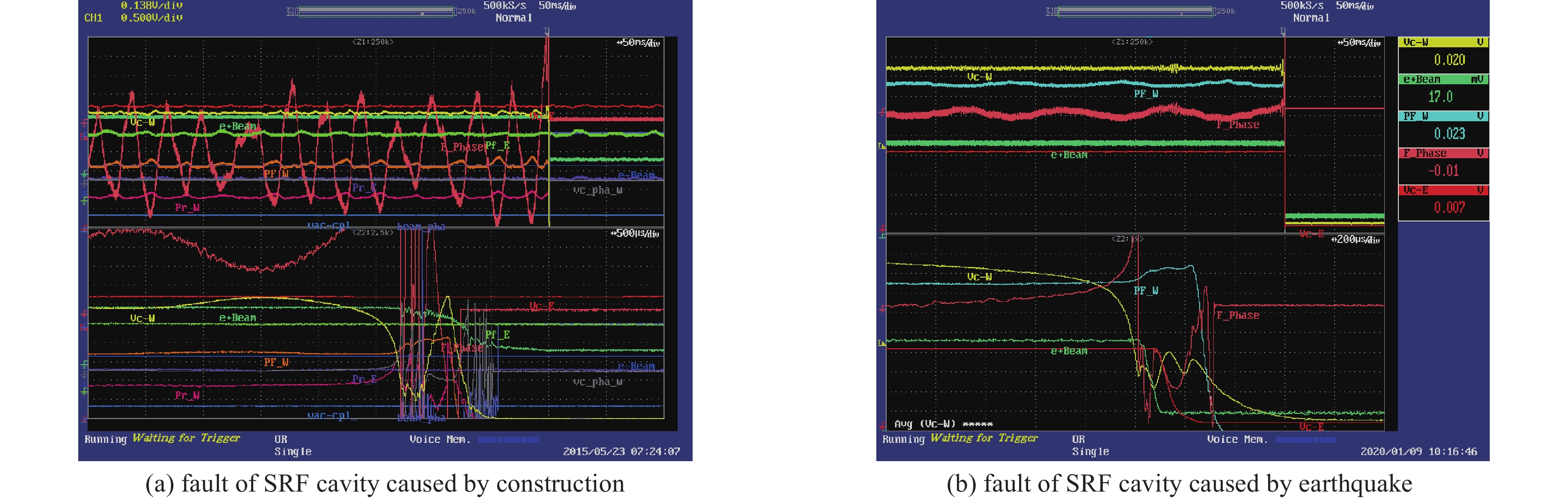
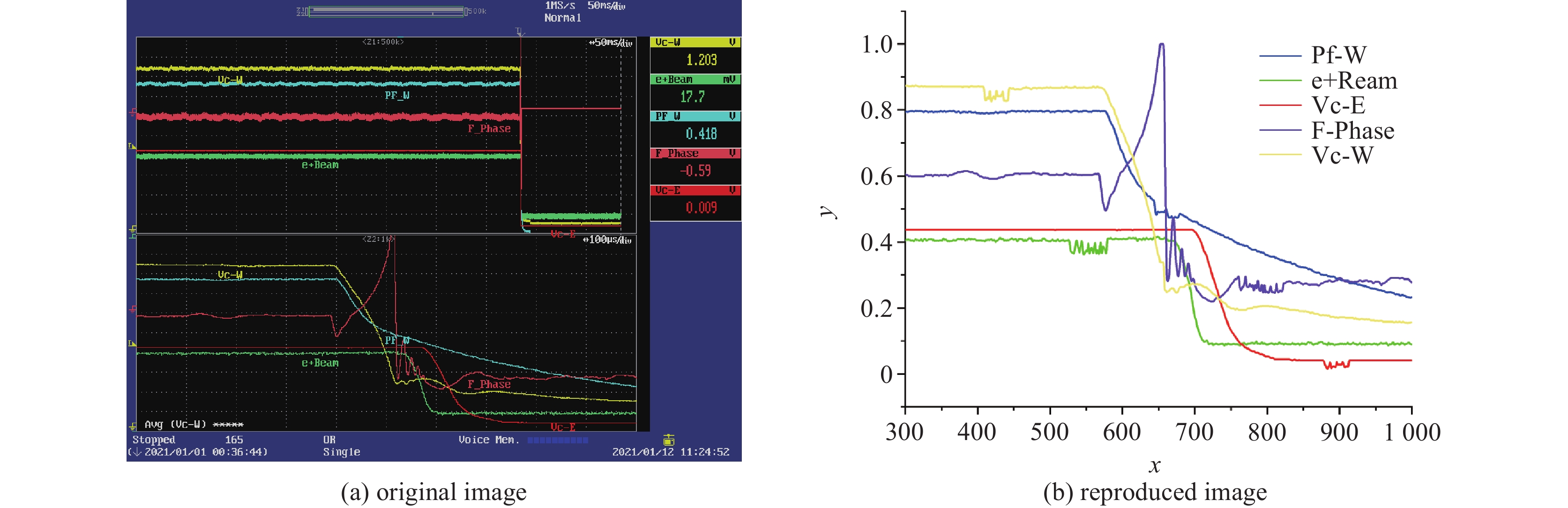
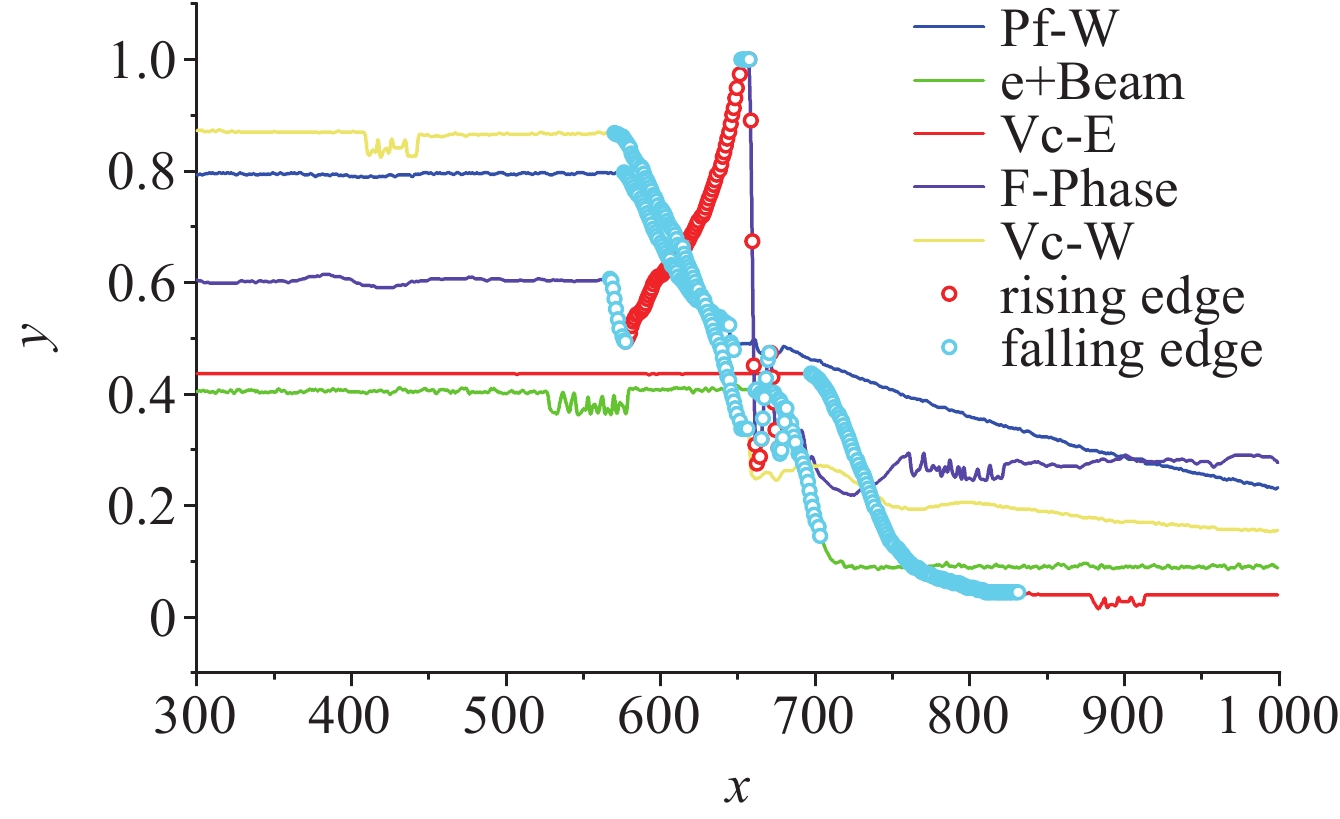
Application of machine learning in BEPCII superconduction radio-frequency cavity fault analysis
-
摘要: 超导腔故障的传统分析方法依赖先验知识,人工和时间成本较高,准确性和一致性较差,并且在处理复杂设备和大量数据时效率较低。机器学习技术能够提高故障分类的准确性和效率,减少主观判断造成的人为误差。研究了基于机器学习算法的超导腔故障分类方法,即,基于BEPCII运行过程中产生的超导腔故障图片数据,通过图片信息提取、特征选择与优化、机器学习算法训练、利用K折交叉验证分析模型准确率与一致性等,实现了对超导腔故障的分类。研究结果表明,随机森林算法、支持向量机与Bagging分类算法在处理故障图片时有更好的分类效果,有监督学习方法的准确性和一致性明显高于无监督学习。研究中实现的故障分类达到了较高的准确率和一致性,有助于快速高效地区分BEPCII超导腔上发生的故障,同时为其他加速器中超导腔故障的诊断提供参考。Abstract: Traditional methods for analyzing superconduction radio-frequency (SRF) cavity faults rely on a priori knowledge, featuring high labor and time costs, poor accuracy and low consistency. They are less efficient when dealing with complex devices and large amounts of data. In this paper, a method for classifying SRF cavity faults based on machine learning algorithms is investigated. Using the SRF cavity fault data generated during the operation of BEPCII, the classification of SRF cavity faults is achieved through image information extraction, feature selection and optimization, machine learning algorithm training, and analyzing the accuracy and consistency of the model via K-fold cross validation. The results of the study show that Random Forest, Support Vector Machine and Bagging algorithms have better classification results when dealing with faulty pictures. The accuracy and consistency of supervised learning methods are significantly higher than those of unsupervised learning. The fault classification realized in this research achieves high accuracy and consistency. It enables to quickly and efficiently distinguish the faults occurring on the SRF cavity of BEPCII. It also provides a reference for the diagnosis of SRF cavity faults in other particle accelerators.
-
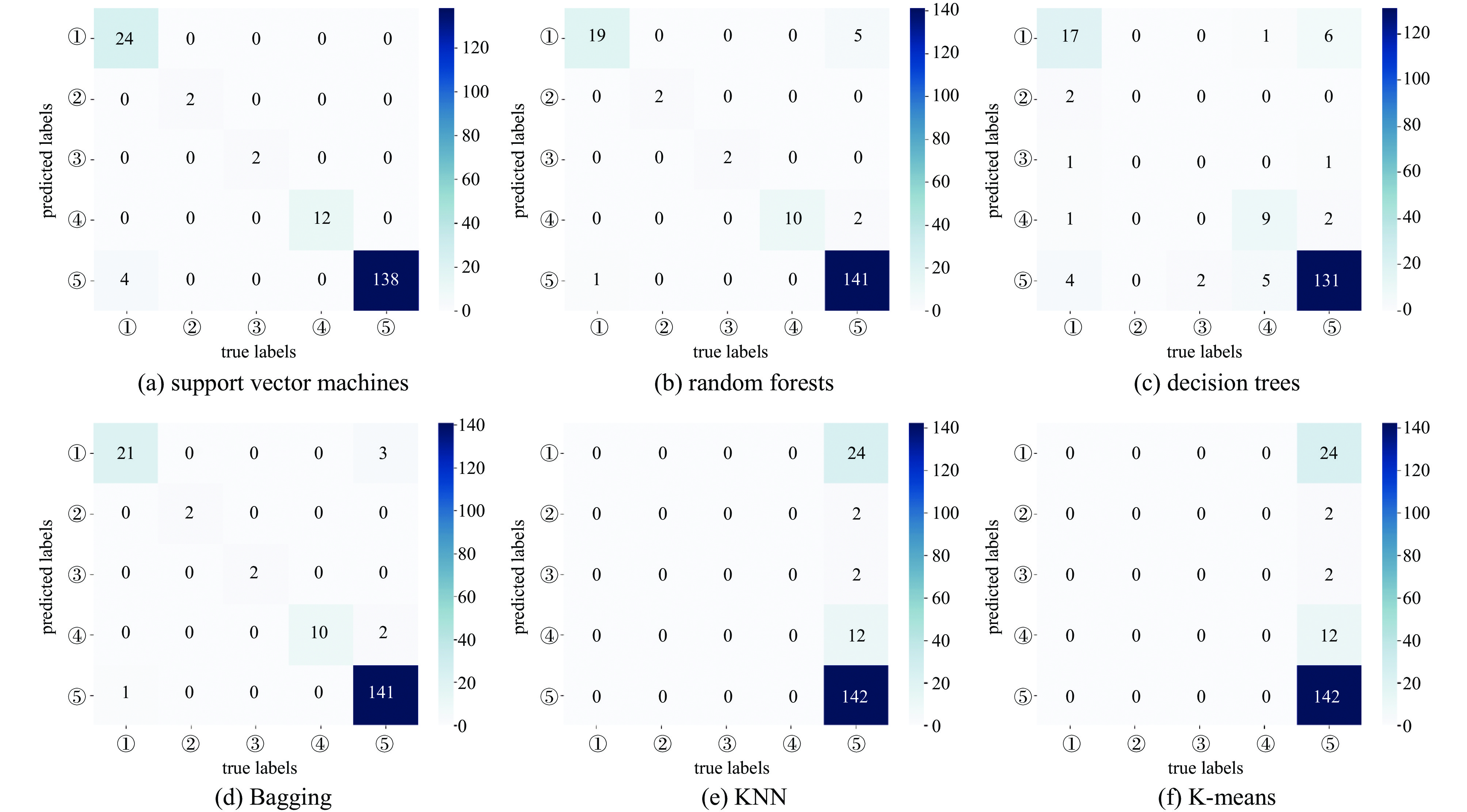
图 6 K折交叉验证后各分类算法的混淆矩阵
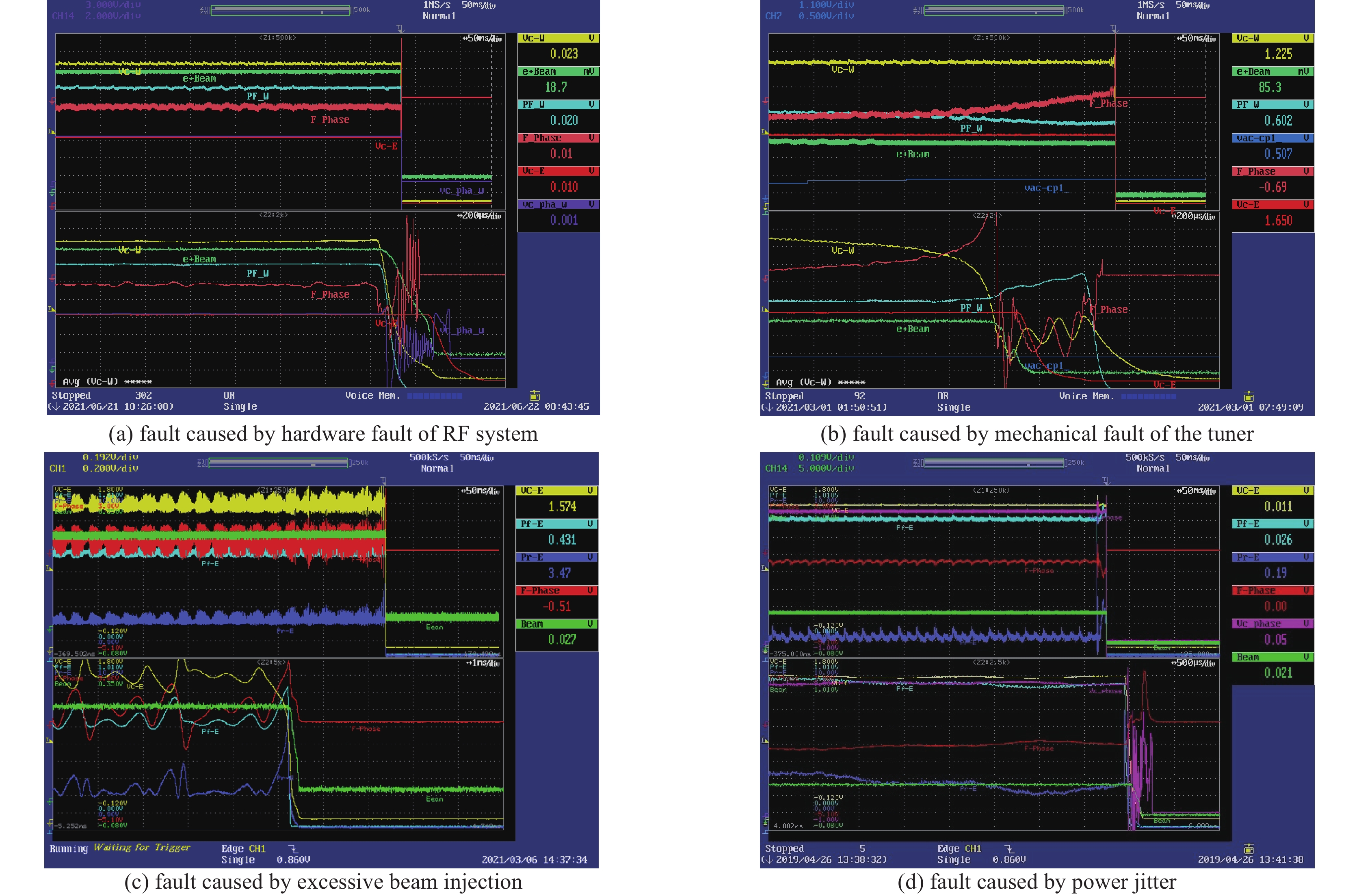
notes: ①—SRF cavity faults caused by failure of RF hardwares ; ②—SRF cavity faults caused by malfunction of the cavity tuner; ③—SRF cavity faults caused by LLRF loop oscillation due to excessive beam injection; ④—SRF cavity faults caused by incident power jitter; ⑤—SRF cavity faults caused by beam loss due to other systems
Figure 6. Confusion matrix for each classification algorithm after K-fold cross-validation
表 1 机器学习算法分类验证精度
Table 1. Validation accuracy of machine learning algorithms
method accuracy/% Kappa coefficient Support Vector Method 96.296 0.913 Random Forest 98.378 0.872 Decision Tree 94.444 0.916 Bagging Classifier 98.148 0.955 K-means 88.235 0.179 K-Nearest Neighbor 86.275 0.385 表 2 BEPCII超导腔故障分类情况
Table 2. Classification of BEPCII SRF cavity faults
method accuracy/% Kappa coefficient Support Vector Method 96.638 0.886 Random Forest 96.722 0.926 Decision Tree 88.893 0.723 Bagging Classifier 95.702 0.933 K-means 77.796 ~0 K-Nearest Neighbor 78.013 ~0 -
[1] 王光伟, 沙鹏, 潘卫民, 等. BEPCII高频系统的建造[J]. 中国物理C, 2008(s1):169-171Wang Guangwei, Sha Peng, Pan Weimin, et al. Construction of the BEPCII RF system[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2008(s1): 169-171 [2] Solopova A, Carpenter A, Powers T, et al. SRF cavity fault classification using machine learning at CEBAF[R]. Newport News: Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF), 2019. [3] Tennant C, Carpenter A, Powers T, et al. Superconducting radio-frequency cavity fault classification using machine learning at Jefferson Laboratory[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2020, 23: 114601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.23.114601 [4] Vidyaratne L, Carpenter A, Powers T, et al. Deep learning based superconducting radio-frequency cavity fault classification at Jefferson laboratory[J]. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 4: 718950. doi: 10.3389/frai.2021.718950 [5] Rahman M M, Iftekharuddin K, Carptenter A, et al. Real-time cavity fault prediction in CEBAF using deep learning[C]//Proceedings of the North American Particle Accelerator Conference. 2022: 687-690. [6] 肖麟阁, 戴建枰, 王群要, 等. BEPCII超导腔失效分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:085105 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190078Xiao Linge, Dai Jianping, Wang Qunyao, et al. Analysis of the failure of BEPCII SRF cavities[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 085105 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190078 [7] 韩晓微. 彩色图像处理关键技术研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2005Han Xiaowei. Study on key technologies of color image processing[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2005 [8] 戴聪聪, 罗小燕, 邵凡, 等. 基于CEEMDAN和AR模型的岩体声发射信号特征提取方法研究[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2018, 47(6):20-24Dai Congcong, Luo Xiaoyan, Shao Fan, et al. Study on extraction method of rock acoustic emission signals based on CEEMDAN and AR model[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2018, 47(6): 20-24 [9] Das K, Behera R N. A survey on machine learning: concept, algorithms and applications[J]. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, 2017, 5(2): 1301-1309. [10] 李小斌, 李世银. AdBagging: 自适应抽样参数在线装袋算法[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2011, 32(12):4095-4099Li Xiaobin, Li Shiyin. AdBagging: adaptive sampling parameters online bagging algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2011, 32(12): 4095-4099 [11] 孔英会, 车辚辚, 苑津莎, 等. 基于小波分解和数据挖掘中决策树算法的电能质量扰动识别方法[J]. 电网技术, 2007, 31(23):78-82Kong Yinghui, Che Linlin, Yuan Jinsha, et al. A power quality disturbance identification method based on wavelet decomposition and decision tree algorithm in data mining[J]. Power System Technology, 2007, 31(23): 78-82 [12] 孙吉贵, 刘杰, 赵连宇. 聚类算法研究[J]. 软件学报, 2008, 19(1):48-61Sun Jigui, Liu Jie, Zhao Lianyu. Clustering algorithms research[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2008, 19(1): 48-61 [13] 张宁, 贾自艳, 史忠植. 使用KNN算法的文本分类[J]. 计算机工程, 2005, 31(8):171-172,185Zhang Ning, Jia Ziyan, Shi Zhongzhi. Text categorization with KNN algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering, 2005, 31(8): 171-172,185 [14] James G, Witten D, Hastie T, et al. An introduction to statistical learning[M]. New York: Springer, 2013: 180-182. [15] Foody G M. Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2002, 80(1): 185-201. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(01)00295-4 [16] Veropoulos K, Campbell I C G, Cristianini N. Controlling the sensitivity of support vector machines[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on AI. 1999: 55-60. -




 下载:
下载: