Optimal wire-array design for underwater electrical wire explosion based on parallel-series wire-array and discharge similarity
-
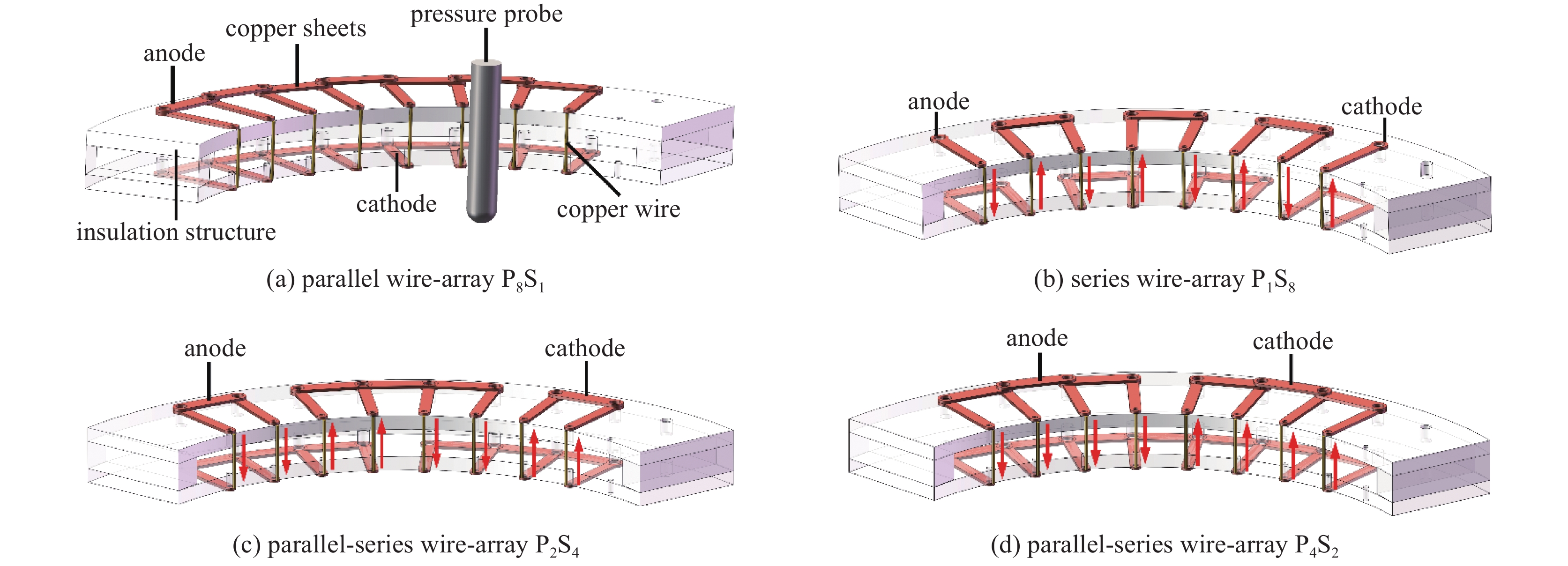
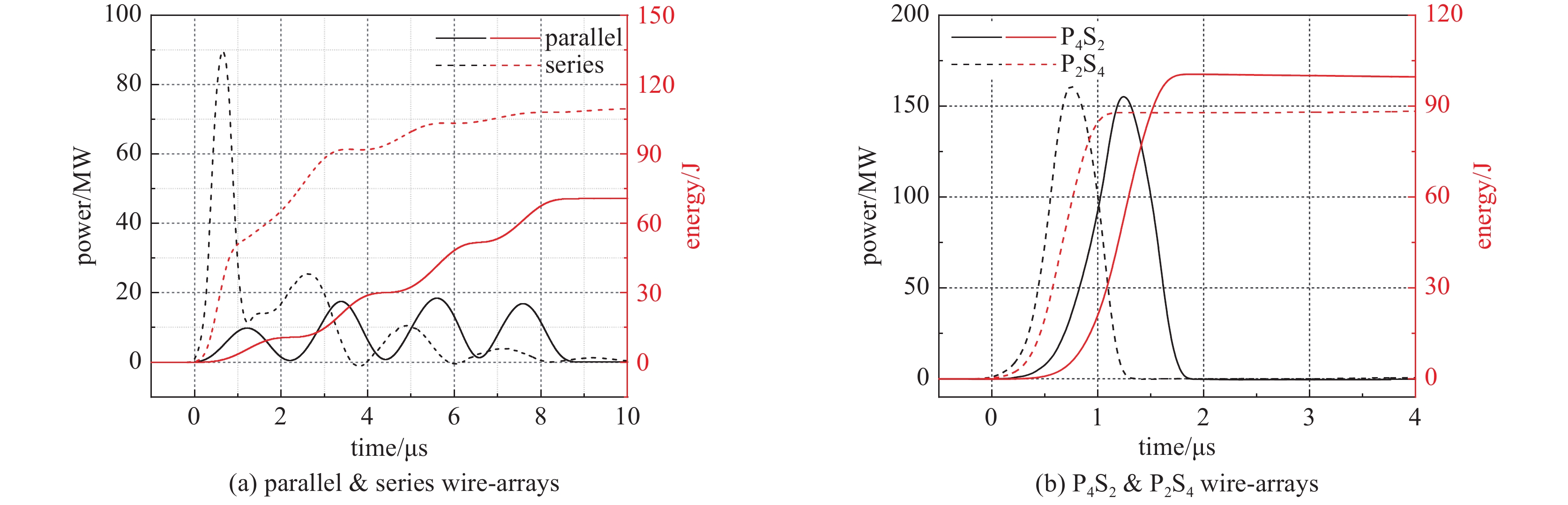
摘要: 为提高水中金属丝电爆炸(水中丝爆)产生的冲击波,将多根丝并联形成丝阵负载,但此方法会降低负载电阻导致沉积功率低。为解决这一问题,通过电流“换向件”设计了总质量不变前提下、整体电阻可变的多种串并联丝阵,提出负载与电源内阻动态匹配是理想放电模式。借助串并联丝阵验证了单丝放电相似性,实现了高电压大装置的小型化验证。通过放电相似性和串并联丝阵,提出水中丝爆丝阵负载优化设计方法,实现了给定能量和金属丝质量下最优负载确定方法。Abstract: To enhance the shock wave generated by underwater electrical wire explosion(UEWE), wires are connected in parallel to form wire-array, but wire-array’s low resistance results in low deposition power. To solve the problem, by using copper sheets, parallel-series wire-arrays with different resistance and same mass were designed, and it was proposed that resistance matching between wire-array and power source is the ideal discharge mode. By parallel-series wire-array, single wire discharge similarity was verified, and miniaturization verification of large devices with high voltage was achieved. With the help of discharge similarity and parallel-series wire-array, the optimal wire-array design of UEWE was proposed at a given energy and wire mass.
-
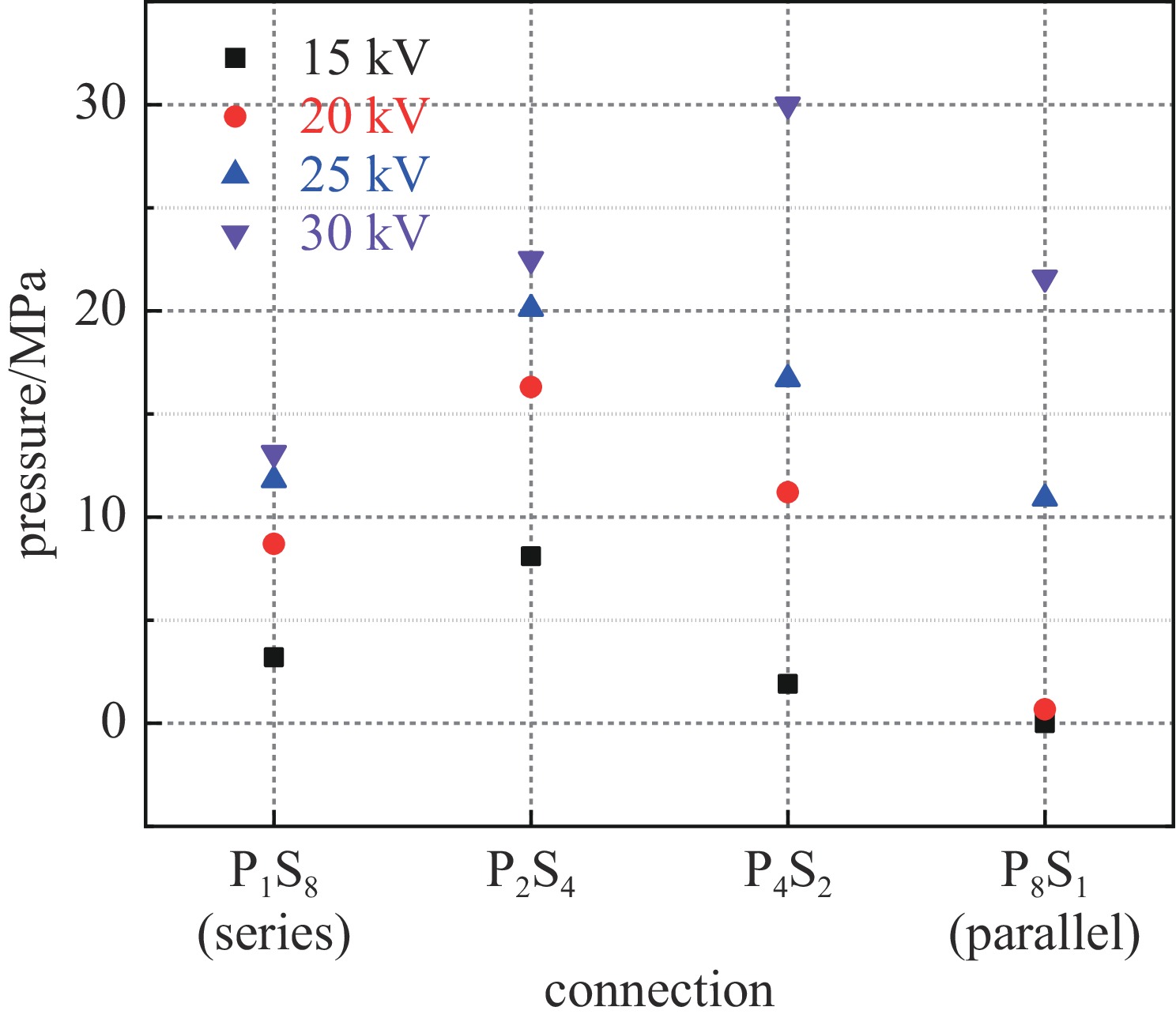
表 1 不同储能下不同丝阵的电爆炸冲击波峰值
Table 1. Shock wave generated by different stored energy and wire-array connection
initial voltage/kV stored energy/J shock wave/MPa P1S8 P2S4 P4S2 P8S1 15 56 3.2 8.1 1.9 ~0 20 100 8.7 16.3 11.0 0.67 25 156 12.0 20.1 17.0 11.00 30 225 13.0 23.0 30.0 22.00 表 2 不同状态下四种丝阵的电阻
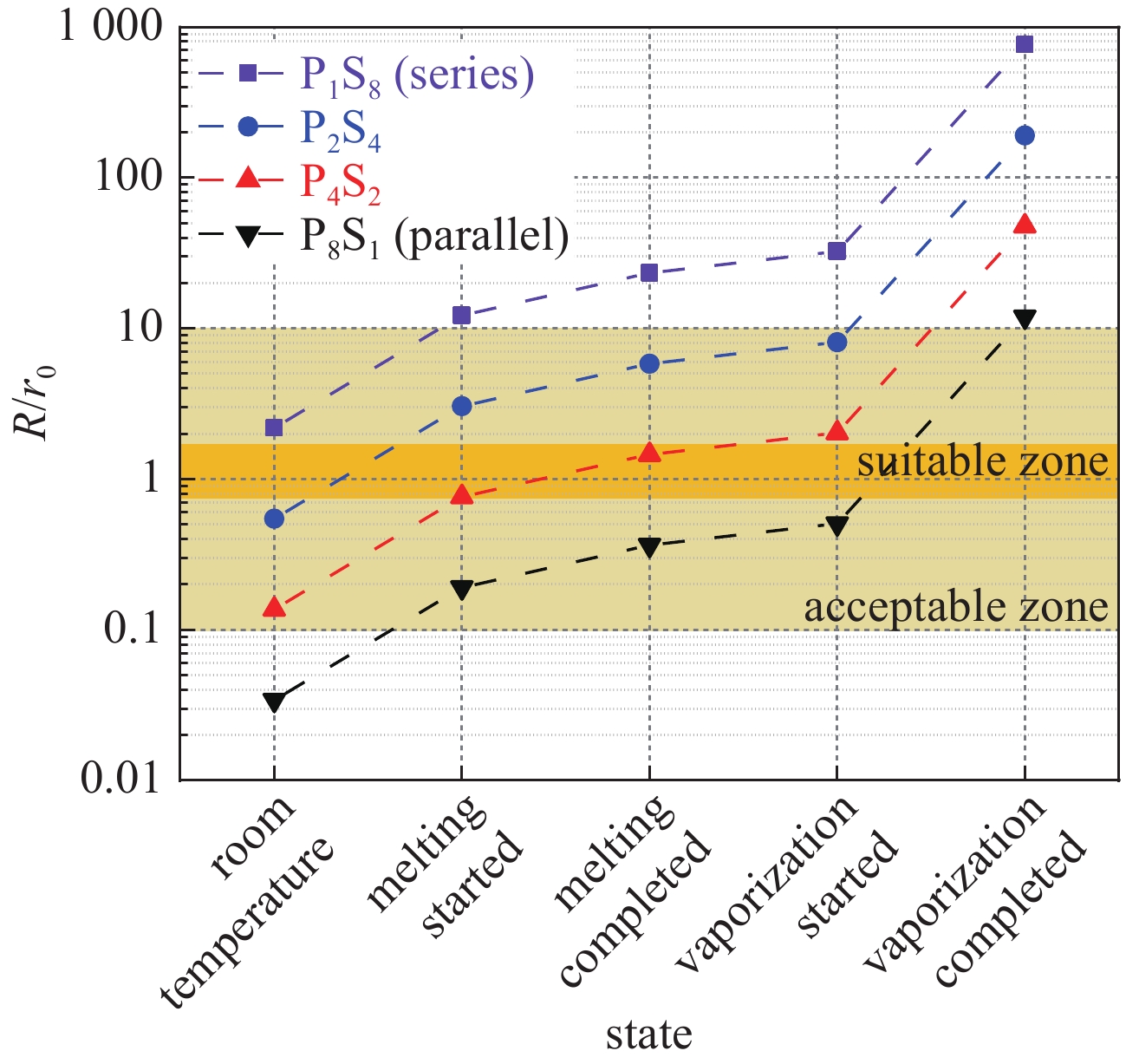
Table 2. Resistance of four wire-arrays at different states
state resistance/Ω P1S8 P2S4 P4S2 P8S1 room temperature 0.36 0.09 0.023 0.0056 melting started 2.0 0.5 0.13 0.032 melting completed 3.9 1.0 0.24 0.060 vaporization started 5.4 1.3 0.33 0.084 vaporization completed 126 32 7.9 2.0 -
[1] Krasik Y E, Grinenko A, Sayapin A, et al. Underwater electrical wire explosion and its applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2008, 36(2): 423-434. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2008.918766 [2] Kolacek K, Prukner V, Schmidt J, et al. A potential environment for lasing below 15 nm initiated by exploding wire in water[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 28(1): 61-67. doi: 10.1017/S0263034609990577 [3] Sheftman D, Krasik Y E. Investigation of electrical conductivity and equations of state of non-ideal plasma through underwater electrical wire explosion[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2010, 17: 112702. doi: 10.1063/1.3497010 [4] Claverie A, Deroy J, Boustie M, et al. Experimental characterization of plasma formation and shockwave propagation induced by high power pulsed underwater electrical discharge[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2014, 85: 063701. doi: 10.1063/1.4879715 [5] Tobe T, Kato M, Obara H. Pressure pulses produced by underwater wire explosions in electric discharge metal forming[J]. Bulletin of JSME, 1979, 22(166): 613-619. doi: 10.1299/jsme1958.22.613 [6] Oyane M, Masaki S. Fundamental study on electrohydraulic forming[J]. Bulletin of JSME, 1964, 7(26): 474-480. doi: 10.1299/jsme1958.7.474 [7] Oyane M, Masaki S. Fundamental study on electrohydraulic forming: II. The effect of kinds of fuse wires and circuit inductance on pressure pulse[J]. Bulletin of JSME, 1965, 8(30): 251-258. doi: 10.1299/jsme1958.8.251 [8] Oyane M, Masaki S. Fundamental study on electrohydraulic forming: III. The effect of diameter of fuse wire and circuit inductance on pressure pulse[J]. Bulletin of JSME, 1965, 8(30): 259-263. doi: 10.1299/jsme1958.8.259 [9] Chace W G, Moore H K. Exploding wires[M]. New York: Plenum Press, 1962: 195-206. [10] Ide M, Irie S, Matsuo N, et al. Research about pulverization of rice using underwater shock wave by electric discharge[C]//2010 Pressure Vessels and Piping Division/K-PVP Conference. 2010: 477-481. [11] Kuraya E, Touyama A, Nakada S, et al. Underwater shockwave pretreatment process to improve the scent of extracted Citrus junos Tanaka (Yuzu) Juice[J]. International Journal of Food Science, 2017, 2017: 2375181. [12] Yasuda A, Kuraya E, Touyama A, et al. Underwater shockwave pretreatment process for improving carotenoid content and yield of extracted carrot (Daucus carota L.) juice[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2017, 211: 15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.04.026 [13] Shimojima K, Higa O, Higa Y, et al. Experimental verification of the softening of the pork using underwater shock waves generated by wire electrical discharges[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2018, 910: 176-179. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.910.176 [14] Prieto F E, Loske A M, Yarger F L. An underwater shock wave research device[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1991, 62(7): 1849-1854. doi: 10.1063/1.1142527 [15] Cho C H, Park S H, Choi Y W, et al. Production of nanopowders by wire explosion in liquid media[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201(9/11): 4847-4849. [16] Cho C, Choi Y W, Kang C, et al. Effects of the medium on synthesis of nanopowders by wire explosion process[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 91: 141501. doi: 10.1063/1.2794724 [17] 张永民, 邱爱慈, 周海滨, 等. 面向化石能源开发的电爆炸冲击波技术研究进展[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(4):1009-1017Zhang Yongmin, Qiu Aici, Zhou Haibin, et al. Research progress in electrical explosion shockwave technology for developing fossil energy[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(4): 1009-1017 [18] Han Ruoyu, Zhou Haibin, Liu Qiaojue, et al. Generation of electrohydraulic shock waves by plasma-ignited energetic materials: I. Fundamental mechanisms and processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2015, 43(12): 3999-4008. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2015.2468064 [19] 邱爱慈, 张永民, 蒯斌, 等. 高功率脉冲技术在非常规天然气开发中应用的设想[C]//第二届中国工程院/国家能源局能源论坛论文集. 北京: 中国工程院, 2012: 1112-1124Qiu Aici, Zhang Yongmin, Kuai Bin, et al. Application of high power pulse technology in unconventional gas development[C]//The 2nd China Academy of Engineering/National Energy Administration Forum. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Engineering, 2012: 1112-1124 [20] 曹落霞, 胡海波, 陈永涛, 等. 磁驱动飞片加载下纯铁的冲击相变和层裂特性[J]. 高压物理学报, 2015, 29(4):248-254 doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2015.04.002Cao Luoxia, Hu Haibo, Chen Yongtao, et al. Shock-induced phase transition and spallation in pure iron under magnetically driven flyer plate loading[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2015, 29(4): 248-254 doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.2015.04.002 [21] Gregory K B, Vidic R D, Dzombak D A. Water management challenges associated with the production of shale gas by hydraulic fracturing[J]. Elements, 2011, 7(3): 181-186. doi: 10.2113/gselements.7.3.181 [22] Grinenko A, Gurovich V T, Krasik Y E. Implosion in water medium and its possible application for the inertial confinement fusion target ignition[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2007, 14: 012701. doi: 10.1063/1.2424885 [23] Tobe T, Kato M, Obara H. Energy consumption at underwater exploding-wire gap in electric discharge metal forming[J]. Bulletin of JSME, 1978, 21(162): 1780-1786. doi: 10.1299/jsme1958.21.1780 [24] Rodriguez G, Roberts J P, Echave J A, et al. Laser shadowgraph measurements of electromagnetically-driven cylindrical shock-wave implosions in water[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 93(3): 1791-1797. doi: 10.1063/1.1535253 [25] Rousskikh A G, Oreshkin V I, Labetsky A Y, et al. Electrical explosion of conductors in the high-pressure zone of a convergent shock wave[J]. Technical Physics, 2007, 52(5): 571-576. doi: 10.1134/S1063784207050064 [26] Krasik Y E, Grinenko A, Sayapin A, et al. Generation of sub-Mbar pressure by converging shock waves produced by the underwater electrical explosion of a wire array[J]. Physical Review E, 2006, 73: 057301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.73.057301 [27] Fedotov-Gefen A, Efimov S, Gilburd L, et al. Extreme water state produced by underwater wire-array electrical explosion[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 96: 221502. doi: 10.1063/1.3446832 [28] Fedotov-Gefen A, Efimov S, Gilburd L, et al. Generation of a 400 GPa pressure in water using converging strong shock waves[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2011, 18: 062701. doi: 10.1063/1.3599425 [29] Antonov O, Gilburd L, Efimov S, et al. Generation of extreme state of water by spherical wire array underwater electrical explosion[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2012, 19: 102702. doi: 10.1063/1.4757984 [30] Gilburd L, Efimov S, Fedotov Gefen A, et al. Modified wire array underwater electrical explosion[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 30(2): 215-224. doi: 10.1017/S0263034611000851 [31] Antonov O, Efimov S, Yanuka D, et al. Generation of converging strong shock wave formed by microsecond timescale underwater electrical explosion of spherical wire array[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102: 124104. doi: 10.1063/1.4798827 [32] Antonov O, Efimov S, Gurovich V T, et al. Diagnostics of a converging strong shock wave generated by underwater explosion of spherical wire array[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 115: 223303. doi: 10.1063/1.4883187 [33] Bland S N, Krasik Y E, Yanuka D, et al. Generation of highly symmetric, cylindrically convergent shockwaves in water[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2017, 24: 082702. doi: 10.1063/1.4994328 [34] Rososhek A, Efimov S, Nitishinski M, et al. Spherical wire arrays electrical explosion in water and glycerol[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2017, 24: 122705. doi: 10.1063/1.5000037 [35] Yanuka D, Rososhek A, Bland S N, et al. Uniformity of cylindrical imploding underwater shockwaves at very small radii[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111: 214103. doi: 10.1063/1.5005174 [36] Yanuka D, Theocharous S, Efimov S, et al. Synchrotron based X-ray radiography of convergent shock waves driven by underwater electrical explosion of a cylindrical wire array[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 125: 093301. doi: 10.1063/1.5089011 [37] Qian Dun, Liu Zhigang, Li Liuxia, et al. Enhancement of shock wave generated by underwater electrical wire-array explosion at a fixed energy and mass of wire-array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2020, 48(10): 3373-3377. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2019.2963424 -




 下载:
下载: