Three-dimensional reconstruction system for transparent samples based on phase retrieval
-
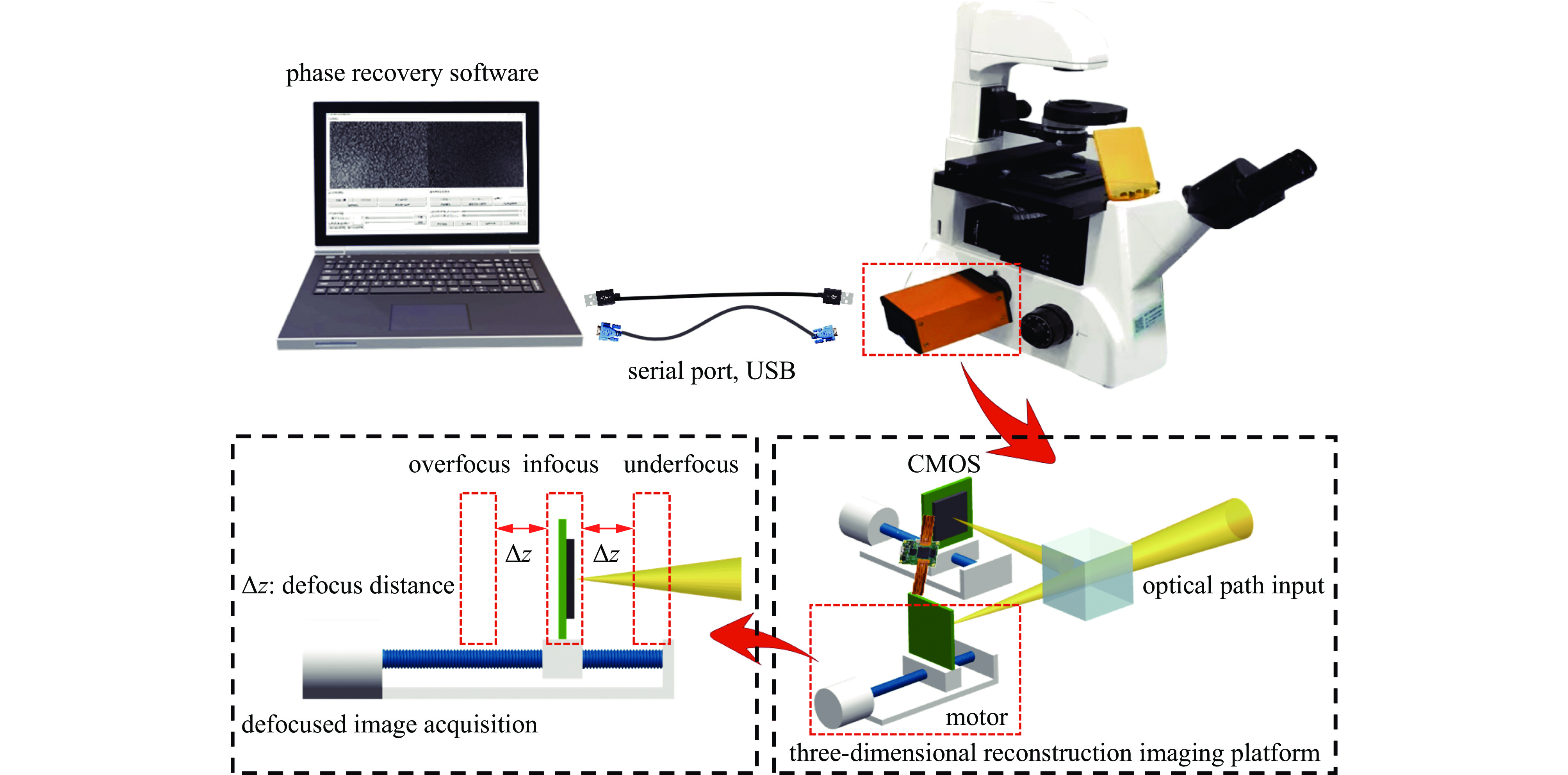
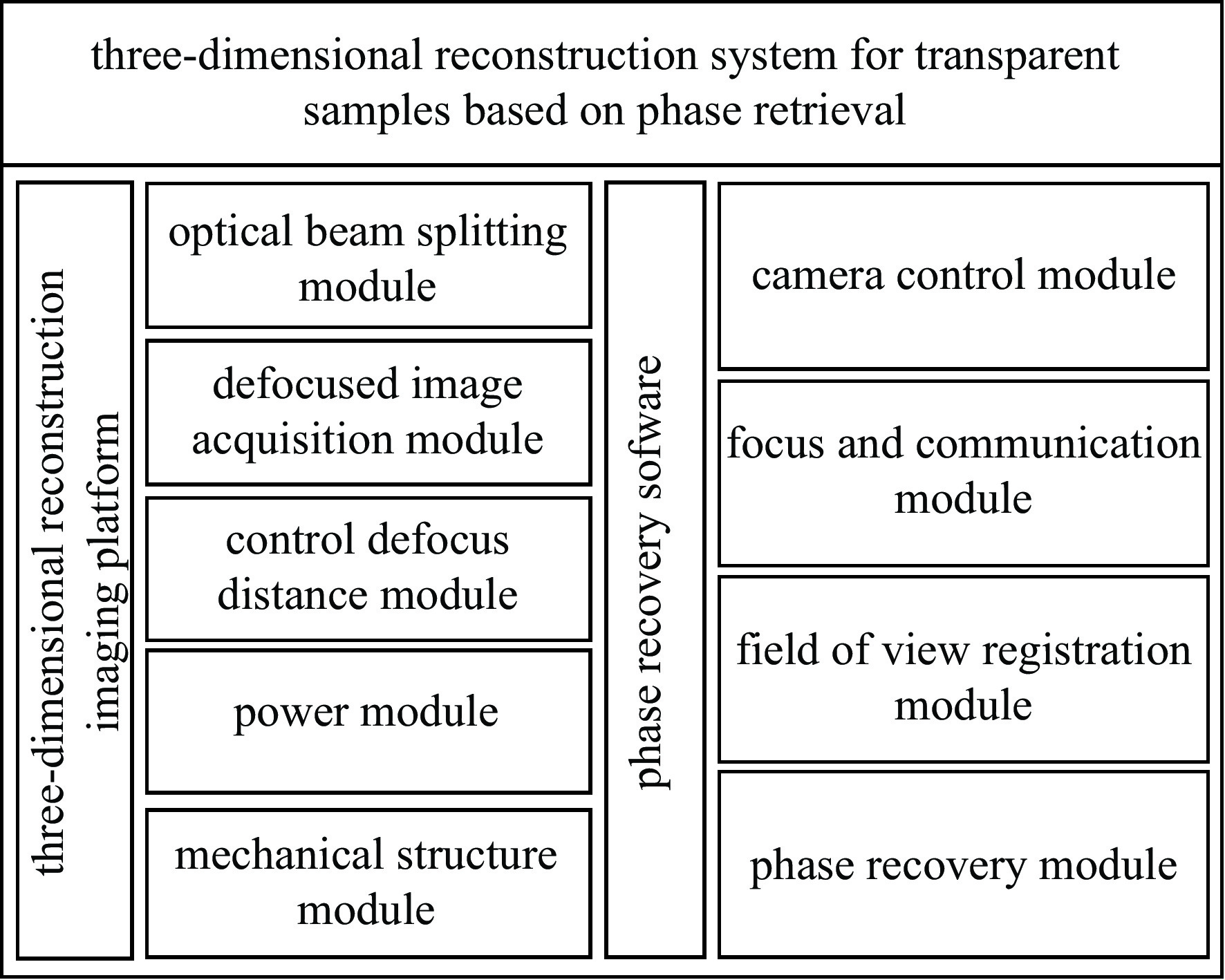
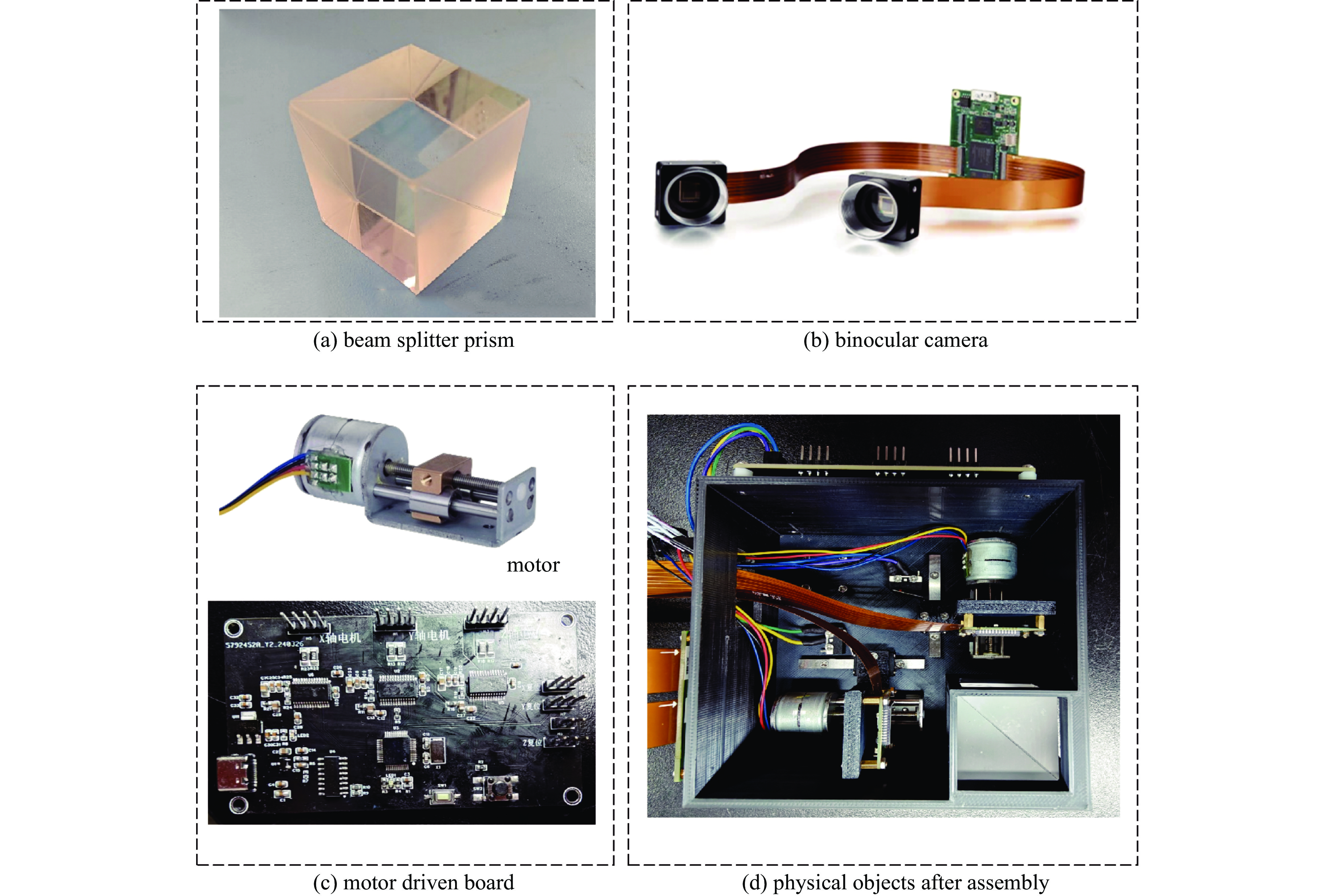
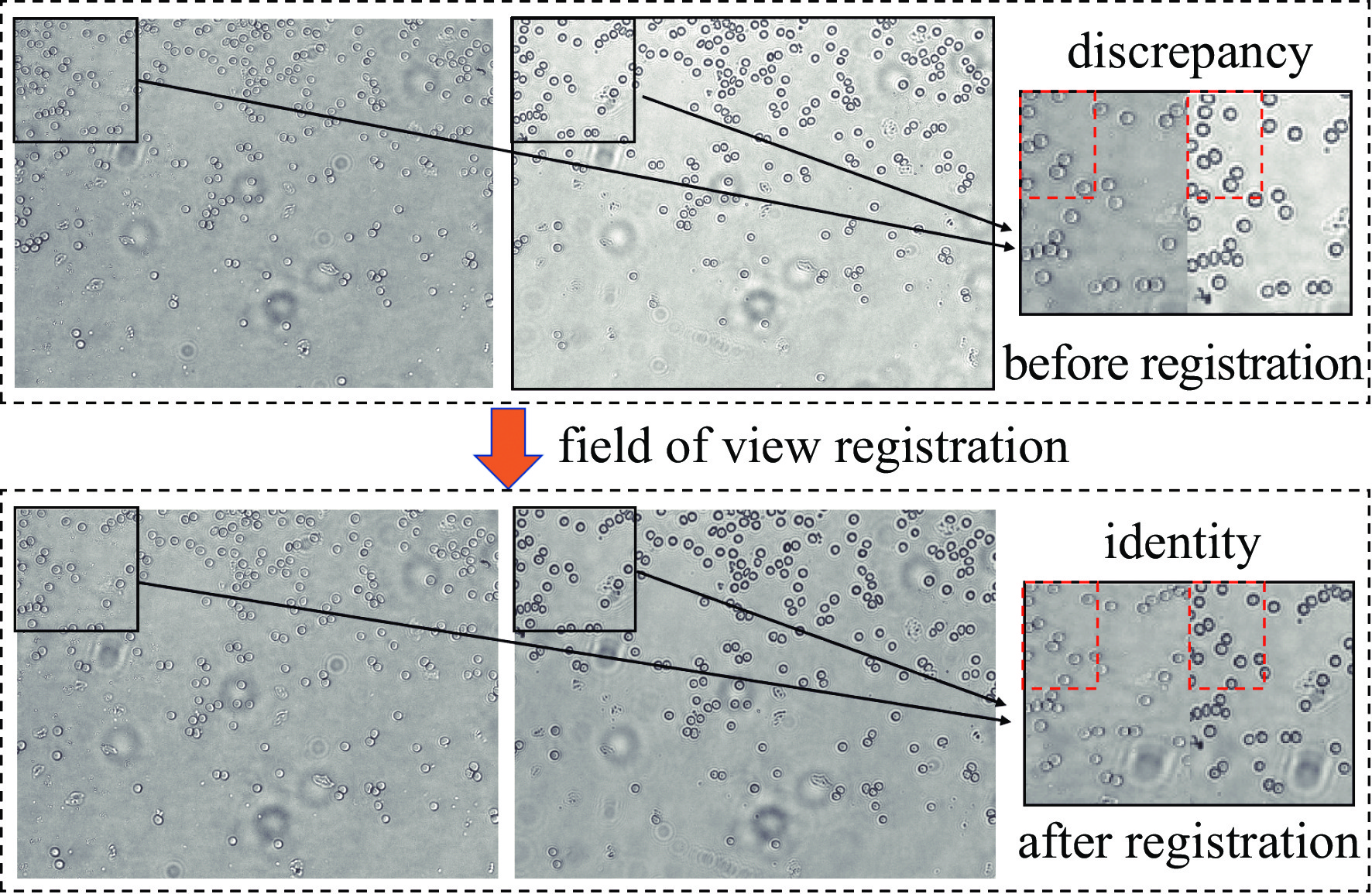
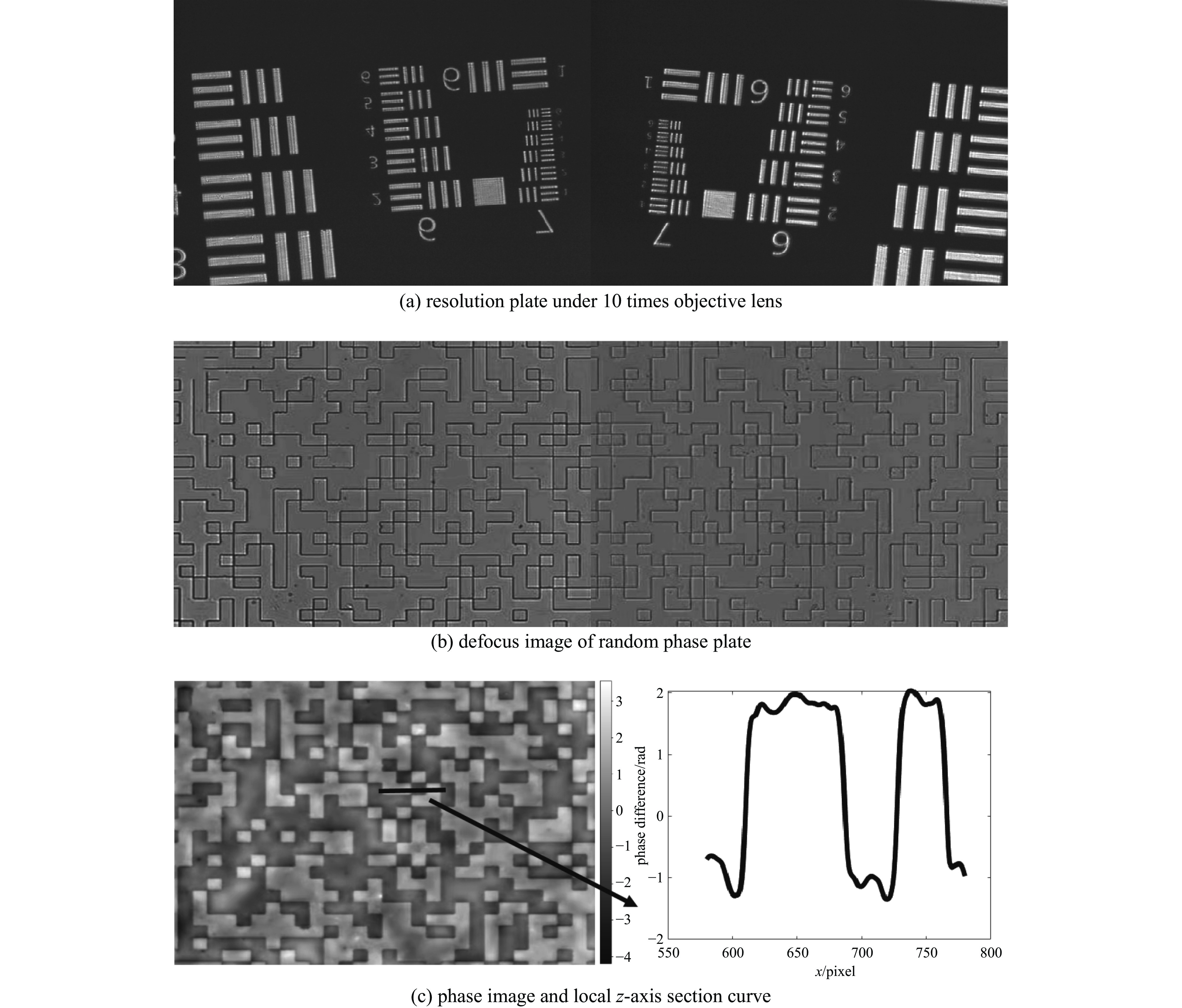
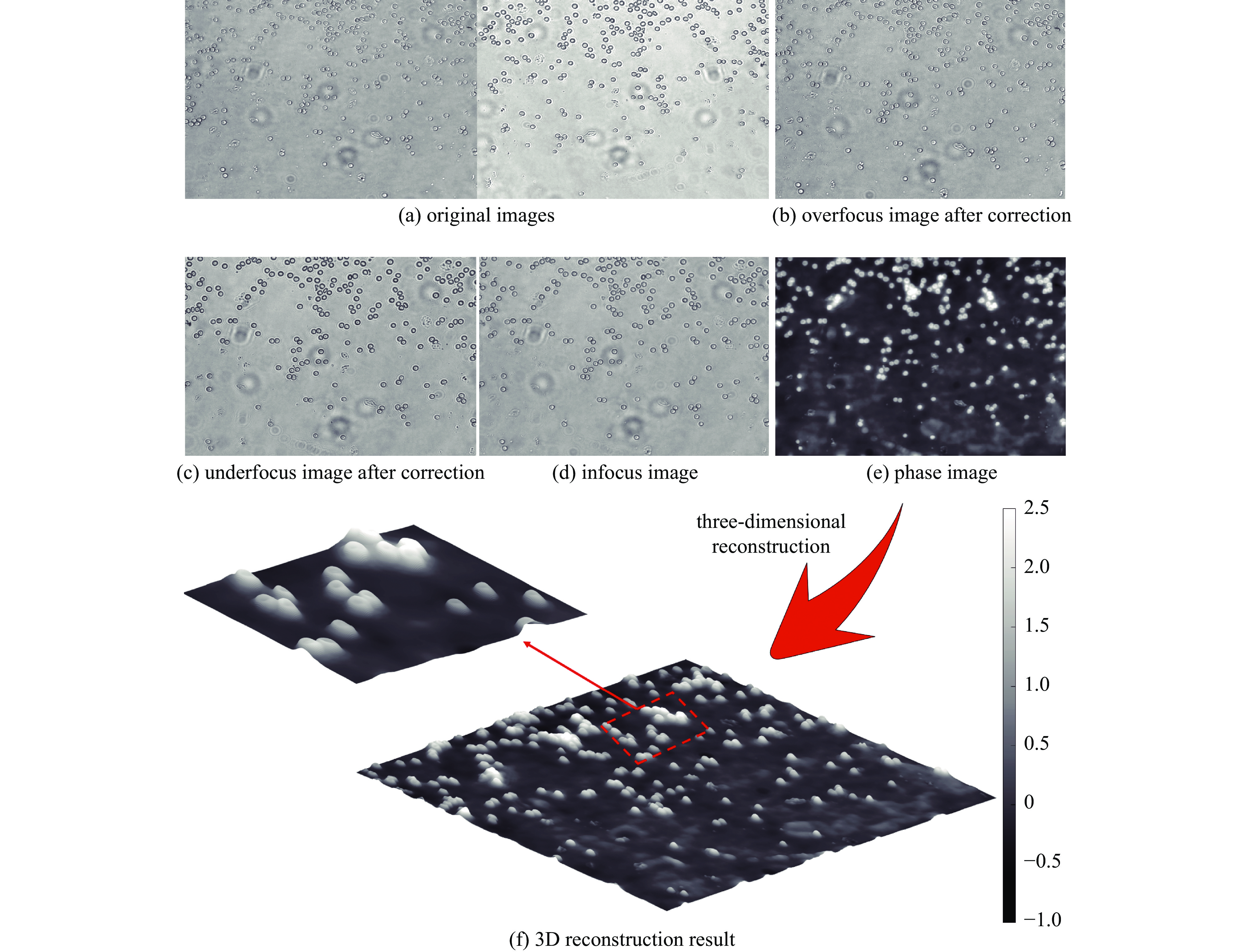
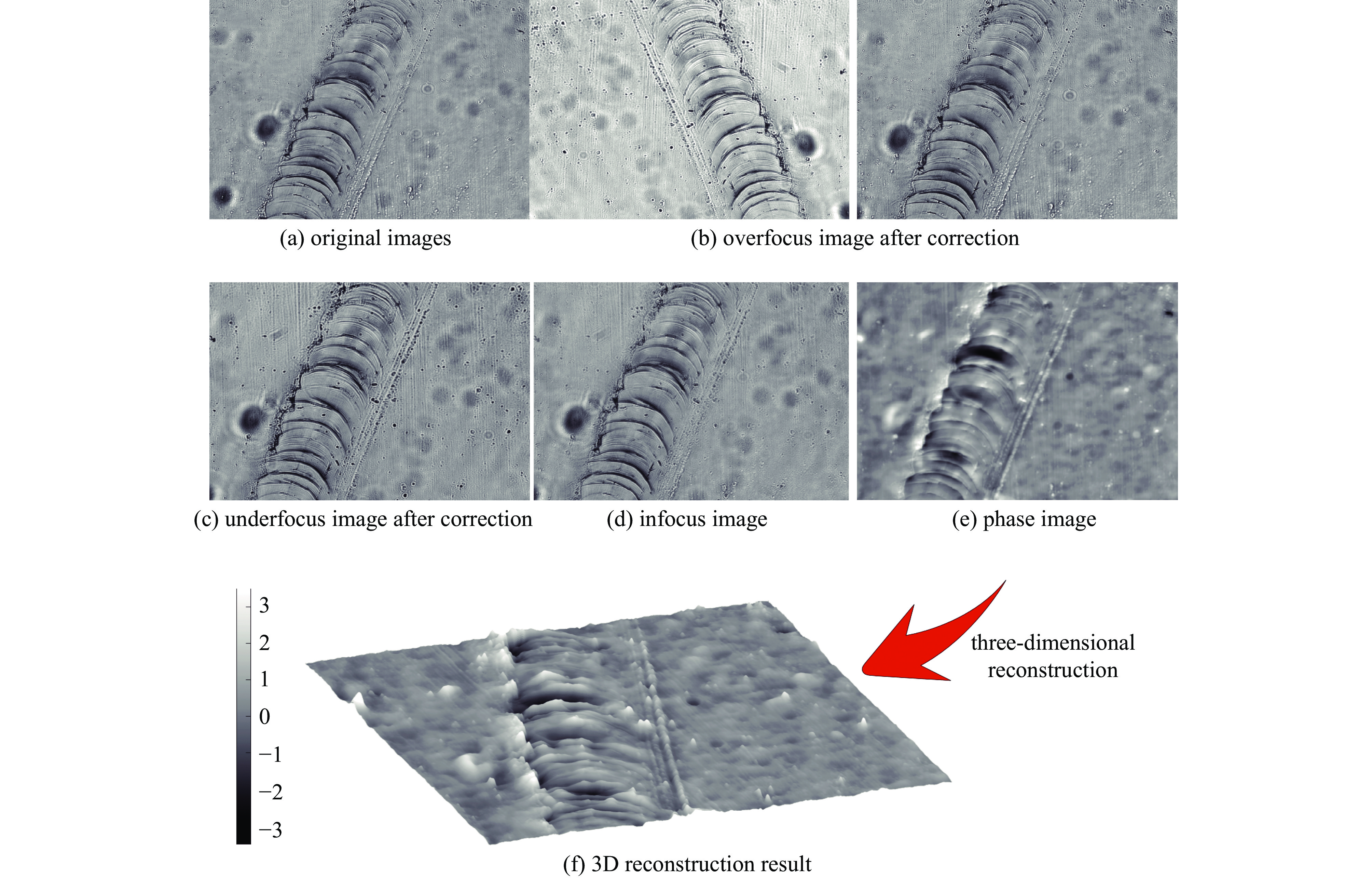
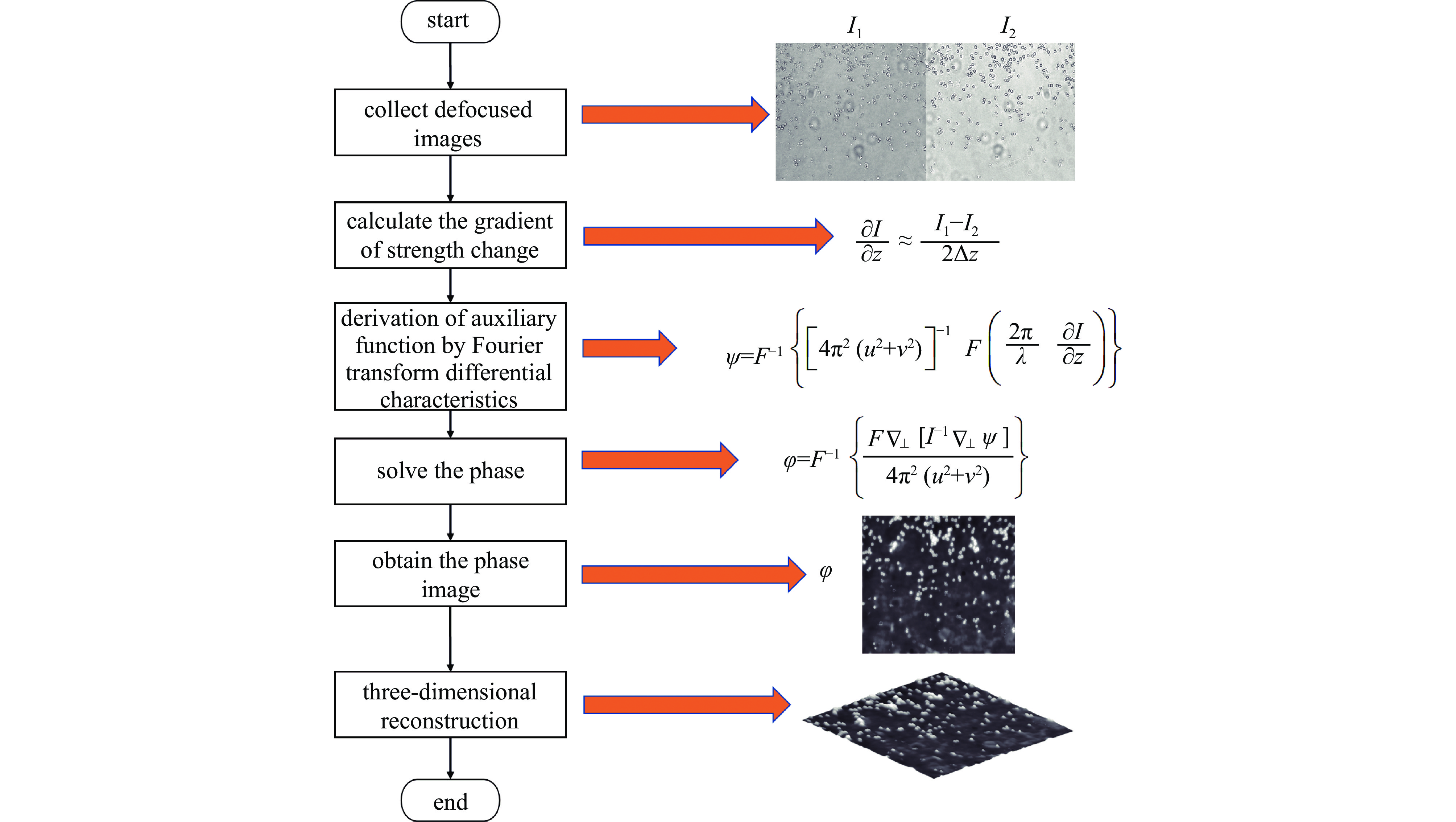
摘要: 为解决传统显微成像技术难以获取无色透明样本结构和厚度的问题,设计了一款小型透明样本3维重建系统。该系统通过对透明样本进行相位恢复,实现3维重建。系统的设计突破了传统光学结构,只需输入携带样本信息的光线,经过分光棱镜分成两路,终由双目相机捕获。系统使用3D打印制作,尺寸仅为110 mm×110 mm×60 mm,成本低廉,并可与传统显微成像设备配合使用。系统内置自动对焦和视场配准算法,只需采集1张过焦和1张欠焦图像,通过求解光强传输方程便可进行相位恢复,从而实现透明样本的3维重建。测试结果显示,10倍物镜下系统的成像分辨率可达2.46 μm,同时相位恢复精确度也能达到基本要求。系统成功对血细胞和载玻片划痕进行了3维重建,证明了系统的可行性与实用性。Abstract: In response to the difficulties posed by traditional microscopy imaging techniques in capturing the structure and thickness of colorless transparent samples, we have designed a miniature three-dimensional reconstruction system for such samples. This innovative system, breaking away from traditional optical structures, performs phase retrieval on transparent samples to achieve three-dimensional reconstruction. It requires only light carrying sample information, which is then bifurcated by a spectroscope and captured by a stereo camera. Constructed using 3D printing technology, the compact system measures just 110 mm×110 mm×60 mm, offering a cost-effective solution that is also compatible with traditional microscopy imaging equipment. It incorporates autofocus and field of view correction algorithms, which, by collecting one over-focused and one under-focused image, solve the transport intensity equation to enable phase retrieval and hence the three-dimensional reconstruction of transparent samples. Test results have shown that the system can achieve an imaging resolution of 2.46 μm under a 10× objective lens, and the phase recovery accuracy can also meet the basic requirements. Furthermore, the successful three-dimensional reconstruction of blood cells and scratches on microscope slides validates the system's feasibility and practicality.
-
表 1 CMOS相机参数表
Table 1. CMOS camera parameters
model transmission mode resolution frames/Hz pixel dimension/(μm×μm) VEN-134-90U3M-D USB3.0 1280 ×1024 ×290 4.8×4.8 -
[1] 左超, 陈钱. 计算光学成像: 何来, 何处, 何去, 何从?[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51:20220110 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220110Zuo Chao, Chen Qian. Computational optical imaging: an overview[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51: 20220110 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220110 [2] Jiang Fuda, Zhang Chonglei. High accuracy quantitative phase imaging based on transport-of-intensity equation[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2023, 169: 107700. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107700 [3] Park Y, Depeursinge C, Popescu G. Quantitative phase imaging in biomedicine[J]. Nature Photonics, 2018, 12(10): 578-589. doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0253-x [4] Zuo Chao, Li Jiaji, Sun Jiasong, et al. Transport of intensity equation: a tutorial[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 135: 106187. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106187 [5] 何璇. 明场、暗场、相衬的多模显微镜成像技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2017He Xuan. Research on multi-mode microscopy imaging technology of brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017 [6] Trattner S, Kashdan E, Feigin M, et al. Image formation of thick three-dimensional objects in differential-interference-contrast microscopy[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2014, 31(5): 968-980. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.31.000968 [7] 左超, 陈钱, 孙佳嵩, 等. 基于光强传输方程的非干涉相位恢复与定量相位显微成像: 文献综述与最新进展[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43:0609002 doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0609002Zuo Chao, Chen Qian, Sun Jiasong, et al. Non-interferometric phase retrieval and quantitative phase microscopy based on transport of intensity equation: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43: 0609002 doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0609002 [8] 桂博瀚, 李常伟. 基于波面分割及多平面相位恢复的定量相位成像技术[J]. 光学学报, 2023, 43:1411002 doi: 10.3788/AOS230451Gui Bohan, Li Changwei. Quantitative phase imaging technology based on wavefront segmentation and multiplane phase retrieval[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2023, 43: 1411002 doi: 10.3788/AOS230451 [9] 张赵. 基于光强传输方程的相位恢复与多模式成像研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2017Zhang Zhao. Phase retrieval and multi-mode imaging based on light intensity transfer equation[D]. Nanjing: University of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2017 [10] Cheng Hong, Wang Jincheng, Gao Yaoli, et al. Phase unwrapping based on transport-of-intensity equation with two wavelengths[J]. Optical Engineering, 2019, 58: 054103. [11] Grant S D, Richford K, Burdett H L, et al. Low-cost, open-access quantitative phase imaging of algal cells using the transport of intensity equation[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2020, 7: 191921. doi: 10.1098/rsos.191921 [12] Chen Chao, Lu Y Yunan, Huang Huachuan, et al. PhaseRMiC: phase real-time microscope camera for live cell imaging[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2021, 12(8): 5261-5271. doi: 10.1364/BOE.430115 [13] Liu Cheng, Wang Shouyu, Veetil S P. Computational optical phase imaging[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2022. [14] Carney S, Khoo T C, Sheikhsofla A, et al. Quantitative phase imaging comparison of digital holographic microscopy and transport of intensity equation phase through simultaneous measurements of live cells[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2023, 166: 107581. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107581 [15] Wang Shouyu, Huang Huachuan, Sun Aihui, et al. Dual-view transport of intensity phase imaging devices for quantitative phase microscopy applications[J]. Sensors & Diagnostics, 2024, 3(3): 381-394. -




 下载:
下载: