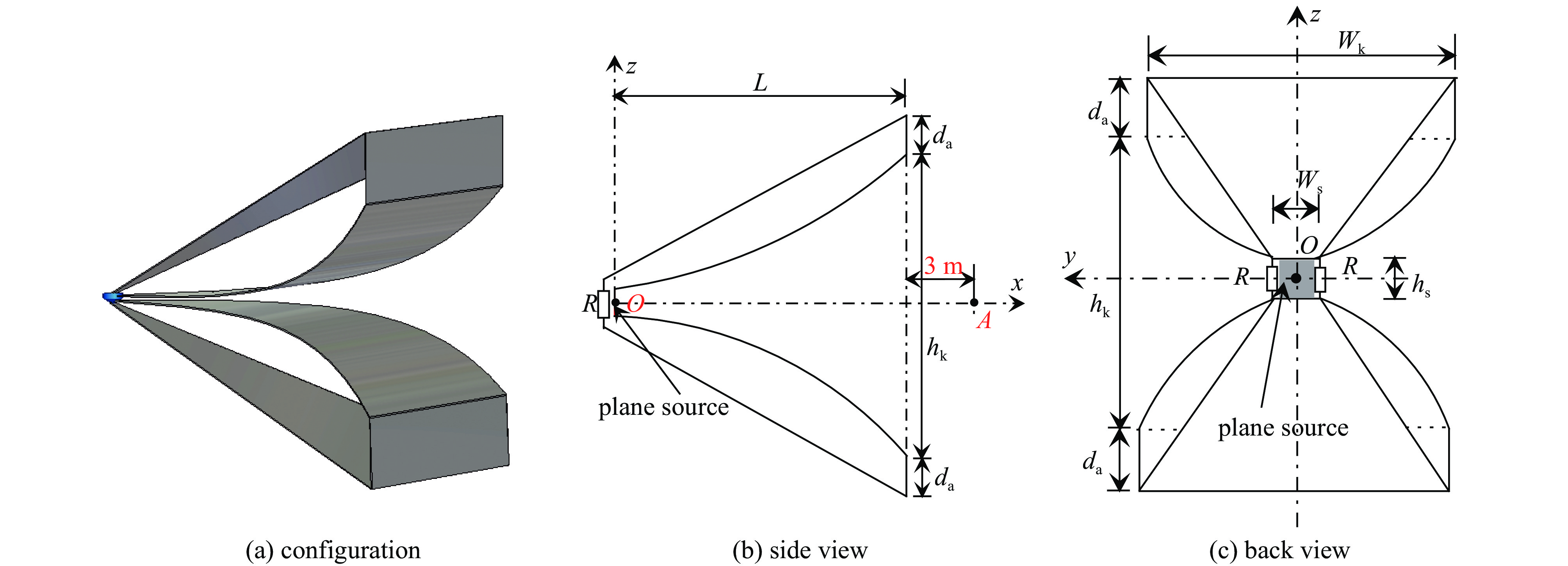
Simulation and optimization of novel movable TEM horn radiating-wave simulator
-
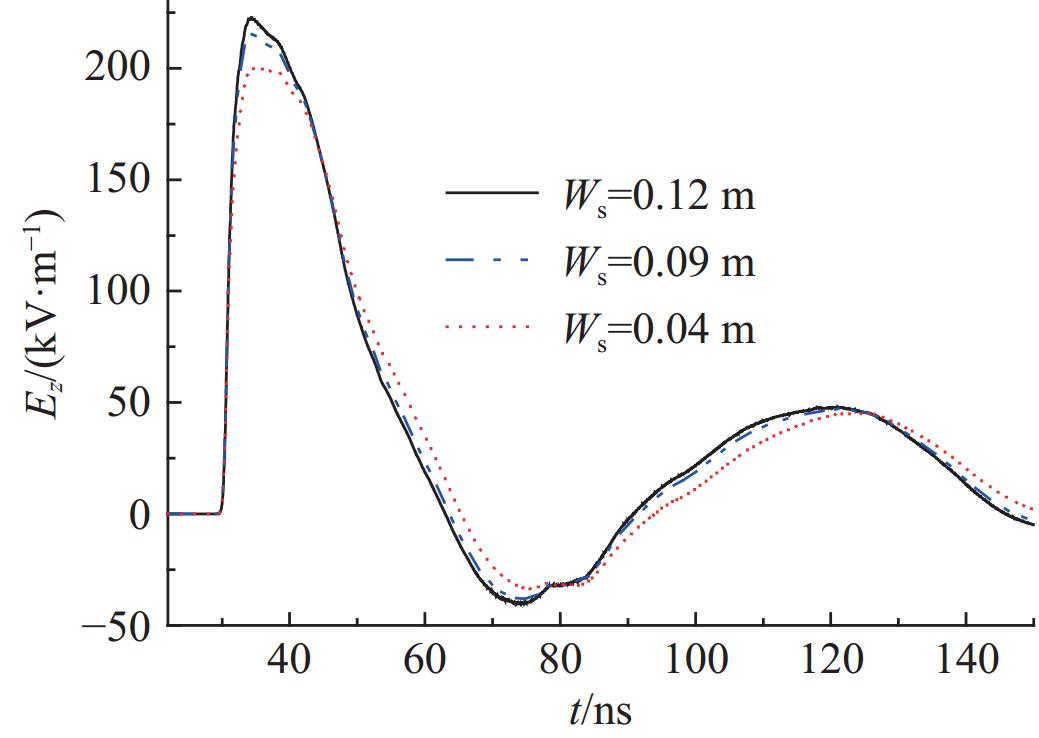
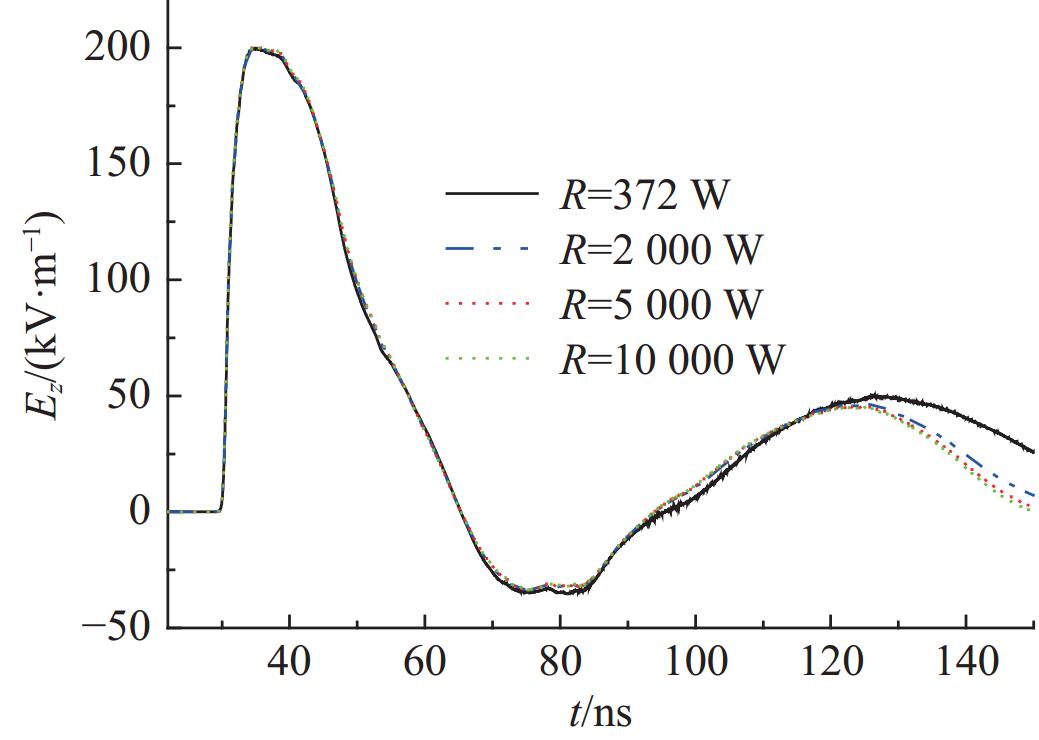
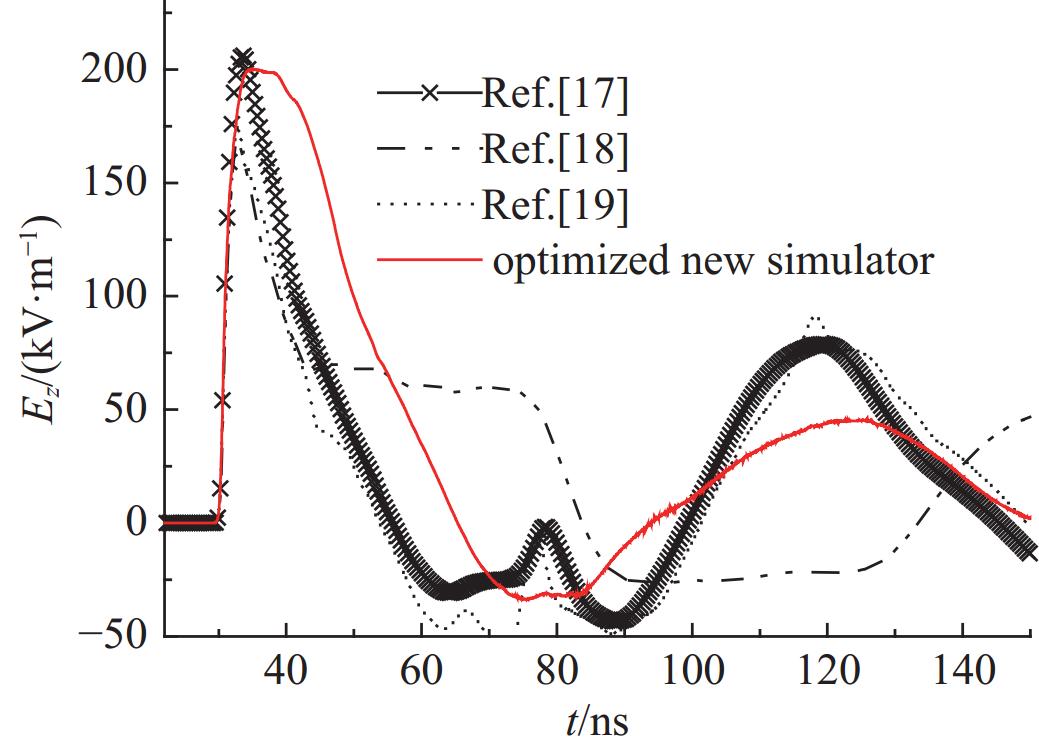
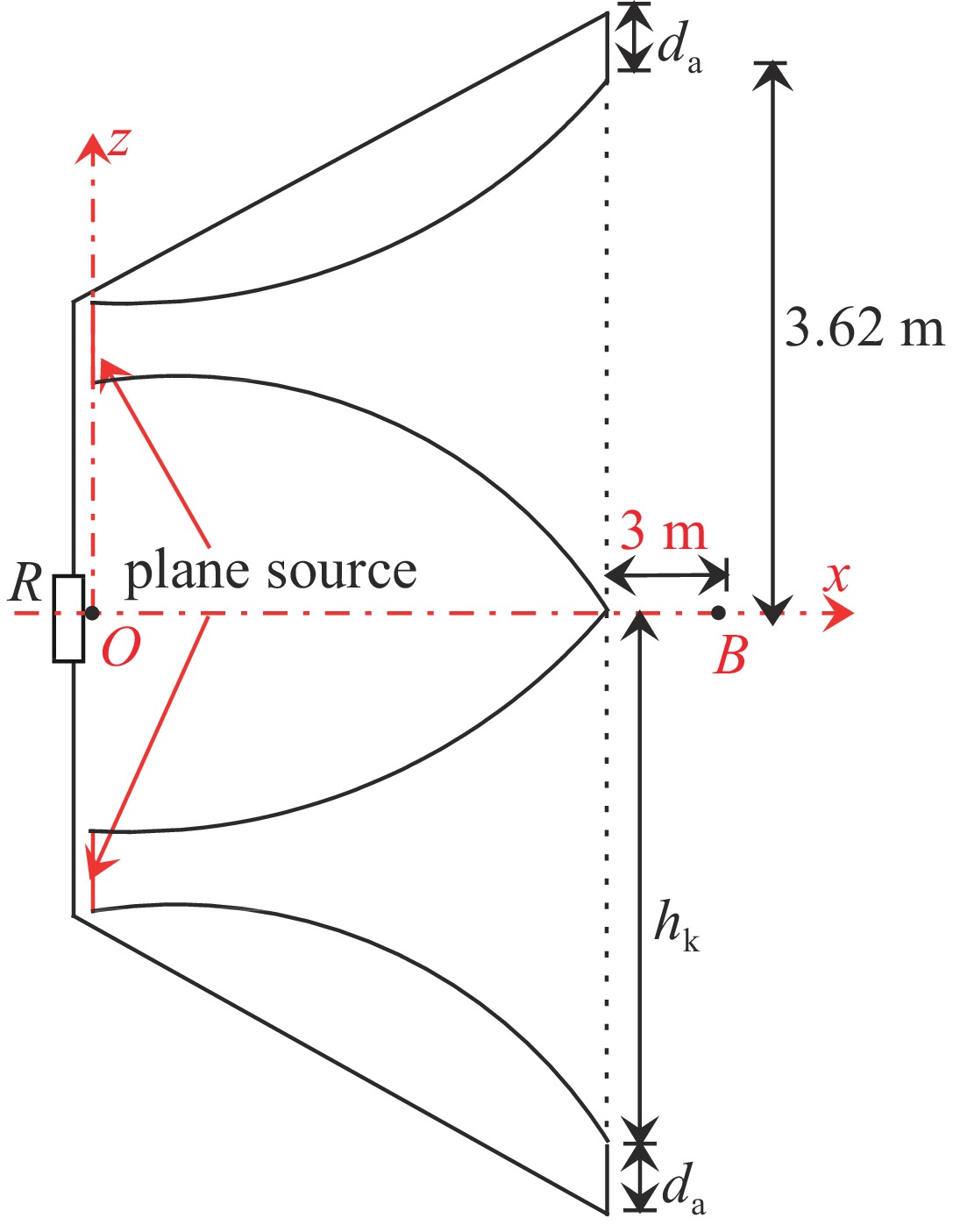
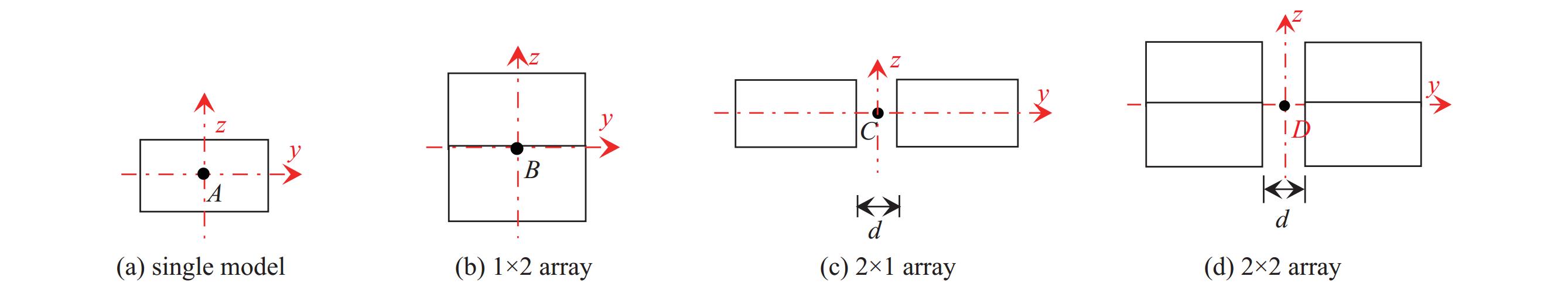
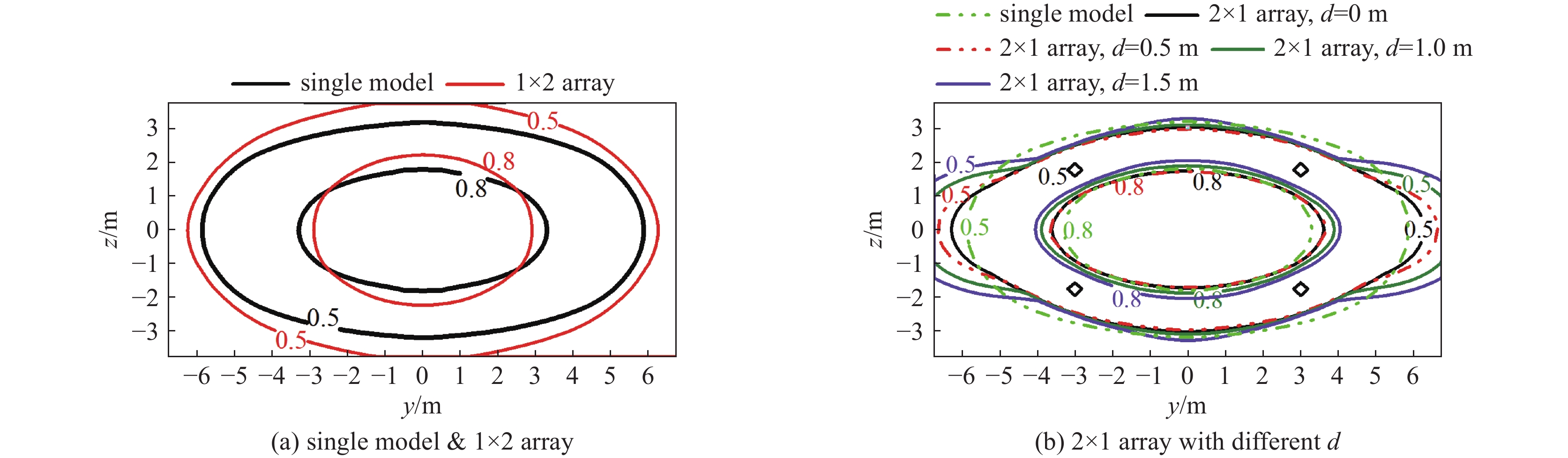
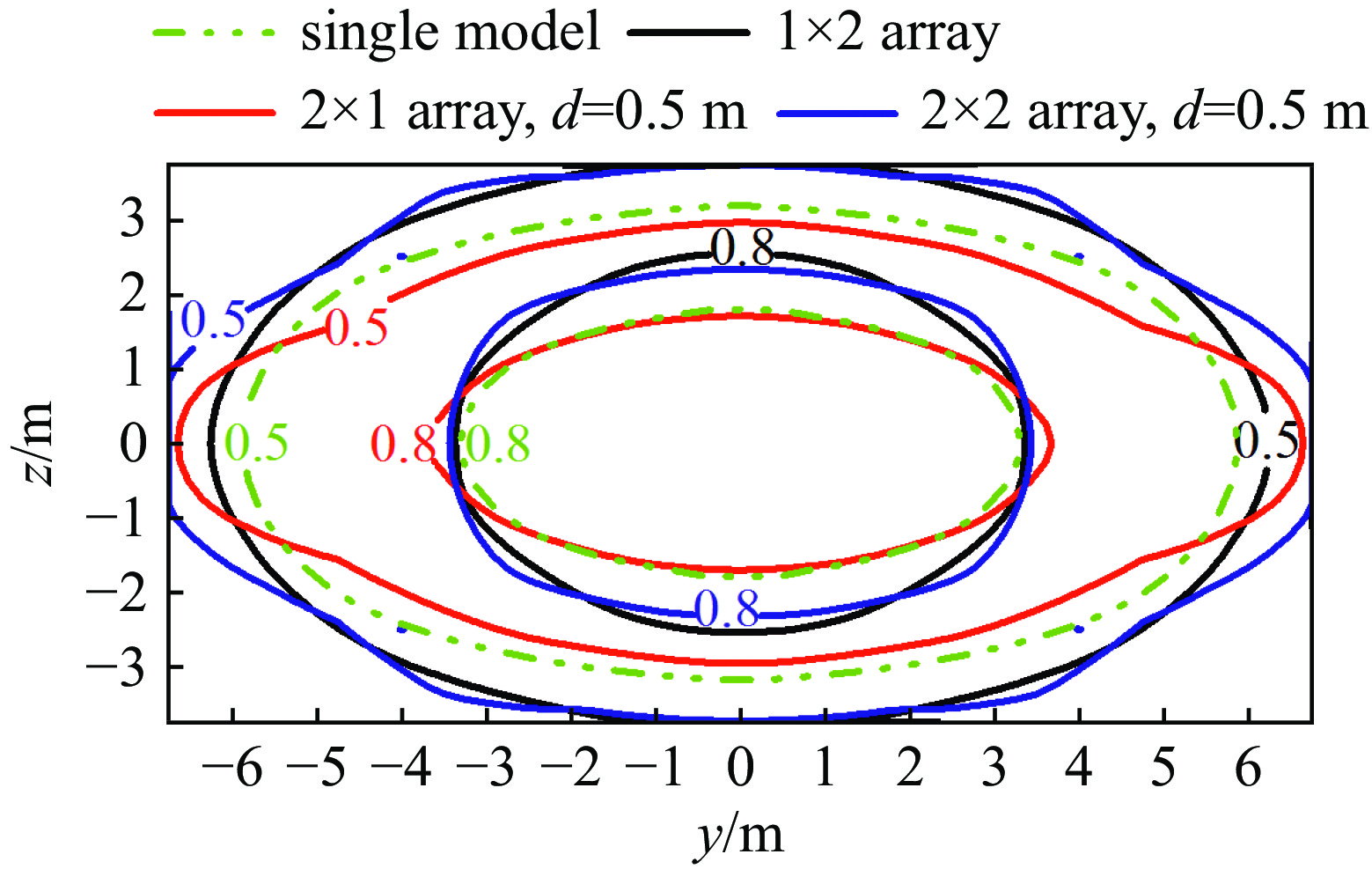
摘要: 为改善基于TEM喇叭的辐射波模拟器的低频辐射特性从而展宽其辐射近场半高宽,首次提出了在指数型TEM喇叭上/下两个极板的端口加上2个金属直板、并通过倾斜金属板和并联电阻相连的新型可移动模拟器的设计方案。基于FDTD方法模拟分析了该新型模拟器的特性参数对其近场辐射性能的影响,并给出了优化后的模拟器及其阵列的辐射特性。计算结果表明:尺寸为6 m×6 m×6.24 m的优化后的新型模拟器在距离口面3 m的中心位置的辐射近场脉宽能达到18.95 ns,而达到相同低频辐射性能的常规模拟器尺寸为9 m×12 m×6.8 m。且与常规模拟器相比,优化后的模拟器的场峰值更大。与前人的研究相比,优化后的模拟器场在保持高峰值的同时,时域波形后延震荡的幅度与主峰的比值明显减小。优化后的模拟器2×2阵列模型的测试平面中心点场峰值最大,且在测试平面上满足6 dB均匀性要求的有效测试区最大;有效测试区在横向上范围最大的是2×2阵列模型,其次是2×1阵列模型;在纵向上范围最大的是2×2阵列模型及1×2阵列模型。Abstract: To improve the low frequency radiation characteristics of the radiating-wave simulator based on transverse electromagnetic (TEM) horn, a novel movable simulator made up of exponential-type TEM horn, two vertical perfect electric conductor (PEC) plates at its aperture, two sloping PEC plates and parallel resistance is designed firstly. The effect of different exponential tapered rates, the height of the two vertical PEC plates, the width of the source port and the parallel resistance at the end of the two sloping PEC plates to the near-field radiation performance of the novel simulator is simulated and optimized by finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method. The radiation characteristics of the optimized novel simulator and its arrays is also given. The calculation results show that, the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the electric field at the testing point which is 3 m away from the optimized novel simulator’s aperture center reaches 18.95 ns, and the optimized novel simulator’s sizes are 6 m×6 m×6.24 m while those of the normal simulator must be 9 m×12 m×6.8 m to get the same low-frequency radiation performance as that of the optimized novel simulator. And higher peak-value of the electric field at the testing point of the optimized novel simulator can be got compared with the normal simulator. In addition, the ratio of the delayed oscillation’s amplitude of the electric field in time-domain at the testing point of the optimized novel simulator to its peak-value is significantly reduced compared with that of the previous studies, while the peak-value of the testing point of the optimized novel simulator keeps high. The electric field’s peak value at the center point in the testing plane of the optimized novel simulator’s 2×2 array model is the largest, and the effective region meeting the requirement of field 6dB uniformity on the testing plane of 2×2 array model has the largest domain; The effective region on the 2×2 array model’s testing plane has the largest horizontal range, followed by 2×1 array model; The effective regions on the testing planes of 2×2 array model and 1×2 array model have the largest vertical range.
-
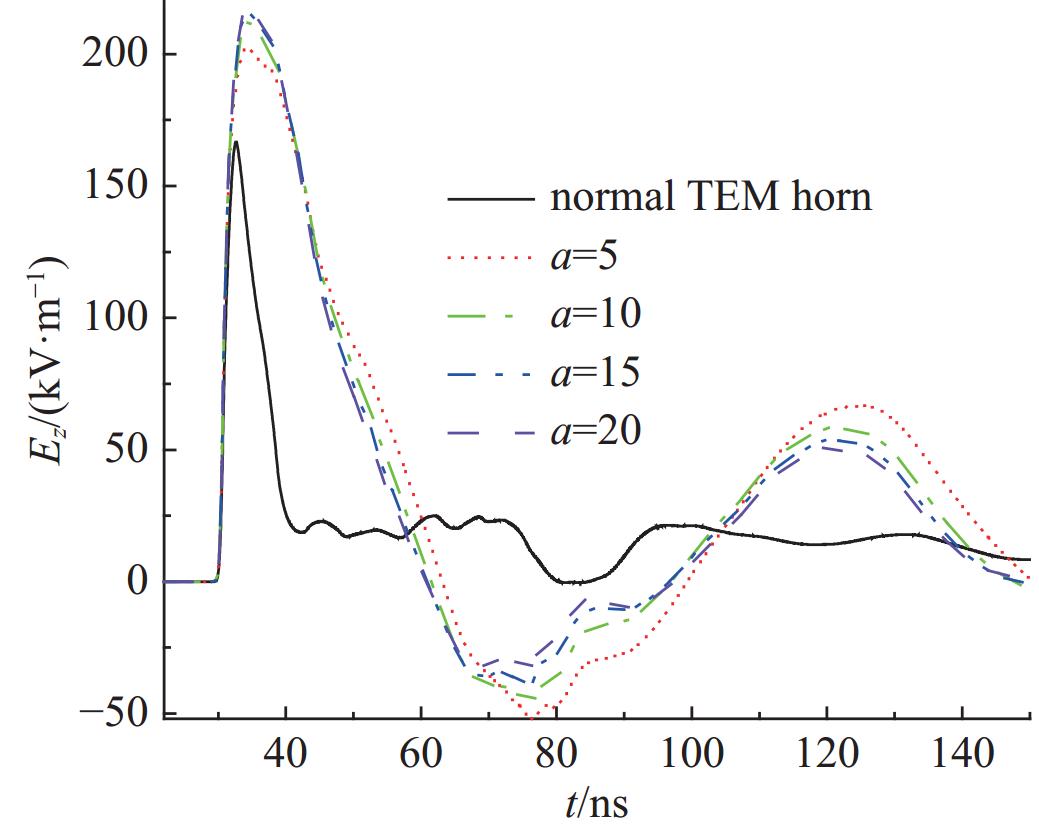
表 1 指数渐变率α不同时测点A的时域场的峰值、半高宽和上升沿
Table 1. Peak-value, rise-time and FWHM of Ez at point A with different α
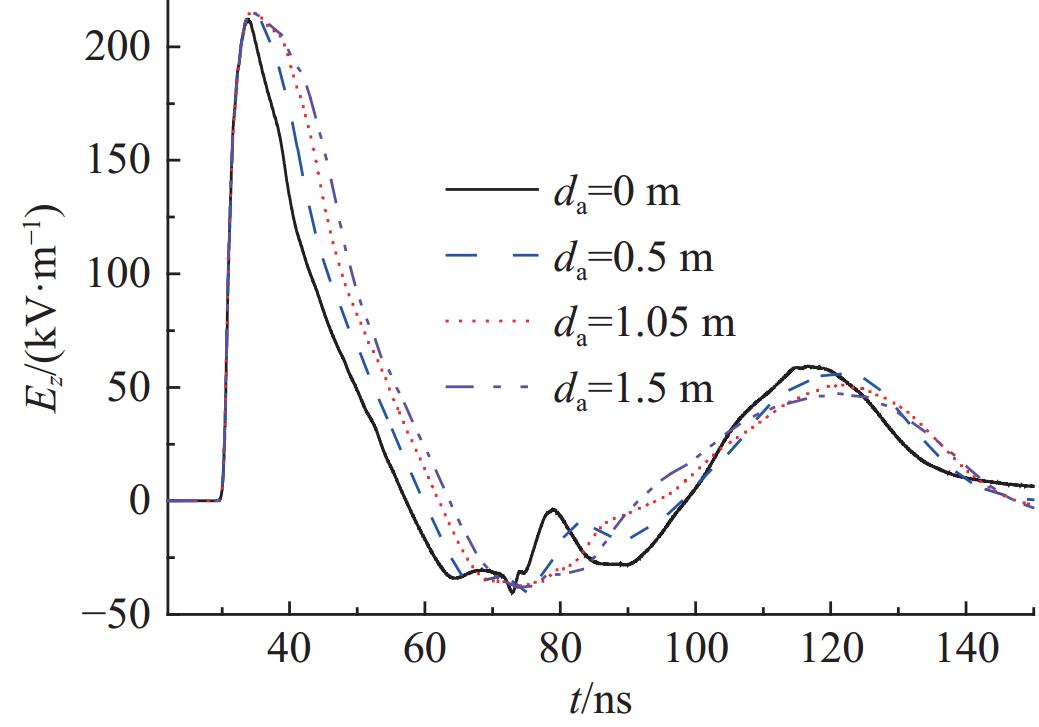
configuration peak-value/(kV·m−1) rise-time/ns FWHM/ns normal TEM 166.67 1.62 6.04 Ref.[15] 168.61 1.64 9.65 novel simulator α=5 202.60 2.08 16.83 α=10 212.04 2.29 15.51 α=15 215.90 2.29 14.81 α=20 218.22 2.28 14.29 表 2 新型模拟器开口处加载金属板的高度da不同时测点A的时域场的峰值、半高宽和上升沿
Table 2. Peak-value, rise-time and FWHM of Ez at point A with different da
da /m peak-value/(kV·m−1) rise-time/ns FWHM/ns 0 212.32 2.10 11.35 0.5 215.78 2.29 13.78 0.75 215.90 2.29 14.81 1.05 215.74 2.30 15.95 1.5 215.51 2.30 17.55 2.0 215.34 2.28 19.35 表 3 优化后的新型模拟器与其他基于TEM喇叭的模拟器测点A的时域场的峰值、半高宽和上升沿的对比
Table 3. Peak-value, rise-time and FWHM of Ez at A point of optimized novel simulator with other simulators
-
[1] 朱湘琴, 王建国, 陈维青, 等. 分布式负载平行板有界波电磁脉冲模拟器的模拟分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:035001 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20142603.35001Zhu Xiangqin, Wang Jianguo, Chen Weiqing, et al. Simulation for flat-plate bounded wave electromagnetic pulse simulator with distributed terminator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 035001 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20142603.35001 [2] 朱湘琴, 王建国, 陈维青, 等. 集总负载平行板有界波电磁脉冲模拟器的并行时域有限差分模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(9):2334-2340 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132509.2334Zhu Xiangqin, Wang Jianguo, Chen Weiqing, et al. Parallelized FDTD Simulation for flat-plate bounded wave EMP simulator with lumped teminator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(9): 2334-2340 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132509.2334 [3] 国海广, 魏光辉, 范丽思, 等. 快沿电磁脉冲模拟器内部垂直极化场分布仿真研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2009, 21(3):403-406Guo Haiguang, Wei Guanghui, Fan Lisi, et al. Simulation study on vertical field distribution of EMP simulator with fast risetime[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2009, 21(3): 403-406 [4] Klaasen J J A. An efficient method for the performance analysis of bounded-wave nuclear EMP simulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 1993, 35(3): 329-338. doi: 10.1109/15.277307 [5] 孙凤杰, 罗学金, 李小伟, 等. 基于时域有限差分法的亚纳秒有界波模拟器数值模拟及分析[J]. 电子工程师, 2008, 34(7):34-37Sun Fengjie, Luo Xuejin, Li Xiaowei, et al. Numerical analysis and design for subnanosecond EMP simulator based on finite difference-time domain method[J]. Electronic Engineer, 2008, 34(7): 34-37 [6] 孙凤杰, 罗学金, 李小伟, 等. 亚纳秒前沿有界波模拟器传输线设计的理论分析与实验[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2008, 20(5):811-814Sun Fengjie, Luo Xuejin, Li Xiaowei, et al. Theoretical analysis and experimental varification on design of transmission line for subnanosecond risetime EMP simulator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2008, 20(5): 811-814 [7] 李云伟, 王泽忠, 刘峰. 有界波电磁脉冲模拟器参数对传播模式的影响[J]. 高电压技术, 2007, 33(5):54-57Li Yunwei, Wang Zezhong, Liu Feng. Influence of parameters of boundary electromagnetic pulse simulator on transmitting mode[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2007, 33(5): 54-57 [8] 朱湘琴, 王建国, 蔡利兵, 等. 辐射波电磁脉冲模拟器笼形天线辐射特性的并行计算[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(6):1597-1601 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112306.1597Zhu Xiangqin, Wang Jianguo, Cai Libing, et al. Parallel computation for radiation characteristics of cage antenna of radiating-wave EMP simulator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(6): 1597-1601 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112306.1597 [9] 朱湘琴, 陈再高, 吴伟, 等. 离散电阻加载的大型垂直极化EMP辐射波模拟器的并行FDTD模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2019, 36(3):349-356Zhu Xiangqin, Chen Zaigao, Wu Wei, et al. Simulation of large vertically polarized EMP radiating wave simulator with discrete resistors using parallel FDTD method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 36(3): 349-356 [10] 田春明, 王建国, 陈雨生, 等. 基于TEM喇叭的辐射波模拟器天线的近场特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2004, 16(5):641-644Tian Chunming, Wang Jianguo, Chen Yusheng, et al. Near-field characteristics of radiating-wave simulator antenna based on TEM horn[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2004, 16(5): 641-644 [11] 王赟, 陈永光, 王庆国, 等. 辐射式核电磁脉冲模拟器TEM喇叭天线[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:1015002 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB201426.015002Wang Yun, Chen Yongguang, Wang Qingguo, et al. Analysis of TEM horn antenna for radiating-wave nuclear electromagnetic pulse simulator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 1015002 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB201426.015002 [12] 王赟, 陈永光, 王庆国, 等. 基于TEM喇叭的辐射波模拟器天线辐射性能研究[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2012, 32(9):1070-1073Wang Yun, Chen Yongguang, Wang Qingguo, et al. Research on antenna radiation performance of radiating-wave simulator antenna based on TEM[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2012, 32(9): 1070-1073 [13] 范丽思, 潘晓东, 王赟. 基于横电磁波天线的高空核电磁脉冲辐射波模拟器设计[J]. 高电压技术, 2012, 38(9):2302-2307Fan Lisi, Pan Xiaodong, Wang Yun. Design of HEMP radiating-wave simulator based on TEM horn[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2012, 38(9): 2302-2307 [14] 栾珊. 超宽带介质加载天线的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2011: 41-44Luan Shan. Research on ultra-wideband dielectric loaded antenna[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2011: 41-44 [15] 朱四桃, 易超龙, 陈昌华, 等. TEM喇叭天线脉冲辐射特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(7):1755-1758 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132507.1755Zhu Sitao, Yi Chaolong, Chen Changhua, et al. Radiation characteristics of TEM horn antenna[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(7): 1755-1758 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132507.1755 [16] Xia Jing, Kong Wa, Wang Gang. Compact UWB probe for near-field microwave target detection and imaging[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing. 2009: 201-204. [17] 葛德彪, 闫玉波. 电磁波时域有限差分方法[M]. 3版. 西安:西安电子科技大学出版社, 2011Ge Debiao, Yan Yubo. Finite-difference time-domain method for electromagnetic waves[M]. 3rd ed. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2011 [18] IEC 61000-4-25, Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)—Part 4-25: testing and measurement techniques—HEMP immunity test methods for equipment and systems[S]. -




 下载:
下载: