Development of distributed all-solid-state waveform adjustable high-voltage pulse generator
-
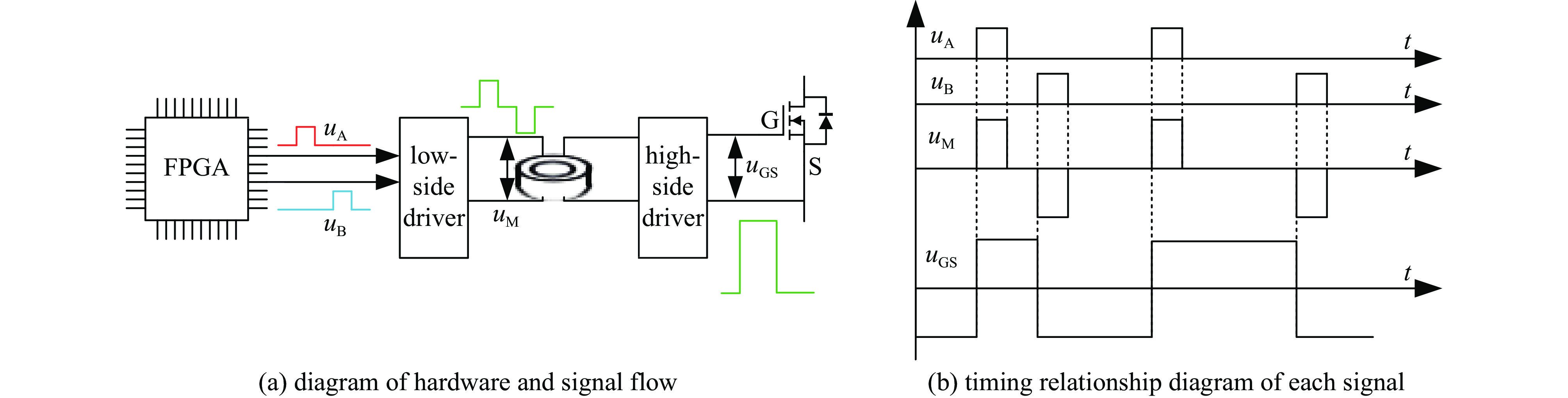
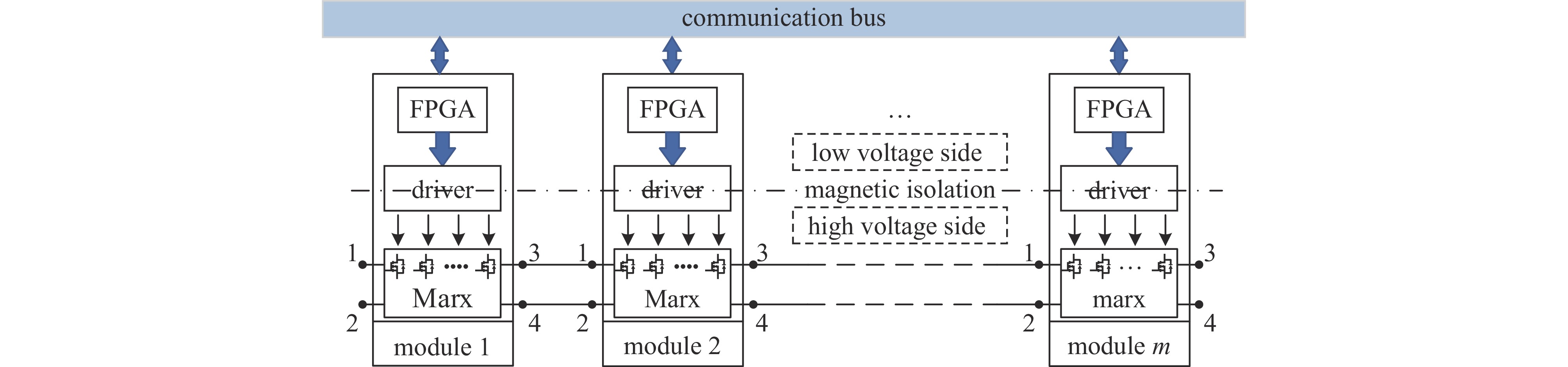
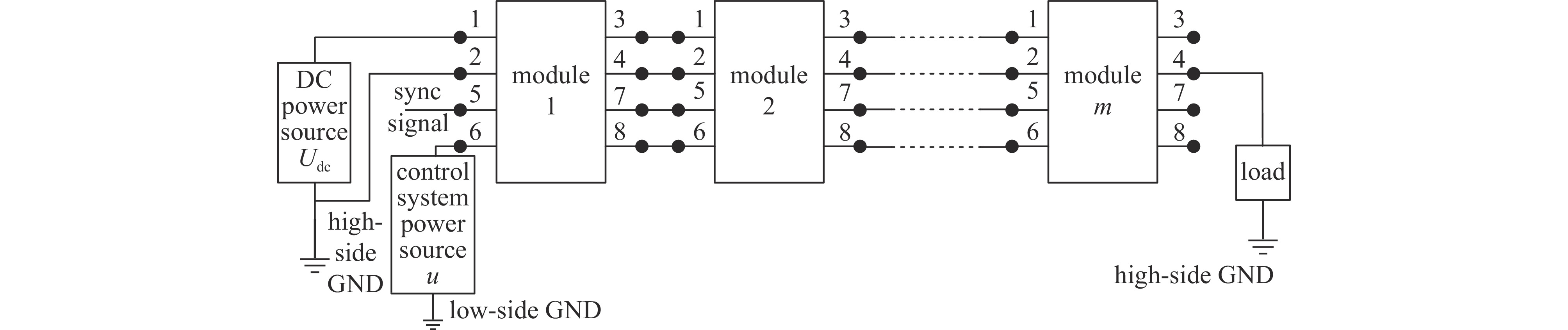
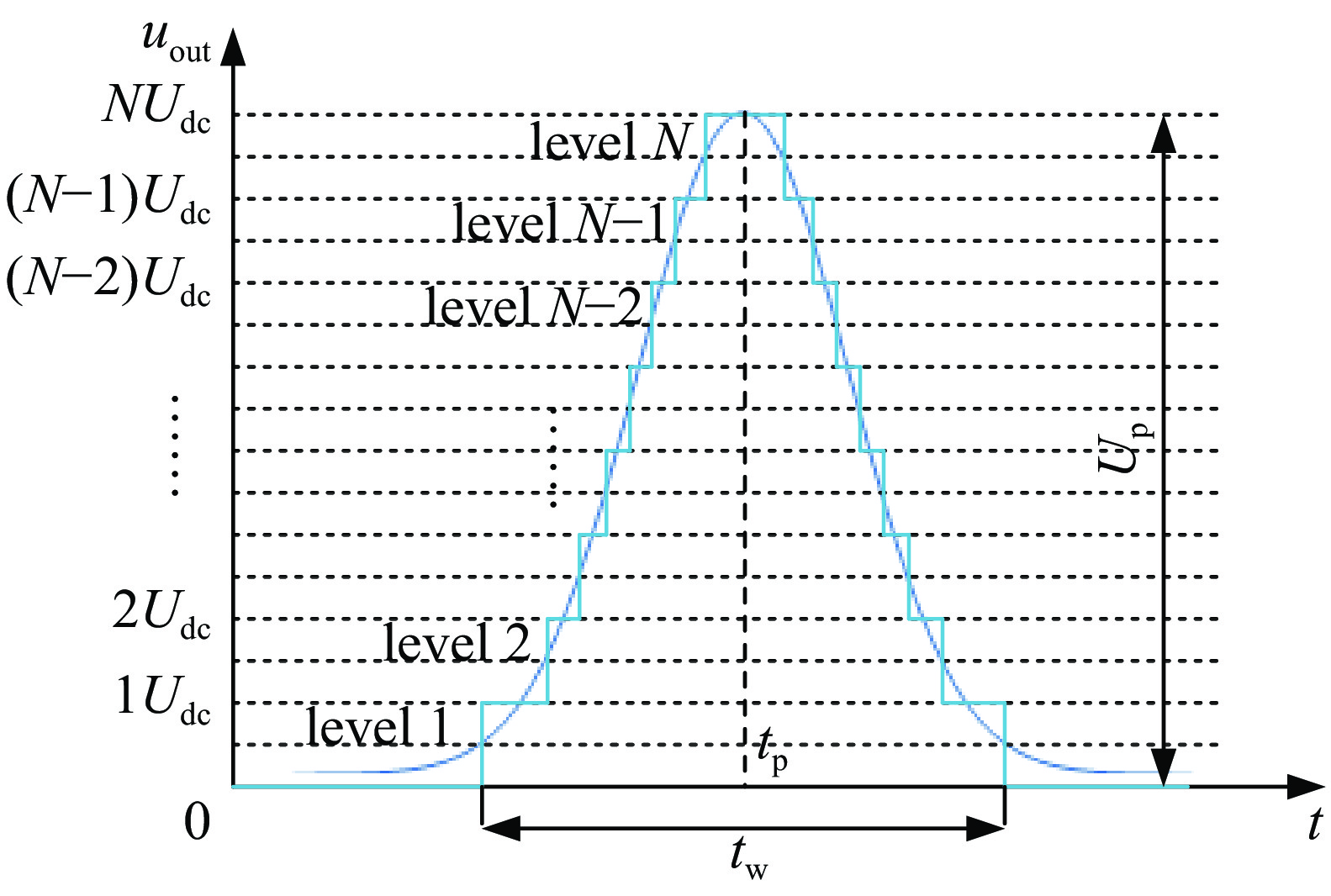
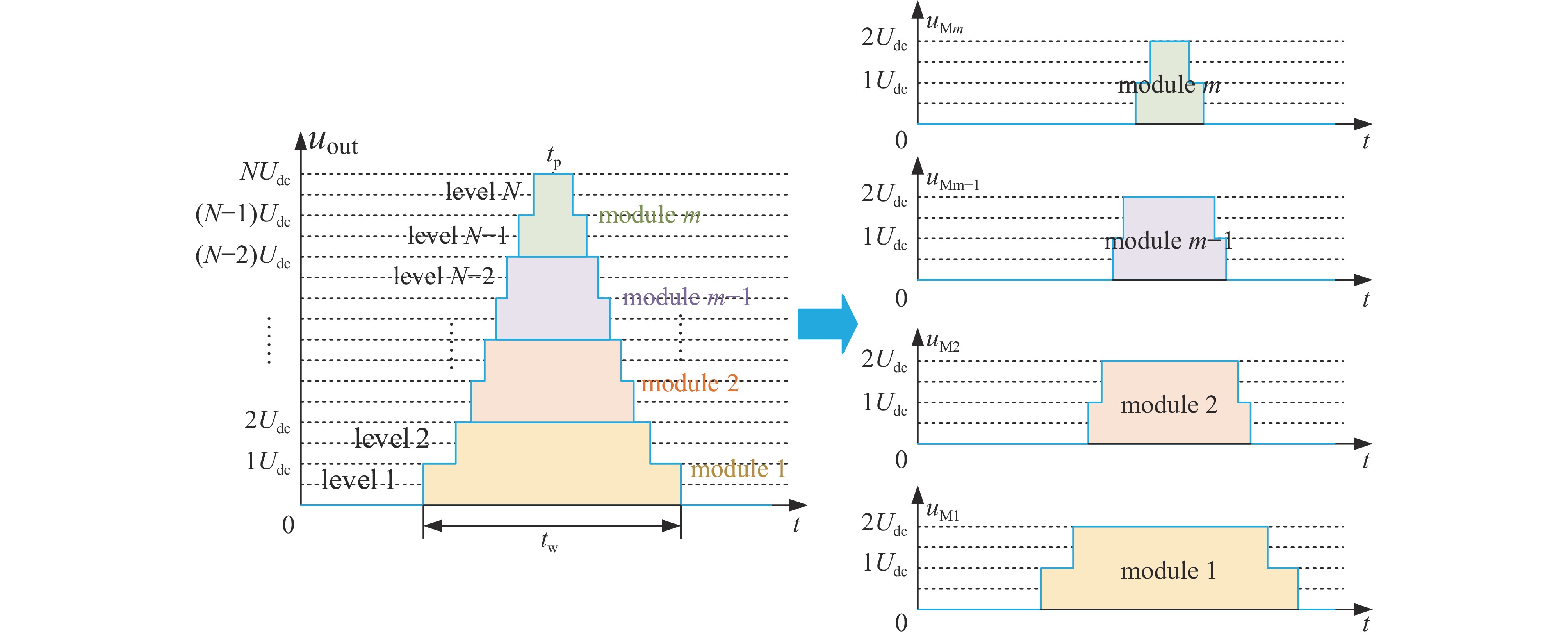
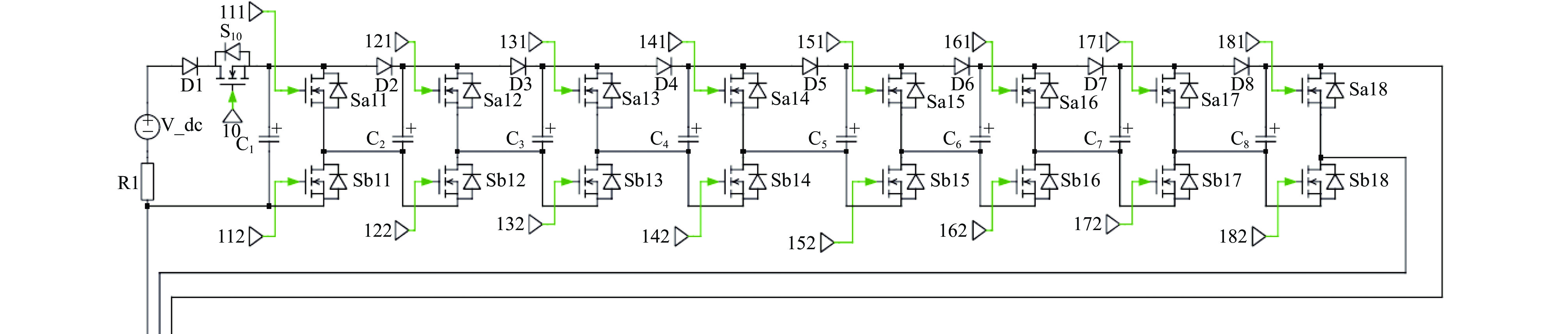
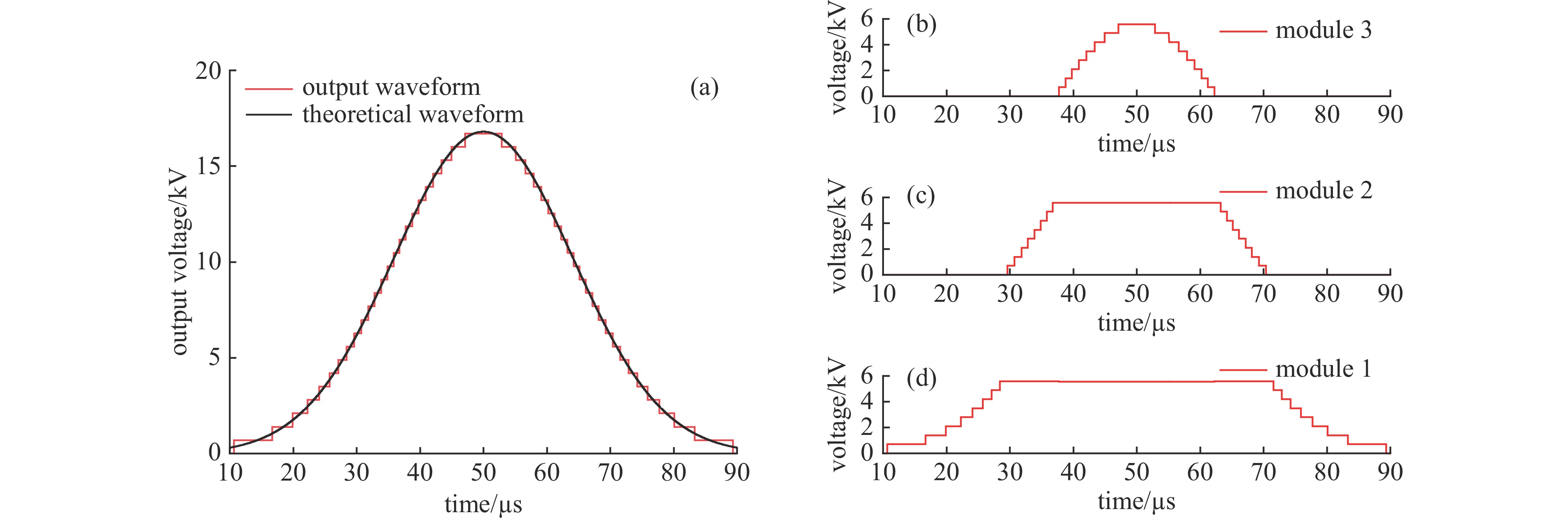
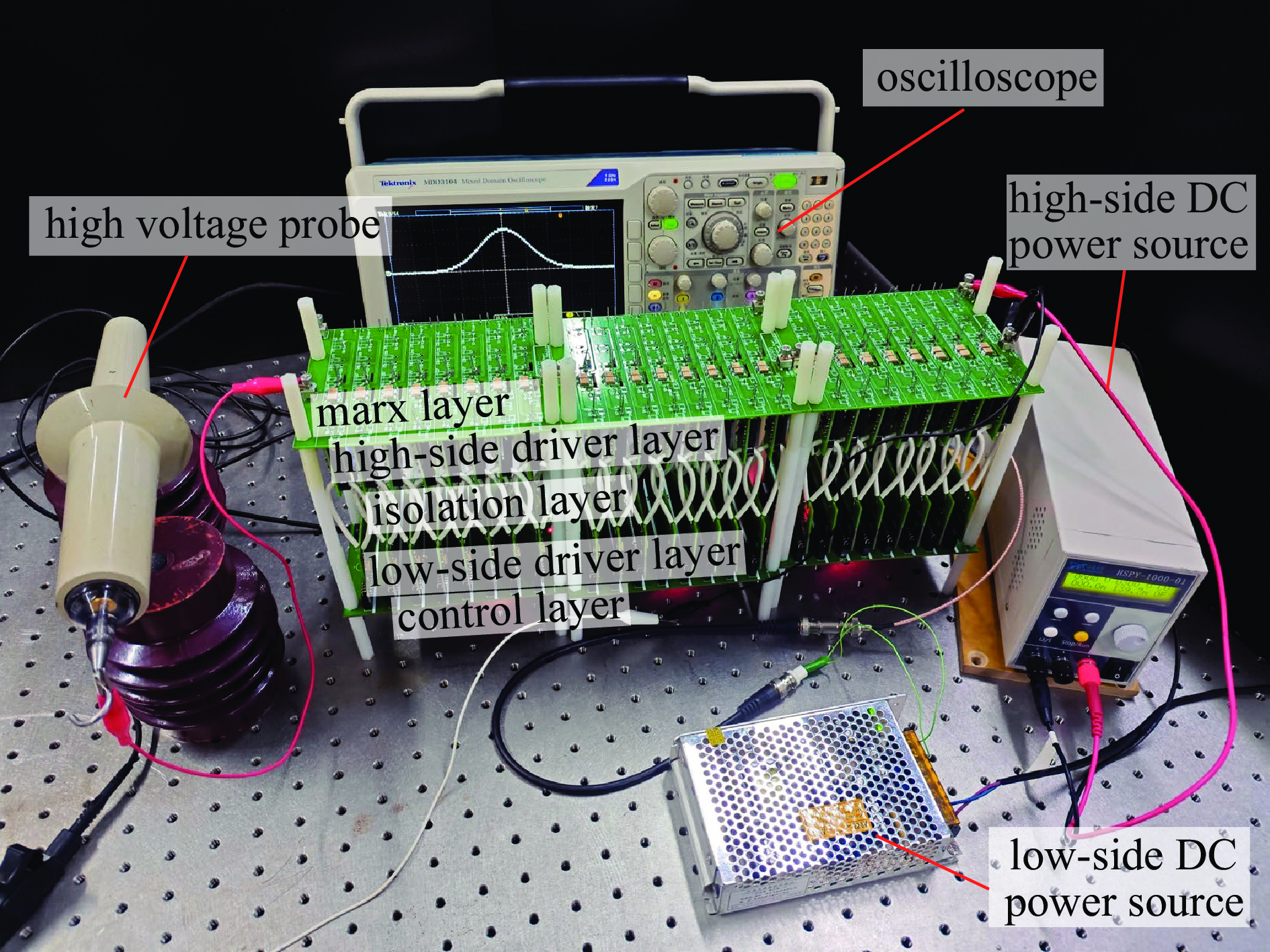
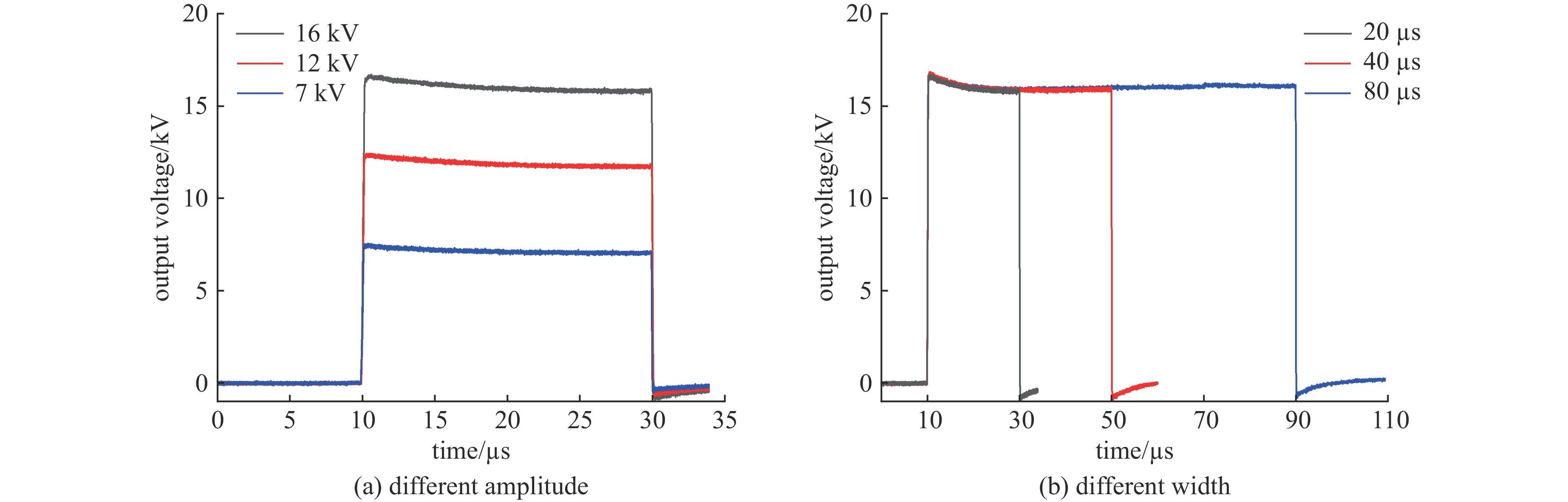
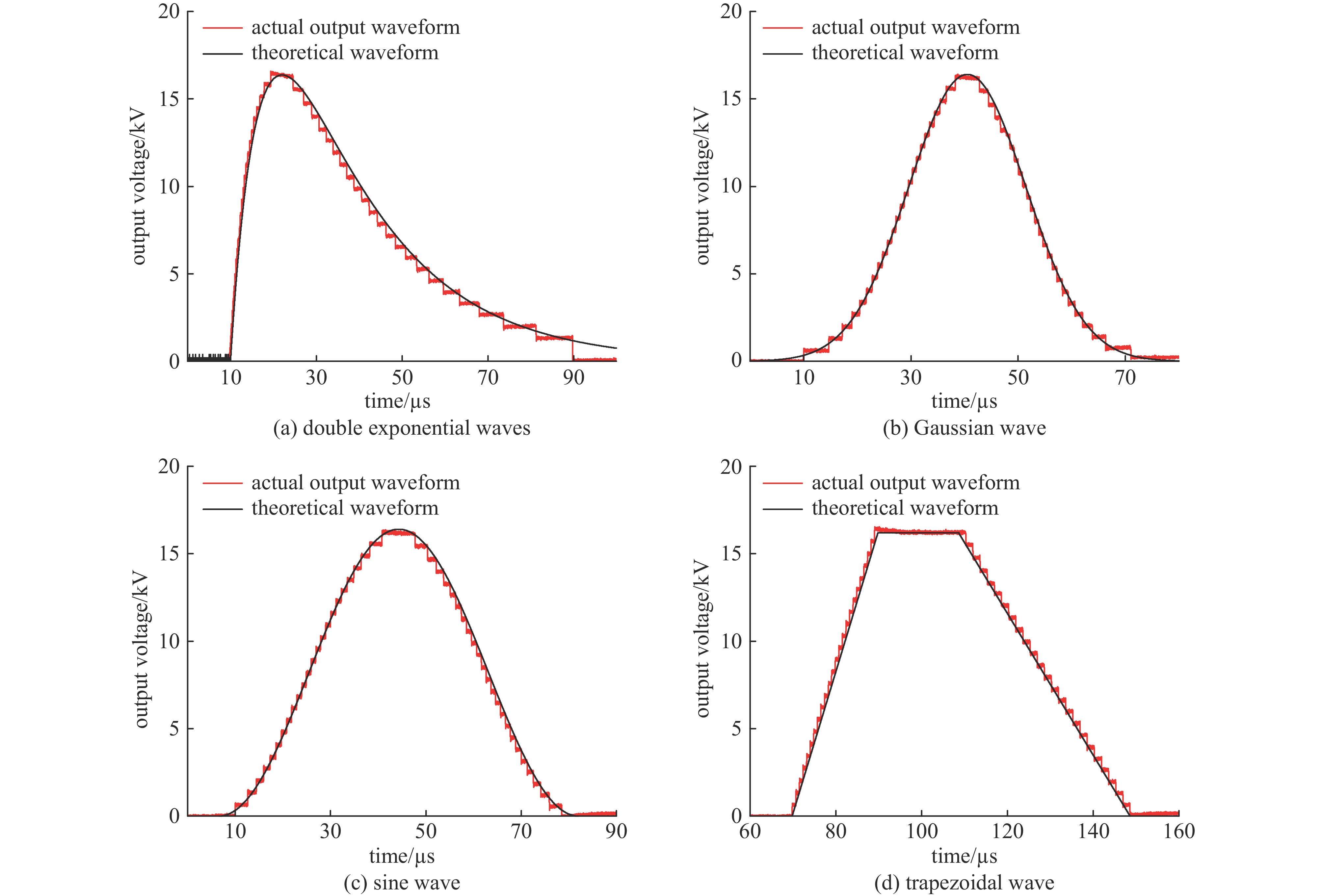
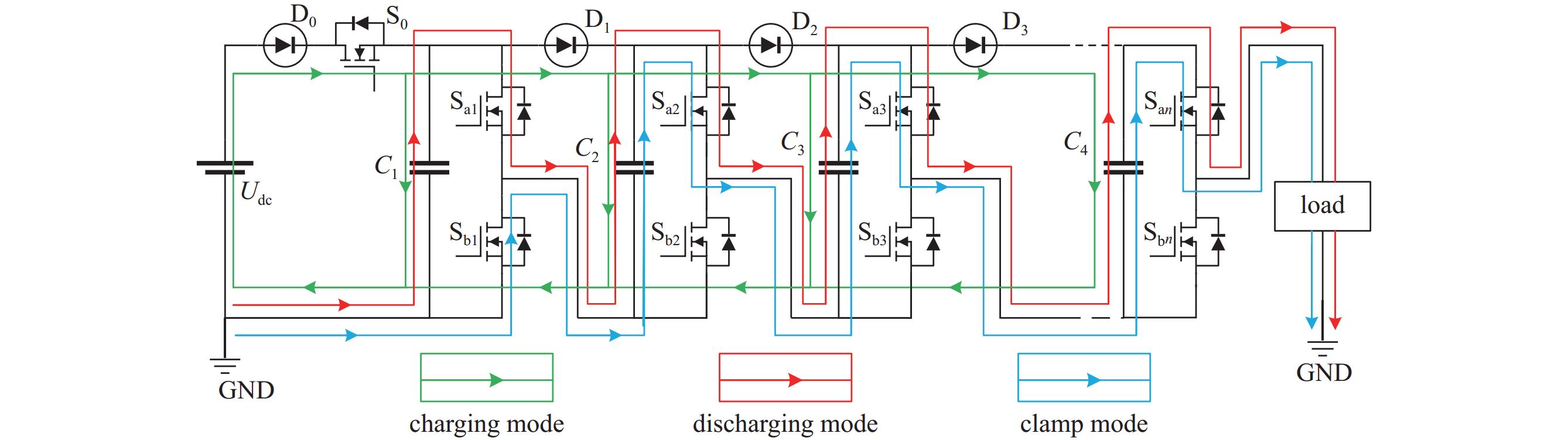
摘要: 为了满足多领域对幅值、脉宽、波形、重复频率等参数的不同要求,基于分布式理念,提出了一种分布式全固态波形可调高压脉冲发生器。该脉冲发生器由多个结构相同的子模块构成,单个模块采用半桥结构的全固态Marx主拓扑,驱动采用磁隔离方案;每个模块具有统一设计的连接端子与通信协议,多个模块可以独立工作,也可以直接串联工作以获得更好的性能。整个装置采用分层式设计,结构紧凑。详细阐述了该发生器的电路拓扑、工作原理与波形产生方法,并搭建了3台8级基本单元的9电平试验样机,串联后可输出25级电平的单极性任意高压脉冲波形,最大输出电压达到16 kV。Abstract: To meet the different requirements of different fields for parameters such as amplitude, pulse width, waveform, and repetition rate, a distributed all-solid-state waveform adjustable high-voltage pulse generator has been developed based on the distributed concept. This pulse generator comprises multiple sub-modules with identical structures. Each module is based on the all-solid-state Marx with the half-bridge structure, while the drive uses a magnetic isolation scheme. Moreover, every module has a uniformly designed connection terminal and communication protocol. Multiple modules can operate independently or directly in series to achieve superior performance. The entire device features a layered design and compact structure. This paper elaborates on the pulse generator's circuit topology, working principle, and waveform generation method. Finally, three 9-level test prototypes with 8-level basic units have been constructed, which can produce a 25-level unipolar arbitrary high-voltage waveform in series. The output peak voltage can reach 16 kV.
-
表 1 主要仿真参数
Table 1. Main simulation parameters
C0/nF load/pF Udc/V tw/μs m n N 100 50 700 80 3 8 24 -
[1] Elgenedy M A, Darwish A, Ahmed S, et al. A transition arm modular multilevel universal pulse-waveform generator for electroporation applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2017, 32(12): 8979-8991. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2017.2653243 [2] Elserougi A A, Massoud A M, Ahmed S. A modular high-voltage pulse-generator with sequential charging for water treatment applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(12): 7898-7907. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2515055 [3] Rezanejad M, Sheikholeslami A, Adabi J. High-voltage pulsed power supply to generate wide pulses combined with narrow pulses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2014, 42(7): 1894-1901. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2014.2323413 [4] Gómez B, Munekata P E S, Gavahian M, et al. Application of pulsed electric fields in meat and fish processing industries: An overview[J]. Food Research International, 2019, 123: 95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.04.047 [5] Ade-Omowaye B I O, Taiwo K A, Eshtiaghi N M, et al. Comparative evaluation of the effects of pulsed electric field and freezing on cell membrane permeabilisation and mass transfer during dehydration of red bell peppers[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2003, 4(2): 177-188. [6] Pang Lei, Ye Mingtian, Li Geqi, et al. A high voltage multi level arbitrary waveform generator for insulation testing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2019, 26(2): 405-411. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2019.007730 [7] Seri P, Wright A, Shaw A, et al. Influence of the voltage waveform’s shape and on-time duration on the dissolved ozone produced by a DBD bubble reactor[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2019, 28: 035001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6595/ab024f [8] Dragonas F A, Neretti G, Sanjeevikumar P, et al. High-voltage high-frequency arbitrary waveform multilevel generator for DBD plasma actuators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2015, 51(4): 3334-3342. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2015.2409262 [9] Wang Xiaoling, Gao Yuan, Zhang Shuai, et al. Nanosecond pulsed plasma assisted dry reforming of CH4: the effect of plasma operating parameters[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 243: 132-144. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.03.193 [10] Wang Yonggang, Yang Shilong, Wu Gaisheng, et al. A novel repetitive high-voltage resonant pulse generator for plasma-assisted milling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2021, 49(8): 2350-2358. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2021.3092417 [11] Jung E A, Lewis R N. A solid state nanosecond pulser using Marx bank techniques[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 1966, 44(2): 224-228. doi: 10.1016/0029-554X(66)90154-6 [12] 饶俊峰, 李成建, 李孜, 等. 全固态高重频高压脉冲电源[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:035001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190005Rao Junfeng, Li Chengjian, Li Zi, et al. All solid state high-frequency and high voltage pulsed power supply[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 035001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190005 [13] Rao Junfeng, Liu Kefu, Qiu Jian. A novel all solid-state sub-microsecond pulse generator for dielectric barrier discharges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2013, 41(3): 564-569. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2012.2228885 [14] Sakamoto T, Akiyama H. Solid-state dual Marx generator with a short pulsewidth[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2013, 41(10): 2649-2653. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2013.2272946 [15] Baek J W, Yoo D W, Rim G H, et al. Solid state Marx generator using series-connected IGBTs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2005, 33(4): 1198-1204. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2005.852409 [16] Camarinha-Matos L M. Technological innovation for sustainability[C]. Costa de Caparica, Portugal: Springer, 2011: 573-580. [17] Rocha L L, Silva J F, Redondo L M. Seven-level unipolar/bipolar pulsed power generator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2016, 44(10): 2060-2064. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2016.2519269 [18] 李戈琦, 庞磊, 孙玮, 等. 采用正负半桥子模块级联拓扑的高压多电平波形发生器[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42(11):3820-3826Li Geqi, Pang Lei, Sun Wei, et al. A high-voltage multilevel waveform generator with cascaded topology of positive and negative half bridge submodules[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42(11): 3820-3826 [19] 姜松, 邱力文, 饶俊峰, 等. 新型全固态高压多电平波形发生器的研制[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:115003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190124Jiang Song, Qiu Liwen, Rao Junfeng, et al. Development of a new all-solid-state high voltage multilevel waveform generator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 115003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190124 [20] Álvarez-Gariburo I, Sarnago H, Lucía Ó, et al. Design and optimization of a SiC-based versatile bidirectional high-voltage waveform generator[C]//2022 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC). 2022: 1333-1337. [21] Zhong Zhengyi, Rao Junfeng, Liu Haotiao, et al. Review on solid-state-based Marx generators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2021, 49(11): 3625-3643. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2021.3121683 [22] Jiang Song, Qiu Liwen, Li Zi, et al. A new all-solid-state bipolar high-voltage multilevel generator for dielectric barrier discharge[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2020, 48(4): 1076-1081. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2020.2975216 [23] Li Liuxia, Liu Kefu, Qiu Jian. Repetitive high voltage rectangular waveform pulse adder for pulsed discharge of capacitive load[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2013, 20(4): 1218-1223. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2013.6571437 [24] Dong Shoulong, Bo Zongqing, Xiang Sizhe, et al. A magnetic isolated drive circuit based on half-bridge for bipolar Marx pulse generator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2023, 51(10): 3188-3197. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2023.3319378 [25] Li Liuxia, Peng Zihuang, Liu Nan, et al. A distributed high-voltage arbitrary waveform generator based on versatile pulsed power module[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2023, 51(8): 2309-2320. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2023.3297116 [26] Canacsinh H, Silva J F, Redondo L M. Fault tolerance capability and semiconductor’s hold-off voltage of solid-state bipolar Marx modulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2017, 45(10): 2661-2666. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2017.2720974 -




 下载:
下载: