Research on spherical graphite cast iron electrode based gas switch
-
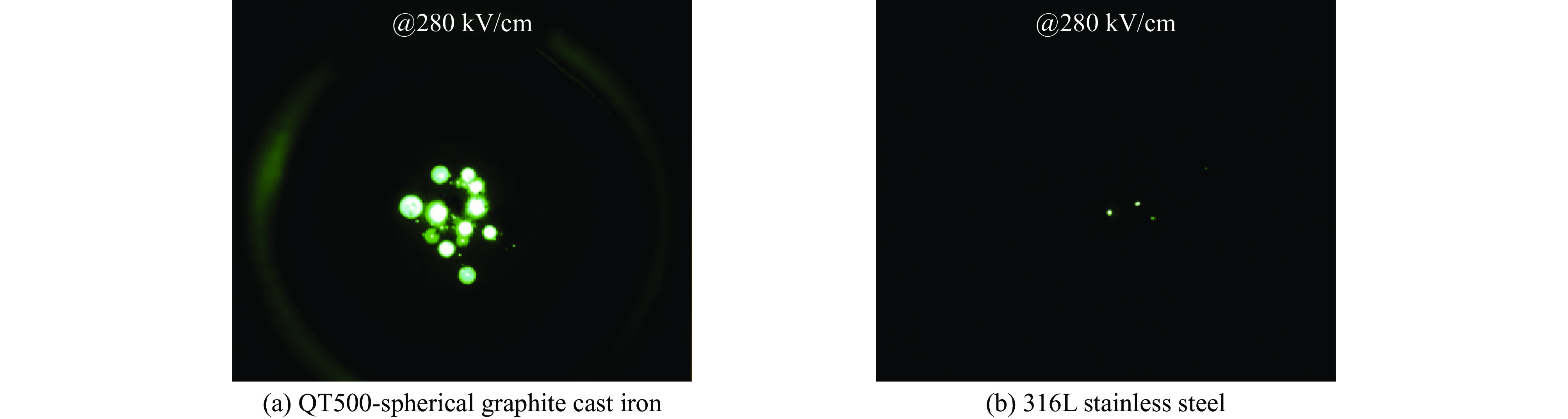
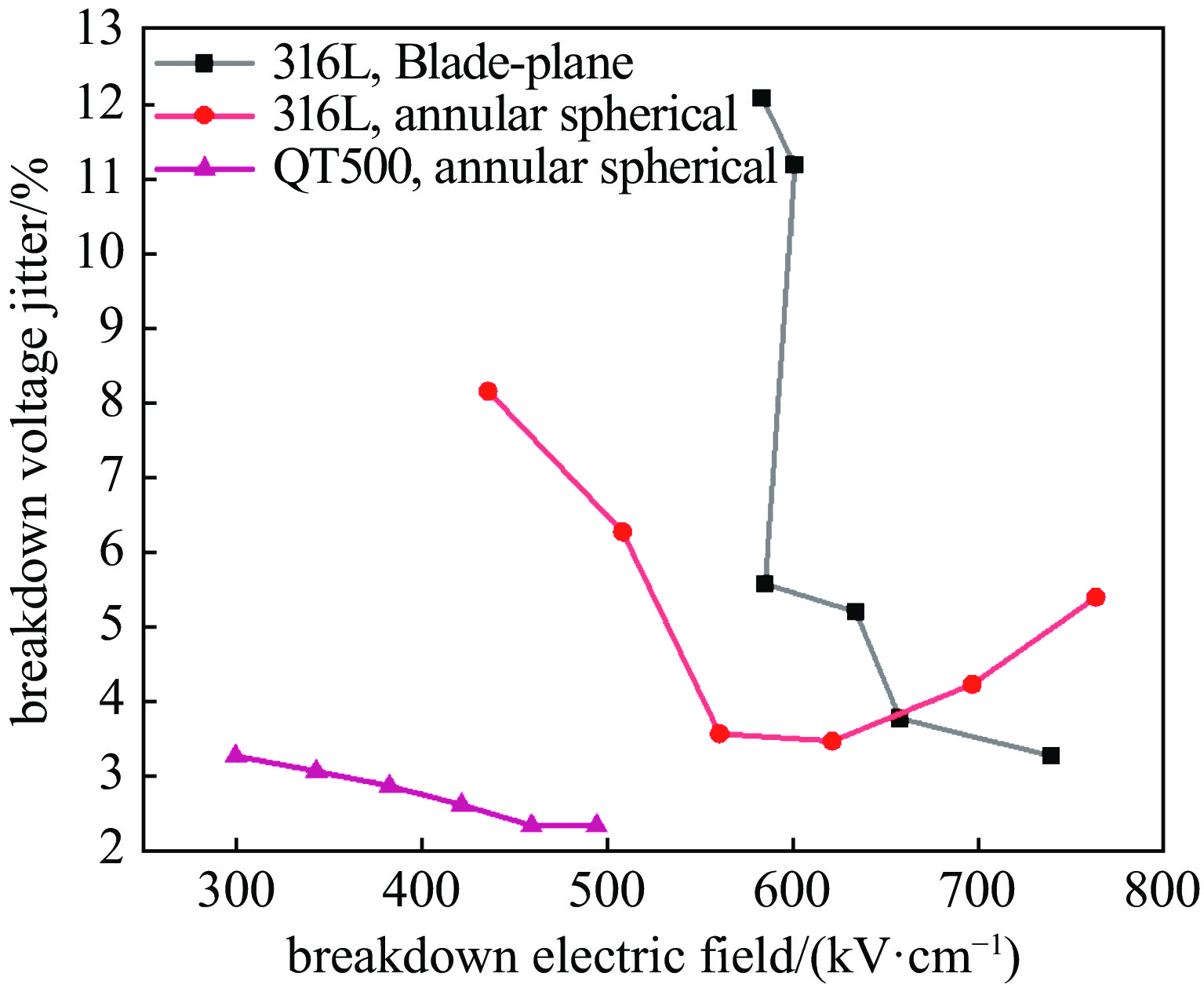
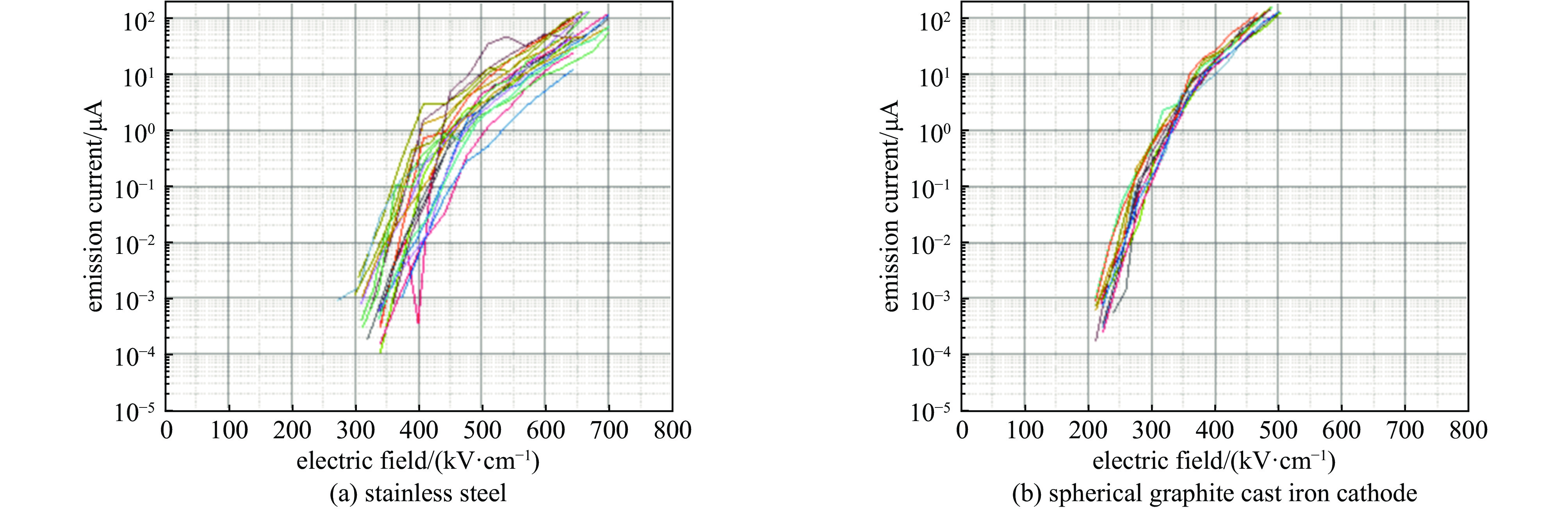
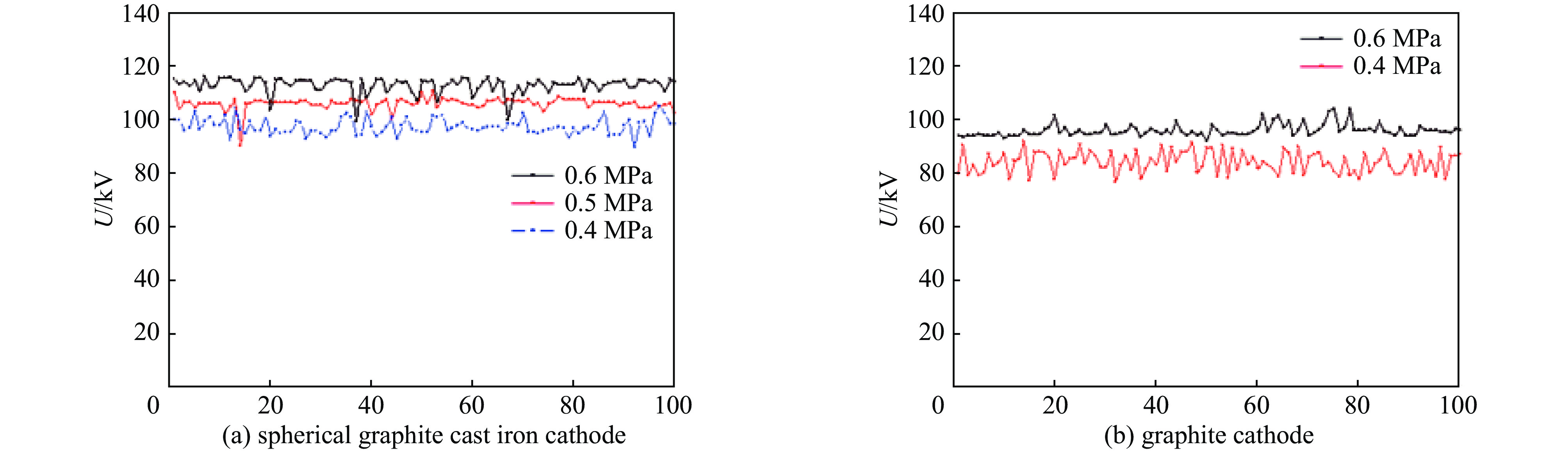
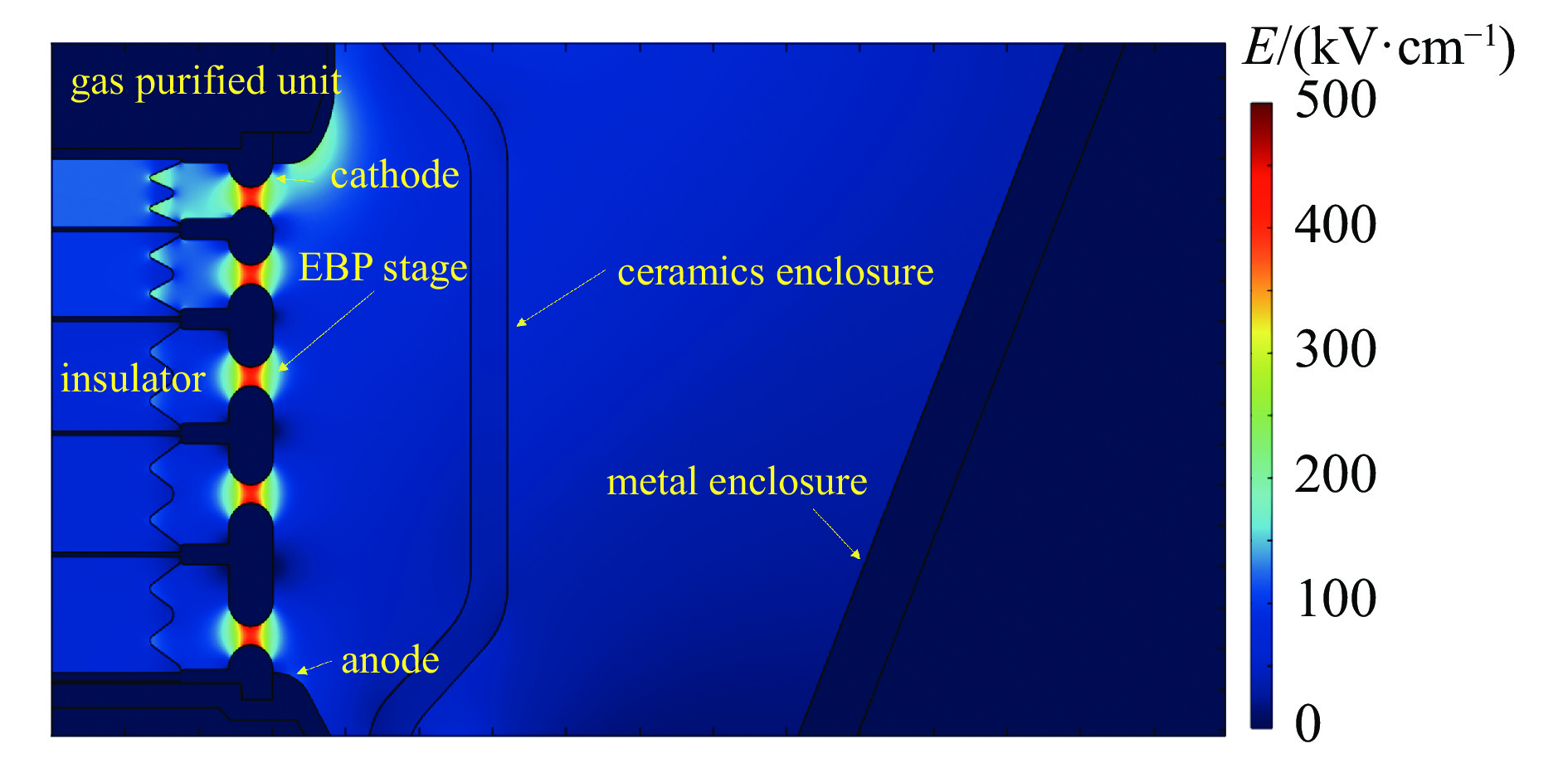
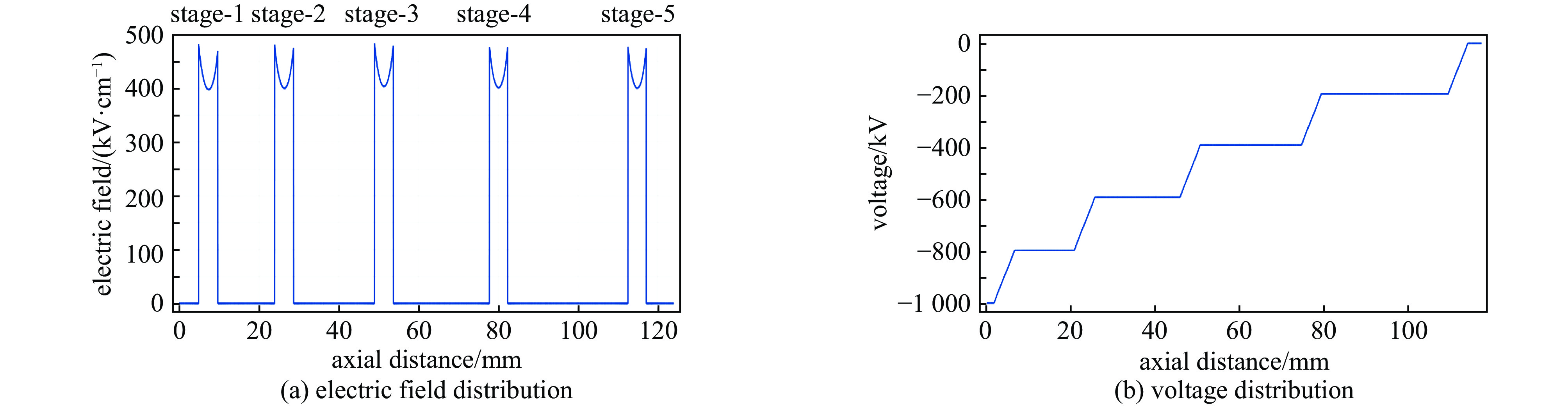
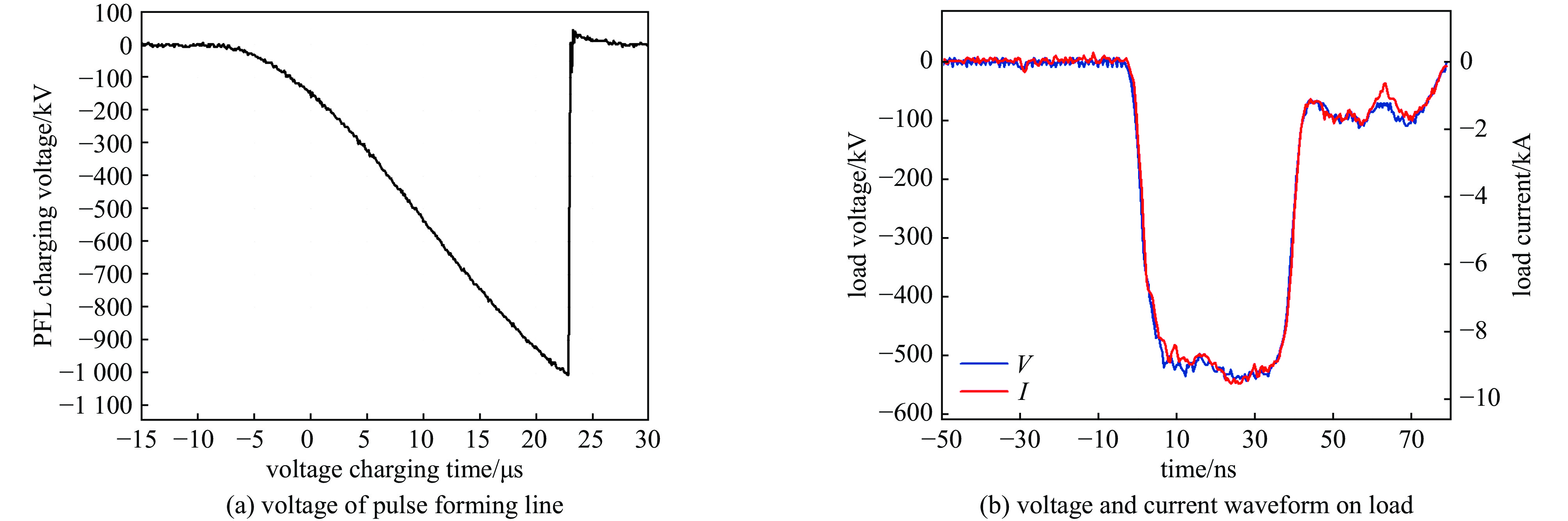
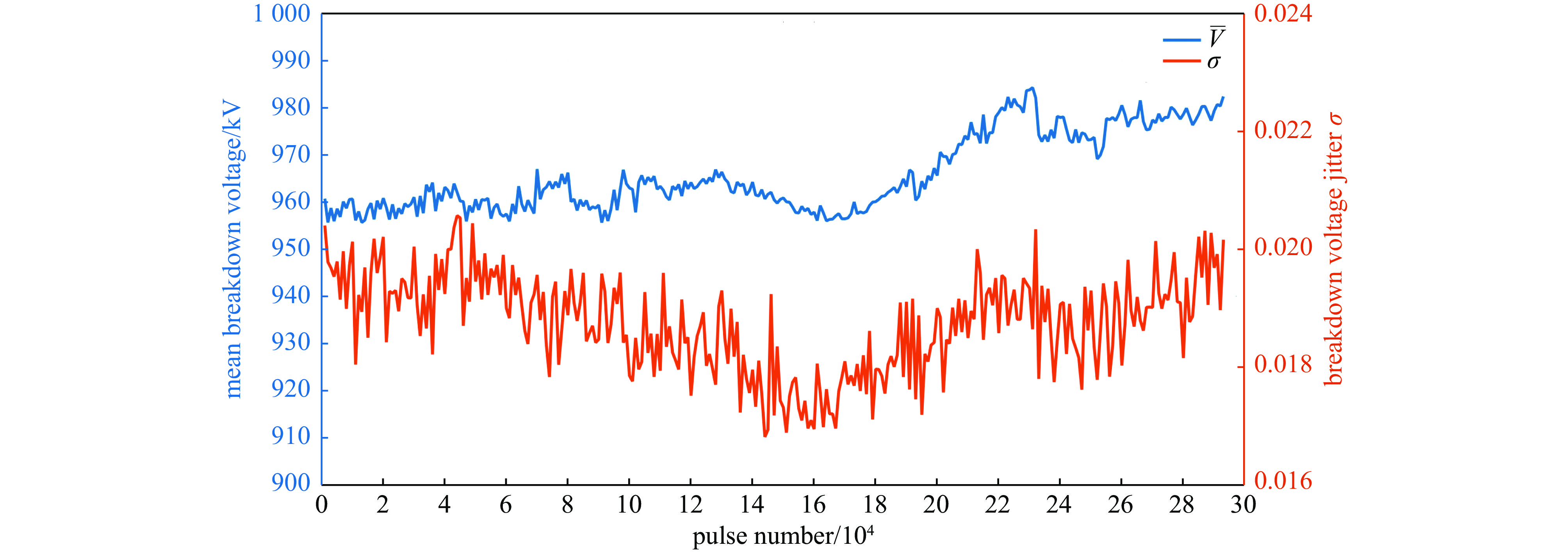
摘要: 高功率容量的气体开关是国内外大型脉冲功率装置的首选,但因气体放电随机性导致的自击穿电压抖动一直以来是脉冲功率装置的瓶颈问题。电极是影响气体开关稳定性和寿命的关键,开关设计总要面临低抖动和长寿命之间的取舍,提出一种兼顾低抖动、长寿命特性的球墨铸铁气体开关。基于对球墨铸铁材料的特性分析,提出球墨均布于电极有利于提高气体开关击穿稳定性的机制,且球状石墨均布于整个电极体内,相比表面结构,具有长寿命的原生优势。设计开展了单级开关稳定性测试实验,结果表明球墨铸铁电极可将传统电极结构3%~4%的重频自击穿抖动有效降低至2.5%。最终利用低抖动球墨电极,设计了5级1 MV等自击穿概率型全密封气体开关,开关抖动进一步降低至2%以下。在测试电压范围960~980 kV,放电电流约9 kA,无维护条件下开展了开关30万脉冲寿命考核,自击穿抖动维持在2%以下,最优达1.7%。开关导通前沿小于5 ns,传输效率大于90%。此结果展现了球墨铸铁作为气体开关电极的应用潜力。Abstract: Gas switches with high power capacity are the first choice for large-scale pulsed power devices at home and abroad, but the self-breakdown voltage jitter due to the randomness of gas discharge has always been the bottleneck problem for pulsed power devices. The electrode is the key to affect the stability and life of the gas switch, and the previous designs had to face the trade-off between low jitter and long life. This paper proposes a spherical graphite cast iron gas switch that takes into account the characteristics of low jitter and long life. Based on the characterization of the spherical graphite cast iron material, it is proposed that the uniform distribution of spherical graphite in the electrode is conducive to the mechanism of improving the breakdown stability of the gas switch, and the spherical graphite is uniformly distributed in the whole electrode, which has the native advantage of long life compared with the surface structure. A single-stage switching stability test experiment was designed and carried out, and the results show that the ductile graphite electrode can effectively reduce the heavy frequency self-breakdown jitter of 3%−4% in the traditional electrode structure to 2.5%. Ultimately, a 5-stage 1 MV equal self-breakdown probability type fully sealed gas switch was designed using low jitter ductile electrodes, and the switching jitter was further reduced to less than 2%. Under the test voltage range of 960-980 kV, discharge current of about 9 kA, and maintenance-free conditions, the switch was tested for 300 000 pulses, and the self-breakdown jitter was maintained at less than 2%, with an optimum of 1.7%. The switch conduction front is less than 5 ns, and the transmission efficiency is more than 90%. The results demonstrate the potential application of spherical graphite cast iron cathodes as gas switches.
-
Key words:
- gas switch /
- low jitter /
- long life /
- spherical graphite cast iron
-
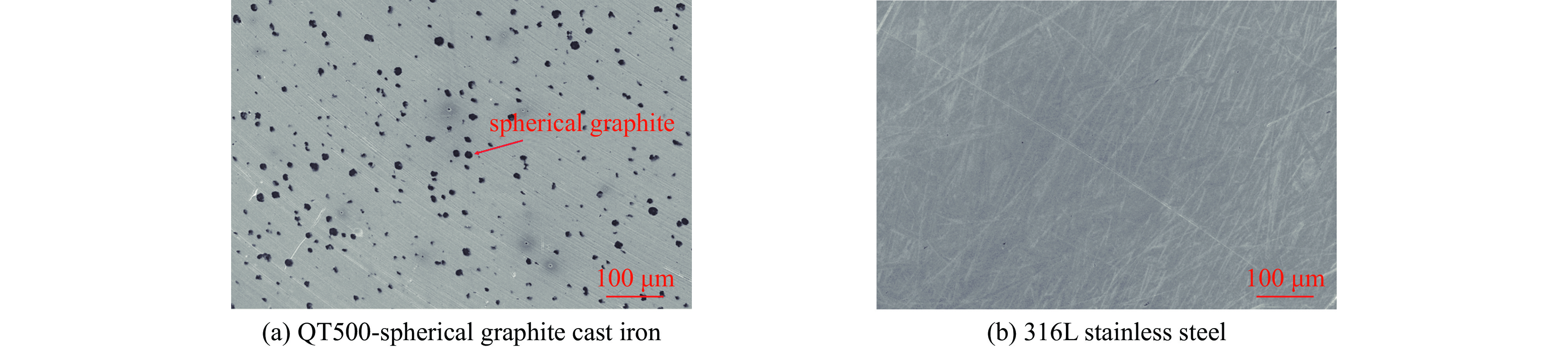
表 1 QT500球墨铸铁材料与316L不锈钢材料性质对比
Table 1. Comparison of material properties between spherical graphite cast iron and stainless steel
material mass fraction/% tensile
strength/MPayield
strength/MPathermal conductivity/
(W∙m−1∙K−1)melting
point/℃hardness/HB metallographic
structureQT500 C: 3.55~3.85;
Si: 2.34~2.86
Mn,S,P,Mg: 0.02~0.04
RE: 0.03~0.05≥500 ≥320 35.7 1200 ~1300 170~230 austenitic stainless steel 316L C: ≤0.03; Si: ≤1.00;
Mn: ≤2.00; S: ≤0.03;
P: ≤0.045; Mo: 2.00~3.00≥480 ≥177 16.3 1375 ~1450 ≤187 ferrite+pearlite 表 2 四个实验组的开关结构
Table 2. Basic structure of 4 experimental groups
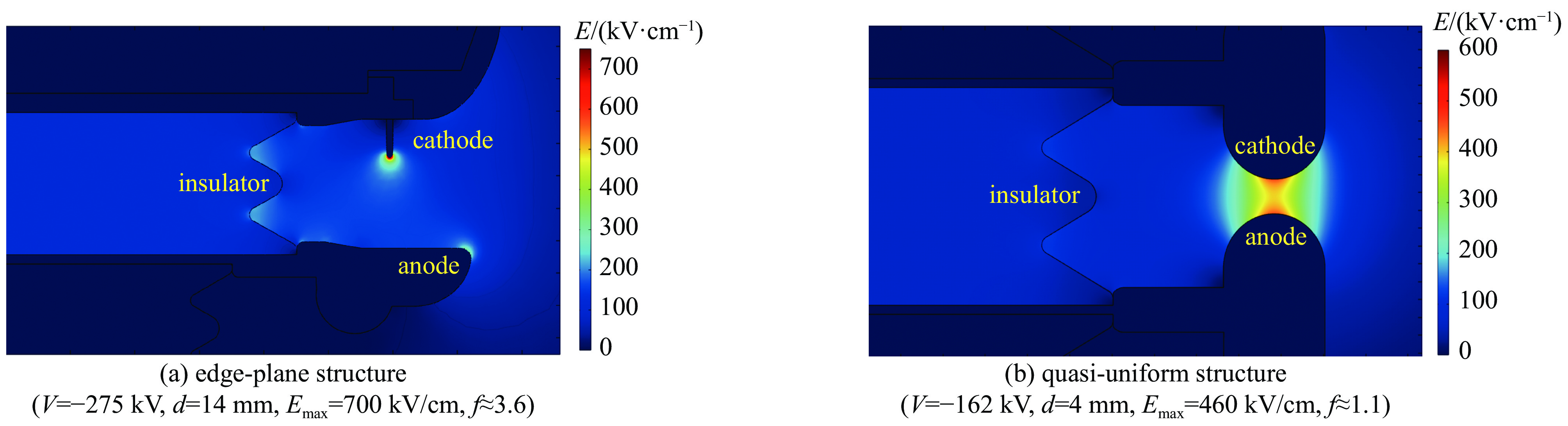
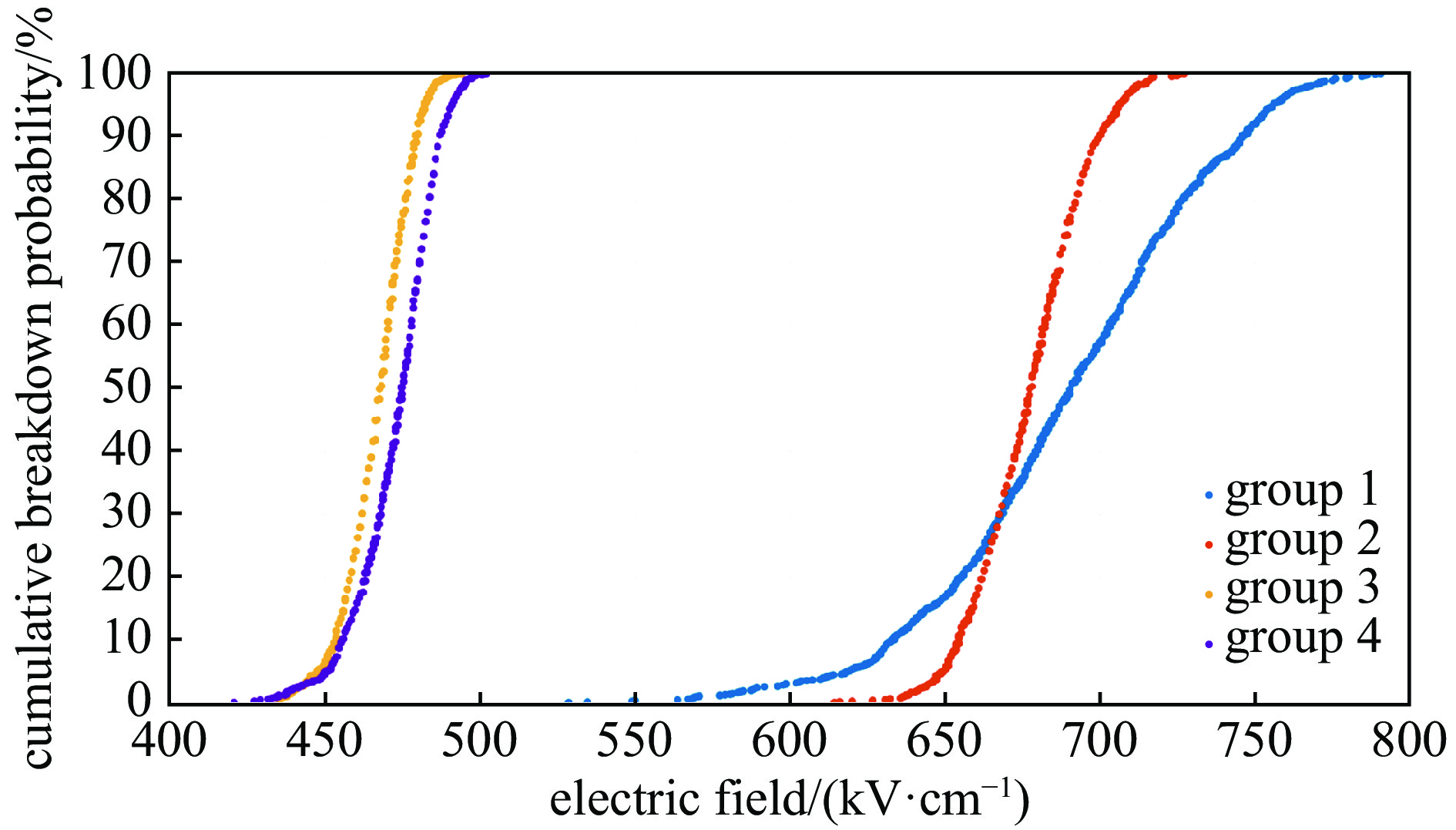
experiment group electrode structure electric field enhancement f cathode material anode material group 1 annular spherical 1.1 316L 316L group 2 blade-plane 3.6 316L 316L group 3 annular spherical 1.1 QT500 QT500 group 4 annular spherical 1.1 QT500 316L -
[1] 刘锡三. 高功率脉冲技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2005Liu Xisan. High pulsed power technology[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2005 [2] 曾正中. 实用脉冲功率技术引论[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 2003Zeng Zhengzhong. Introduction to practical pulsed power technology[M]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 2003 [3] 周传明, 刘国治, 刘永贵, 等. 高功率微波源[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2007Zhou Chuanming, Liu Guozhi, Liu Yonggui, et al. High-power microwave sources[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2007 [4] Martin T H, Guenther A H, Kristiansen M. J. C. Martin on pulsed power[M]. New York: Springer, 1996. [5] Lehr J, Ron P. Foundations of pulsed power technology[M]. New York: Wiley-IEEE Press, 2017. [6] Jones Jr C H, Crewson W F J, Naff J T, et al. An analytical model for the high voltage rope switch[R]. Pulsar Associates Switching Note 19, 1973. [7] Maenchen J, Lehr J M, Warne L K, et al. Fundamental science investigations to develop a 6-MV laser triggered gas switch for ZR: first annual report[R]. SAND2007-0217, 2007. [8] Beveridge J R, MacGregor S J, Given M J, et al. A corona-stabilised plasma closing switch[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2009, 16(4): 948-955. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2009.5211838 [9] Gao Pengcheng, Su Jiancang, Zeng Bo, et al. A low-jitter self-break repetitive multi-stage gas switch[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88: 024705. doi: 10.1063/1.4973420 [10] 曾搏, 苏建仓, 等. 一种陶瓷封装V/N触发多级气体开关[C]//第十一届全国高功率微波会议. 2017Zeng Bo, Su Jiancang, et al. A ceramic package V/N triggers a multi-stage gas switch[C]//The 11th National High Power Microwave Conference. 2017 [11] Su Jiancang, Zeng Bo, Gao Pengcheng, et al. A voltage-division-type low-jitter self-triggered repetition-rate switch[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87: 105118. doi: 10.1063/1.4963659 [12] Shang Wei, Su Jiancang, Zeng Bo, et al. A 1-MV low-jitter high-reliability multi-stage equal breakdown probability gas switch[J]. Physica Scripta, 2023, 98: 015013. doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/aca846 [13] 罗维熙, 丛培天, 孙铁平, 等. 电极材料对气体火花开关静态性能的影响[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28:015022 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.015022Luo Weixi, Cong Peitian, Sun Tieping, et al. Influence of electrode materials on static performance of gas spark switch[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 015022 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.015022 [14] 戴宏宇, 沈昊, 李黎. 石墨电极气体开关中等离子体弧区碳氧反应效率研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:065015 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210084Dai Hongyu, Shen Hao, Li Li. Research on plasma arc oxidation efficiency of spark gap switch with graphite electrodes[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 065015 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210084 [15] Zeng Fanzheng, Li Song, Zhang Quancai, et al. Investigation on a self-breakdown repetitive gap switch based on the graphite electrodes with TiC surface modification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2022, 50(3): 709-714. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2022.3148320 [16] Wang Gang, Su Jiancang, Zhang Xibo, et al. Impulse-breakdown characteristics of a high-power gas switch based on graphene cathode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2019, 47(10): 4567-4571. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2019.2919350 [17] 孙钧. 介质掺杂爆炸发射阴极研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2006Sun Jun. Study on dielectric doped explosion emission cathode[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2006 [18] 孙钧, 刘国治, 林郁正, 等. 阴极金属微凸起电场增强因子数值模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2005, 17(8):1183-1186Sun Jun, Liu Guozhi, Lin Yuzheng, et al. Numerical simulation of electric field enhancement factor of metallic microprotrusion[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2005, 17(8): 1183-1186 [19] 吴平. 结构场增强爆炸发射阴极研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2017Wu Ping. Research on explosive emission cathode with structural field enhancement[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2017 [20] Wu Ping, Sun Jun. Emission current from a single micropoint of explosive emission cathode[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2016, 23: 013111. doi: 10.1063/1.4940334 [21] 吴德海. 球墨铸铁[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2006Wu Dehai. Spherical graphite cast iron[M]. Beijing: China Water Power Press, 2006 [22] Meek J M. A theory of spark discharge[J]. Physical Review, 1940, 57(8): 722-728. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.57.722 [23] Raether H. Electron avalanches and breakdown in gases[M]. London: Butterworths, 1964. [24] Loeb L B. Fundamental processes of electrical discharge in gases[M]. New York: Wiley, 1939. [25] Li Yutai, Fu Yangyang, Liu Zhigang, et al. Observation of electron runaway in a tip-plane air gap under negative nanosecond pulse voltage by PIC/MCC simulation[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2022, 31: 045027. doi: 10.1088/1361-6595/ac5ec9 [26] Kunhardt E E, Tzeng Y. Development of an electron avalanche and its transition into streamers[J]. Physical Review A, 1988, 38(3): 1410-1421. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.38.1410 [27] Tan Nongchao, Wu Ping, Hua Ye, et al. Mechanism analysis of field electron emission of titanium[J]. Physica Scripta, 2023, 98: 045005. doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/acbe78 [28] Tan Nongchao, Wu Ping, Sun Jun, et al. Experimental study on the influence of grain boundary on breakdown in relativistic backward wave oscillator[J]. Physica Scripta, 2023, 98: 105535. doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/acfac7 [29] Wu Yue, Su Jiancang, Qiu Xudong, et al. Review of metallic microprotrusion model and microdielectrics model in vacuum[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2023, 51(12): 3492-3499. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2023.3331849 -




 下载:
下载: