Analysis of the influence of key parameters of step-frequency radar on false alarm signal
-
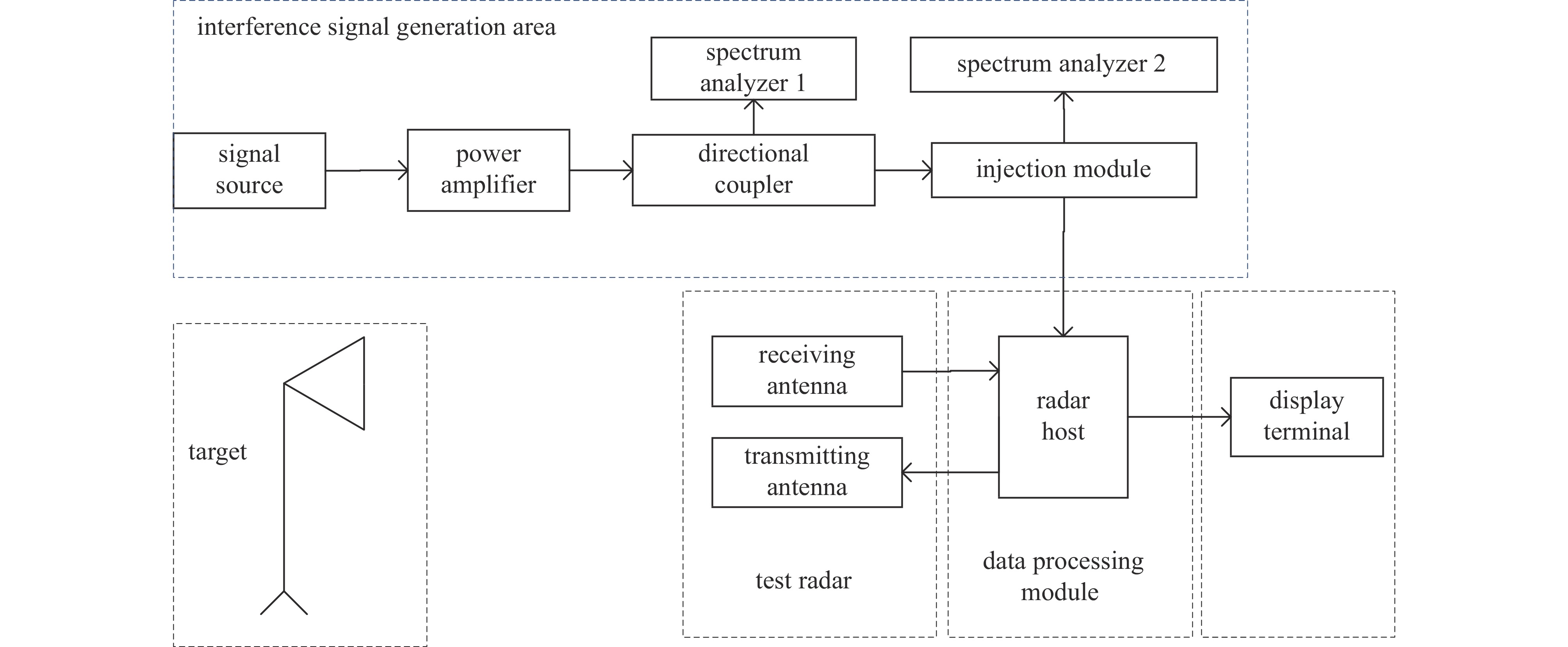
摘要: 为掌握雷达装备关键参数对虚警信号的影响规律,揭示虚警信号产生的本质原因,针对雷达装备在复杂电磁干扰中出现的多虚警信号问题,以某型步进频雷达为受试对象,理论阐明虚警干扰的作用机理和虚警目标的成像特征。理论与试验测定相结合,选取单频连续波为电磁干扰源,采用注入等效替代电磁辐射的试验方法,总结归纳雷达关键参数跳频间隔和频率步进对虚警信号影响规律。结果表明:受试雷达在单频电磁干扰作用下会产生能量较集中的虚警信号;受试雷达频率步进选取10 kHz、跳频时间0.05 ms时,虚警电平随干扰频偏的变化规律较稳定,信号幅度损失较小,该参数取值可作为控制参数的最优取值,依据该结果能够为后续开展雷达装备在多频电磁环境下的试验评估提供技术支撑。Abstract: Aiming at the problem of multiple false alarm signals of radar equipment in complex electromagnetic interference, in order to get the influence law of key parameters of radar equipment on false alarm signals, and to reveal the essential causes of false alarm signals, taking a type of stepper frequency ranging radar as the test object, this paper theoretically explains the mechanism of false alarm interference and the imaging characteristics of false alarm targets. Combining theoretical and experimental measurements, single-frequency continuous wave is selected as the source of electromagnetic interference, and the test method of injecting equivalent alternative electromagnetic radiation is adopted to summarize and generalize the influence of the critical radar parameters including frequency hopping interval and stepping frequency on the false alarm signal. The results show that the single-frequency electromagnetic interference of the test radar generates false alarm signal. When the frequency stepping of the tested radar is selected as 10 kHz and the frequency hopping time is 0.05 ms, the variation of false alarm level with interference frequency offset is relatively stable, and the signal amplitude loss is relatively small. The values can be used as the optimal control parameter values, and on this basis, it can provide technical support for subsequent experimental evaluation of radar equipment in multi frequency electromagnetic environments.
-
表 1 不同干扰强度下虚警信号测试数据
Table 1. Test data of false alarm signal under different interference strengths
U1/dBmV R1/m U2/dBmV R2/m E1=6 dBV/m E2=17.5 dBV/m 19.12 4506.0 20.70 4586.0 19.10 3330.0 20.80 2756.0 19.13 2769.0 20.73 3580.0 19.12 1384.0 20.68 2860.0 19.13 633.7 20.73 932.9 19.12 3256.0 20.70 3456.0 19.10 3344.0 20.66 3243.0 19.12 1819.0 20.70 2016.0 19.13 783.7 20.71 689.3 19.00 1123.0 20.68 4586.0 表 2 虚警信号测试数据 (E1=20.6 dBV/m)
Table 2. False alarm signal test data (E1=20.6 dBV/m)
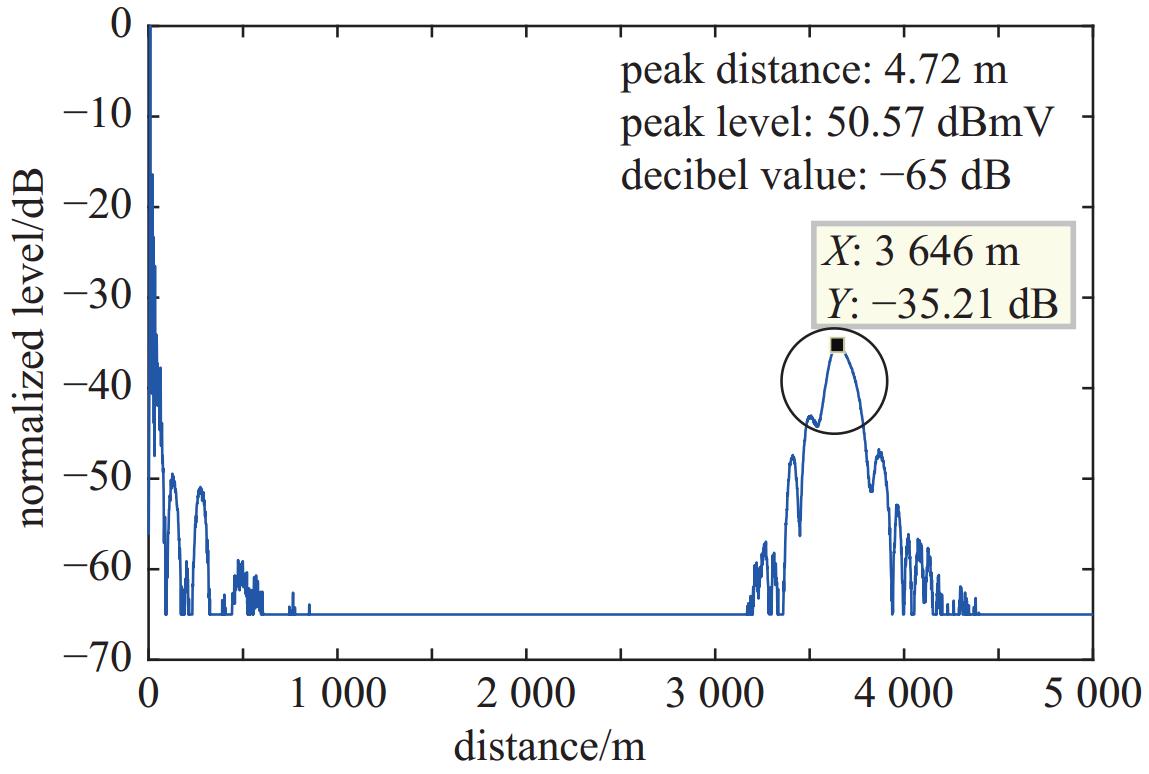
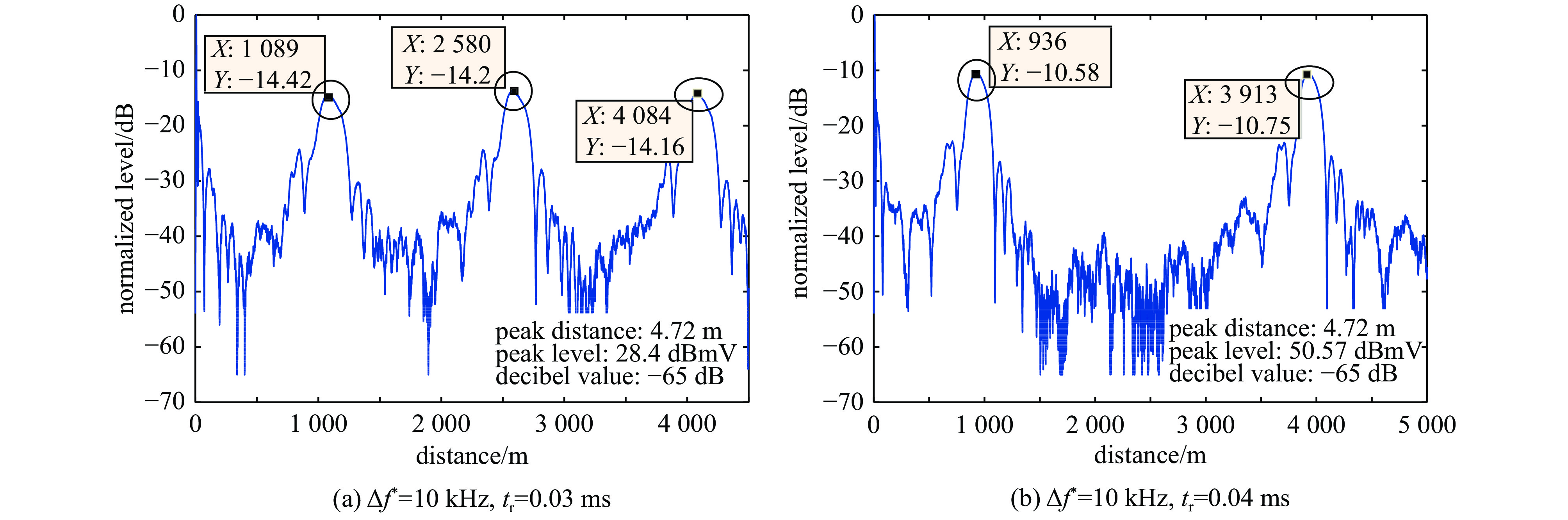
tr/ms n' Um/dBmV R/m ΔR 0.05 1 24.67 2077.0 — 0.04 4 18.5 419.2 ΔR1= 1519.8 m18.5 1939.0 ΔR2= 1517.0 m18.3 3456.0 ΔR3= 1490.0 m18.4 4946.0 ΔR≈ 1508.0 m0.03 3 19.2 1364.0 ΔR1= 1504.0 m19.2 2868.0 ΔR2= 1518.0 m19.2 4386.0 ΔR≈ 1511.0 m0.02 2 19.6 1155.0 ΔR≈ 1502.0 m19.5 2657.0 0.01 1 17.7 965.1 — 表 3 虚警信号测试数据(E2=32.6 dBV/m)
Table 3. False alarm signal test data (E2=32.6 dBV/m)
tr/ms n' Um/dBmV R/m ΔR 0.05 1 24.8 2033.0 — 0.04 4 18.6 242.9 ΔR1= 1499.1 m 18.6 1742.0 ΔR2= 1503.0 m 18.7 3245.0 ΔR3= 1494.0 m 18.6 4739.0 ΔR≈ 1498.7 m 0.03 3 19.2 713.6 ΔR1= 1496.4 m 19.3 2210.0 ΔR2= 1514.0 m19.2 3724.0 ΔR≈ 1510.2 m0.02 2 19.4 1402.0 ΔR≈ 1501.0 m19.5 2903.0 0.01 1 17.7 553.4 — 表 4 虚警信号测试数据(Δf2=40 MHz)
Table 4. False alarm signal test data (Δf2=40 MHz)
tr/ms n' Um/dBmV R/m ΔR 0.05 1 21.23 1983.0 — 0.04 4 14.6 500.9 ΔR1= 1498.1 m 14.8 1999.0 ΔR2= 1503.0 m 14.9 3502.0 ΔR3= 1495.0 m 14.6 4997.0 ΔR≈ 1498.7 m 0.03 3 14.8 609.6 ΔR1= 1493.7 m 15.0 2103.0 ΔR2= 1497.0 m 15.0 3600.0 ΔR≈ 1495.4 m 0.02 2 15.0 383.9 ΔR≈ 1504.0 m 15.1 1888.0 0.01 1 13.2 499.4 — 注:表中ΔR1、ΔR2、ΔR3分别代表出现多虚警目标时,第n′个和第n′+1个(n′=1,2,3)之间的间隔,ΔR表示对间隔取平均。 表 5 虚警信号测试数据(Δf *=10 kHz,Δf1=0 MHz)
Table 5. False alarm signal test data (Δf *=10 kHz,Δf2=0 MHz)
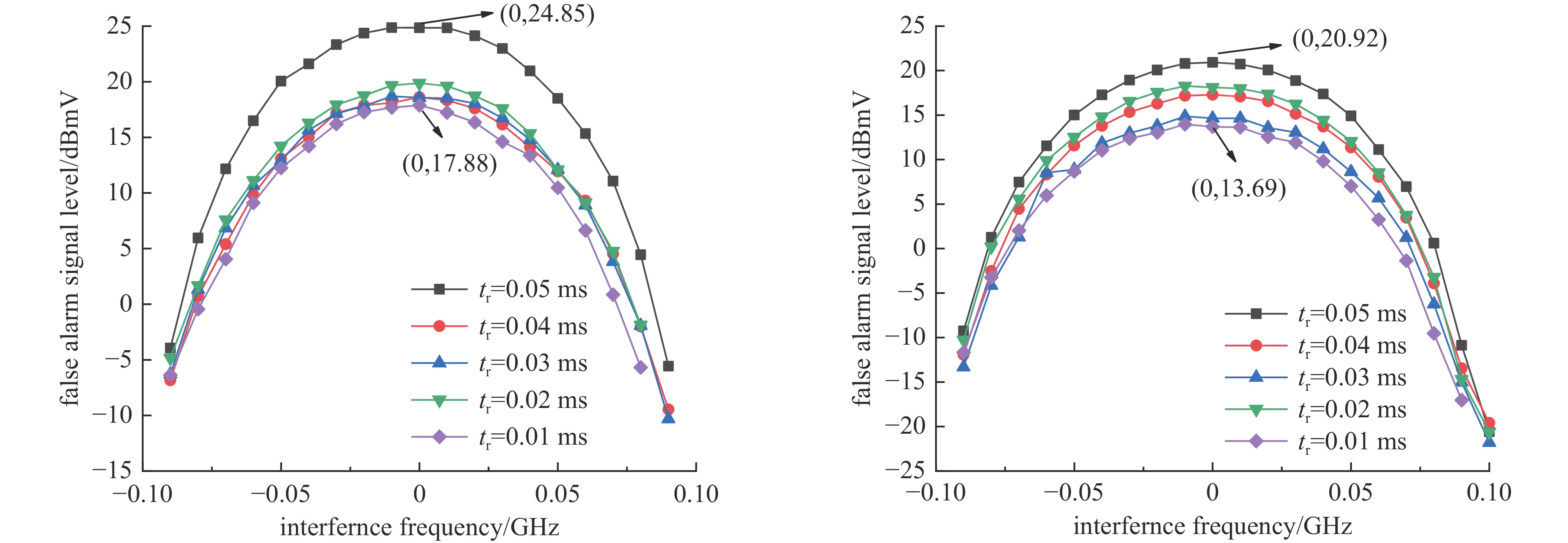
tr/ms n' ΔR/m U1/dBmV E1=17.6 dBV/m E1=20.6 dBV/m E1=26.6 dBV/m 0.05 1 — 20.7 20.9 21.1 0.04 2 3000 16.9 17.3 17.1 0.03 3 1500 14.7 14.9 14.8 0.02 1 — 18.2 18.1 18.4 0.01 1 — 13.9 13.7 13.9 表 6 虚警信号测试数据(Δf *=10 kHz,Δf2=−60 MHz)
Table 6. False alarm signal test data (Δf *=10 kHz,Δf2=−60 MHz)
tr/ms n' ΔR/m U2/dBmV E2=17.6 dBV/m E2=20.6 dBV/m E2=26.6 dBV/m 0.05 1 — 17.1 17.2 17.4 0.04 2 3000 13.6 13.7 13.8 0.03 3 1500 11.2 10.7 11.1 0.02 1 — 14.0 14.4 14.6 0.01 1 — 9.3 9.8 10.5 -
[1] 任仕召, 魏光辉, 潘晓东, 等. 典型雷达装备带内连续波辐射效应试验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32:053005 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.190471Ren Shizhao, Wei Guanghui, Pan Xiaodong, et al. Experimental study on radiation effect of in-band continuous wave on typical radar equipment[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 053005 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.190471 [2] 马立云, 王玉明, 陈亚洲. 连续波对激光雷达的电磁干扰效应[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:123012 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210385Ma Liyun, Wang Yuming, Chen Yazhou. Continuous-wave electromagnetic environment effects on laser radar[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 123012 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210385 [3] Olivier K, Cilliers J E, du Plessis M. Design and performance of wideband DRFM for radar test and evaluation[J]. Electronics Letters, 2011, 47(14): 824-825. doi: 10.1049/el.2011.0362 [4] 李文臣, 黄烽, 杨会民, 等. 雷达噪声干扰和多假目标干扰效能分析[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2013, 8(4):403-406 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2013.04.015Li Wenchen, Huang Feng, Yang Huimin, et al. Efficiency analysis of radar noise jamming and multiple false target jamming[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2013, 8(4): 403-406 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2013.04.015 [5] 李楠. 雷达干扰多假目标欺骗效果研究[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2020, 40(1):65-68Li Nan. Study on jamming effect of multiple false targets with radar[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2020, 40(1): 65-68 [6] 徐磊, 俞成龙, 陈旭. 一种基于DRFM的针对LFM雷达的自适应复合干扰技术[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2021, 44(2):18-22,60Xu Lei, Yu Chenglong, Chen Xu. An adaptive composite jamming technology to LFM radar based on DRFM[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2021, 44(2): 18-22,60 [7] Soumekh M. SAR-ECCM using phase-perturbed LFM chirp signals and DRFM repeat jammer penalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 191-205. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603414 [8] 周治宇, 饶彬, 谢晓霞. 对LFM-PC雷达的分布式合成欺骗干扰效果分析[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2020, 18(1):24-29 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2018184Zhou Zhiyu, Rao Bin, Xie Xiaoxia. Analysis of the effect on distributed synthetic deception jamming to LFM-PC radar[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2020, 18(1): 24-29 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2018184 [9] 黄天奇, 王布宏, 田继伟. 集中式组网雷达的假目标欺骗干扰优化方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(7):1484-1490 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.07.08Huang Tianqi, Wang Buhong, Tian Jiwei. False target deception jamming optimized method for centralized netted radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(7): 1484-1490 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.07.08 [10] 袁天, 罗震明, 刘晨, 等. 基于欺骗噪声复合干扰的组网雷达对抗方法[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2019, 41(6):69-74Yuan Tian, Luo Zhenming, Liu Chen, et al. Antagonistic method of deception and noise complex jamming against netted radar[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2019, 41(6): 69-74 [11] 于恒力, 张林让, 刘洁怡, 等. 一种异构组网雷达系统抗欺骗式假目标方法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2019, 48(5):706-710 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.05.007Yu Hengli, Zhang Linrang, Liu Jieyi, et al. A method against deception-false-target jamming based on isomerous netted radar[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019, 48(5): 706-710 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.05.007 [12] GJB 403.7-87, 舰载雷达通用技术条件电磁兼容性要求和测试方法[S]GJB 403.7-87, General technical specification of shipborne radars electromagnetic compatibility requirements and measurements[S] [13] GJB 8312-2015, 舰船雷达对抗系统通用规范[S]GJB 8312-2015, General specification for radar electronic warfare system of shipborne[S] [14] 赵宏泽, 魏光辉, 杜雪, 等. 雷达装备二阶互调伪信号干扰效应预测模型[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35:083001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230089Zhao Hongze, Wei Guanghui, Du Xue, et al. Prediction model of second-order intermodulation pseudo-signal interference effect for radar equipment[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 083001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230089 [15] Du Xue, Wei Guanghui, Zhao Hongze, et al. Research on continuous wave electromagnetic effect in swept frequency radar[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 4862451. [16] 毛二可, 龙腾, 韩月秋. 频率步进雷达数字信号处理[J]. 航空学报, 2001, 22(s1):16-25 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2001.z1.003Mao Erke, Long Teng, Han Yueqiu. Digital signal processing of stepped frequency radar[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2001, 22(s1): 16-25 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2001.z1.003 [17] 龙腾, 毛二可, 何佩琨. 调频步进雷达信号分析与处理[J]. 电子学报, 1998, 26(12):84-88 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1998.12.019Long Teng, Mao Erke, He Peikun. Analysis and processing of modulated frequency stepped radar signal[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1998, 26(12): 84-88 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1998.12.019 [18] 龙腾, 李眈, 吴琼之. 频率步进雷达参数设计与目标抽取算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2001, 23(6):26-31 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2001.06.008Long Teng, Li Dan, Wu Qiongzhi. Design methods for step frequency waveform and the target pick-up algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2001, 23(6): 26-31 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2001.06.008 [19] 周国富, 毛二可. 频率调制对雷达线性调频脉冲压缩性能的影响[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2008, 28(3):256-259Zhou Guofu, Mao Erke. Effect of frequency modulation on the performance of pulse compression in radar linear frequency modulation[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2008, 28(3): 256-259 [20] 贺志毅, 郝祖全, 朱淮城. 步进跳频信号跳频间隔的选取分析[J]. 现代雷达, 2003, 25(8):23-25,36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2003.08.008He Zhiyi, Hao Zuquan, Zhu Huaicheng. A study on the selection of stepped-frequency interval[J]. Modern Radar, 2003, 25(8): 23-25,36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2003.08.008 [21] Du Xue, Wei Guanghui, Zhao Kai, et al. Research on dual-frequency electromagnetic false alarm interference effect of a typical radar[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(9): 3574. doi: 10.3390/s22093574 [22] GJB 8848-2016, 系统电磁环境效应试验方法[S]GJB 8848-2016, Electromagnetic environmental effects test methods for systems[S] [23] GJB 151B-2013, 军用设备和分系统电磁发射和敏感度要求与测量[S]GJB 151B-2013, Electromagnetic emission and susceptibility requirements and measurements for military equipment and subsystems[S] -




 下载:
下载: