Study on resistance to high current electron beam bombardment of different types of graphite
-
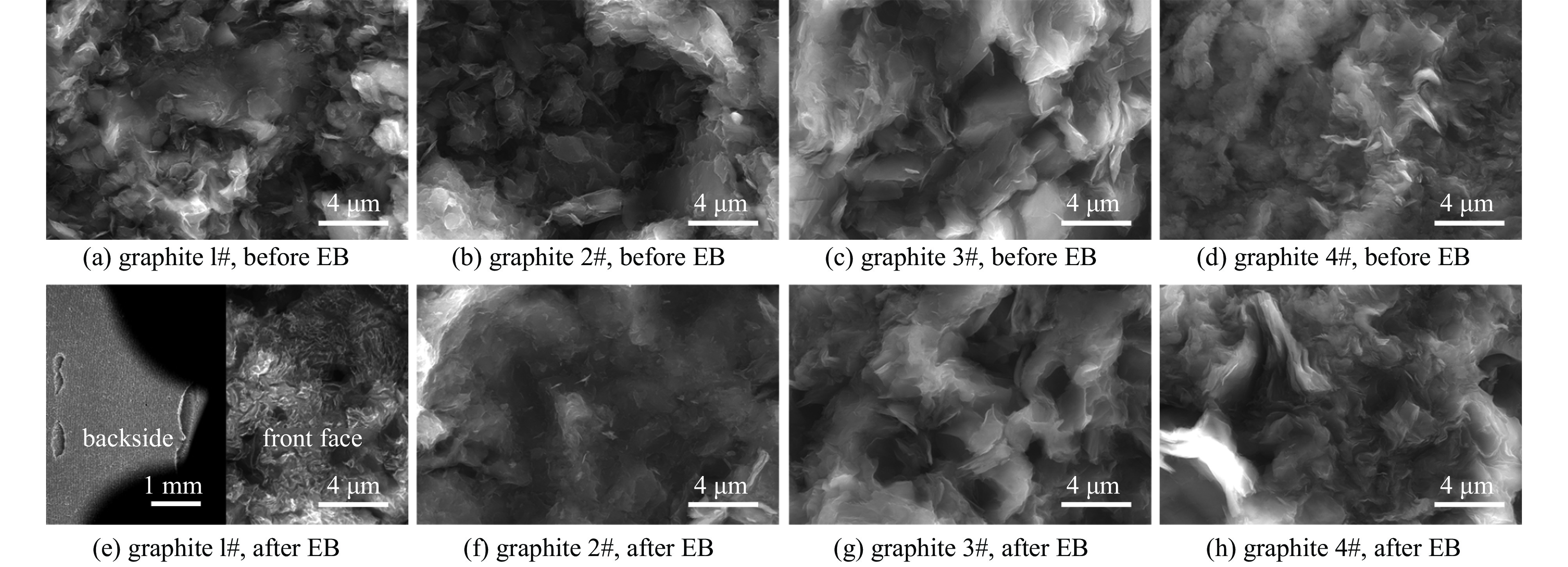
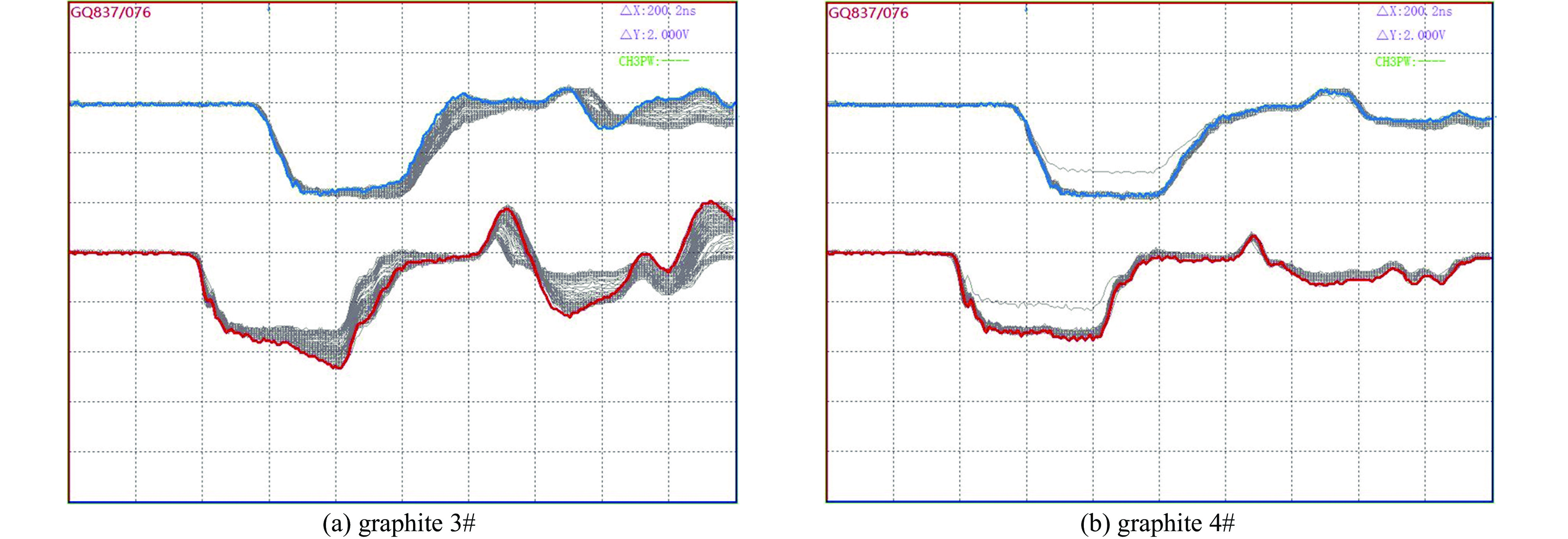
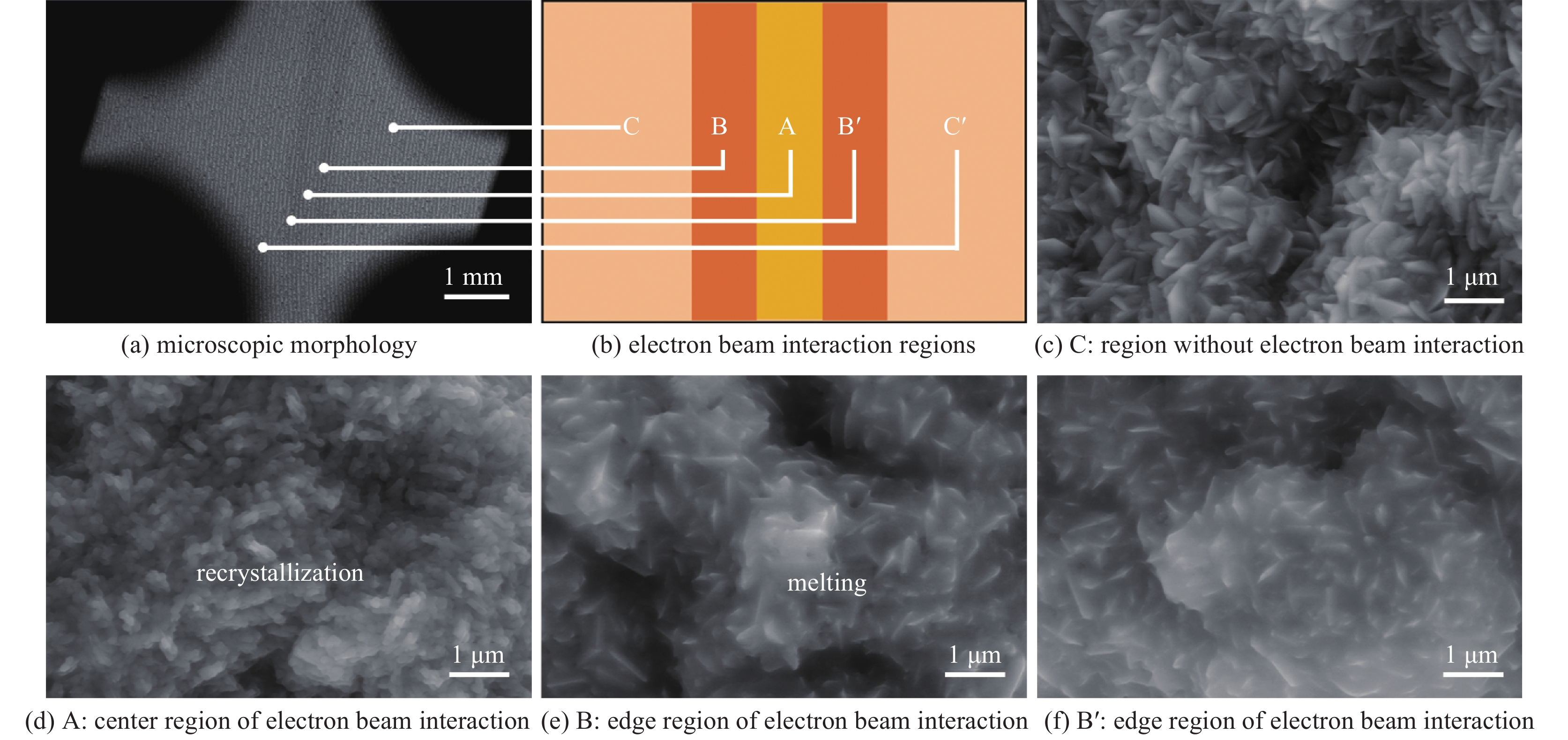
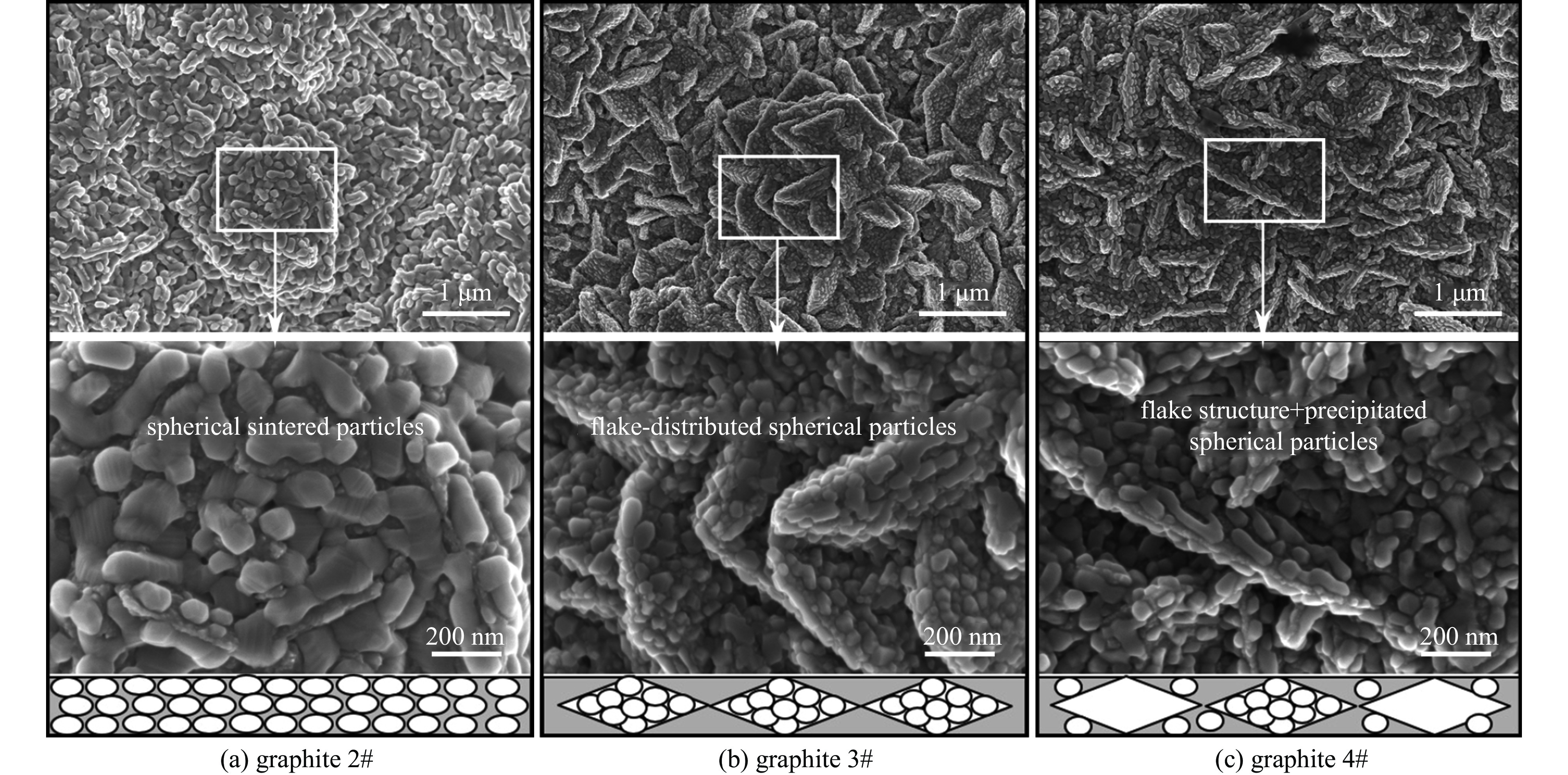
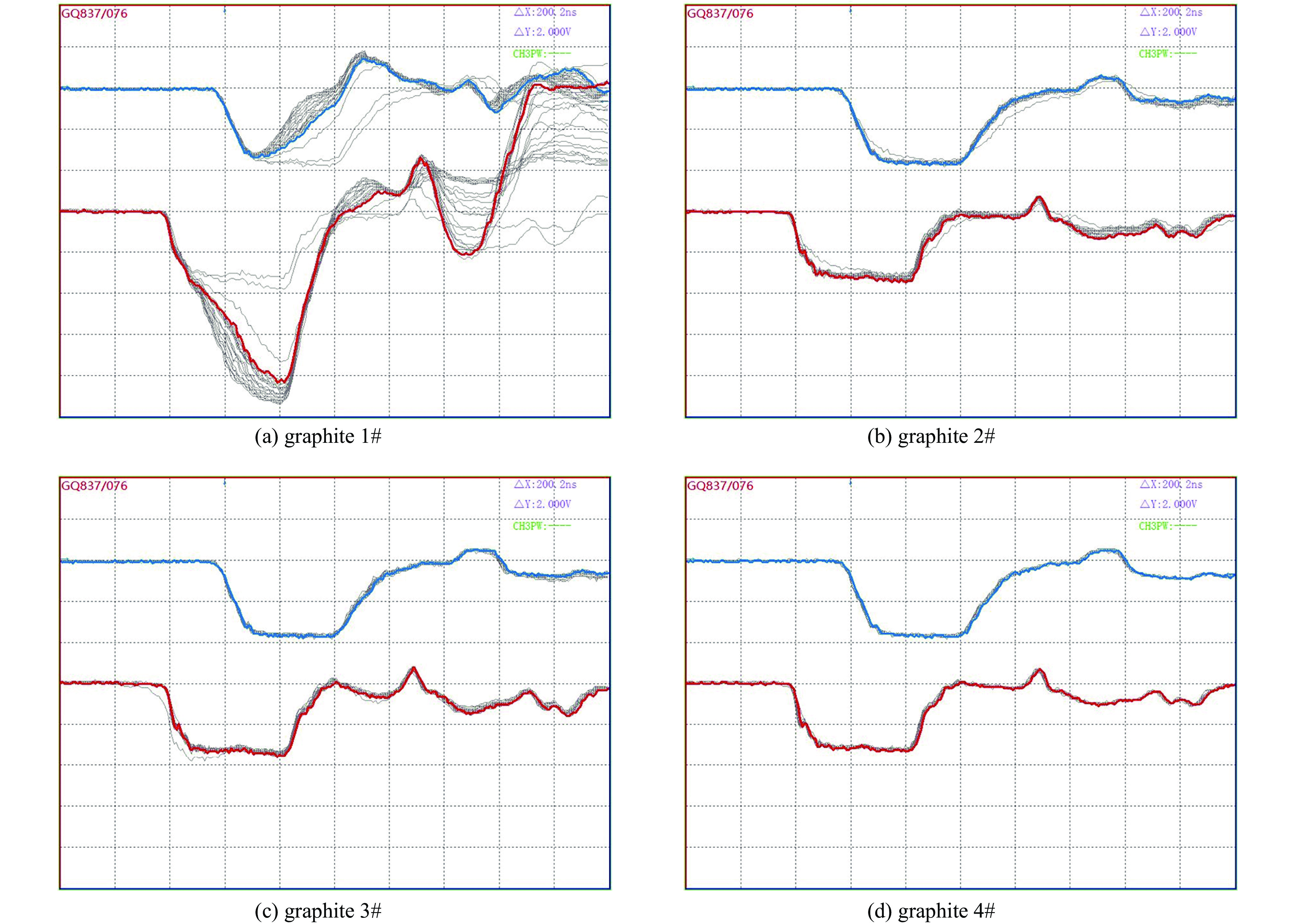
摘要: 石墨因组成元素的原子序数较低、熔点极高、导热性能优异、化学稳定性高及抗热冲击能力较强等诸多优点, 已成为相对论返波管中关键部件收集极的首选材料。对4种具有代表性的高纯石墨及其各自碳化钛涂层改性材料作为强流电子束二极管中的阳极进行了耐强流电子束轰击性能考核。结果表明,4种石墨在电压为860 kV、电流为11 kA、脉宽为40 ns的电子束轰击下二极管的电流表现出明显的差异,石墨4#即使电子束脉冲作用167次,电流曲线也未表现出明显异常,而其他三种石墨的电流曲线均出现不同程度的尾蚀。通过石墨表面碳化钛涂层的烧蚀实验进一步验证了石墨的差异性,表明石墨的热导率对其抗烧蚀性能具有重要的影响。石墨的热导率越高,碳化钛熔融析出再结晶程度越低,说明石墨的抗烧蚀性能越好。石墨4#具有优异的耐电子束轰击性能,在相对论返波管收集极领域具有重要的应用前景。Abstract: In this paper, four typical types of high purity graphite and their titanium carbide coating modified materials were tested as anodes in high current electron beam diodes. The results show that the currents of the diodes were obviously different when the graphite anodes were under electron beam bombardment with voltage 860 kV, current 11 kA and pulse width 40 ns. The current curve for graphite 4# was normal even after interaction of 167 electron pulses while the other graphite current curves showed different degrees of tail erosion. The ablative experiments of titanium carbide coating on graphite further verified the difference of the graphite, indicating that the thermal conductivity of graphite has an important effect on its ablative resistance. The higher the thermal conductivity of graphite, the lower the degree of recrystallization of titanium carbide, the better the corrosion resistance of graphite. Therefore, graphite 4# has an excellent resistance to electron beam bombardment and would be promising for application as collector materials in relativistic traveling wave tubes.
-
Key words:
- collector /
- graphite /
- electron beam bombardment /
- titanium carbide coating /
- thermal conductivity
-
表 1 不同型号石墨的物理参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of different graphite
type density/
(g·cm−3)resistivity/
(10−5 Ω·m)bending
strength/MPacompressive
strength/MPathermal expansion
coefficient/(10−6 K−1)thermal conductivity/
(W·m−1·K−1)graphite 1# 1.89 1.88 72 147 8.09 70 graphite 2# 1.91 1.46 80 160 5.50 65 graphite 3# 1.84 1.76 100 148 5.25 95 graphite 4# 1.91 1.18 85 140 5.11 120 表 2 不同石墨物理参数的影响
Table 2. Effects of physical parameters of different graphite
influencing factor reference graphite type
(resistance to electron beam bombardment)whether it is main
influencing factorinfluence 1#
(poor)2#
(medium)3#
(good)4#
(excellent)density √ √ √ √ no ― resistivity ― √ √ ― no ― bending strength √ √ ― √ no ― compressive strength √ ― √ √ no ― thermal expansion coefficient √ √ √ √ yes the greater coefficient of thermal expansion,
the greater risk of particle sheddingthermal conductivity ― √ √ √ yes the higher thermal conductivity, the better
resistance to electron beam bombardment -
[1] Chen Y, Mankowski J, Walter J, et al. Cathode and anode optimization in a virtual cathode oscillator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2007, 14(4): 1037-1044. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2007.4286545 [2] 陈昌华, 刘国治, 宋志敏, 等. 引导磁场对相对论返波管微波功率的影响[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2000, 12(6):745-748Chen Changhua, Liu Gouzhi, Song Zhimin, et al. Effects of axial guiding magnetic field on microwave power of relativistic backward oscillators[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2000, 12(6): 745-748 [3] 陈昌华, 刘国治. 相对论返波管导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021Chen Changhua, Liu Gouzhi. Introduction to relativistic backward wave oscillator[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021 [4] Tan Nongchao, Wu Ping, Hua Ye, et al. Mechanism of radio frequency breakdown on metal surfaces in relativistic backward wave oscillator[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2021, 28: 022107. doi: 10.1063/5.0035386 [5] 夏文锋, 张冬晓, 刘启晨, 等. 一种新型高功率轻小型化脉冲驱动源研制[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14:030506Xia Wenfeng, Zhang Dongxiao, Liu Qichen, et al. A novel lightweight and miniaturized high power pulse drive source[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 030506 [6] Parson J, Dickens J, Walter J, et al. Gas evolution of nickel, stainless steel 316 and titanium anodes in vacuum sealed tubes[C]//2012 IEEE International Power Modulator and High Voltage Conference. 2012: 239-240. [7] Roy A, Menon R, Mitra S, et al. Plasma expansion and fast gap closure in a high power electron beam diode[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2009, 16: 053103. doi: 10.1063/1.3129802 [8] 霍少飞, 孙钧, 梁玉钦, 等. 不锈钢电子束收集极的损伤能量密度阈值[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:063008 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.063008Huo Shaofei, Sun Jun, Liang Yuqin, et al. Damage threshold of energy density of stainless steel electron beam collector[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 063008 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.063008 [9] 谭维兵, 李小泽, 李爽, 等. 永磁约束二极管阳极管头轰击现象研究[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14:040508 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2023.040508Tan Weibing, Li Xiaoze, Li Shuang, et al. Bombardment mark on the anode head of diode under permanent magnetic field[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 040508 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2023.040508 [10] 华叶. 碳化物改性石墨材料的强流电子束发射和收集特性研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2019Hua Ye. Research on the emission and collection characteristics of intense electron beams for carbide modified graphite materials[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2019 [11] He Juntao, Cao Yibing, Zhang Jiande, et al. Effects of intense relativistic electron beam on the microwave generation in a foilless low-impedance transit-time oscillator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2012, 40(6): 1622-1631. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2012.2192484 [12] Shiffler D, Nation J A, Schachter L, et al. A high-power two stage traveling-wave tube amplifier[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1991, 70(1): 106-113. doi: 10.1063/1.350322 [13] Chen Changhua, Tang Yunsheng, Liu Wenyuan, et al. Resistance to intense electron beam bombardment of TiC/Graphite: numerical modeling and experimental investigation[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(1): 361-366. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.141 [14] 唐运生, 陈昌华, 刘文元, 等. 沉积温度对TiC涂层微观形貌及导电性能的影响[J]. 现代应用物理, 2020, 11:020801 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2020.020801Tang Yunsheng, Chen Changhua, Liu Wenyuan, et al. Effect of deposition temperature on morphology and conductivity of TiC coatings[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2020, 11: 020801 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2020.020801 [15] Shulov V A, Engelko V I, Mueller G, et al. Mechanisms of element redistribution into the surface layer of refractory alloy parts during their irradiation by intense pulsed electron beams[C]//2004 International Conference on High-Power Particle Beams. 2004: 647-650. [16] Nusinovich G S, Kashyn D G, Antonsen T M. Effect of metallic dust on operation of repetition-rate high-power microwave devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2011, 39(8): 1680-1683. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2011.2154346 [17] Zhou Yichun, Duan Zhuping, Yang Qibing. Thermal shock wave and spall fracture caused by an electron beam[J]. Natural Science Journal of Xiangtan University, 1997, 19(2): 117-128. [18] Wong B T, Mengüç M P, Vallance R R. Thermal conduction induced by electron-beam[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, 50(25/26): 5099-5107. [19] Nishikawa S, Sawada M, Marukawa Y, et al. Thermal erosion of graphite by pulsed electron beam[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1991, 179/181: 176-179. doi: 10.1016/0022-3115(91)90055-C [20] Robin J E, Srivastava R D. High-energy electron-beam deposition onto a hot graphite surface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1973, 22(4): 153. doi: 10.1063/1.1654592 [21] 谌继明, 刘翔, 肖征贤, 等. 掺杂石墨在高能激光束和电子束作用下的热冲击行为[J]. 核科学与工程, 2002, 22(1):47-52 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-0918.2002.01.009Chen Jiming, Liu Xiang, Xiao Zhenxian, et al. Thermal shock behavior of doped graphites tested by high energy laser beam and electron beam[J]. Chinese Journal of Nuclear Science and Engineering, 2002, 22(1): 47-52 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-0918.2002.01.009 -




 下载:
下载: