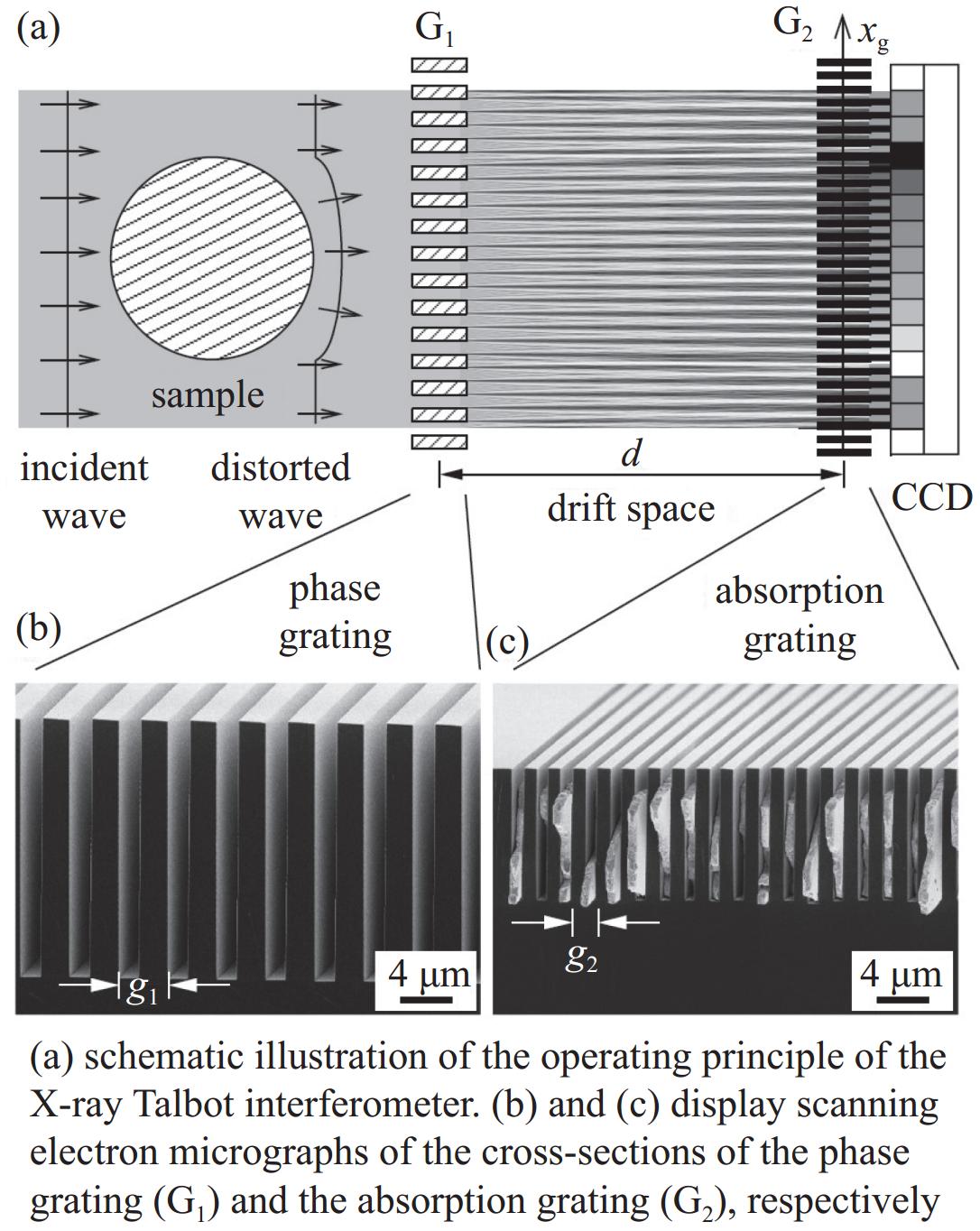
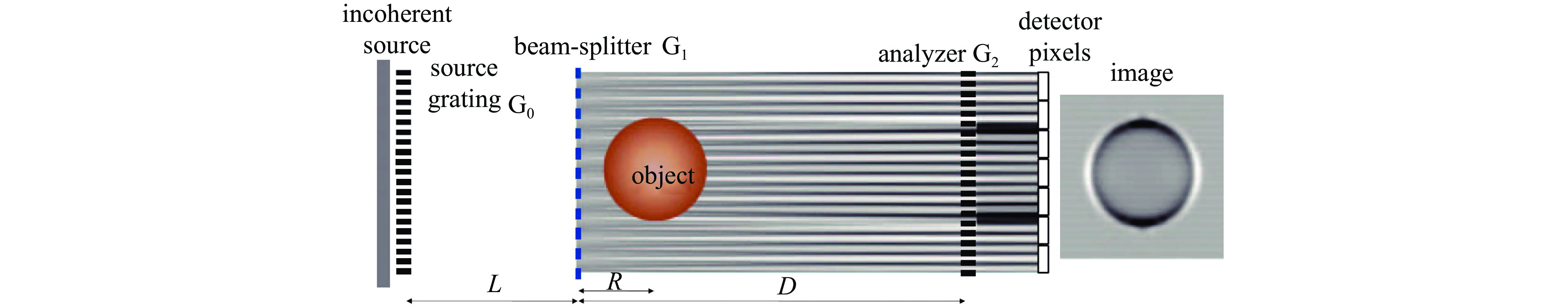
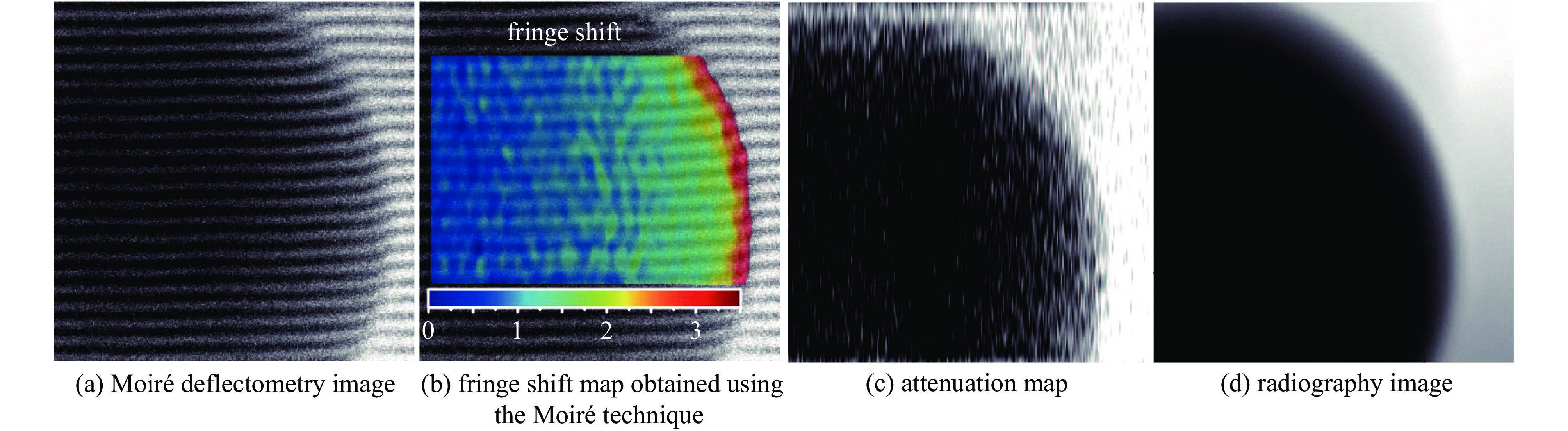
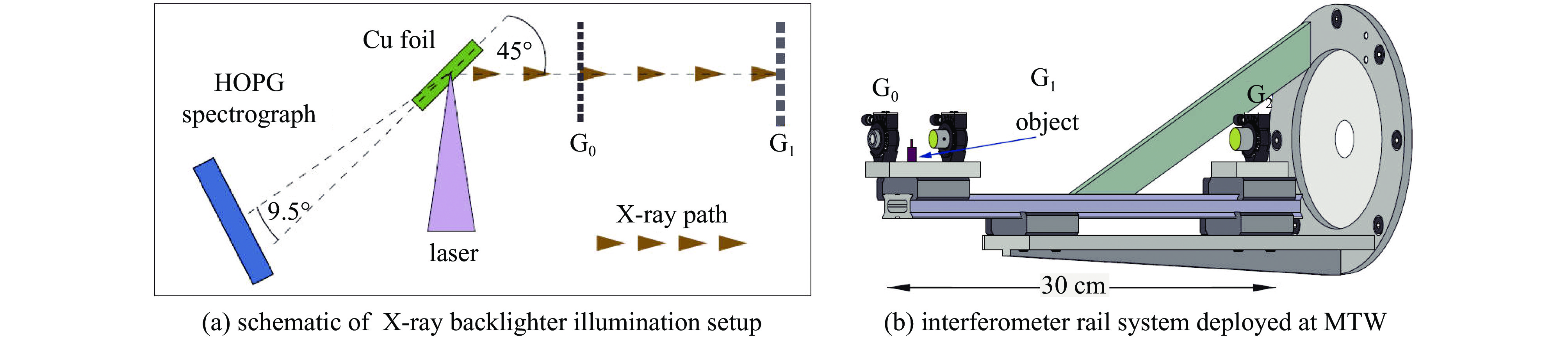
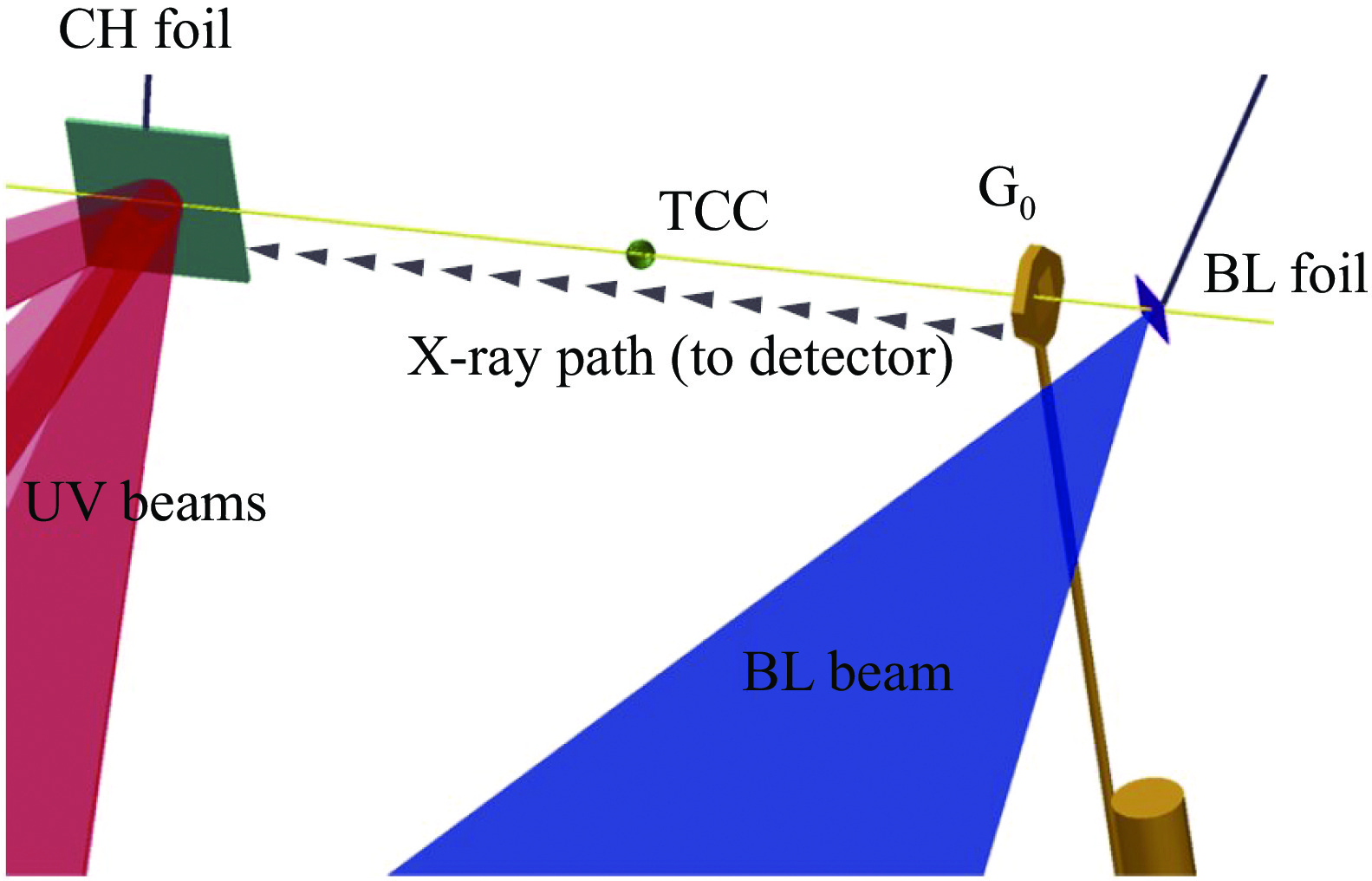
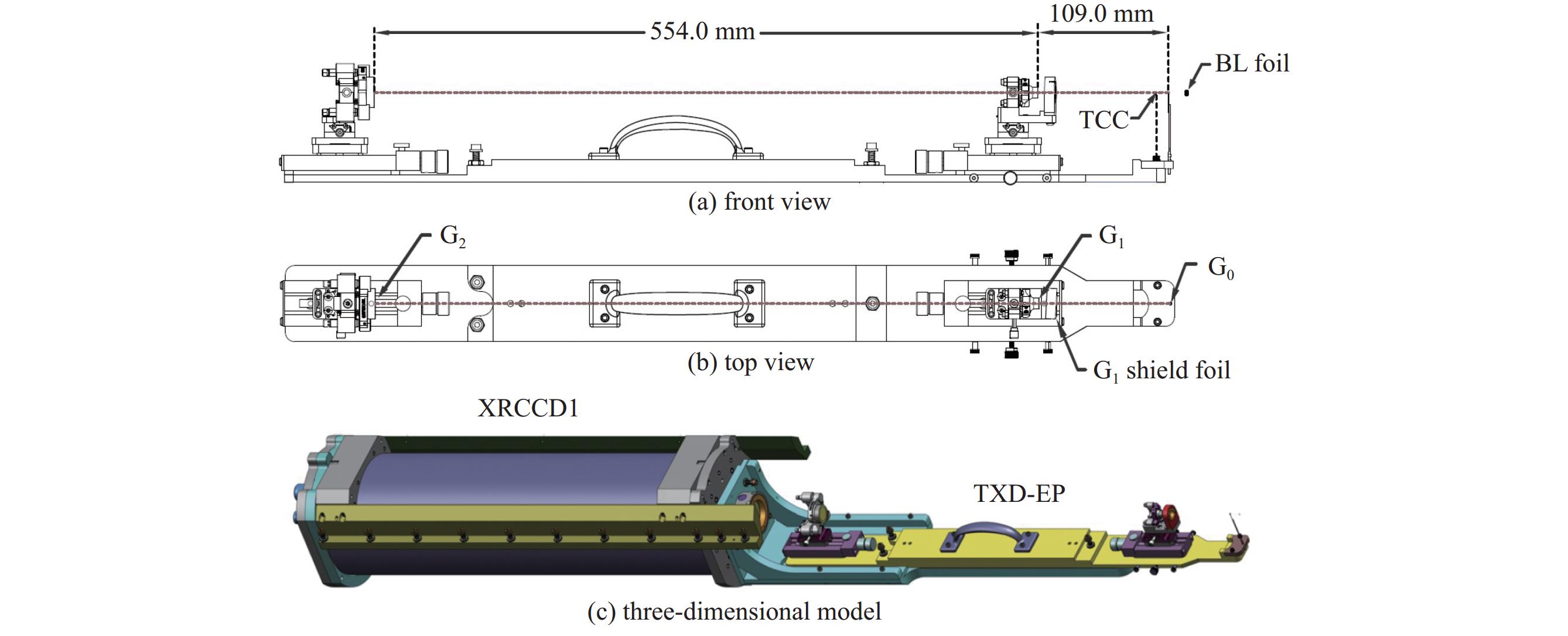
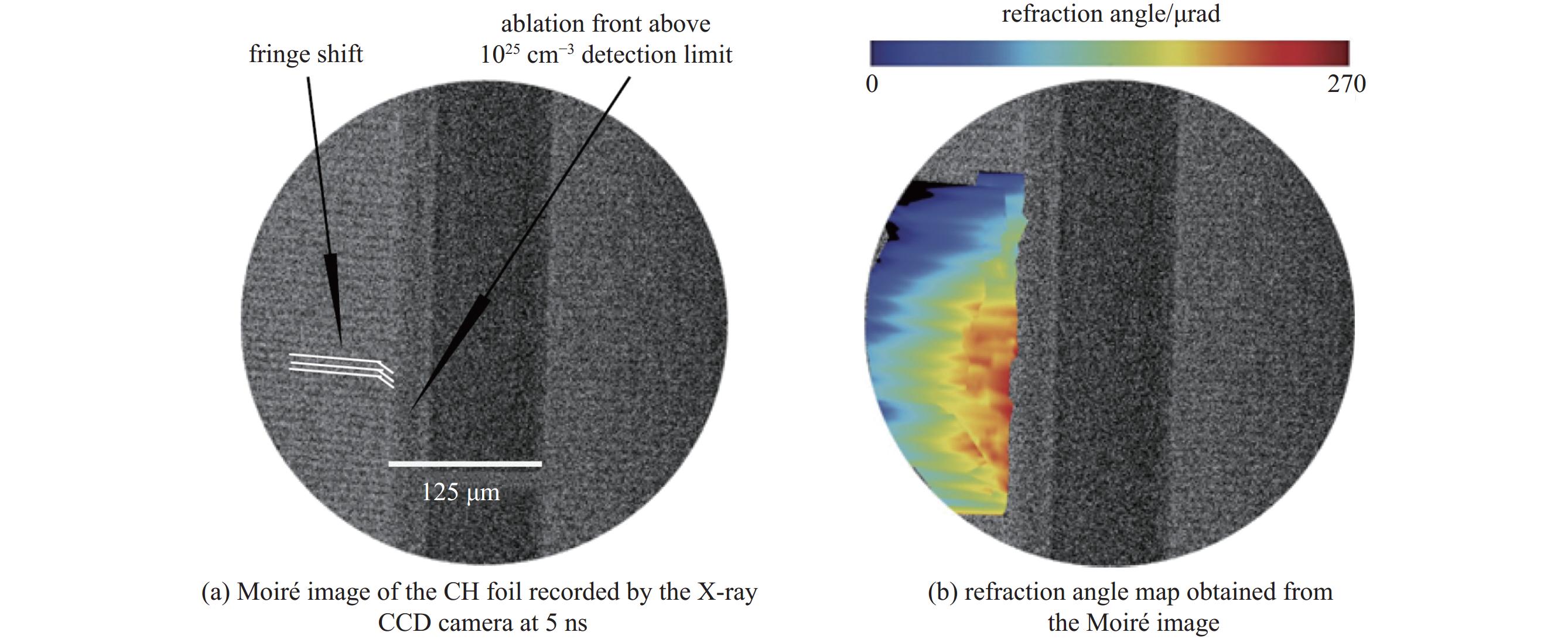
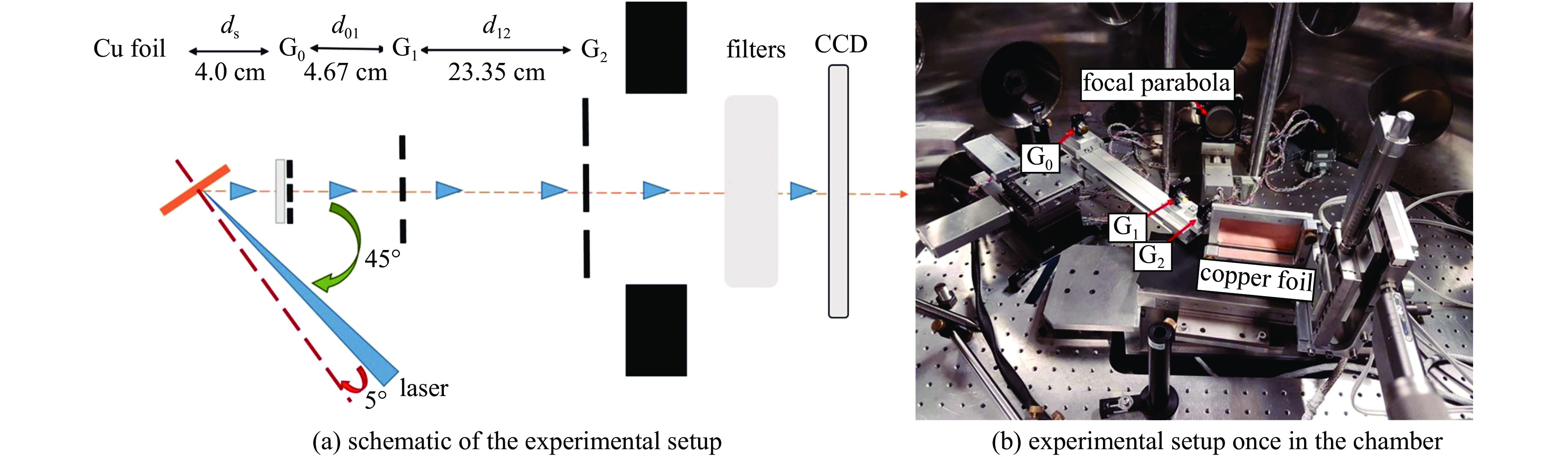
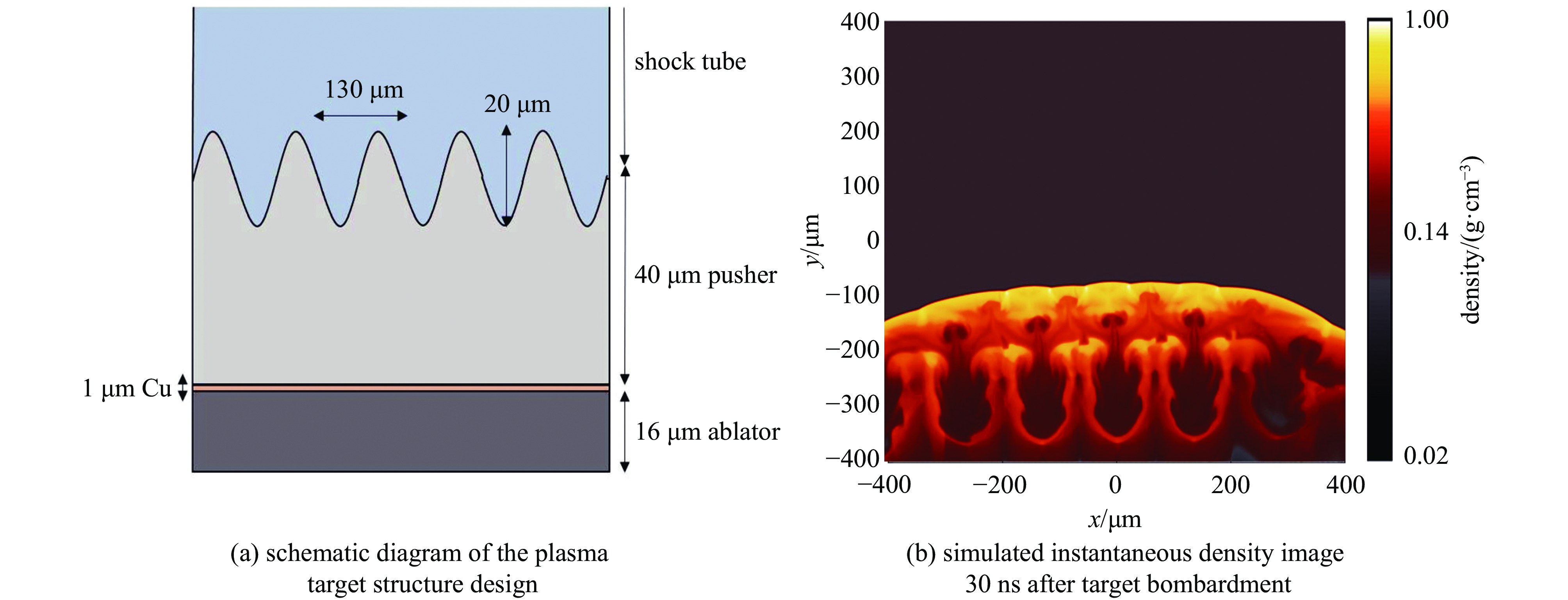
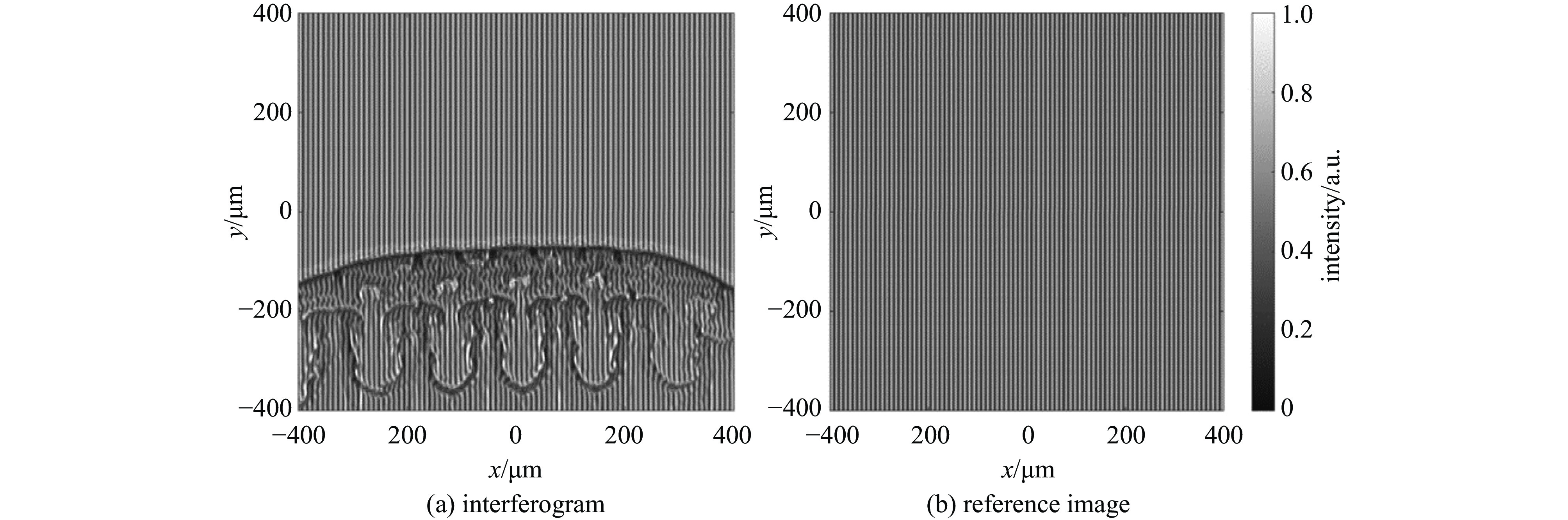
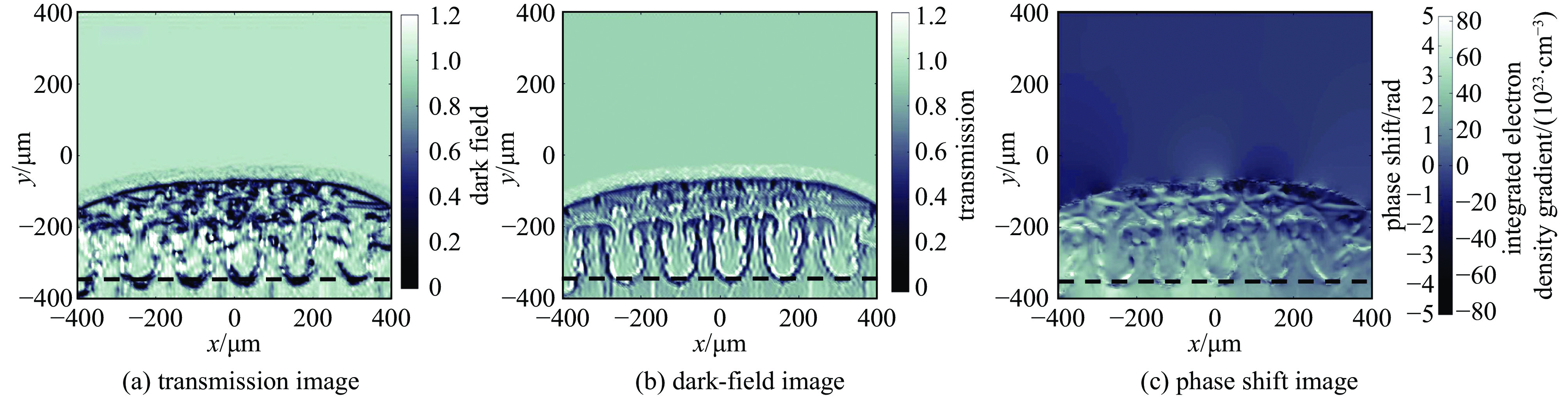
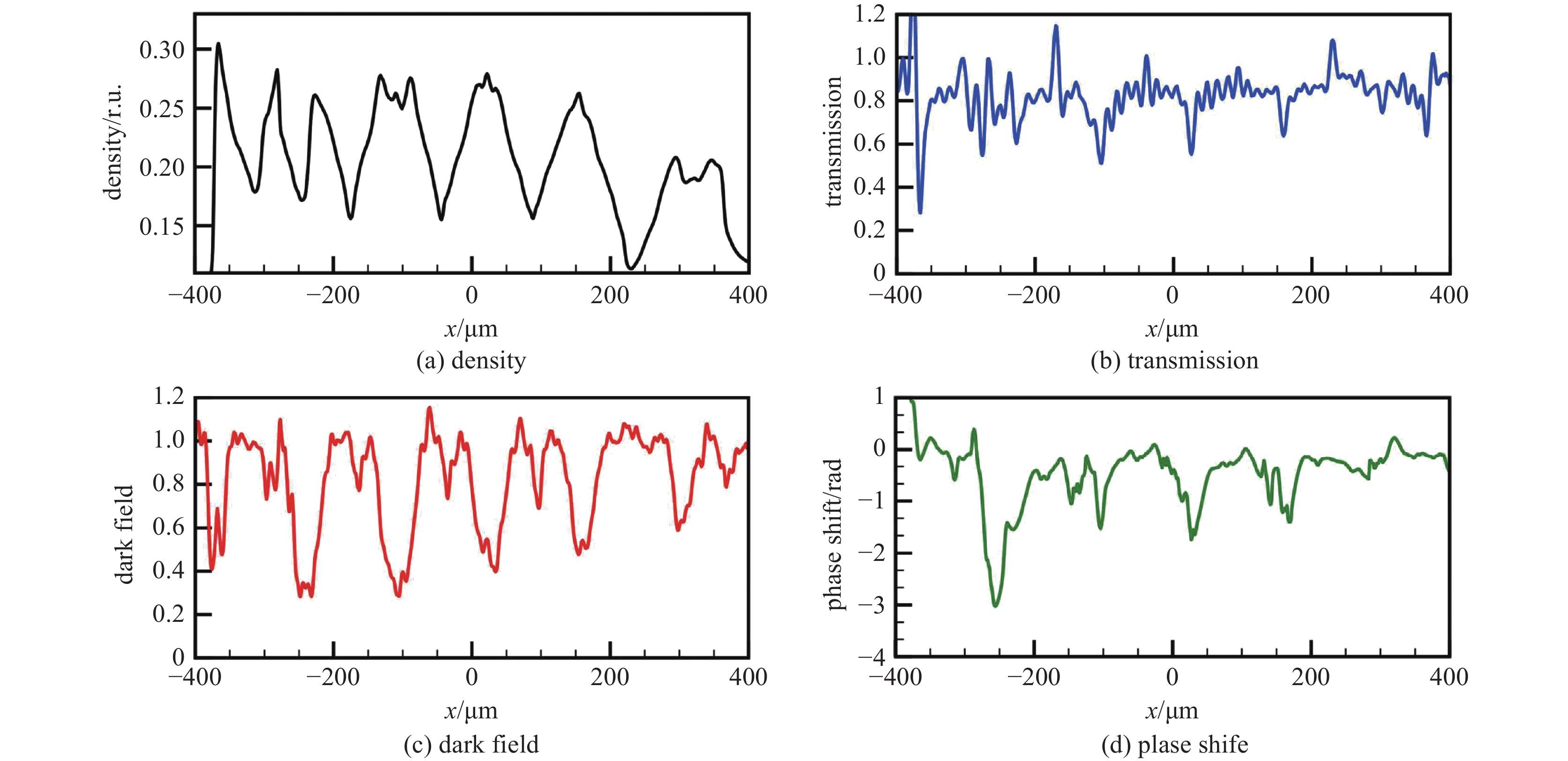
| [1] |
Momose A, Fukuda J. Phase-contrast radiographs of nonstained rat cerebellar specimen[J]. Medical Physics, 1995, 22(4): 375-379. doi: 10.1118/1.597472
|
| [2] |
McMorrow D, Als-Nielsen J. Elements of modern X-ray physics[M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
|
| [3] |
杜杨, 刘鑫, 雷耀虎, 等. X射线光栅微分相衬成像视场分析[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65:058701 doi: 10.7498/aps.65.058701Du Yang, Liu Xin, Lei Yaohu, et al. Quantitative analysis of the field of view for X-ray differential phase contrast imaging[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65: 058701 doi: 10.7498/aps.65.058701
|
| [4] |
Momose A. Recent advances in X-ray phase imaging[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 44(9A): 6355-6367.
|
| [5] |
李镜, 刘文杰, 朱佩平, 等. 基于光栅相衬成像的扇束螺旋CT重建算法[J]. 光学学报, 2010, 30(2):421-427 doi: 10.3788/AOS20103002.0421Li Jing, Liu Wenjie, Zhu Peiping, et al. Reconstruction algorithm of fan-beam helical X-ray computer tomography based on grating imaging[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2010, 30(2): 421-427 doi: 10.3788/AOS20103002.0421
|
| [6] |
王振天. 常规X光源光栅成像相关方法和技术研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2010Wang Zhentian. Research on methods and technologies for grating-based imaging with conventional X-ray sources[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2010
|
| [7] |
Momose A, Kawamoto S, Koyama I, et al. Demonstration of X-ray Talbot interferometry[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 42: L866. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.42.L866
|
| [8] |
Takeda Y, Yashiro W, Suzuki Y, et al. X-ray phase imaging with single phase grating[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 46: L89. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.46.L89
|
| [9] |
Weitkamp T, Diaz A, David C, et al. X-ray phase imaging with a grating interferometer[J]. Optics Express, 2005, 13(16): 6296-6304. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.006296
|
| [10] |
Weitkamp T, Nöhammer B, Diaz A, et al. X-ray wavefront analysis and optics characterization with a grating interferometer[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86: 054101. doi: 10.1063/1.1857066
|
| [11] |
Pfeiffer F, Weitkamp T, Bunk O, et al. Phase retrieval and differential phase-contrast imaging with low-brilliance X-ray sources[J]. Nature Physics, 2006, 2(4): 258-261. doi: 10.1038/nphys265
|
| [12] |
Pfeiffer F, Bech M, Bunk O, et al. Hard-X-ray dark-field imaging using a grating interferometer[J]. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(2): 134-137. doi: 10.1038/nmat2096
|
| [13] |
韩跃平, 陈志强, 张丽, 等. 基于Talbot干涉的X射线光栅成像技术研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2012, 49:070002Han Yueping, Chen Zhiqiang, Zhang Li, et al. Developments of X-ray grating imaging based on Talbot interferometry[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2012, 49: 070002
|
| [14] |
Momose A, Yashiro W, Takeda Y, et al. Phase tomography by X-ray Talbot interferometry for biological imaging[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2006, 45(6R): 5254-5262. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.45.5254
|
| [15] |
Stutman D, Finkenthal M. Talbot-Lau X-ray interferometry for high energy density plasma diagnostic[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2011, 82: 113508. doi: 10.1063/1.3660808
|
| [16] |
Pérez-Callejo G, Bouffetier V, Ceurvorst L, et al. TIA: a forward model and analyzer for Talbot interferometry experiments of dense plasmas[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2022, 29: 043901. doi: 10.1063/5.0085822
|
| [17] |
Hutchinson I H. Principles of plasma diagnostics: second edition[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2002, 44(12): 2603. doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/44/12/701
|
| [18] |
Talbot H F. LXXVI. Facts relating to optical science. No. IV[J]. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, 1836, 9(56): 401-407. doi: 10.1080/14786443608649032
|
| [19] |
Weitkamp T, David C, Kottler C, et al. Tomography with grating interferometers at low-brilliance sources[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 6318, Developments in X-ray Tomography V. 2006.
|
| [20] |
Weitkamp T, Diaz A, Nohammer B, et al. Moiré interferometry formulas for hard X-ray wavefront sensing[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5533, Advances in Mirror Technology for X-Ray, EUV Lithography, Laser, and Other Applications II. 2004.
|
| [21] |
Weitkamp T, Diaz A, Nohammer B, et al. Hard X-ray phase imaging and tomography with a grating interferometer[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5535, Developments in X-ray Tomography IV. 2004.
|
| [22] |
Lider V V. Talbot and Talbot–Lau X-ray interferometers[J]. Uspekhi Fizicheskikh Nauk, 2023, 66(10): 987-1007. doi: 10.3367/UFNe.2022.12.039283
|
| [23] |
Myers G R, Mayo S C, Gureyev T E, et al. Polychromatic cone-beam phase-contrast tomography[J]. Physical Review A, 2007, 76: 045804. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.76.045804
|
| [24] |
Thüring T, Modregger P, Pinzer B R, et al. Towards X-ray differential phase contrast imaging on a compact setup[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 7961, Medical Imaging 2011: Physics of Medical Imaging. 2011.
|
| [25] |
Olbinado M P, Harasse S, Yashiro W, et al. X-ray Talbot-Lau interferometer for high-speed phase imaging and tomography using white synchrotron radiation[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2012, 1466(1): 266-271.
|
| [26] |
Luo Ronghui, Wu Zhao, Xiong Ying, et al. Optimization of grating duty cycle in non-interferometric grating-based X-ray phase contrast imaging[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88: 085102. doi: 10.1063/1.4996507
|
| [27] |
Mousavi Ajarostaghi S S, Zaboli M, Javadi H, et al. A review of recent passive heat transfer enhancement methods[J]. Energies, 2022, 15: 986. doi: 10.3390/en15030986
|
| [28] |
Thuering T, Stampanoni M. Performance and optimization of X-ray grating interferometry[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2014, 372: 20130027. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2013.0027
|
| [29] |
Birnbacher L, Willner M, Velroyen A, et al. Experimental realisation of high-sensitivity laboratory X-ray grating-based phase-contrast computed tomography[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 24022. doi: 10.1038/srep24022
|
| [30] |
Vila-Comamala J, Romano L, Jefimovs K, et al. High sensitivity X-ray phase contrast imaging by laboratory grating-based interferometry at high Talbot order geometry[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(2): 2049-2064. doi: 10.1364/OE.414174
|
| [31] |
Donath T, Chabior M, Pfeiffer F, et al. Inverse geometry for grating-based X-ray phase-contrast imaging[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 106: 054703. doi: 10.1063/1.3208052
|
| [32] |
Valdivia M P, Stutman D, Finkenthal M. Talbot-Lau based Moiré deflectometry with non-coherent sources as potential High Energy Density plasma diagnostic[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 114: 163302. doi: 10.1063/1.4827186
|
| [33] |
Valdivia M P, Stutman D, Finkenthal M. Moiré deflectometry using the Talbot-Lau interferometer as refraction diagnostic for high energy density plasmas at energies below 10 keV[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2014, 85: 073702. doi: 10.1063/1.4885467
|
| [34] |
Valdivia M P, Stutman D, Stoeckl C, et al. Talbot-Lau X-ray deflectometer electron density diagnostic for laser and pulsed power high energy density plasma experiments (invited)[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87: 11D501. doi: 10.1063/1.4959158
|
| [35] |
Valdivia M P, Stutman D, Stoeckl C, et al. An X-ray backlit Talbot-Lau deflectometer for high-energy-density electron density diagnostics[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87: 023505. doi: 10.1063/1.4941441
|
| [36] |
Valdivia M P, Stutman D, Stoeckl C, et al. Talbot–Lau X-ray deflectometry phase-retrieval methods for electron density diagnostics in high-energy density experiments[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(2): 138-145. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.000138
|
| [37] |
Schuster M, Ludwig V, Akstaller B, et al. A fast alignment method for grating-based X-ray phase-contrast imaging systems[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2019, 14: P08003. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/14/08/P08003
|
| [38] |
Valdivia M P, Stutman D, Stoeckl C, et al. Implementation of a Talbot–Lau X-ray deflectometer diagnostic platform for the OMEGA EP laser[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2020, 91: 023511. doi: 10.1063/1.5123919
|
| [39] |
Valdivia M P, Stutman D, Stoeckl C, et al. Talbot-Lau X-ray deflectometer: refraction-based HEDP imaging diagnostic[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92: 065110. doi: 10.1063/5.0043655
|
| [40] |
Bouffetier V, Ceurvorst L, Valdivia M P, et al. Proof-of-concept Talbot–Lau X-ray interferometry with a high-intensity, high-repetition-rate, laser-driven K-alpha source[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(27): 8380-8387. doi: 10.1364/AO.398839
|
| [41] |
Weitkamp T. XWFP: an X-ray wavefront propagation software package for the IDL computer language[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5536, Advances in Computational Methods for X-Ray and Neutron Optics. 2004.
|
| [42] |
Tzeferacos P, Fatenejad M, Flocke N, et al. FLASH MHD simulations of experiments that study shock-generated magnetic fields[J]. High Energy Density Physics, 2015, 17: 24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.hedp.2014.11.003
|
| [43] |
Rigon G, Casner A, Albertazzi B, et al. Rayleigh-Taylor instability experiments on the LULI2000 laser in scaled conditions for young supernova remnants[J]. Physical Review E, 2019, 100: 021201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.100.021201
|
| [44] |
Tzeferacos P, Rigby A, Bott A F A, et al. Laboratory evidence of dynamo amplification of magnetic fields in a turbulent plasma[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 591. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02953-2
|




 下载:
下载: