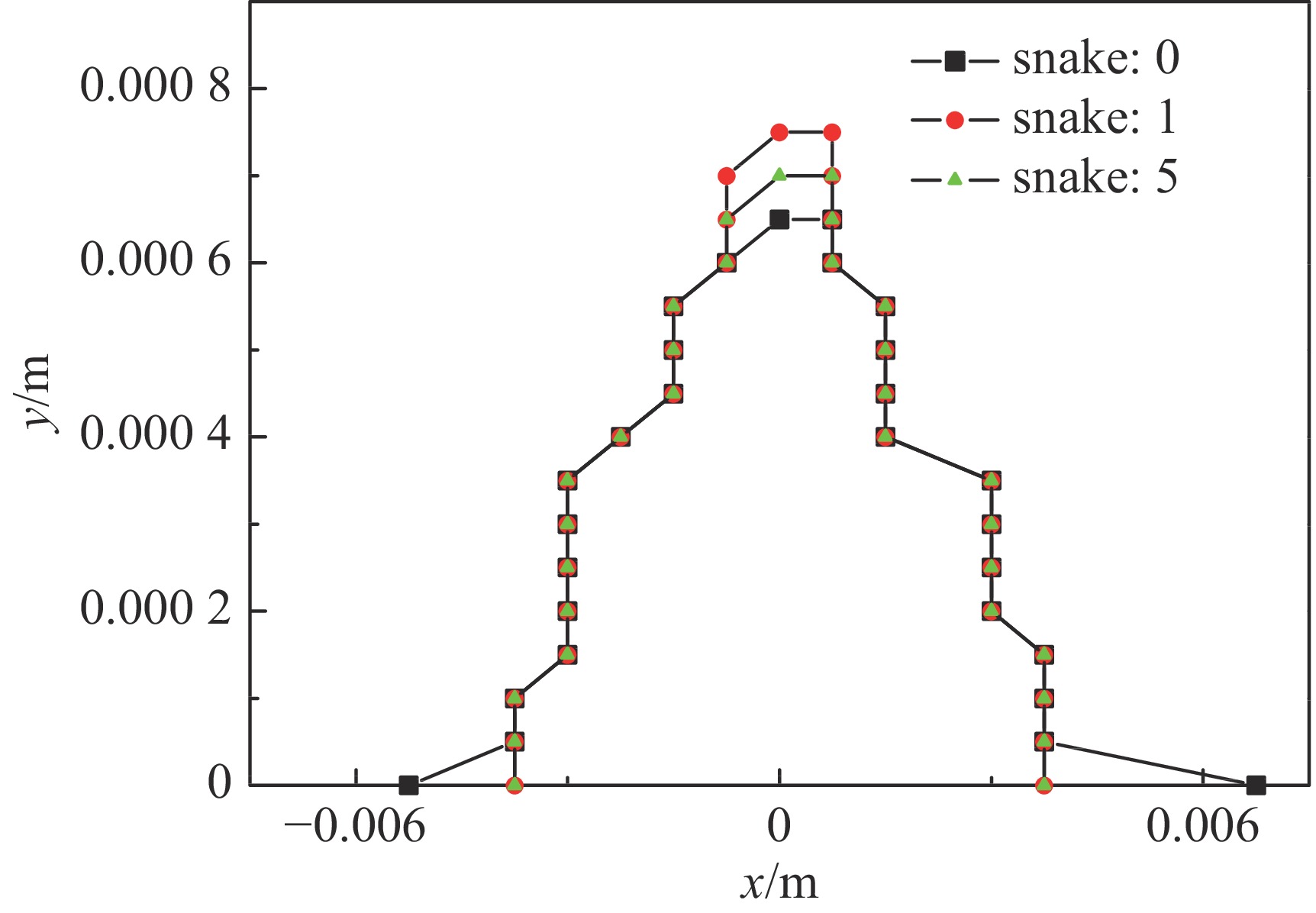
摘要: 在环形对撞机中等方位角间隔安装奇数个西伯利亚蛇是用来获得纵向极化束对撞的通常方案。根据超级陶粲装置的特点,选取螺线管型西伯利亚蛇作为维持束流极化的装置。详细介绍了如何把粒子群优化算法与螺线管蛇去耦合和光学匹配问题相结合,对它进行快速优化设计,并对设计结果进行了展示。结果显示,基于粒子群算法的螺线管蛇优化设计有效且高效。Abstract: Installing an odd number of Siberian snakes at equal azimuth intervals in a circular collider is a common scheme for obtaining longitudinally polarized beam collisions. In this paper, the solenoid Siberian snake is selected as the device to preserve beam polarization in the Super Tau-Charm Facility according to its characteristics. The paper introduces in detail how to combine particle swarm optimization algorithm with decoupling and optical matching problem of solenoid snake to design it quickly and optimally, and presents the design results. The results show that the optimization design of solenoid snake based on particle swarm optimization algorithm is effective and efficient.
-
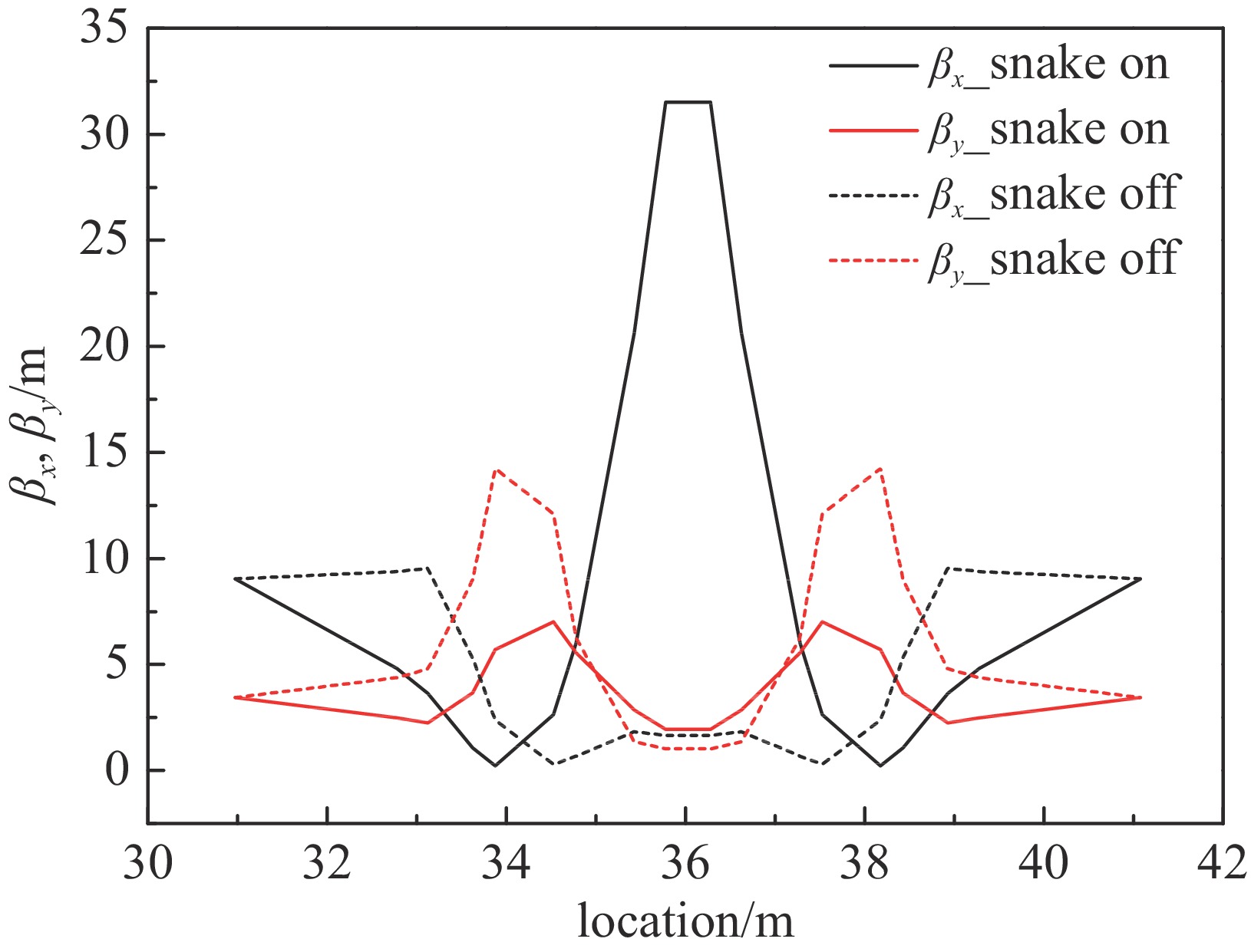
表 1 ±I螺线管蛇装置主要设计参数
Table 1. Main design parameters of ±I solenoid snake
solenoid ks /m−1 solenoid L/m K1/m−2 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 snake on 0.8722 1.8×2 2.38494523 − 1.78215169 0.12879834 2.08811998 snake off 0 1.8×2 2.24210204 − 2.69629201 2.93748997 0.07303464 -
[1] Raimondi P. Status on super-b effort[C]//3rd Workshop on Super Flavor Factory based on Linear Collider Technology (Super B III). 2006. [2] Zobov M, Alesini D, Biagini M E, et al. Test of “crab-waist” collisions at the DAΦNE Φ factory[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104: 174801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.174801 [3] Anashin V V, Anisenkov A V, Aulchenko V M, et al. Super charm-tau factory conceptual design report part two (collider, injector)[R]. Novosibirsk, Russia: BINP SB RAS, 2018. [4] Biagini M E, Boni R, Boscolo M, et al. Tau/Charm factory accelerator report[R]. Frascati: INFN, 2013. [5] Zhao Zhengguo. Introduction to future high intensity collider @ 2-7 GeV in China[C]//Workshop on Physics at Future High Intensity Collider @ 2-7GeV in China. 2015. [6] 黄光顺, 李澄, 李海波, 等. 2~7GeV高亮度正负电子对撞机的物理研究[J]. 科学通报, 2017, 62(12):1226-1232 doi: 10.1360/N972016-00398Huang Guangshun, Li Cheng, Li Haibo, et al. Physics on the high intensive electron position accelerator at 2~7 GeV[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(12): 1226-1232 doi: 10.1360/N972016-00398 [7] Luo Qing, Xu Derong. Progress on preliminary conceptual study of HIEPA, a super Tau-Charm factory in China[C]//9th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2018: 422-424. [8] Lee S Y. Spin dynamics and snakes in synchrotrons[M]. River Edge: World Scientific Press, 1997. [9] Mane S R, Shatunov Y M, Yokoya K. Spin-polarized charged particle beams in high-energy accelerators[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2005, 68(9): 1997-2265. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/68/9/R01 [10] Derbenev Y S, Kondratenko A M, Serednyakov S I, et al. Radiative polarization: obtaining, control, using[J]. Particle Accelerators, 1978, 8: 115-126. [11] Mane S R, Shatunov Y M, Yokoya K. Siberian Snakes in high-energy accelerators[J]. Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics, 2005, 31(9): R151-R209. doi: 10.1088/0954-3899/31/9/R01 [12] Kondratenko A M, Kovalenko A D, Kondratenko M A, et al. Comparison of solenoid, helix and dipole Siberian snake in the NICA collider[C]//Joint Institute for Nuclear Research XV Workshop on High Energy Spin Physics. 2013. [13] Thomas L H. The motion of the spinning electron[J]. Nature, 1926, 117: 514. [14] Bargmann V, Michel L, Telegdi V L. Precession of the polarization of particles moving in a homogeneous electromagnetic field[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1959, 2(10): 435-436. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.2.435 [15] Zhelents A A, Litvinenko V N. On the compensation of solenoid field effects by quadrupole lenses[R]. DESY L-TRANS-289, 1984: 1-8. [16] Iselin F C. The MAD program (methodical accelerator design) version 8.13 physical methods manual[M]. Geneva: Eurpean Organization for Nuclear Research, 1994. [17] Liujckx G, Van Amersfoort P W, Boer-Rookhuizen H, et al. Polarized electrons in the AmPS storage ring[C]//Proceedings of the 1997 Particle Accelerator Conference. 1997: 1063-1065. [18] Zwart T, Ivanov P, Shatunov Y, et al. A spin control system for the south hall ring at the bates linear accelerator center[C]//Proceedings of the 1995 Particle Accelerator Conference. 1995: 600-602. [19] Koop I A, Otboev A V, Shatunov P Y, et al. Spin transparent Siberian snake and spin rotator with solenoids[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2007, 915(1): 948-954. [20] Kennedy J, Eberhart R C. Particle swarm optimization[C]//IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. 1995: 1942-1948. [21] Zhang Tong, Huang Xiaobiao. Numerical optimization of a low emittance lattice cell[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2019, 923: 55-63. [22] Jiao Yi, Xu Gang. Optimizing the lattice design of a diffraction-limited storage ring with a rational combination of particle swarm and genetic algorithms[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2017, 41: 027001. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/41/2/027001 [23] Lan Jieqin, Luo Qing, Zhang Chun, et al. Design of beam optics for a super tau-charm factory[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2021, 16: T07001. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/16/07/T07001 -




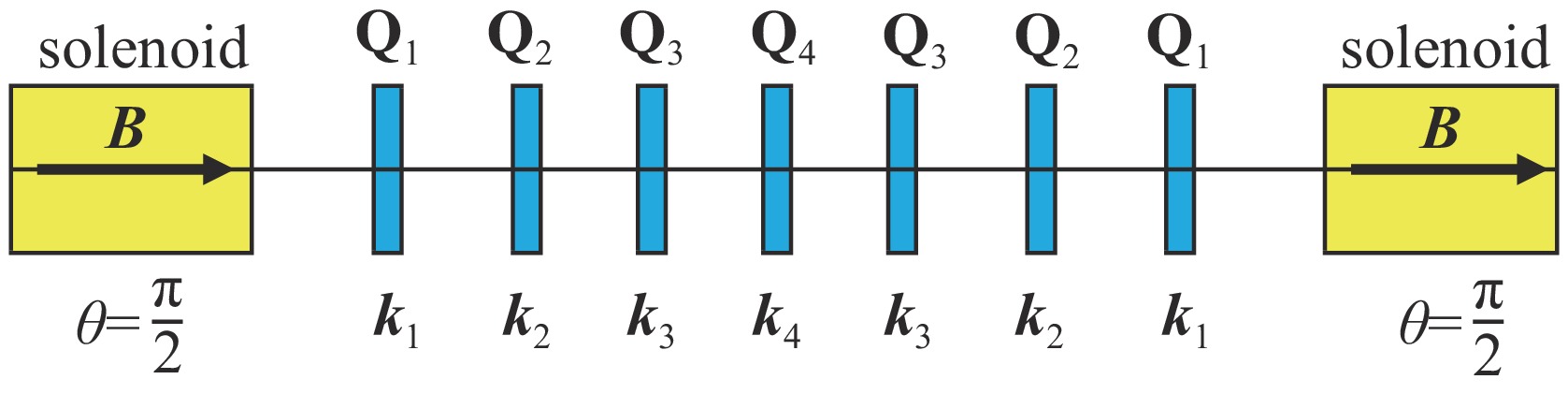
 下载:
下载: