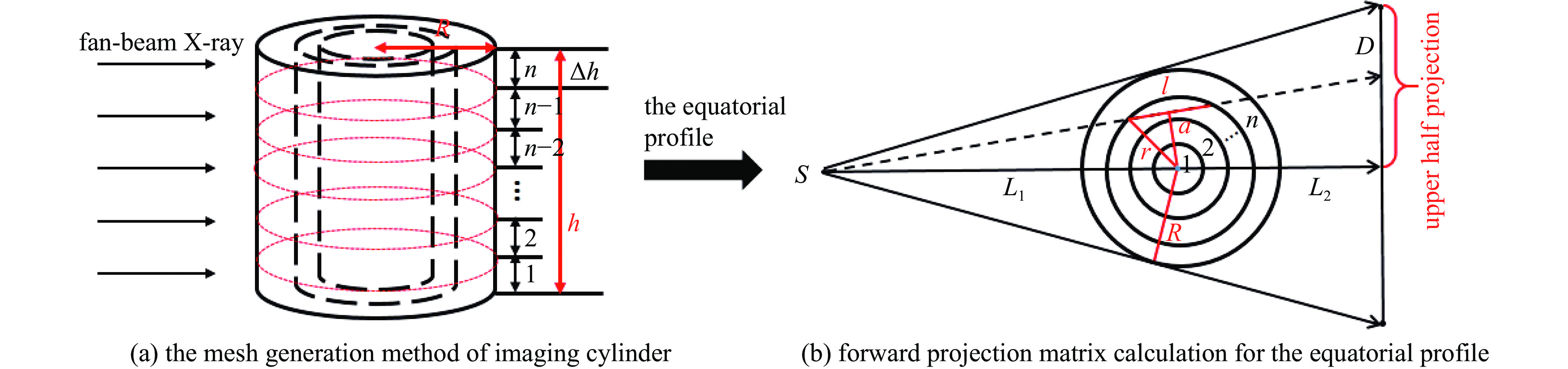
Research on uncertainty quantification of single-view CT nonlinear image reconstruction
-
摘要: 闪光照相技术可以对快速物理过程进行诊断,但由于是瞬时照相,获得的投影数量稀少。考虑视角典型受限(即一个视角)的情况下,CT图像重建不确定度量化方法的研究。目前的单视角CT图像重建不确定度量化方法通常假设在线性光程方程中含有高斯噪声的模型,但这种物理模型过于简化。从朗博比尔定律(Lambert-Beer’s law)出发,构建了关于透射率的指数衰减方程及其高斯噪声项,得到更合理的非线性图像重建模型,推导得到相应的非线性后验概率密度函数,然后利用RTO算法以及Gibbs算法对该后验概率进行抽样,通过统计抽样样本得到图像重建的平均值及其不确定度。为了验证新方法的有效性,给出了模拟数据,并与基于光程方程的线性图像重建结果进行了对比,结果表明基于透射率方程的非线性图像重建方法具有更好的不确定度估计潜力。Abstract: Flash radiography enables the diagnosis of rapid physical processes, yet the instantaneous nature of image acquisition results in a severely limited number of projections. This study investigates uncertainty quantification methods for computed tomography (CT) image reconstruction under the typical scenario of a single projection view. Current approaches for single-view CT uncertainty quantification often adopt oversimplified physical models, assuming linearized optical path equations with Gaussian noise. To address this limitation, we derive a more realistic nonlinear reconstruction framework based on the Lambert-Beer’s law, constructing an exponential attenuation model for transmittance with an integrated Gaussian noise term. This formulation yields a nonlinear posterior probability density function, which is subsequently sampled using the Randomize-Then-Optimize (RTO) algorithm combined with Gibbs sampling. The reconstructed image and its associated uncertainty are obtained through statistical analysis of the sampled data. Numerical simulations validate the proposed method, with comparative results against conventional linearized models demonstrating its superior potential for accurate uncertainty estimation in image reconstruction.
-
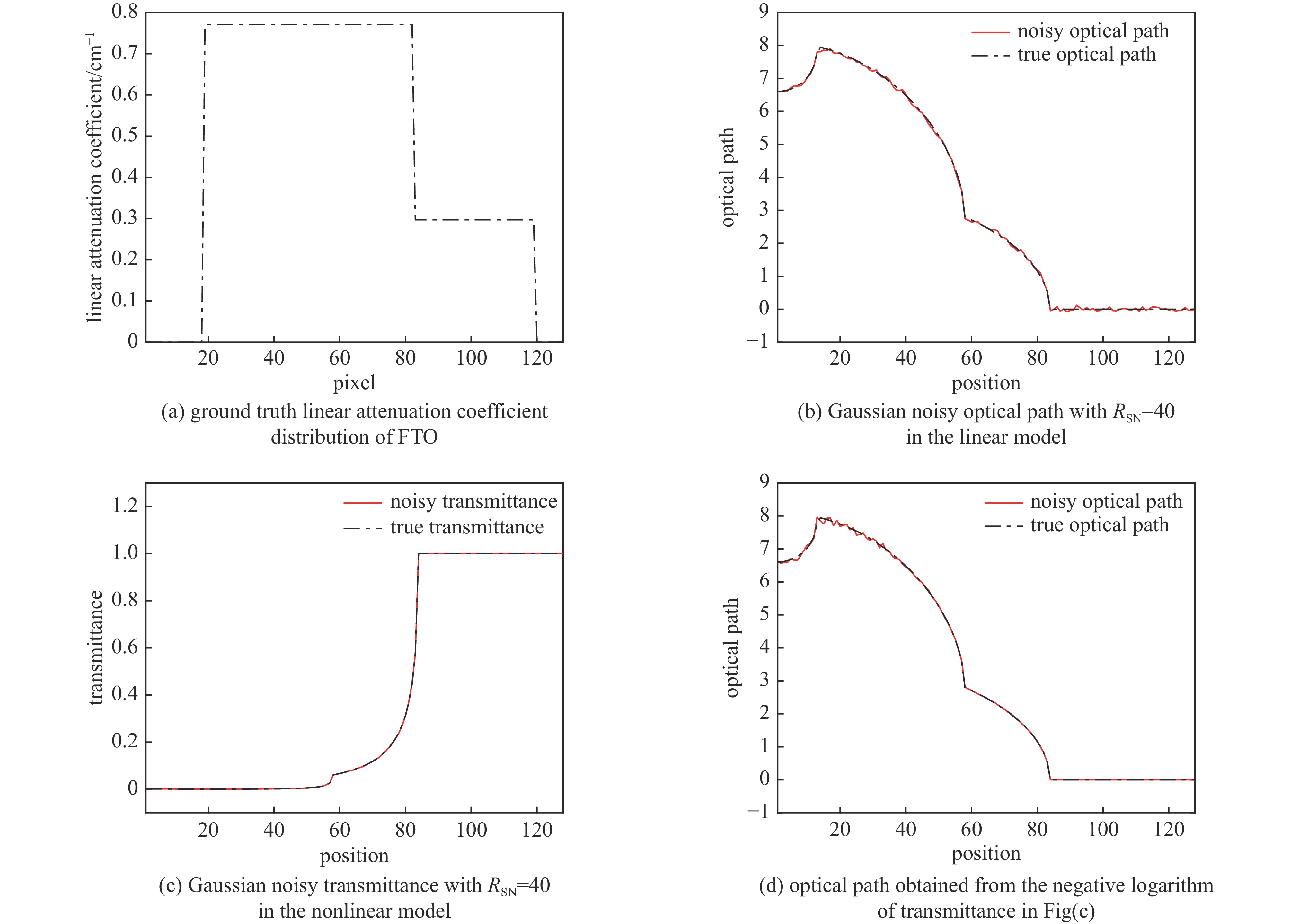
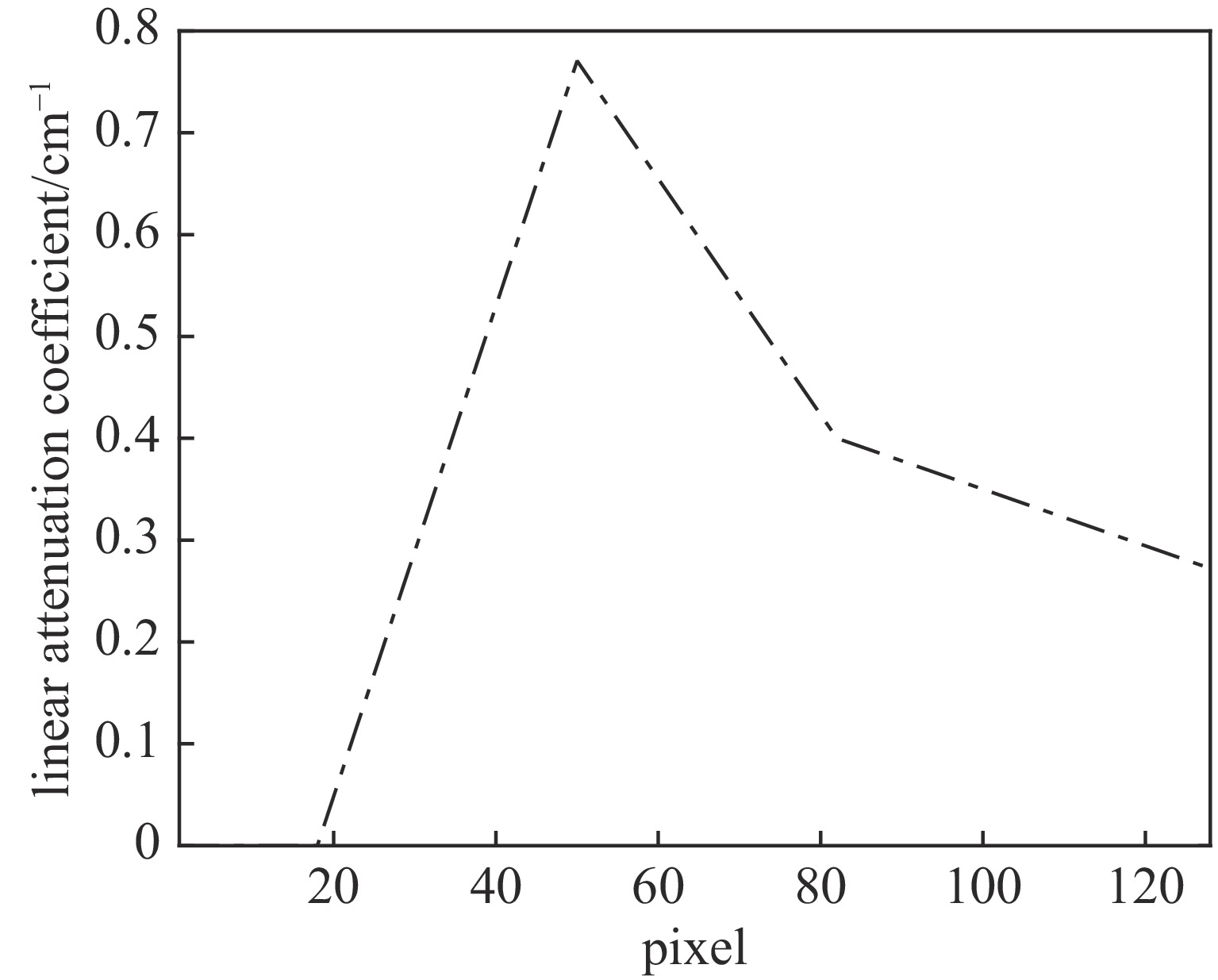
图 2 FTO的真实线性衰减系数分布、含噪声的光程分布与真值的对比以及含噪声的透射率分布与真值的对比;在图(b)中,可以看到噪声是独立同分布的;在图(c)中,噪声则难以看见;而在图(d)中,噪声是清晰可见的
Figure 2. Ground truth linear attenuation coefficient distribution of FTO, the comparison between the noisy optical path and the true value, and the comparison between the noisy transmittance and the true value; in Fig (b), the noise is independently and equally distributed; in Fig (c), the noise is difficult to see; however in Fig (d), the noise is clearly visible
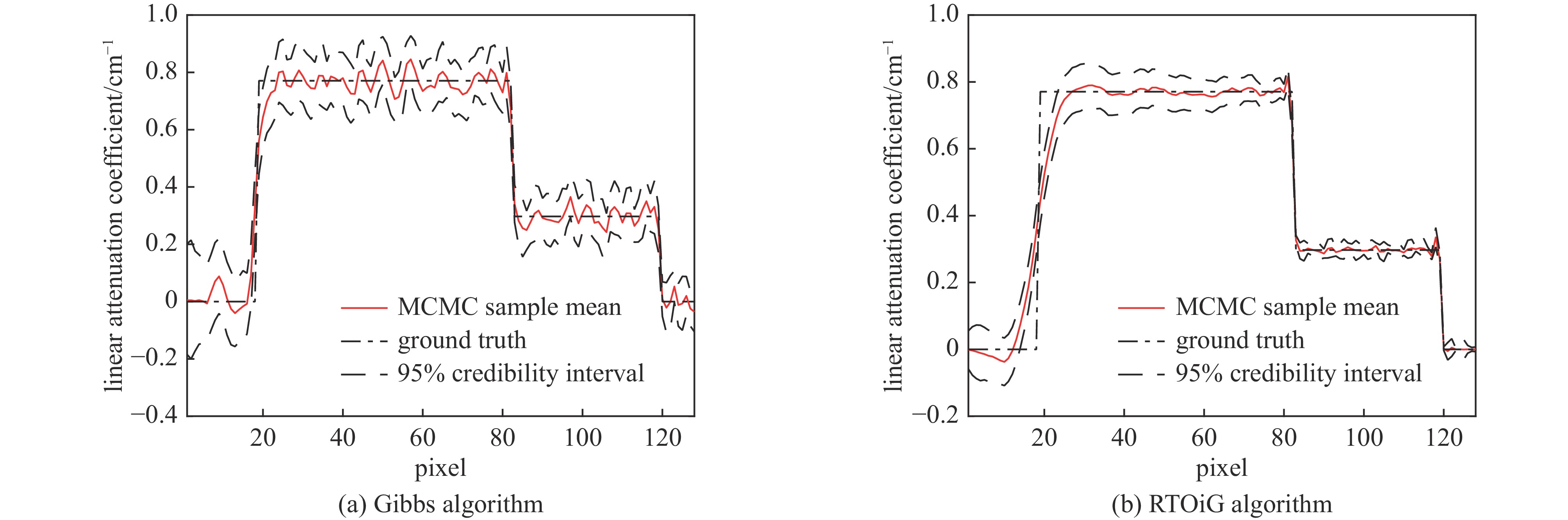
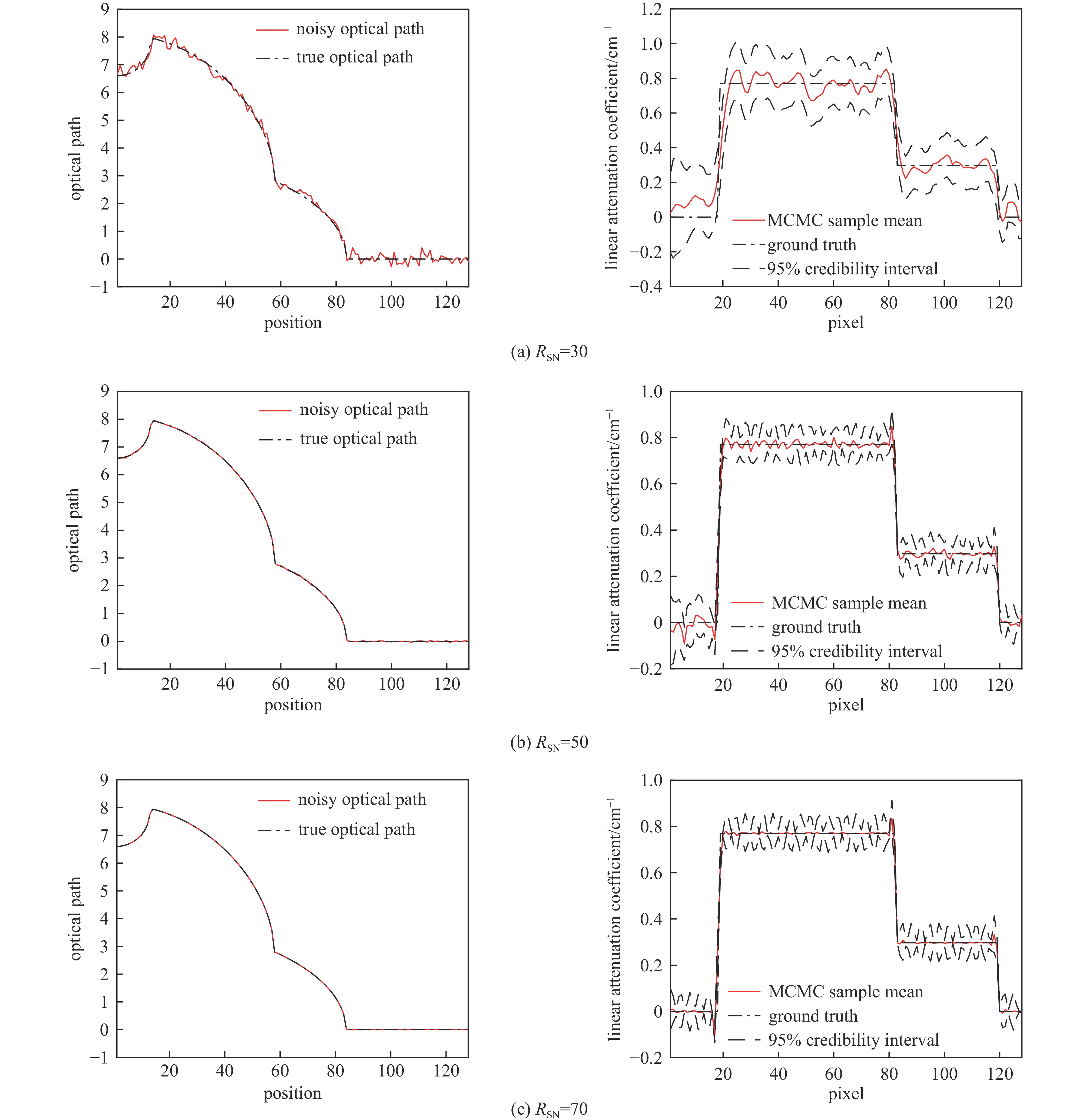
图 7 N=
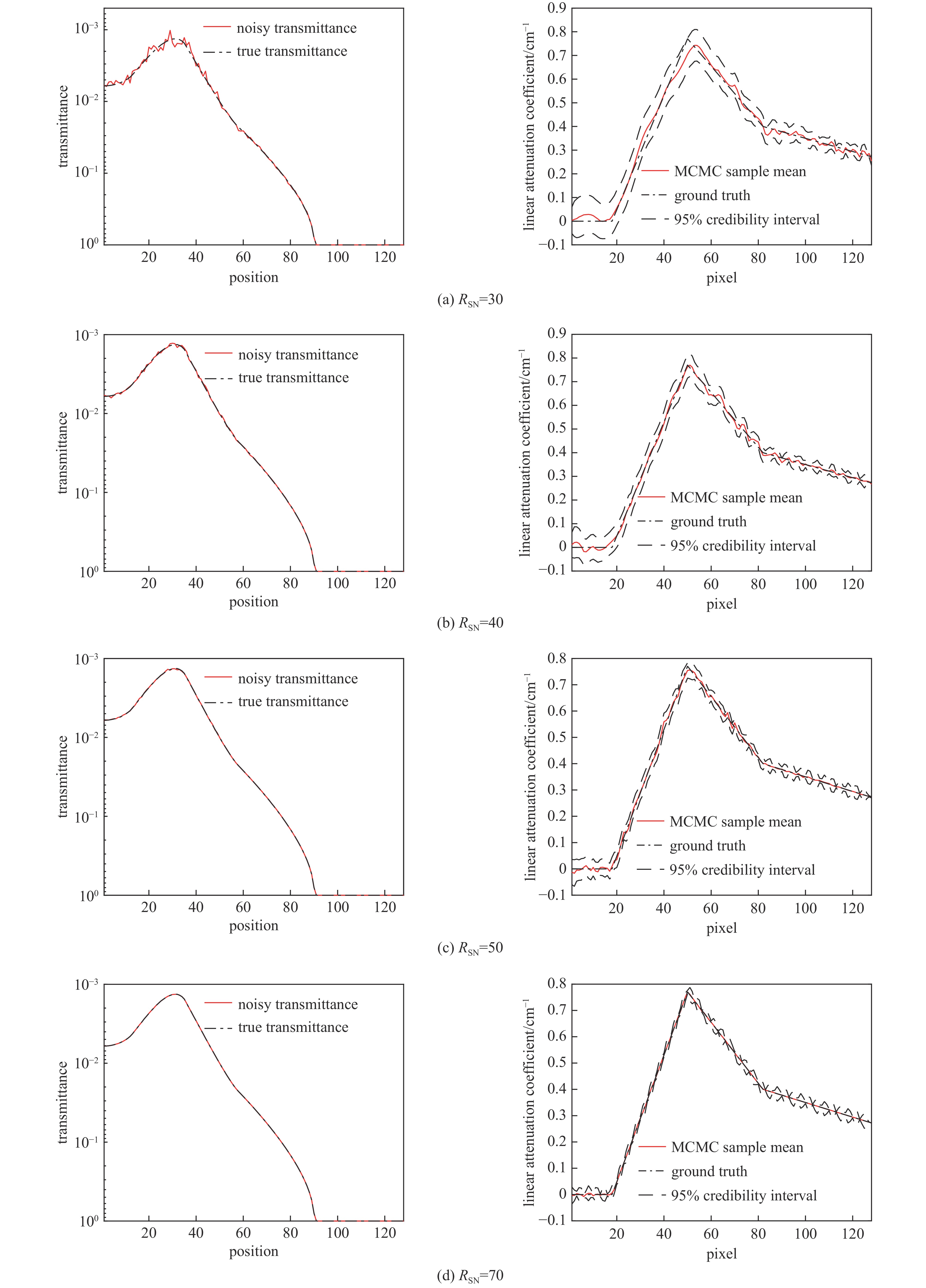
10000 ,退火数5000 ,不同RSN的情况下,模拟生成的含噪透射率(注意此时y轴是对数坐标)以及RTOiG算法重建得到的FTO线性衰减系数的均值和不确定度Figure 7. The noisy transmittance generated by simulation (note that the y axis is logarithmic coordinate), and the mean and uncertainty of FTO linear attenuation coefficient reconstructed by RTOiG algorithm under different RSN, for N=
10000 and burn-in number of5000 图 10 N=
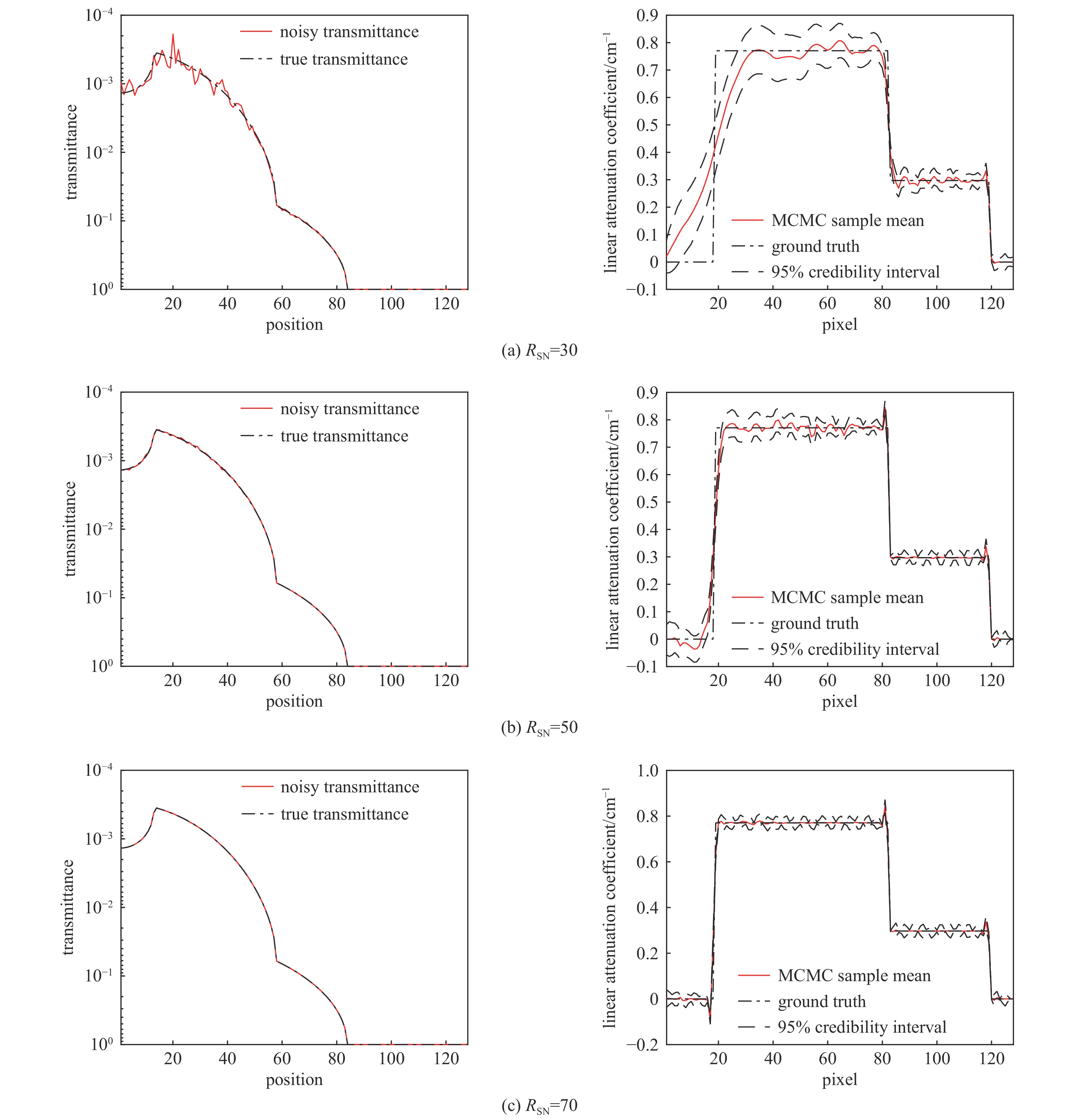
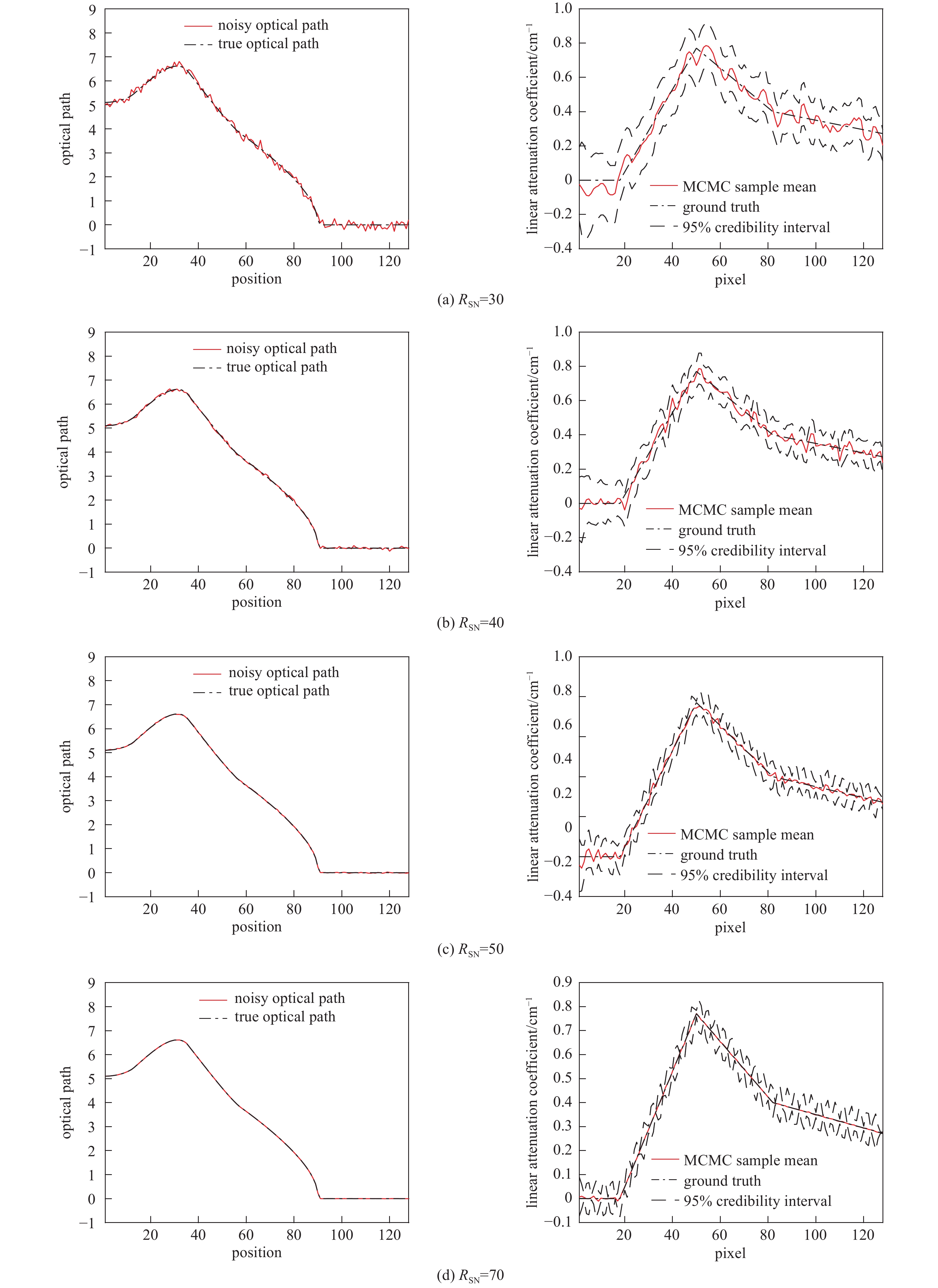
10000 ,退火数5000 ,不同RSN的情况下,模拟生成的含噪透射率(注意此时y轴是对数坐标)以及RTOiG算法重建得到的pcv-STO线性衰减系数的均值和不确定度Figure 10. The noisy transmittance generated by simulation (note that the y axis is logarithmic coordinate), and the mean and uncertainty of pcv-STO linear attenuation coefficient reconstructed by RTOiG algorithm under different RSN, for N=
10000 and burn-in number of5000 表 1 关于FTO客体MCMC重建结果均值与真值的均方根误差(RMSE)对比
Table 1. Comparison of root mean square error (RMSE) between mean of MCMC reconstruction and ground truth of FTO
SNR RMSE/% linear Gibbs non-linear RTOiG 30 12.87 17.71 40 8.73 11.03 50 5.71 7.97 70 4.97 4.96 表 2 关于pcv-STO客体MCMC重建结果均值与真值的均方根误差(RMSE)对比
Table 2. Comparison of root mean square error (RMSE) between mean of MCMC reconstruction and ground truth of pcv-STO
SNR RMSE/% linear Gibbs non-Linear RTOiG 30 10.08 4.45 40 6.27 2.45 50 3.32 1.71 70 0.59 0.39 -
[1] 马勋, 邓建军, 姜苹, 等. 流体动力学实验用闪光X光机研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:010201 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20142601.10201Ma Xun, Deng Jianjun, Jiang Ping, et al. Review of flash X-ray generator applied to hydrokinetical experiments[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 010201 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20142601.10201 [2] 管永红, 王鹏来, 景越峰. 基于贝叶斯准则的闪光照相图像重建[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(9):2495-2498 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112309.2495Guan Yonghong, Wang Penglai, Jing Yuefeng. Reconstruction of flash radiographic image based on Bayesian approach[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(9): 2495-2498 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112309.2495 [3] 管永红, 景越峰. 基于自适应准则的闪光照相图像重建[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2009, 21(2):260-264Guan Yonghong, Jing Yuefeng. Adaptive reconstruction of flash radiographic image[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2009, 21(2): 260-264 [4] 景越峰, 刘军, 管永红. 改进的约束共轭梯度闪光照相图像重建算法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(8):2201-2204 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112308.2201Jing Yuefeng, Liu Jun, Guan Yonghong. Improved constrained conjugate gradient reconstruction algorithm for flash radiographic image[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(8): 2201-2204 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112308.2201 [5] 景越峰, 管永红, 张小琳. 基于约束优化的闪光照相图像重建算法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28:094002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.150498Jing Yuefeng, Guan Yonghong, Zhang Xiaolin. Constrained optimization reconstruction for flash radiographic image[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 094002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.150498 [6] Howard M, Fowler M, Luttman A, et al. Bayesian Abel inversion in quantitative X-ray radiography[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2016, 38(3): B396-B413. doi: 10.1137/15M1018721 [7] 王忠淼, 刘军, 景越峰, 等. 基于贝叶斯分层模型的MCMC方法在闪光图像重建中的应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30:114004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.180123Wang Zhongmiao, Liu Jun, Jing Yuefeng, et al. Applications of MCMC method based on Bayesian hierarchical model in flash radiography reconstruction[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 30: 114004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.180123 [8] Li Xinge, Xu Haibo, Zheng Na, et al. Uncertainty quantification of density reconstruction using MCMC method in high-energy X-ray radiography[J]. Communications in Computational Physics, 2020, 27(5): 1485-1504. doi: 10.4208/cicp.OA-2019-0060 [9] Bardsley J M. MCMC-based image reconstruction with uncertainty quantification[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2012, 34(3): A1316-A1332. doi: 10.1137/11085760X [10] Siddon R L. Prism representation: a 3D ray-tracing algorithm for radiotherapy applications[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 1985, 30(8): 817-824. [11] 刘进, 张小琳, 景越峰, 等. 含系统模糊的闪光照相正向成像技术研究及应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:044003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.044003Liu Jin, Zhang Xiaolin, Jing Yuefeng, et al. Research and application of forward imaging technology with systemic blur[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 044003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.044003 [12] Bardsley J M, Solonen A, Haario H, et al. Randomize-then-optimize: a method for sampling from posterior distributions in nonlinear inverse problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2014, 36(4): A1895-A1910. doi: 10.1137/140964023 [13] 景越峰, 张小琳, 管永红, 等. 基于约束共轭梯度的高能闪光照相图像复原算法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2009, 21(2):277-280Jing Yuefeng, Zhang Xiaolin, Guan Yonghong, et al. Constrained conjugate gradient algorithm for image restoration in high-energy radiography[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2009, 21(2): 277-280 [14] Díaz-Francés E, Rubio F J. On the existence of a normal approximation to the distribution of the ratio of two independent normal random variables[J]. Statistical Papers, 2013, 54(2): 309-323. doi: 10.1007/s00362-012-0429-2 [15] Asaki T J, Chartrand R, Vixie K R, et al. Abel inversion using total-variation regularization[J]. Inverse Problems, 2005, 21(6): 1895-1903. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/21/6/006 [16] 钱伟新, 刘瑞根, 王婉丽, 等. 基于广义变分正则化的闪光照相图像重建算法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2009, 21(12):1903-1907Qian Weixin, Liu Ruigen, Wang Wanli, et al. Generalized variation-based regularization algorithm for image reconstruction in high energy X-ray radiography[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2009, 21(12): 1903-1907 -




 下载:
下载: