In-situ calibration of the efficiency of a yttrium activation detection system by the accelerator-based DD fusion neutron source
-
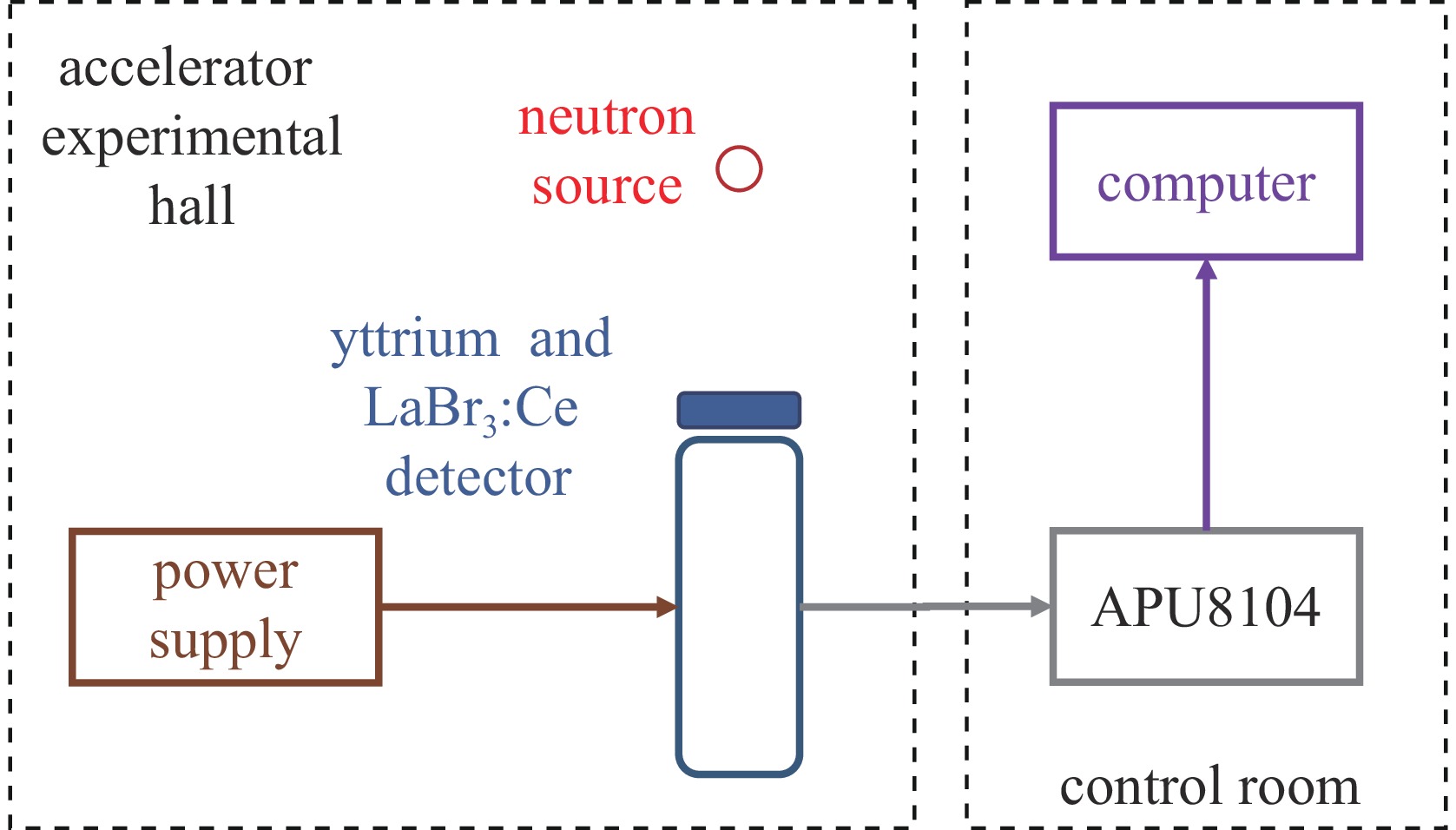
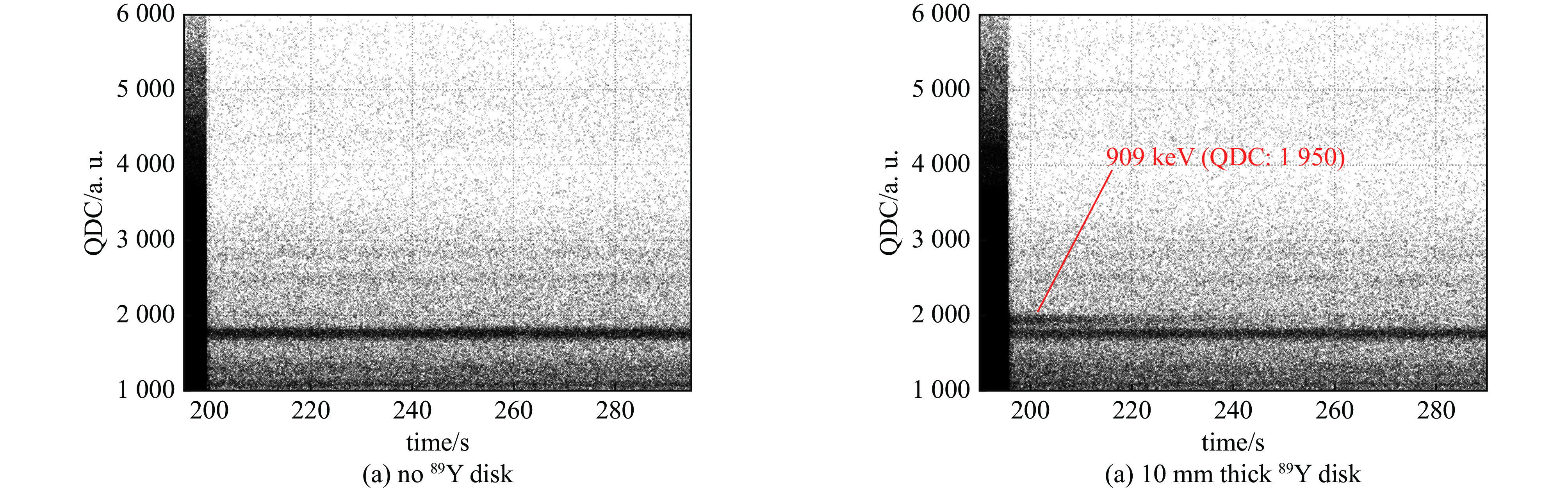
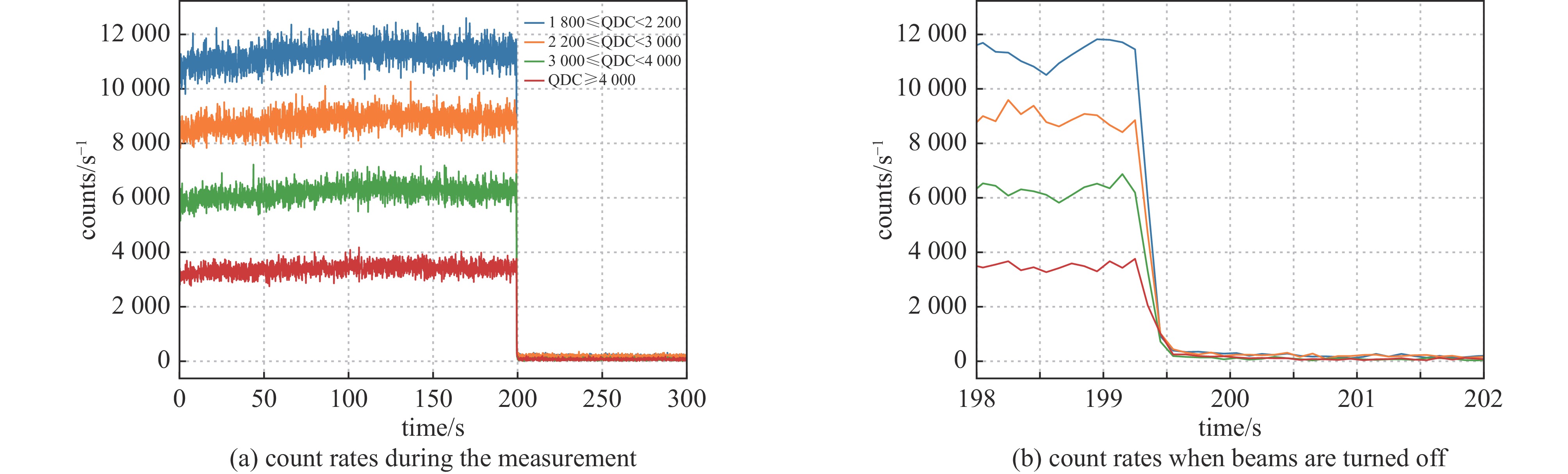
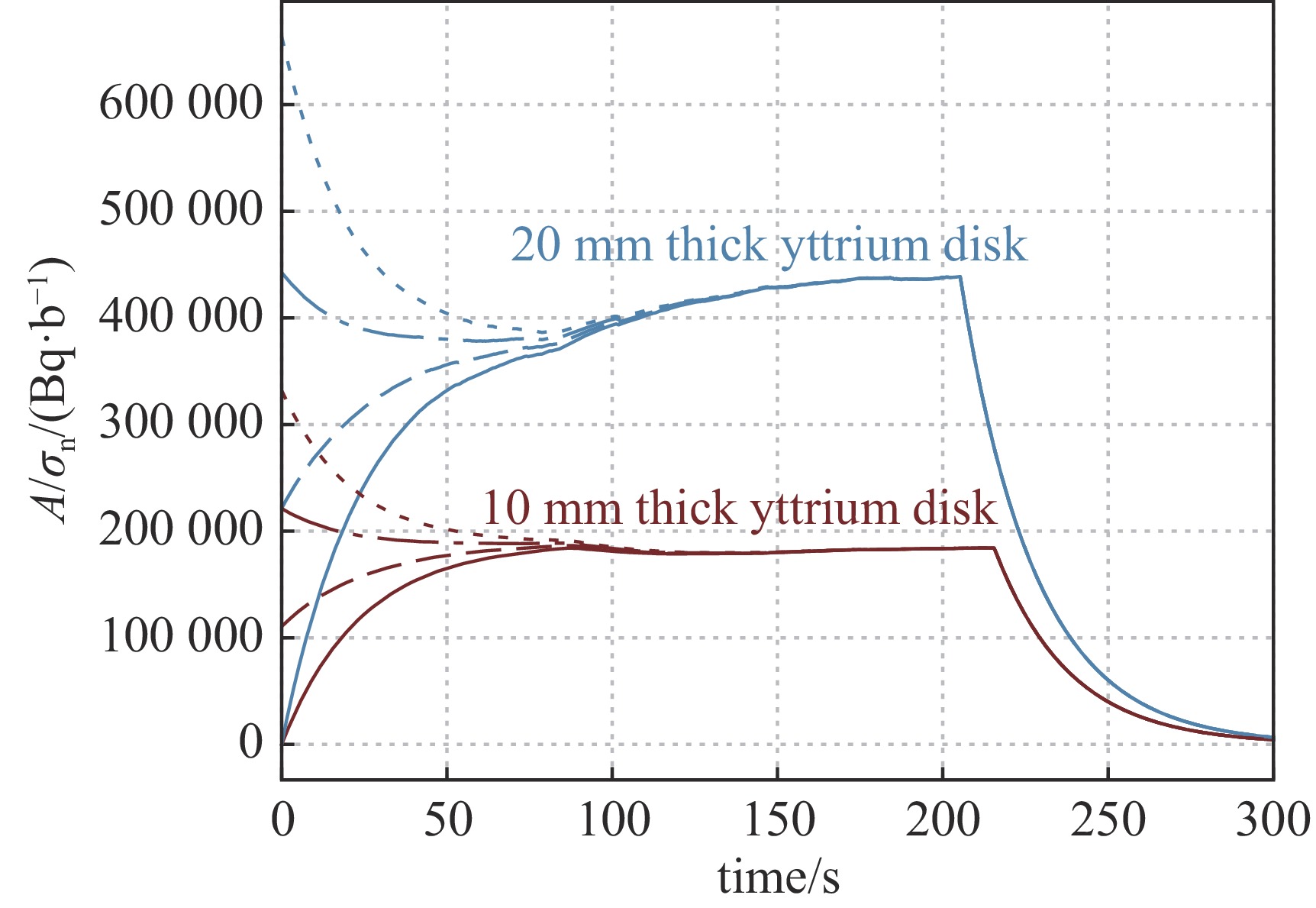
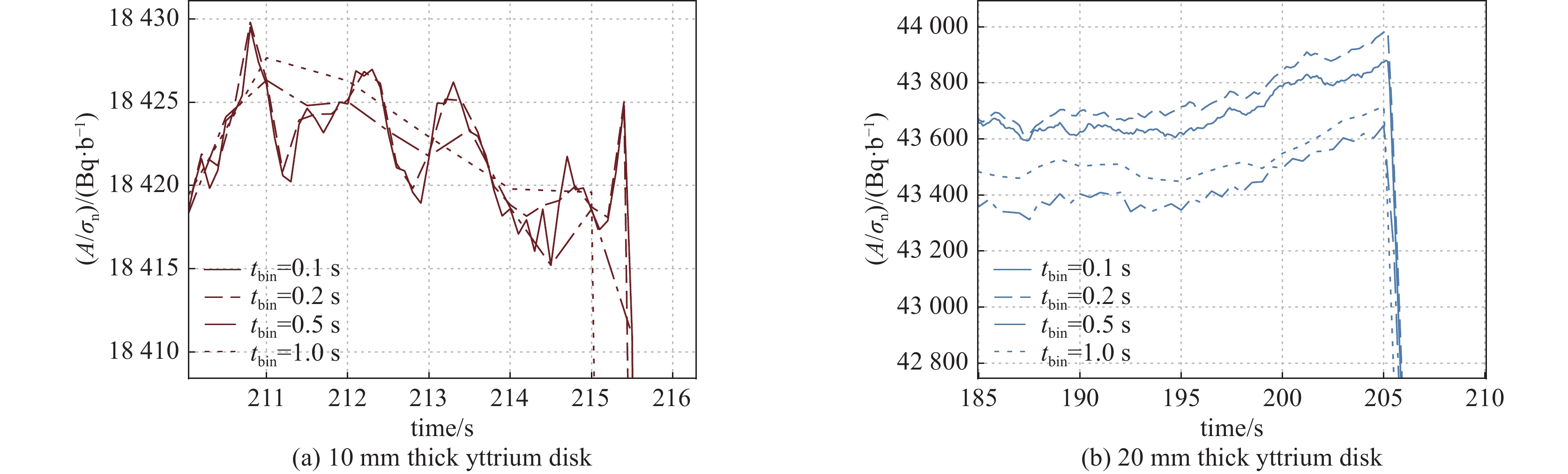
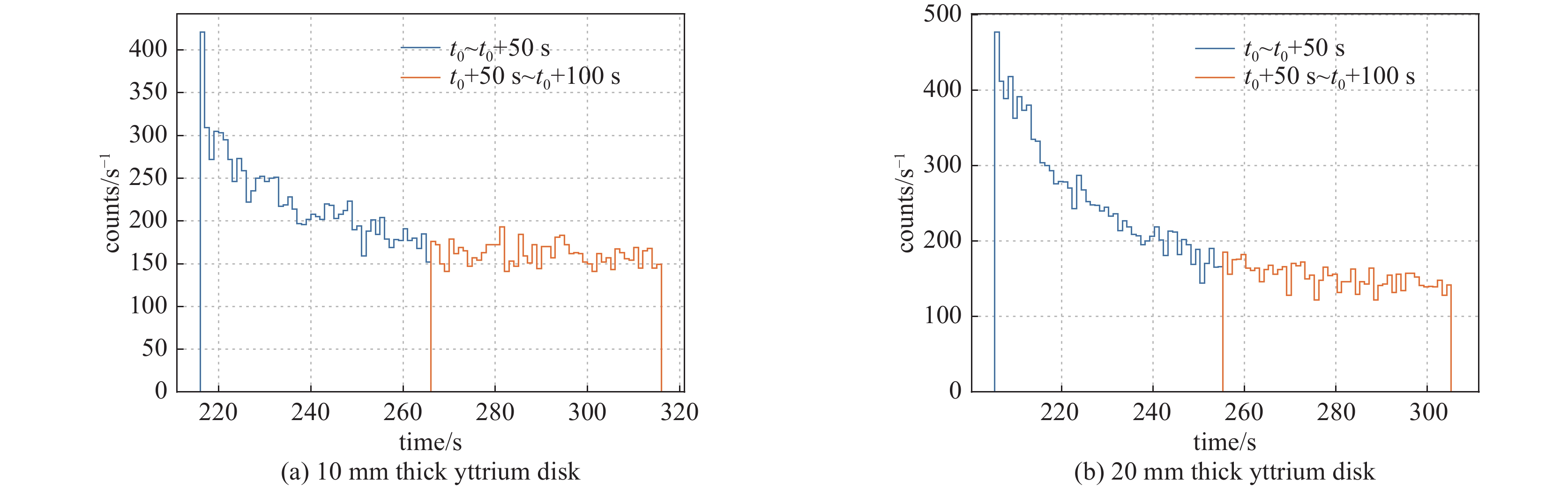
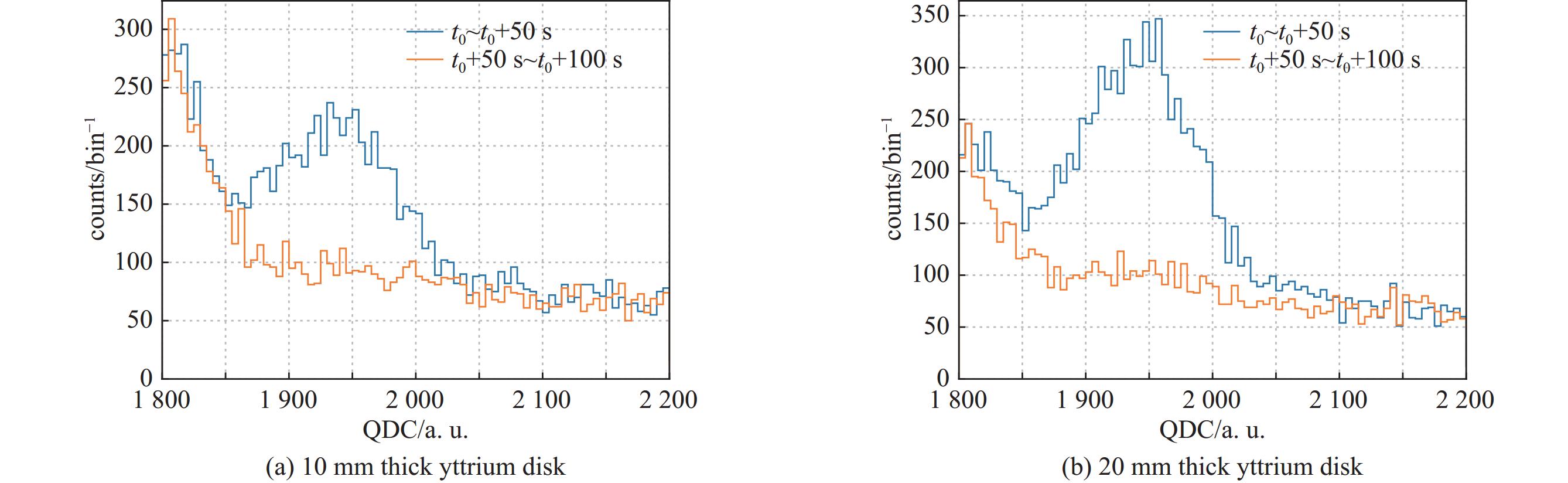
摘要: 在包括激光惯性约束聚变(ICF)、Z箍缩及稠密等离子聚焦(DPF)等脉冲聚变装置上,活化法作为中子通量测量与产额诊断的手段,得到了广泛的应用。利用无机闪烁体探测器,测量89Y核与中子非弹散反应产生的909 keV的单能伽马射线,可以实现DD中子通量的准确测量。采用金属钇作为活化靶,利用LaBr3:Ce闪烁体伽马探测器建立了中子活化原位探测系统。针对钇活化核半衰期仅有15.663 s的特点,对其在连续束流辐照下的累积过程进行了物理分析,建立了通过加速器DD中子源进行入射中子探测效率标定的实验方法。实验中,利用伽马探测器兼顾中子通量监测与活化伽马测量,模拟了钇靶活度随中子通量变化的过程,实现了该活化探测系统对入射中子探测效率的原位标定。Abstract: On the pulsed fusion sources such as laser ICF device, Z pinch facility and dense plasma focus device, the neutron activation method are widely applied, which can measure the neutron flux and diagnose the neutron yield from the source. Based on the inorganic scintillation detector, the 909 keV monoenergetic gammas, which are emitted from decay of the activated yttrium nuclei after the inelastic scattering on neutrons, can be measured, and the flux of the DD fusion neutrons can be diagnosed. In this work, an activation detection system using yttrium is developed, in which the LaBr3:Ce scintillator detector is chosen as the gamma sensitive material. The accumulation process of yttrium activation products under continuous irradiation has been physically analyzed, with respect to their half-life of only 15.663 s. An experimental method of calibrating the incident neutron detection efficiency by accelerator-based DD neutron source is thus established. In the experiments, the gamma detector is served as both neutron flux rate monitor and activation gamma measurements. The variation of radiation activity of the yttrium target with the neutron flux rate are simulated. Therefore, the in-situ calibration of the detection efficiency of this yttrium activation system for incident neutrons is achieved, with an accuracy of about 3.8%.
-
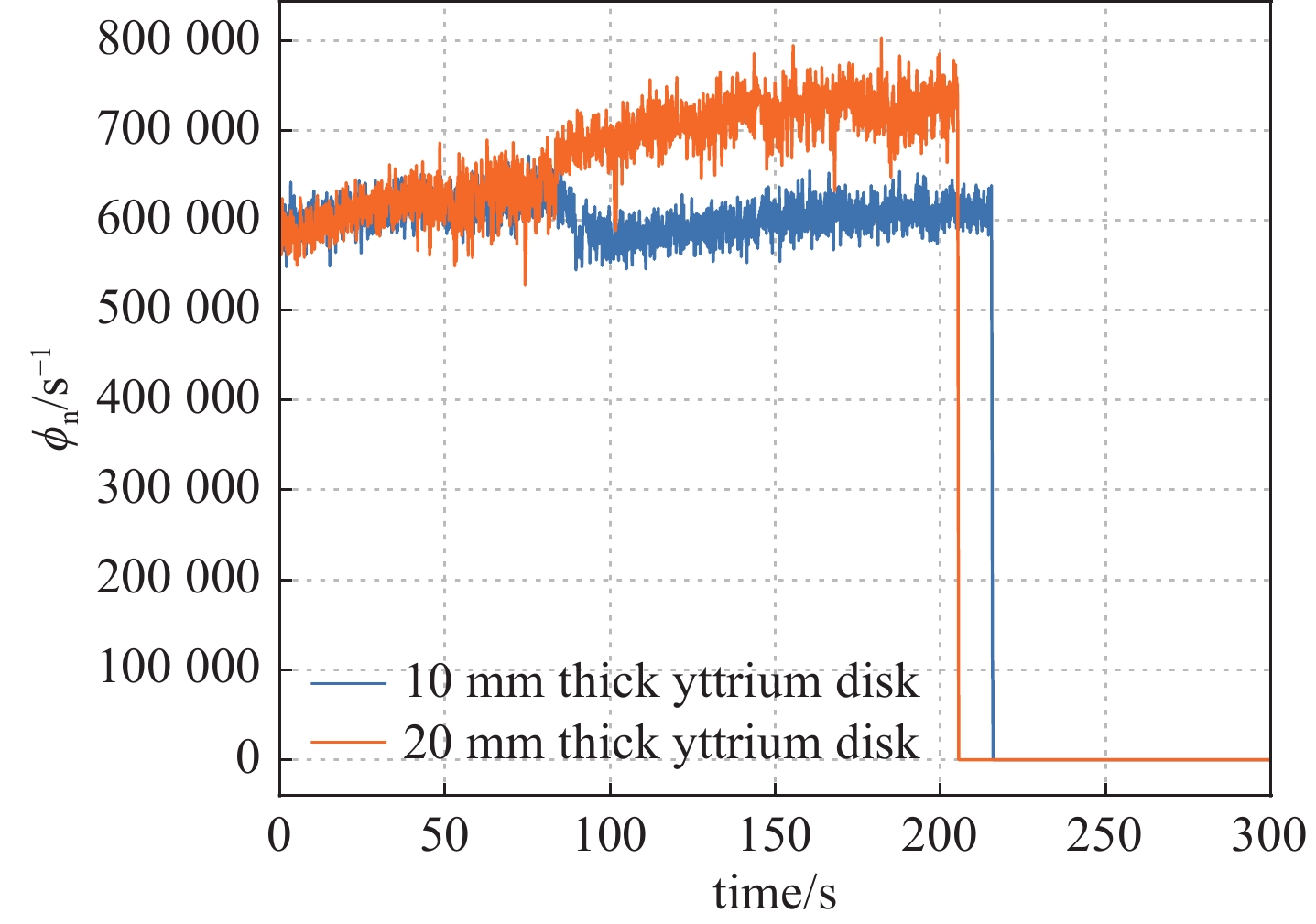
表 1 两种靶厚的中子活化探测系统标定结果
Table 1. Results of calibration with 2 different thickness of the yttrium disk
No. thickness/mm n1 n2 ϕn(t0)/s−1 η 1 10 11196 8047 6.09×105 2.29×10−4 2 20 12832 7594 7.25×105 3.20×10−4 -
[1] Frenje J A. Nuclear diagnostics for Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF) plasmas[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2020, 62: 023001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6587/ab5137 [2] Wang Feng, Jiang Shaoen, Ding Yongkun, et al. Recent diagnostic developments at the 100 kJ-level laser facility in China[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2020, 5: 035201. doi: 10.1063/1.5129726 [3] Bionta R M, Grim G P, Hahn K D, et al. Real-time nuclear activation detectors for measuring neutron angular distributions at the National Ignition Facility[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92: 043527. doi: 10.1063/5.0042869 [4] Cikhardt J, Klir D, Shishlov A V, et al. Neutron fluence distribution in experiments with 3 MA deuterium gas-puff z-pinch[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2020, 27: 072705. doi: 10.1063/5.0008108 [5] Hahn K D, Chandler G A, Ruiz C L, et al. Fusion-neutron measurements for magnetized liner inertial fusion experiments on the Z accelerator[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2016, 717: 012020. [6] Springham S V, Verma R, Zaw M S N, et al. Plasma focus neutron energy and anisotropy measurements using zirconium–beryllium pair activation detectors[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2021, 988: 164830. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2020.164830 [7] Cooper G W, Ruiz C L. NIF total neutron yield diagnostic[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2001, 72(1): 814-817. [8] Hahn K D, Cooper G W, Ruiz C L, et al. Fusion-neutron-yield, activation measurements at the Z accelerator: design, analysis, and sensitivity[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2014, 85: 043507. doi: 10.1063/1.4870779 [9] Jednorog S, Laszynska E, Batistoni P, et al. Activation measurements in support of the 14 MeV neutron calibration of JET neutron monitors[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2017, 125: 50-56. doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2017.10.024 [10] Cheon M S, Kim C S, Cho S, et al. Investigation of the capsule detection method at the irradiation end of the ITER neutron activation system[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2021, 78(7): 574-579. doi: 10.1007/s40042-021-00083-5 [11] 宋仔峰, 陈家斌, 唐琦, 等. 氘氘中子产额铟活化诊断方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(5):1165-1168 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122405.1165Song Zifeng, Chen Jiabin, Tang Qi, et al. DD neutron yield diagnosis by indium activation[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(5): 1165-1168 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122405.1165 [12] Li Kai, Hu Liqun, Zhong Guoqiang, et al. Development of neutron activation system on EAST[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2020, 91: 013503. [13] Ruiz C L, Styron J D, Fehl D L, et al. Novel beryllium-scintillator, neutron-fluence detector for magnetized liner inertial fusion experiments[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2019, 22: 042901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.22.042901 [14] Roshan M V, Springham S V, Rawat R S, et al. Absolute measurements of fast neutrons using yttrium[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2010, 81: 083506. doi: 10.1063/1.3478020 [15] Jednorog S, Szydlowski A, Bienkowska B, et al. The application of selected radionuclides for monitoring of the D–D reactions produced by dense plasma-focus device[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2014, 301(1): 23-31. doi: 10.1007/s10967-014-3131-0 [16] Song Zifeng, Chen Jiabin, Liu Zhongjie, et al. The calibration of the DD neutron indium activation diagnostic[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2015, 17(4): 337-339. doi: 10.1088/1009-0630/17/4/14 [17] Li Kai, Hu Liqun, Zhong Guoqiang, et al. Calibration of the gamma-ray measurement procedure in the EAST neutron activation system[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2019, 148: 111278. [18] Jednorog S, Laszynska E, Bienkowska B, et al. A new concept of fusion neutron monitoring for PF-1000 device[J]. Nukleonika, 2017, 62(1): 17-22. doi: 10.1515/nuka-2017-0003 [19] 李凯. 基于铟硅活化法的EAST聚变中子产额诊断研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2020: 25-28Li Kai. Research of EAST fusion neutron yield diagnostic based on indium and silicon activation method[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2020: 25-28 [20] 朱通华, 刘荣, 蒋励, 等. D-D中子源产额的大角度伴随质子监测技术研究[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2007, 27(1):141-144,166 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2007.01.038Zhu Tonghua, Liu Rong, Jiang Li, et al. The associated proton monitoring technique study of D-D source neutron yields at the large angle[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2007, 27(1): 141-144,166 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2007.01.038 [21] Cazzaniga C, Nocente M, Tardocchi M, et al. Response of LaBr3(Ce) scintillators to 2.5 MeV fusion neutrons[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2013, 84: 123505. doi: 10.1063/1.4847056 [22] Xi Hao, Liang Chuan, Zhang F Q, et al. A pulse current generator for dense plasma focus[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2021, 16: P12021. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/16/12/P12021 -




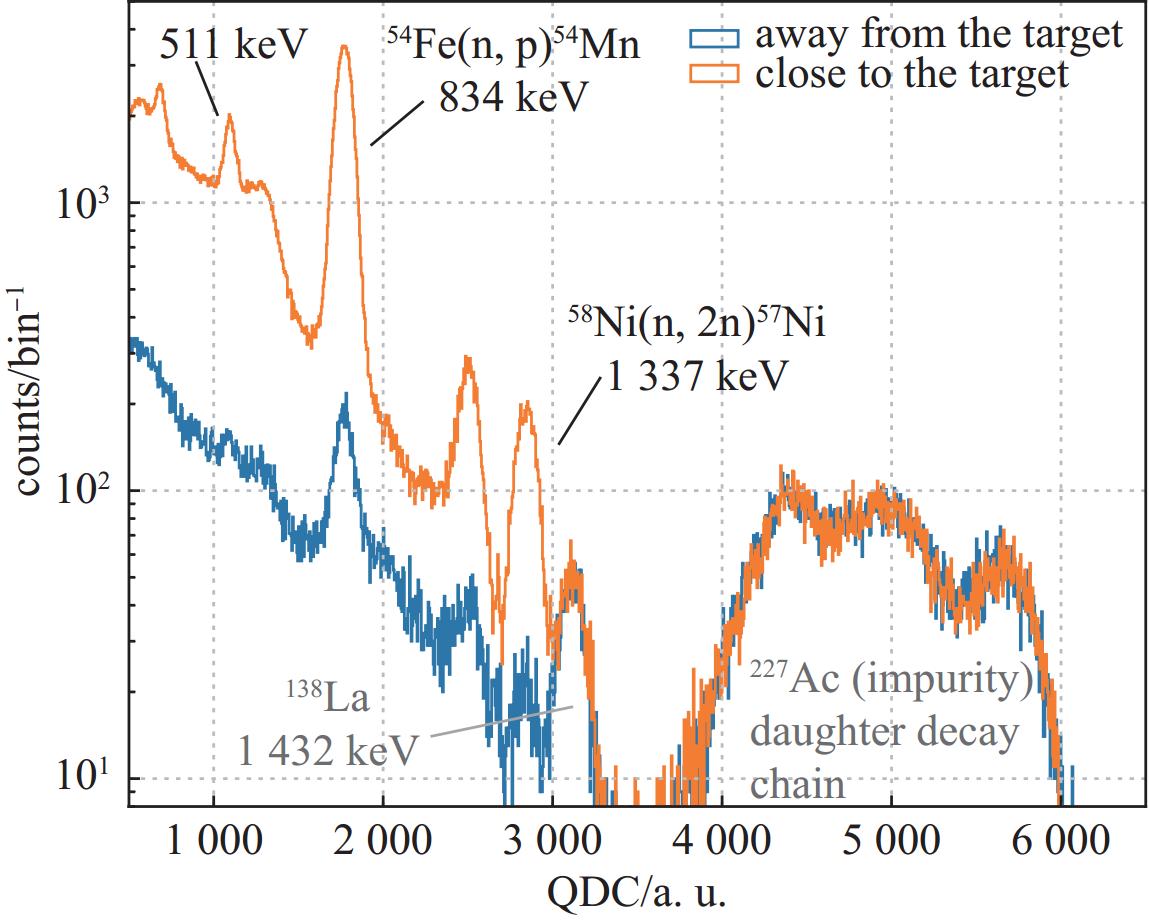
 下载:
下载: