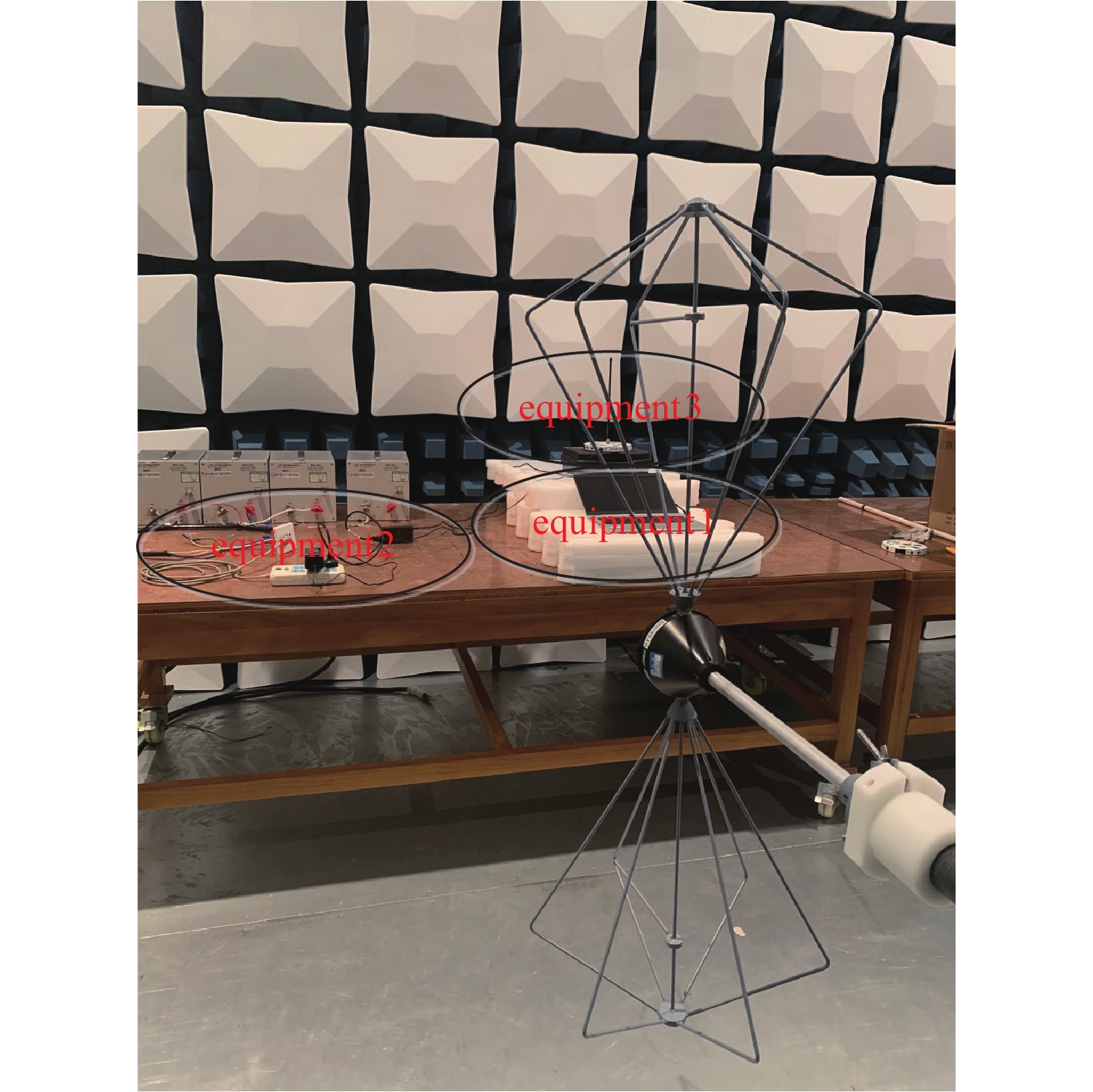
Prediction of system-level electric field radiated emission based on ANN reverse model
-
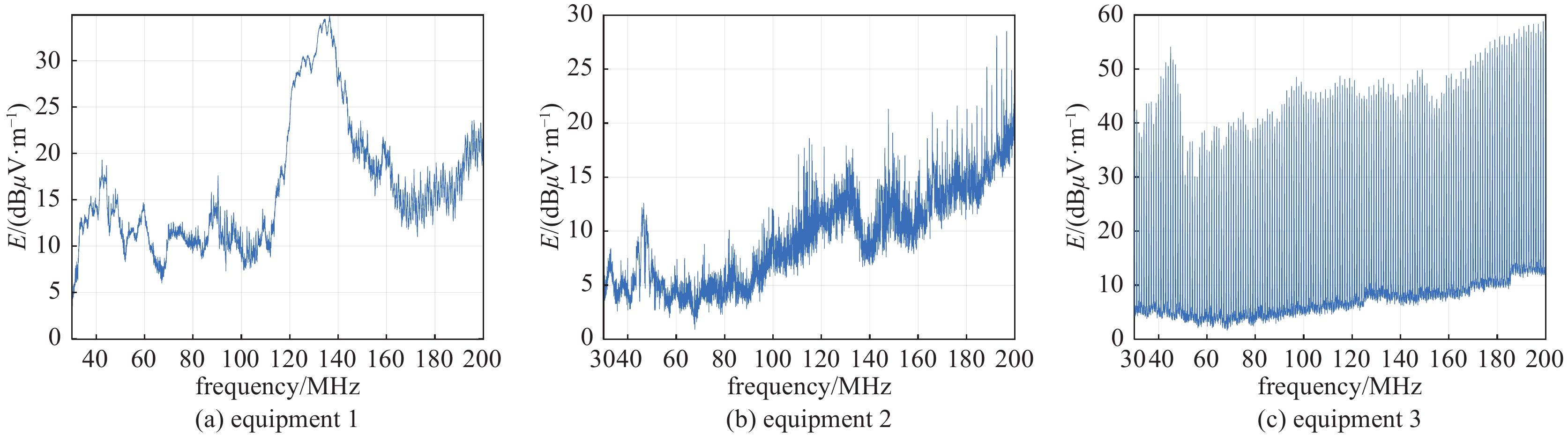
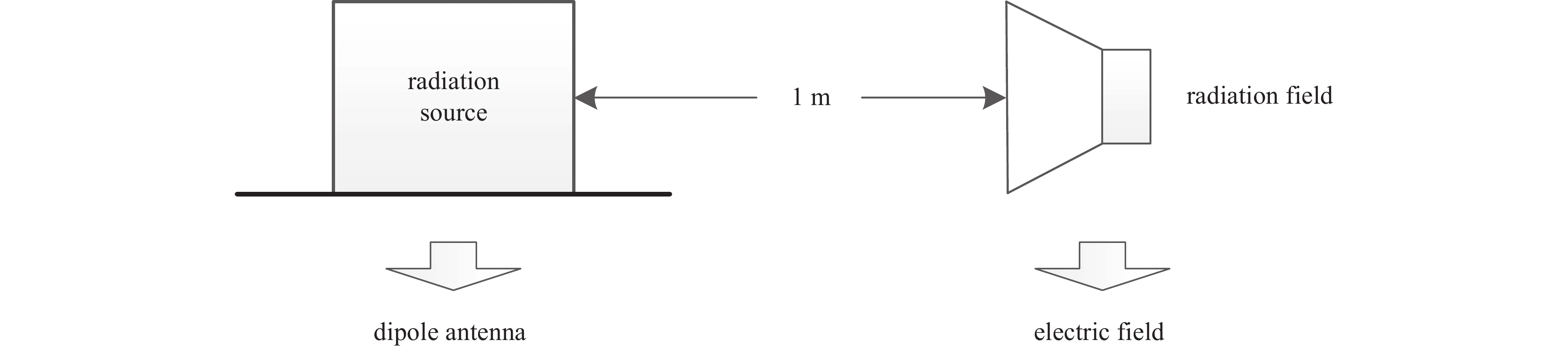
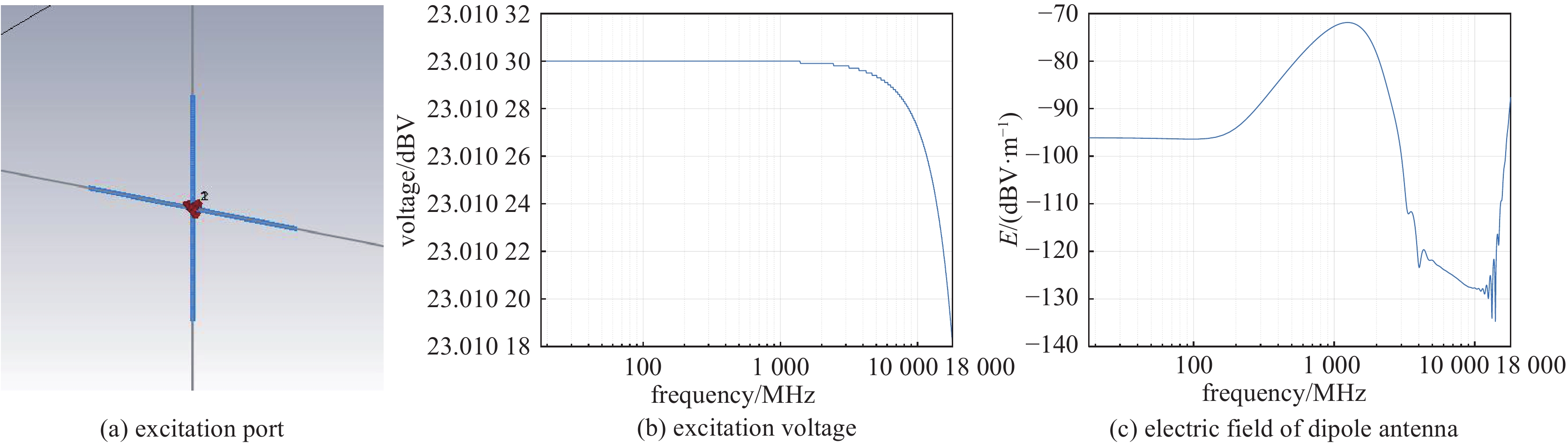
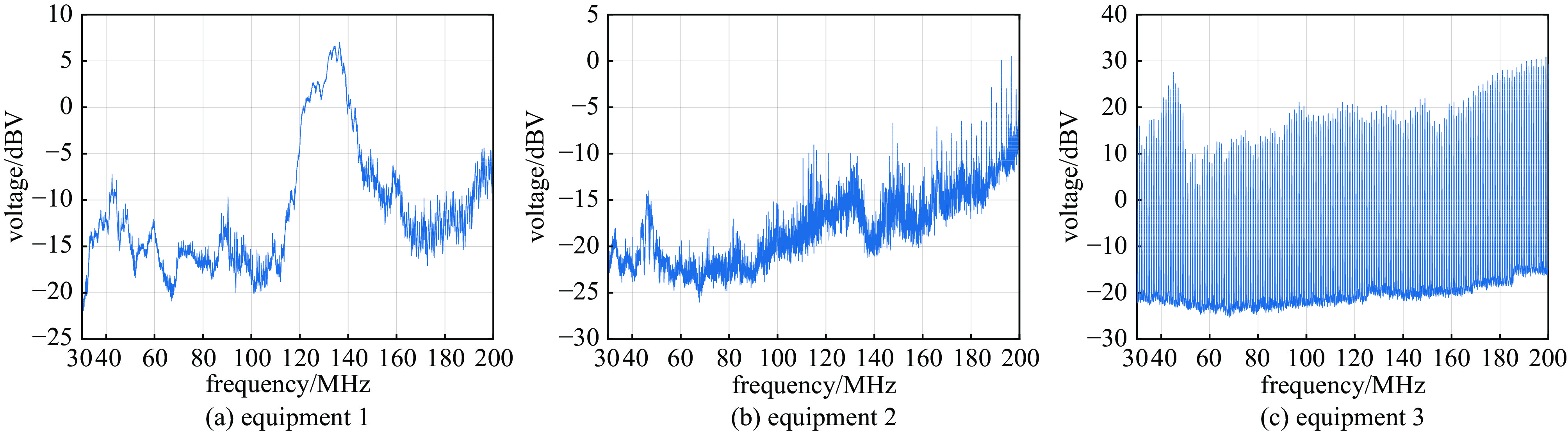
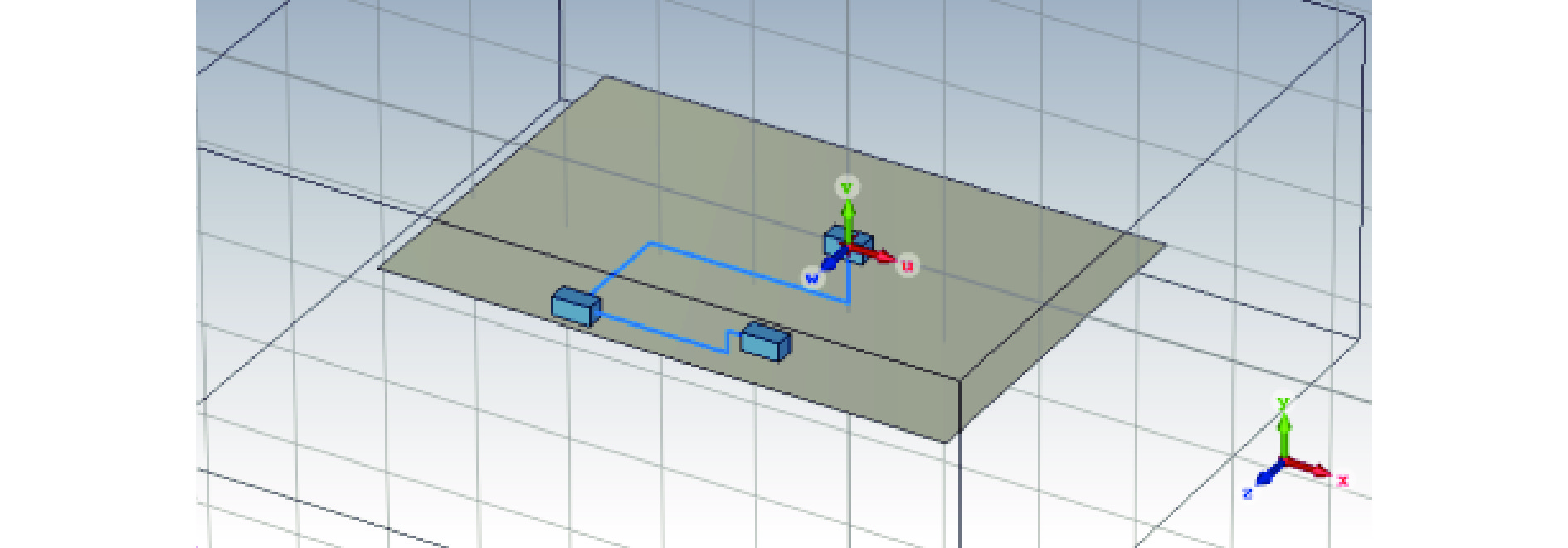
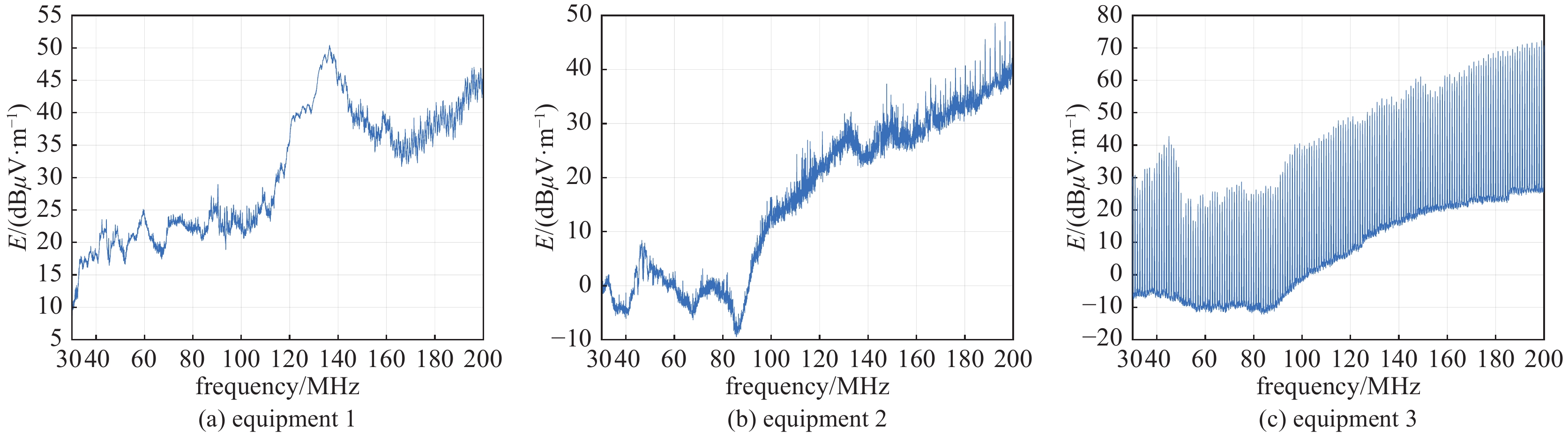
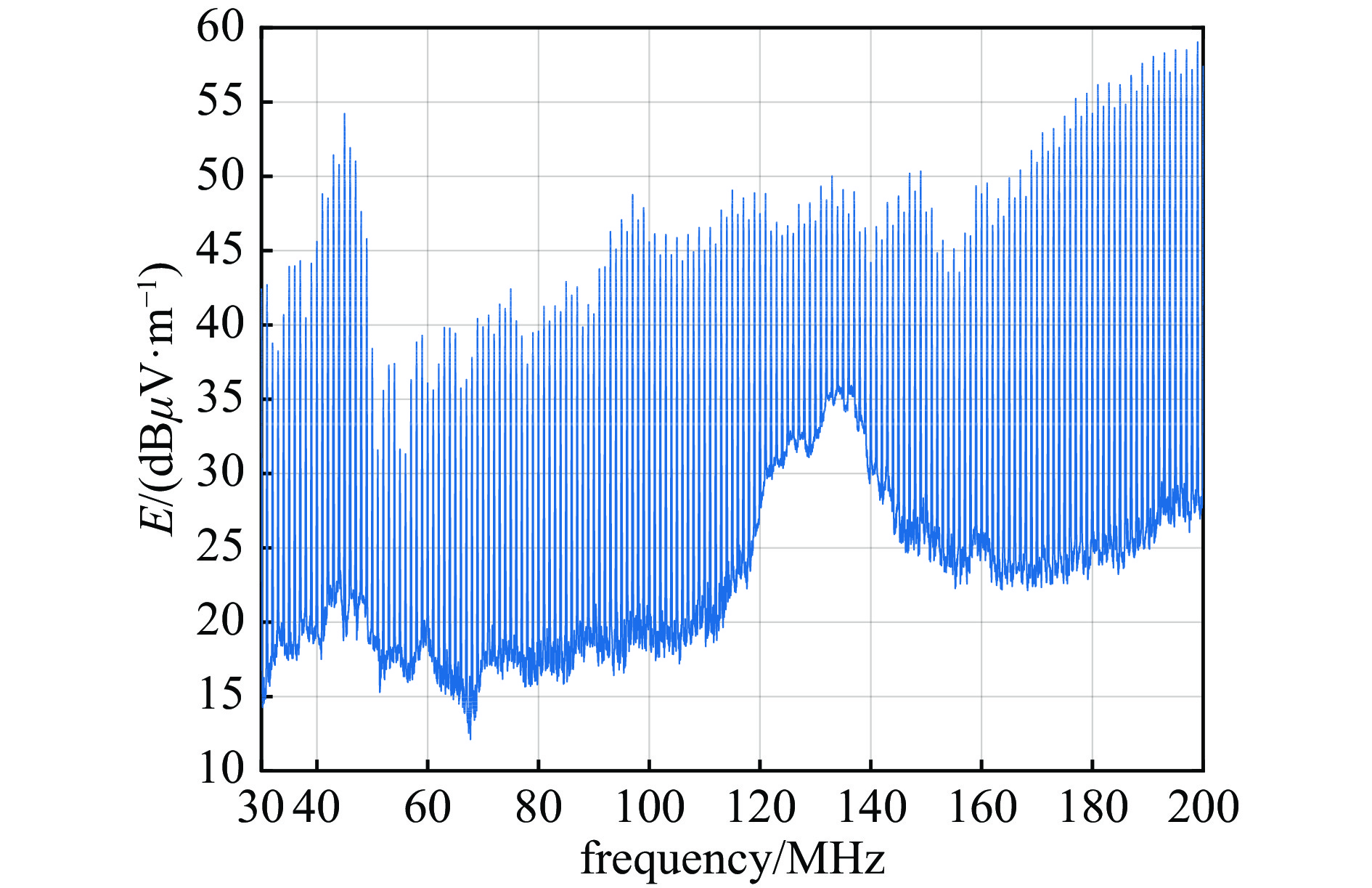
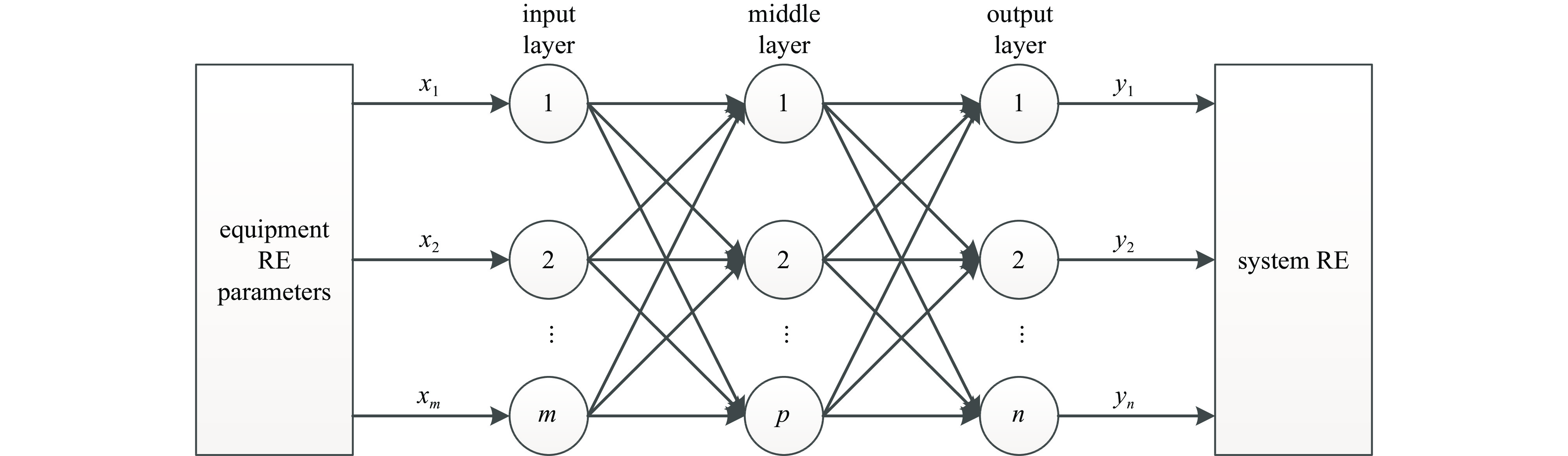
摘要: 针对多设备叠加系统级电磁兼容性问题,提出了一种基于神经网络反向模型的复杂系统电磁干扰预测新方法。首先实测单设备电场辐射发射数据,通过噪声源辐射发射等效性原理仿真多设备叠加的系统级电场辐射发射,获取训练样本集。选择各设备辐射场强、频率、坐标为输入参数,以系统级电场辐射发射为输出参数,建立基于Levenberg-Marquardt (LM)算法的三层逆向传播(BP)神经网络的反向模型,将神经网络的输入、输出反向,寻找验证误差最小的备选神经网络作为最终的神经网络,并结合试位法和共轭梯度法等数值求解算法计算神经网络输出。结果表明,该模型仿真的验证误差较传统三层LM-BP神经网络改善明显,其中采用共轭梯度法求解的神经网络反向模型将验证误差由
0.4159 %减小到了0.0997 %。该方法不仅不依赖于复杂的神经网络结构,且在有限的训练数据规模下提高了模型精度,为舰船、卫星、飞机等电子信息平台的电磁兼容性评估提供了一种新的高效解决途径。Abstract: To address the issue of system-level electromagnetic compatibility, a new method of predicting electromagnetic interference of complex systems based on artificial neural network (ANN) reverse model is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the electric field radiated emission (RE) of single equipment is measured. The training data of system-level RE are obtained by simulation based on the equivalence principle of radiated emission. Frequency, RE and coordinate of each single equipment are selected as the input variables, and the system-level RE is the output variable. A reverse model of the three-layer back-propagation (BP) ANN with Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) algorithm is established by exchanging the input–output variables. The alternative ANN with minimum validation error is searched as the ultimate ANN. The numerical root-finding algorithm (regular-falsi method and conjugate gradient method) are adopted to calculate the RE of multi equipments. The results show that the validation error of this reverse model is significantly improved compared to the traditional three-layer LM-BP ANN. Especially, the ANN reverse model based on conjugate gradient method reduces the validation error from0.4159 % to0.0997 %. This method is independent of complex ANN structures, and improves simulation accuracy with limited training data, which provides a new efficient and feasible solution for electromagnetic compatibility evaluation of electronic information platforms such as ships, satellites, and aircrafts. -
表 1 验证数据集
Table 1. Validation dataset
No. f/MHz x1 y1 z1 E1/(dBuV/m) x2 y2 z2 E2/(dBuV/m) x3 y3 z3 E3/(dBuV/m) Etotal/(dBuV/m) 1 30 0 0 −100 4.3 1000 120 −100 4.3 1050 310 −750 42.2 31.939571 2 70 0 0 −100 10.9 1000 120 −100 3.2 1050 310 −750 39.4 40.123183 3 100 0 0 −100 9.2 1000 120 −100 10.7 1050 310 −750 45.2 53.036382 4 130 0 0 −100 30.5 1000 120 −100 11.5 1050 310 −750 45.3 60.507379 5 160 0 0 −100 19.9 1000 120 −100 11.6 1050 310 −750 48.3 64.899009 6 200 0 0 −100 20.9 1000 120 −100 17.3 1050 310 −750 57.2 77.367965 7 30 0 100 −200 4.3 900 200 −200 4.3 1000 400 −600 42.2 35.062737 8 70 0 100 −200 10.9 900 200 −200 3.2 1000 400 −600 39.4 43.601726 9 100 0 100 −200 9.2 900 200 −200 10.7 1000 400 −600 45.2 56.07834 10 130 0 100 −200 30.5 900 200 −200 11.5 1000 400 −600 45.3 62.877408 … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … 25 30 −200 0 −400 4.3 1200 150 −150 4.3 1200 200 −800 42.2 32.92811 26 70 −200 0 −400 10.9 1200 150 −150 3.2 1200 200 −800 39.4 40.90428 27 100 −200 0 −400 9.2 1200 150 −150 10.7 1200 200 −800 45.2 54.0078 28 130 −200 0 −400 30.5 1200 150 −150 11.5 1200 200 −800 45.3 61.66204 29 160 −200 0 −400 19.9 1200 150 −150 11.6 1200 200 −800 48.3 65.79797 30 200 −200 0 −400 20.9 1200 150 −150 17.3 1200 200 −800 57.2 77.72475 表 2 不同训练样本数量下的模型验证误差及相关性系数
Table 2. Validation error and relative coefficient of different number of training dataset
number of training dataset validation error/% relative coefficient 30 7.7008 0.85303 100 0.8713 0.87193 200 0.4159 0.95546 500 0.0059 0.99809 1000 3.4247E-5 0.99977 10000 2.2718E-5 0.99991 表 3 备选神经网络
Table 3. Alternative neural network
No. alternative neural network validation error/% 1 x1,c=fann,1(y, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 0.149589782 2 x2,c=fann,2(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 0.000017400 3 x3,c=fann,3(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 0.096499053 4 x4,c=fann,4(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 0.003367234 5 x5,c=fann,5(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 3.945121882 6 x6,c=fann,6(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 0.000000768 7 x7,c=fann,7(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 0.20383497 8 x8,c=fann,8(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 0.000812276 9 x9,c=fann,9(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 26.19090216 10 x10,c=fann,10(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 8.284504188 11 x11,c=fann,11(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 0.061618247 12 x12,c=fann,12(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 0.430195851 13 x13,c=fann,13(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9, x10, x11, x12, x13) 10.20954216 表 4 预测结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of prediction results
No. Etotal/(dBμV·m−1) CST simulation traditional
LM-BP ANNANN reverse model
(conjugate gradient method)ANN reverse model
(regular-falsi method)1 31.94 45.64 30.34 31.04 2 40.12 52.91 38.11 39.00 3 53.04 56.41 52.91 51.55 4 60.51 48.03 60.33 58.81 5 64.90 58.98 65.98 63.08 6 77.37 60.86 76.63 75.20 7 35.06 54.04 26.02 34.08 8 43.60 55.38 36.43 42.38 9 56.08 60.12 49.31 54.51 10 62.88 56.28 65.89 61.11 11 67.58 60.84 66.36 65.68 12 80.09 63.85 74.17 77.84 13 33.37 60.00 33.68 32.44 14 40.88 62.78 41.72 39.73 15 53.74 60.13 53.21 52.23 16 60.87 61.54 60.15 59.17 17 65.84 65.62 66.13 63.99 18 78.86 68.21 78.36 76.65 19 32.80 47.91 27.05 31.88 20 41.02 53.70 37.33 39.87 21 53.80 55.91 48.49 52.29 22 61.09 52.69 59.88 59.38 23 65.67 59.85 60.61 63.83 24 78.14 64.56 65.75 75.95 25 32.93 58.02 31.77 32.00 26 40.90 57.64 38.76 39.76 27 54.01 56.90 53.70 52.49 28 61.66 60.12 60.52 59.93 29 65.80 61.43 67.04 63.95 30 77.72 66.63 77.63 75.55 -
[1] 赵辉. 系统电磁兼容[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2019Zhao Hui. System electromagnetic compatibility[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2019 [2] Kraft C H. Modeling leakage through finite apertures with TLM[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility. 1994: 73-76. [3] Kunz K S, Luebbers R J. The finite difference time domain method for electromagnetics[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1993. [4] Cerri G, De Leo R, Primiani V M. Theoretical and experimental evaluation of the electromagnetic radiation from apertures in shielded enclosure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 1992, 34(4): 423-432. doi: 10.1109/15.179275 [5] 李永明, 祝言菊, 李旭, 等. 电磁兼容的人工神经网络预测技术分析[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2008, 31(11):1313-1316,1322Li Yongming, Zhu Yanju, Li Xu, et al. Artificial neural networks-based prediction of electromagnetic compatibility problems[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2008, 31(11): 1313-1316,1322 [6] Shi Dan, Gao Yougang. A new method for identifying electromagnetic radiation sources using backpropagation neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2013, 55(5): 842-848. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2012.2237176 [7] Shi Dan, Fang Wei, Zhang Fangfei, et al. A novel method for intelligent EMC management using a “knowledge base”[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2018, 60(6): 1621-1626. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2018.2797053 [8] Kuo M J, Lin T C. Dynamical optimal training for behavioral modeling of nonlinear circuit elements based on radial basis function neural network[C]//Proceedings of 2008 Asia-Pacific Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility and 19th International Zurich Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility. 2008. [9] Li Xu, Yu Jihui, Zhu Yanju, et al. Prediction of electromagnetic compatibility problems based on artificial neural networks[C]//Proceedings of 2008 World Automation Congress. 2008. [10] Belkacem F T, Bensetti M, Laour M, et al. The analytical, numerical and neural network evaluation versus experimental of electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of a rectangular enclosure with apertures[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Cybernetic Intelligent Systems. 2010. [11] Devabhaktuni V, Bunting C F, Green D, et al. A new ANN-based modeling approach for rapid EMI/EMC analysis of PCB and shielding enclosures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2013, 55(2): 385-394. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2012.2214223 [12] Chahine I, Kadi M, Gaboriaud E, et al. Using neural networks for predicting the integrated circuits susceptibility to conducted electromagnetic disturbances[C]//Proceedings of 2007 18th International Zurich Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility. 2007: 13-16. [13] Burghardt F, Garbe R. Introduction of artificial neural networks in EMC[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Signal Integrity and Power Integrity. 2018. [14] Hager W W, Zhang Hongchao. A new conjugate gradient method with guaranteed descent and an efficient line search[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2005, 16(1): 170-192. doi: 10.1137/030601880 [15] 丛爽. 面向MATLAB工具箱的神经网络理论与应用[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009Cong Shuang. Neural network theory and applications with MATLAB toolboxes[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2009 -





 下载:
下载: