Analysis based on simulation of kicker working at high repetition frequency with transmission line structure
-
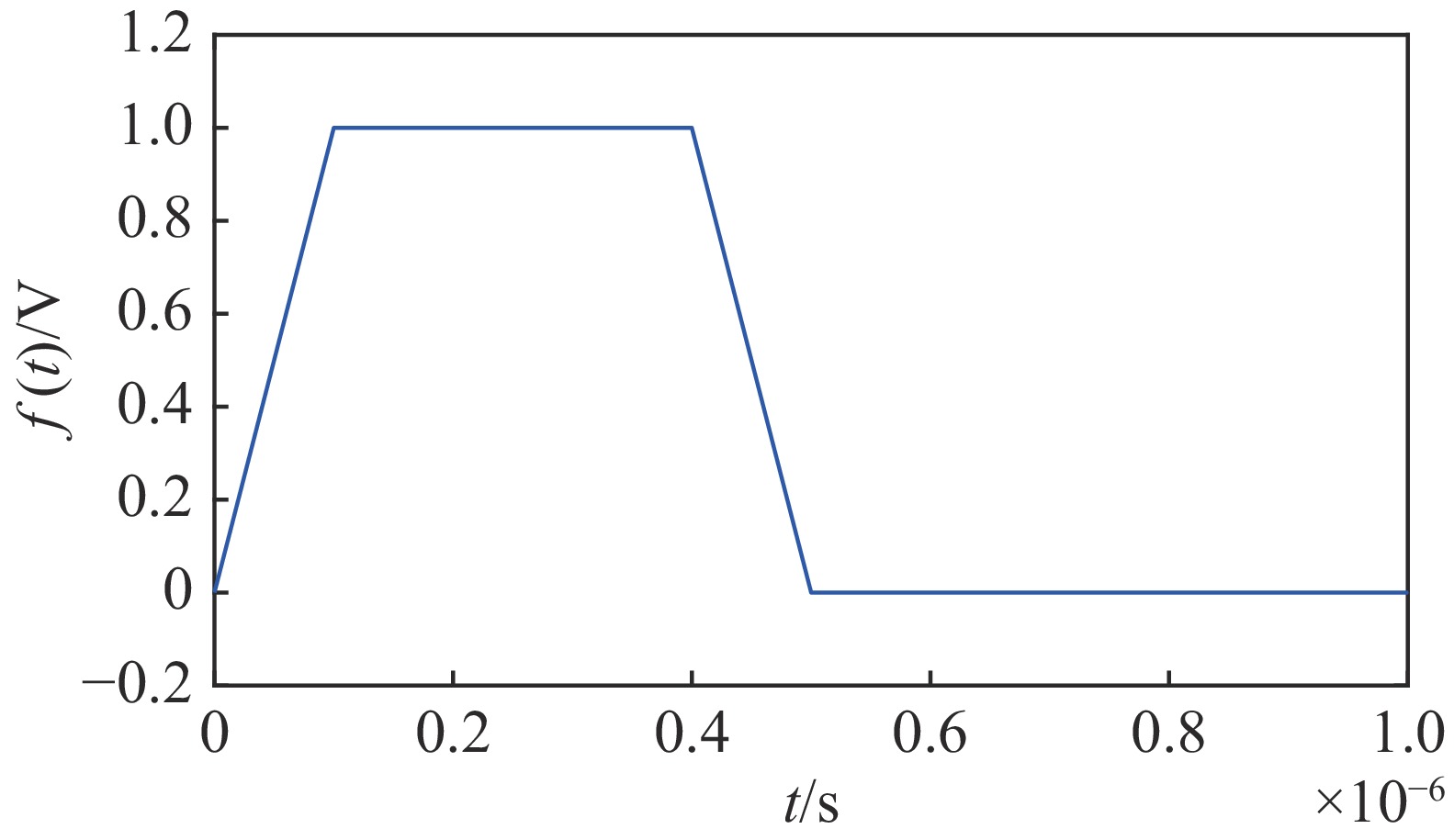
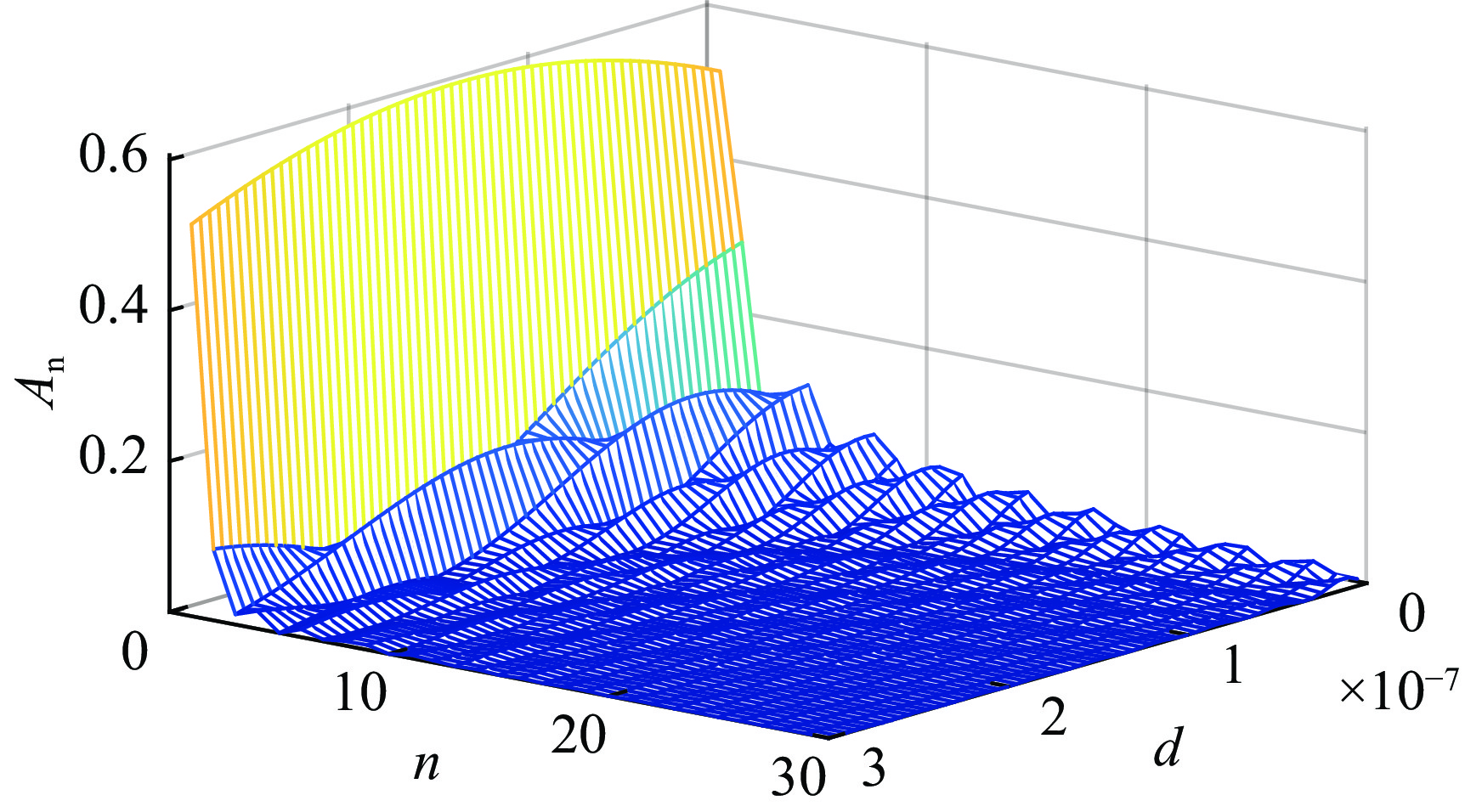
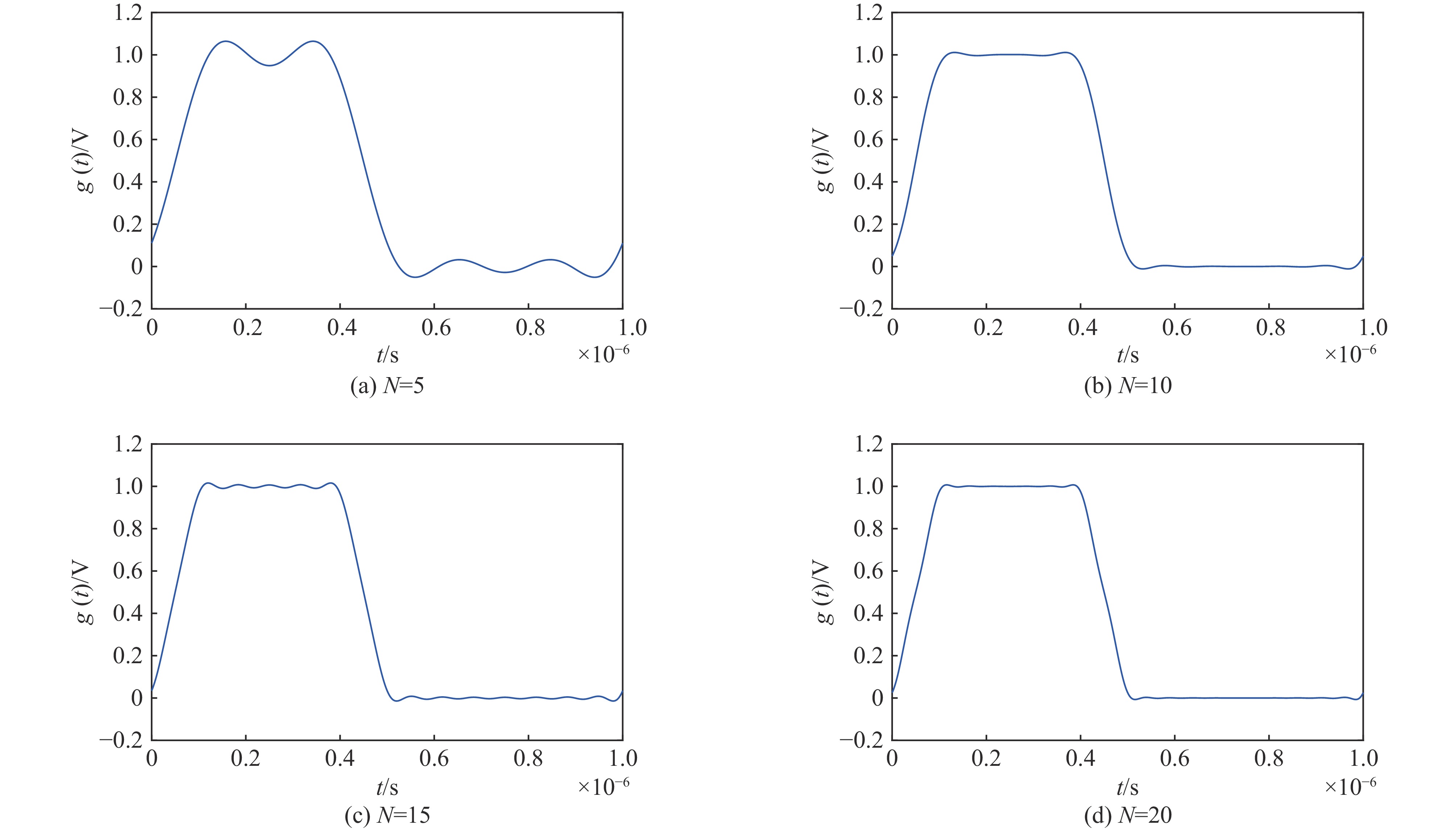
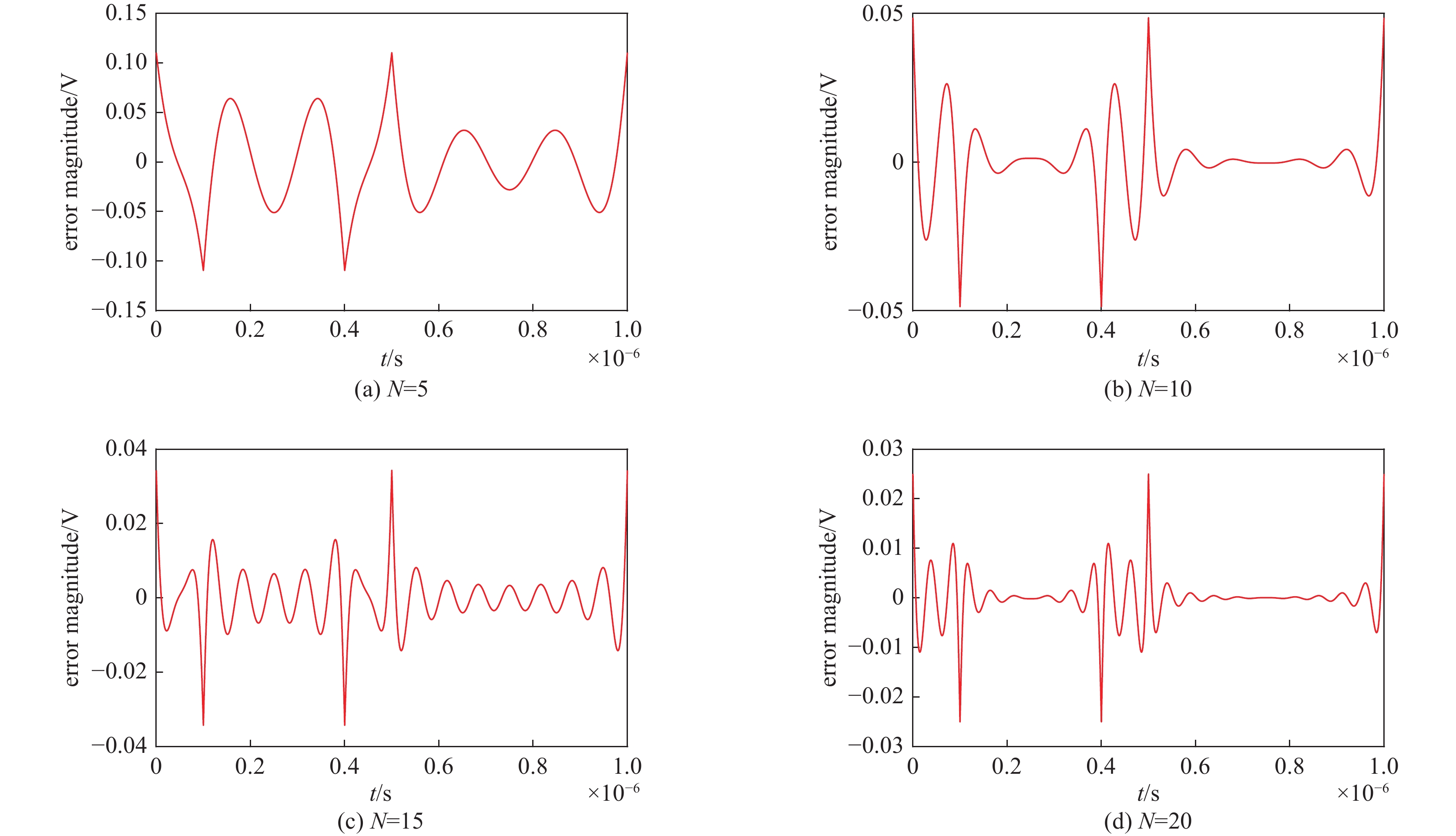
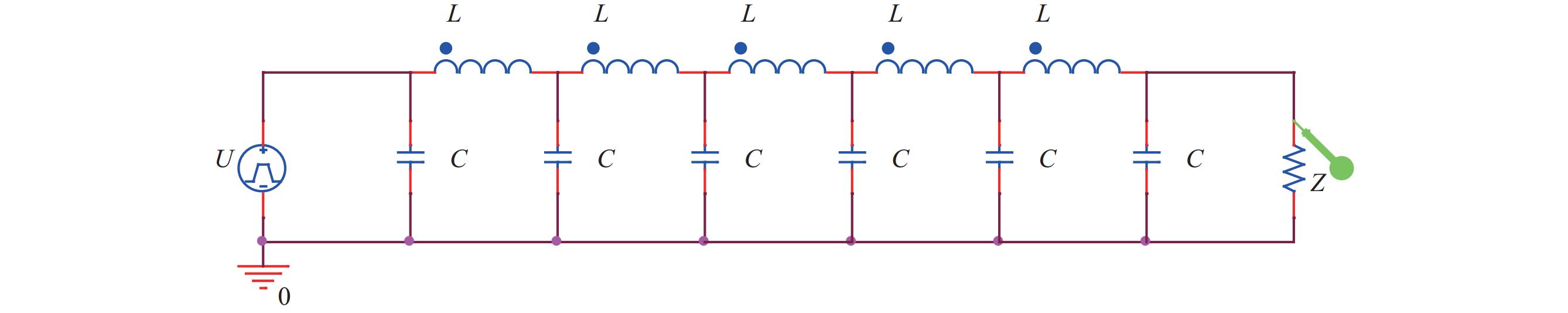
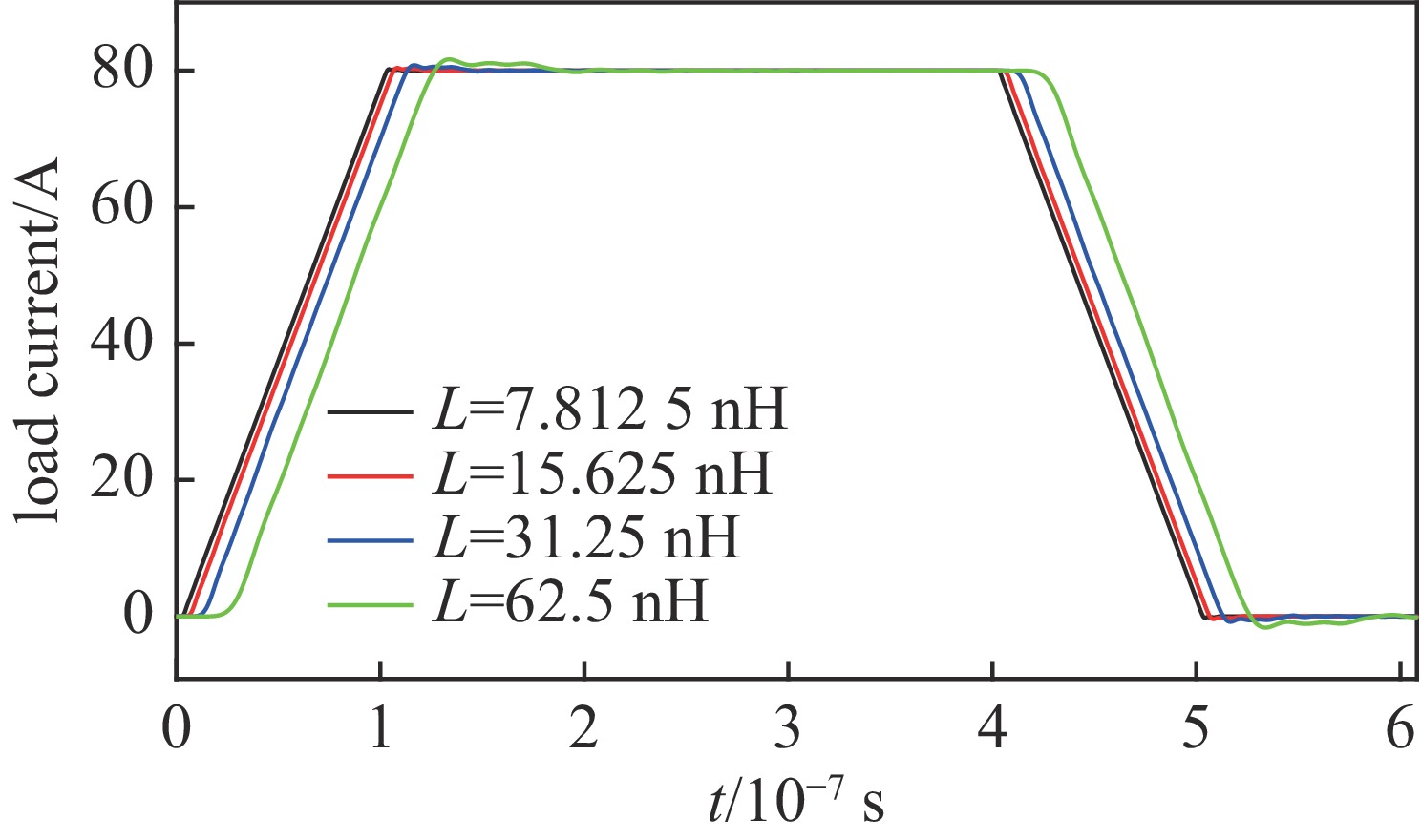
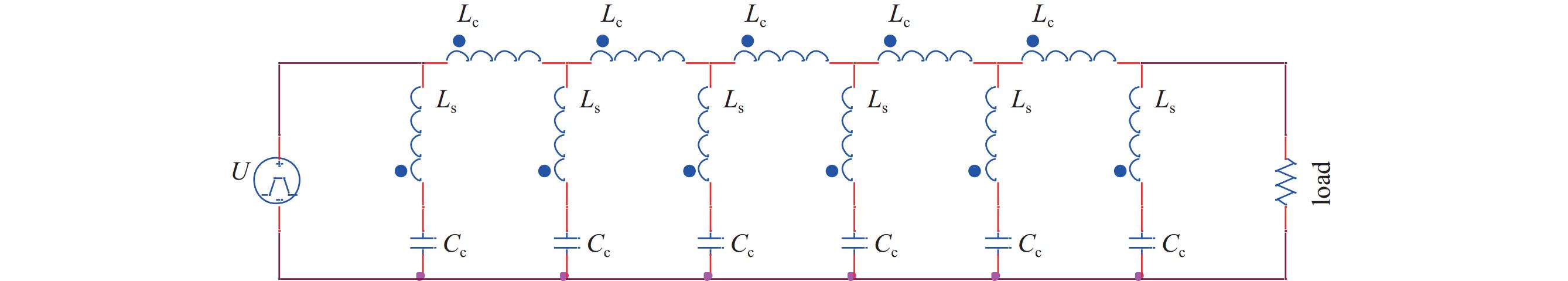
摘要: 深圳中能高重复频率X射线自由电子激光(S3FEL)需要MHz的高重复频率高稳定性冲击磁铁(Kicker)系统,传输线结构冲击磁铁系统是实现高重复频率的有效途径。但传输线结构冲击磁铁的波形稳定性不足限制了该类型冲击磁铁在大型粒子加速器中的应用。为改善上述不足,基于传输线结构冲击磁铁的输入波形和电路结构参数开展了研究,利用傅里叶分析等数学工具分析了影响冲击磁铁工作波形稳定性的主要因素,揭示了冲击磁铁理想波形的谐波次数与传输线结构冲击磁铁截止频率之间的关系。在此基础上,提出一种减小冲击磁铁实际波形与理想波形偏差的方法。该方法通过调整冲击磁铁输入波形参数或者传输线结构冲击磁铁截止频率,在一定范围内可以获得冲击磁铁理想的工作波形。为验证上述关系,用电路仿真软件对冲击磁铁不同工作波形和不同电路参数进行了仿真。仿真结果证实了上述关系且验证了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: Shenzhen’s medium-energy high-repetition-rate X-ray free electron laser (Shenzhen Superconducting Soft X-ray Free Electron Laser, S3FEL) requires 1 MHz high-repetition-rate and high-stability kicker. Transmission line structure kicker is an effective way to achieve high repetition rate. However, the insufficient waveform stability of the transmission line structure kicker limits the application of this type of kicker in large particle accelerators. To solve the above problem, this paper studies the input waveform and circuit structure parameters of the transmission line structure kicker. It analyzes the main factors affecting the stability of kicker’s working waveform using mathematical tools such as Fourier analysis, and reveals the relationship between the harmonic order of kicker ideal waveform and the cut-off frequency of kicker transmission line structure. On this basis, this paper proposes a method to reduce the deviation between the actual waveform and the ideal waveform of kicker. This method can obtain the ideal working waveform of kicker within a certain range by adjusting the input waveform parameters or the cut-off frequency of kicker. To verify the above relationship, this paper uses circuit simulation software to simulate different waveforms and different circuit parameters of kicker. The simulation results verify that the above relationship revealed and confirm the effectiveness of the method mentioned.
-
Key words:
- transmission line structure /
- kicker /
- high repetition rate /
- Fourier series /
- cut-off frequency
-
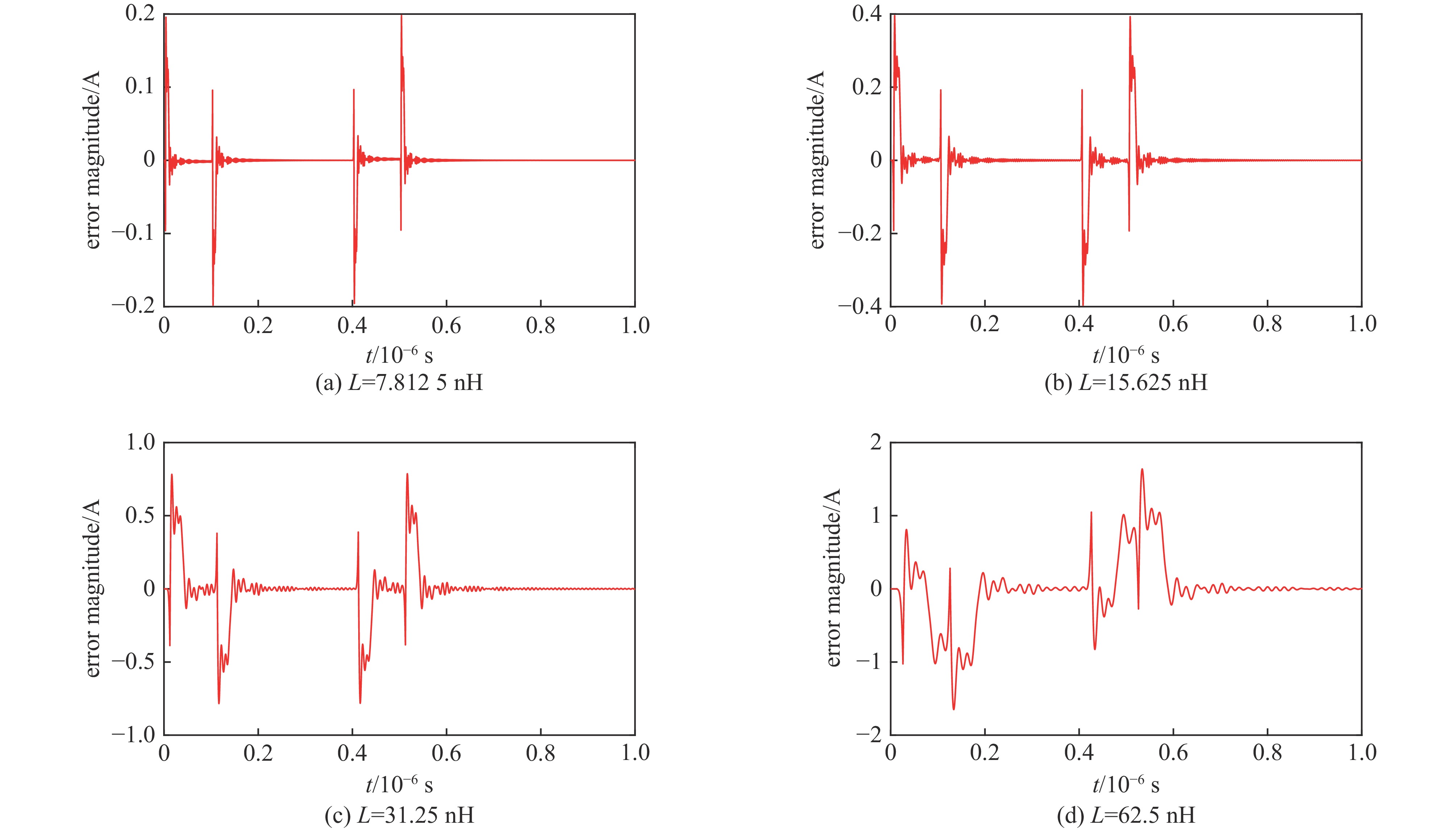
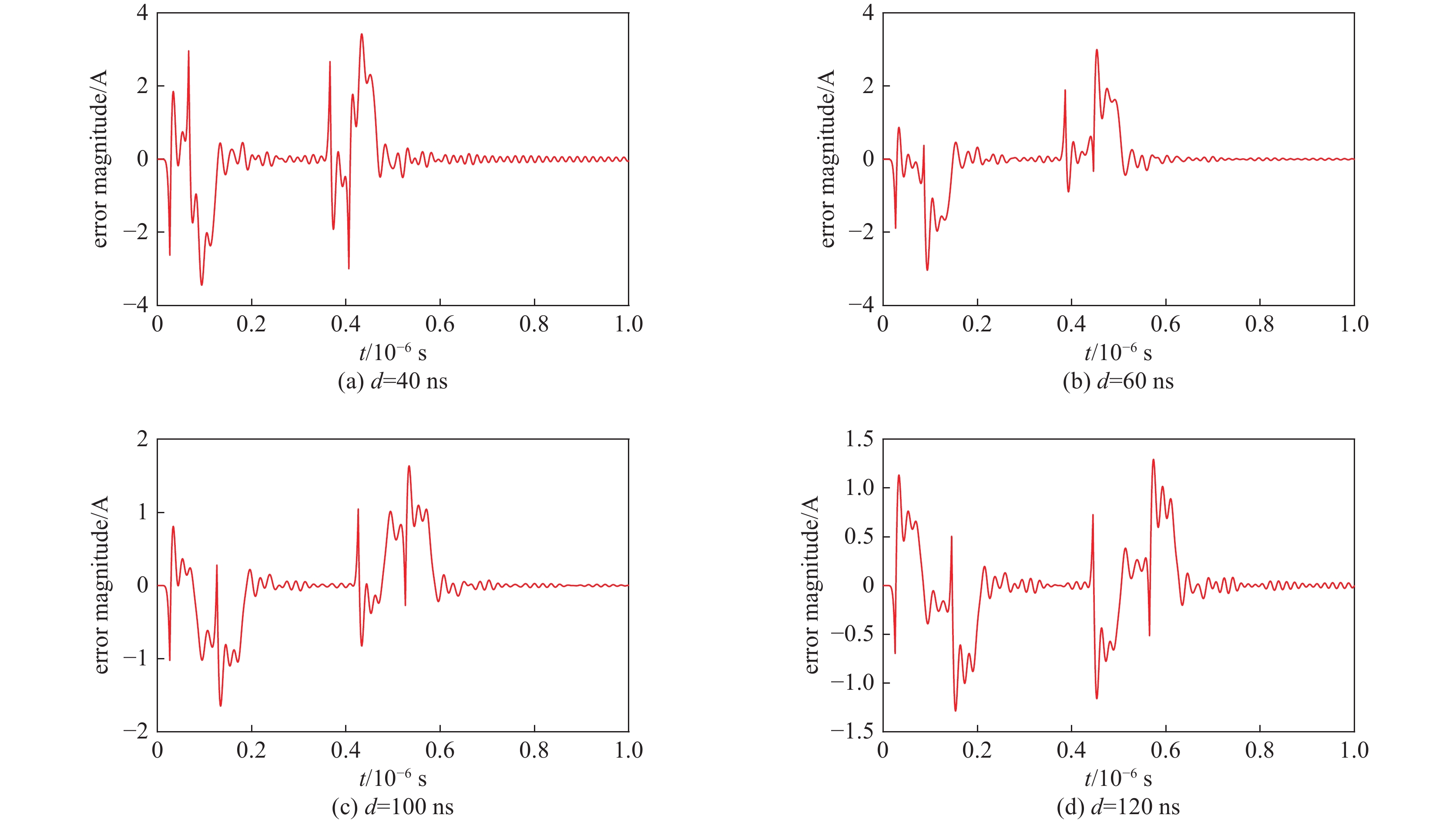
表 1 d=100 ns时,不同L的脉冲电流平顶稳定性
Table 1. Flat-top stability of pulse current when d=100 ns, L has different values
L/nH standard deviation time range of error data/µs 7.8125 0.000292 0.2-0.4 15.625 0.001918 0.203-0.403 31.25 0.006951 0.209-0.409 62.5 0.04593 0.222-0.422 表 2 L=
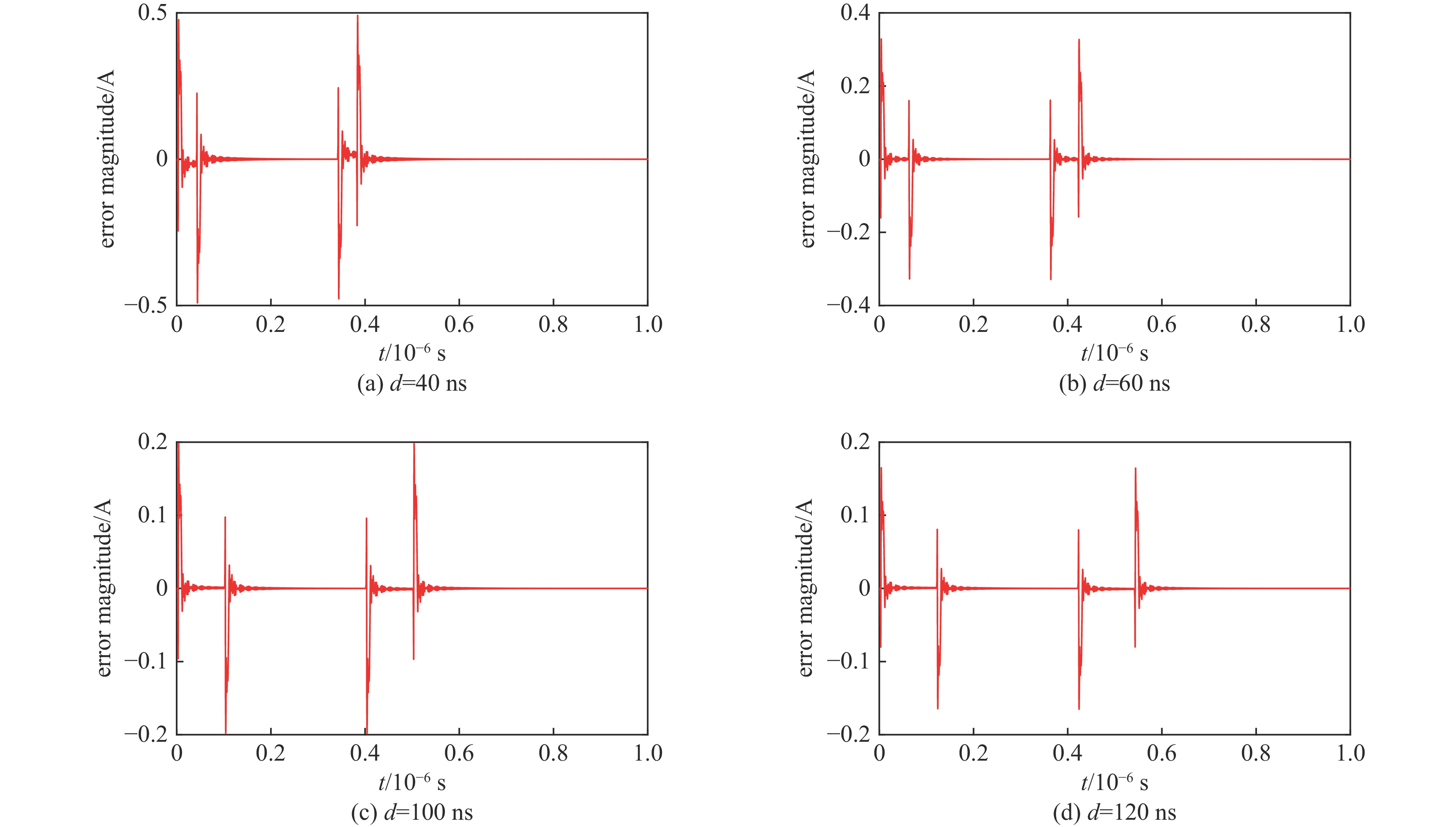
7.8125 nH时,不同d的脉冲电流平顶稳定性Table 2. The flat-top stability of pulse current when L=
7.8125 nH, d is 40, 60, 100, 120 nsd/ns standard deviation time range of error data/µs 40 0.001007 0.14-0.34 60 0.000417 0.16-0.36 100 0.000292 0.2-0.4 120 0.00025 0.22-0.42 表 3 L=62.5 nH时,不同d的脉冲电流平顶稳定性
Table 3. Flat-top stability of pulse current when L=62.5 nH, d is 40, 60, 100, 120 ns
d/ns standard deviation time range of error data/µs 40
600.148448 0.098411 0.14-0.34
0.16-0.36100 0.049833 0.2-0.4 120 0.04615 0.22-0.42 -
[1] Ducimetière L. Advances of transmission line kicker magnets[C]//Proceedings of the 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2005: 235-239. [2] Lin Munan, Wu Y W, Huang L S, et al. Fast injection and extraction kicker system design for High rEpetition rate Muon Source at CSNS[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2021, 16: P08010. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/16/08/P08010 [3] Barnes M J, Ducimetière L, Fowler T, et al. Injection and extraction magnets: kicker magnets[C]//Proceedings of the CERN Accelerator School CAS 2009: Specialised Course on Magnets. 2009: 141-166. [4] Beukers T, Nguyen M, Tang Tao. Discrete element transmission line beam spreader kickers for LCLS-II[C]//2018 IEEE International Power Modulator and High Voltage Conference (IPMHVC). 2018: 151-155. [5] Armenta R B, Barnes M J, Blackmore E W, et al. Design concept for AGS injection kicker upgrade to 2 GeV[C]//Proceedings of the 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2005: 1380-1382. [6] Armenta R B, Barnes M J, Blackmore E W, et al. Electromagnetic modeling of the AGS A10 injection kicker magnet[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2006, 16(2): 293-296. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2005.864458 [7] Barnes M J, Wait G D. Low power measurements on an AGS injection kicker magnet[C]//2007 IEEE Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC). 2007: 2188-2190. [8] Fukuoka S, Fan K, Ishii K, et al. Development of a fast compensation kicker system for J-PARC main-ring injection[C]//Proceedings of IPAC 2013. 2013: 684-686. [9] Fan K, Ishii K, Fukuoka S, et al. Ferrite property effects on a fast kicker magnet[C]//Proceedings of the 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Nagoya, 2013). 2013: 845-847. [10] 吴官健, 王磊, 王冠文, 等. 环形正负电子对撞机注入引出分布参数型冲击磁铁设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35:054002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220364Wu Guanjian, Wang Lei, Wang Guanwen, et al. Design of injection and extraction delay-line kicker magnet for circular electron-positron collider[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 054002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220364 [11] Schröder G. Fast pulsed magnet systems[M]//Chao A W, Tigner M. Handbook of Accelerator Physics and Engineering. Geneva: World Scientific Press, 1999: 460-466. [12] Chmielińska A, Barnes M J. Helical beam screen for the Future Circular Collider for hadrons injection kicker magnets[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2020, 23: 041002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.23.041002 [13] Ohkawa T, Chiba Y, Wakasugi M. Development of the kicker magnet for muses[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2005, 547(2/3): 287-293. [14] Barnes M J, Wait G D. Comparison of measured and predicted inductance per cell for a travelling wave kicker magnet[C]//Proceedings of the 5th European Particle Accelerator Conference. 1996: 2588-2590. [15] 刘超, 尚雷, 刘祖平, 等. 冲击磁铁脉冲发生器技术分析[J]. 高电压技术, 2008, 34(3):480-483Liu Chao, Shang Lei, Liu Zuping, et al. Technology of pulse generators for kicker magnets[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2008, 34(3): 480-483 [16] Shinde R S, Pareek P, Gaud V, et al. Studies of prototype transmission line extraction kicker magnet for booster synchrotron[C]//Proceeding of InPAC-2011: DAE-BRNS Indian Particle Accelerator Conference. 2011. -




 下载:
下载: