Simulation of harmonic lasing self-seeded free electron laser
-
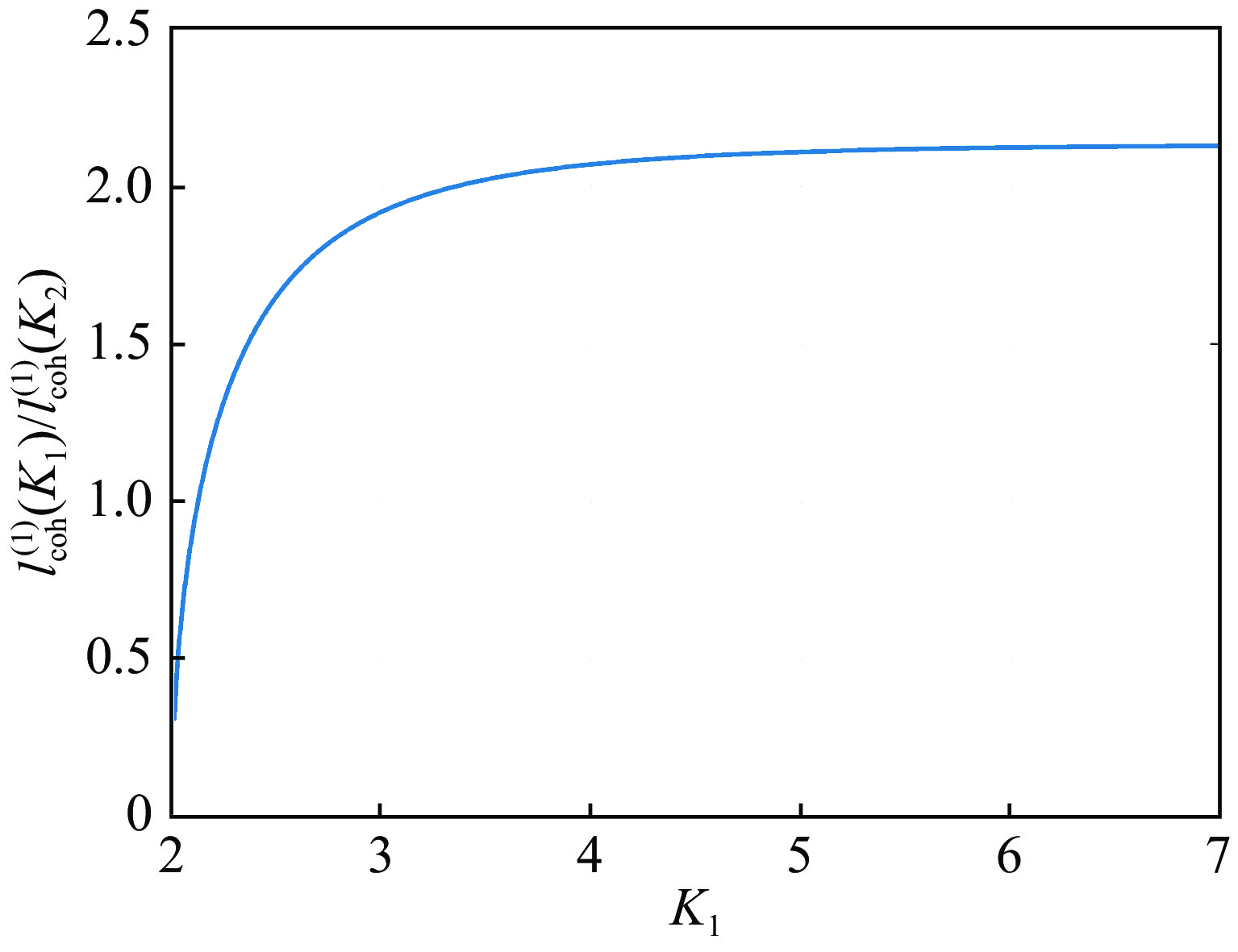
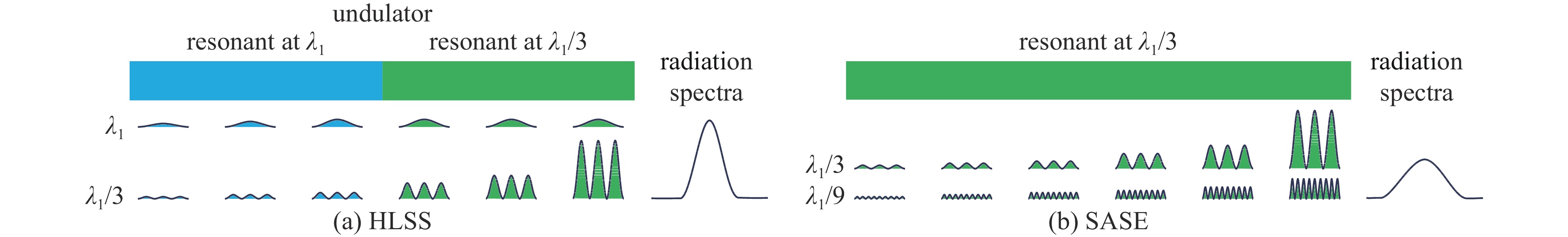
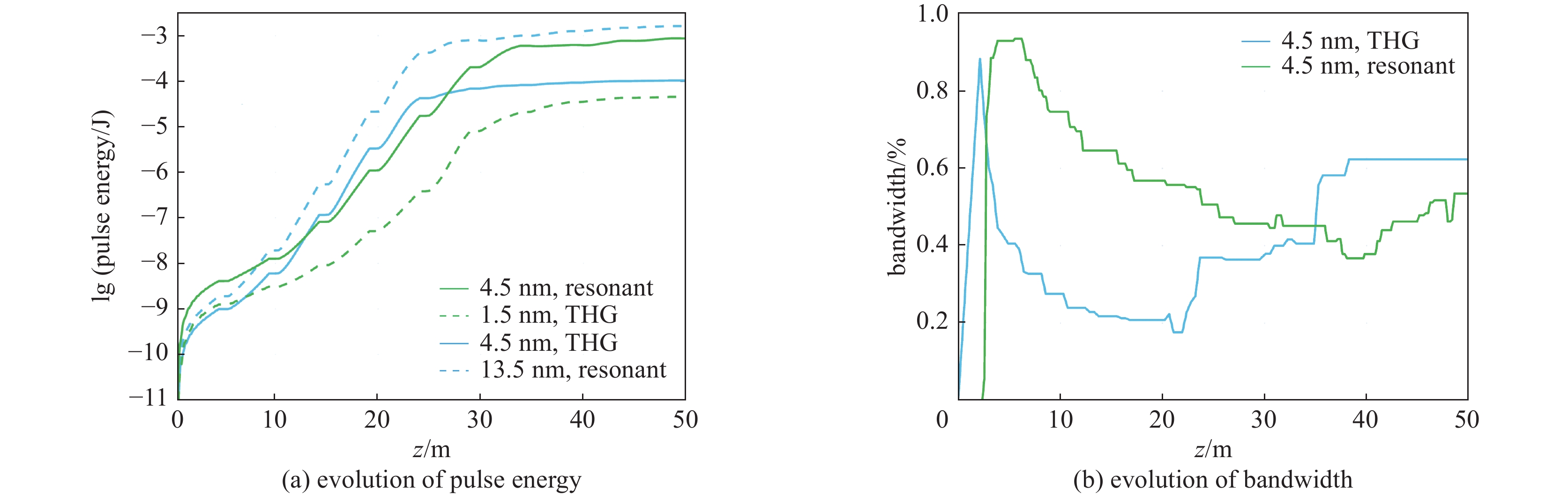
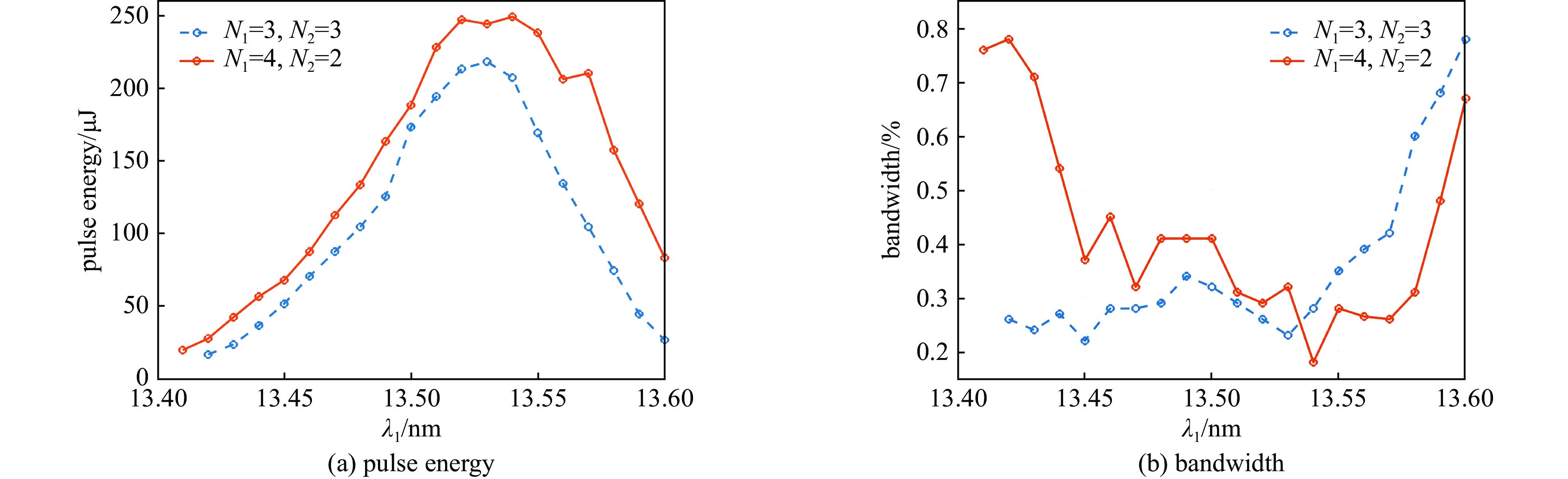
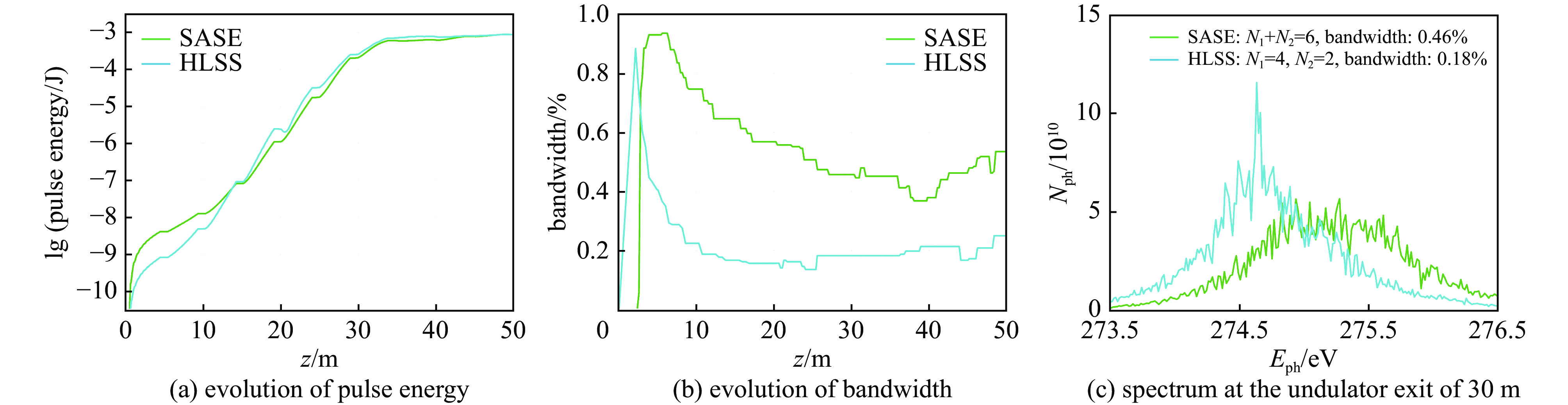
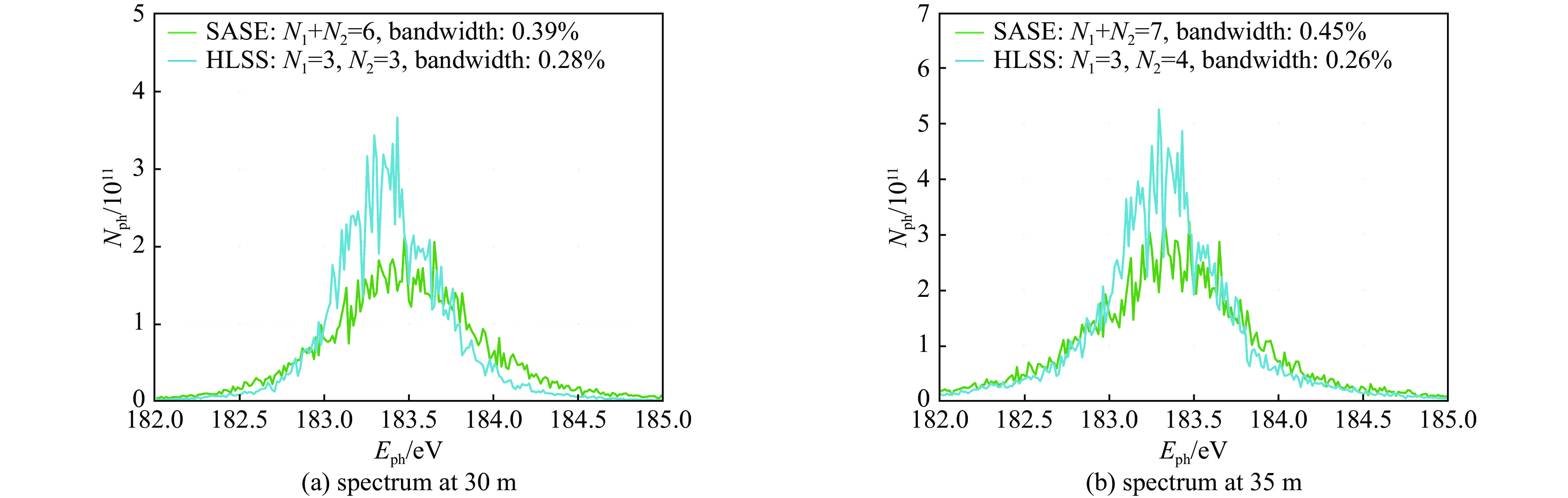
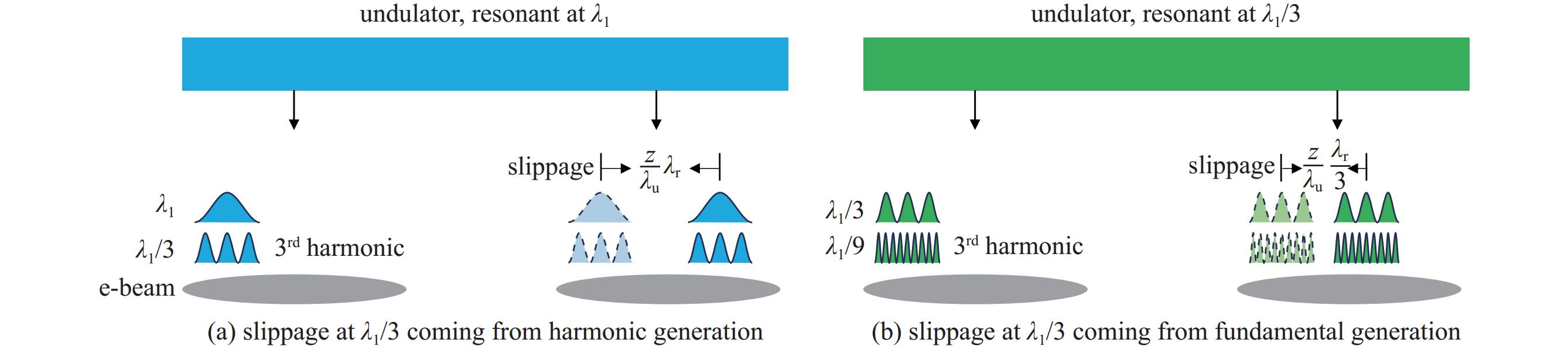
摘要: 在自由电子激光(FEL)中,谐波驱动自种子(HLSS)可以减小自放大自发辐射(SASE)机制的辐射带宽、提高X射线波段FEL的谱亮度,其原理已被FLASH、PAL、European XFEL等实验室验证。HLSS可改善SASE FEL的相干性,但同时相对SASE并没有提出新的硬件需求,因此可以很方便地应用于国内在建或运行在SASE机制的自由电子激光装置。本文对HLSS方案实现窄带宽效果的原理进行了归纳,给出了波荡器参数的定量条件;随后使用深圳中能高重复频率X射线自由电子激光的典型参数进行模拟,模拟结果表明在出光波长为4.5 nm与6.75 nm时,HLSS的带宽减小至SASE的1/2左右,同时谱亮度提高至2倍左右。Abstract: Among free electron laser (FEL) schemes, the Harmonic Lasing Self-Seeded (HLSS) scheme can reduce the radiation bandwidth of self amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) and improve the spectral brightness of FEL in X-ray band. The principle of HLSS has been verified at FLASH, PAL, European XFEL and other laboratories. The HLSS scheme can improve the coherence of a SASE FEL without additional hardware, so it can be easily applied to domestic facilities under construction or running in SASE scheme. In this paper, the principle of the HLSS scheme to achieve narrow bandwidth is summarized, and the quantitative conditions of the undulator parameters are given. Typical parameters of Shenzhen superconducting soft X-ray free electron laser are used to simulate the HLSS scheme. Simulation results show that the bandwidth in the HLSS scheme can be reduced to about 1/2 of the bandwidth in SASE, and the spectral brightness can increase to about 2 times, when the output wavelengths are 4.5 nm and 6.75 nm.
-
表 1 模拟用到的参数
Table 1. Parameters for simulation
beam energy/GeV energy spread/% current/A beam length/$ {\text{μ}}$m normalized emittance /$ {\text{μ}}$rad period/cm period number FODO length/m 2.53 0.012 800 65 0.39 4.3 93 10 -
[1] Feldhaus J, Saldin E L, Schneider J R, et al. Possible application of X-ray optical elements for reducing the spectral bandwidth of an X-ray SASE FEL[J]. Optics Communications, 1997, 140(4/6): 341-352. [2] Pellegrini C, Reiche S, Rosenzweig J, et al. Optimization of an X-ray SASE-FEL[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2001, 581(1): 221-228. [3] Feng Chao, Deng Haixiao. Review of fully coherent free-electron lasers[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2018, 29: 160. doi: 10.1007/s41365-018-0490-1 [4] Zhao Zhentang, Wang Dong, Gu Qiang, et al. SXFEL: a soft X-ray free electron laser in China[J]. Synchrotron Radiation News, 2017, 30(6): 29-33. doi: 10.1080/08940886.2017.1386997 [5] Geloni G, Saldin E, Samoylova L, et al. Coherence properties of the European XFEL[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2010, 12: 035021. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/12/3/035021 [6] Galayda J N. The LCLS-II: a high power upgrade to the LCLS[R]. Menlo Park: SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, 2018. [7] Macias I J B, Düsterer S, Ivanov R, et al. Study of temporal, spectral, arrival time and energy fluctuations of SASE FEL pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(7): 10491-10508. doi: 10.1364/OE.419977 [8] Geloni G, Kocharyan V, Saldin E. A novel self-seeding scheme for hard X-ray FELs[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2011, 58(16): 1391-1403. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2011.586473 [9] Xiang Dao, Ding Yuantao, Huang Zhirong, et al. Purified self-amplified spontaneous emission free-electron lasers with slippage-boosted filtering[J]. Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, 2013, 16: 010703. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.16.010703 [10] Wu Jiacong, Marinelli A, Pellegrini C. Generation of longitudinally coherent ultra high power X-ray FEL pulses by phase and amplitude mixing[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Free Electron Laser Conference. 2012: 237-240. [11] McNeil B W J, Thompson N R, Dunning D J. Transform-limited X-ray pulse generation from a high-brightness self-amplified spontaneous-emission free-electron laser[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110: 134802. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.134802 [12] Schneidmiller E A, Yurkov M V. Harmonic lasing in X-ray free electron lasers[J]. Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, 2012, 15: 080702. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.15.080702 [13] Schneidmiller E A, Faatz B, Kuhlmann M, et al. First operation of a harmonic lasing self-seeded free electron laser[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2017, 20: 020705. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.20.020705 [14] Nam I, Min C K, Kim C, et al. Soft X-ray harmonic lasing self-seeded free electron laser at Pohang Accelerator Laboratory X-ray free electron laser[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 112: 213506. doi: 10.1063/1.5030443 [15] Schneidmiller E A, Brinker F, Decking W, et al. Observation of harmonic lasing in the Angstrom regime at European X-ray Free Electron Laser[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2021, 24: 030701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.24.030701 [16] Wang Xiaofan, Zeng Li, Shao Jiahang, et al. Physical design for Shenzhen Superconducting Soft X-ray free-electron laser (S3FEL)[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2023: 1852-1855. [17] 金光齐, 黄志戎, 瑞安·林德伯格. 同步辐射与自由电子激光——相干X射线产生原理[M]. 黄森林, 刘克新, 译. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2018Kim K J, Huang Zhirong, Lindberg R. Synchrotron radiation and free-electron lasers: principles of coherent X-ray generation[M]. Huang Senlin, Liu Kexin, trans. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2018 [18] McNeil B W J, Robb G R M, Poole M W, et al. Harmonic lasing in a free-electron-laser amplifier[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 96: 084801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.084801 [19] Isono F, Schroeder C, van Tilborg J, et al. Frequency redshift of seeded FEL radiation generated with a low-energy chirped electron beam[C]//APS Division of Plasma Physics Meeting. 2021: GO05.011. -






 下载:
下载: