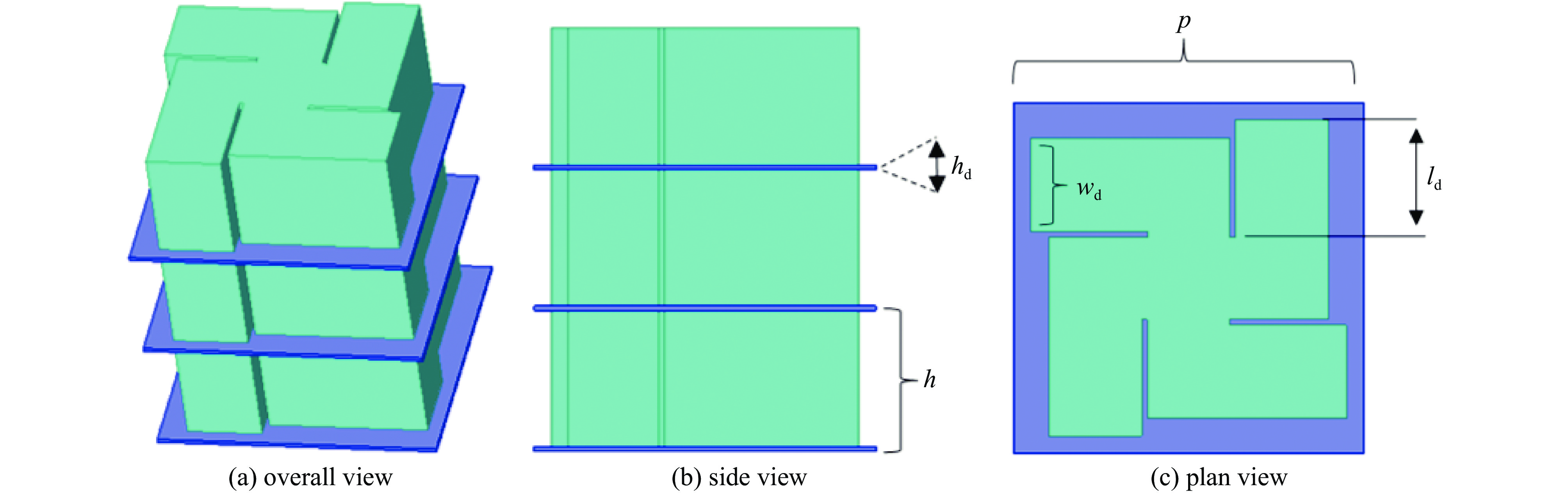
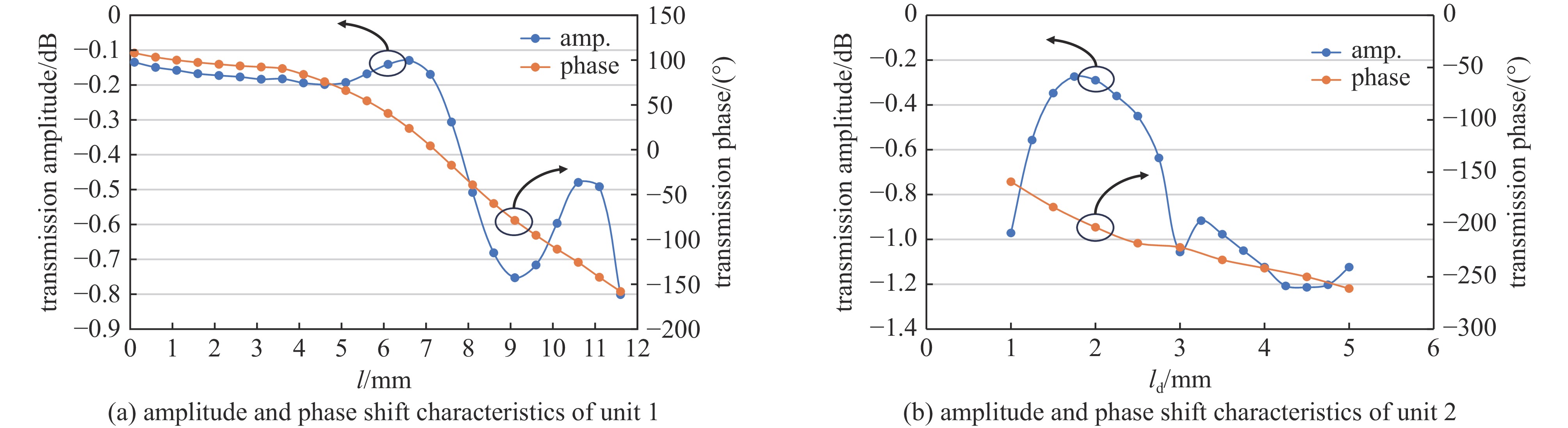
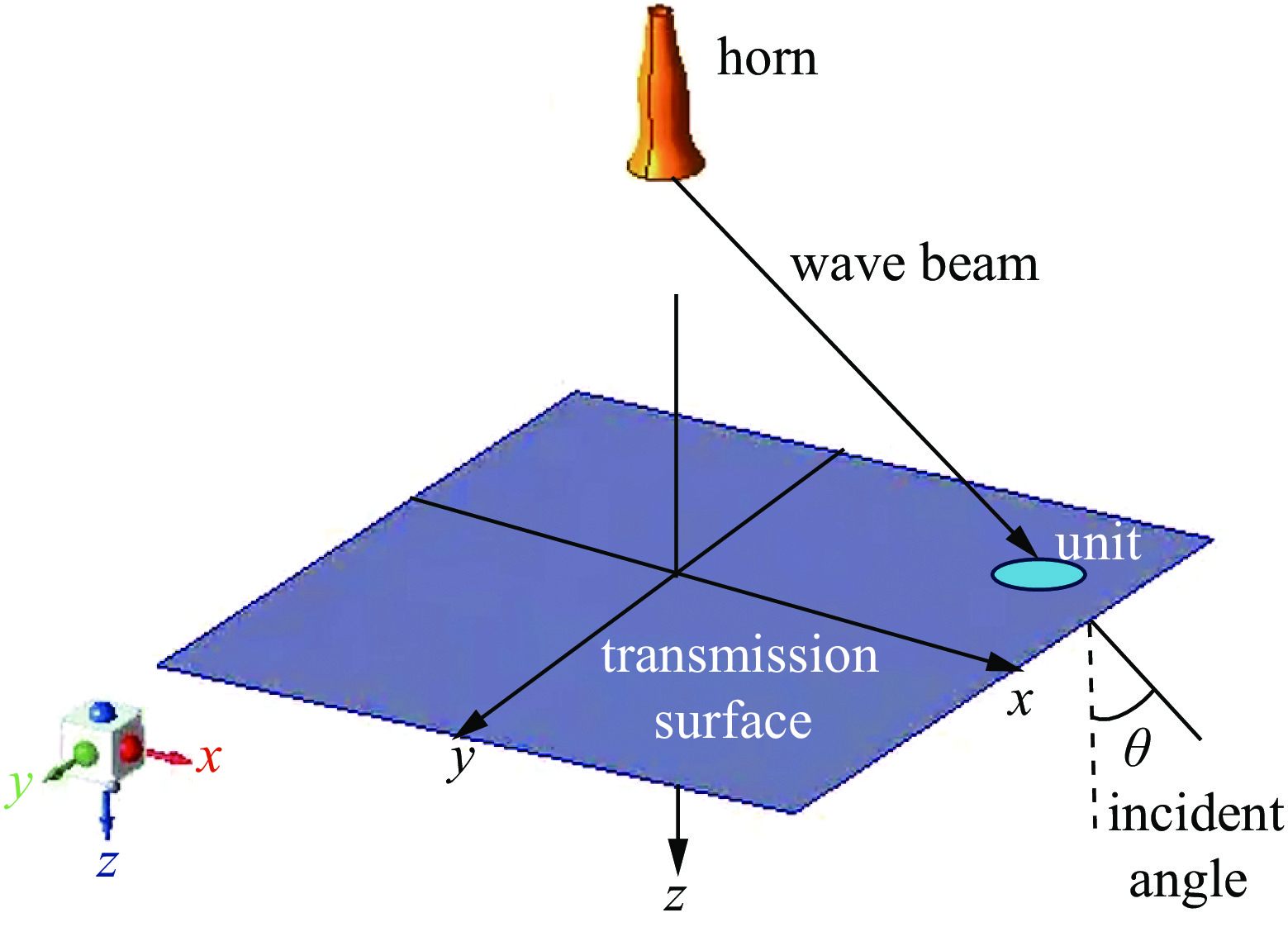
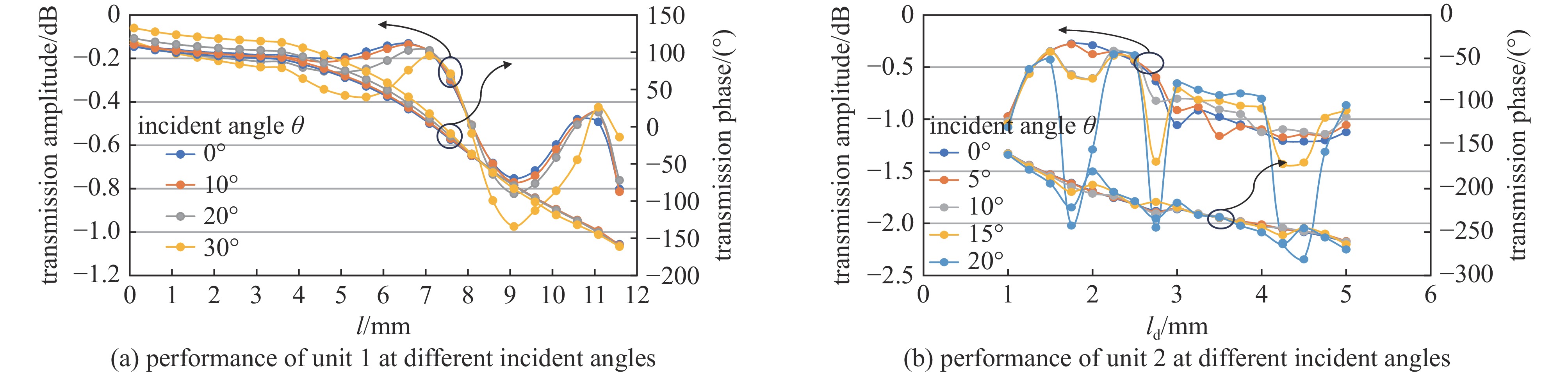
All-dielectric lens array antenna for high-power microwave applications
-
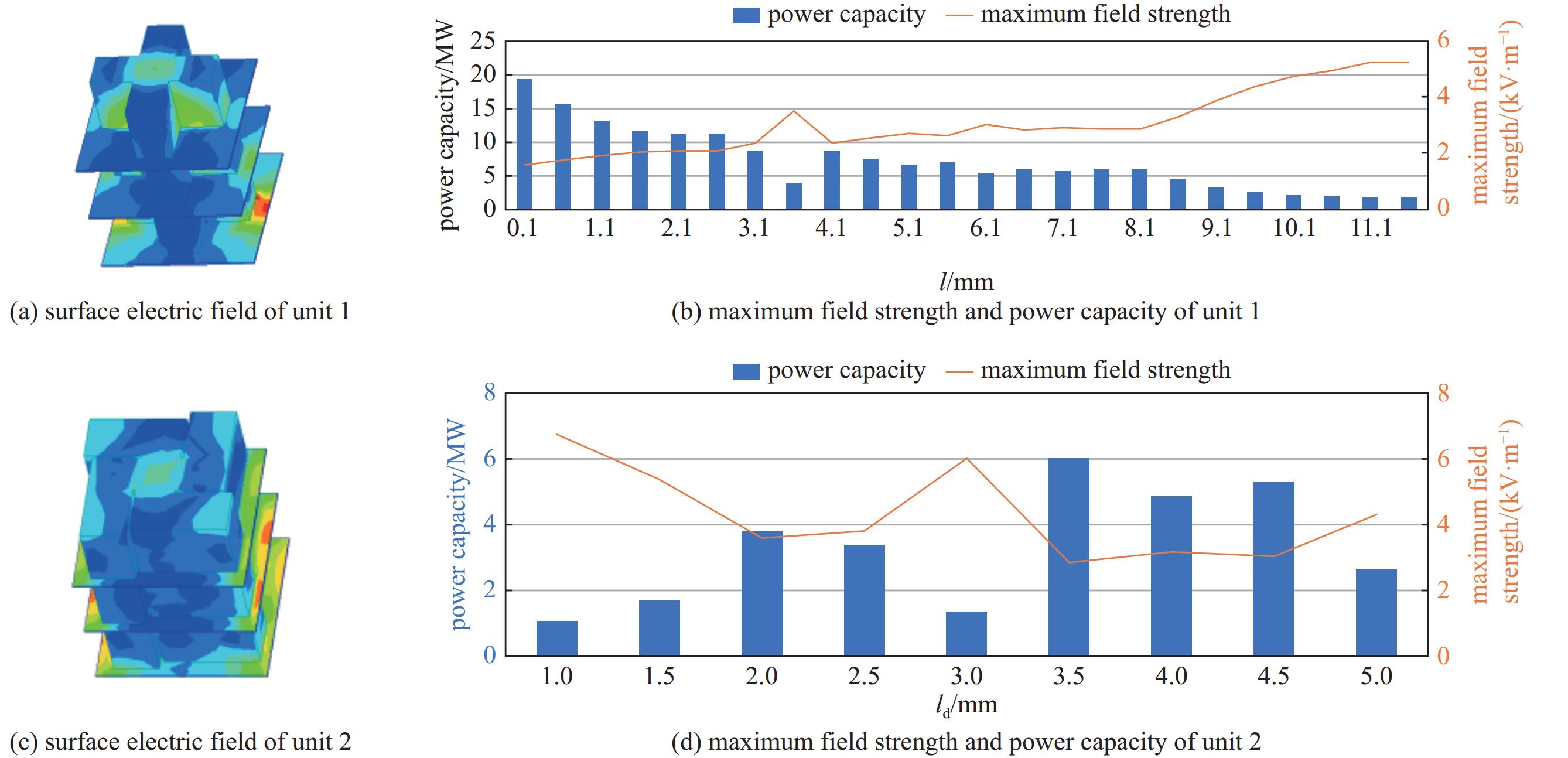
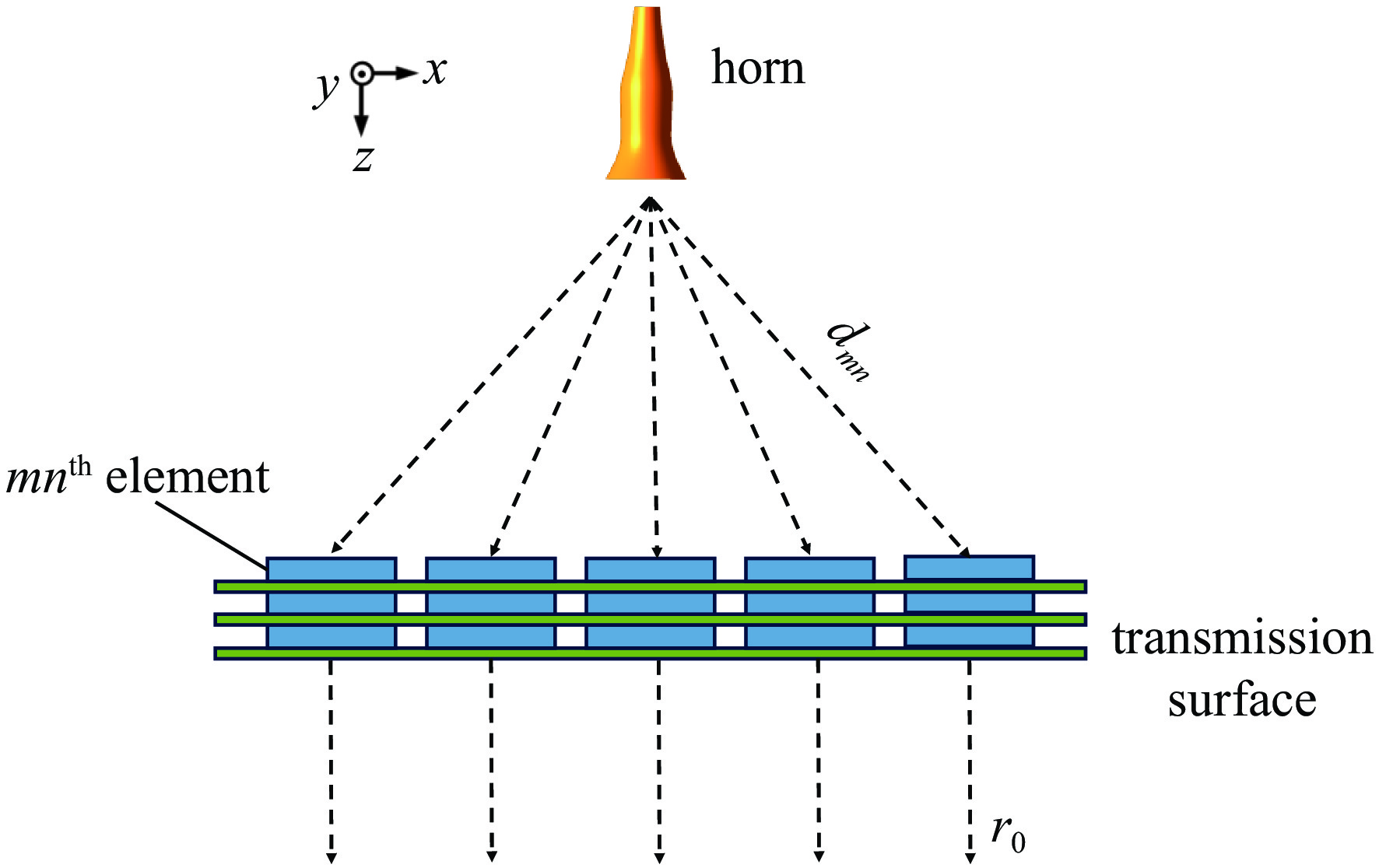
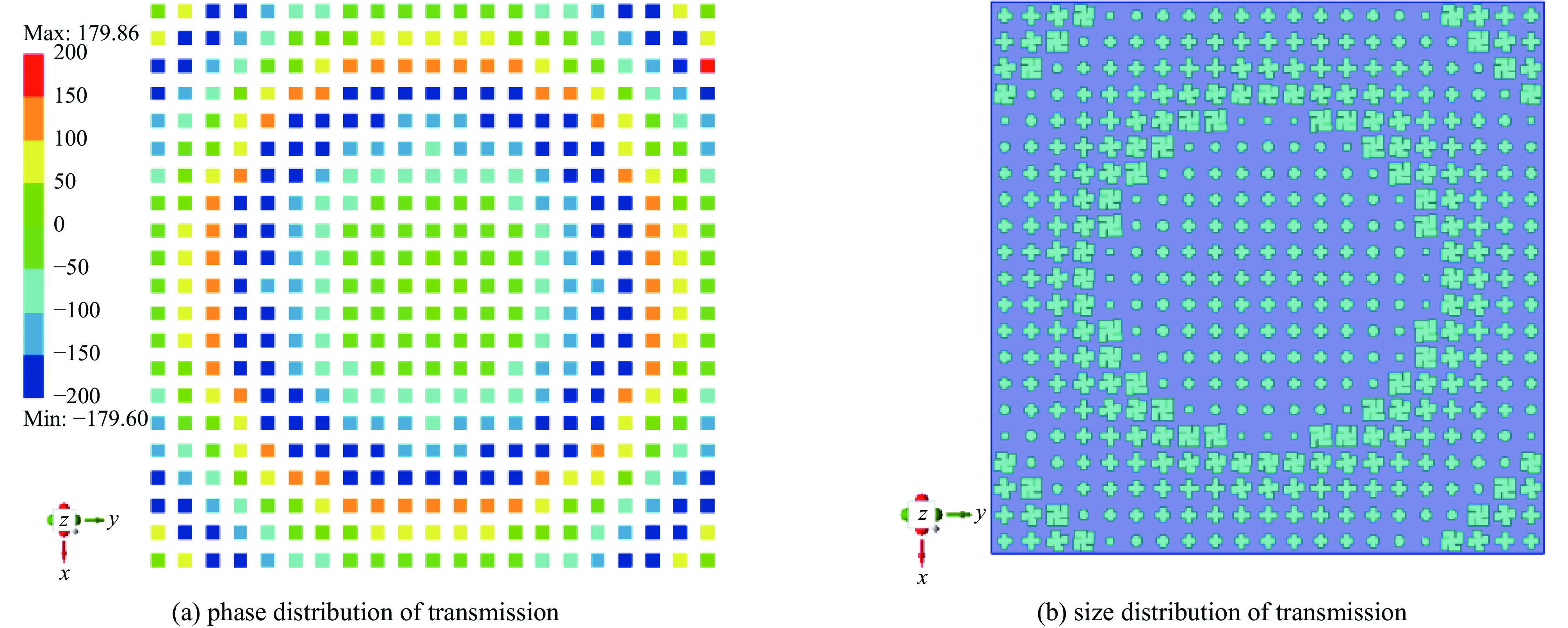
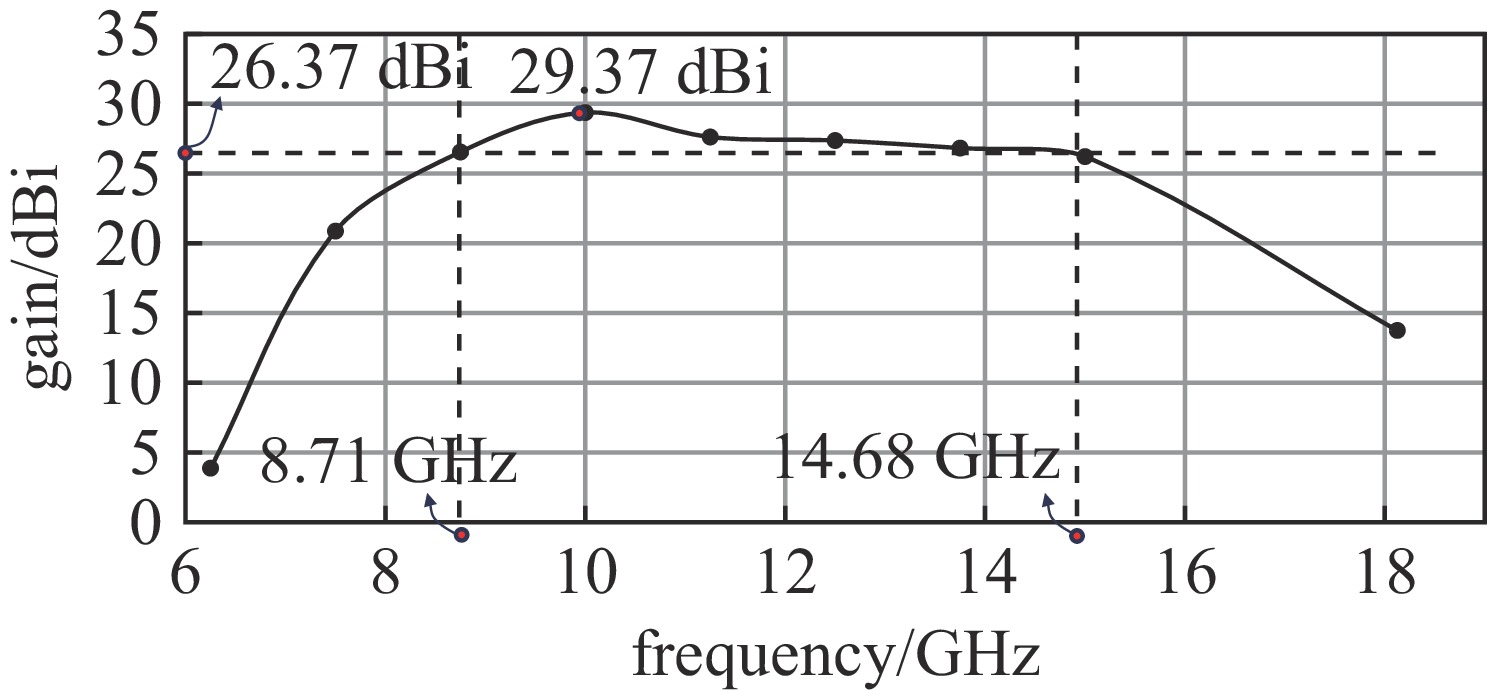
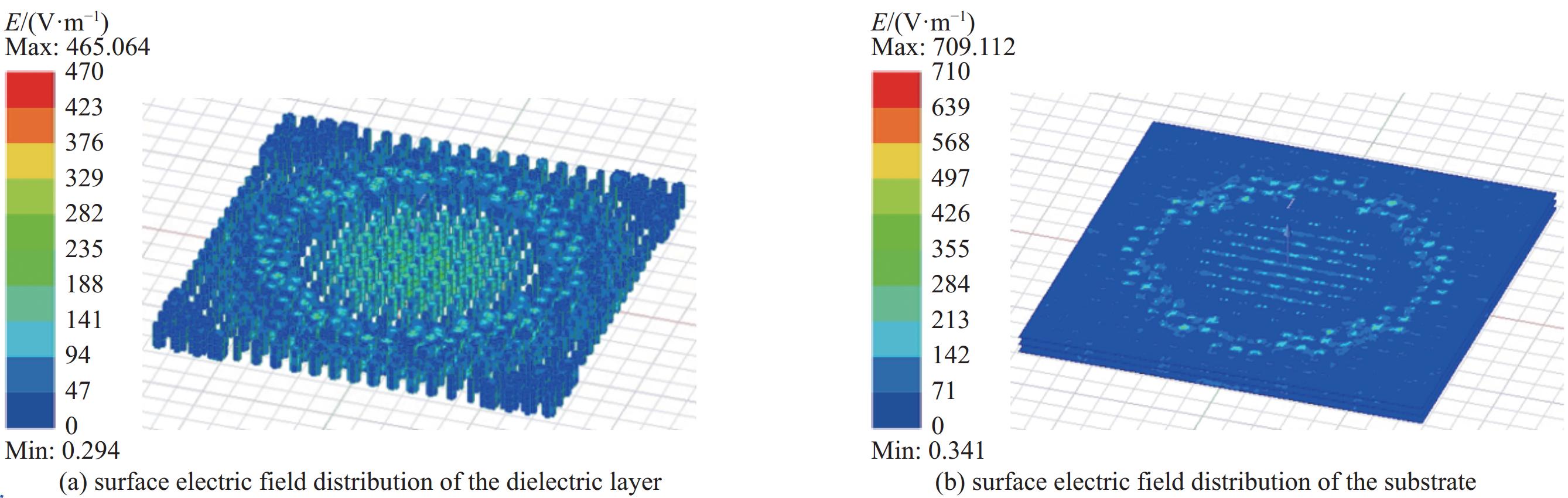
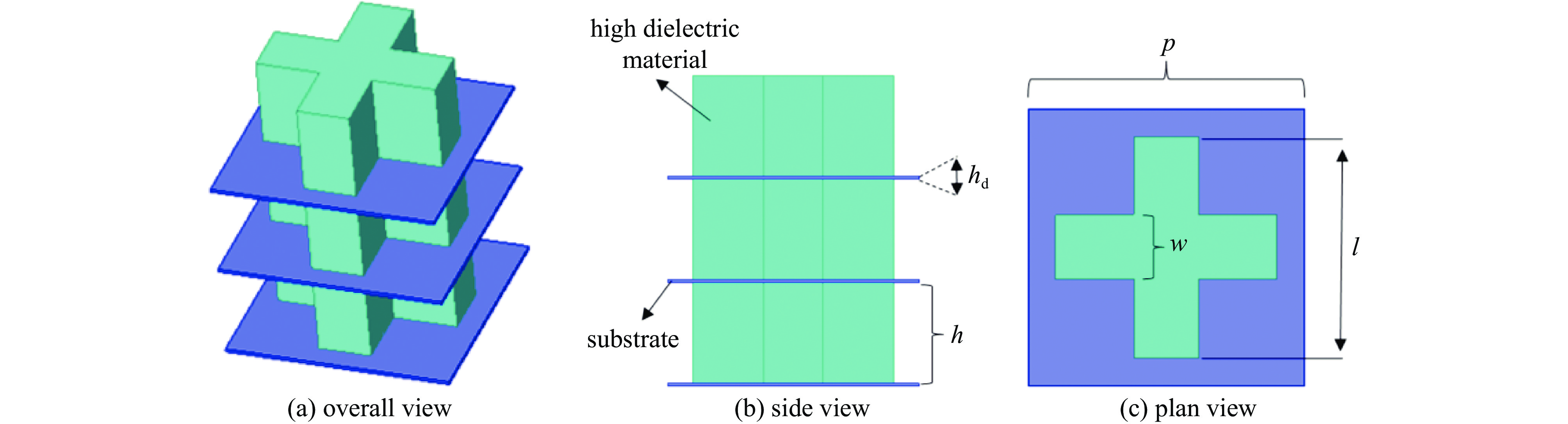
摘要: 为了实现透镜阵列天线所需的移相范围,设计了两种不同的单元结构,通过优化参数,在保证良好的传输幅值的基础上实现相移范围的互补。为了探索在高功率微波系统应用,对两种单元的功率容量也开展了详细研究。在无限周期情况下,随着单元尺寸变化,单元功率容量范围为1.08~19.37 MW;通过研制口径为315 mm×315 mm的透镜天线来构建有限周期条件,并仿真计算得到该天线最大功率容量为226.553 MW,功率密度可以达到
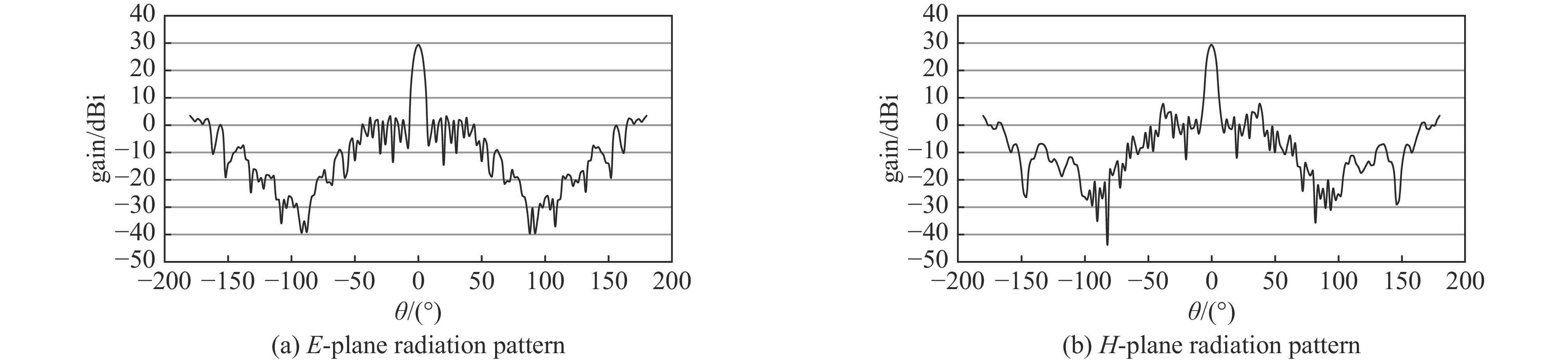
2283.23 W/mm2,并且该天线在中心频点10 GHz处峰值增益可达到29.37 dBi,口径效率为62.43%,副瓣电平约为−21.54 dBi。结果表明所提出单元的有效性与正确性,也说明设计的透镜阵列天线不仅具有良好的辐射特性,同时具有MW量级的功率容量。Abstract: An all-dielectric high-power microwave lens array antenna is proposed in this paper. To achieve the required phase shift range of the lens array antenna, two different cell structures are designed and by optimizing the parameters, complementary phase shift ranges are achieved on the basis of ensuring good transmission amplitude. To explore the application in high power microwave systems, a detailed study of the power capacity of the two units is also carried out . Firstly, in the infinite period case, with the change of cell size, the cell power capacity ranges from 1.08−19.37 MW; secondly, the finite period condition is constructed by developing the lens antenna with an aperture of 315 mm×315 mm, and the simulation calculates to obtain that the antenna’s maximum power capacity is 226.553 MW, the power density can reach2283.23 W/mm2, and the antenna can reach a peak gain of 29.37 dBi at the central frequency point of 10 GHz, the aperture efficiency of 62.43%, and the sub-flap level of about −21.54 dBi . The above results show the validity and correctness of the proposed unit, and also indicate that the designed lens array antenna not only has good radiation characteristics, but also has a power capacity of MW magnitude.-
Key words:
- high-power lens array antenna /
- high power capacity /
- high gain /
- all dielectric /
- aperture efficiency
-
表 1 阵列天线性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of array antennas
reference type gain/dBi area/(mm×mm) aperture efficiency/% Ed/(MV/m) Pc/MW band width/% [7] leaky waveguide 26.20 800×53.08 76.20 3.38 200.00 — [8] all-metal 32.80 500×500 54.59 50.00 2679.08 — [11] all-metal 23.70 189×189 50.60 3.00/80.00 0.50/358.00 24.2(1-dBi) [12] dielectric- metal 27.58 80×80 52.33 3.00 13.99 26.4(3-dBi) [20] all-metal 21.80 160×320 — 7.00 12.00 — this work all-dielectric 29.37 315×315 62.43 7.00 226.60 51.0(3-dBi) -
[1] Benford J, Swegle J A, Schamiloglu E. High power microwaves[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Taylor & Francis, 2007: 66-70. [2] Gold S G, Nusinovich G S. Review of high-power microwave source research[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1997, 68(11): 3945-3974. doi: 10.1063/1.1148382 [3] Zhang Jun, Jin Zhenxing, Yang Jianhua, et al. Recent advance in long-pulse HPM sources with repetitive operation in S-, C-, and X-bands[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2011, 39(6): 1438-1445. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2011.2129536 [4] 许亮, 袁成卫, 张强. 紧凑型宽带高功率微波悬板阵列天线研究[C]//2019年全国天线年会论文集(上册). 2019: 449-451Xu Liang, Yuan Chengwei, Zhang Qiang. Research on compact broadband high-power microwave suspended plate array antenna[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 National Antenna Conference (Volume I). 2019: 449-451 [5] Vlasov S N, Orlova I M. Quasioptical transformer which transforms the waves in a waveguide having a circular cross section into a highly directional wave beam[J]. Radiophysics and Quantum Electronics, 1974, 17(1): 115-119. doi: 10.1007/BF01037072 [6] Courtney C C, Baum C E. The coaxial beam-rotating antenna (COBRA): Theory of operation and measured performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2000, 48(2): 299-309. doi: 10.1109/8.833080 [7] 李佳伟, 黄文华, 梁铁柱, 等. 基于漏波波导的X波段高功率微波天线[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(8):2125-2129 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112308.2125Li Jiawei, Huang Wenhua, Liang Tiezhu, et al. Design and simulation of X-band HPM antenna based on leaky waveguide[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(8): 2125-2129 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112308.2125 [8] 赵旭浩, 毕绍锋, 张建德, 等. 伸缩式全金属反射阵列扫描天线[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:043004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210340Zhao Xuhao, Bi Shaofeng, Zhang Jiande, et al. Scalable all-metal reflective array beam scanning antenna[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 043004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210340 [9] Sun Yunfei, Dang Fangchao, Yuan Chengwei, et al. A beam-steerable lens antenna for Ku-band high-power microwave applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(11): 7580-7583. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2979282 [10] Zhao Xuelong, Yuan Chengwei, Liu Lie, et al. All-metal beam steering lens antenna for high power microwave applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(12): 7340-7344. [11] Kong Gexing, Li Xiangqiang, Wang Qingfeng, et al. A wideband reconfigurable dual-branch helical reflectarray antenna for high-power microwave applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(2): 825-833. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3016379 [12] 张治强, 赵加宁, 李芳, 等. 宽带Ka波段平面反射阵列天线设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:083001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220037Zhang Zhiqiang, Zhao Jianing, Li Fang, et al. Design of a broadband Ka-band reflectarray antenna[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 083001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220037 [13] Wang Shaofei, Xie Yanzhao, Qiu Yangxin. A kind of tightly coupled array with nonuniform short-circuited branches for the radiation of UWB pulses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2023, 71(3): 2259-2267. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2023.3240624 [14] Yu Longzhou, Yuan Chengwei, He Juntao, et al. Beam steerable array antenna based on rectangular waveguide for high-power microwave applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2019, 47(1): 535-541. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2018.2884290 [15] Goulas A, Zhang Shiyu, McGhee J R, et al. Fused filament fabrication of functionally graded polymer composites with variable relative permittivity for microwave devices[J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 193: 108871. [16] Shahrubudin N, Lee T C, Ramlan R. An overview on 3D printing technology: technological, materials, and applications[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 35: 1286-1296. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2019.06.089 [17] Wu Gengbo, Zeng Yuansong, Chan K F, et al. 3-D printed terahertz lens with circularly polarized focused near field[C]//2019 13th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP). 2019: 1-4. [18] Massaccesi A, Pirinoli P, Bertana V, et al. 3D-printable dielectric transmitarray with enhanced bandwidth at millimeter-waves[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 46407-46418. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2865353 [19] Zainud-Deen S H, Gaber S M, Malhat H A, et al. B10. Multilayer dielectric resonator antenna transmitarray for near-field and far-field fixed RFID reader[C]//2012 29th National Radio Science Conference (NRSC). 2012: 81-88. [20] 龚鸿州, 张建德, 袁成卫, 等. 一种高功率微波宽带紧耦合偶极子阵列天线[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:013009 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230139Gong Hongzhou, Zhang Jiande, Yuan Chengwei, et al. A tightly coupled dipole array antenna with high power and broadband[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 013009 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230139 [21] Fröhlich H, Paranjape B V. Dielectric breakdown in solids[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society. Section B, 1956, 69(1): 21-32. doi: 10.1088/0370-1301/69/1/304 -




 下载:
下载: