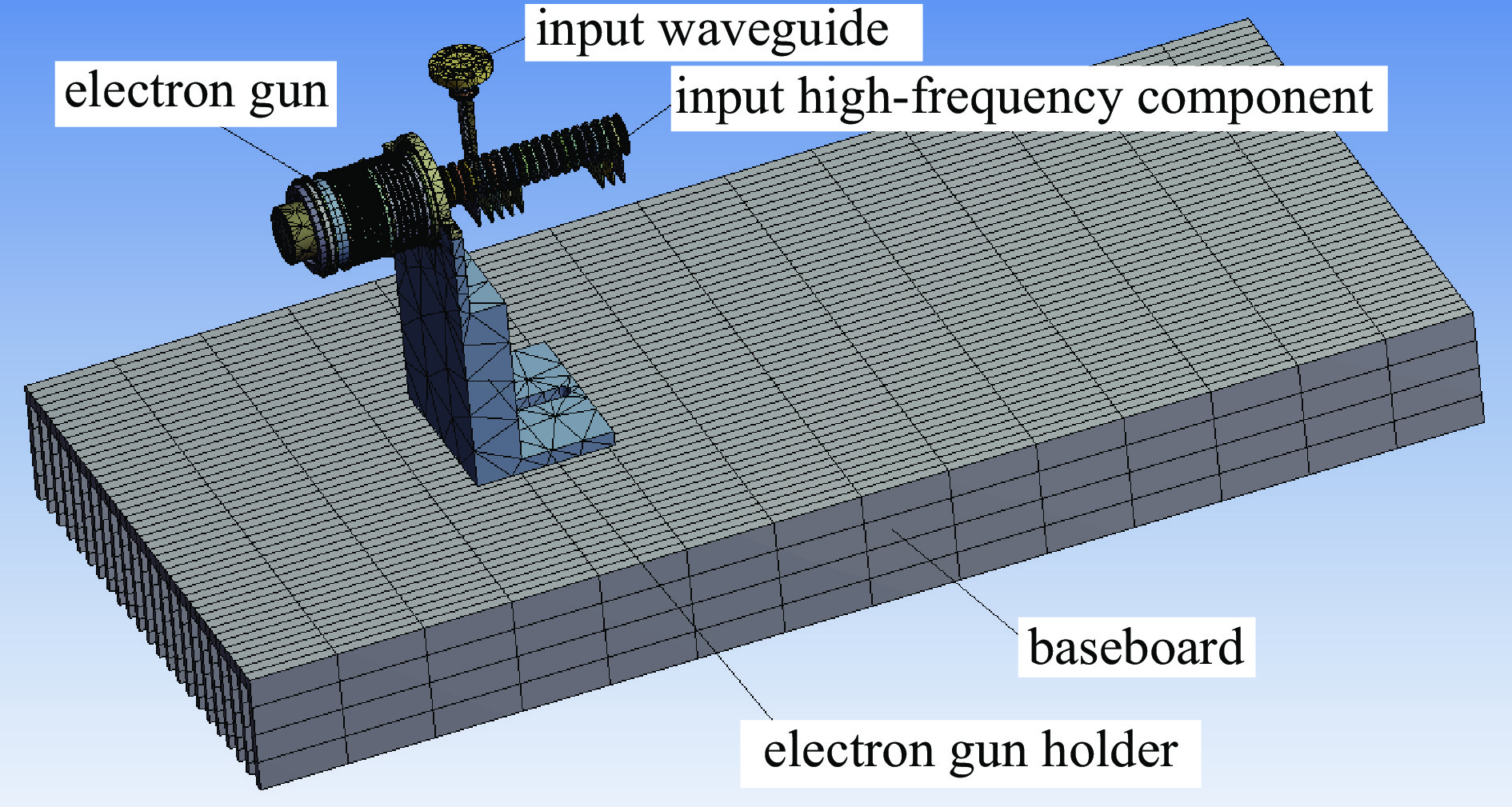
Influence of thermal radiation on cathode temperature of traveling wave tubes
-
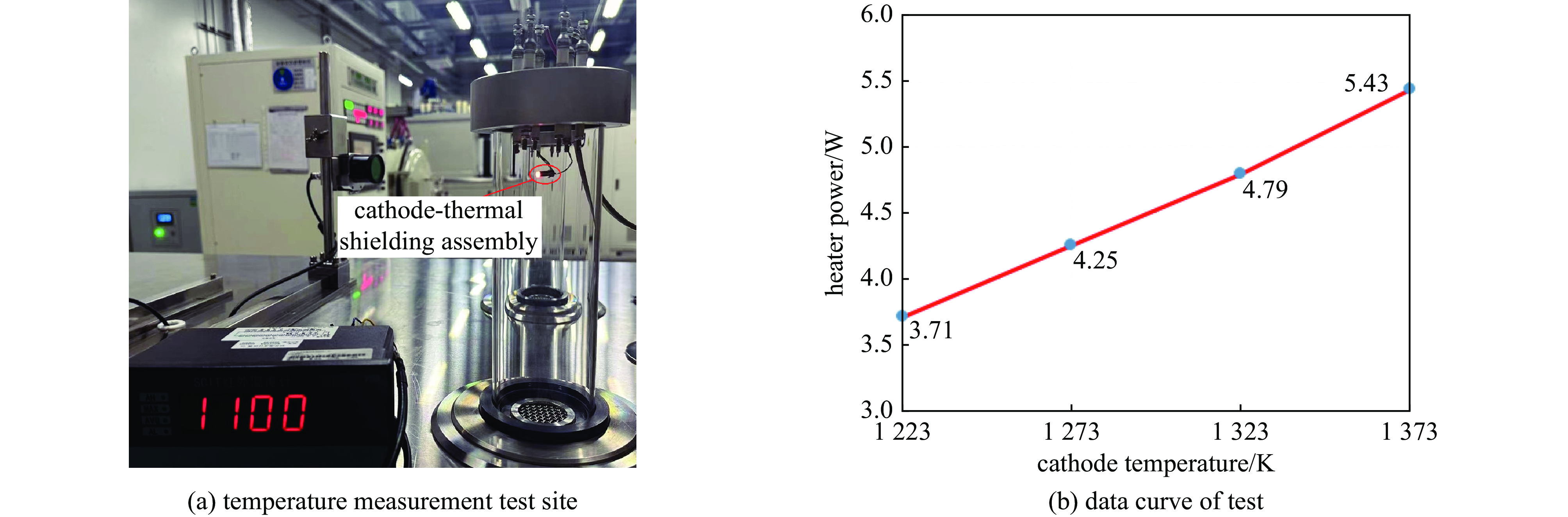
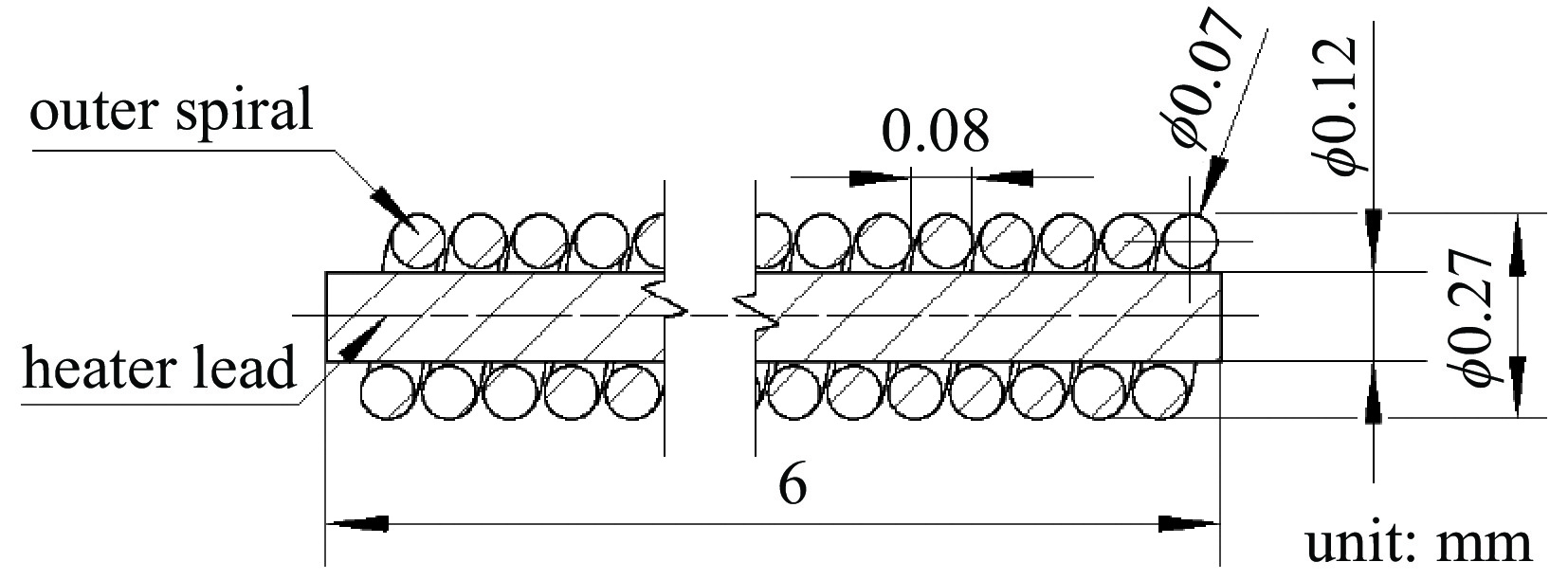
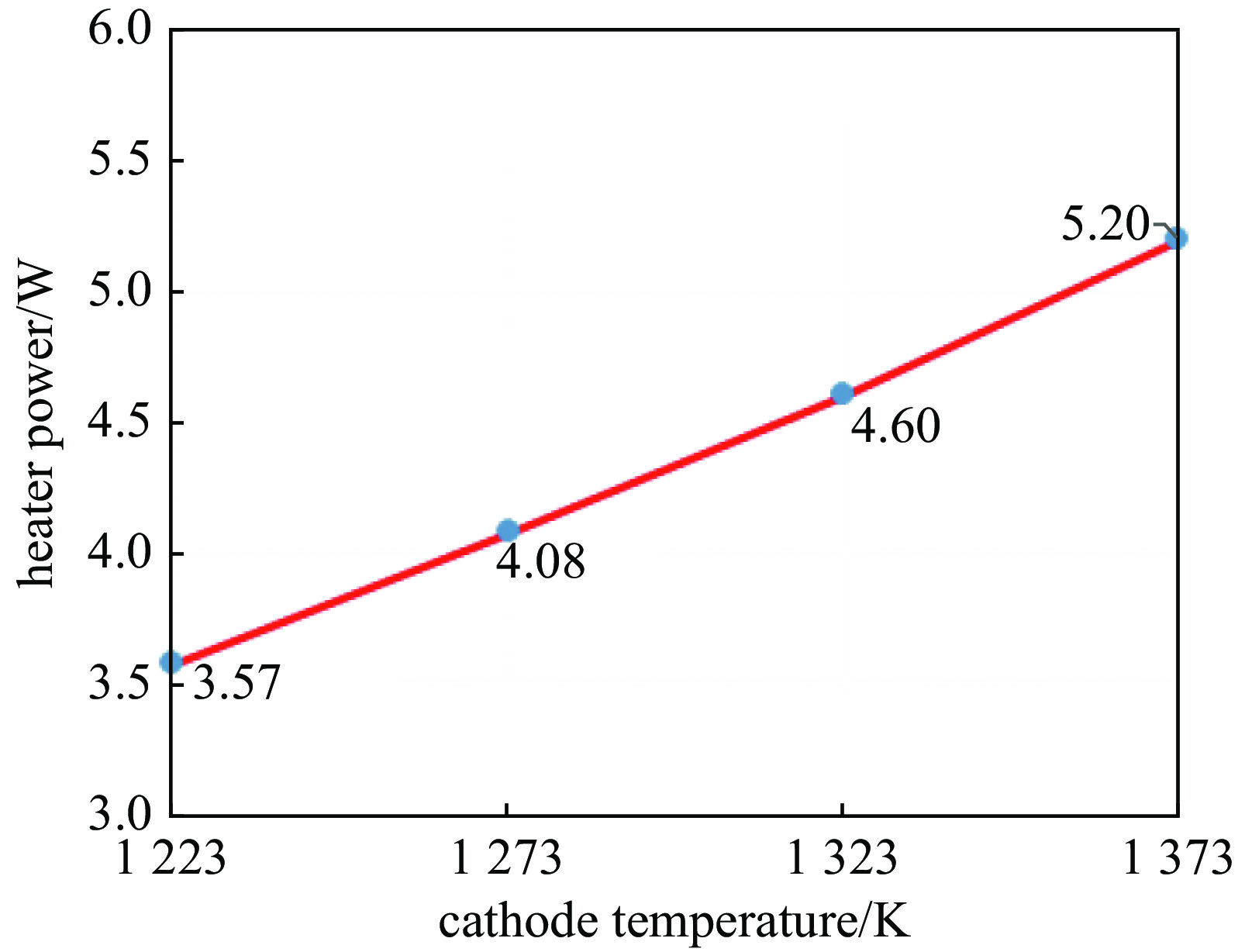
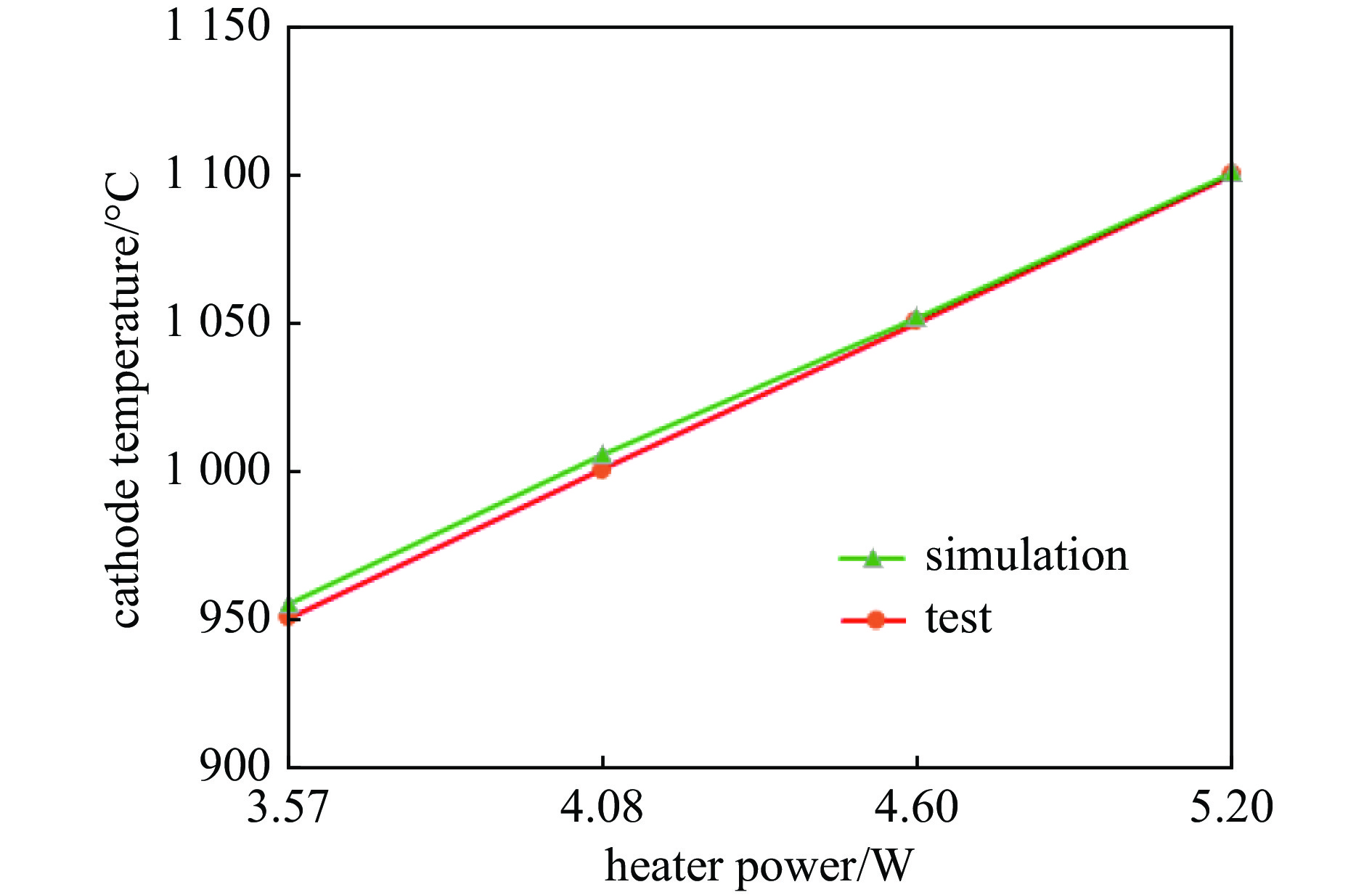
摘要: 由于行波管工作时无法直接测量阴极温度,目前主要通过组件测温和电子枪热仿真确定阴极工作温度。热辐射不仅是电子枪热量传递的主要途径之一,也是产生热损耗的主要因素,因而热辐射是电子枪热分析不可忽略的因素。对热损耗进行了定量分析,考虑了接触热阻和热损耗,建立了全面的热辐射边界,对阴极-热屏组件进行热仿真,通过调整零件表面发射率拟合了阴极-热屏组件测温实验数据曲线,得到了行波管电子枪高温区域零件表面的发射率,分析了热损耗、零件表面发射率对阴极温度的影响,并通过电子枪热平衡实验验证了所得发射率数值的正确性,进而得到了更准确的电子枪温度分布云图。研究表明,阴极温度950~
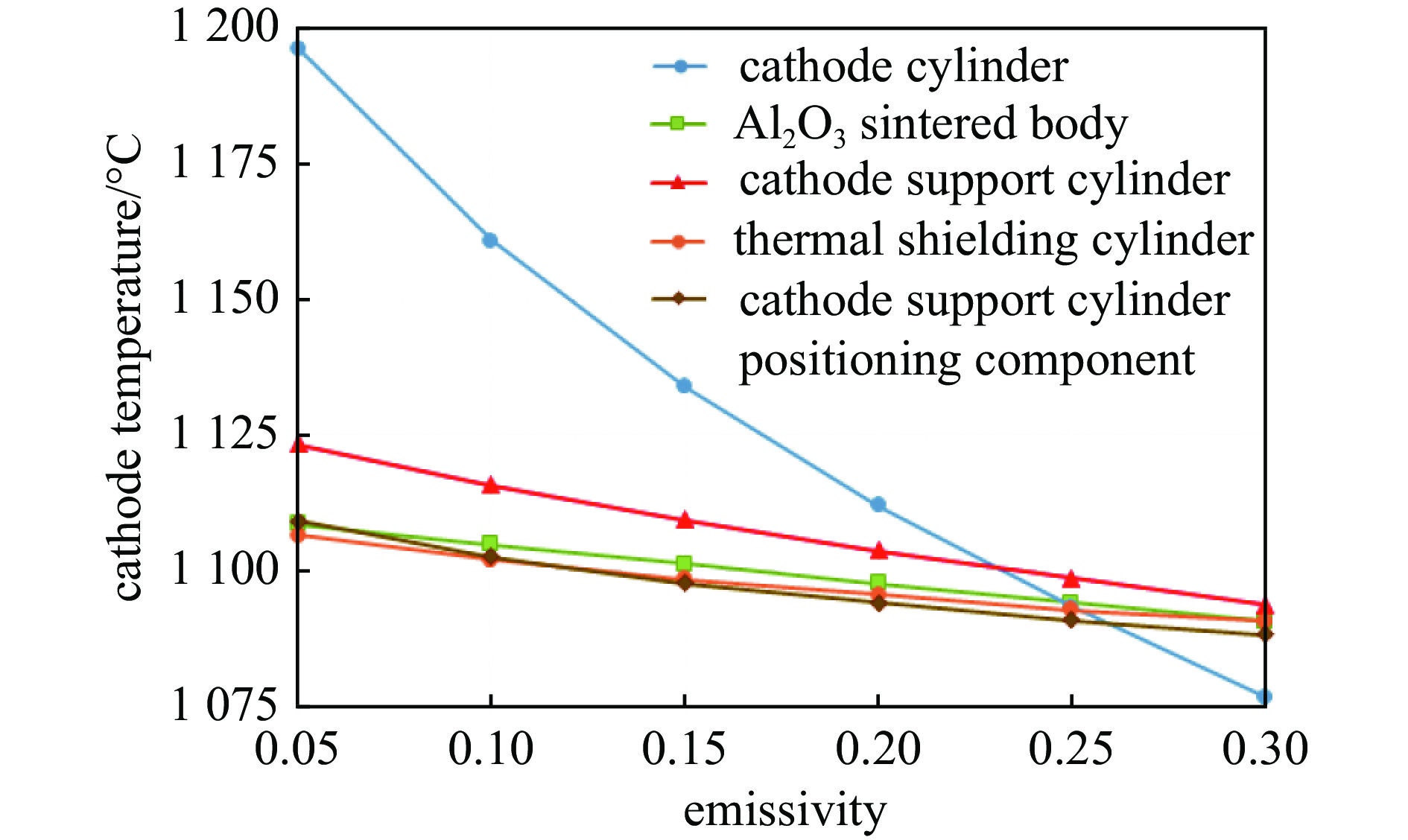
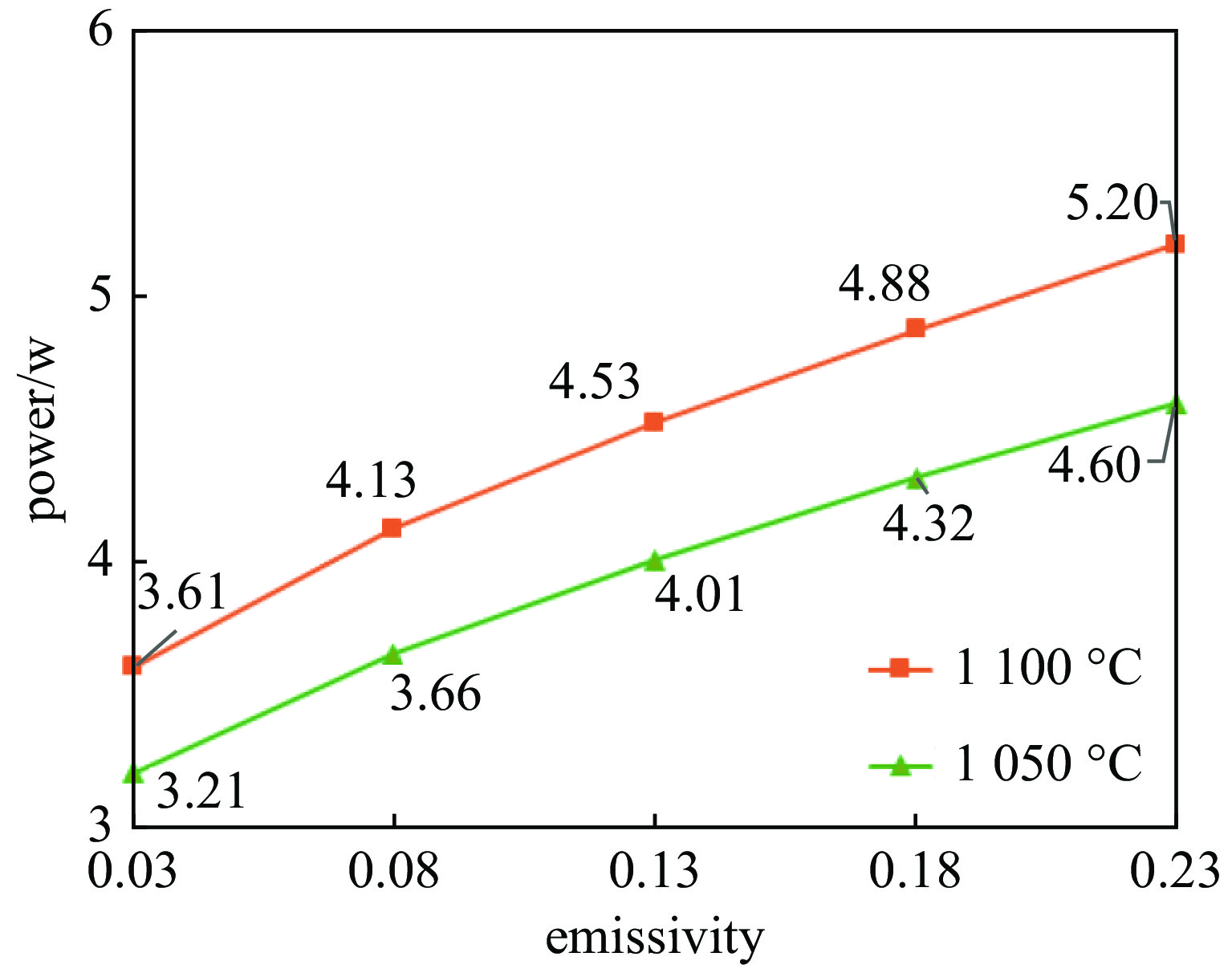
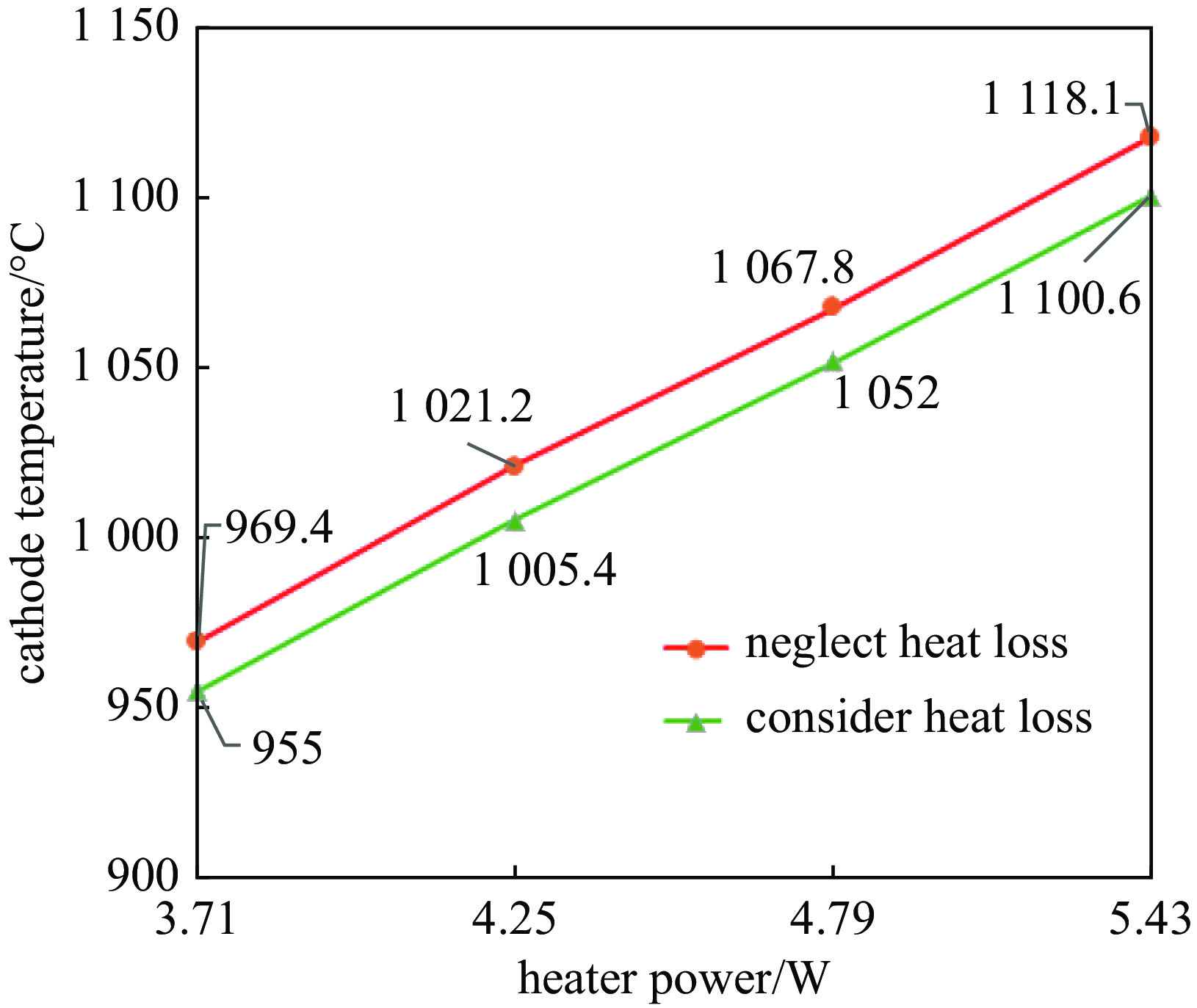
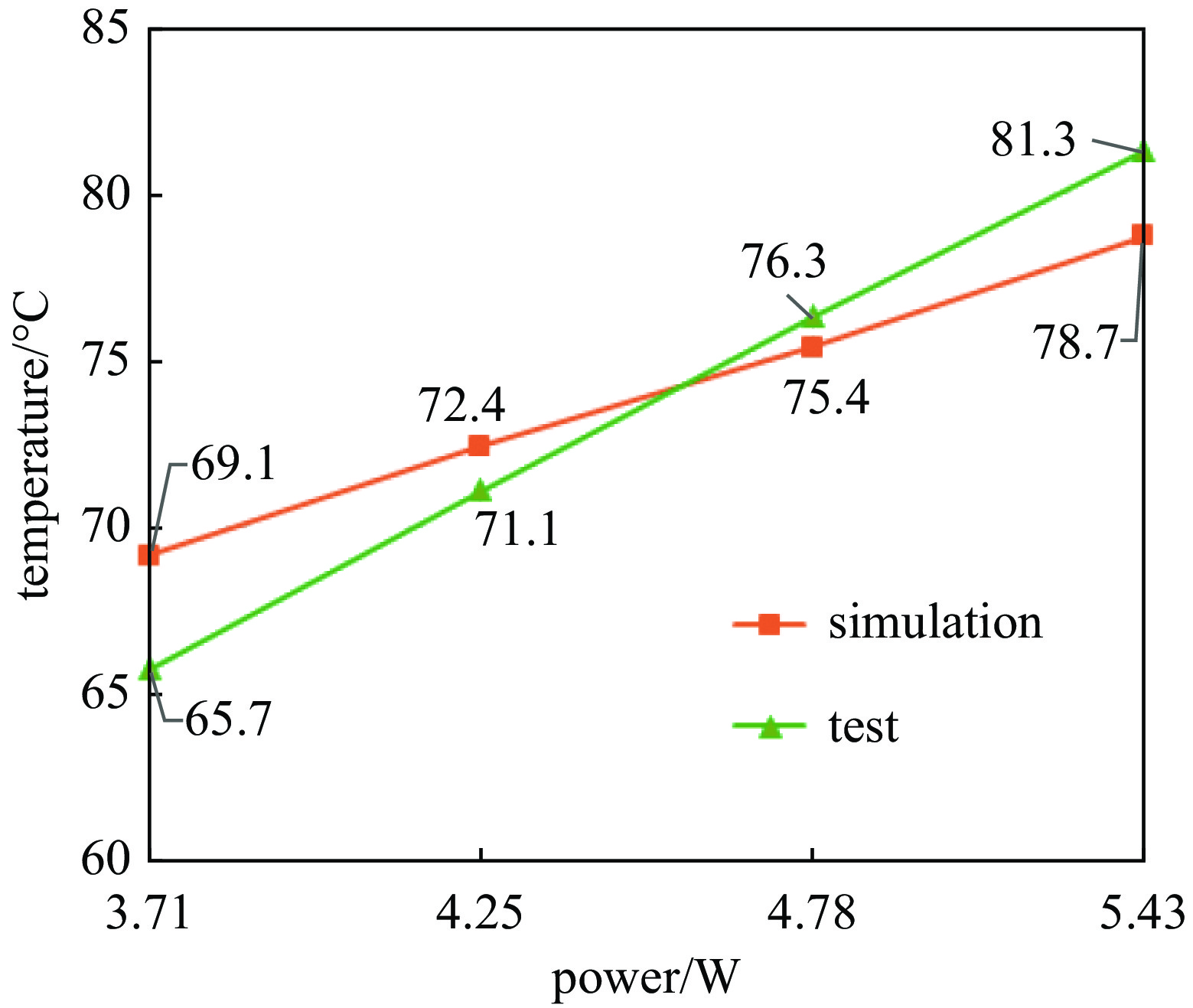
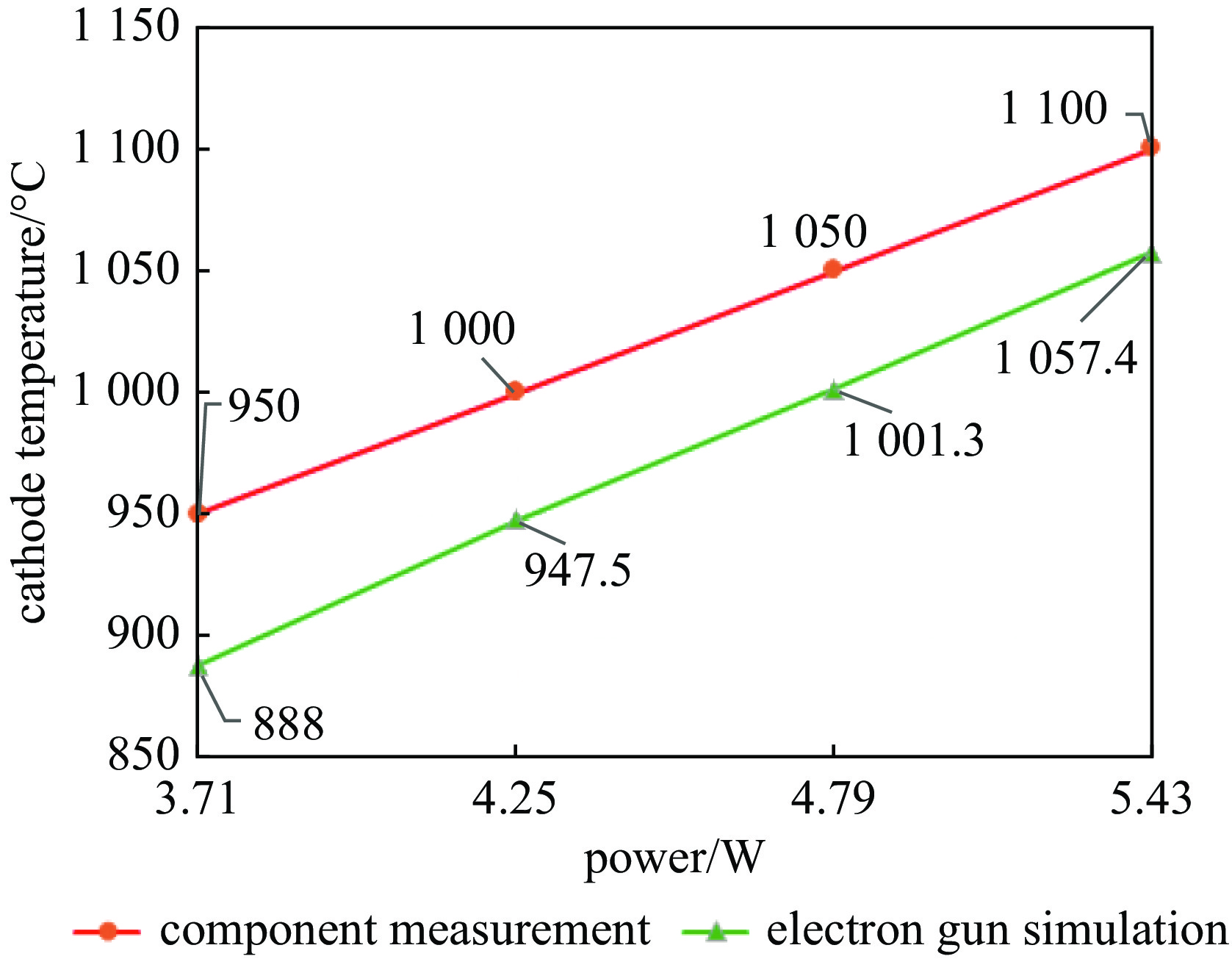
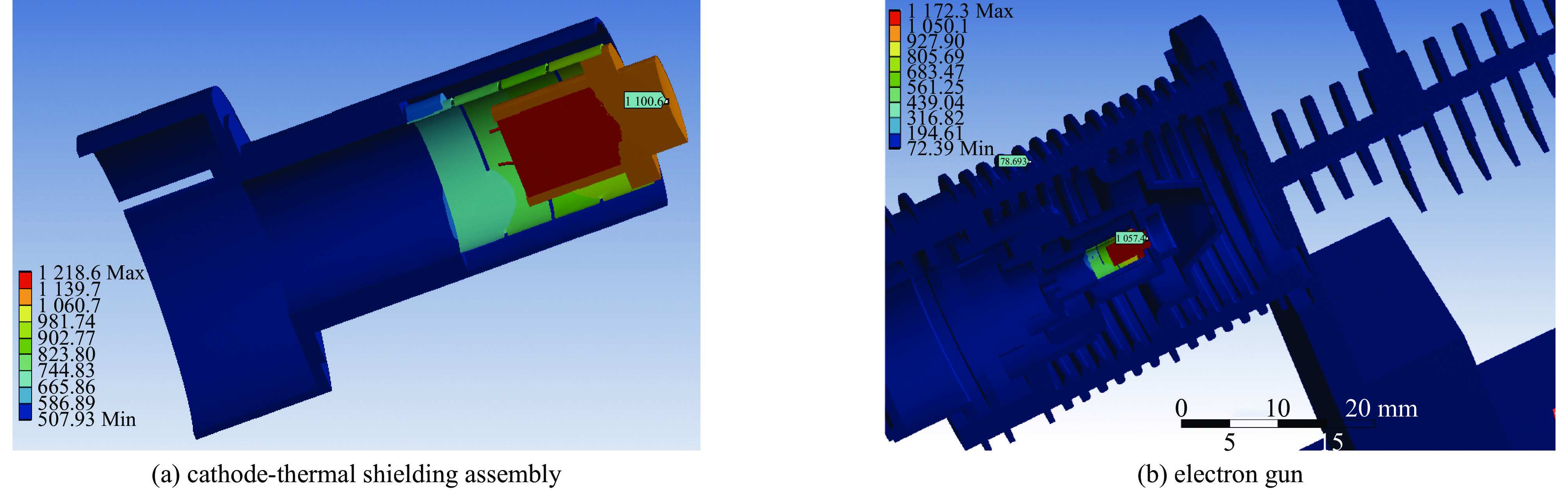
1100 ℃时其表面发射率为0.65;电子枪零件表面发射率越大,阴极温度越低,阴极筒表面发射率对阴极温度影响最大;温度越高热子热损耗越大,不考虑热损耗仿真得到的阴极表面温度偏高14.4~17.5 ℃;组件测温得到的阴极表面温度比整管时高42~62 ℃。Abstract: The working temperature of the cathode, as the electron source of traveling wave tubes (TWTs), directly impacts the performance, stability and lifespan of TWTs. Since the cathode’s temperature cannot be directly measured during TWT operation, it is primarily determined through component temperature measurement and electron gun thermal simulation. Thermal radiation is a significant heat transfer mode in the electron gun and a major factor in heat loss. Therefore, it cannot be ignored in the thermal analysis of the electron gun. The heat loss was quantitatively analyzed, the thermal simulation of cathode-thermal shielding assembly was conducted considering contact thermal resistance and heat loss, establishing a comprehensive thermal radiation boundary. The temperature measurement test data curve of the cathode-thermal shielding assembly was fitted by adjusting the surface emissivity of the parts to obtain its value in high-temperature regions of TWT electron guns. The impact of surface emissivity and heat loss on cathode temperature was analyzed, and the accuracy of obtained emissivity value was verified through a heat equilibrium test of electron gun, and then a more precise distribution cloud map of the electron gun was obtained. The research results show that the surface emissivity of cathode is 0.65 when the temperature is between 950 and1100 ℃. Besides, the higher the surface emissivity of electron gun components, the lower the cathode temperature, and the surface emissivity of the cathode cylinder has the greatest impact on the cathode temperature; the higher the temperature, the greater the heat loss of the heater. Without considering heat loss, the simulated cathode surface temperature is 14.4−17.5 ℃ higher. The surface temperature of the cathode obtained by component temperature measurement is 42−62 ℃ higher than that of the entire tube.-
Key words:
- traveling wave tube /
- cathode /
- thermal radiation /
- heat loss /
- emissivity
-
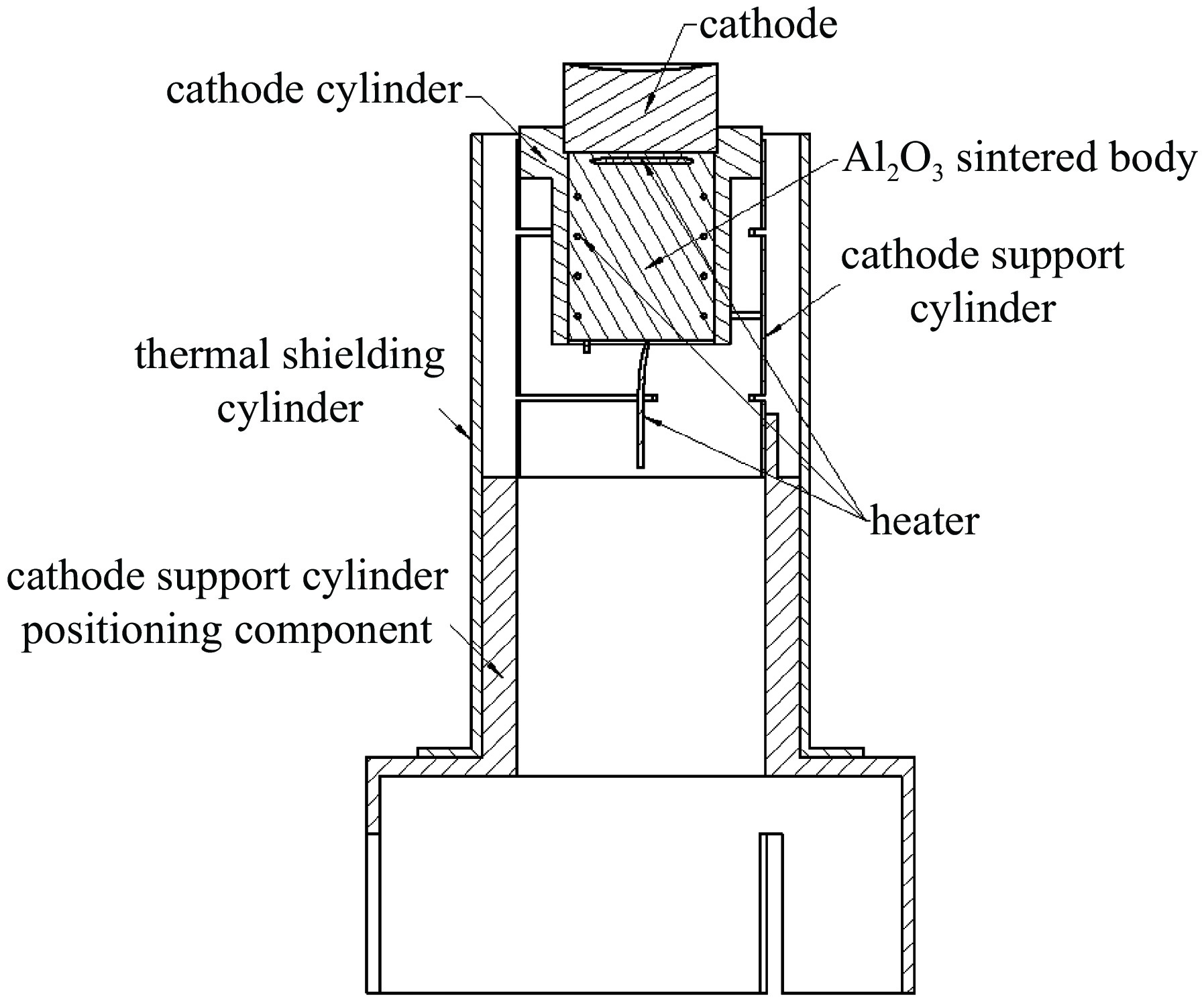
表 1 电子枪热仿真时需要设置的发射率
Table 1. Emissivity for thermal simulation of electron guns
part material emissivity cathode M-type ε1 Al2O3 sintered body Al2O3 ε2 cathode cylinder Mo ε3 cathode support cylinder Mo ε3 thermal shielding cylinder 4J36 ε4 cathode support cylinder positioning component 4J36 ε4 表 2 热损耗数据
Table 2. Heat loss data
T/K I/A ρ/(10−5 Ω·mm) ε Qgenerate/W Qloss/W 1323 0.696 55.84 0.153 0.14 0.13 1373 0.738 57.44 0.162 0.16 0.17 1423 0.777 59.00 0.171 0.18 0.20 1473 0.818 60.56 0.180 0.21 0.24 表 3 钨的发射率测量数据统计
Table 3. Measurement data statistics of tungsten emissivity
author temperature/K wavelength/μm ε1 compared to the value of
the target conditionLü Zheng[27] 3000 2.1~2.4 0.68~0.69 much larger Yao Longqing[28] 1300 0.65 0.46 larger Yu Kun[29] 873 3 0.25 much smaller Cagran C[30] 973~ 1283 2.2 0.26 slightly smaller Seifter A[31] 1800 0.65 0.54 much larger Brodu E[32] 1300 ~1500 0.6~2.8 0.36~0.39 similar 表 4 钼的发射率测量数据统计
Table 4. Measurement data statistics of molybdenum emissivity
表 5 铁镍合金、铁和钢的发射率测量数据统计
Table 5. Measurement data statistics of iron nickel alloy, iron and steel emissivity
表 6 建立的热辐射边界条件
Table 6. Established thermal radiation boundary conditions
correlation radiation face absorbing face emissivity estimate to ambient cathode emitting surface and exposed side ambience ε1 0.46~0.75 to ambient bottom surface of Al2O3 sintered body ambience ε2 0.15~0.2 to ambient upper and lower end faces of cathode cylinder ambience ε3 0.15~0.3 surface to surface outer surface of cathode cylinder internal surface of cathode support cylinder ε3 0.15~0.3 surface to surface outer surface of cathode support cylinder internal surface of thermal shielding cylinder ε3 0.15~0.3 to ambient outer surface of thermal shielding cylinder ambience ε4 0.1~0.2 to ambient inner and outer surfaces of the cathode support
cylinder positioning componentambience ε4 0.1~0.2 表 7 通过热仿真确定的发射率数值
Table 7. Emissivity values determined through thermal simulation
part material emissivity value cathode M-type ε1 0.65 Al2O3 sintered body Al2O3 ε2 0.16 cathode cylinder Mo ε3 0.23 cathode support cylinder Mo ε3 0.23 thermal shielding cylinder 4J36 ε4 0.12 thermal shielding cylinder positioning component 4J36 ε4 0.12 -
[1] 姚若妍, 唐涛, 赵国庆, 等. 螺旋线行波管慢波结构设计及注波互作用模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:063030 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.063030Yao Ruoyan, Tang Tao, Zhao Guoqing, et al. Design of slow-wave structure and beam-wave interaction simulation for helix traveling-wave tube[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 063030 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.063030 [2] 李莹, 边兴旺, 张琳, 等. G波段行波管电子枪设计与实验[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2023, 21(7):895-900Li Ying, Bian Xingwang, Zhang Lin, et al. Design and experiment research on electron gun of G band traveling wave tube[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2023, 21(7): 895-900 [3] 廖复疆. 真空电子技术: 信息化武器装备的心脏[M]. 2版. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2008: 181Liao Fujiang. Vacuum electronics: the heart of information equipment[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2008: 181 [4] 姚列明, 杨中海, 肖礼. 行波管电子枪设计中的热分析[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2005, 34(4):470-473 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2005.04.011Yao Lieming, Yang Zhonghai, Xiao Li. Thermal analysis in the design of electronic gun[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2005, 34(4): 470-473 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2005.04.011 [5] 程诚, 程道喜, 郑曙昕, 等. 新型热阴极电子枪加热结构热分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(7):1607-1609 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102207.1607Cheng Cheng, Cheng Daoxi, Zheng Shuxin, et al. Thermal analysis of heating structure for thermionic cathode electron gun[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(7): 1607-1609 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102207.1607 [6] Xu S X, Hou X W, Wang Z D, et al. Thermal analysis of electron gun for W-band gyro-traveling-wave amplifier[J]. Journal Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2018, 37(3): 275-277,283. [7] Bhat K S, Sreedevi K, Ravi M. Thermal analysis of electron gun for travelling wave tubes[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2006, 253(2): 679-682. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.12.154 [8] Sharma R K, Sinha A K, Sharma S M, et al. Thermal analysis of electron gun for a miniature helix TWT[J]. IETE Technical Review, 2000, 17(5): 269-274. doi: 10.1080/02564602.2000.11416915 [9] 戴景民, 王新北. 材料发射率测量技术及其应用[J]. 计量学报, 2007, 28(3):232-236Dai Jingmin, Wang Xinbei. Review of emissivity measurement and its applications[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2007, 28(3): 232-236 [10] 刘波, 郑伟, 李海洋. 材料表面发射率测量技术研究进展[J]. 红外技术, 2018, 40(8):725-732Liu Bo, Zheng Wei, Li Haiyang. Research and progress on material surface emissivity measurement[J]. Infrared Technology, 2018, 40(8): 725-732 [11] 张树养. 影响红外测温的主要因素分析研究[J]. 工业计量, 2023, 33(5):16-20Zhang Shuyang. Analysis and research on the main factors affecting infrared temperature measurement[J]. Industrial Metrology, 2023, 33(5): 16-20 [12] 于坤, 刘玉芳, 赵跃进. 光谱发射率测量标准参考材料研究进展[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(11):2911-2915Yu Kun, Liu Yufang, Zhao Yuejin. Review of normal spectral emissivity standard reference materials[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(11): 2911-2915 [13] 陈梦朝. 高温合金红外光谱发射率特性研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2022: 2-3Chen Mengchao. Research on infrared spectral emissivity characteristics of superalloys[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022: 2-3 [14] Pan Y J, Dong W, Lin H. Progress on spectral emittance measurement at temperature over 1000℃[C]//The 7th National Academic Exchange Conference on Temperature Measurement and Control. 2015: 105-113. [15] 万志, 任建伟, 李宪圣, 等. 一种红外光谱发射率测量装置的研制[J]. 发光学报, 2008, 29(1):200-203Wan Zhi, Ren Jianwei, Li Xiansheng, et al. The development of a kind of apparatus for measuring infrared spectral emissivity[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2008, 29(1): 200-203 [16] 宋芳芳, 张国兴, 何小琦, 等. 行波管阴极组件动态热耗散分析及优化设计[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2006, 26(2):118-122Song Fangfang, Zhang Guoxing, He Xiaoqi, et al. Dynamic thermal dissipation of cathode module in electron gun of traveling wave tube[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2006, 26(2): 118-122 [17] 阴生毅, 王宇, 王欣欣. 钨粉分级及其在M型阴极上的应用[J]. 中国钨业, 2010, 25(2):31-33Yin Shengyi, Wang Yu, Wang Xinxin. The tungsten powder grading and its application on M-type cathodes[J]. China Tungsten Industry, 2010, 25(2): 31-33 [18] Lucken J A. Some aspects of circuit power dissipation in high power CW helix traveling-wave tubes, part Ⅰ: general theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 1969, 16(9): 813-820. doi: 10.1109/T-ED.1969.16858 [19] 孟鸣凤, 俞世吉, 徐振英, 等. 行波管阴极热子组件结构的热分析[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2009, 29(5):513-516Meng Mingfeng, Yu Shiji, Xu Zhenying, et al. Thermal analysis of differently-structured cathode-heater assemblies in traveling wave tube[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2009, 29(5): 513-516 [20] 景天虎. 螺旋钢筋纯螺旋段长度的计算[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2006, 18(9):217-220Jing Tianhu. Calculation of the pure spiral section length of spiral steel bars[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2006, 18(9): 217-220 [21] 黄美超. 钨铼高温热电偶合金的热性质[J]. 功能材料, 1975, 18(1):73-74Huang Meichao. Thermal properties of tungsten rhenium high-temperature thermocouple alloy[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 1975, 18(1): 73-74 [22] 张依雨, 魏义学, 孟晓君. 行波管电子枪稳态热分析仿真模型参数设置方法[J]. 真空电子技术, 2015(2):46-49Zhang Yiyu, Wei Yixue, Meng Xiaojun. Parameters setting method of steady-state thermal analysis model of electron gun for traveling wave tubes[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2015(2): 46-49 [23] 曹鼎汉. 维恩位移定律及其应用[J]. 红外技术, 1994, 16(2):46-48Cao Dinghan. Wien’s displacement law and its application[J]. Infrared Technology, 1994, 16(2): 46-48 [24] 余其铮. 辐射换热原理[M]. 北京: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2000: 34Yu Qizheng. Radiation heat transfer principle[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2000: 34 [25] 张宇峰. 材料发射率测量技术与应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2021: 8Zhang Yufeng. Measurement technology and application of material emissivity[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2021: 8 [26] 熊磊, 曾鸣, 周波, 等. 涂层半球发射率影响因素的研究[J]. 节能技术, 2021, 39(5):426-431Xiong Lei, Zeng Ming, Zhou Bo, et al. Influence factors of hemispherical emissivity of coatings[J]. Energy Conservation Technology, 2021, 39(5): 426-431 [27] 吕正, 代彩红, 于家琳. 钨的光谱发射率测量[J]. 现代测量与实验室管理, 2004, 12(2):9-11Lv Zheng, Dai Caihong, Yu Jialin. Measurement of spectral emissivity of tungsten[J]. China Inspection Body & Laboratory, 2004, 12(2): 9-11 [28] 姚隆卿, 贺履平, 郝玉才, 等. 金属材料的高温热物理性能测试[J]. 工程热物理学报, 1984, 2(2):185-187Yao Longqing, He Luping, Hao Yucai, et al. A method for measuring multiple thermalphysical properties of metallic materials at high temperature[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 1984, 2(2): 185-187 [29] 于坤, 石瑞涛, 张会燕, 等. 纯钨红外光谱发射率特性研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(1):107-112Yu Kun, Shi Ruitao, Zhang Huiyan, et al. Experimental investigation of infrared spectral emissivity of pure tungsten[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(1): 107-112 [30] Cagran C, Pottlacher G, Rink M, et al. Spectral emissivities and emissivity X-points of pure molybdenum and tungsten[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2005, 26(4): 1001-1015. doi: 10.1007/s10765-005-6680-1 [31] Seifter A, Sachsenhofer F, Pottlacher G. A fast laser polarimeter improving a microsecond pulse heating system[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2002, 23(5): 1267-1280. doi: 10.1023/A:1019852506410 [32] Brodu E, Balat-Pichelin M, Sans J L, et al. Evolution of the emissivity of tungsten at high temperature with and without proton bombardment[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 84: 305-316. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2014.10.050 [33] 葛绍岩, 那鸿悦. 热辐射性质及其测量[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 8-9Ge Shaoyan, Na Hongyue. Thermal radiation properties and measurement[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989: 8-9 [34] 于志强, 邵文生, 李季, 等. M型阴极寿命特性分析[J]. 真空电子技术, 2014(6):32-35,65Yu Zhiqiang, Shao Wensheng, Li Ji, et al. Life characteristic analysis of M-type dispenser cathodes[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2014(6): 32-35,65 [35] 柯维娜, 朱定强, 蔡国飙. 金属光谱发射率的仿真与分析[J]. 航空学报, 2010, 31(11):2139-2145Ke Weina, Zhu Dingqiang, Cai Guobiao. Simulation and analysis of spectral emissivity of metals[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2010, 31(11): 2139-2145 [36] 圆山重直. 传热学[M]. 王世学, 张信荣, 译. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2011: 108Yuanshan C. Heat transfer[M]. Wang Shixue, Zhang Xinrong, trans. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2011: 108 [37] 徐艺寒. 钼的光谱发射率特性研究[D]. 郑州: 河南师范大学, 2019: 19-20Xu Yihan. A research on the spectral emissivity of molybdenum[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Normal University, 2019: 19-20 [38] Taylor J E. The variation with wavelength of the spectral emissivity of iron and molybdenum[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1952, 42(1): 33-36. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.42.000033 [39] 朱映山, Herve P, 常海萍. 金属在高温状态下复折射率的确定[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2008, 29(12):2097-2100 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2008.12.032Zhu Yingshan, Herve P, Chang Haiping. Determination of complex refractive index of metal at high temperature[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2008, 29(12): 2097-2100 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2008.12.032 [40] Brodu E, Balat-Pichelin M, Sans J L, et al. Efficiency and behavior of textured high emissivity metallic coatings at high temperature[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 83: 85-94. [41] Wilthan B, Cagran C, Pottlacher G, et al. Normal spectral emissivity at 684.5nm of the liquid binary system Fe-Ni[J]. Monatshefte für Chemie, 2005, 136(11): 1971-1976. [42] 白银雪. 铁镍合金熔融光谱发射率特性研究[D]. 新乡: 河南师范大学, 2022: 38-39Bai Yinxue. Study on characteristics of melting spectral emissivity of Fe-Ni alloy[D]. Xinxiang: Henan Normal University, 2022: 38-39 [43] 于坤, 刘玉芳, 贾光瑞, 等. 影响钢表面红外光谱发射率的因素分析[J]. 红外技术, 2011, 33(5):289-292 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8891.2011.05.010Yu Kun, Liu Yufang, Jia Guangrui, et al. Analysis on factors affecting the infrared spectral emissivity of steel surface[J]. Infrared Technology, 2011, 33(5): 289-292 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8891.2011.05.010 [44] 卞伯绘. 辐射换热的分析与计算[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1988: 29Bian Baihui. Analysis and calculation of radiation heat transfer[M]. Beijing: Tsing University Press, 1988: 29 [45] GB/T 34515-2017, 航天器热平衡实验方法[S]GB/T 34515-2017, Thermal balance test method for spacecraft[S] [46] 王龙升. 高温条件下材料光谱发射率测量研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2014: 2-8Wang Longsheng. Study on the measurement of material spectral emissivity at high temperature[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2014: 38 [47] 肖斌安, 龚烈航, 曾锐. 金属红外发射率的分析和仿真研究[J]. 红外技术, 2008, 30(6):358-360Xiao Bin’an, Gong Liehang, Zeng Rui. Analysis and simulation of metallic infrared emissivity[J]. Infrared Technology, 2008, 30(6): 358-360 [48] Haugh M J. Radiation thermometry in the aluminum industry[M]//DeWitt D P, Nutter G D. Theory and practice of radiation thermometry. New York: Wiley, 1988: 905-971. -




 下载:
下载: