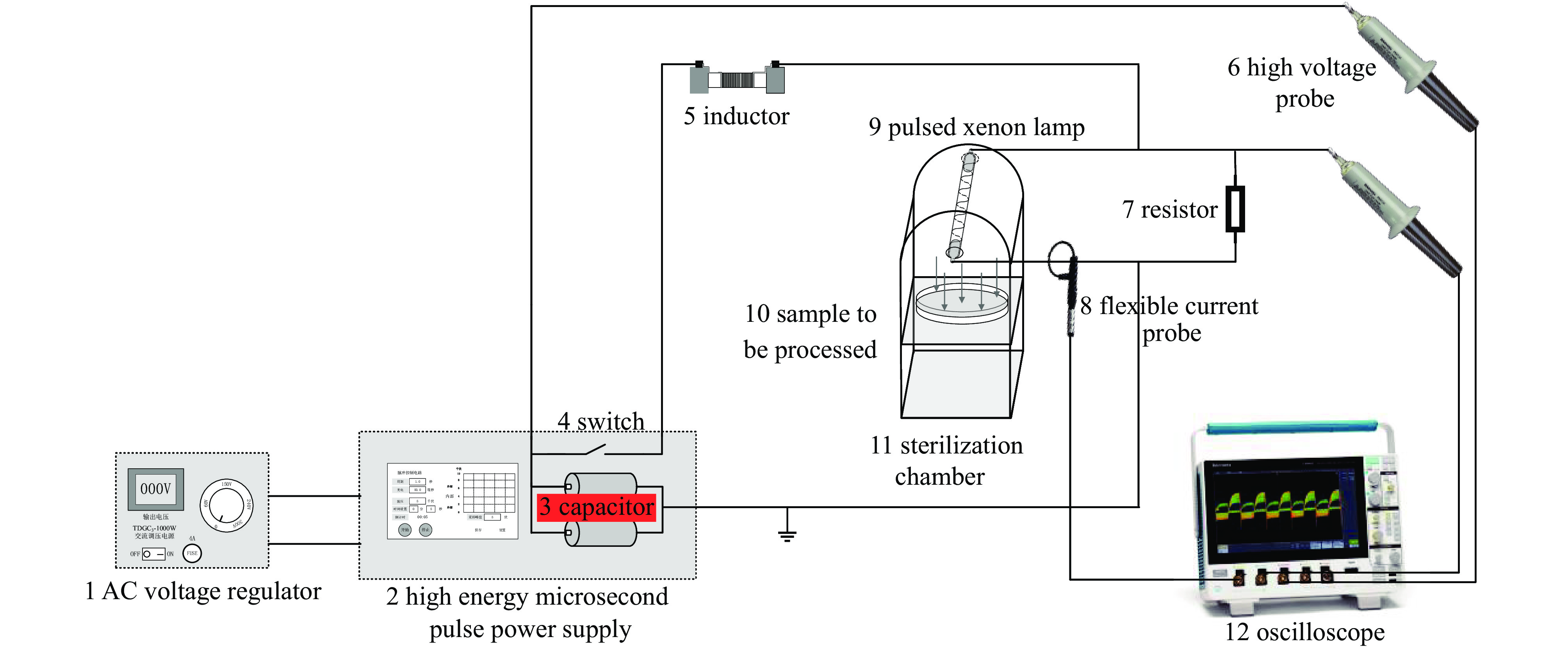
Experimental study on Escherichia coli treatment by pulsed xenon lamp
-
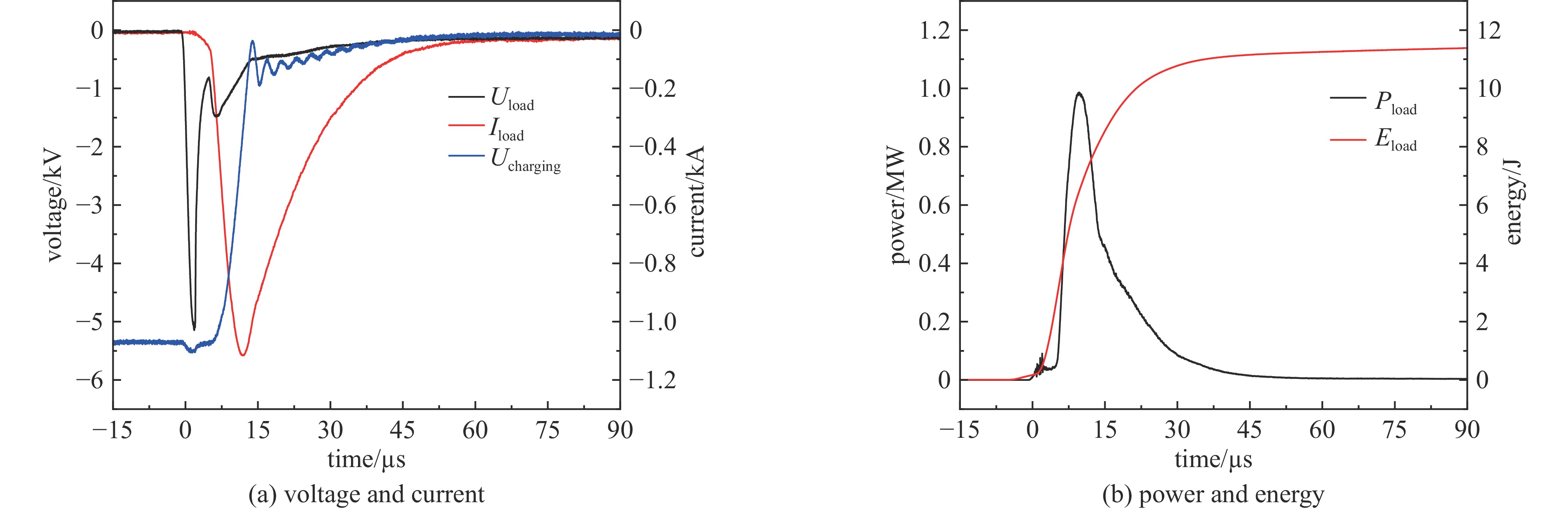
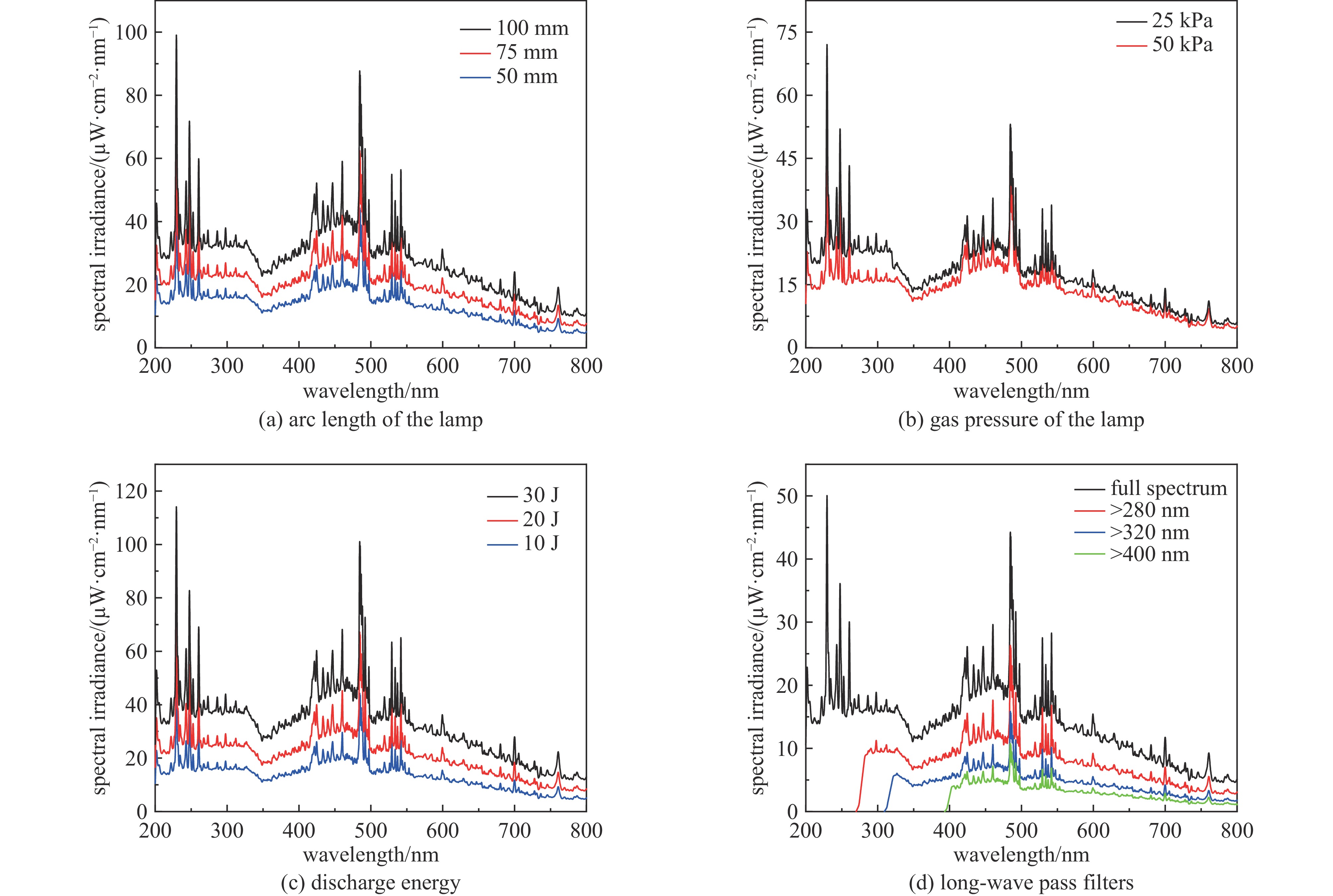
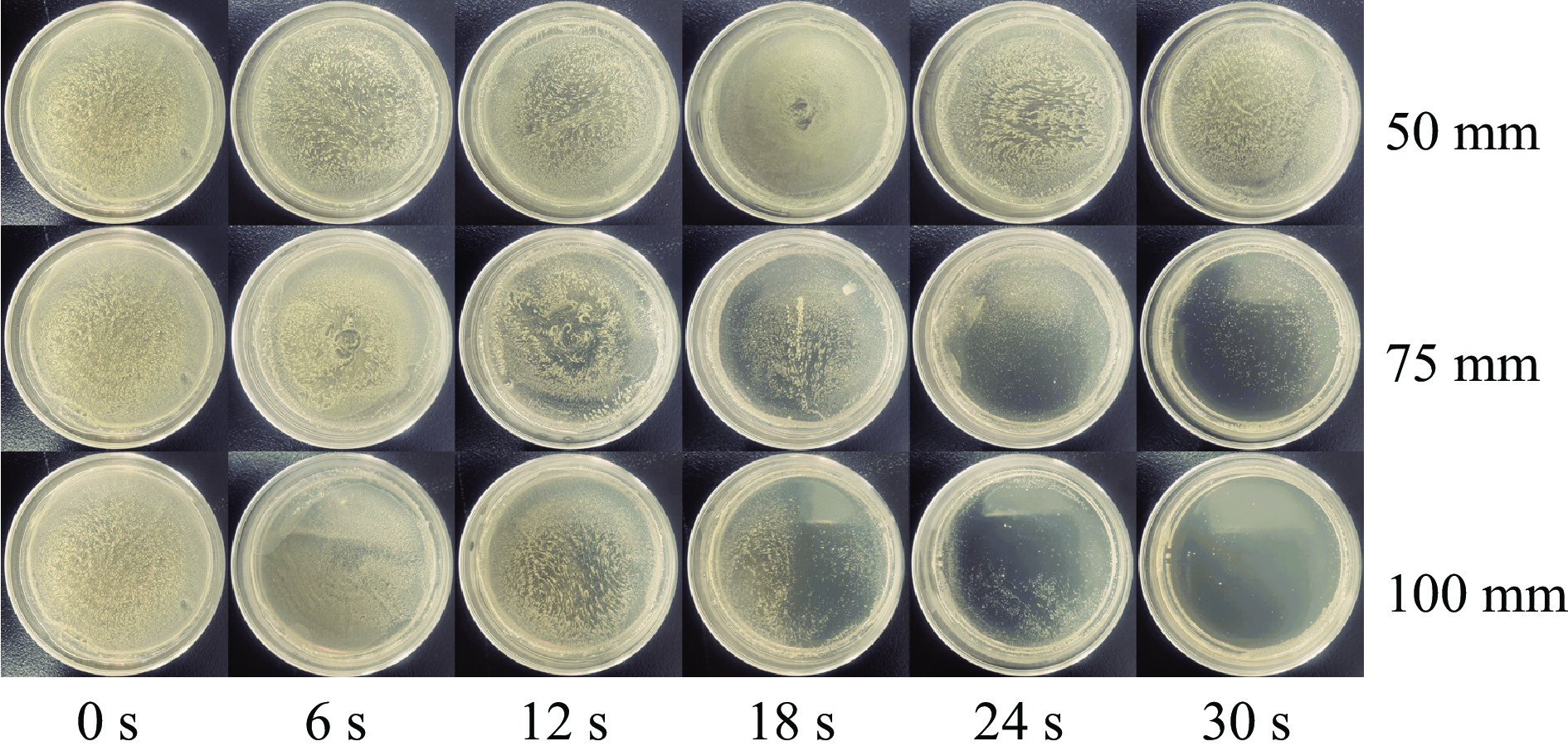
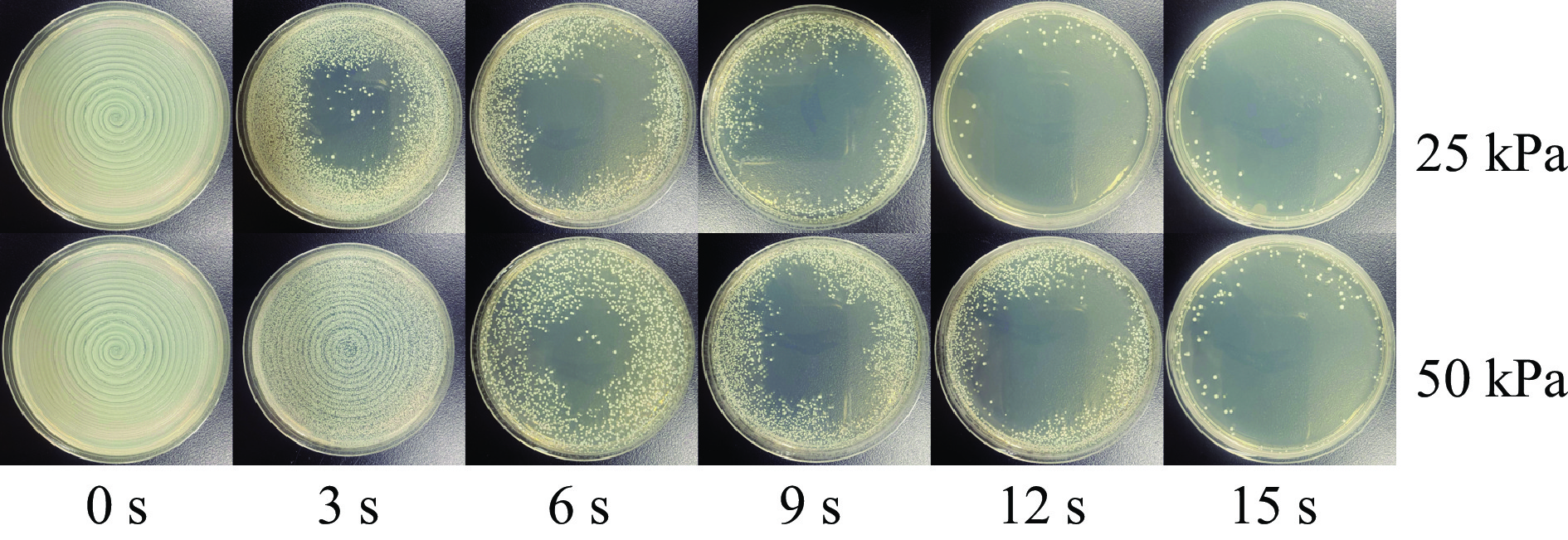
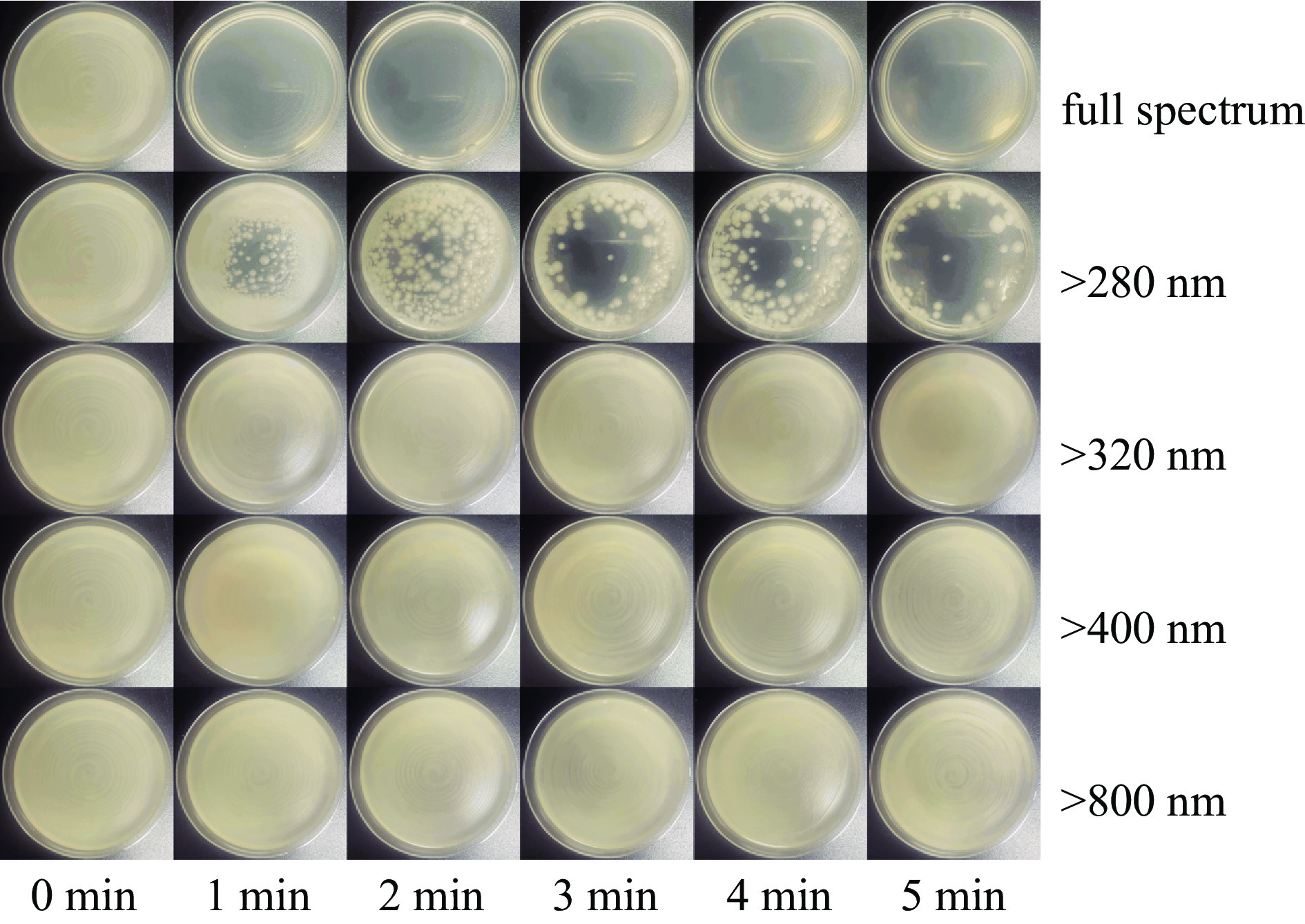
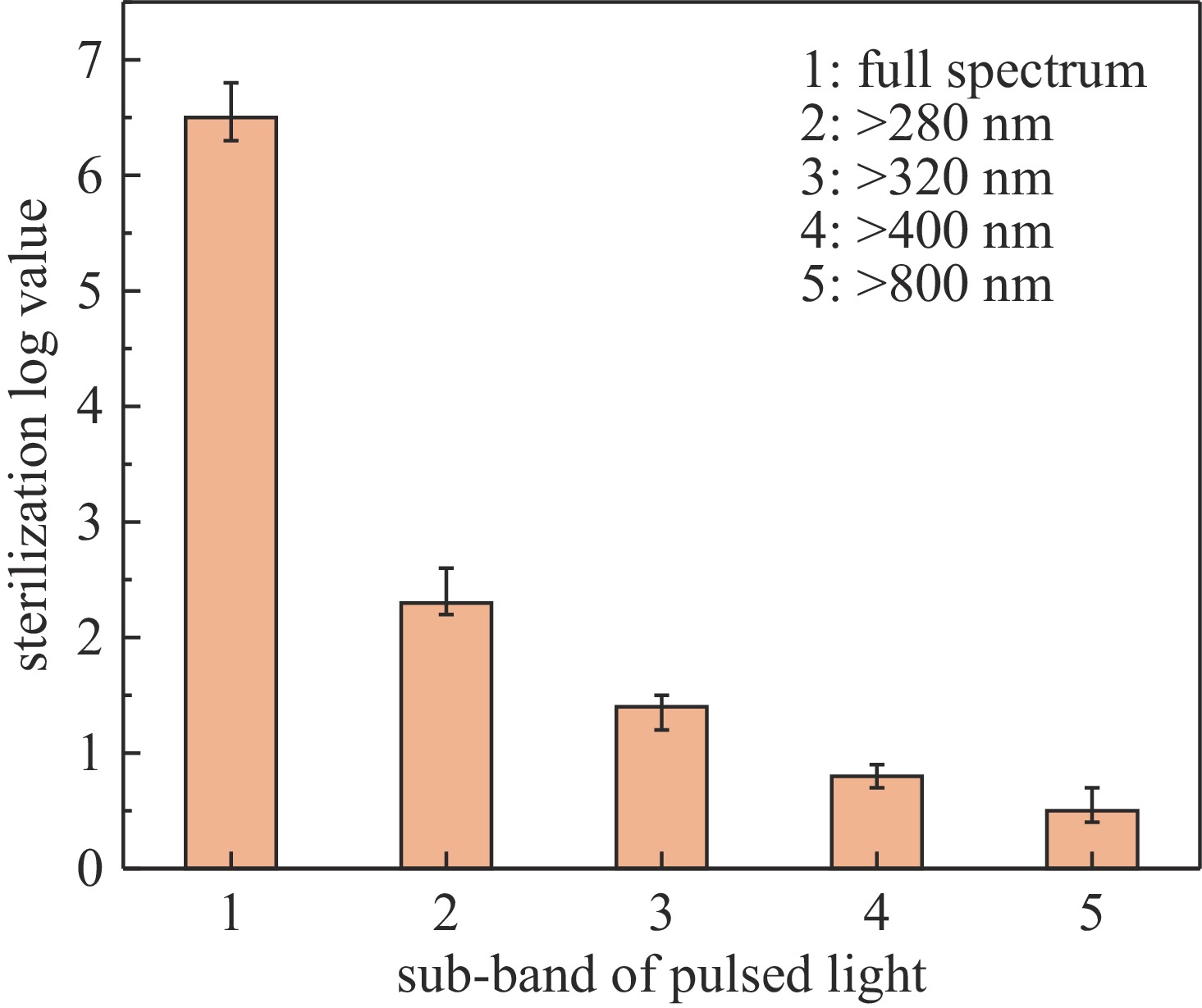
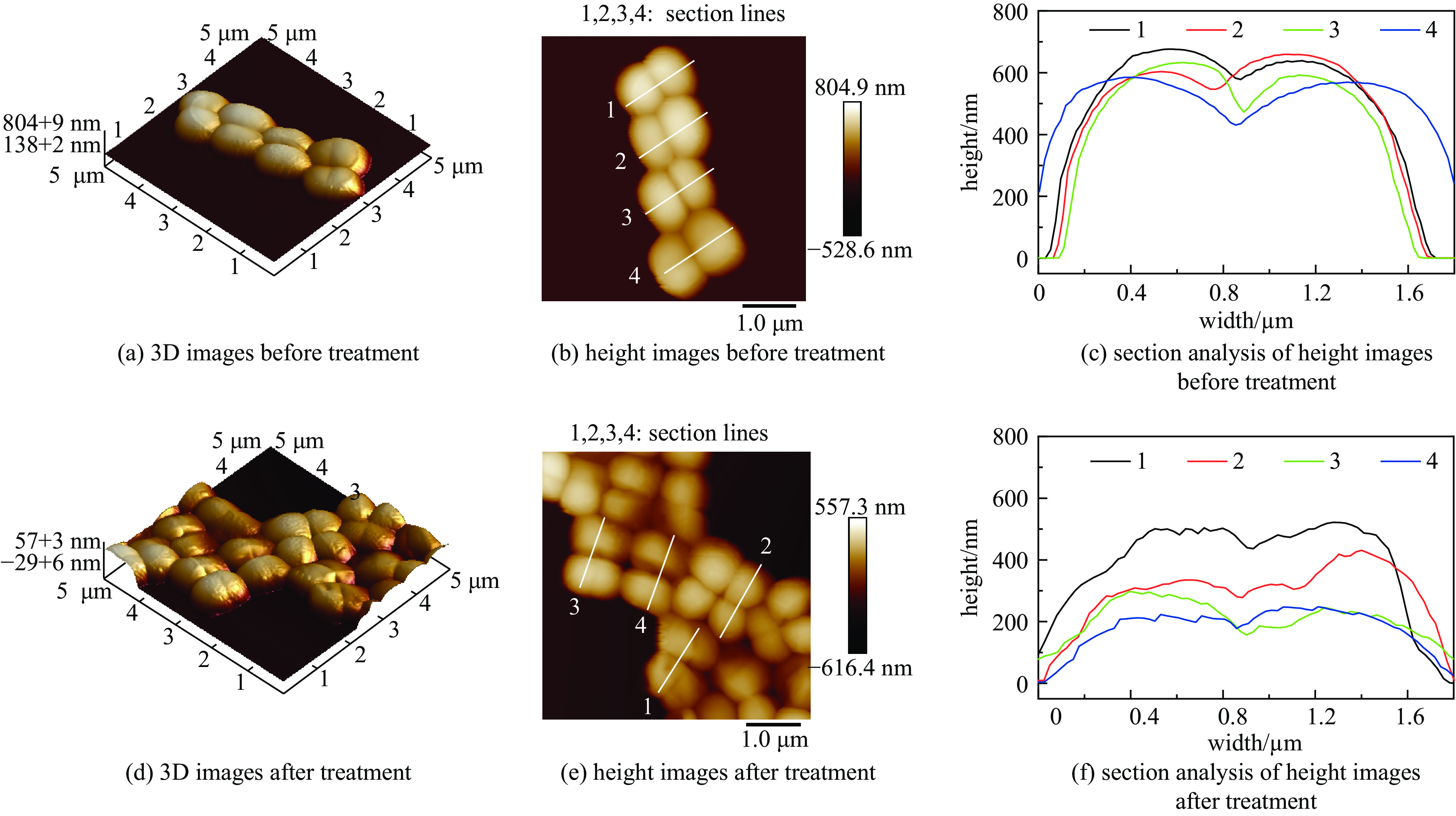
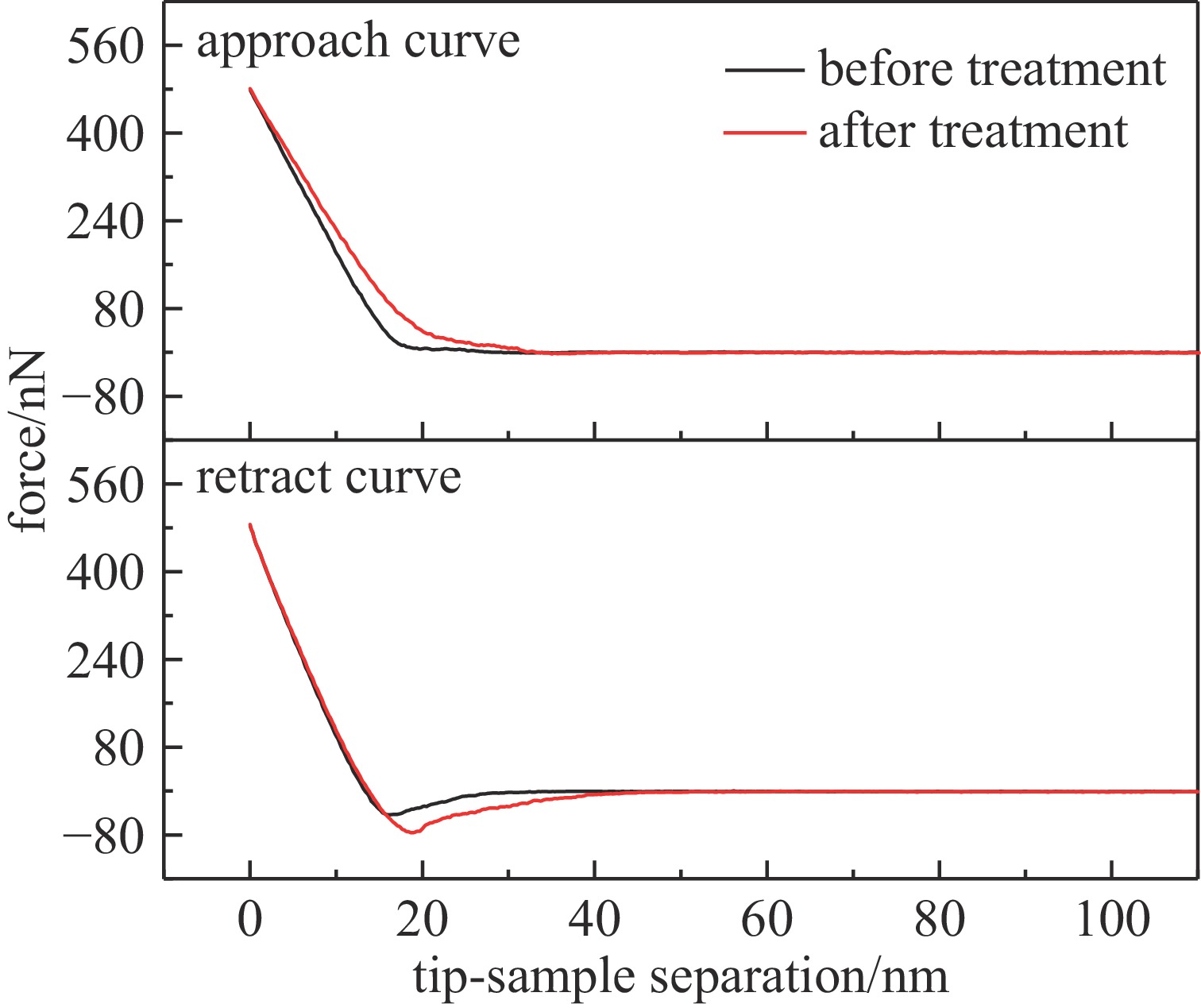
摘要: 为优化脉冲氙灯灭菌装置性能,基于自主研发的微秒脉冲电源系统,研究了不同规格的定制氙灯及其光谱范围对灭菌效果的影响。结果表明:弧长50 mm、气压50 kPa的氙灯的紫外-可见部分光谱中,UV波段占38.5%,UVC波段占17.6%。增大弧长、减小气压均可提高光谱强度,后者还可提高UV比例。弧长100 mm,气压50 kPa的氙灯在放电能量为20 J时,处理3 s可使覆盖范围内的大肠杆菌基本全部失去活性。灭菌效率与灯管弧长、放电能量呈正相关,与灯管气压呈负相关。氙灯辐射光的不同波段均有灭菌作用,UV波段灭菌对数值占87.7%,小于280 nm波段占64.6%。原子力显微镜结果显示,脉冲氙灯可以改变细菌菌体形貌和力学性质,使菌体萎缩,增大表面粗糙度、菌体弹性和粘附力。Abstract: To optimize the performance of the pulsed xenon lamp sterilization device, the influence of spectral range and specifications of lamps on the sterilization effect is studied based on a self-developed high-energy microsecond pulse power supply and xenon lamps with different specifications. The results show that in the UV-visible spectrum of a xenon lamp with an arc length of 50 mm and a pressure of 50 kPa, the UV accounts for 38.5% and the UVC accounts for 17.6%. Increasing the arc length and decreasing the pressure can both increase the spectral intensity, and the latter can also increase the ratio of UV. The xenon lamp with an arc length of 100 mm and a pressure of 50 kPa can basically inactivate all Escherichia coli in 3 seconds with a discharge energy of 20 J. The sterilization rate is positively correlated with arc length and discharge energy of the lamp, negatively correlated with pressure. The all bands of xenon lamp radiation have sterilization effects, with UV accounting for 87.7% and the wavelength band less than 280 nm accounting for 64.6%. The AFM images show that pulsed xenon lamp changed the morphology and mechanical properties of Escherichia coli, hence the bacteria shrank, their surface roughness, elasticity, and adhesion increased.
-
Key words:
- pulsed xenon lamp /
- surface sterilization /
- pulse discharge /
- intense pulsed light /
- Escherichia coli
-
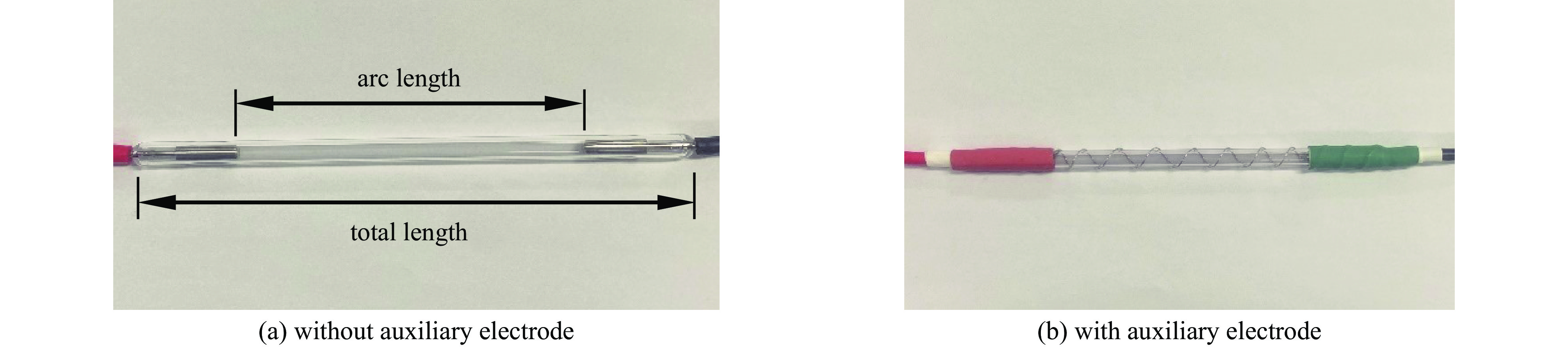
表 1 不同规格脉冲氙灯的尺寸参数
Table 1. Dimensional parameters of different pulsed xenon lamps
total length/mm arc length/mm gas pressure/kPa outer diameter/mm 110 50 25 7.0 110 50 50 7.0 135 75 25 7.0 135 75 50 7.0 160 100 25 7.0 160 100 50 7.0 表 2 处理前后大肠杆菌的粗糙度
Table 2. The roughness of Escherichia coli before and after treatment
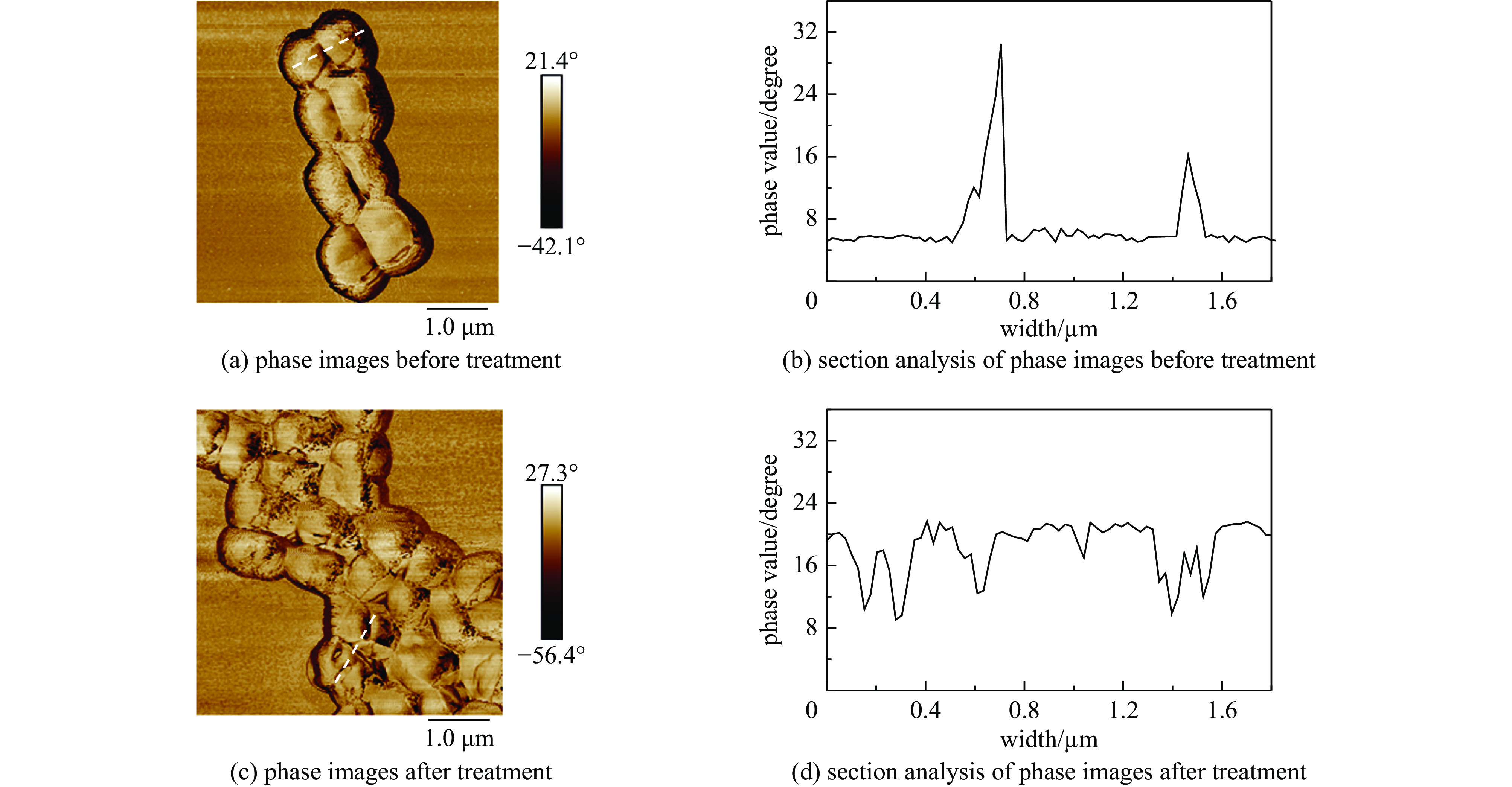
No. before treatment after treatment Ra Rq Ra Rq 1 17.5 21.4 19.8 24.5 2 18.1 22.3 24.8 31.0 3 16.3 20.5 19.9 24.7 4 16.4 20.1 18.5 23.2 5 19.2 25.7 22.5 29.7 6 15.5 18.7 22.0 31.4 7 19.0 23.6 25.4 29.3 8 16.7 20.4 20.1 25.7 9 17.6 22.4 22.3 28.3 10 18.6 22.5 19.6 24.2 average 17.5 21.8 21.5 27.2 standard deviation 1.2 1.9 2.2 2.9 -
[1] 郑超. 低温等离子体和脉冲电场灭菌技术[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013Zheng Chao. Non-thermal plasma and pulsed electric field induced disinfection[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013 [2] Júnior L M, Cristianini M, Anjos C A R. Packaging aspects for processing and quality of foods treated by pulsed light[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 2020, 44: e14902. [3] 廖云辉. 脉冲氙灯空气杀菌效果的实验研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018Liao Yunhui. Experimental study on the air disinfection by pulsed xenon lamp[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2018 [4] Uslu G, Demirci A, Regan J M. Disinfection of synthetic and real municipal wastewater effluent by flow-through pulsed UV-light treatment system[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2016, 10: 89-97. [5] Hwang H J, Park J Y, Chung M S, et al. Microbial inactivation in fresh and minimally processed foods by intense pulsed light (IPL) treatment[J]. Food Science and Biotechnology, 2021, 30(7): 939-948. doi: 10.1007/s10068-021-00937-5 [6] Tao Tingting, Ding Chao, Han Nengneng, et al. Evaluation of pulsed light for inactivation of foodborne pathogens on fresh-cut lettuce: effects on quality attributes during storage[J]. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 2019, 21: 100358. [7] Zhang Baiqing, Sun Bingxin, Ma Fengming, et al. The design and theoretical analysis of major components of pulse light sterilization equipment[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 37: 260-267. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2012.04.237 [8] Garvey M, Rowan N J. Pulsed UV as a potential surface sanitizer in food production processes to ensure consumer safety[J]. Current Opinion in Food Science, 2019, 26: 65-70. [9] Ferrario M, Guerrero S, Alzamora S M. Study of pulsed light-induced damage on Saccharomyces cerevisiae in apple juice by flow cytometry and transmission electron microscopy[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2014, 7(4): 1001-1011. doi: 10.1007/s11947-013-1121-9 [10] Artíguez M L, de Marañón I M. Inactivation of spores and vegetative cells of Bacillus subtilis and Geobacillus stearothermophilus by pulsed light[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2015, 28: 52-58. [11] Huang Yaoxin, Ye Mu, Cao Xinang, et al. Pulsed light inactivation of murine norovirus, Tulane virus, Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella in suspension and on berry surfaces[J]. Food Microbiology, 2017, 61: 1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2016.08.001 [12] Jang H, Nguyen M C, Noh S, et al. UV laser sterilization of Bacillus atrophaeus spores on ceramic tiles[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(1): 1446-1450. [13] Pellicer J A, Navarro P, Gómez-López V M. Pulsed light inactivation of polygalacturonase[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 271: 109-113. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.194 [14] Jabeen A, Rayees B, Masoodi F A. Pulsed light technology: a novel method for food preservation[J]. International Food Research Journal, 2014, 21(3): 839-848. [15] Hilton S T, de Moraes J O, Moraru C I. Effect of sublethal temperatures on pulsed light inactivation of bacteria[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2017, 39: 49-54. [16] Faghihzadeh F, Anaya N M, Hadjeres H, et al. Pulse UV light effect on microbial biomolecules and organic pollutants degradation in aqueous solutions[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 216: 677-683. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.176 [17] Xie Shuge, Shen Diya, Yuan Qing, et al. Effects of electrical pulse width and output irradiance on intense pulse light inactivation[J]. Bioengineering, 2022, 9(12): 730. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9120730 [18] Cassar J R, Mills E W, Demirci A. Characterization of pulsed light for microbial inactivation[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2022, 334: 111152. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2022.111152 [19] 王纯冰, 孔庆财, 徐伟, 等. 脉冲强光对流动水中大肠杆菌的杀灭效果研究[J]. 食品科技, 2011, 36(4):36-40,44Wang Chunbing, Kong Qingcai, Xu Wei, et al. Inactivation of E. coli in water using flow-through pulsed light treatment system[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2011, 36(4): 36-40,44 [20] Paskeviciute E, Buchovec I, Luksiene Z. High-power pulsed light for decontamination of chicken from food pathogens: a study on antimicrobial efficiency and organoleptic properties[J]. Journal of Food Safety, 2011, 31(1): 61-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4565.2010.00267.x [21] 杨浩, 宋涛, 赵慧平, 等. 大肠杆菌在原子力显微镜下的观测及其形貌[J]. 武汉工程大学学报, 2012, 34(12):8-12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2012.12.003Yang Hao, Song Tao, Zhao Huiping, et al. Imaging and morphology of Escherichia coli using atomic force microscopy[J]. Journal of Wuhan Institute of Technology, 2012, 34(12): 8-12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2012.12.003 [22] 马梦佳, 陈玉云, 闫志强, 等. 原子力显微镜在纳米生物材料研究中的应用[J]. 化学进展, 2013, 25(1):135-144 doi: 10.7536/PC120714Ma Mengjia, Chen Yuyun, Yan Zhiqiang, et al. Applications of atomic force microscopy in nanobiomaterials research[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2013, 25(1): 135-144 doi: 10.7536/PC120714 -




 下载:
下载: