Simulation research on high resolution X-ray diagnosis technology based on diffraction imaging
-
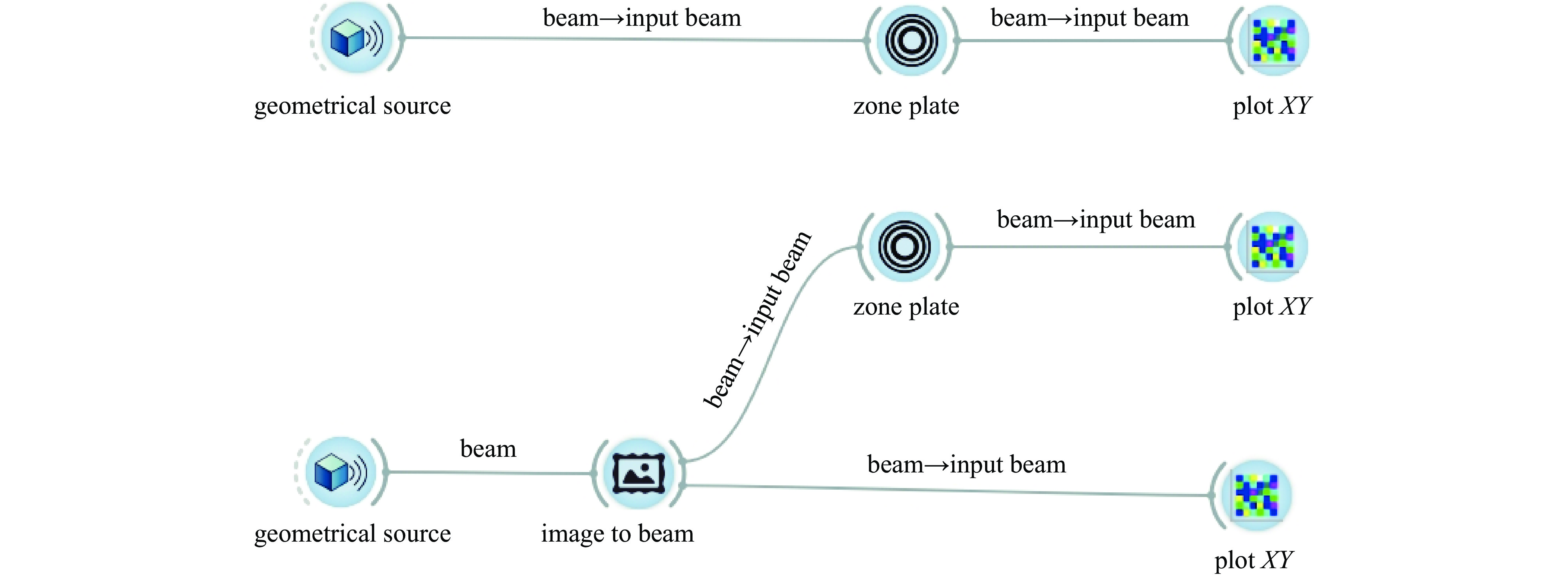
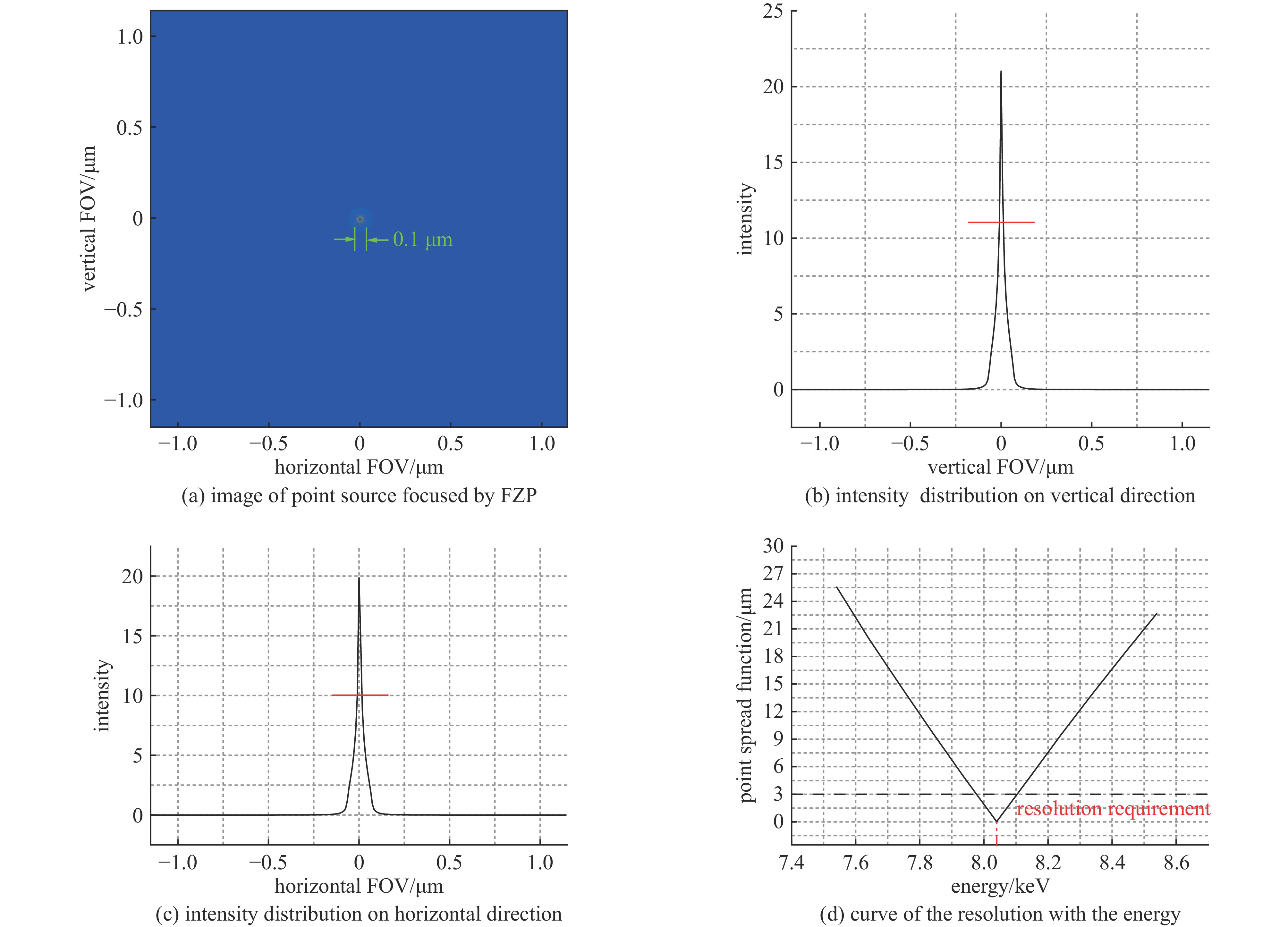
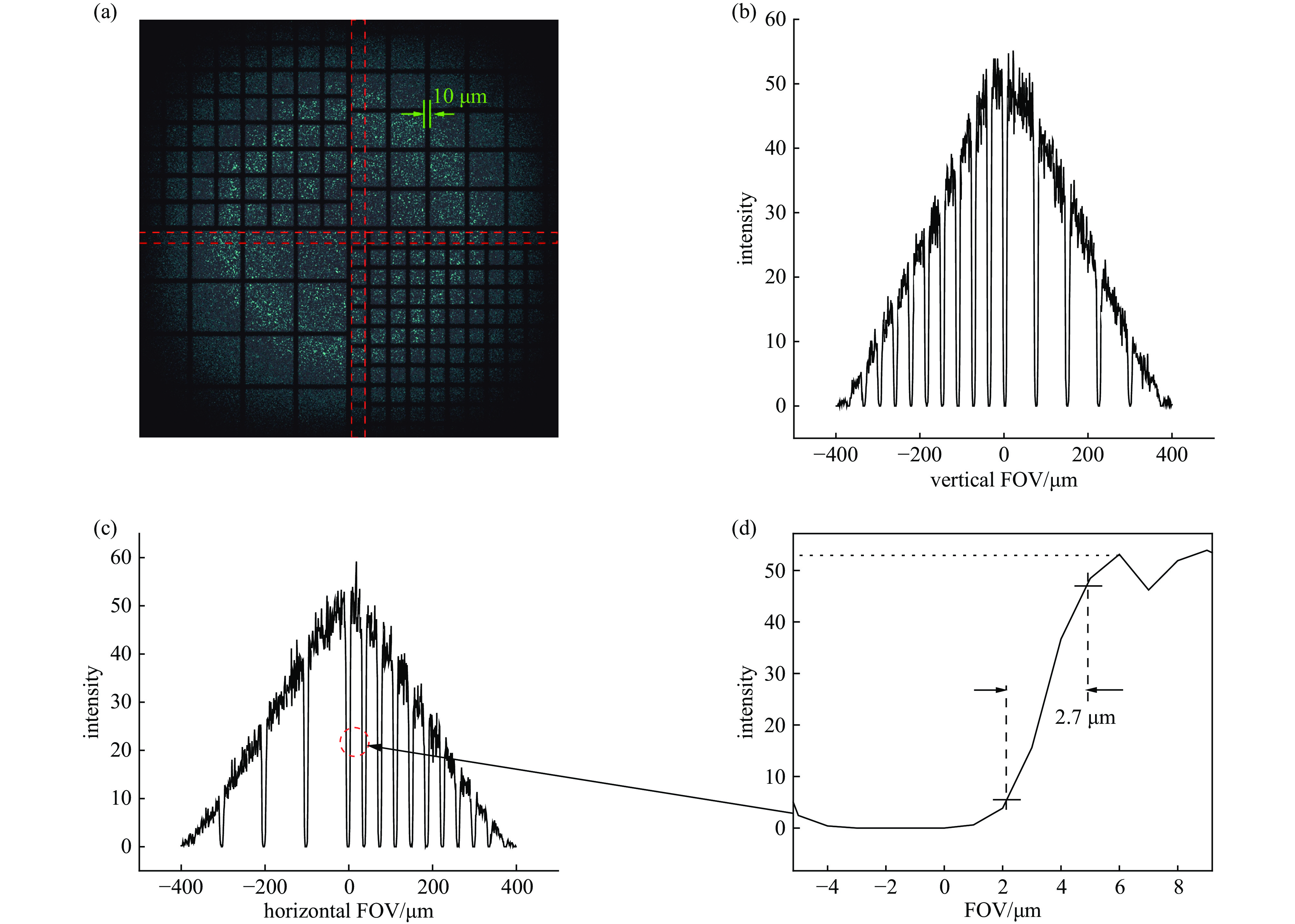
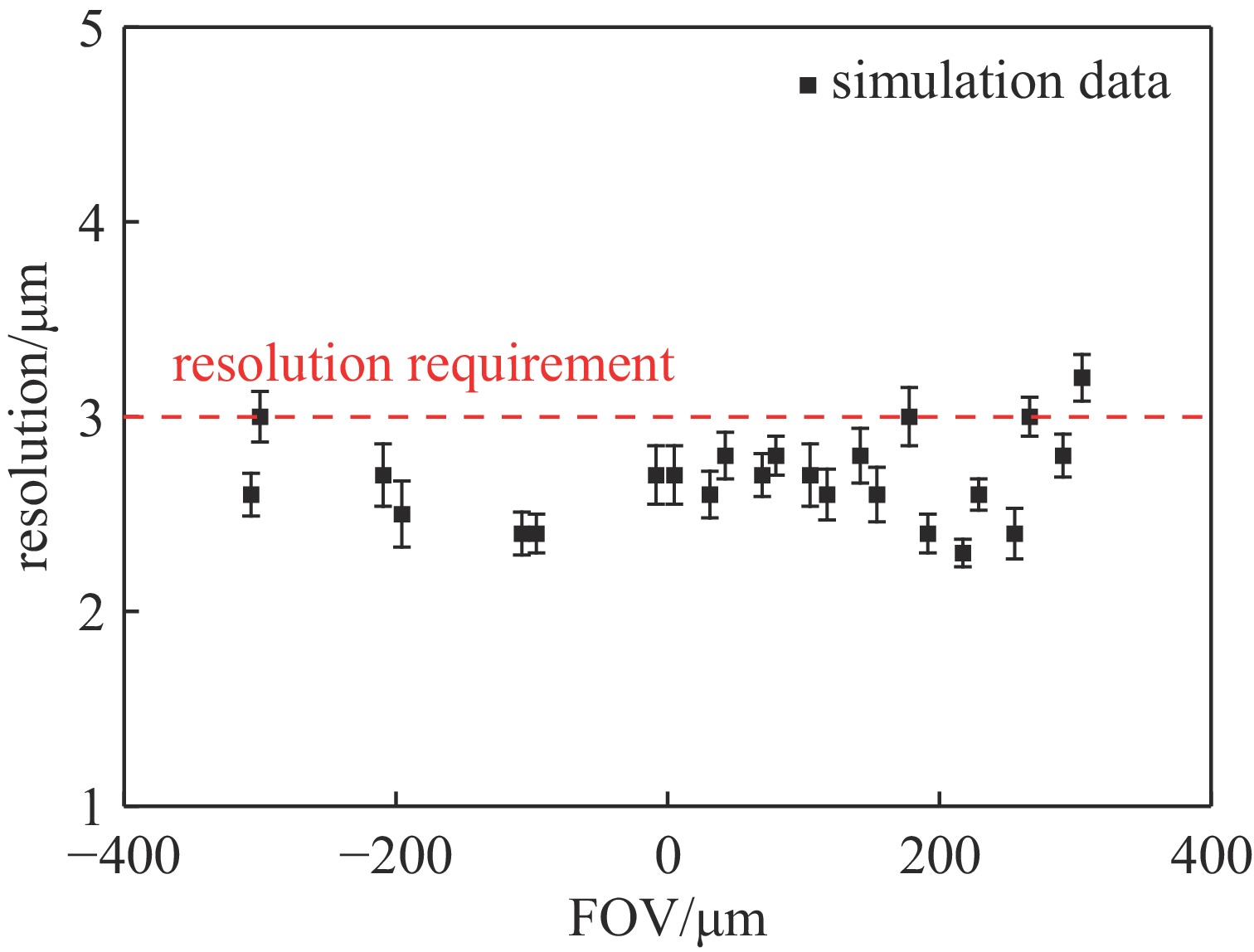
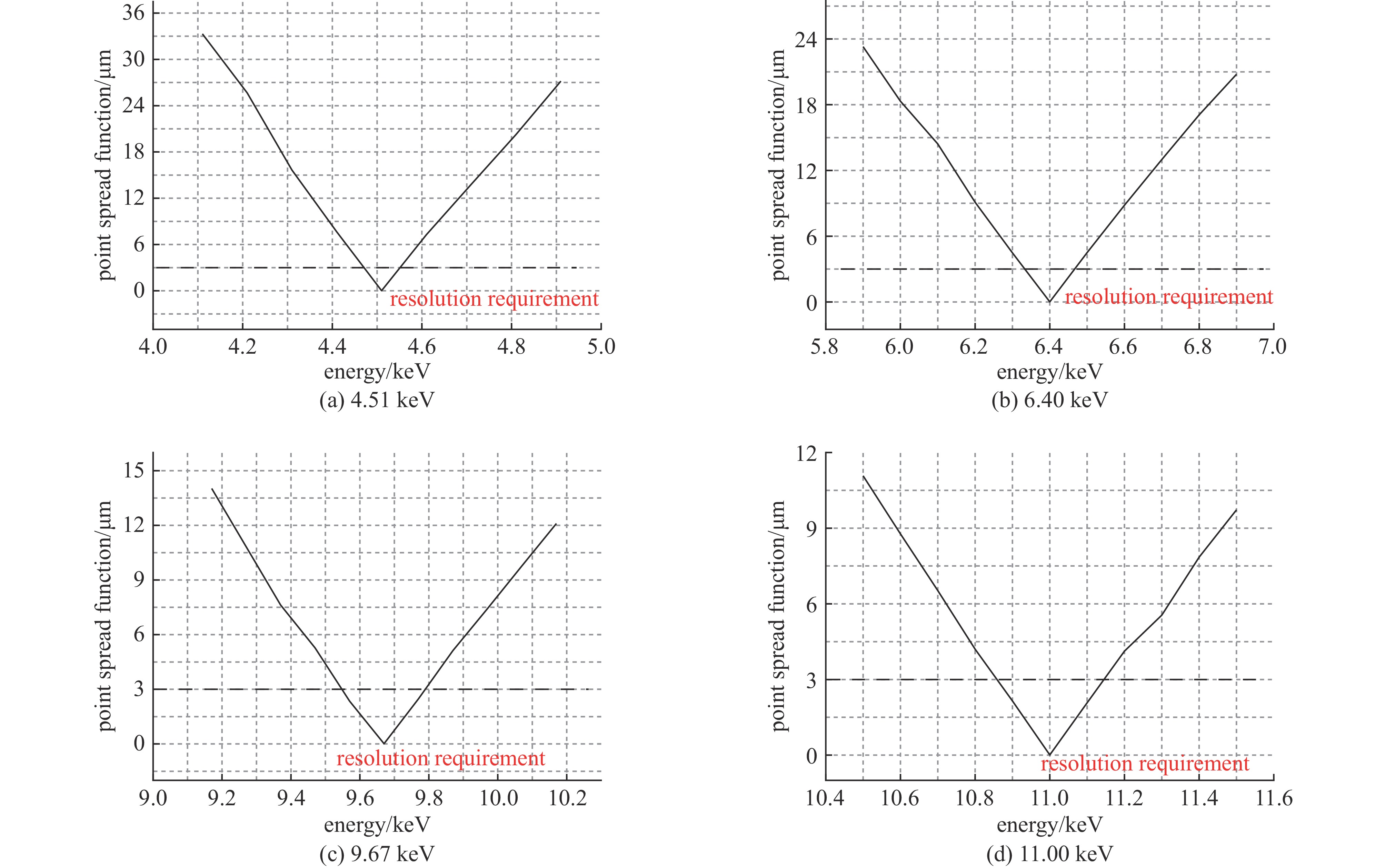
摘要: 为了研究激光聚变内爆中出现的流体力学不稳定性问题,需要具备大视场、高分辨率的X射线诊断技术。菲涅耳波带片(FZP)是一种圆形非周期光栅结构,可实现X射线的高空间分辨率成像。开展了基于衍射成像的高分辨X射线诊断技术仿真研究,展示了FZP对于流体力学不稳定性问题的应用前景。基于衍射理论建立FZP理论模型,根据诊断实验环境,设计了工作能点为8.04 keV下的FZP结构参数。基于光学仿真模型,对FZP成像色差问题进行模拟,给出了空间分辨与光谱带宽的关系,仿真结果表明,光源带宽小于0.2 keV,FZP的分辨率优于3 μm。通过网格背光成像仿真表明,FZP在0.8 mm视场内,可以实现优于3 μm的分辨。Abstract: To study the hydrodynamic instability in laser fusion implosion, X-ray diagnostic technology with large field of view and high resolution is needed. Fresnel zone plate (FZP) is a kind of circular aperiodic grating structure, which can realize high spatial resolution imaging of X-ray. In this paper, the simulation research of high-resolution X-ray diagnosis technology based on diffraction imaging is carried out, showing the application prospects of FZP for hydrodynamic instability research. Based on the diffraction theory, the theoretical model of FZP is established, and the structural parameters of FZP with working energy point of 8.04 keV are designed according to the diagnostic experimental environment. Based on the optical simulation model, the color difference of FZP imaging is simulated, and the relationship between spatial resolution and spectral bandwidth is given. The simulation results show that the bandwidth of light source is less than 0.2 keV, and the resolution of FZP is better than 3 μm. The simulation of grid backlight imaging shows that FZP can achieve good resolution (less than 3 μm) within 0.8 mm field of view.
-
Key words:
- thermonuclear fusion /
- X-ray imaging diagnosis /
- fluid instability growth /
- FZP /
- OASYS model simulation
-
表 1 模拟实验基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of simulation experiment
energy/keV diameter/μm $ \mathrm{\Delta }{r}_{n} $/nm $ {r}_{1} $/μm M N 8.04 433.5 67.7 5.42 20 1600 表 2 中文表题
Table 2. Basic parameters of multi energy points simulation experiment
energy/keV diameter/μm $ \mathrm{\Delta }{r}_{n} $/nm $ {{r}}_{1} $/μm M N 4.51 579.0 90.5 7.24 20 1600 6.40 486.0 76.0 6.07 20 1600 9.67 395.4 61.0 4.94 20 1600 11.00 370.7 58.0 4.63 20 1600 -
[1] Do A, Pickworth L A, Kozioziemski B J, et al. Fresnel zone plate development for X-ray radiography of hydrodynamic instabilities at the National Ignition Facility[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(34): 10777-10785. doi: 10.1364/AO.408569 [2] Do A, Kozioziemski B J. Fresnel zone plate point spread function approximation for zeroth order mitigation in millimetric field of view X-ray imaging[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2022, 93: 103507. doi: 10.1063/5.0101691 [3] Do A, Angulo A M, Hall G N, et al. X-ray imaging of Rayleigh–Taylor instabilities using Fresnel zone plate at the National Ignition Facility[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92: 053511. doi: 10.1063/5.0043682 [4] 陈志峰. 梁铨廷教授著《物理光学》及其配套教材评介[J]. 求知导刊, 2017(6):155Chen Zhifeng. Liang Quanting, Physical Optics[J]. Guide to Knowledge, 2017(6): 155 [5] Born M, Wolf E. Principles of optics: electromagnetic theory of propagation, interference and diffraction of light[M]. 7th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013. [6] 徐向东, 洪义麟, 付绍军, 等. X射线波带片的制作及其应用[J]. 光学技术, 1999(2):22-25 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.1999.02.002Xu Xiangdong, Hong Yilin, Fu Shaojun, et al. X ray zone plates fabrication and its application[J]. Optical Technology, 1999(2): 22-25 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.1999.02.002 [7] Suzuki Y, Takeuchi A, Takano H, et al. Performance test of Fresnel zone plate with 50 nm outermost zone width in hard X-ray region[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 44: 1994. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.44.1994 [8] Takeuchi A, Uesugi K, Uesugi M, et al. High-energy X-ray nanotomography introducing an apodization Fresnel zone plate objective lens[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92: 023701. doi: 10.1063/5.0020293 [9] Chao W L, Kim J, Rekawa S, et al. Demonstration of 12 nm resolution Fresnel zone plate lens based soft X-ray microscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(20): 17669-17677. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.017669 [10] Chu Y S, Yi J M, De Carlo F, et al. Hard-X-ray microscopy with Fresnel zone plates reaches 40 nm Rayleigh resolution[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92: 103119. doi: 10.1063/1.2857476 [11] Attwood D. Soft X-rays and extreme ultraviolet radiation: principles and applications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999. [12] Do A, Briat M, Baton S D, et al. Two-channel high-resolution quasi-monochromatic X-ray imager for Al and Ti plasma[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89: 113702. doi: 10.1063/1.5042069 [13] Do A, Troussel P, Baton S D, et al. High-resolution quasi-monochromatic X-ray imaging using a Fresnel phase zone plate and a multilayer mirror[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88: 013701. doi: 10.1063/1.4973296 [14] Guilbaud O, Edwards M, Klisnick A, et al. Near-field imaging of Ni-like silver transient collisional X-ray laser[C]//Soft X-Ray Lasers and Applications V. 2003: 17-28. [15] Rus B, Mocek T, Präg A R, et al. Multi-millijoule, deeply saturated X-ray laser at 21.2 nm for applications in plasma physics[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2002, 44: B207. doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/44/12B/315 -





 下载:
下载: