Design of a miniaturized high-isolation dual-frequency antenna based on quarter-mode substrate integrated waveguide
-
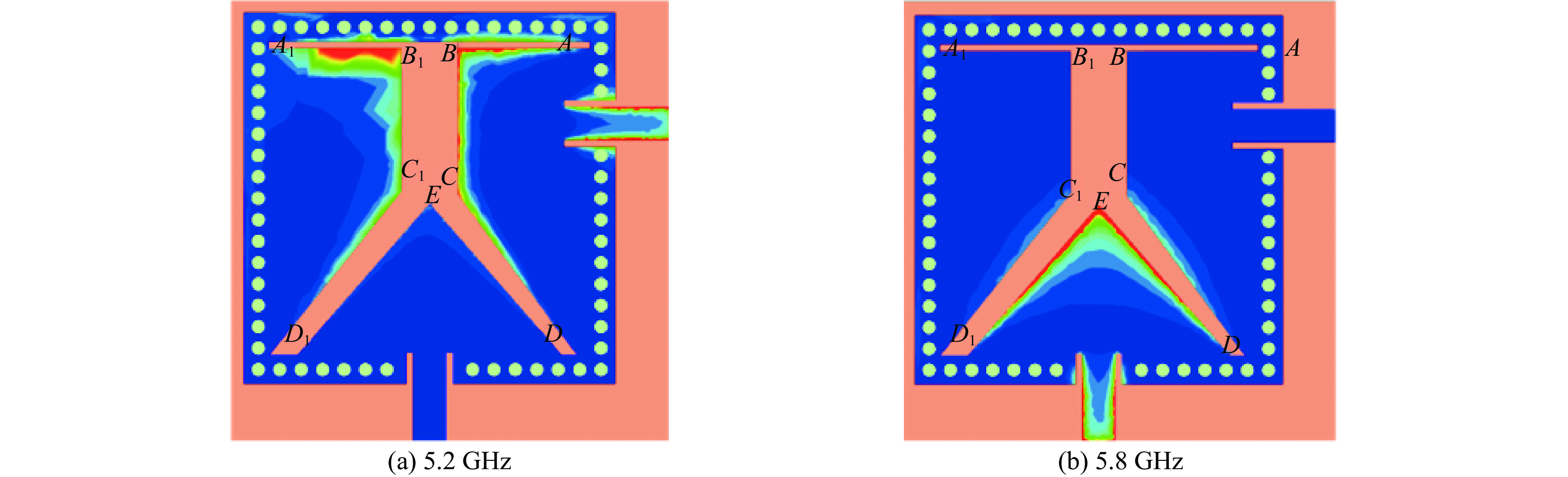
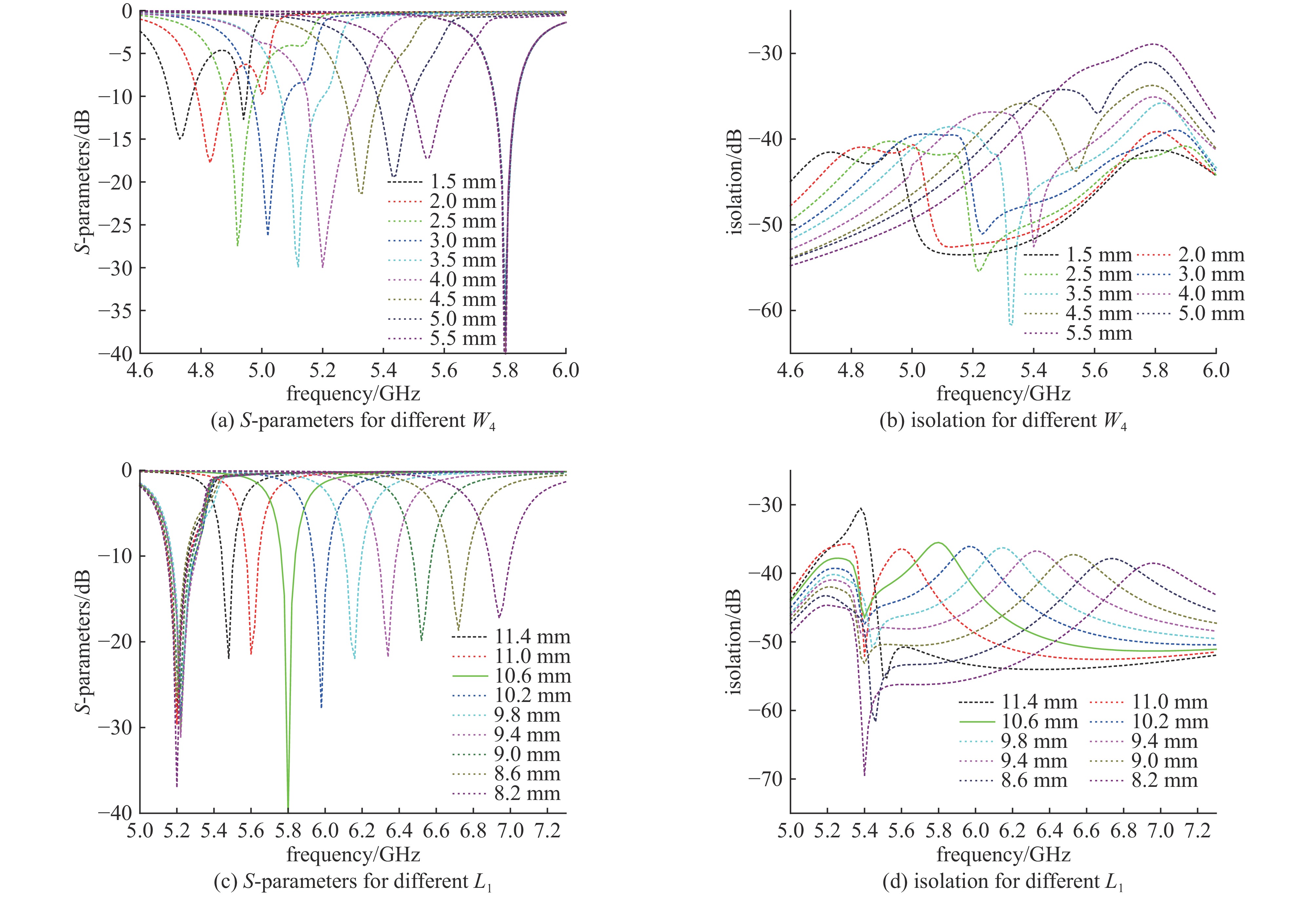
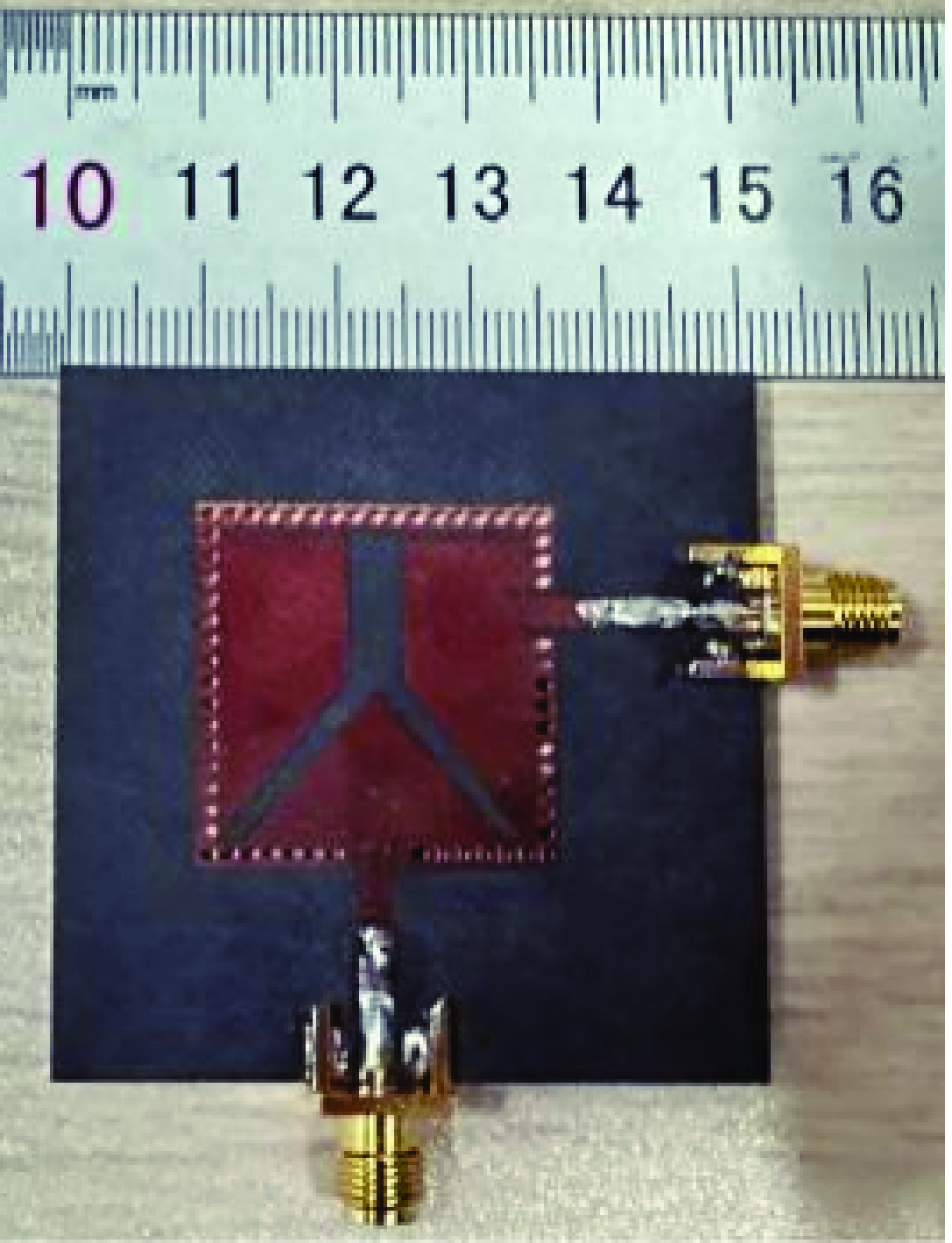
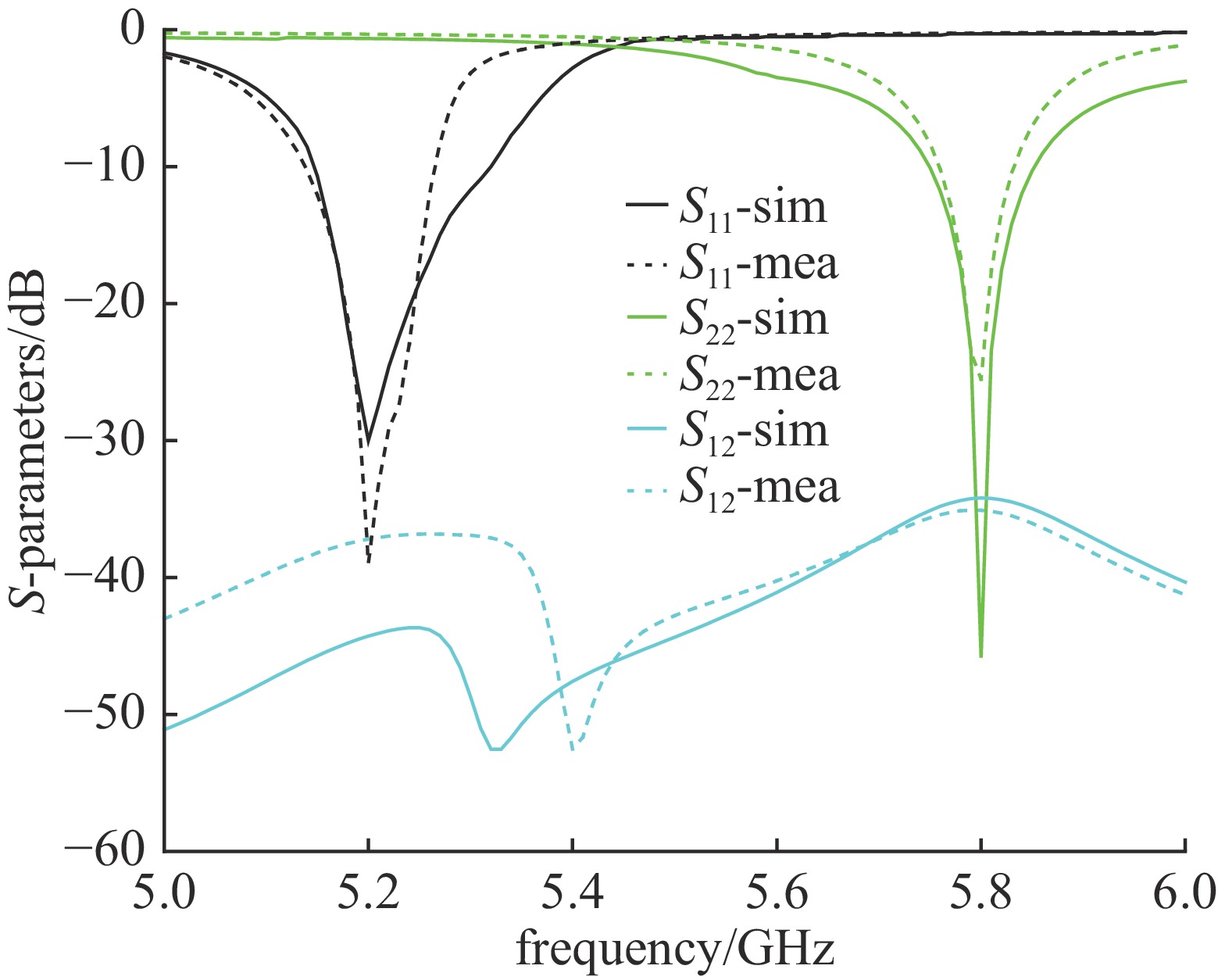
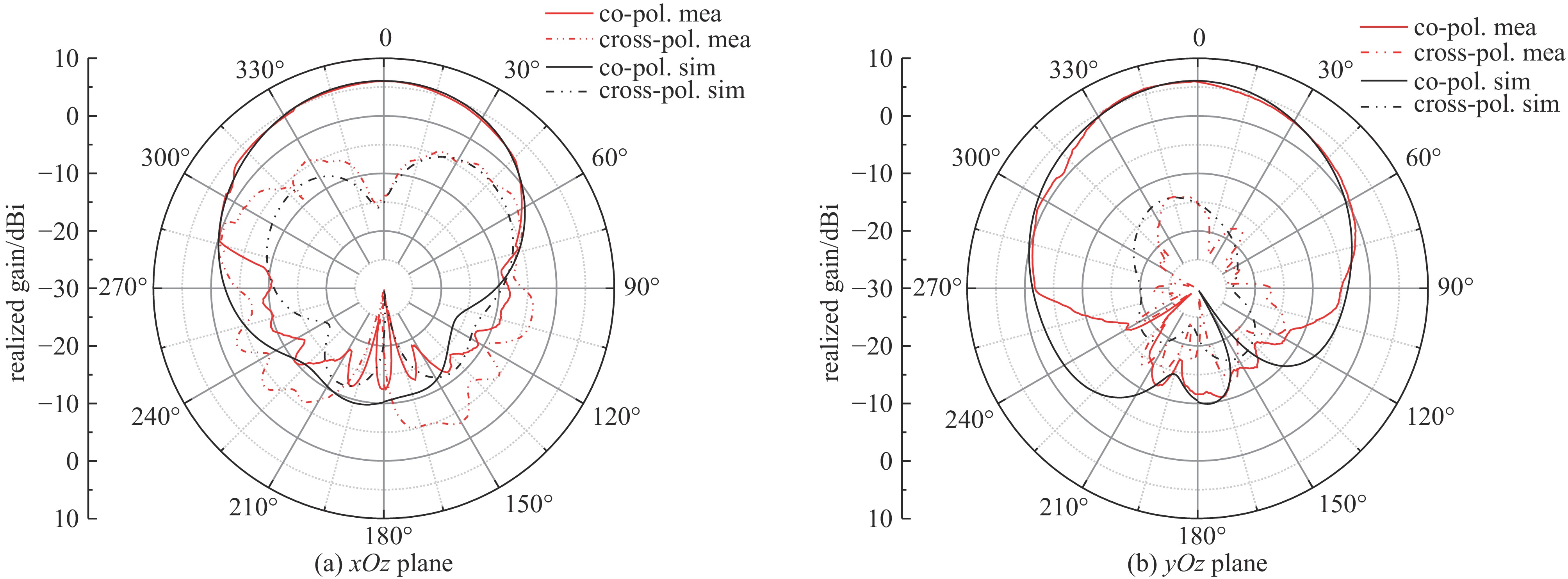
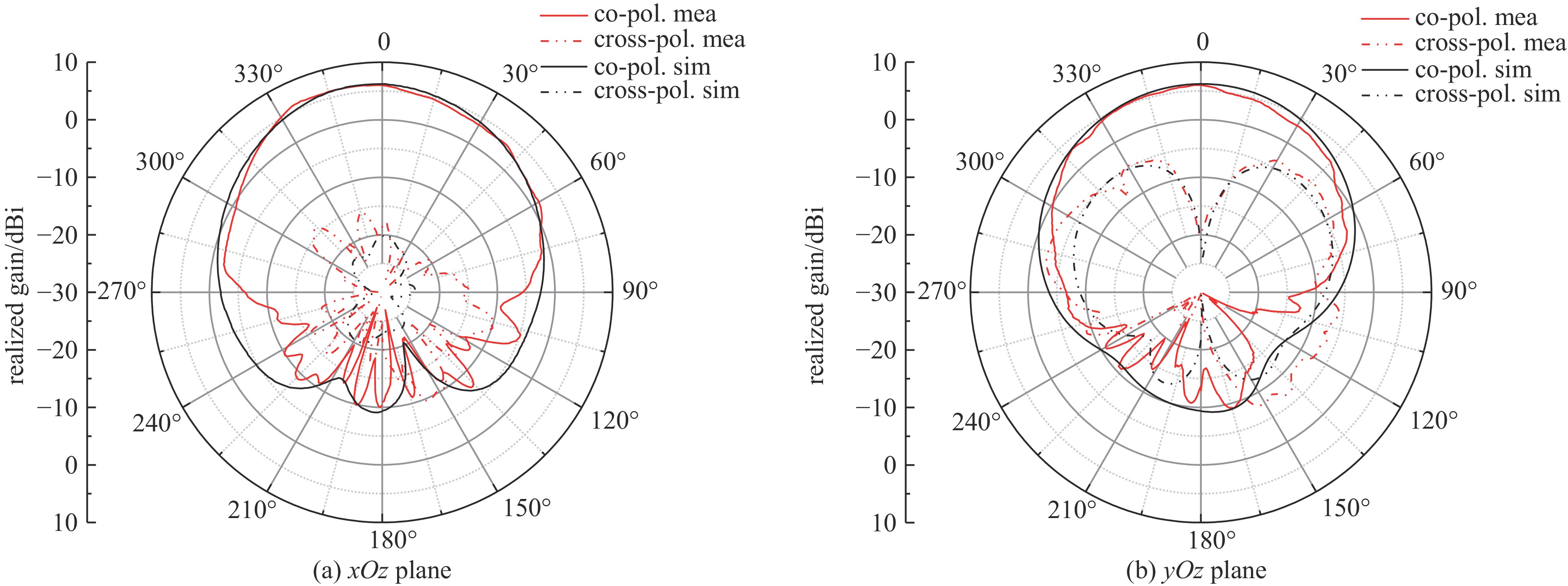
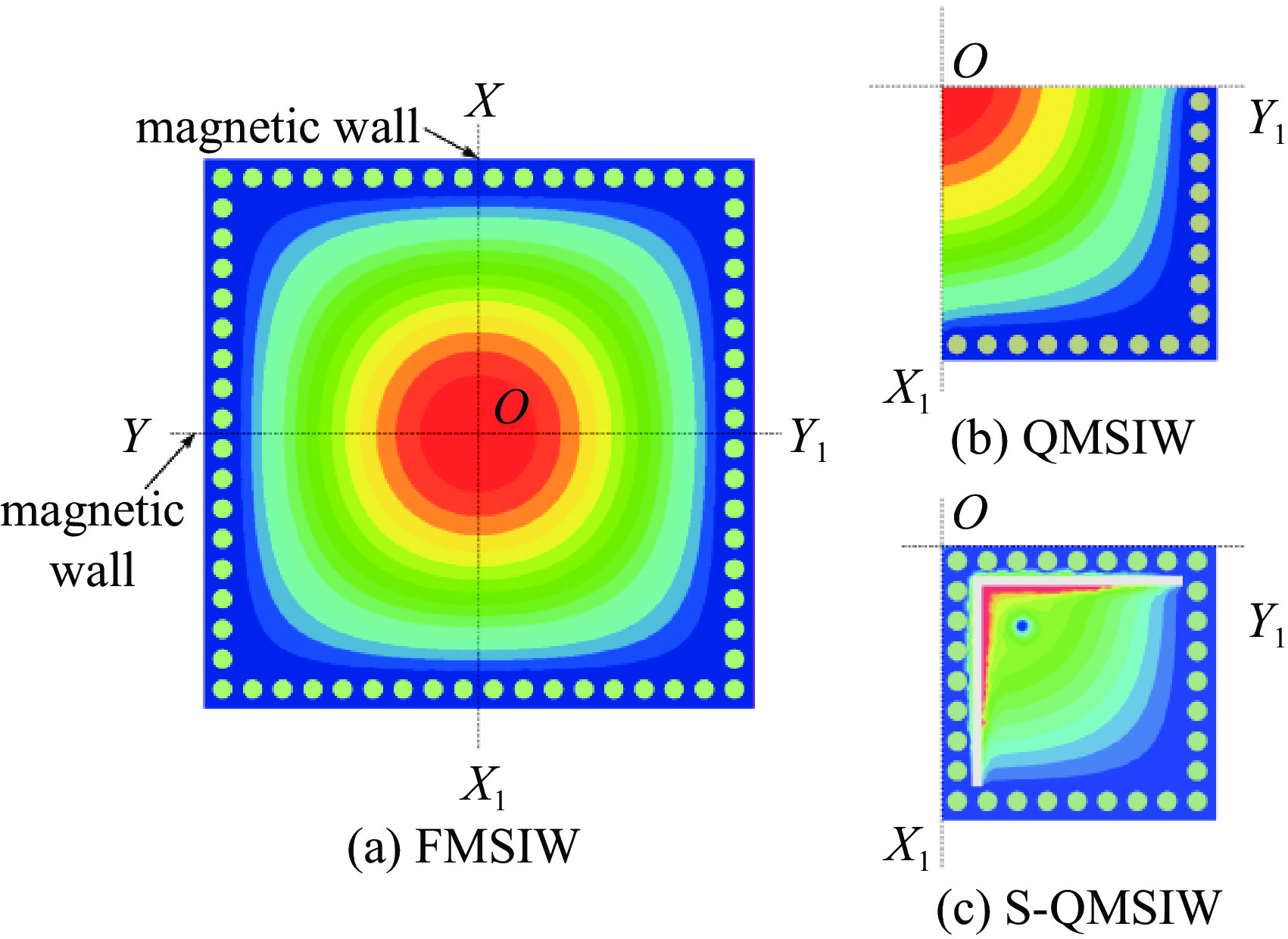
摘要: 设计实现了一种基于四分之一模基片集成波导(Quarter-Mode Substrate Integrated Waveguide, QMSIW)应用于5.2 GHz/5.8 GHz的双频天线。采用QMSIW结构,在保持了基片集成波导(SIW)的低损耗、低剖面等特性的情况下,减小了天线的体积。通过在QMSIW腔体上添加两排金属化通孔并刻蚀两条矩形槽以及不对称Y形槽,减小其尺寸并实现较高的隔离度。经过测试,天线在5.2 GHz和5.8 GHz的增益分别为6.0和6.1 dBi,交叉极化比分别大于20 dB和25 dB。所设计的天线实现了良好的小型化和大于34 dB的高隔离度,尺寸为0.42λ0×0.42λ0×0.01λ0。实物测试结果与仿真结果吻合良好。
-
关键词:
- 四分之一模基片集成波导 /
- 高隔离 /
- 双频 /
- 小型化天线
Abstract: A dual-band antenna based on the quarter-mode substrate integrated waveguide (QMSIW) operating at 5.2GHz and 5.8GHz is designed and implemented. The QMSIW structure reduces the volume of the antenna while maintaining the characteristics of low loss and low profile of the substrate integrated waveguide (SIW). By adding two rows of metallized through holes to the QMSIW and etching two rectangular slots and asymmetric Y-shaped slots, the size is reduced and high isolation is achieved. After testing, the antenna gains at 5.2 GHz and 5.8 GHz are 6.0 and 6.1 dBi, respectively, with cross-polarization ratios greater than 25 dB and 20 dB, respectively. The proposed antenna achieves good miniaturization and high isolation (greater than 34 dB), with dimensions of 0.42λ0×0.42λ0× 0.01λ0. The test results agree well with the simulation results. -
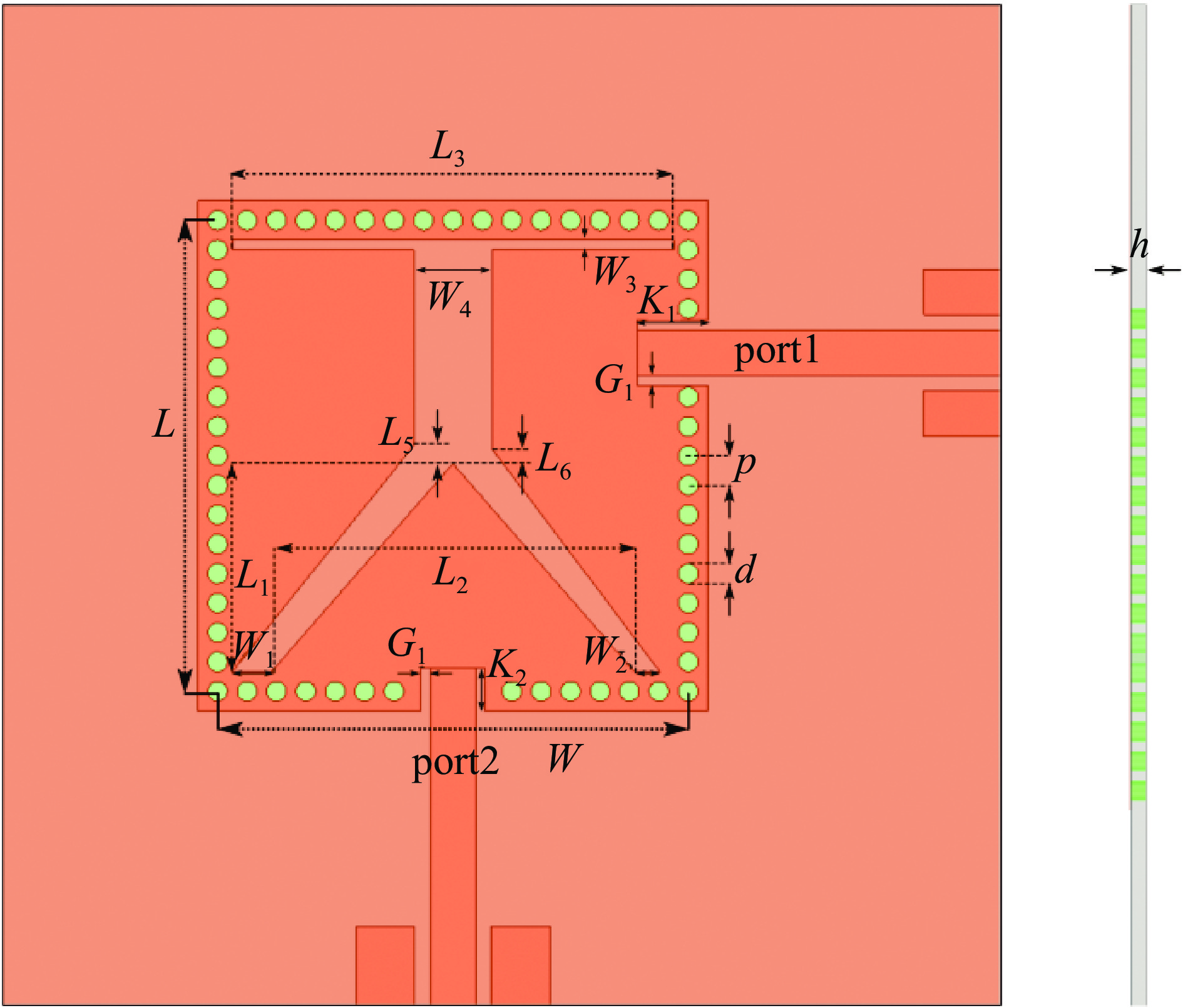
表 1 天线尺寸参数
Table 1. Parameters of the antenna
(mm) L L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 W 24 10.6 18.5 22.5 10 0.9 0.7 24 W1 W2 W3 W4 G1 G2 K1 K2 2 1.3 0.5 4 0.5 0.5 2.6 2 d p h 1 1.5 0.787 表 2 与其他双频天线的比较
Table 2. Comparison with other dual band antennas
antennas frequency/GHz isolation/dB gain/dBi front-to-back ratio FTBR/dB size Ref [5] 5.2/5.8 >28 6.97/6.2 − 0.83λ×0.90λ0×0.03λ0 Ref [6] 8.7/10.5 >20 5.11/7 >11.2 0.81λ0×0.81λ0×0.05λ0 Ref [10] 11.23/11.72 >14 5.6/5.9 >14 0.54λ0×0.48λ0×0.03λ0 Ref [13] 3.56/4.4 >24 5.3/4.45 − 0.43λ0×0.43λ0×0.02λ0 this work 5.2/5.8 >34 6.0/6.1 >15.6 0.42λ0×0.42λ0×0.01λ0 -
[1] Chaturvedi D, Kumar A. A QMSIW cavity-backed self-diplexing antenna with tunable resonant frequency using CSRR slot[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2024, 23(1): 259-263. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2023.3323008 [2] Gayen R K, Midya P, Ghosh S, et al. Design of a ‘U’ slot substrate-integrated waveguide cavity-backed self-diplexing antenna[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International IOT, Electronics and Mechatronics Conference. 2020: 1-4. [3] Khan A A, Mandal M K. Compact self-diplexing antenna using dual-mode SIW square cavity[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2019, 18(2): 343-347. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2018.2890790 [4] Kumar A, Chaturvedi D, Raghavan S. Design and experimental verification of dual-fed, self-diplexed cavity-backed slot antenna using HMSIW technique[J]. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 2019, 13(3): 380-385. [5] Chaturvedi D, Kumar A, Raghavan S. A nested SIW cavity-backing antenna for Wi-Fi/ISM band applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(4): 2775-2780. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2896670 [6] Agrawal M, Kumar T. Wideband SIW based self-diplexing antenna using parasitic slots[C]//Proceedings of 2021 Second International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems. 2021: 649-652. [7] Kumar A, Singh A K, Kumar M. A 25/28 GHz modified π-shaped SIW-based self-diplexing antenna with low frequency ratio for 5G applications[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE Indian Conference on Antennas and Propagation. 2021: 1039-1042. [8] Dash S K K, Cheng Q S, Barik R K, et al. A compact substrate integrated self-diplexing antenna for WiFi and ISM band applications[C]//Proceedings of 2020 50th European Microwave Conference. 2021: 232-235. [9] Kumar A, Raghavan S. Planar cavity-backed self-diplexing antenna using two-layered structure[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research Letters, 2018, 76: 91-96. [10] Priya S, Kumar K, Dwari S, et al. Circularly polarized self-diplexing SIW cavity backed slot antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(3): 2387-2392. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2938576 [11] Sun Y X, Wu D, Fang X S, et al. Compact quarter-mode substrate-integrated waveguide dual-frequency millimeter-wave antenna array for 5G applications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2020, 19(8): 1405-1409. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2020.3003305 [12] Lai M, Kong Y D. A simple dual-band antenna using half mode substrate integrated waveguide technique with low cross polarization[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium. 2020: 1-3. [13] Reddy M G, Pradhan N C, Karthikeyan S S. Fluidically reconfigurable SIW based self-diplexing antenna for sub-6 GHz band applications[C]//Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications. 2022: 1-5. [14] Naseri H, PourMohammadi P, Melouki N, et al. Substrate integrated waveguide-based dual-polarized self-diplexing antenna array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2023, 70(8): 2839-2843. [15] Zheng Yan, Zhu Yilong, Wang Zhan, et al. Compact, wide stopband, shielded hybrid filter based on quarter-mode substrate integrated waveguide and microstrip line resonators[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2021, 31(3): 245-248. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2020.3049048 [16] Wang Xiang, Zhu Xiaowei, Tian Ling, et al. Design and experiment of filtering power divider based on shielded HMSIW/QMSIW technology for 5G wireless applications[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 72411-72419. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2920150 [17] Kumar A, Chaturvedi D, Raghavan S. Dual-band, dual-fed self-diplexing antenna[C]//Proceedings of 2019 13th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation. 2019: 1-5. -




 下载:
下载: