Cleanliness control of vacuum system in high-flux laser device
-
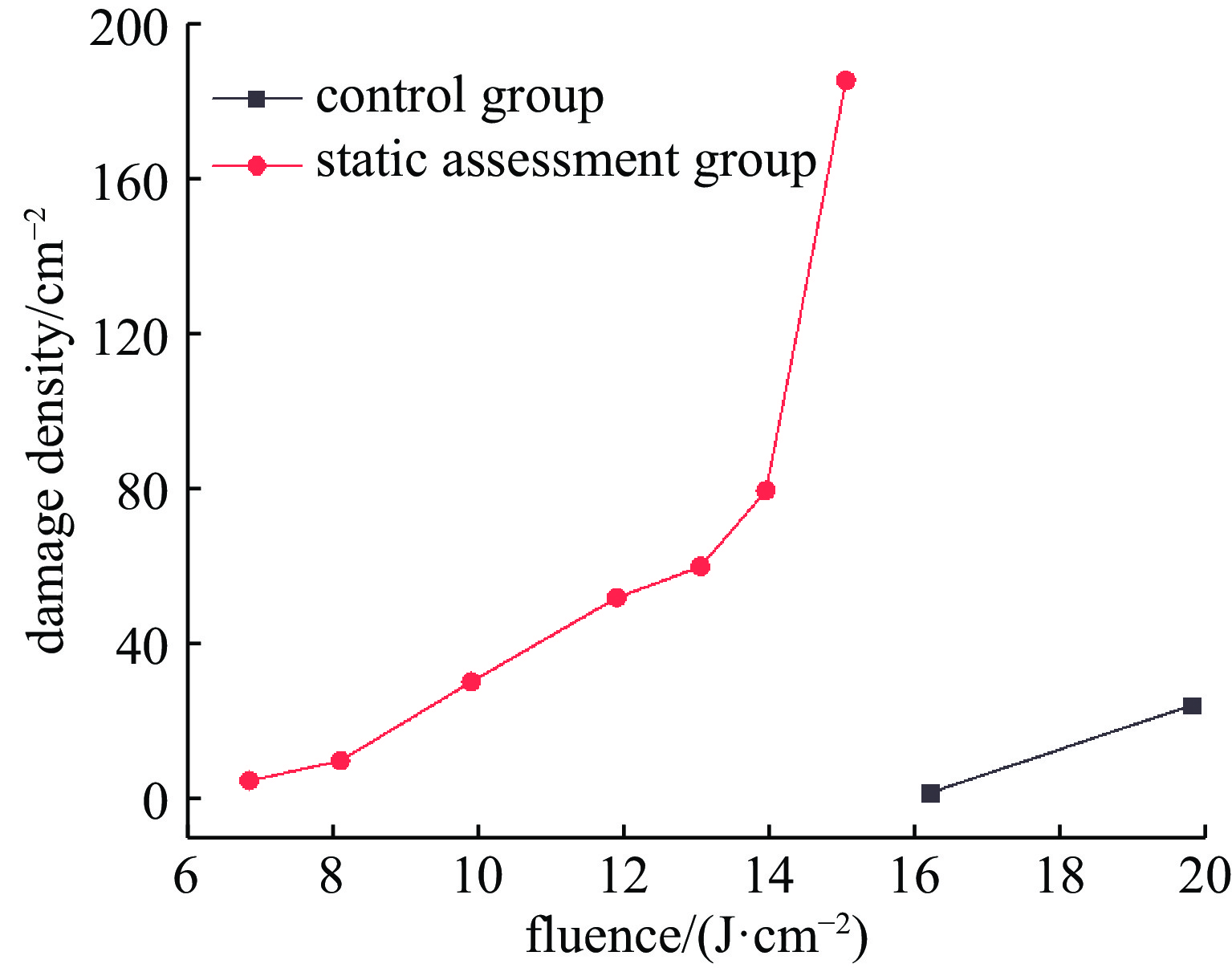
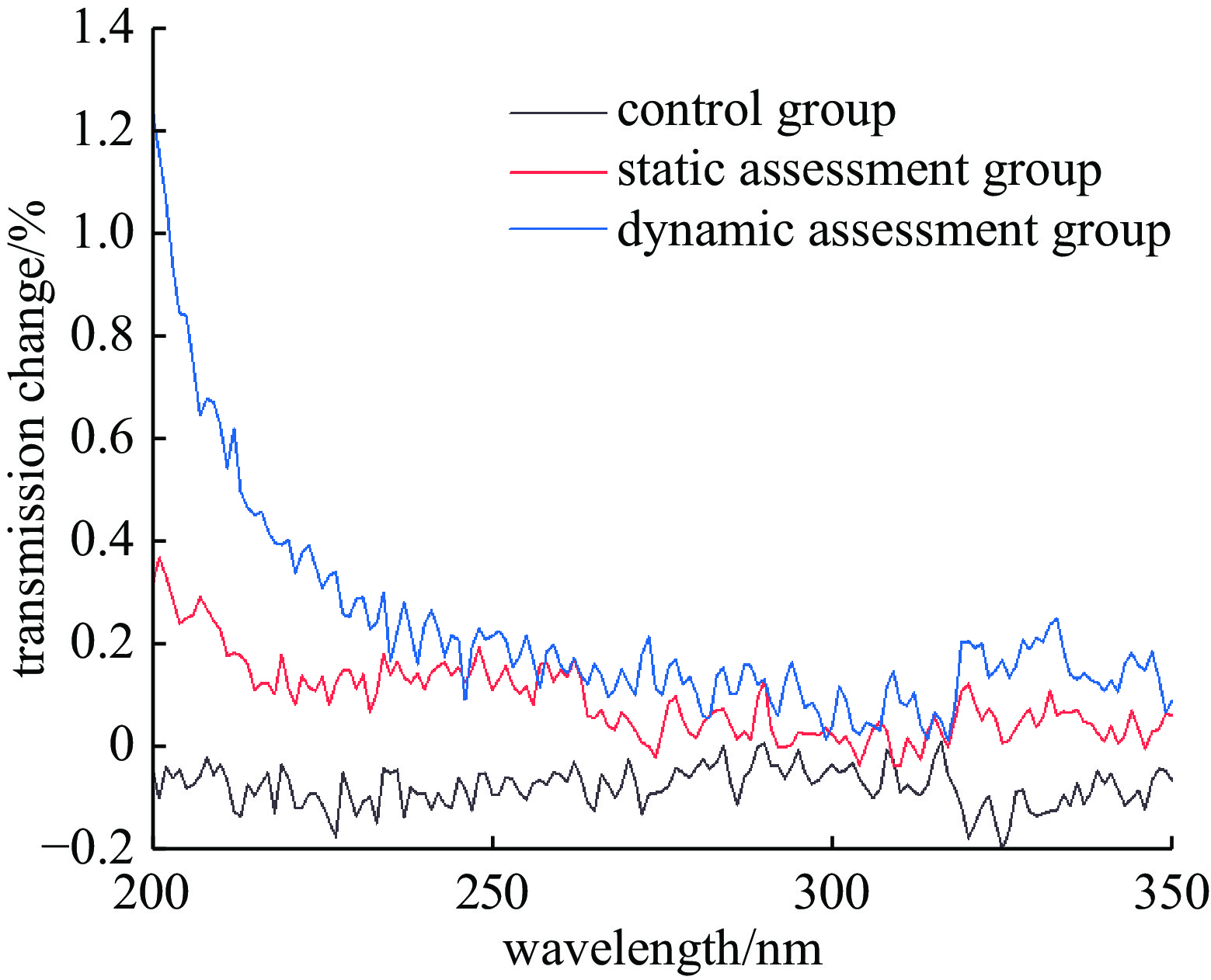
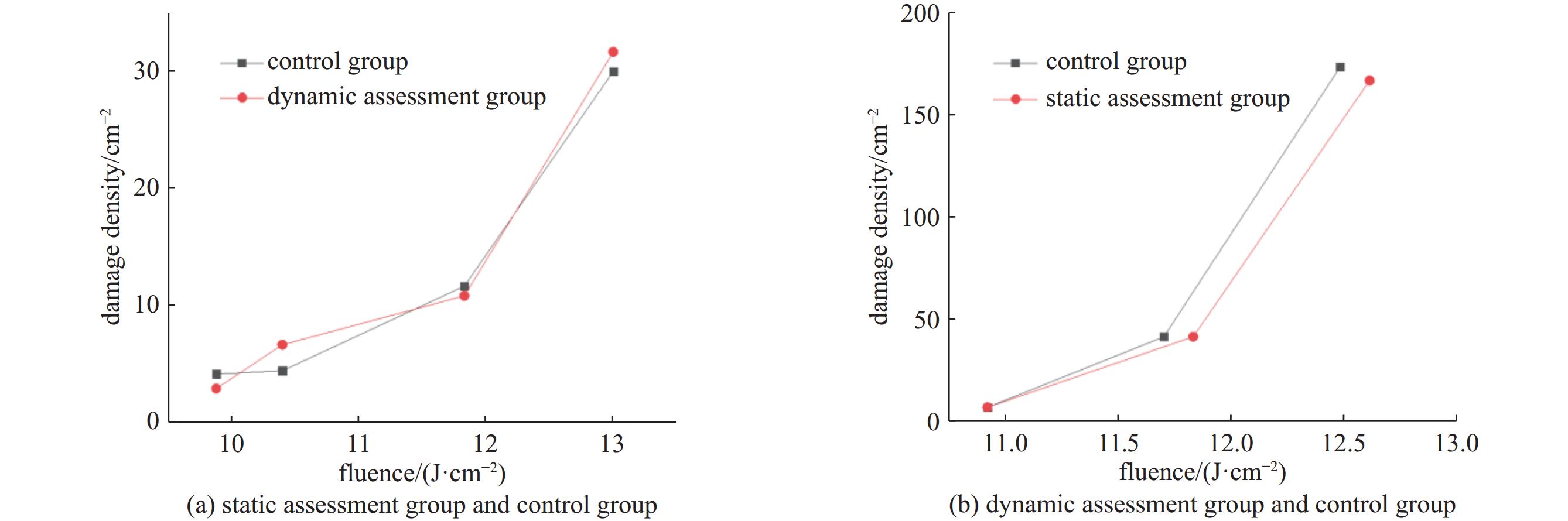
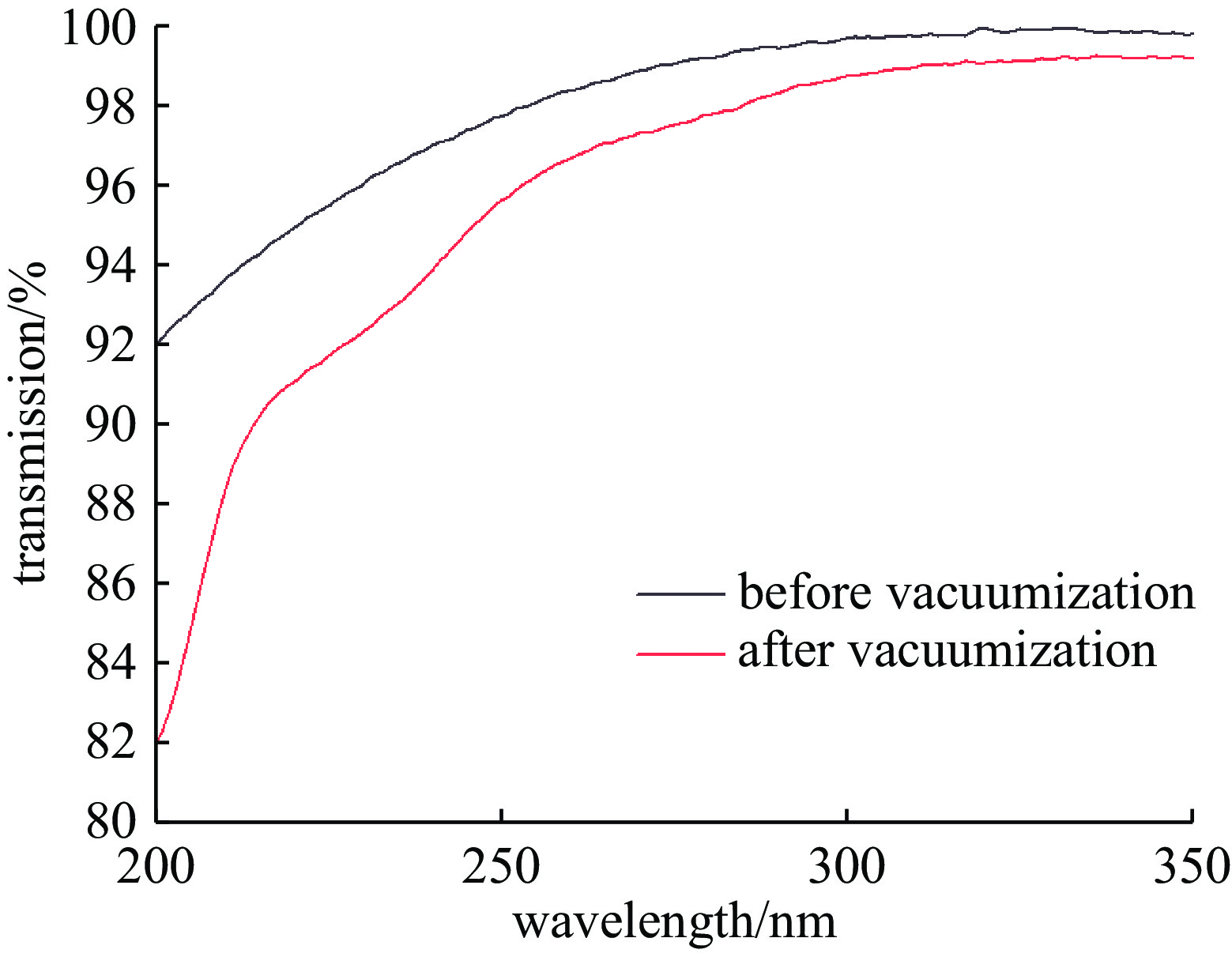
摘要: 在高通量激光装置真空系统运行过程中,泵组润滑油在真空环境下产生的分子污染可能扩散沉积在光学系统元件表面,在高通量激光辐照下诱导损伤,降低光学元件负载能力。针对真空系统洁净度控制开展研究,构建了包括真空泵组优化、增加低温冷阱吸附、增加冷阱在线加热再生工艺的真空系统洁净度控制方法。实验研究结果表明:真空系统经过120 h连续运行后,平均24 h非挥发性残留物表面沉积量维持在2.86×10−9 g/cm2洁净水平,熔石英光学试片考核组和对照组在350 nm处的透过率以及12.3 J/cm2通量以下的损伤密度曲线基本一致,证明了该方法的有效性。Abstract: During the operation of vacuum system in high-flux laser device, molecular contamination generated by the pump lubricating oil in the vacuum environment may diffuse and deposit on the surface of optical system components, induce damage under high-flux laser irradiation, and reduce the devices’ load capacity. Research has been conducted on the cleanliness control of vacuum systems, and a series of technical measures have been developed to control the vacuum system cleanliness, including optimizing the vacuum pump group, increasing low-temperature cold trap adsorption, and adding online heating regeneration technology for the cold trap. The experimental research results show that after 120 h of continuous operation, the average surface deposition of non-volatile residues in the vacuum system reaches a clean level of 2.86 × 10−9 g/cm2 after 24 h; The transmittance at 350 nm and the damage density curve below 12.3 J/cm2 flux of the fused quartz optical test piece assessment group and control group are basically consistent, proving the effectiveness of this method.
-
Key words:
- high-flux laser device /
- vacuum system /
- cleanliness /
- optical components /
- transmittance /
- damage density
-
表 1 考核组和对照组条件对比
Table 1. Comparison of conditions between the assessment group and the control group
optical component group conditions control group placed vertically in a PTFE storage box in a class 100 laboratory, at atmospheric pressure, room temperature, and relative humidity of 60% static assessment
groupplaced vertically in the pipeline of vacuum clean validation experimental system in a class 10000 laboratory, the vacuum unit and cold trap are not running, at atmospheric pressure, room temperature, and relative humidity of 60%dynamic assessment
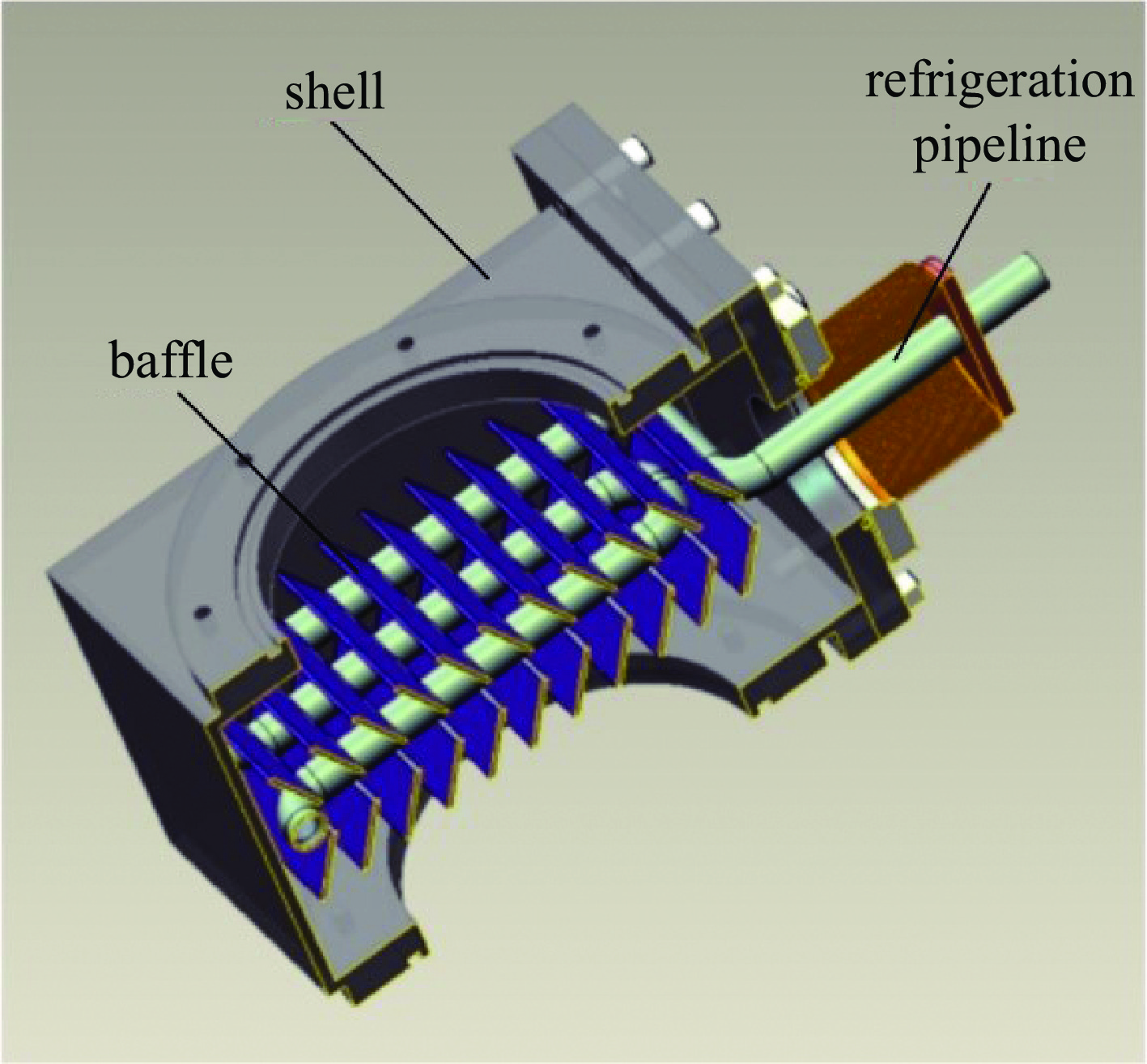
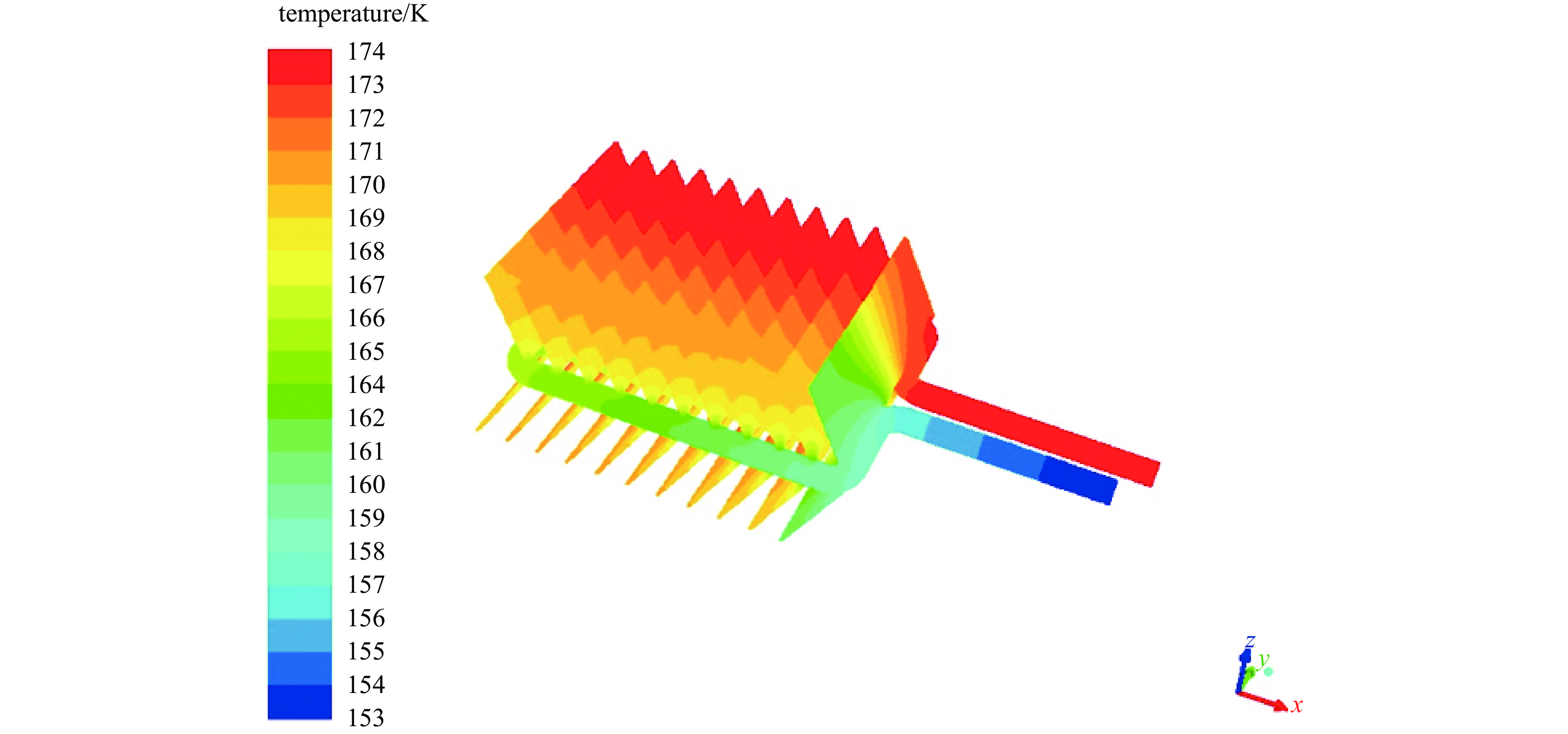
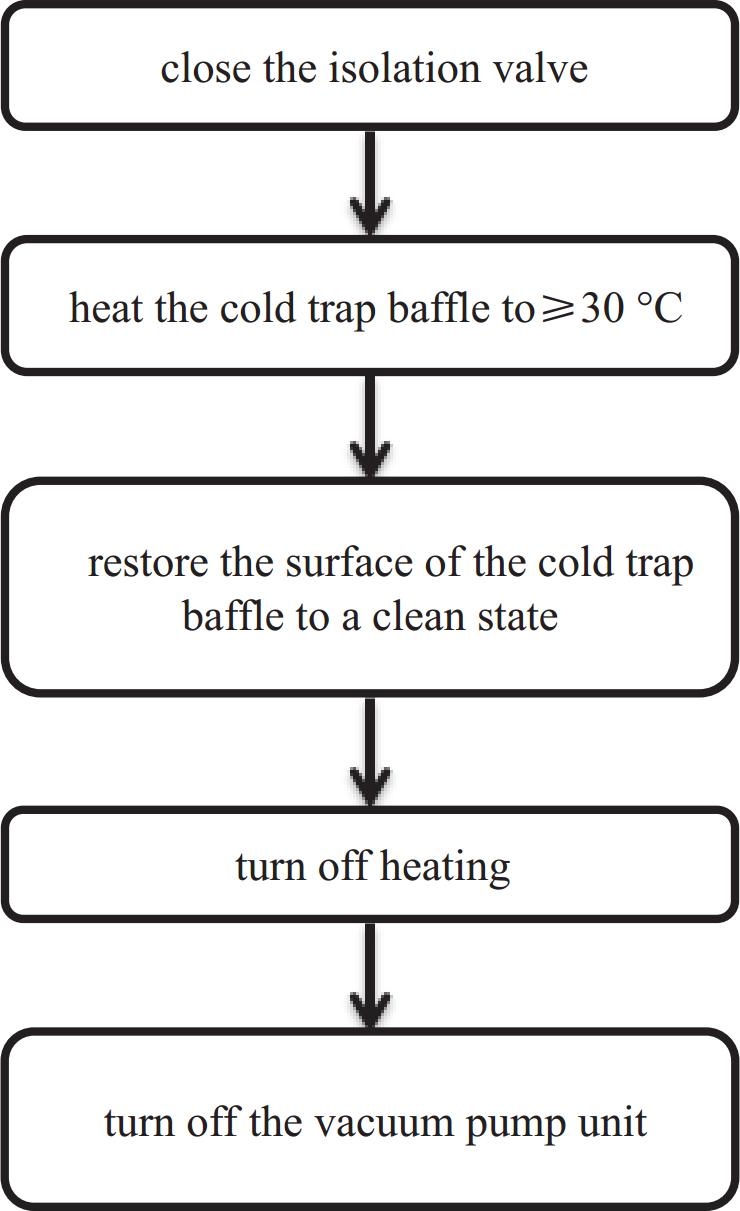
groupplaced vertically in the pipeline of vacuum clean validation experimental system in a class 10000 laboratory, the vacuum unit and cold trap are running,with a vacuum degree of 4.0 × 10−1 Pa and a working temperature of −100 ℃ for the cold trap表 2 非挥发性残留物表面沉积量实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of surface deposition of non-volatile residues
optical component group total surface deposition of non-volatile
residues after 120 h/(g·cm−2)average surface deposition of non-volatile
residues over 24 h/(g·cm−2)static assessment group 2.20×10−9 4.40×10−10 dynamic assessment group 1.43×10−8 2.86×10−9 -
[1] Manes K R, Spaeth M L, Adams J J, et al. Damage mechanisms avoided or managed for NIF large optics[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 146-249. doi: 10.13182/FST15-139 [2] Nicolaizeau M, Miquel J L. LMJ status: fifth bundle commissioning and PW class laser coupling[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 10898, High Power Lasers for Fusion Research V. 2019: 1089802. [3] Bass M. When everything damaged and we didn’t know why[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 10805, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials 2018: 50th Anniversary Conference. 2018: 1080504. [4] 许彬, 李斌成, 高椿明, 等. 真空环境下低损耗高反射光学元件性能退化特性[J]. 激光技术, 2020, 44(6):768-772Xu Bin, Li Bincheng, Gao Chunming, et al. Performance degradation of low-loss highly-reflective mirrors under vacuum environment[J]. Laser Technology, 2020, 44(6): 768-772 [5] Pryatel J A, Gourdin W H, Frieders S C, et al. Cleaning practices and facilities for the National Ignition Facility (NIF)[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 9237, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials. 2014: 92372H. [6] 焦子龙, 庞贺伟, 易忠, 等. 卫星真空热试验污染物成分分析[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2009, 26(3):240-243Jiao Zilong, Pang Hewei, Yi Zhong, et al. The identification of molecular contaminant in thermal vacuum test[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2009, 26(3): 240-243 [7] 张洪波, 刘天雄, 李长江. 卫星热真空试验微波开关分子污染防护研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2011, 20(5):125-130Zhang Hongbo, Liu Tianxiong, Li Changjiang. Research on prevention of molecular contamination of microwave switches in thermal vacuum test for satellite[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2011, 20(5): 125-130 [8] 刘天雄, 罗成, 朱剑涛, 等. 热真空试验中分子污染敏感单机的失效机理及对策[J]. 航天器工程, 2014, 23(1):47-52Liu Tianxiong, Luo Cheng, Zhu Jiantao, et al. Failure mechanism and countermeasure of unit sensitive to molecular contamination in thermal vacuum test[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2014, 23(1): 47-52 [9] 焦子龙, 姜利祥, 孙继鹏, 等. 空间光学系统真空热试验污染控制经验综述[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2015, 32(4):445-450 doi: 10.12126/see.2015.04.020Jiao Zilong, Jiang Lixiang, Sun Jipeng, et al. Overview of contamination controls for space-based optical systems in thermal vacuum tests[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2015, 32(4): 445-450 doi: 10.12126/see.2015.04.020 [10] 焦子龙, 姜利祥, 孙继鹏, 等. 星载激光雷达系统污染增强损伤效应及防护试验研究[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2017, 34(4):419-423Jiao Zilong, Jiang Lixiang, Sun Jipeng, et al. Tests for contamination enhanced and laser-induced damage in spaceborne lidar system and its prevention[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2017, 34(4): 419-423 [11] Pryatel J A, Gourdin W H, Hampton G J, et al. Qualification of materials for applications in high fluence lasers[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 6403, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials. 2007: 640329. [12] 牛龙飞, 尤辉, 吕海兵, 等. 激光系统用密封圈除气对真空光学元件性能影响[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35:061004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220390Niu Longfei, You Hui, Lü Haibing, et al. Influence of vacuum baking O-rings on optical properties of laser system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 061004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220390 [13] 赵飞, 张晓妹, 刘鸣, 等. 多重接触式静密封泄漏特性定量分析模型[J]. 机械工程师, 2022(12):45-17,50Zhao Fei, Zhang Xiaomei, Liu Ming, et al. Quantitative analysis model for leakage characteristics of multi-contact static seal[J]. Mechanical Engineer, 2022(12): 45-17,50 [14] Henrist M, Cucchiaro A, Domken I, et al. The space simulation facilities at IAL SPACE[C]//Proceedings of 16th Space Simulation Conference Confirming Spaceworthiness Into the Next Millennium. 1990: 314-322. [15] Straka S, Peters W, Hasegawa M, et al. Development of molecular adsorber coatings[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 7794, Optical System Contamination: Effects, Measurements, and Control 2010. 2010: 77940C. [16] Miller P E, Thorsness C B, Ertel J, et al. Use of silica gel as a getter for the protection of sol-gel coated optics: concept verification[R]. Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Lab. , 2014. [17] 王先荣, 颜则东. 分子凝结与凝结表面温度的关系机理研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2004, 25(3):327-329Wang Xianrong, Yan Zedong. The mechanism research upon the relationship between molecular condensation and sensitive surface temperature[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2004, 25(3): 327-329 [18] 杨东升, 臧卫国, 于钱. 低温石英天平在材料放气污染特性测试中的应用[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2005, 22(5):300-303 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2005.05.011Yang Dongsheng, Zang Weiguo, Yu Qian. Application of low temperature QCM to outgassing contamination characteristics detection of spacecraft materials[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2005, 22(5): 300-303 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2005.05.011 [19] 刘玉魁. 真空工程设计[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2016Liu Yukui. Design of vacuum engineering[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2016 [20] ISO 11254-2: 2001, Lasers and laser-related equipment – determination of laser-induced damage threshold of optical surfaces[S]. -




 下载:
下载: