RF design of C-band photocathode electron gun for Southern Advanced Photon Source
-
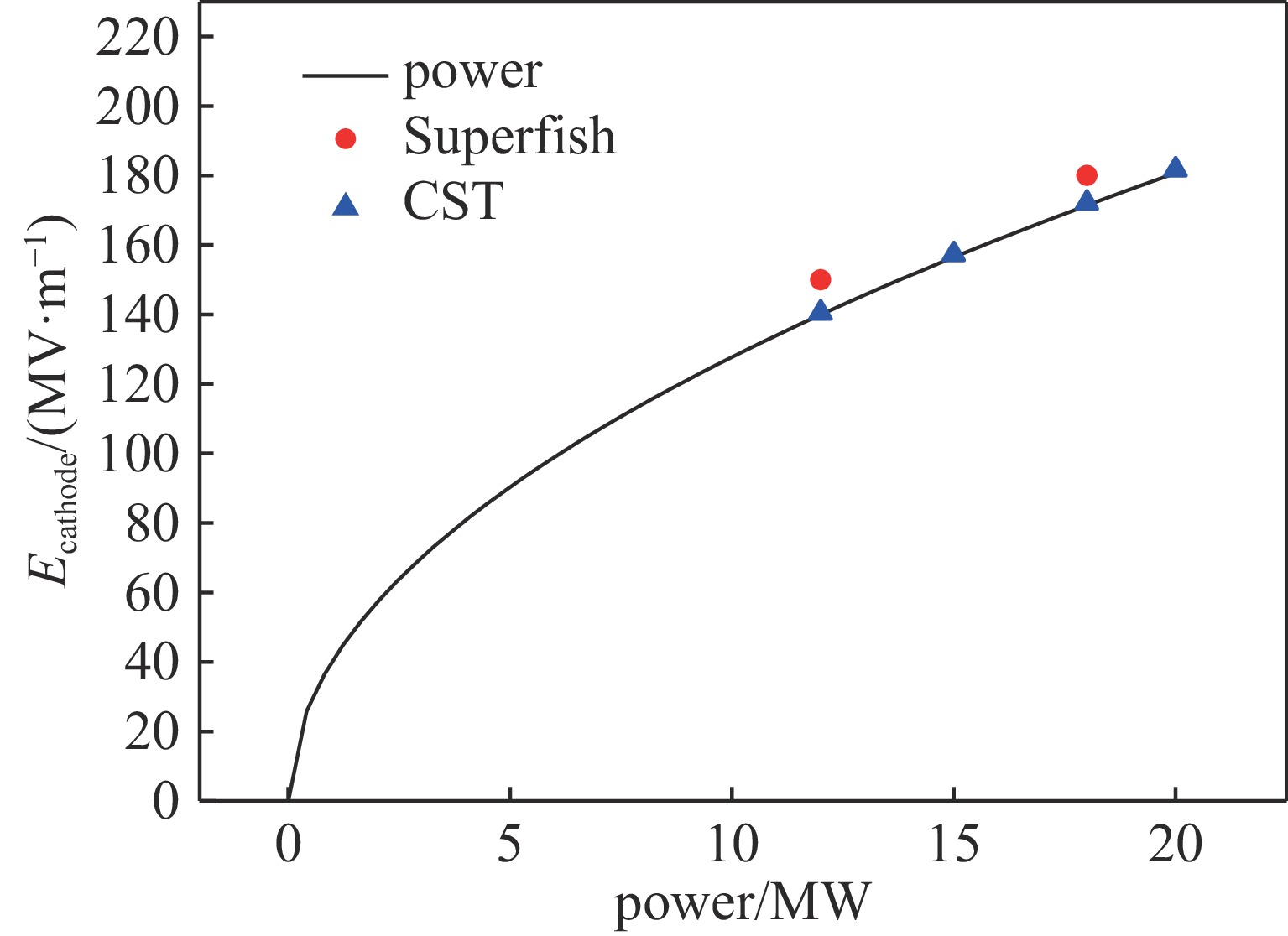
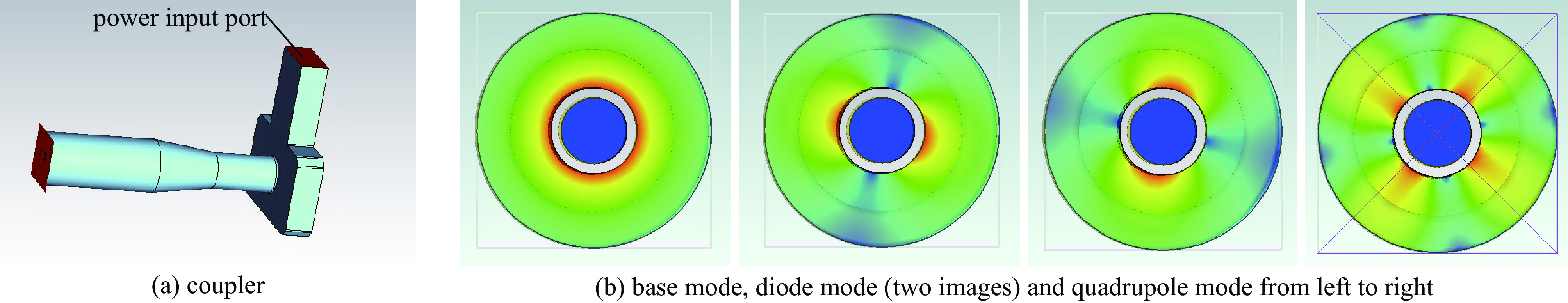
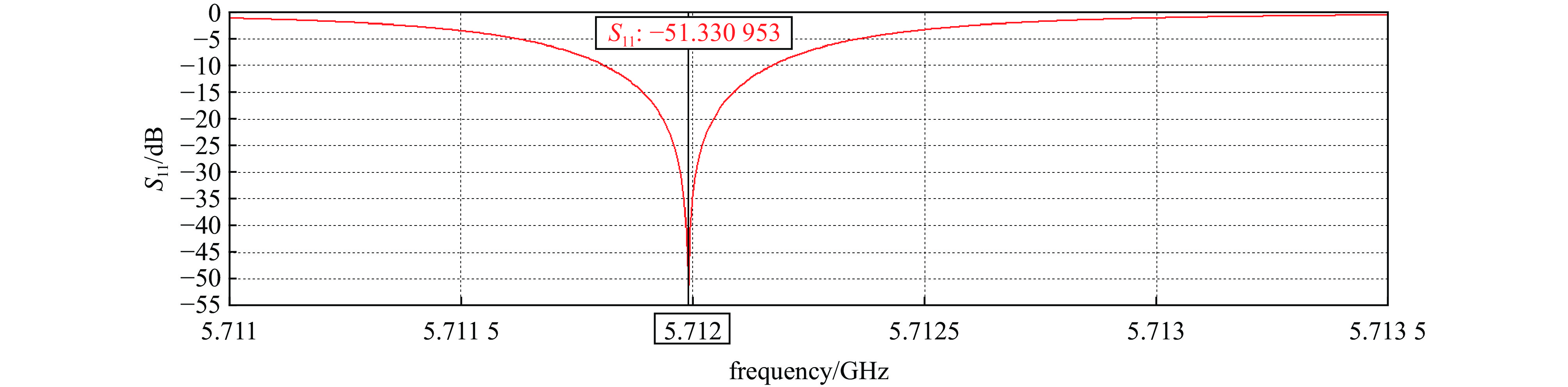
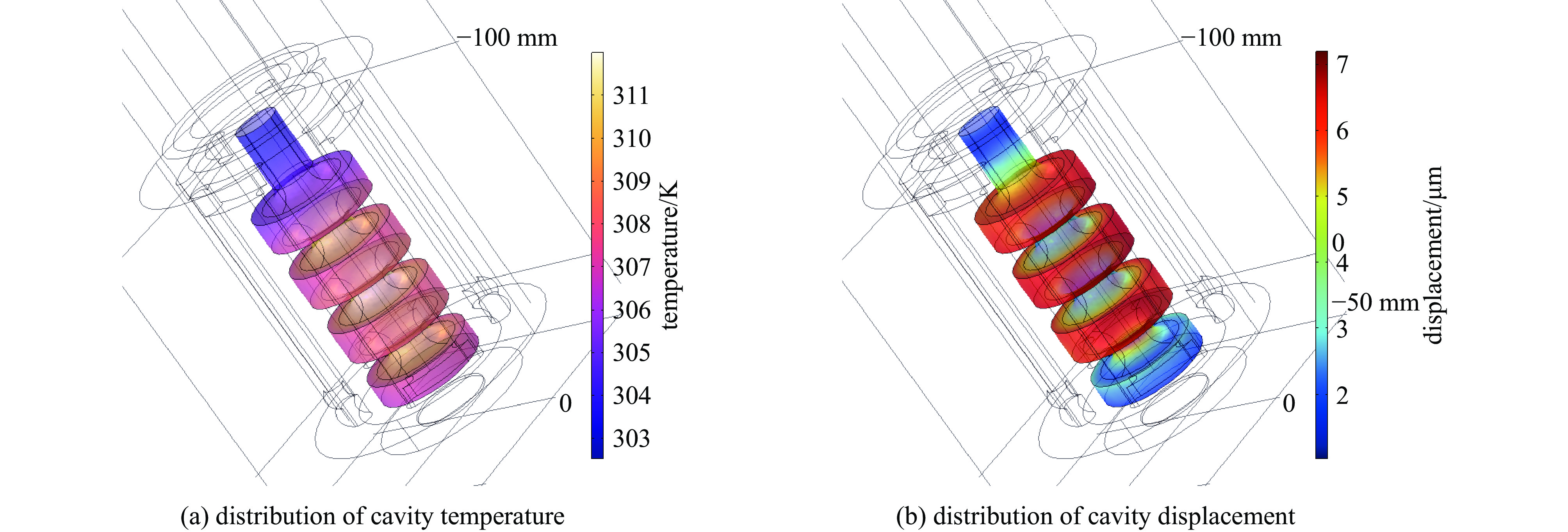
摘要: 作为南方先进光源直线段注入器重要设备,开展了C波段光阴极电子枪研究,包括驻波腔微波设计和耦合器设计。其中驻波腔采用3.6腔结构,π模加速模式,工作频率为5.712 GHz;耦合器采用同轴耦合方式。利用Superfish及CST完成了腔体微波结构设计,优化盘片的形状,降低腔体表面最大电场,从而有利于提高腔体加速场强;利用COMSOL开展了腔体水冷系统的分析,优化设计水路,减少腔体由于功率负载所造成的频率偏移, 控制腔体温度的上升,保持腔体最大温升小于20 ℃。在18.15 MW的入腔功率下,阴极面最高场强为180 MV/m,腔体表面最大场强与阴极面场强比值约为
0.9346 ,腔体Q值大于10 000。通过对耦合器的设计,抑制二极模和四极模的传输,S11参数小于−40 dB。Abstract: The C-band photocathode electron gun is designed. As one of important equipments for the linear injector of the Southern Advanced Photon Source. This paper discusses its RF and coupler design. The C-band electron gun has a working frequency of 5.712 GHz, a 3.6-cell structure, a π-mode acceleration mode, and it adopts a coaxial coupling method. The CST and Superfish codes are used to optimize the cavity microwave structure, reducing the surface electric field of the cavity to enhance the accelerating field strength and suppressing the multimode transmission. Furthermore, COMSOL Multiphysics is applied to analyze the cavity cooling system, reducing frequency drift caused by the cavity heating. Additionally, a water cooling design for the cavity ensures that the maximum temperature rise of the cavity is less than 20 ℃. Under an input power of 18.15 MW, the acceleration gradient of 180 MV/m on the cathode surface is achieved, the ratio of the acceleration gradient to the cathode surface electric field is approximately 0.93, and the cavity quality factor is greater than10000 . The design of the coupler suppresses the transmission of dipole and quadrupole modes, with the S11 parameter being less than −40 dB.-
Key words:
- Southern Advanced Photon Source /
- photocathode electron gun /
- RF structure /
- coupler /
- C-band
-
表 1 电子枪仿真微波参数
Table 1. RF parameters of electron gun
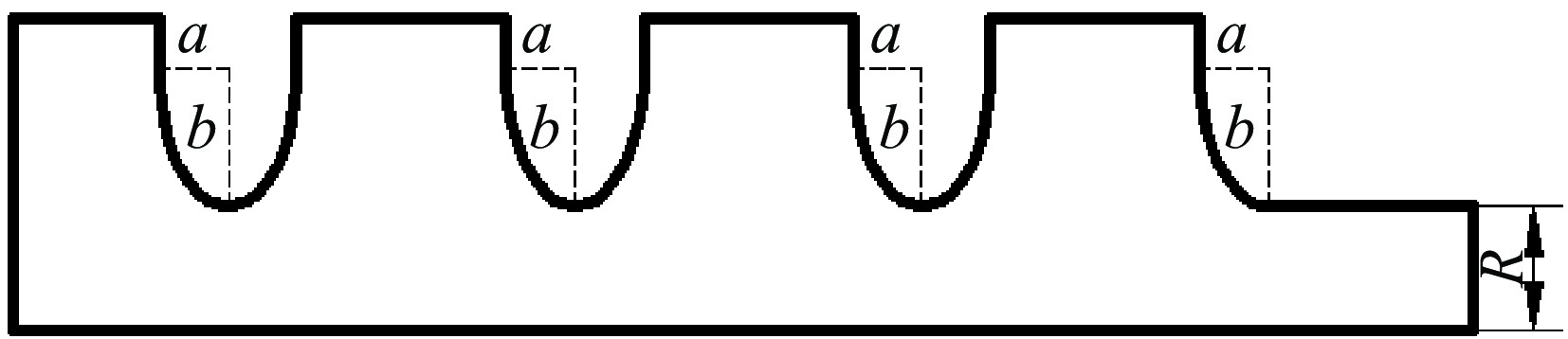
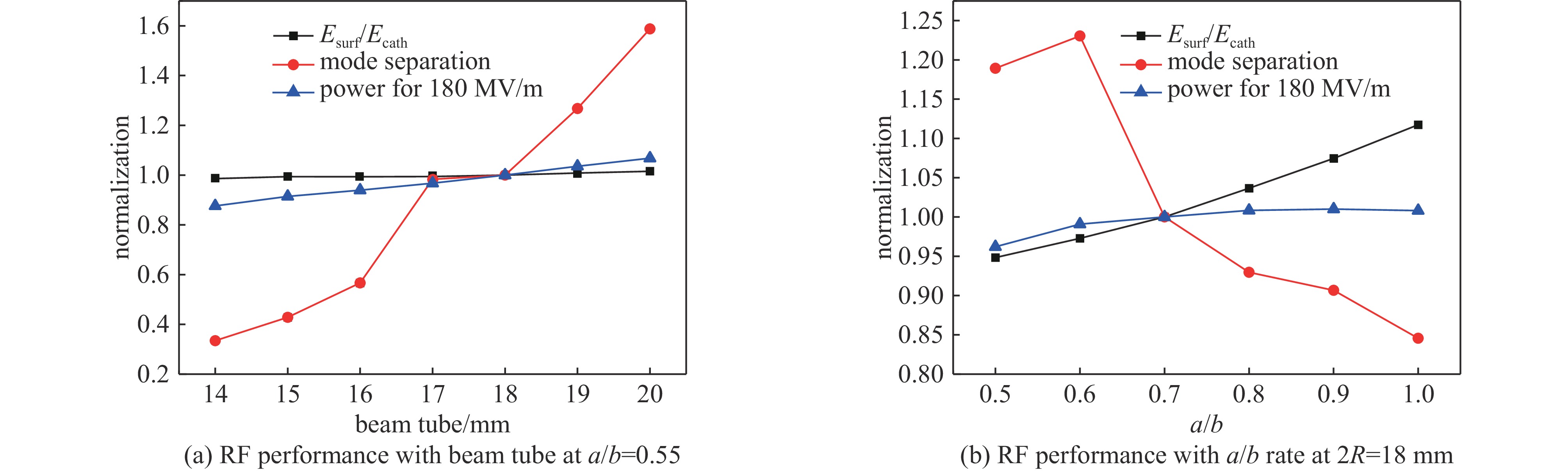
a/b a/mm b/mm mode separation/MHz Esurf/Ecath effective shunt impedance/(MΩ/m) Q value power/MW 0.50 5.0 10.0 24.81 0.9470 48.685 11575.1 17.58 0.55 5.5 10.0 21.837 0.9346 46.775 11252.3 18.15 0.60 6.0 10.0 21.937 0.9353 44.467 10901.5 18.83 0.70 6.0 8.57 17.829 0.9614 43.687 10691.0 19.00 表 2 腔体结构各尺寸敏感度分析
Table 2. Cavity dimension and sensitivity
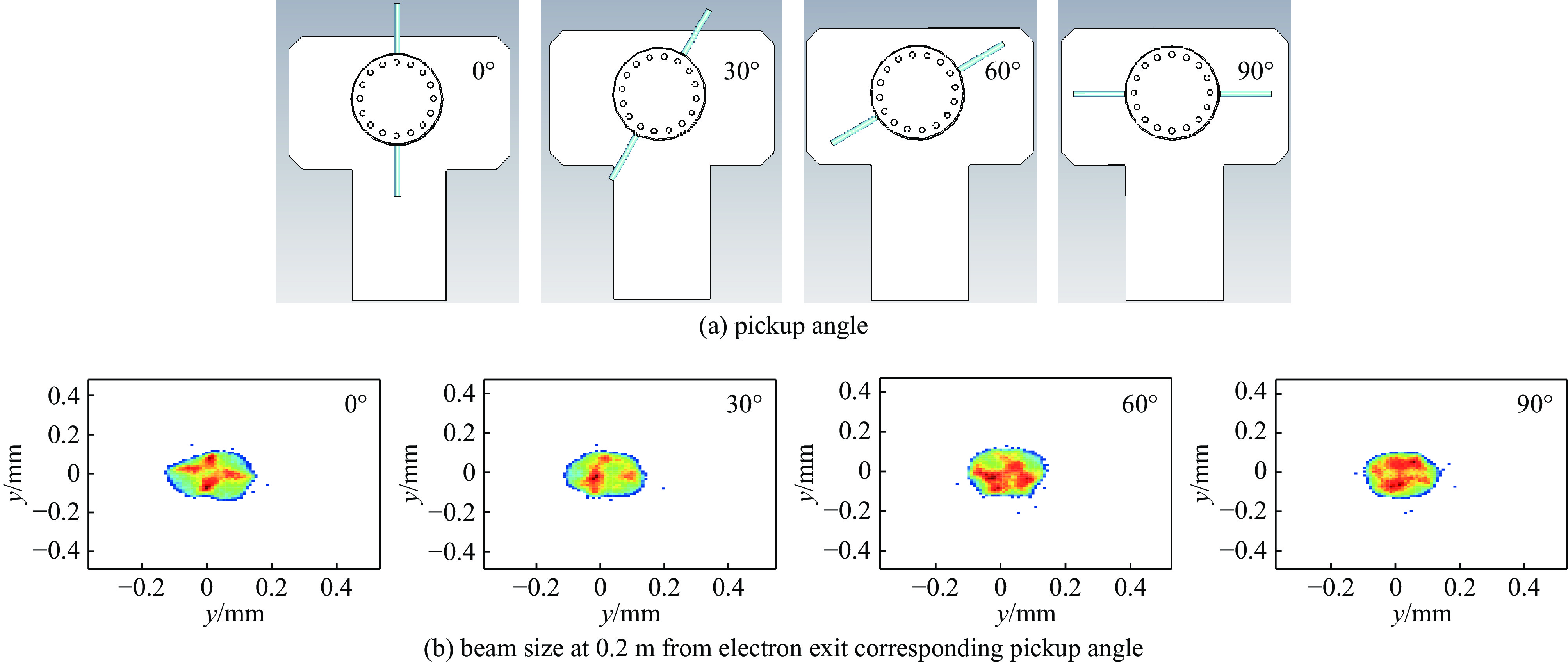
size/mm sensitivity/(MHz·mm−1) cavity diameter 45.053 140.800 beam tube diameter 18.000 50.400 single cell length 26.242 42.400 semi short axis 5.500 14.100 semi long axis 10.000 22.100 表 3 不同角度下X、Y方向束流的发射度
Table 3. X and Y direction beam emittance at different angle
angle of pickup/(°) emittance of X direction/(mm·mrad) emittance of Y direction/(mm·mrad) no pickup 0.198 0.187 0 0.210 0.228 30 0.223 0.203 60 0.207 0.199 90 0.219 0.195 表 4 腔体入水温度的变化对腔体结构及微波参数的影响
Table 4. Water temperature and RF parameters
Twater/℃ ΔTcavity/℃ ΔDcavity/μm Δf/MHz flatness of E-field/% 25.0 14 7 −1.3 1 22.5 12 6 −1.1 2 20.0 10 5 −0.9 3 -
[1] Arthur J, Anfinrud P, Audebert P, et al. LCLS-conceptual design report for the LCLS project[EB/OL]. 2002(2002-04-08). http://www-ssrl.slac.stanford.edu/lcls/cdr/. [2] Materlik G, Tschentscher T. TESLA technical design report Part 5: the X-ray free electron laser[EB/OL]. 2001. http://tesla.desy.de/newpages/TDRD/PartV/xfel.html. [3] Poole M W, Bennett S L, Bowler M A, et al. 4GLS: a new type of fourth generation light source facility[C]//Proceedings of 2003 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2003: 189-191. [4] Corlett J N, Barletta W A, DeSantis S, et al. A recirculating linac-based facility for ultrafast X-ray science[C]//Proceedings of 2003 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2003: 186-188. [5] Park S J, Park J H, Parc Y W, et al. Status of PPI (Pohang Photo-Injector) for PAL XFEL[C]//Proceedings of 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2005: 1733-1735. [6] Kramer D. Closing in on the design of the BESSY-FEL[C]//Proceedings of 2003 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2003: 1083-1085. [7] 周奎, 李鹏, 周征, 等. 中物院太赫兹自由电子激光装置现状及升级计划[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:104013 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220091Zhou Kui, Li Peng, Zhou Zheng, et al. Status and upgrade plan of CAEP THz-FEL facility[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 104013 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220091 [8] 贾豪彦, 黄森林, 焦毅, 等. 超快X射线自由电子激光研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:054001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220056Jia Haoyan, Huang Senlin, Jiao Yi, et al. Research advances in ultrafast X-ray free-electron lasers[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 054001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220056 [9] Vogt M, Faatz B, Feldhaus J, et al. The free-electron laser FLASH at DESY[C]//Proceedings of IPAC2013. 2013: 1167-1169. [10] Altarelli M. The European X-ray free-electron laser: toward an ultra-bright, high repetition-rate X-ray source[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2015, 3: e18. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2015.17 [11] Emma P, Akre R, Arthur J, et al. First lasing and operation of an ångstrom-wavelength free-electron laser[J]. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4(9): 641-647. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.176 [12] Prat E, Abela R, Aiba M, et al. A compact and cost-effective hard X-ray free-electron laser driven by a high-brightness and low-energy electron beam[J]. Nature Photonics, 2020, 14(12): 748-754. doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-00712-8 [13] Alesini D, Cardelli F, Castorina G, et al. Design of a full C-band injector for ultra-high brightness electron beam[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2019: 1979-1982. [14] Liu Xiaohan, Tang Chuanxiang, Qian Houjun, et al. Design of a compact C-band high brightness photoinjector for an ultra-fast electron diffraction[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(36): 4577-4581. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-6079-5 [15] Schaer M, Bettoni S, Citterio A, et al. Study of a C-band standing-wave gun for the SwissFEL injector[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2014: 698-700. [16] Chen Tingjue, Pei Yuanji, Song Yifan. Design and simulation of a C-band photocathode RF gun with a coaxial coupler for UEM[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2017: 525-527. [17] Wang Lin, Fang Wencheng, Tan Jianhao, et al. Design, fabrication and cold-test results of a 3.6 cell C-band photocathode RF gun for SXFEL[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A, 2021, 1003: 165320. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2021.165320 [18] Liu Xingguang, Li Xiao, Jiang Shiming, et al. A C-band test platform for the development of RF photo cathode and high gradient accelerating structures[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2023: 1995-1998. [19] 姜世民, 陆志军, 刘星光, 等. C波段光阴极电子枪驱动激光整形研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:104003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240162Jiang Shimin, Lu Zhijun, Liu Xingguang, et al. Study of drive laser shaping system for C-band photocathode RF gun[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 104003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240162 [20] Poisson Superfish[EB/OL]. https://laacg.lanl.gov/laacg/services/. [21] CST Studio Suite. Computer Simulation Technology (CST)[EB/OL]. https://3ds.com. [22] COMSOL Multiphysics software[EB/OL]. https://Comsol.com. [23] 程诚, 程道喜, 郑曙昕, 等. 新型热阴极电子枪加热结构热分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(7):1607-1609 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102207.1607Cheng Cheng, Cheng Daoxi, Zheng Shuxin, et al. Thermal analysis of heating structure for thermionic cathode electron gun[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(7): 1607-1609 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102207.1607 [24] Rao T, Dowell D H. An engineering guide to photoinjectors[EB/OL]. 2014(2014-03-28). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1403.7539. -




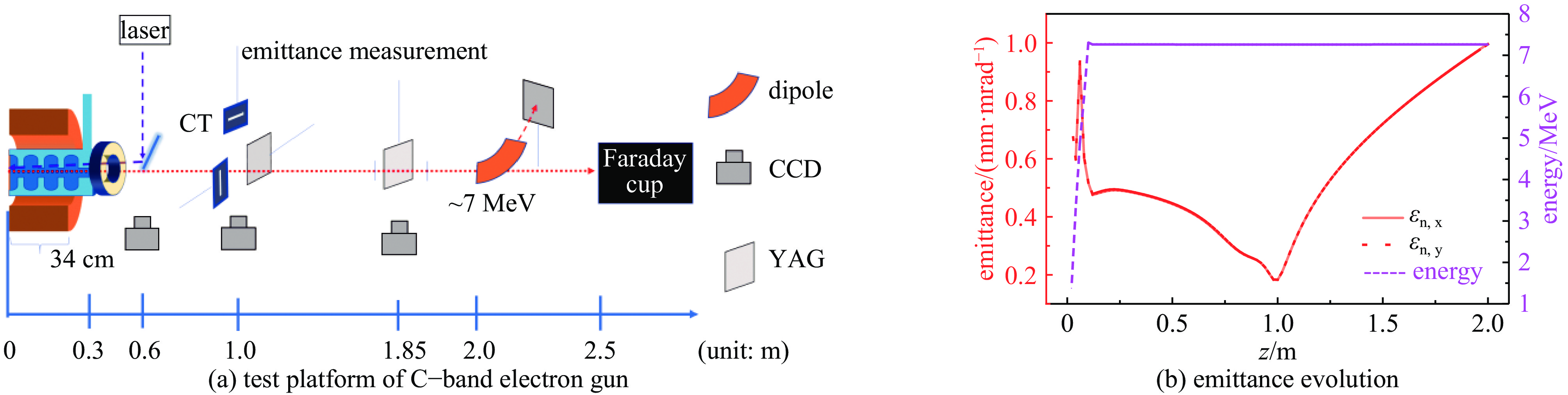
 下载:
下载: