Design of machine protection system for BNCT02 accelerator
-
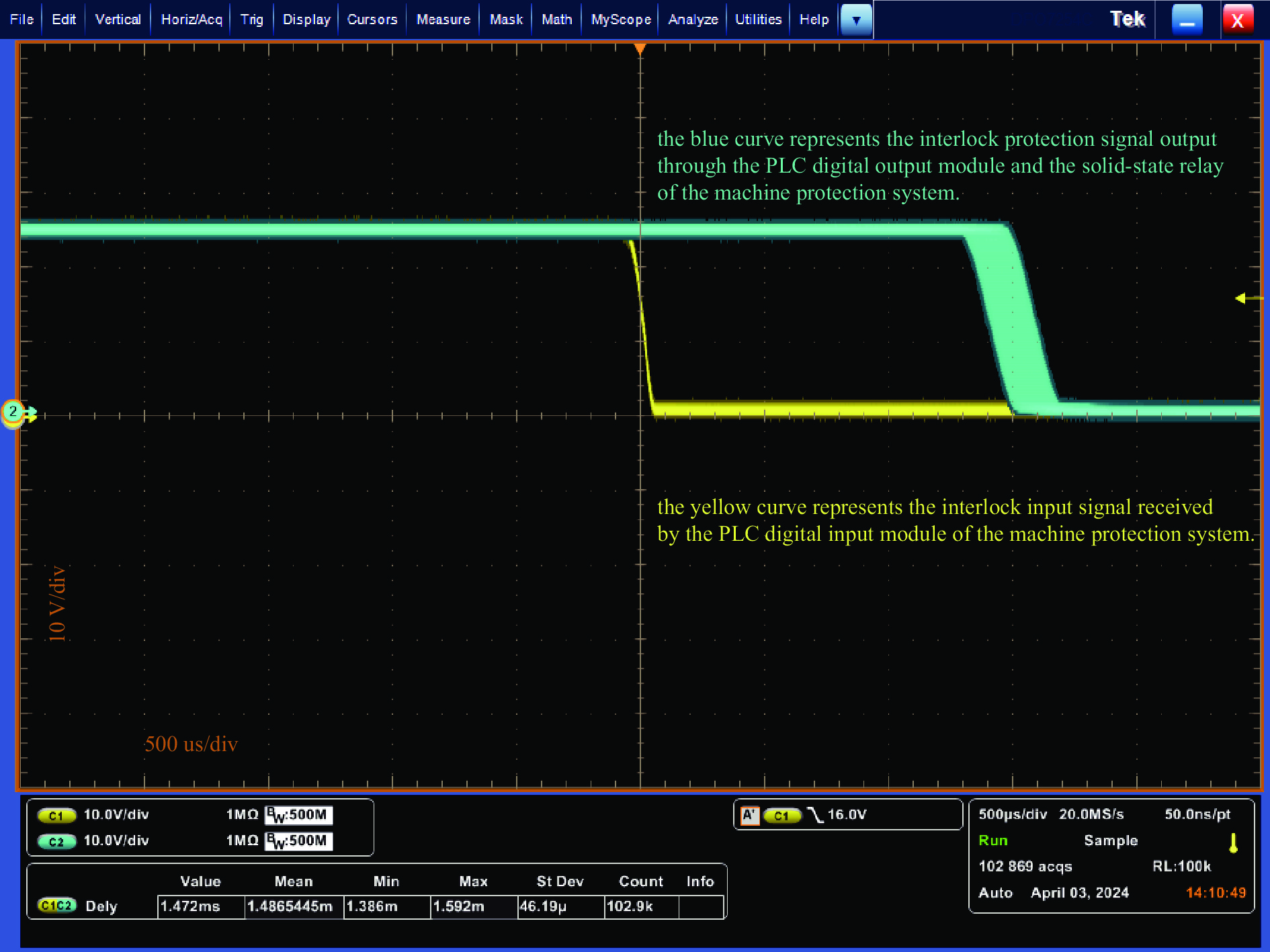
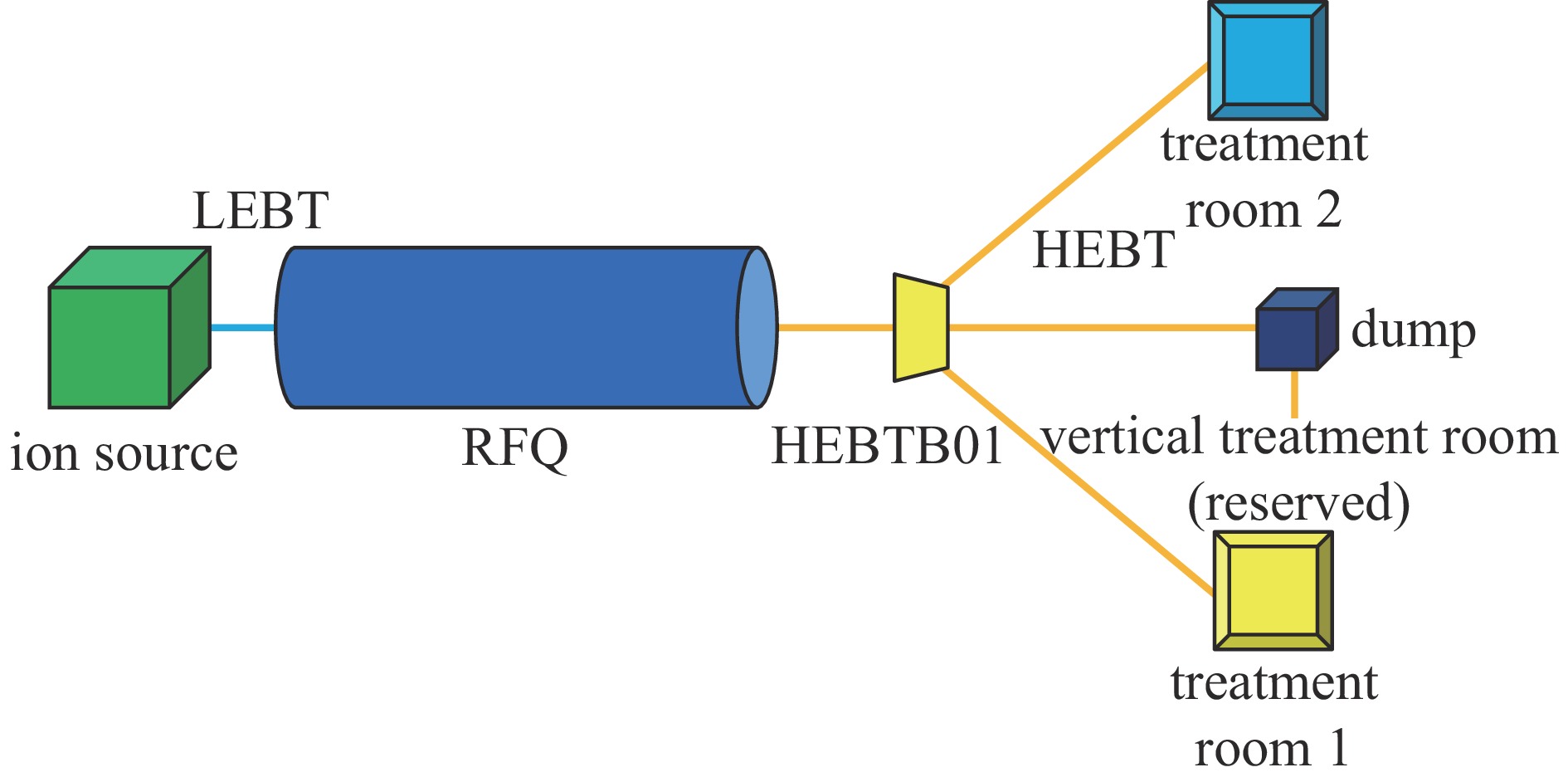
摘要: 中国科学院高能物理研究所第二台硼中子俘获治疗(BNCT02)加速器主要由1台离子源、1条低能束流传输线、1台射频四极加速器和3条高能束流传输线组成。为了保障BNCT02加速器的安全运行,设计了基于横河PLC和实验物理及工业控制系统(EPICS)软件工具包的机器保护系统。为了增强安全性,该系统采用了冗余设计,由两套完全独立且主要输入、输出信号一致的子系统构成。测试结果表明,BNCT02加速器机器保护系统的响应时间小于1.6 ms,且具有稳定可靠性高的特点,满足BNCT02加速器运行的需要。
-
关键词:
- 硼中子俘获治疗 /
- 加速器 /
- 机器保护系统 /
- 实验物理及工业控制系统
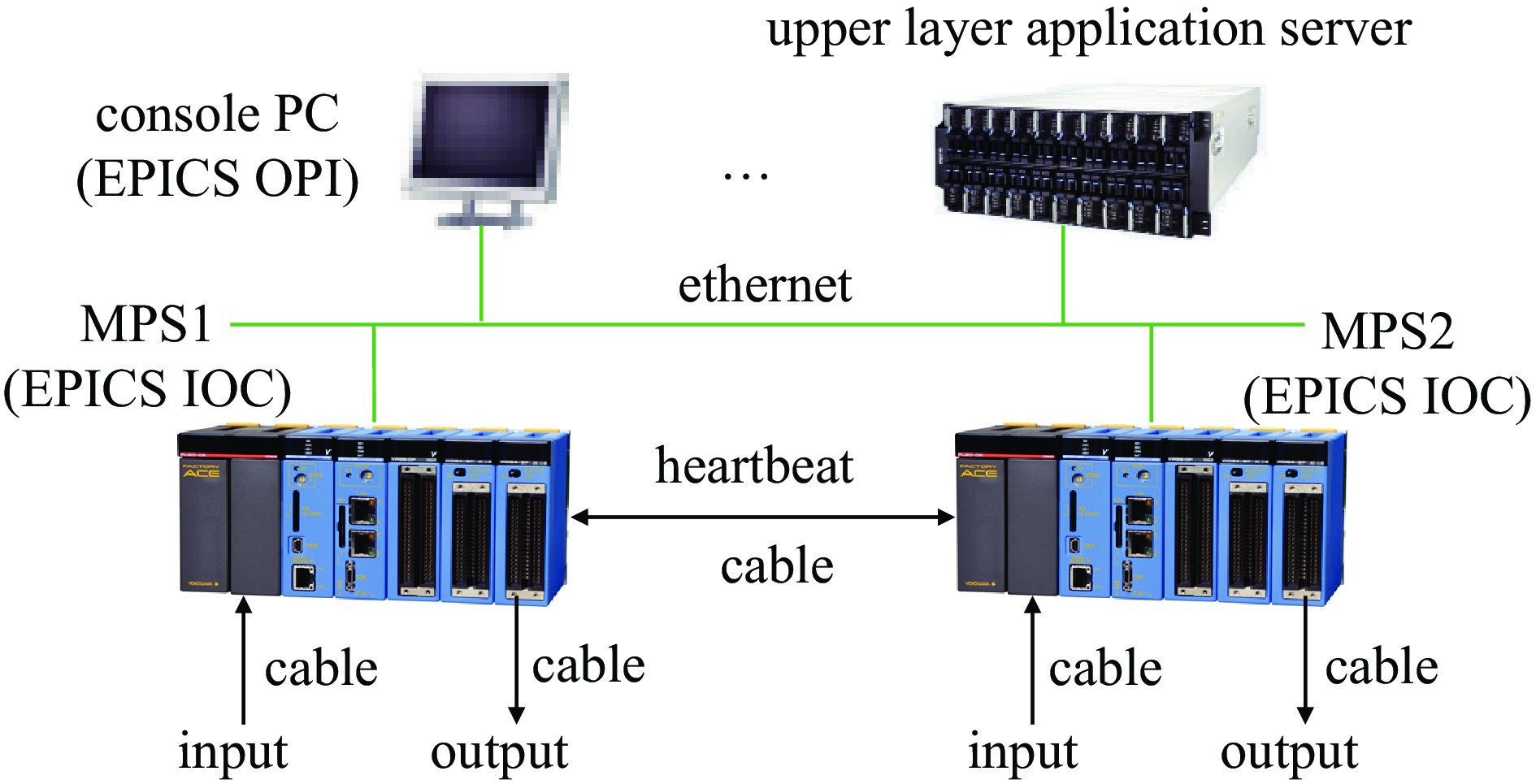
Abstract: The RF linac dedicated to boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT02) in our institute is mainly composed of an ion source, a low energy beam transport line, a radio frequency quadrupole accelerator and three high energy beam transport lines. To ensure the safe operation of the BNCT02 accelerator, a machine protection system (MPS) was designed based on Yokogawa PLC and Experimental Physics and Industrial Control System (EPICS) software toolkit. The MPS adopts a redundant design, consisting of two completely independent subsystems with consistent main input and output signals. The test results show that the response time of the MPS is less than 1.6 ms, and it has the characteristics of high stability and reliability, which meets the operational requirements of the BNCT02 accelerator. -
表 1 机器保护系统的主要输入信号数量
Table 1. Numbers of main input signals of the machine protection system
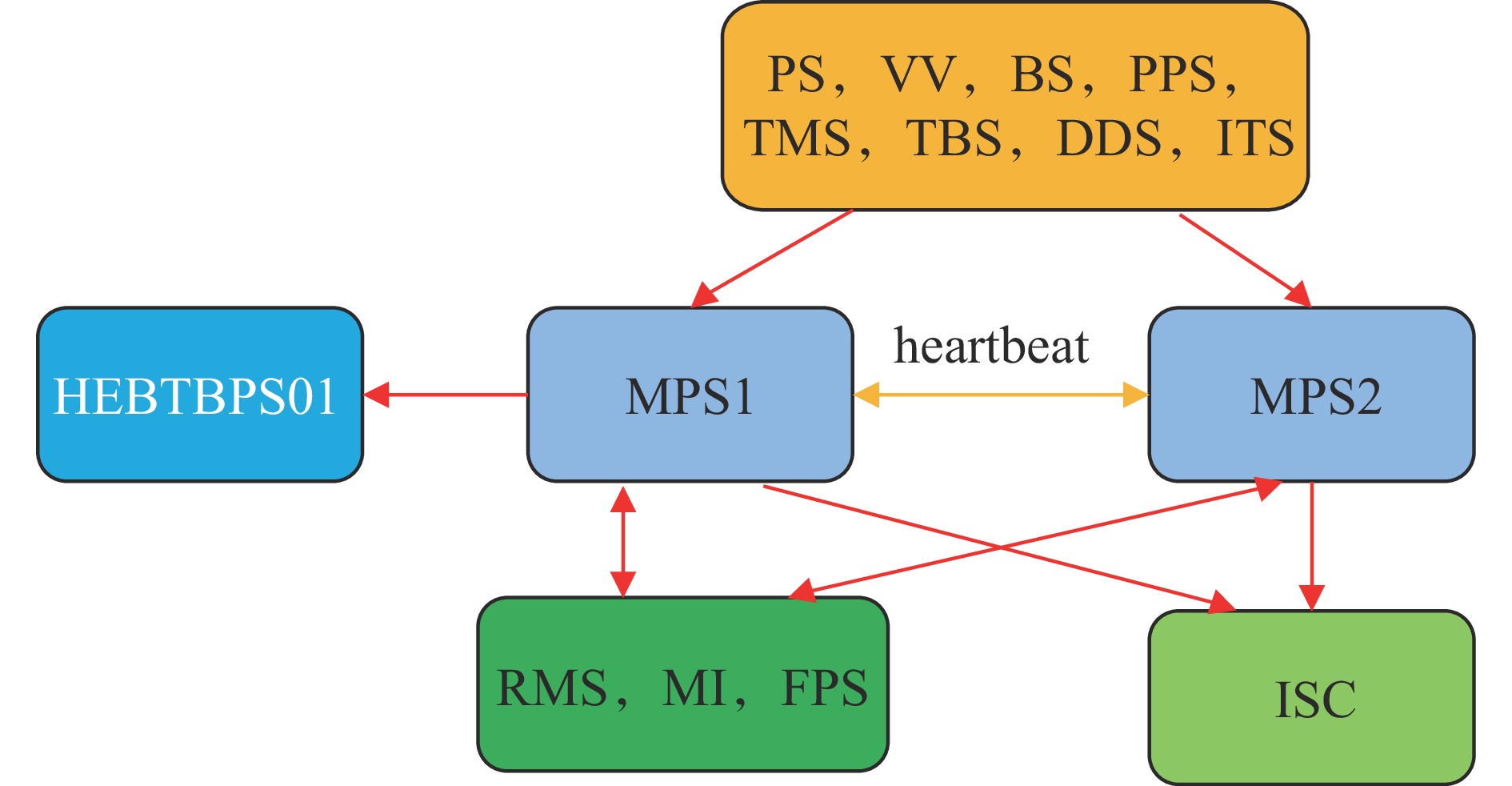
subsystem number of signals PS VV BS RMS PPS TMS TBS MI DDS ITS FPS total MPS1 47 8 2 10 5 4 2 4 2 2 2 88 MPS2 31 8 2 9 4 4 2 4 2 2 1 69 表 2 机器保护系统的主要输出信号数量
Table 2. Numbers of main output signals of the machine protection system
subsystem number of signals ISC RMS MI FPS HEBTBPS01 total MPS1 2 1 2 1 3 9 MPS2 2 1 2 1 0 6 表 3 机器模式与需就绪子区对应关系
Table 3. Relationship between machine mode and sub areas
machine mode linac sub area dump sub area treatment room 1 sub area treatment room 2 sub area ion source mode / / / / dump mode √ √ / / treatment room 1 mode √ / √ / treatment room 2 mode √ / / √ 表 4 机器模式与HEBTBPS01状态信号对应关系
Table 4. Relationship between machine mode and HEBTBPS01 status signal
machine mode power on power off positive negative current raised fault error exceeding limit ion source mode / / / / / / / dump mode × √ / / × √ / treatment room 1 mode √ × √ × √ √ √ treatment room 2 mode √ × × √ √ √ √ 表 5 机器模式与PPS控制区对应关系
Table 5. Relationship between machine mode and PPS control areas
machine mode accelerator
control areatreatment room 1
control areatreatment room 2
control areavertical beam transport
line control areaion source mode √ / / √ dump mode √ / / √ treatment room 1 mode √ √ / √ treatment room 2 mode √ / √ √ -
[1] Nakagawa Y, Hatanaka H. Boron neutron capture therapy: clinical brain tumor studies[J]. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 1997, 33(1): 105-115. [2] Nakagawa Y, Pooh K, Kobayashi T, et al. Clinical review of the Japanese experience with boron neutron capture therapy and a proposed strategy using epithermal neutron beams[J]. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 2003, 62(1/2): 87-99. [3] Kato I, Ono K, Sakurai Y, et al. Effectiveness of BNCT for recurrent head and neck malignancies[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2004, 61(5): 1069-1073. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2004.05.059 [4] 傅世年, 梁天骄, 陈和生. BNCT中子源的研发现况与展望[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(14):1471-1478 doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1254Fu Shinian, Liang Tianjiao, Chen Hesheng. Status and outlook: Research and development on the neutron source for BNCT[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(14): 1471-1478 doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1254 [5] 陈和生, 邢更妹. 硼中子俘获治疗的发展机遇与挑战: 含硼药物的研发[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(14):1469-1470 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0474Chen Hesheng, Xing Gengmei. Opportunities and challenges in boron neutron capture therapy: development of boron-containing drugs[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(14): 1469-1470 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0474 [6] 欧阳华甫, 肖永川, 刘盛进, 等. BNCT加速器设计和调试[J]. 白城师范学院学报, 2020, 34(2):1-9Ouyang Huafu, Xiao Yongchuan, Liu Shengjin, et al. Designing and commissioning of BNCT accelerator[J]. Journal of Baicheng Normal University, 2020, 34(2): 1-9 [7] 欧阳华甫, 肖永川, 曹秀霞, 等. BNCT02加速器设计及离子源调试[J]. 白城师范学院学报, 2022, 36(5):1-8Ouyang Huafu, Xiao Yongchuan, Cao Xiuxia, et al. Designing of BNCT02 accelerator and commissioning of ECR ion source[J]. Journal of Baicheng Normal University, 2022, 36(5): 1-8 [8] 赵籍九, 尹兆升. 粒子加速器技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006Zhao Jijiu, Yin Zhaosheng. Particle accelerator technology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006 [9] 李明涛, 张玉亮, 袁月, 等. CSNS加速器一键开关机程序设计和实现[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35:084001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230014Li Mingtao, Zhang Yuliang, Yuan Yue, et al. Design and implementation of one key on/off program at the accelerator of CSNS[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 084001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230014 [10] 张玉亮, 李明涛, 吴煊, 等. 加速器故障分析软件及其在CSNS应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:074004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210001Zhang Yuliang, Li Mingtao, Wu Xuan, et al. A software based post mortem system and its application in CSNS[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 074004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210001 [11] 朱文超, 林汉尚, 周泽然, 等. 基于嵌入式EPICS的中子监测仪研制[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:026001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200168Zhu Wenchao, Lin Hanshang, Zhou Zeran, et al. Development of a neutron monitor based on embedded EPICS[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 026001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200168 [12] Zhang Yuliang, Jin Dapeng, Zhu Peng, et al. The accelerator control system of CSNS[J]. Radiation Detection Technology and Methods, 2020, 4(4): 478-491. doi: 10.1007/s41605-020-00203-y [13] Zhang Yuliang, Kang Mingtao, Jin Dapeng, et al. The run management system for CSNS[J]. Radiation Detection Technology and Methods, 2019, 3: 35. doi: 10.1007/s41605-019-0116-0 [14] 程司农, 张昭, 朱鹏, 等. 基于高精度时间数据的加速器故障分析样机设计[J]. 核技术, 2022, 45:100203 doi: 10.11889/j.0253-3219.2022.hjs.45.100203Cheng Sinong, Zhang Zhao, Zhu Peng, et al. Design of accelerator failure analysis system prototype based on high precision time data[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2022, 45: 100203 doi: 10.11889/j.0253-3219.2022.hjs.45.100203 [15] 洪春霞, 周平, 滑文强, 等. 上海光源小角X射线散射实验站自动校准系统研究[J]. 核技术, 2021, 44:010102 doi: 10.11889/j.0253-3219.2021.hjs.44.010102Hong Chunxia, Zhou Ping, Hua Wenqiang, et al. Automatic calibration system of small angle X-ray scattering experiment station at SSRF[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2021, 44: 010102 doi: 10.11889/j.0253-3219.2021.hjs.44.010102 [16] 曾孟麒, 尹亮, 尹聪聪, 等. 基于EPICS的SHINE束线站定时设备控制系统[J]. 核技术, 2023, 46:070102 doi: 10.11889/j.0253-3219.2023.hjs.46.070102Zeng Mengqi, Yin Liang, Yin Congcong, et al. Development and implementation of an EPICS-based timing equipment control system for SHINE beamlines and endstations[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2023, 46: 070102 doi: 10.11889/j.0253-3219.2023.hjs.46.070102 [17] 张根灿. 上海质子治疗装置注入器远程控制系统的构建[D]. 上海: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海应用物理研究所), 2018Zhang Gencan. The construction of remote control system for proton injector of Shanghai proton therapy facility[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Science, 2018 [18] 温特. 基于EPICS的HUST-PTF束损探测研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2020Wen Te. Design of an EPICS based beam loss detection for HUST-PTF[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2020 [19] 何泳成, 王春红, 赵卓, 等. 基于F3RP61的嵌入式EPICS IOC应用研究与实现[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2012, 32(1):17-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2012.01.004HE Yongcheng, WANG Chunhong, ZHAO Zhuo, et al. Research and implementation of embedded EPICS IOC based on F3RP61[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2012, 32(1): 17-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2012.01.004 -




 下载:
下载: