Research progress on high-brightness electron source drive laser system
-
摘要: 光阴极电子源是先进加速器装置最为关键的部件,驱动激光的品质参数是电子源性能的首要决定因素。近年来,电子加速器装置的束流指标不断提升,要求驱动激光具备高功率、高稳定性等特点和时空分布调控的功能,这对驱动激光系统的放大、选频、倍频、时空整形等模块提出了更高的需求。国内外主要研究机构根据其电子源的需求采用了相应的技术路线,在重复频率、激光波长、单脉冲能量和时空分布整形等方面各有特点。本文介绍了高亮度电子源驱动激光的主要技术路线和国内外发展现状,分析了典型的驱动激光方案,并讨论了驱动激光系统的未来发展趋势,以期为相关装置的规划和建设提供参考。Abstract: Photocathode electron sources play a crucial role in advanced accelerator facilities. Recent advancements in electron accelerator facilities have continually pushed the parameter boundaries of electron sources, which in turn necessitate photocathode drive lasers that possess high power, high stability, and the ability to control spatiotemporal distributions. For such a purpose, lots of efforts have been made to achieve high-quality amplification, harmonic generation, and spatiotemporal shaping of the drive laser systems. This paper presents a comprehensive review of the primary technological approaches and status of drive lasers for high-brightness electron sources worldwide. Analysis of representative drive laser schemes and discussion on the future trends are also included, aiming to provide a helpful reference for planning and developing high-performance photocathode drive laser system.
-
Key words:
- photocathode laser /
- laser amplification /
- laser harmonic generation /
- laser shaping /
- laser stability
-
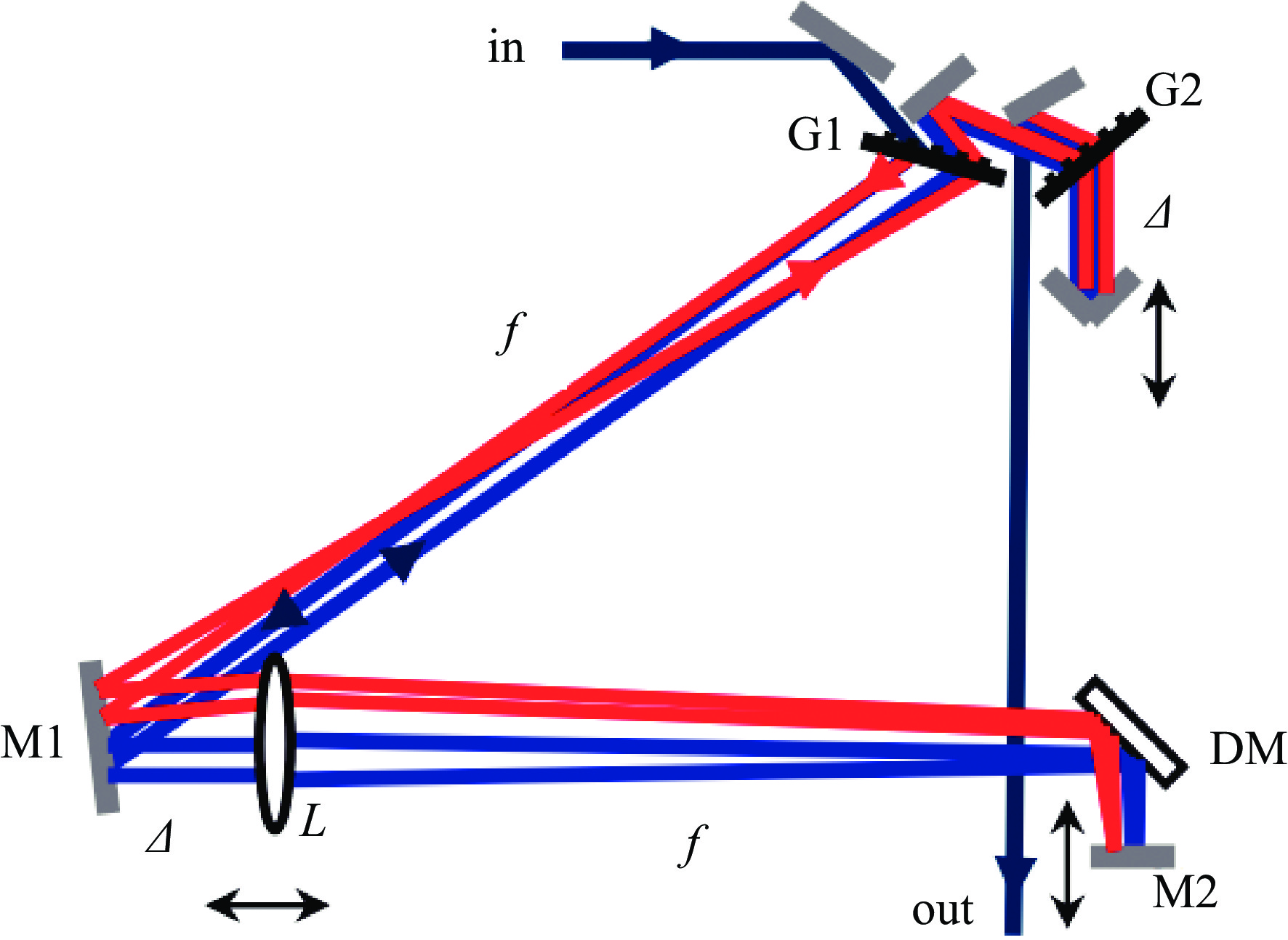
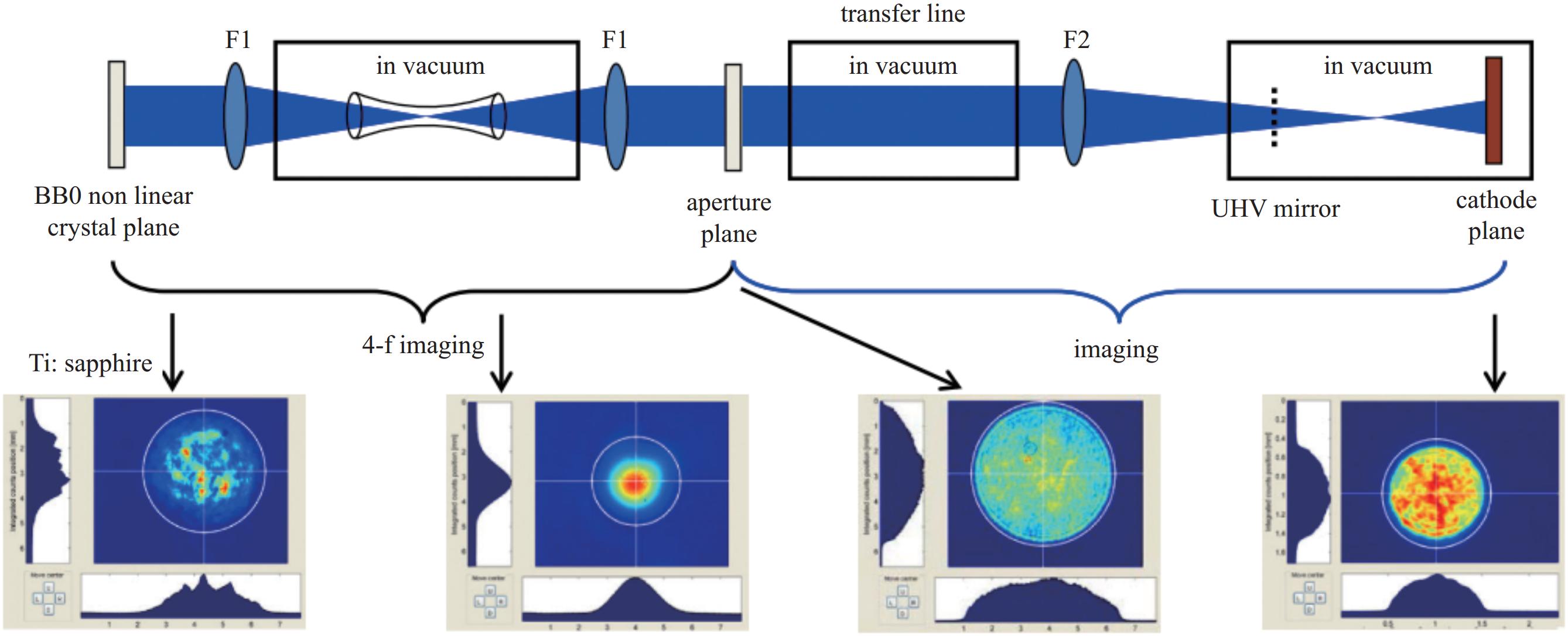
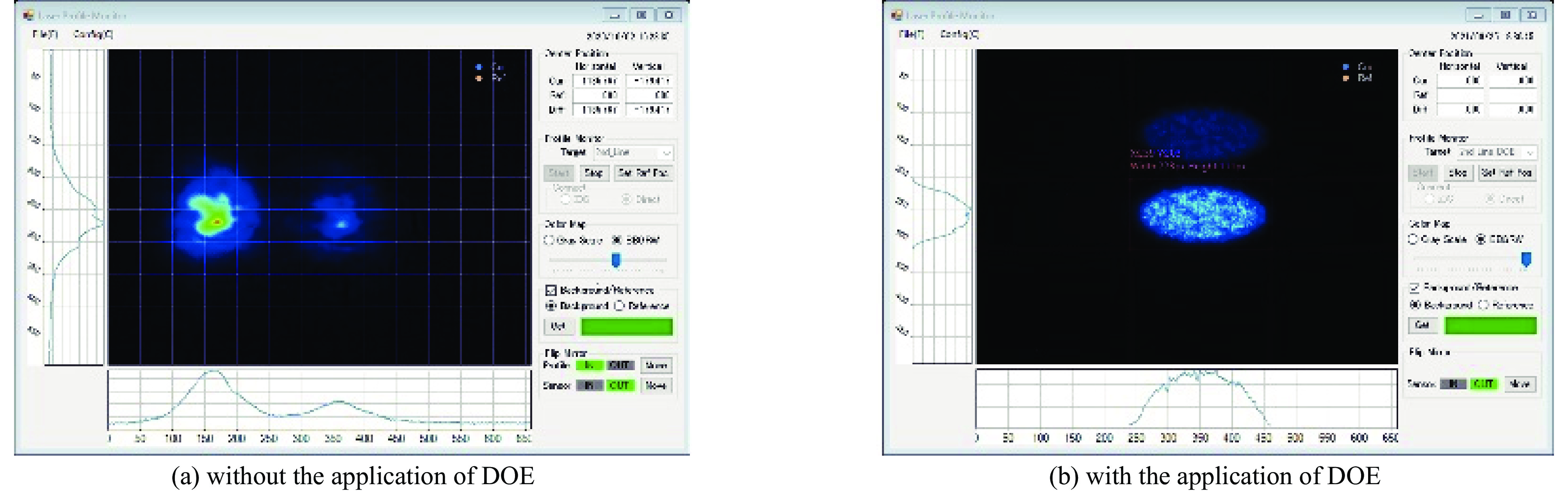
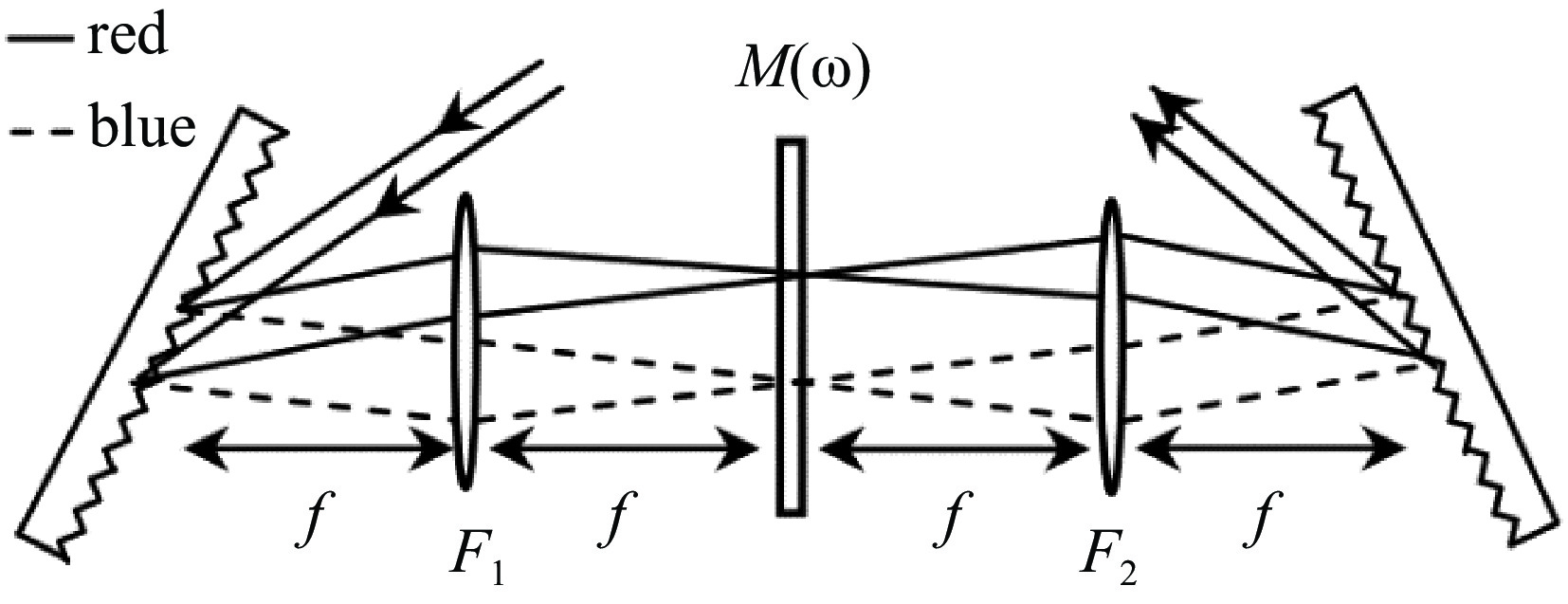
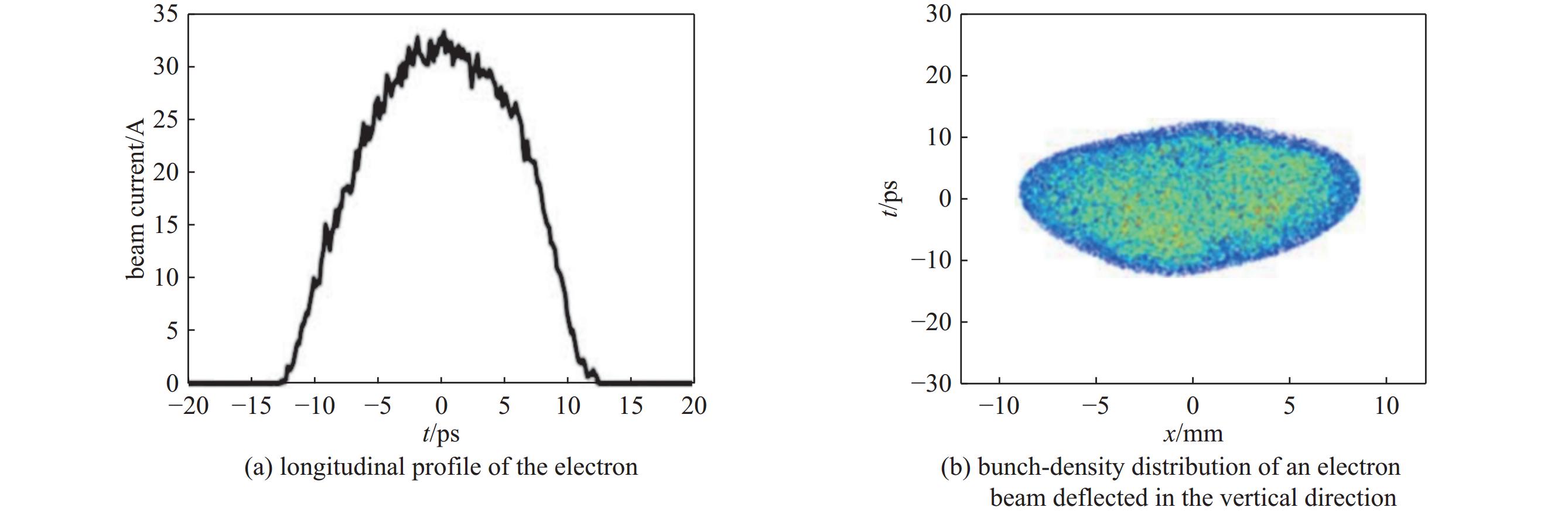
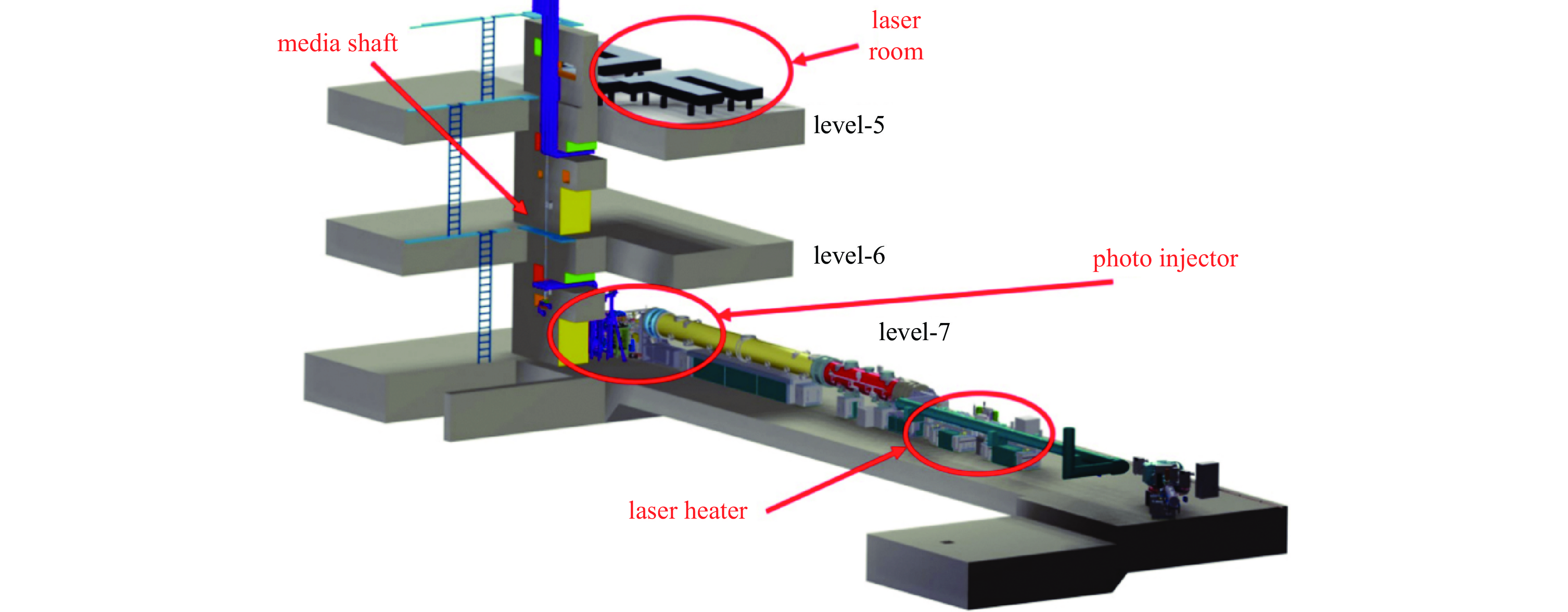
图 19 EuXFEL注入器布局图[16]
Figure 19. Injector building layout at EuXFEL[16]
表 1 典型装置Ⅰ类放大器输出参数
Table 1. Output parameters of class Ⅰ amplifiers in typical facilities
facility amplifier center wavelength/nm pulse energy/mJ repetition rate/Hz SXFEL Ti:sapphire 800.0 10.0 10/50 HALF Ti:sapphire 800.0 13.0 1~100 TTX Ti:sapphire 800.0 200.0 10 SAPS Ti:sapphire 800.0 13.0 1~100 PAL-XFEL Ti:sapphire 770.0 20.8 120 FERMI Ti:sapphire 783.0 18.0 50 SwissFEL Yb:CaF2 1 041.3 2.4 10 SuperKEKB Yb-doped fiber/Nd:YAG hybrid 1 064.0 20.0 1~25 表 2 典型装置Ⅱ类放大器输出参数
Table 2. Output parameters of class Ⅱ amplifiers in typical facilities
facility amplifier center wavelength/nm pulse energy/μJ repetition rate/MHz FLASH Yb-doped fiber/Yb:YAG hybrid 1030 180 1 EuXFEL Nd:YVO4 1064 50 0.5/1.13/2.25/4.5 LCLS-II Yb-doped fiber 1030 50 0~0.929 DC-SRF-II Yb-doped fiber 1030 20 1 S3FEL Yb-doped fiber 1030 50 1 SHINE Yb-doped fiber 1030 150 1 表 3 典型装置Ⅲ类放大器输出参数
Table 3. Output parameters of class Ⅲ amplifiers in typical facilities
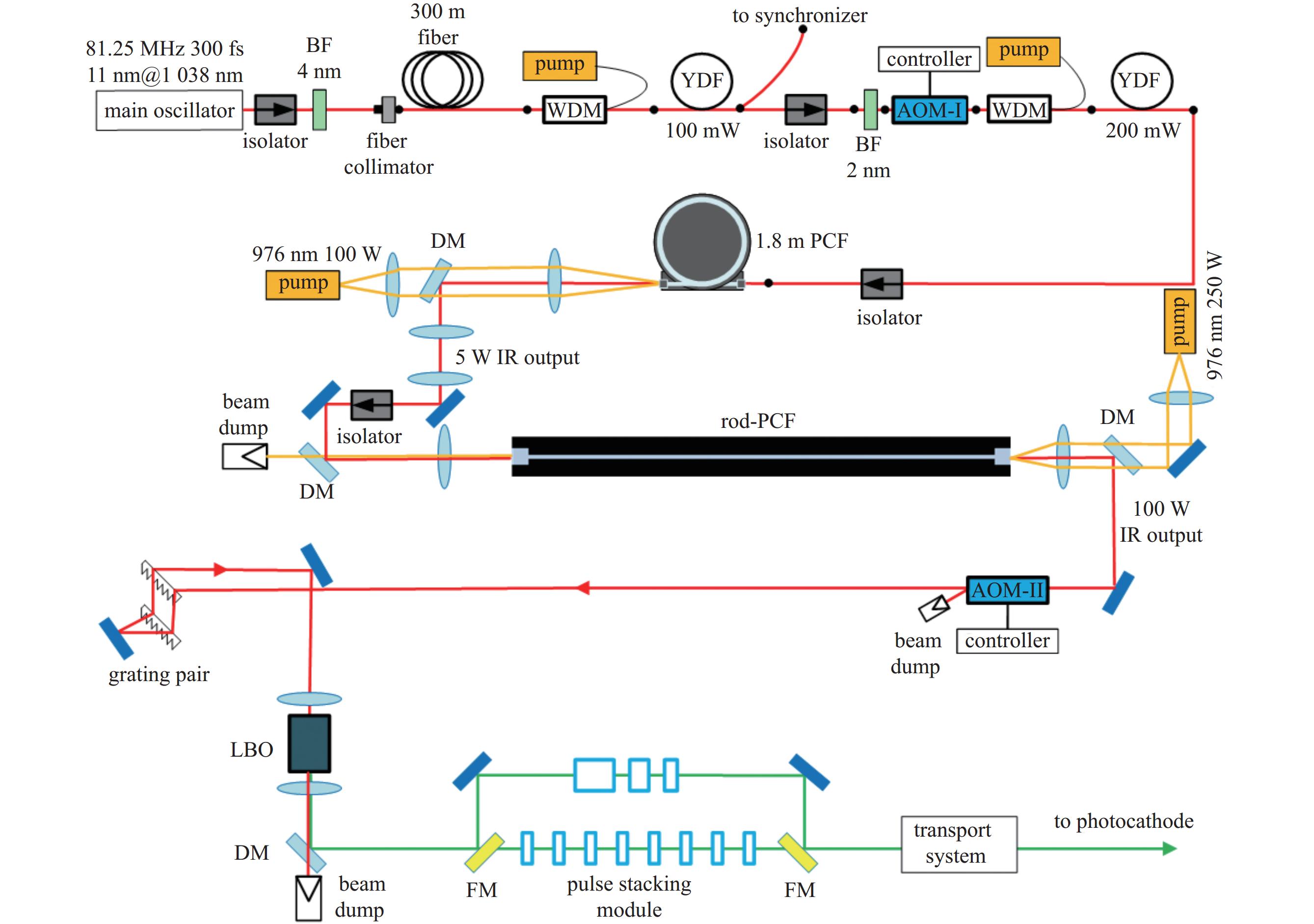
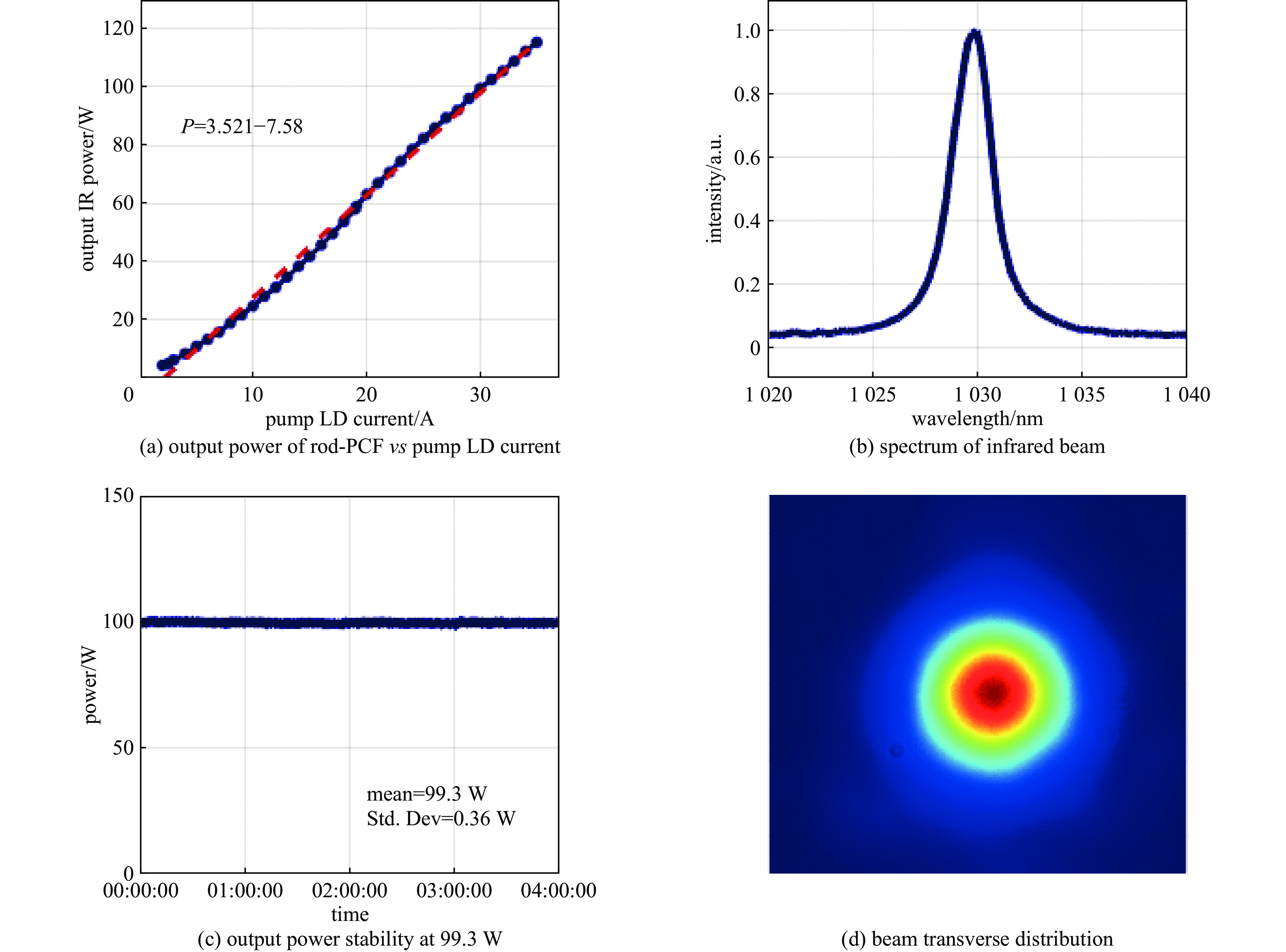
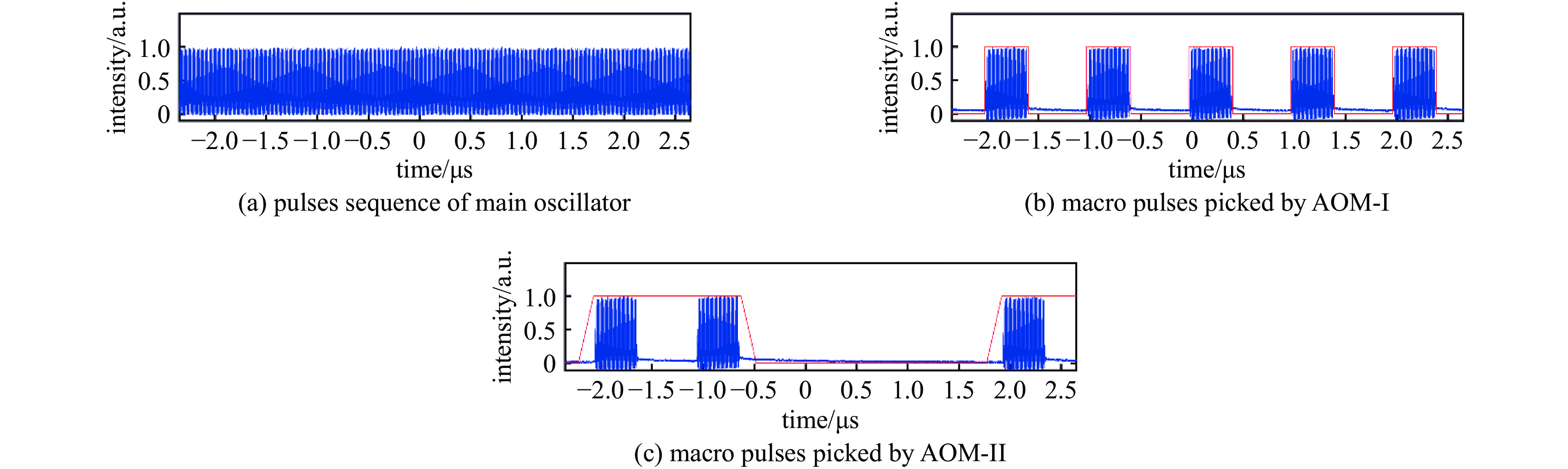
facility amplifier center wavelength/nm average power/W repetition rate/MHz Cornell-ERL Yb-doped fiber 1040 167.0 1300 PAPS Yb-doped fiber 1030 116.3 81.25/100/ 1300 KEK-ERL Yb-doped fiber (solid-state oscillator) 1064 50.0 1300 DC-SRF-II Yb-doped fiber 1030 99.3 81.25 表 4 典型装置倍频模块输出参数
Table 4. Output parameters of harmonic generation module in typical facilities
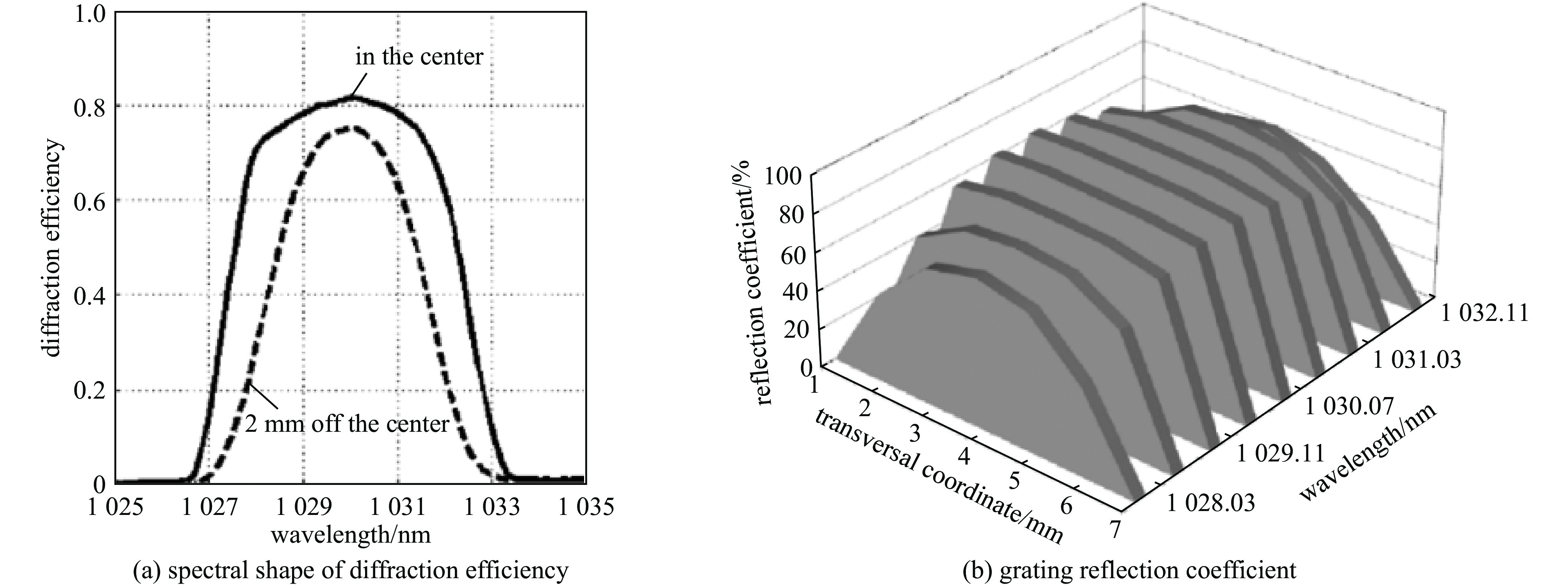
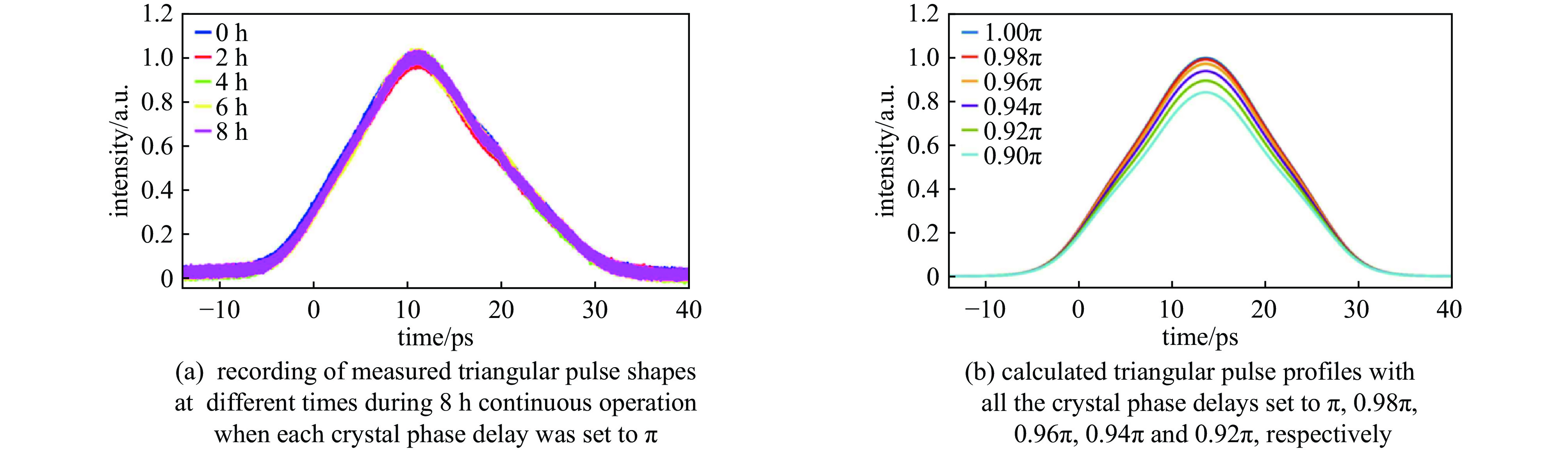
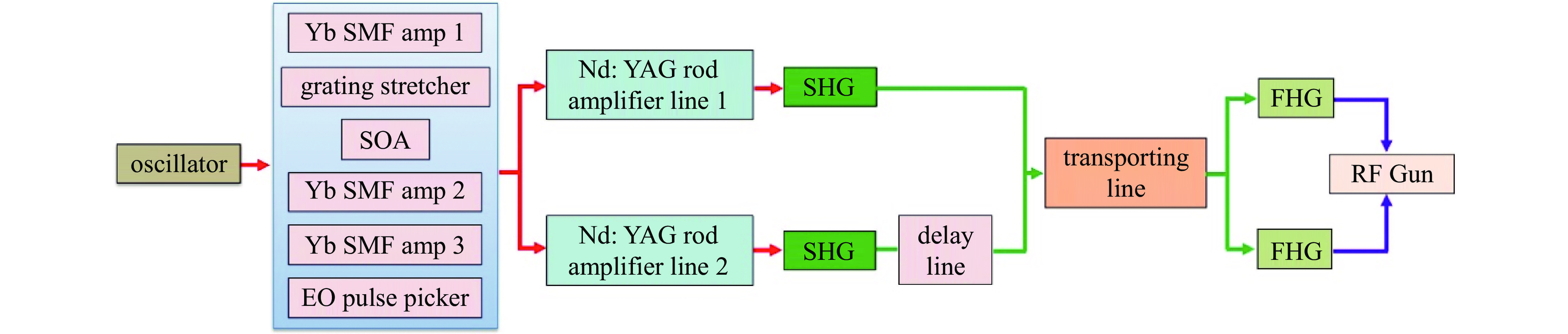
facility frequency conversion method crystal center wavelength/nm pulse energy repetition rate FLASH FHG LBO+BBO 257.5 6.1 μJ/11.2 μJ 1 MHz LCLS-II FHG BBO 257.5 300 nJ 0~0.929 MHz S3FEL FHG BBO 257.5 2 μJ 1 MHz SHINE FHG LBO+BBO 257.5 2 μJ 1 MHz SwissFEL FHG BBO 260 600 μJ 10 Hz EuXFEL FHG LBO+BBO 266 5 μJ 4.5 MHz SuperKEKB FHG BBO 266 1 mJ 25 Hz TTX THG BBO 266.7 1 mJ 10 Hz SXFEL THG BBO 266.7 1.2 mJ 10 Hz/50 Hz HALF THG BBO 266.7 2 mJ 1~100 Hz SAPS THG BBO 266.7 2 mJ 1~100 Hz FERMI THG BBO 261 2.3 mJ 50 Hz DC-SRF-II SHG LBO 515 2 μJ/170 nJ 1 MHz/81.25 MHz Cornell-ERL SHG LBO 520 95 nJ 1.3 GHz KEK-ERL SHG LBO 532 0.77 nJ 1.3 GHz PAPS SHG LBO 515 492 nJ 81.25 MHz -
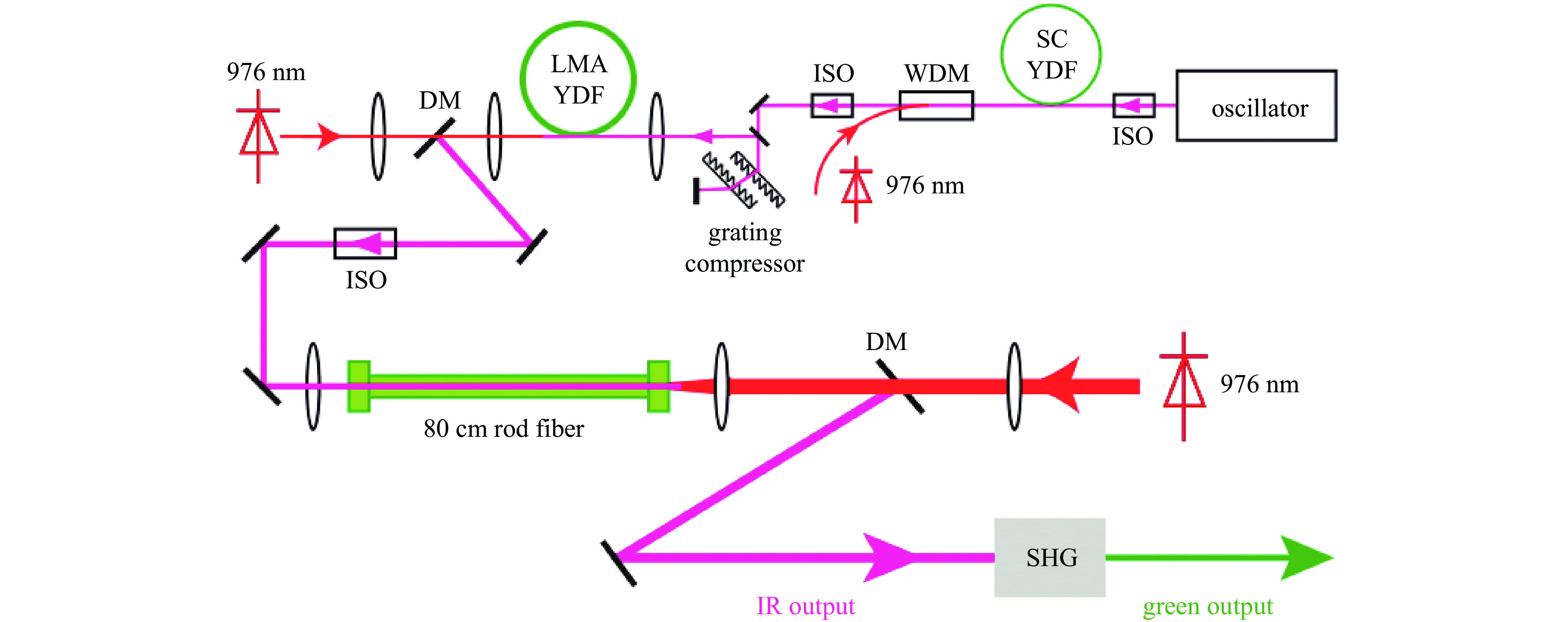
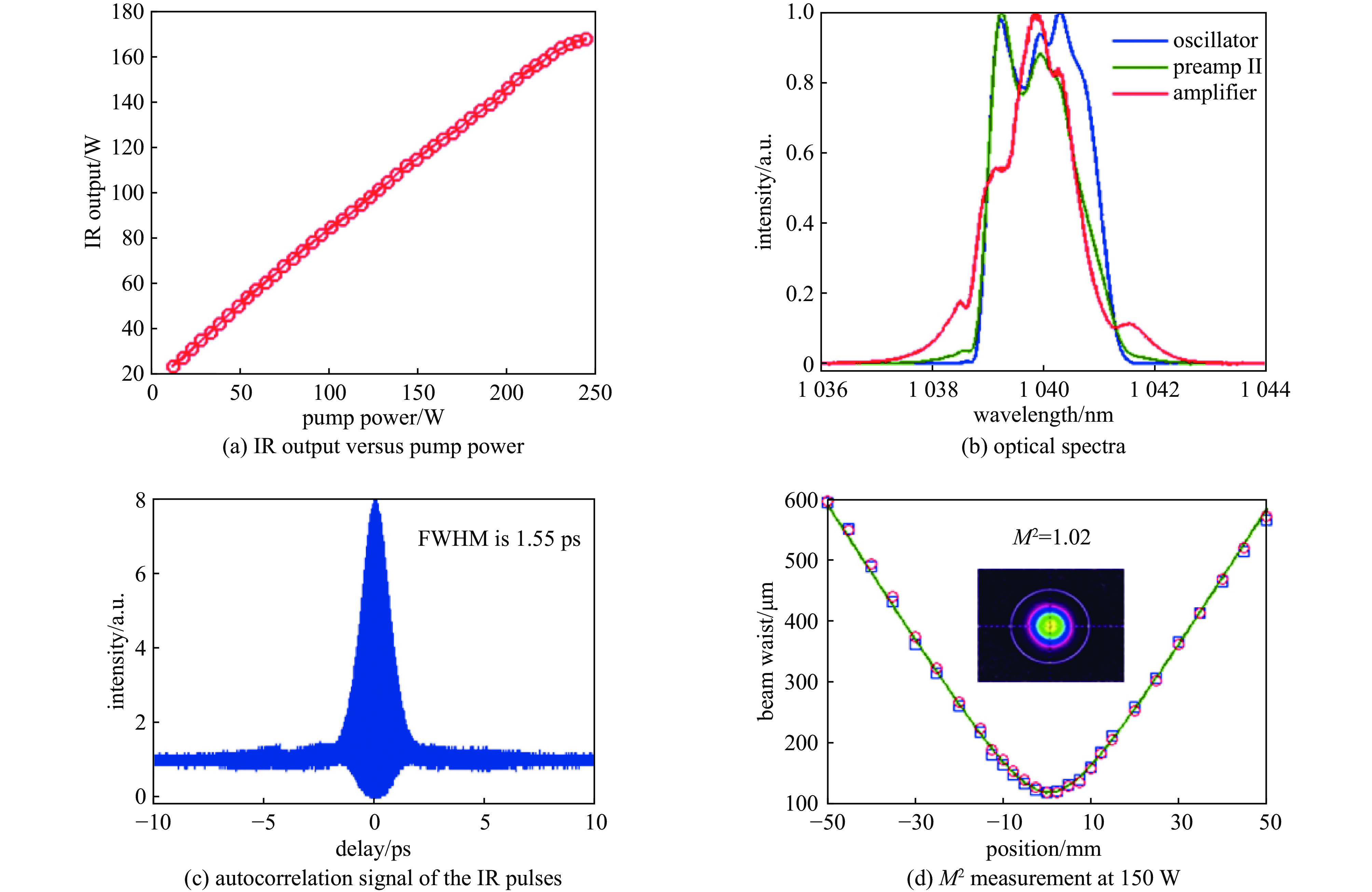
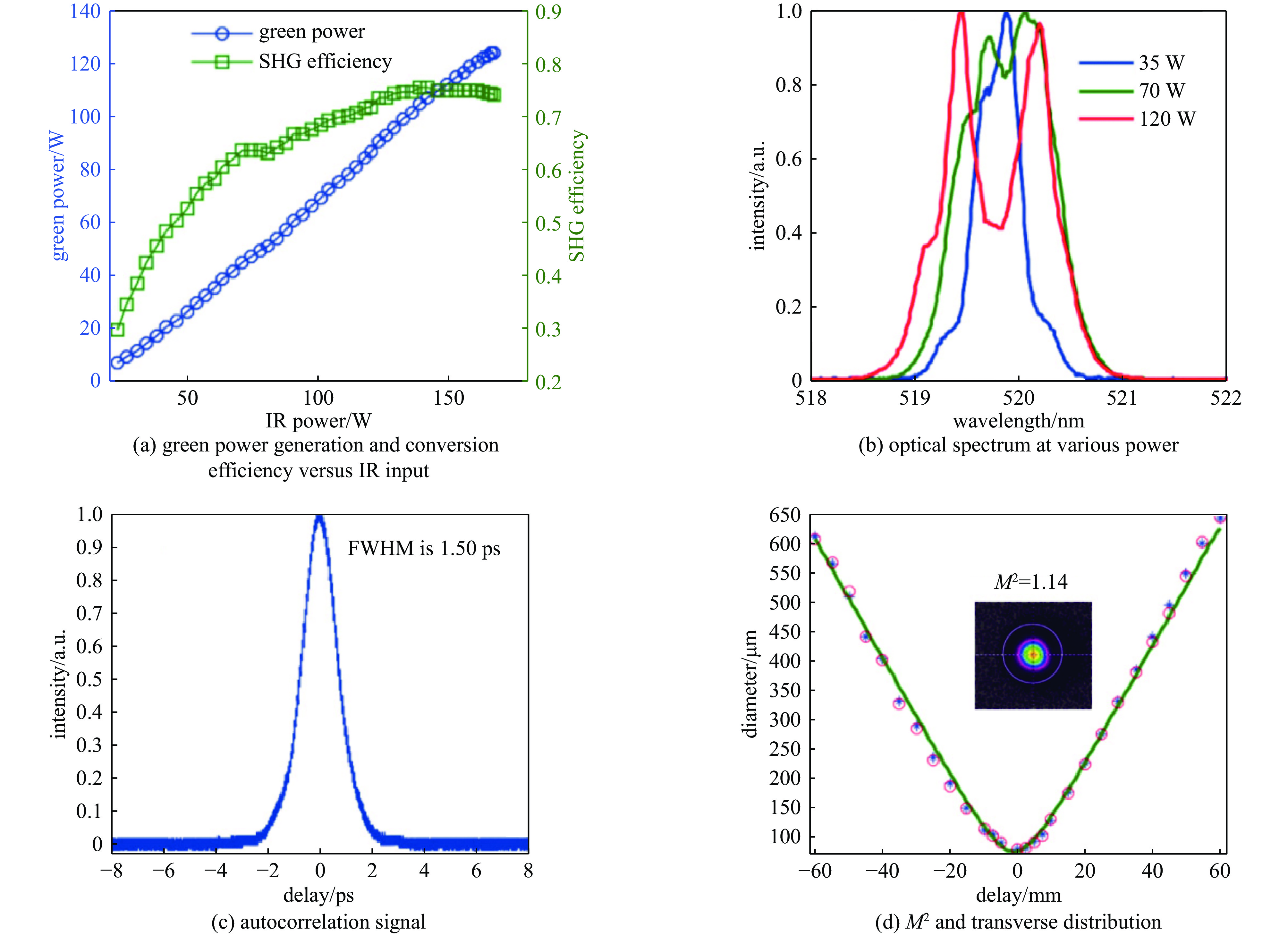
[1] 黄森林, 刘克新, 赵夔, 等. 直流-射频超导光阴极电子枪[J]. 科学通报, 2023, 68(9):1036-1046 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-1091Huang Senlin, Liu Kexin, Zhao Kui, et al. DC-SRF photocathode gun[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(9): 1036-1046 doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-1091 [2] 刘志, 万唯实, 王东. 中国光子大科学装置的发展[J]. 自然杂志, 2024, 46(3):161-172 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2024.03.001Liu Zhi, Wan Weishi, Wang Dong. Development of large-scale user facilities for photon science in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2024, 46(3): 161-172 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2024.03.001 [3] Ackermann W, Asova G, Ayvazyan V, et al. Operation of a free-electron laser from the extreme ultraviolet to the water window[J]. Nature Photonics, 2007, 1(6): 336-342. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.76 [4] Decking W, Abeghyan S, Abramian P, et al. A MHz-repetition-rate hard X-ray free-electron laser driven by a superconducting linear accelerator[J]. Nature Photonics, 2020, 14(6): 391-397. doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-0607-z [5] Cinquegrana P, Demidovich A, Kurdi G, et al. The seed laser system of the FERMI free-electron laser: design, performance and near future upgrades[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2021, 9: e61. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2021.49 [6] Lee J, Ko I S, Han J H, et al. Parameter optimization of PAL-XFEL injector[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2018, 72(10): 1158-1165. doi: 10.3938/jkps.72.1158 [7] Milne C J, Schietinger T, Aiba M, et al. SwissFEL: the Swiss X-ray Free Electron Laser[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7: 720. doi: 10.3390/app7070720 [8] Hutton A. Energy-recovery linacs for energy-efficient particle acceleration[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2023, 5(12): 708-716. doi: 10.1038/s42254-023-00644-6 [9] Zhao Z T, Wang Z, Feng C, et al. Energy recovery linac based fully coherent light source[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 23875. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03354-0 [10] Akemoto M, Arakawa D, Asaoka S, et al. Construction and commissioning of the compact energy-recovery linac at KEK[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2018, 877: 197-219. [11] Filippetto D, Musumeci P, Li Renkai, et al. Ultrafast electron diffraction: Visualizing dynamic states of matter[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2022, 94: 045004. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.94.045004 [12] Xie Huamu. Overview of the semiconductor photocathode research in China[J]. Micromachines, 2021, 12: 1376. doi: 10.3390/mi12111376 [13] Zhou Feng, Adolphsen C, Dowell D, et al. Overview of CW electron guns and LCLS-II RF gun performance[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2023, 11: 1150809. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2023.1150809 [14] Feng Lie, Li Chunlei, Liu Bo, et al. Drive laser system for shanghai soft X-ray Free Electron Laser[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2021: 4403-4405. [15] Zhang Rui, Kumano H K, Toyotomi N, et al. Laser system for SuperKEKB RF gun in phase III commissioning[C]//Proceedings of the 13th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2022: 2914-2916. [16] Winkelmann L, Choudhuri A, Grosse-Wortmann U, et al. The European XFEL photocathode laser[C]//Proceedings of the 39th International Free Electron Laser Conference. 2019: 423-426. [17] Zhang Baichao, Li Xiaoshen, Liu Qi, et al. High repetition-rate photoinjector laser system for S3FEL[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2023, 11: 1181862. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2023.1181862 [18] Zhao Zhi, Dunham B M, Bazarov I, et al. Generation of 110 W infrared power and 65W green power from a 1.3-GHz sub-picosecond fiber amplifier[C]//Proceedings of 2012 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics. 2012: 1-2. [19] Zhao Zhi, Dunham B M, Wise F W. Generation of 167 W infrared and 124 W green power from a 1.3-GHz, 1-ps rod fiber amplifier[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(21): 25065-25070. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.025065 [20] Zhao Z, Sheehy B, Minty M. Generation of 180 W average green power from a frequency-doubled picosecond rod fiber amplifier[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(7): 8138-8143. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.008138 [21] 李孝燊, 徐金强, 孙大睿. 高能所光阴极驱动激光系统研制[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30:021001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.170344Li Xiaoshen, Xu Jinqiang, Sun Darui. Drive laser system for a photocathode at IHEP[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 30: 021001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.170344 [22] Li Xiaoping, Wang Jiuqing, Xu Jinqiang, et al. Constructions and preliminary HV conditioning of a photocathode direct-current electron gun at IHEP[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2017, 34: 072901. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/34/7/072901 [23] Xu Hang, Xu Jinqiang, Li Xiaoping, et al. High power drive laser system for photocathode at IHEP[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(18): 29550-29556. doi: 10.1364/OE.438199 [24] 吴桐, 徐航, 徐金强, 等. 强流目标的DC-SRF-II光阴极驱动激光系统设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:104018 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220244Wu Tong, Xu Hang, Xu Jinqiang, et al. Design of the photocathode drive laser system for high current electron beam operation of DC-SRF-II gun[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 104018 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220244 [25] Jia H, Li T, Wang T, et al. High performance operation of a direct-current and superconducting radio-frequency combined photocathode gun[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2406.00659, 2024. [26] Wang Tianyi, Xu Hang, Liu Zhongqi, et al. Advanced drive laser system for a high-brightness continuous-wave photocathode electron gun[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(6): 9699-9709. doi: 10.1364/OE.515063 [27] Li Chunlei, Dai Xiaolei, Deng Haixiao, et al. Photoinjector drive laser temporal shaping for Shanghai Soft X-ray Free Electron Laser[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2021: 1674-1677. [28] Li Chen, Akcaalan O, Frede M, et al. Photocathode laser development for superconducting X-ray ree electron lasers at DESY[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2021: 3599-3601. [29] Gilevich S, Alverson S, Carbajo S, et al. The LCLS-II photo-injector drive laser system[C]//Proceedings of 2020 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics. 2020: 1-2. [30] Schietinger T, Pedrozzi M, Aiba M, et al. Commissioning experience and beam physics measurements at the SwissFEL Injector Test Facility[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2016, 19: 100702. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.19.100702 [31] 李成, 汪文星, 李伟伟, 等. 光阴极微波电子枪驱动激光整形与传输系统[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:094002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210091Li Cheng, Wang Wenxing, Li Weiwei, et al. Drive laser shaping and transport system for photocathode RF gun[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 094002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210091 [32] Yan Lixin, Hua Jianfei, Du Yingchao, et al. UV pulse trains by α-BBO crystal stacking for the production of THz-rap-rate electron bunches[J]. Journal of Plasma Physics, 2012, 78(S4): 429-431. [33] Liu Fangming, Huang Senlin, Si Shangyu, et al. Generation of picosecond pulses with variable temporal profiles and linear polarization by coherent pulse stacking in a birefringent crystal shaper[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(2): 1467-1478. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.001467 [34] Mohr C, Winkelmann L, Chu H, et al. Flexible pulse-train amplitude shaping for the European XFEL photoinjector laser[C]//Proceedings of the 8th EPS-QEoD Europhoton Conference. 2018. [35] Zhao Zhi, Dunham B M, Wise F W. Generation of 150 W average and 1 MW peak power picosecond pulses from a rod-type fiber master oscillator power amplifier[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2014, 31(1): 33-37. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.31.000033 [36] Zhang R, Zhou X, Yoshida M, et al. Study on stable and high output energy laser system for RF-gun at SuperKEKB injector[C]//Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan. 2017: 1201-1204. [37] 姜世民, 陆志军, 刘星光, 等. C波段光阴极电子枪驱动激光整形研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:104003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240162Jiang Shimin, Lu Zhijun, Liu Xingguang, et al. Study of drive laser shaping system for C-band photocathode RF gun[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 104003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240162 [38] Zhang Haiming, Wang Jian, Liu Zhengzheng, et al. Design of HUST-UED femtosecond laser delivery system[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 12959, AOPC 2023: Laser Technology and Applications; and Optoelectronic Devices and Integration. 2023: 129590A. [39] Yan L X, Du Yingchao, Du Qiang, et al. TW Laser system for Thomson scattering X-ray light source at Tsinghua University[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2009, 33: 154. [40] Hong J, Han J H, Park S J, et al. A study on low emittance injector and undulator for PAL-XFEL[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2015, 3: e21. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2015.18 [41] Penco G, Allaria E, Badano L, et al. Optimization of a high brightness photoinjector for a seeded FEL facility[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2013, 8: P05015. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/8/05/P05015 [42] Zhou Xiangyu, Natsui T, Yoshida M, et al. Ytterbium fiber and disk laser of RF gun for SuperKEKB[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2014: 2415-2417. [43] Zhang Rui, Zhou Xiangyu, Honda Y, et al. Hybrid Yb/Nd laser system for RF gun in SuperKEKB phase II and phase III commissioning[C]//Proceedings of the10th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2019: 3663-3666. [44] Zhang Rui, Zhou Xiangyu, Kumano H, et al. Yb/Nd hybrid laser system for RF gun in SUPERKEKB phase II[C]//Proceedings of the 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan. 2018. [45] Zhang Rui, Yoshida M, Natsui T, et al. Improvements of the laser system for RF-gun at SuperKEKB injector[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2015: 1598-1600. [46] Jauregui C, Limpert J, Tünnermann A. High-power fibre lasers[J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(11): 861-867. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.273 [47] Richardson D J, Nilsson J, Clarkson W A. High power fiber lasers: current status and future perspectives [Invited][J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2010, 27(11): B63-B92. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.27.000B63 [48] Chen Shengping, Chen Hongwei, Hou Jing, et al. 100 W all fiber picosecond MOPA laser[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(26): 24008-24012. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.024008 [49] Dupriez P, Finot C, Malinowski A, et al. High-power, high repetition rate picosecond and femtosecond sources based on Yb-doped fiber amplification of VECSELs[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(21): 9611-9616. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.009611 [50] Limpert J, Deguil-Robin N, Manek-Hönninger I, et al. High-power picosecond fiber amplifier based on nonlinear spectral compression[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30(7): 714-716. doi: 10.1364/OL.30.000714 [51] Honda Y. Development of a photo-injector laser system for KEK ERL test accelerator[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2012: 1530-1532. [52] Cui Zijian, Sun Mingying, Liu De’an, et al. High-peak-power picosecond deep-UV laser sources[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(24): 43354-43370. doi: 10.1364/OE.474513 [53] Turcicova H, Novak O, Muzik J, et al. Laser induced damage threshold (LIDT) of β-barium borate (BBO) and cesium lithium borate (CLBO)-overview[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2022, 149: 107876. [54] Mironov S Y, Andrianov A V, Gacheva E I, et al. Spatio-temporal shaping of photocathode laser pulses for linear electron accelerators[J]. Physics-Uspekhi, 2017, 60(10): 1039-1050. doi: 10.3367/UFNe.2017.03.038143 [55] Chung M, Qin H, Davidson R C. Generalized Kapchinskij-Vladimirskij 的的 distribution and envelope equation for high-intensity beams in a coupled transverse focusing lattice[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103: 224802.Chung M, Qin H, Davidson R C. Generalized Kapchinskij-Vladimirskij 的的 distribution and envelope equation for high-intensity beams in a coupled transverse focusing lattice[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103: 224802 [56] Kuzmin I, Mironov S, Gacheva E, et al. Shaping triangular picosecond laser pulses for electron photoinjectors[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2019, 16: 015001. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/aaef95 [57] Danailov M B, Demidovich A, Ivanov R, et al. Laser systems for next generation light sources[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd Particle Accelerator Conference. 2009: 122-126. [58] Danailov M B, Demidovich A, Ivanov R, et al. Performance of the Fermi FEL photoinjector laser[C]//Proceedings of the 29th International Free Electron Laser Conference. 2008: 358-361. [59] Tournois P. Acousto-optic programmable dispersive filter for adaptive compensation of group delay time dispersion in laser systems[J]. Optics Communications, 1997, 140(4/6): 245-249. [60] Froehly C, Colombeau B, Vampouille M. II shaping and analysis of picosecond light pulses[J]. Progress in Optics, 1983, 20: 63-153. [61] 刘芳铭. 光阴极驱动激光时空任意整形研究[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2020Liu Fangming. Research on spatiotemporal arbitrary shaping of photocathode driven laser[D]. Beijing: Peking University, 2020 [62] Luiten O J, van der Geer S B, de Loos M J, et al. How to realize uniform three-dimensional ellipsoidal electron bunches[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93: 094802. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.094802 [63] Sharma A K, Tsang T, Rao T. Theoretical and experimental study of passive spatiotemporal shaping of picosecond laser pulses[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2009, 12: 033501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.12.033501 [64] 冯立文, 王天一, 贾豪彦, 等. 北京大学DC-SRF-II注入器光阴极驱动激光系统[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:104016 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210343Feng Liwen, Wang Tianyi, Jia Haoyan, et al. Peking University’s DC-SRF-II photoinjector drive laser system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 104016 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210343 [65] Mironov S Y, Potemkin A K, Gacheva E I, et al. Shaping of cylindrical and 3D ellipsoidal beams for electron photoinjector laser drivers[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(7): 1630-1635. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.001630 [66] Rublack T, Good J, Khojoyan M, et al. First results attained with the quasi 3-D ellipsoidal photo cathode laser pulse system at the high brightness photo injector PITZ[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC2015). 2015: 1522-1525. [67] Mironov S Y, Poteomkin A K, Gacheva E I, et al. Generation of 3D ellipsoidal laser beams by means of a profiled volume chirped Bragg grating[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2016, 13: 055003. doi: 10.1088/1612-2011/13/5/055003 [68] Prat E, Abela R, Aiba M, et al. A compact and cost-effective hard X-ray free-electron laser driven by a high-brightness and low-energy electron beam[J]. Nature Photonics, 2020, 14(12): 748-754. doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-00712-8 [69] Kaiser F, Köhler S, Peters F, et al. UV laser beam stabilization system for the European XFEL electron injector laser beamline[C]//Proceedings of 2015 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO). 2015: 1-2. [70] Zhang R, Yoshida M, Zhou X, et al. Improvement of stable and high output energy laser system for RF-gun at SUPERKEKB injector. Chiba, Japan, 2016. [71] Alkeskjold T T, Laurila M, Scolari L, et al. Single-mode ytterbium-doped large-mode-area photonic bandgap rod fiber amplifier[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(8): 7398-7409. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.007398 [72] Jansen F, Stutzki F, Otto H J, et al. Thermally induced waveguide changes in active fibers[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(4): 3997-4008. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.003997 [73] Laurila M, Jørgensen M M, Hansen K R, et al. Distributed mode filtering rod fiber amplifier delivering 292W with improved mode stability[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(5): 5742-5753. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.005742 [74] Laurila M, Saby J, Alkeskjold T T, et al. Q-switching and efficient harmonic generation from a single-mode LMA photonic bandgap rod fiber laser[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(11): 10824-10833. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.010824 -




 下载:
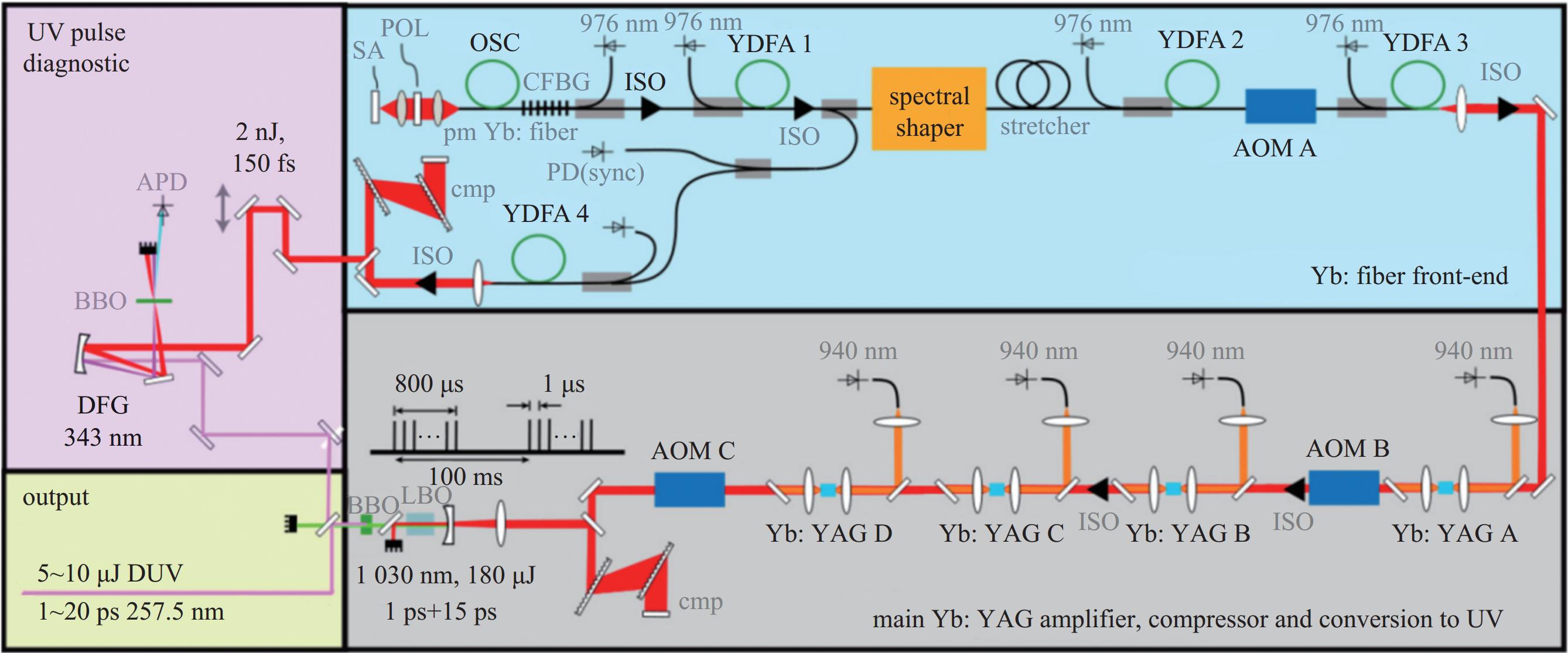
下载: