Study of drive laser shaping system for C-band photocathode RF gun
-
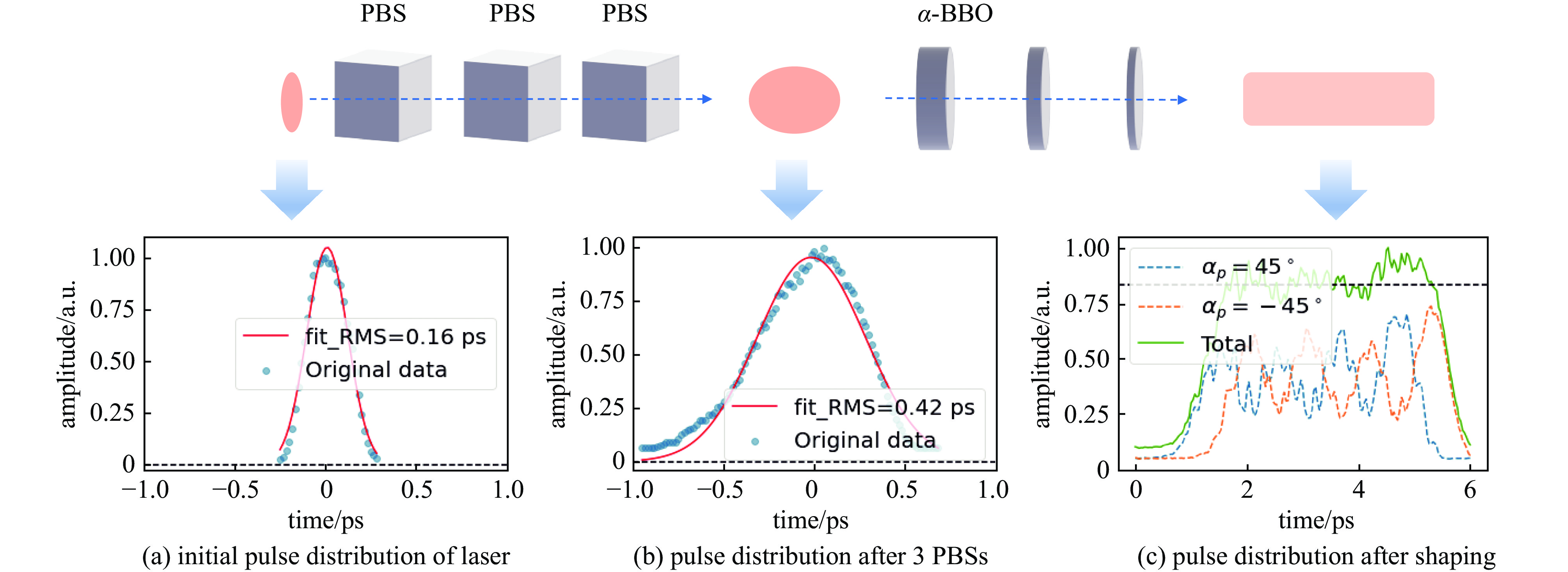
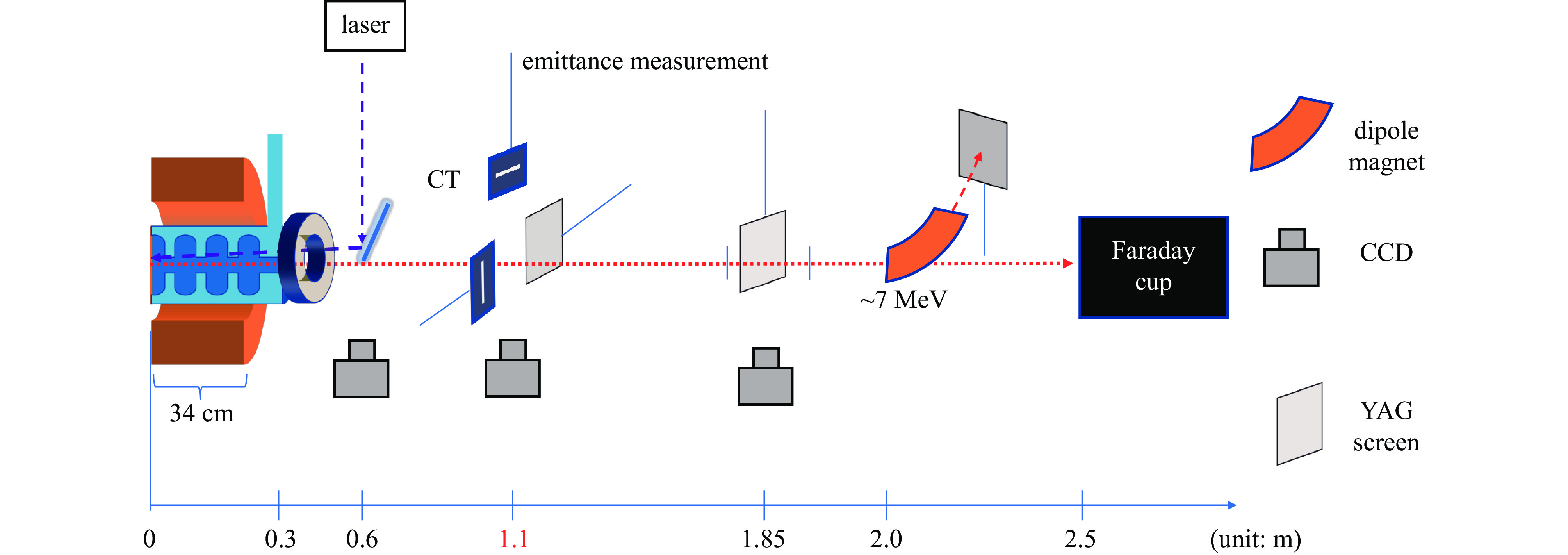
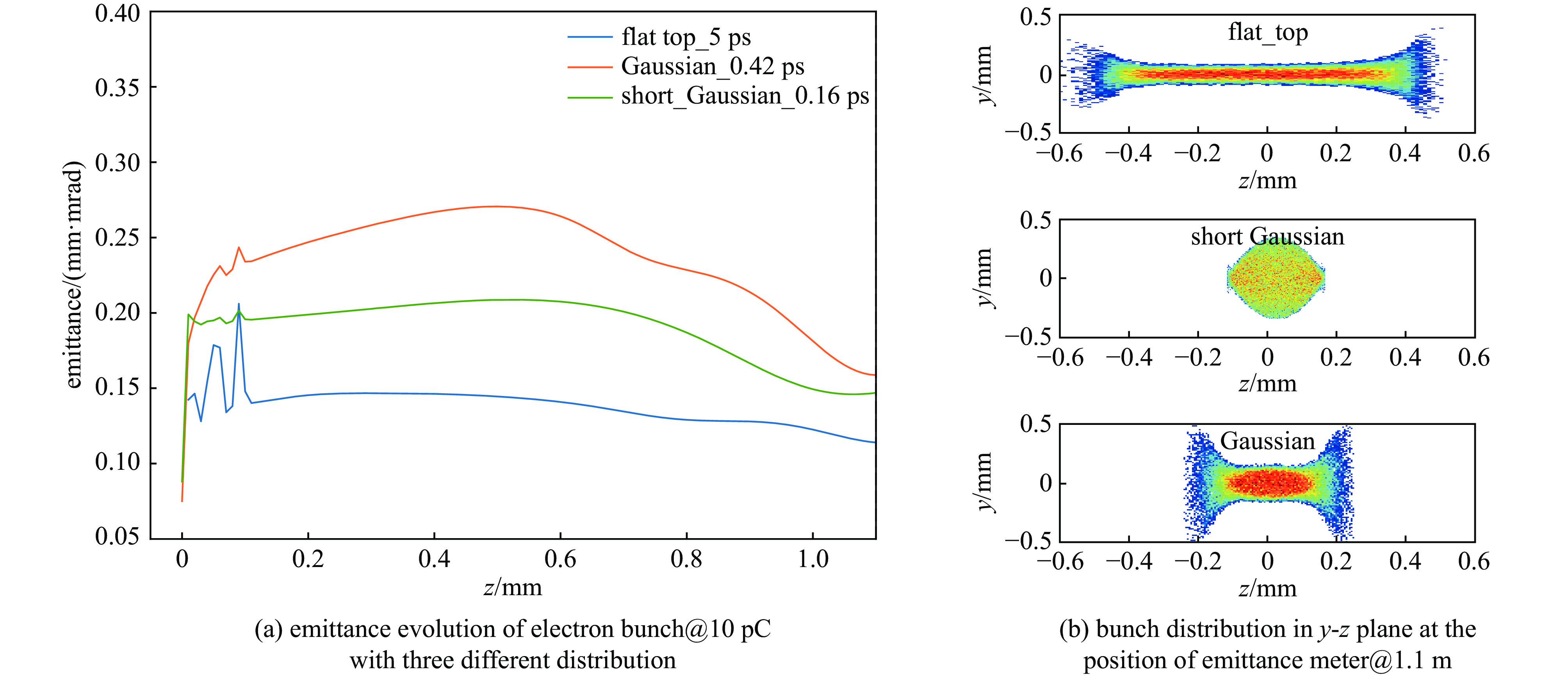
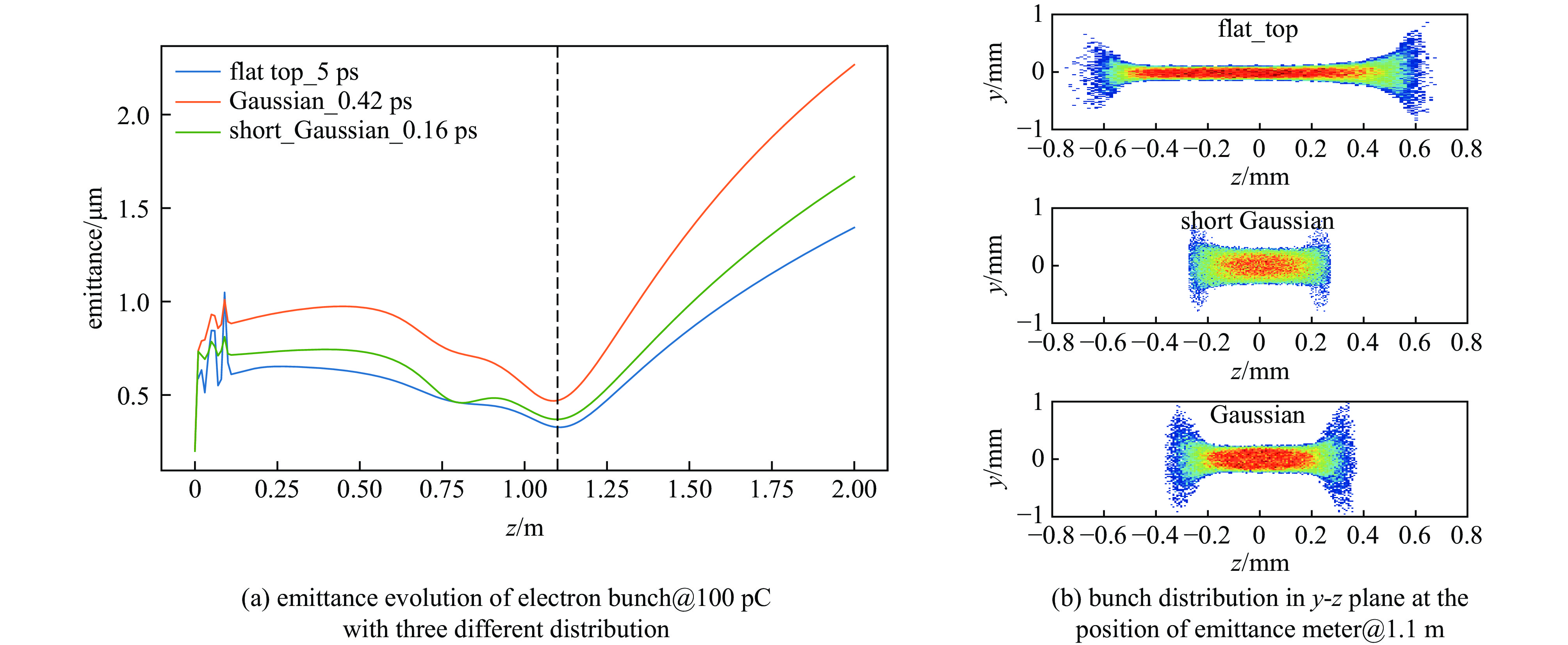
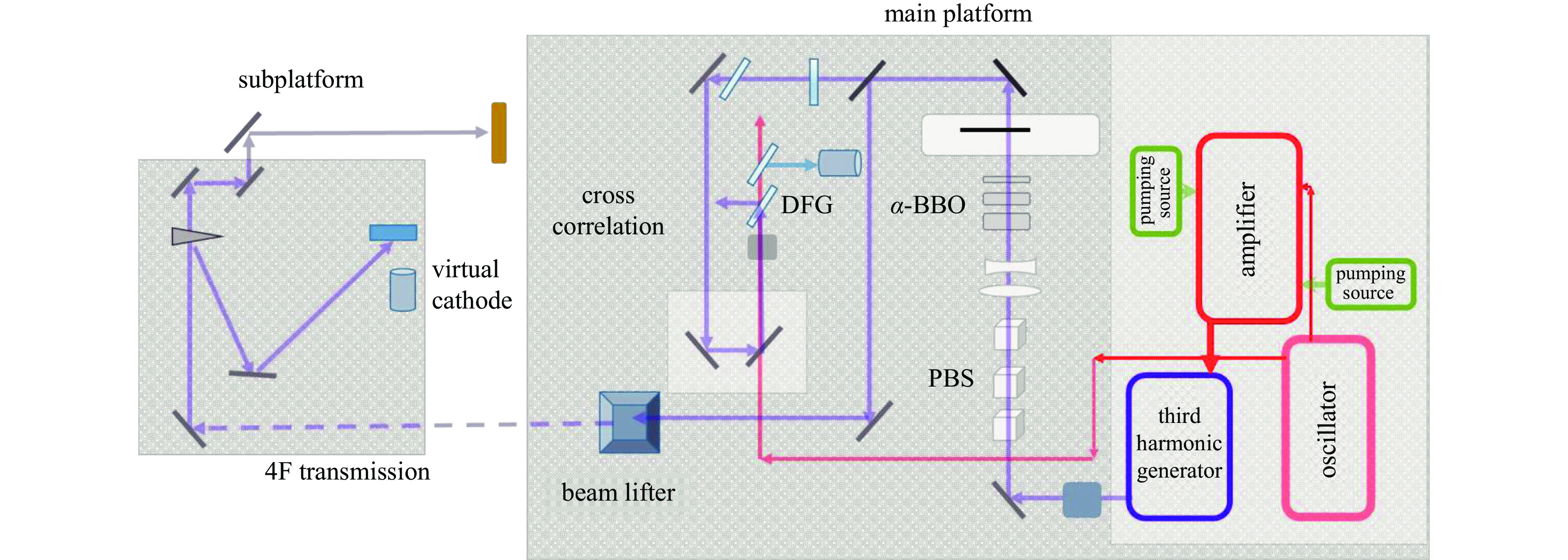
摘要: 在光阴极电子枪系统当中,驱动激光的时空整形是实现束流低发射度的关键之一。基于南方光源预研项目C波段光阴极电子枪测试平台,介绍了驱动激光系统的布局与测试相关内容。测试平台于国内首次采用初始RMS脉冲长度为160 fs的266 nm激光作为驱动激光,利用双折射晶体的脉冲时间延迟完成对激光脉冲纵向时间整形,并配备多个孔径的可调光阑实现对束流的横向尺寸的调节。经过整形,激光平台可以提供纵向RMS长度为160 fs、420 fs的高斯脉冲激光与半高全宽为5 ps的平顶分布脉冲激光,根据激光测试结果,简要分析了不同脉冲分布对于束流发射度演化以及脉冲分布的影响,不仅为后续光阴极电子枪束流调试提供了指导,并对初始脉冲分布对空间电荷力的影响实现更加深入的研究提供了支持。Abstract: In photocathode electron gun system, the space-time shaping of the laser is one of the important parts to achieve low emittance of the beam. Based on the C-band photocathode electron gun test platform of the Southern Advanced Photon Source pre-research project, the layout and testing of the drive laser system are introduced in this paper. A 266 nm laser with an initial RMS pulse length of 160 fs is first used as the driving laser in the test platform in China. The longitudinal time of the laser pulse is shaped by the pulse time delay of the birefringent crystal, and the transverse beam is realized by an adjustable diaphragm with multiple apertures. After shaping, the laser platform can provide a Gaussian pulse with a longitudinal RMS length of 160 fs and 420 fs, and a flat-top distributed pulse laser with FWHM of 5 ps. According to the laser test results, the influence of different pulse distributions on beam emittance evolution and pulse distribution is briefly analyzed in this paper. It provides not only a guidance for the photocathode electron gun commissioning, but also support for further research on the effect of initial pulse distribution on space charge force.
-
Key words:
- photocathode RF gun /
- C-band /
- laser shaping /
- birefringent crystal /
- emittance
-
表 1 激光系统参数要求
Table 1. Parameters required for drive laser system
wavelength/nm pulse energy in cathode/µJ RMS radius/mm FWHM/ps longitudinal distribution 266 ≥150 ≤0.15 ≤5 flat-top 表 2 激光器参数
Table 2. Parameters of drive laser
element wavelength/nm pulse RMS width/fs repetition rate/Hz pulse energy/mJ oscillator 800 100 79.33×106 15×10−6 amplifier 800 − 1~100 13 third harmonic generator 266 160 1~100 2 表 3 α-BBO晶体的参数
Table 3. Parameters of α-BBO
No. wavelength/nm L/mm time delay/ps 1 266 0.71 0.6 2 266 1.42 1.2 3 266 2.84 2.4 -
[1] Rao T S, Dowell D H. An engineering guide to photoinjectors(2013)[M/OL]. Available at:. https://arxiv.org/abs/1403.7539. [2] Li Cheng, Wang Wenxing, Zhang Haoran, et al. Few-femtosecond MeV electron bunches for ultrafast electron diffraction[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2022, 17: 064012. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.17.064012 [3] Ackermann W, Asova G, Ayvazyan V, et al. Operation of a free-electron laser from the extreme ultraviolet to the water window[J]. Nature Photonics, 2007, 1(6): 336-342. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.76 [4] Schaap B H, De Vos T D C, Smorenburg P W, et al. Photon yield of superradiant inverse Compton scattering from microbunched electrons[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2022, 24: 033040. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/ac59eb [5] Zheng Lianmin, Du Yingchao, Zhang Zhe, et al. Development of S-band photocathode RF guns at Tsinghua University[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2016, 834: 98-107. [6] Xu Hanxun, Shi Jiaru, Du Yingchao, et al. Development of an L-band photocathode RF gun at Tsinghua University[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2021, 985: 164675. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2020.164675 [7] Fang Wencheng, Gu Qiang, Sheng Xing, et al. Design, fabrication and first beam tests of the C-band RF acceleration unit at SINAP[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2016, 823: 91-97. [8] Limborg-Deprey C, Adolphsen C, McCormick D, et al. Performance of a first generation X-band photoelectron RF gun[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2016, 19: 053401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.19.053401 [9] Bettoni S, Divall M C, Ganter R, et al. Impact of laser stacking and photocathode materials on microbunching stability in photoinjectors[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2020, 23: 024401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.23.024401 [10] Limborg-Deprey C, Bolton P R. Optimum electron distributions for space charge dominated beams in photoinjectors[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2006, 557(1): 106-116. [11] Zhou Feng, Brachmann A, Emma P, et al. Impact of the spatial laser distribution on photocathode gun operation[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2012, 15: 090701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.15.090701 [12] 李成, 汪文星, 李伟伟, 等. 光阴极微波电子枪驱动激光整形与传输系统[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:094002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210091Li Cheng, Wang Wenxing, Li Weiwei, et al. Drive laser shaping and transport system for photocathode RF gun[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 094002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210091 [13] Rublack T, Khojoyan M, Krasilnikov M, et al. Development of a quasi 3-D ellipsoidal photo cathode laser system for PITZ[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC 2014). 2014: 3. [14] Mironov S Y, Potemkin A K, Gacheva E I, et al. Shaping of cylindrical and 3D ellipsoidal beams for electron photoinjector laser drivers[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(7): 1630-1635. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.001630 [15] Musumeci P, Moody J T, England R J, et al. Experimental generation and characterization of uniformly filled ellipsoidal electron-beam distributions[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100: 244801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.244801 [16] Liu Xingguang. A C-band test platform for the development of RF photo cathode and high gradient accelerating structures[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2023: 1995-1998. [17] Liu X G, Jiao Y, Li B B, et al. Preliminary design of the full energy Linac injector for the southern advanced photon source[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2021. [18] Floettmann K. ASTRA: a space charge tracking algorithm version 3.2[M]. Hamburg: DESY, 2017. -




 下载:
下载: