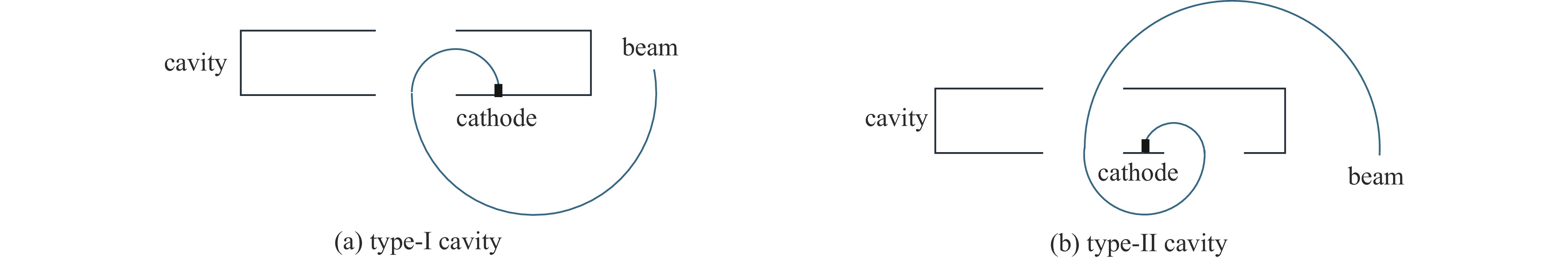
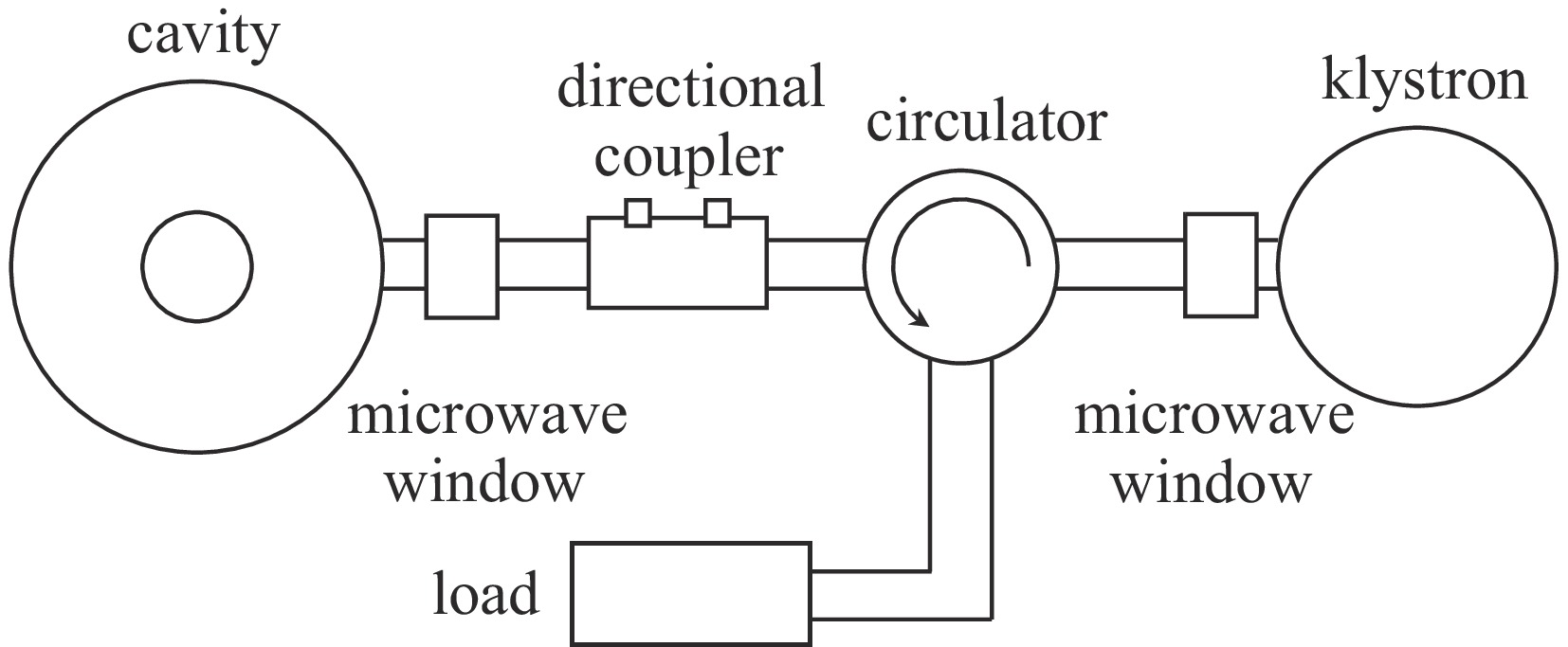
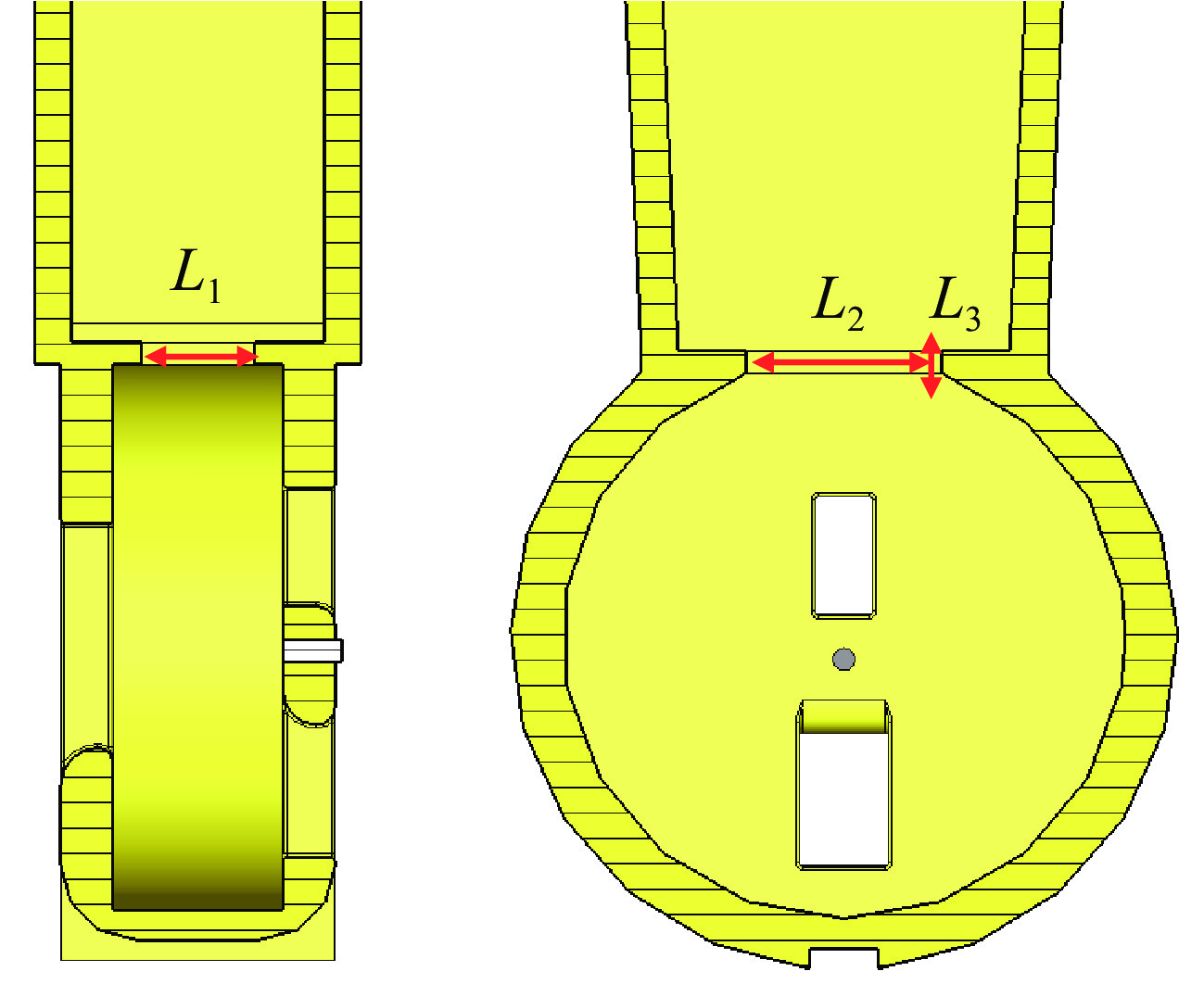
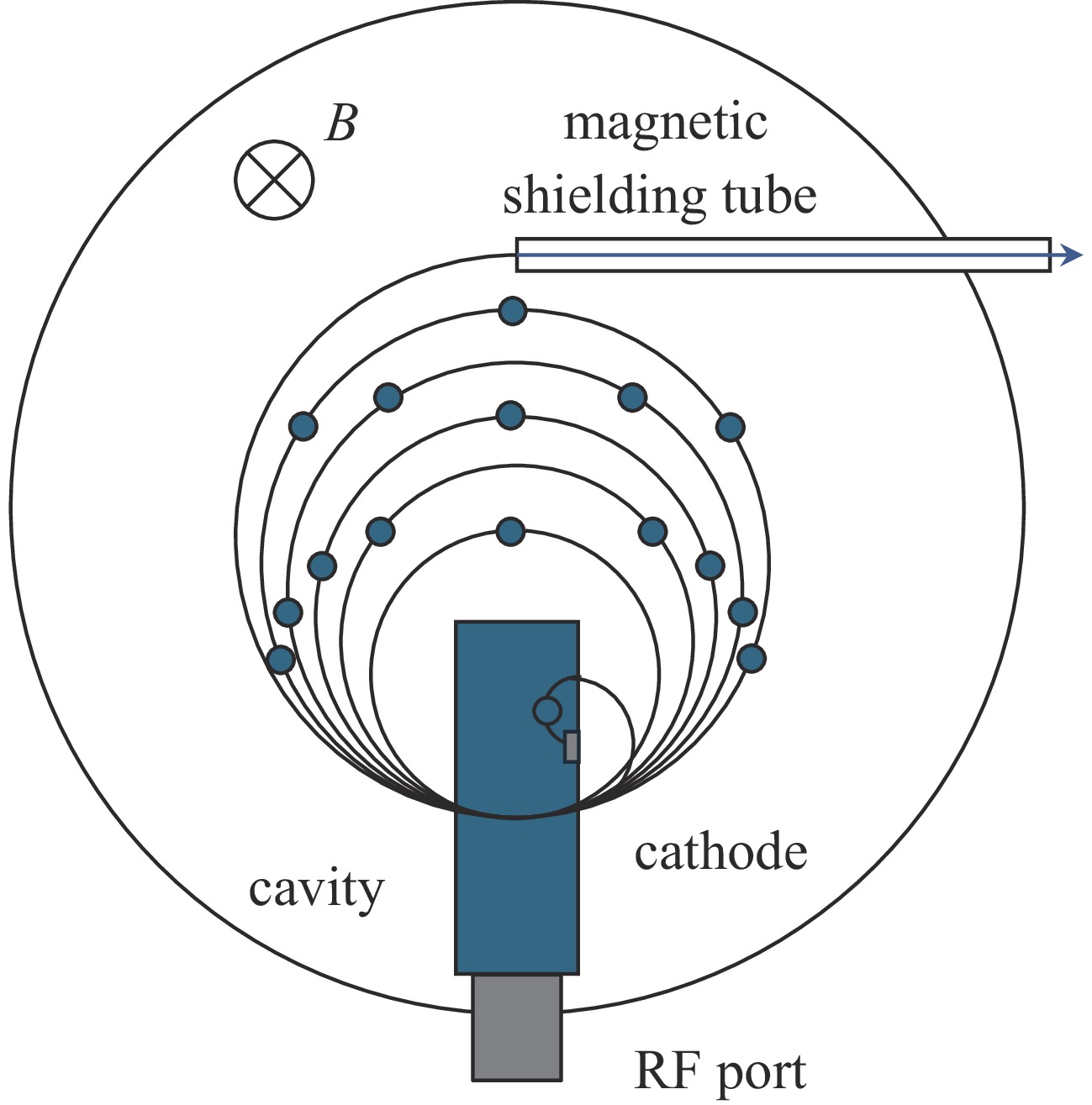
Simulation design of an S-band 6 MeV compact microtron
-
摘要: 安徽省先进光子源实验室正在研制一台S波段6 MeV紧凑型电子回旋加速器,可以用于驱动紧凑型微焦点X射线源或用于驱动紧凑型太赫兹自由电子激光。为了得到更紧凑的加速器设计,利用CST电磁工作室对电子回旋加速器二型谐振腔进行了设计与计算,谐振腔工作频率为
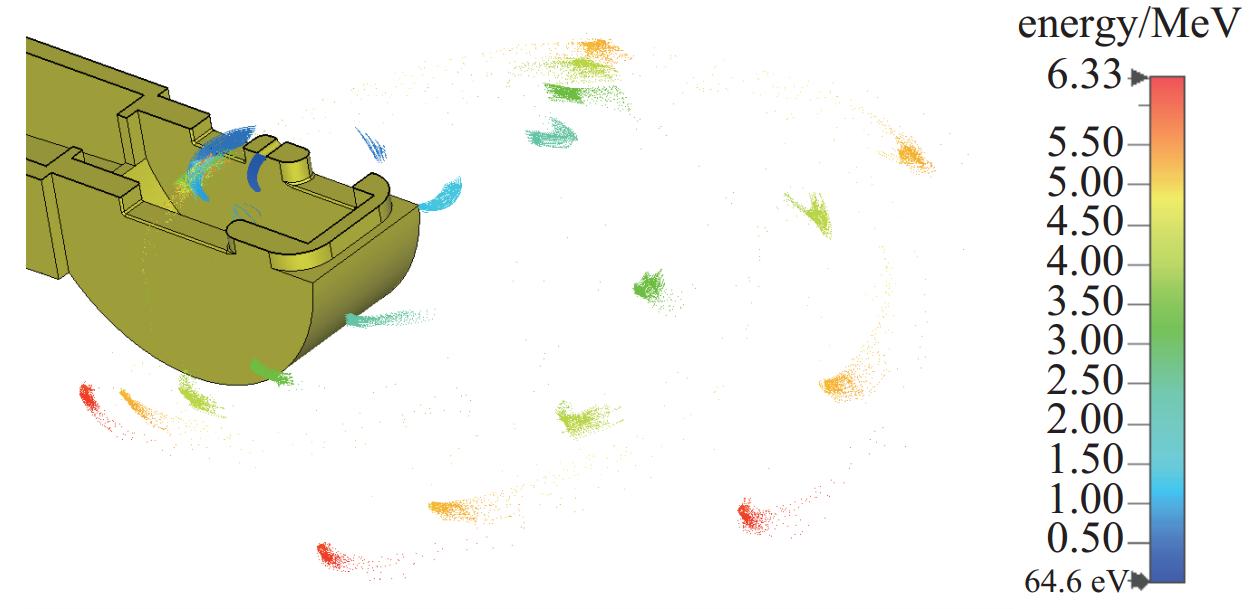
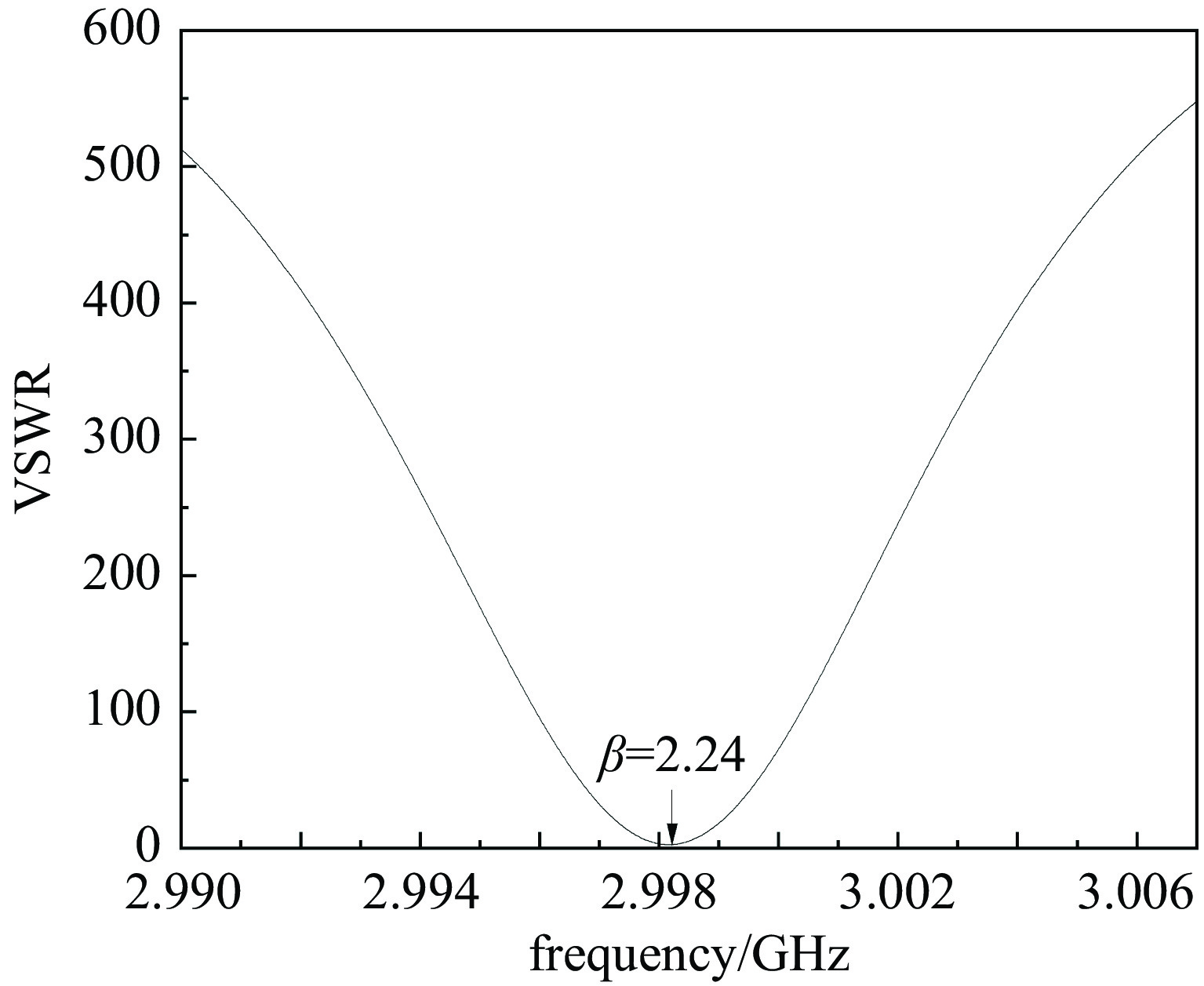
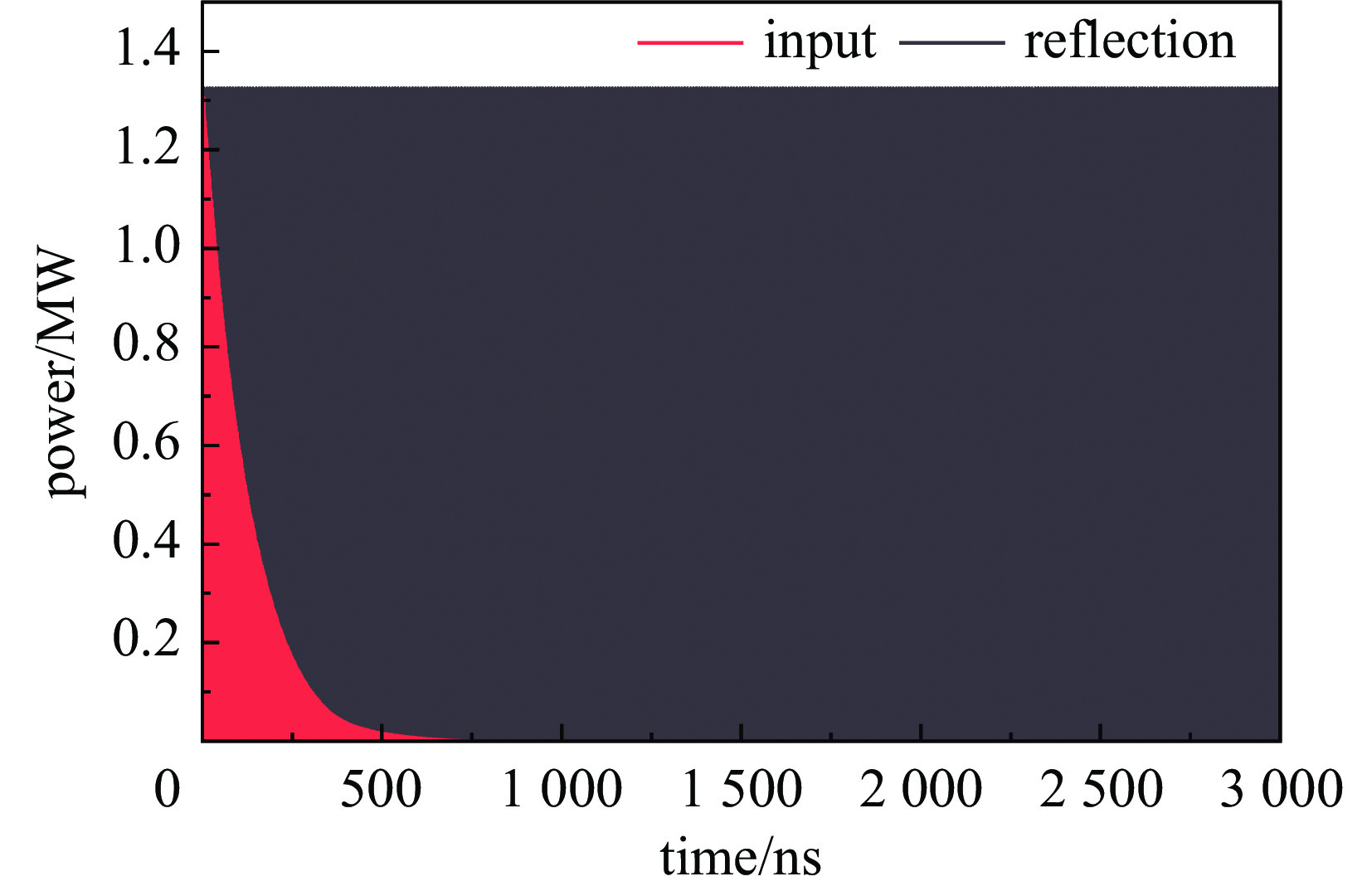
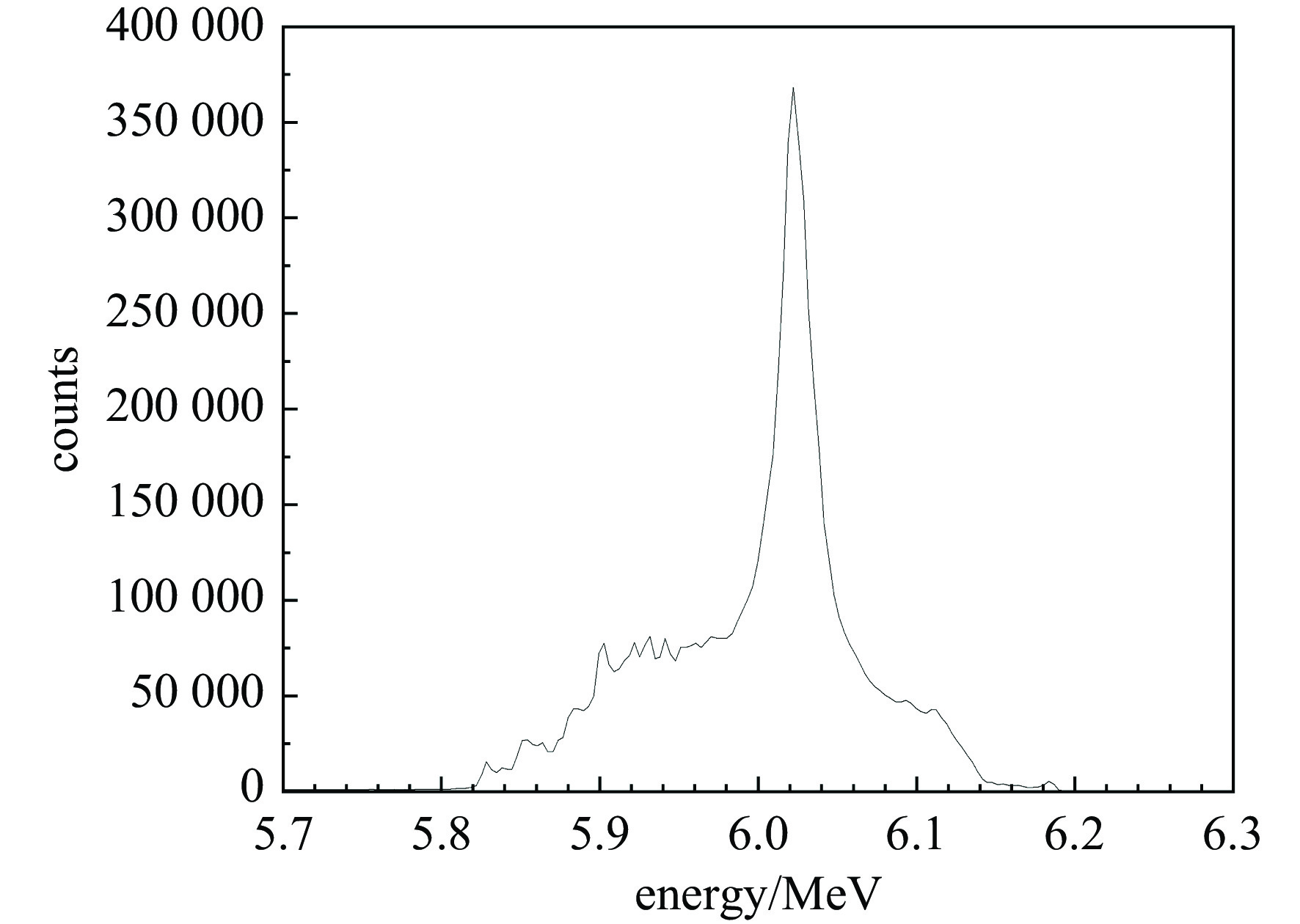
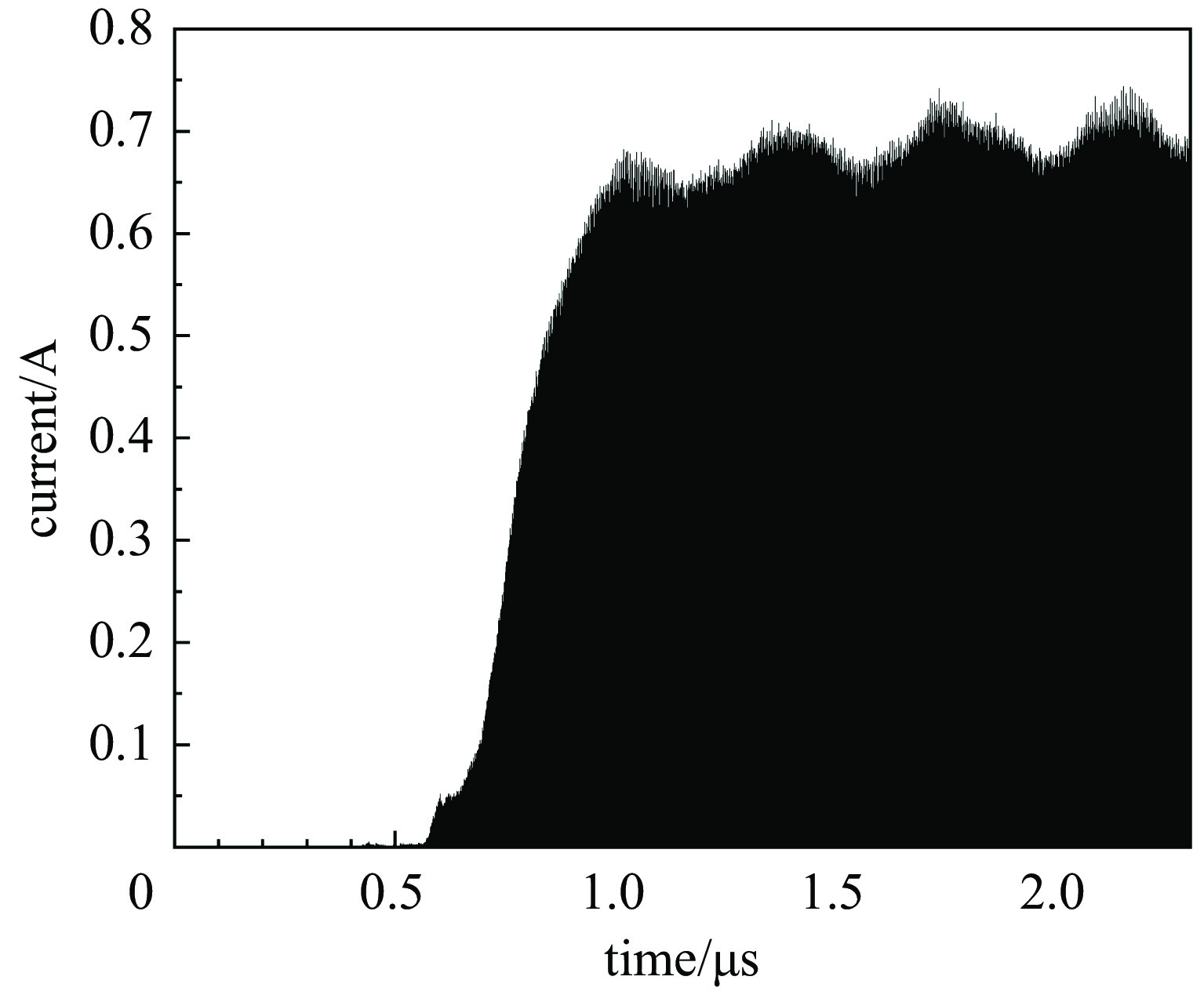
2998.2 MHz,在谐振腔间隙可获得1 MV以上的加速电压,使电子单圈能量增益可达0.9 MeV左右。同时,利用CST粒子工作室对内嵌式热阴极谐振腔的电子产生与加速过程进行了仿真计算,研究了微波功率幅度、磁场强度、热阴极发射位置、束流通道对电子回旋加速器的影响,完成了考虑束流负载情况下的耦合器设计,得到了稳态运行时的谐振腔工作参数。仿真结果表明,束流负载到达稳态时,在热阴极发射能力为20 A/cm2的情况下,可引出流强为 24 mA,束流能量为6.02 MeV,能散约为0.64%,束流横向均方根尺寸为3.3 mm×1.8 mm。Abstract: The Anhui Laboratory of Advanced Photon Science and Technology has beer developing a 6 MeV compact microtron, which can be used to drive compact microfocus X-ray sources or compact terahertz free electron lasers. To achieve a more compact accelerator design, the CST Electromagnetic suite was used to design and calculate the second type RF cavity of the microtron. The frequency of the RF cavity is2998.2 MHz, and an accelerating voltage of over 1 MV can be obtained in the RF cavity gap. The electron energy gain can reach about 0.9 MeV per pass. At the same time, CST Particle Studio was used to simulate the electron generation and acceleration process in the ultra-high frequency cavity with thermionic cathode. The effects of microwave power amplitude, magnetic field strength, cathode emission position, and beam channel on the microtron were studied. The coupler design considering beam loading was also completed, and the operating parameters of the RF cavity during steady-state operation were obtained. The simulation results show that when the beam loading reaches steady state, with a cathode emission capacity of 20 A/cm2, a current of 24 mA can be induced, a beam energy of 6 MeV, an energy spread of 0.64%, and a transverse RMS size of 3.3 mm × 1.8 mm can be obtained.-
Key words:
- microtron /
- RF cavity /
- beam simulation /
- beam loading /
- coupling coefficient
-
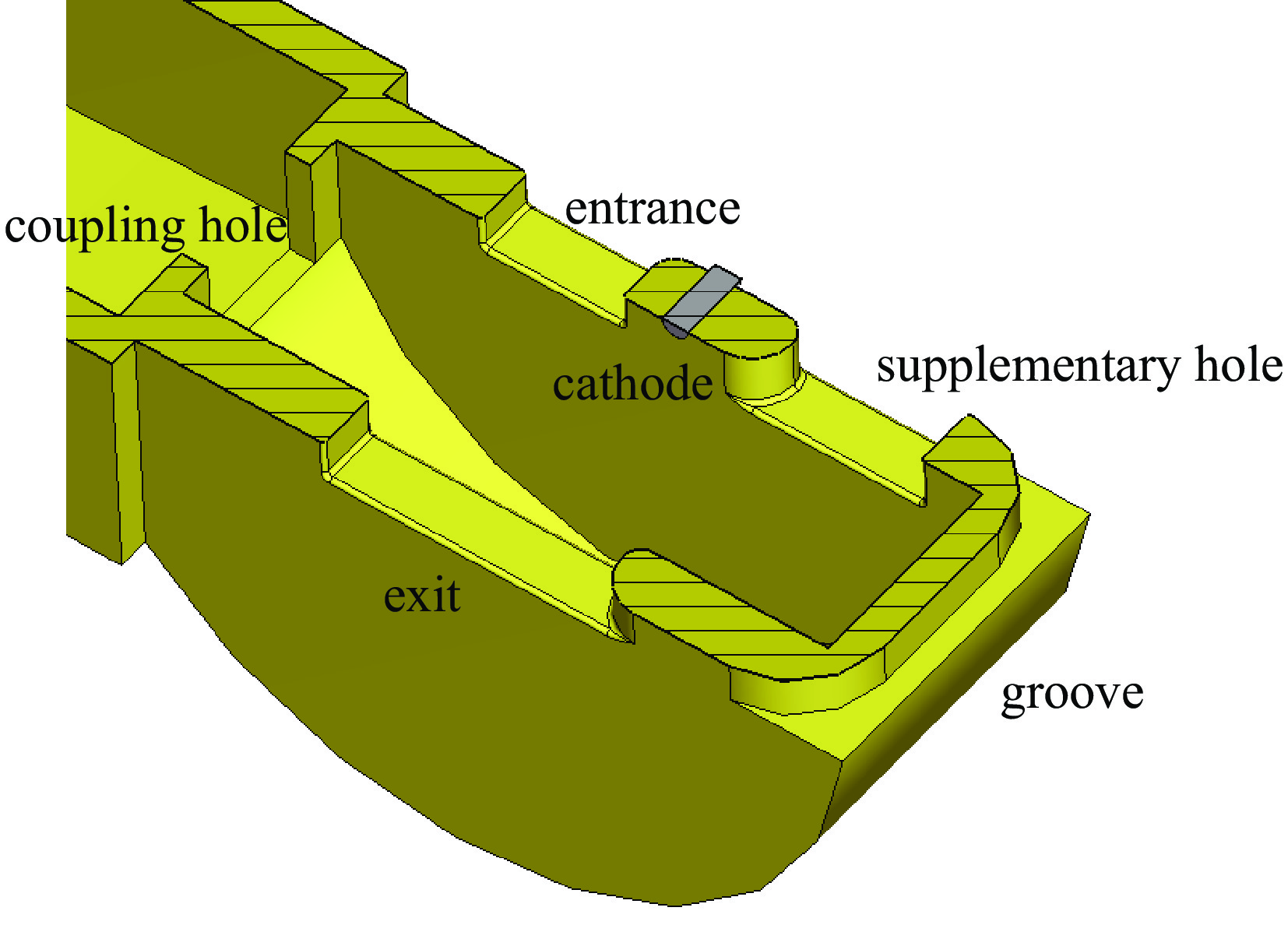
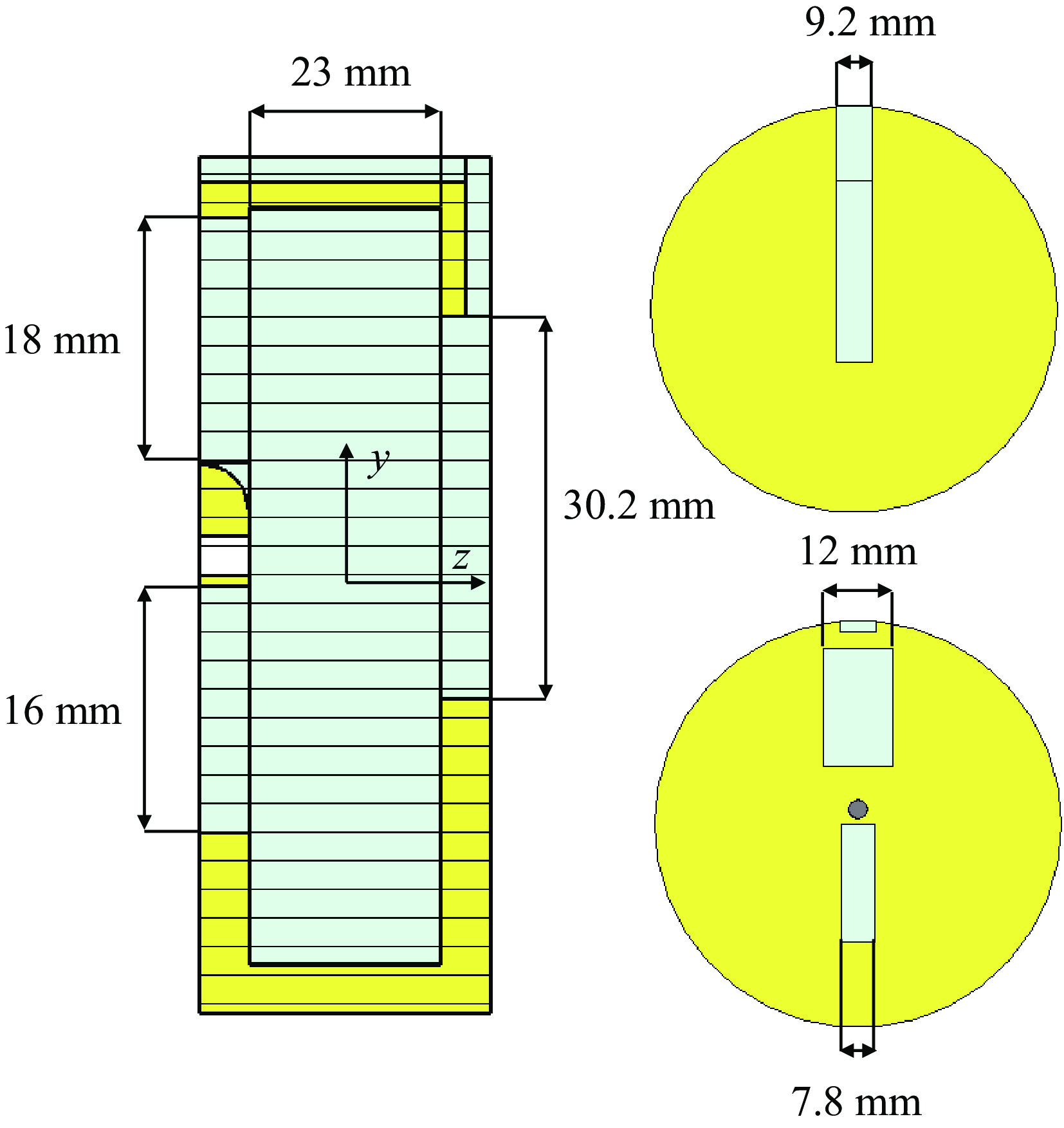
表 1 S波段驻波腔尺寸
Table 1. Size of S-band type-II cavity
radius/mm gap/mm cathode position/mm supplementary/mm entrance/mm exit/mm 37.991 23 3 12 × 18 7.8 × 16 9.2 × 30.2 表 2 驻波腔主要工作参数
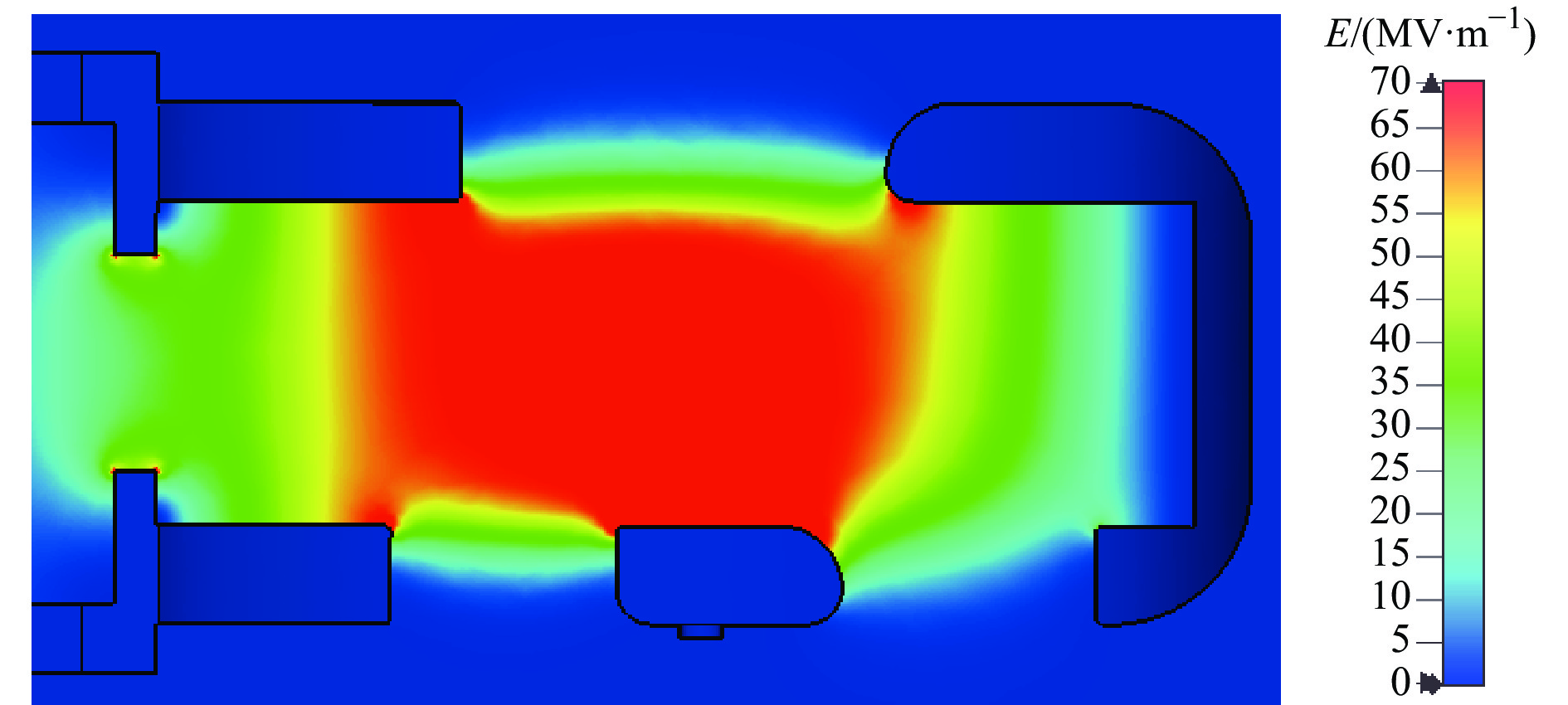
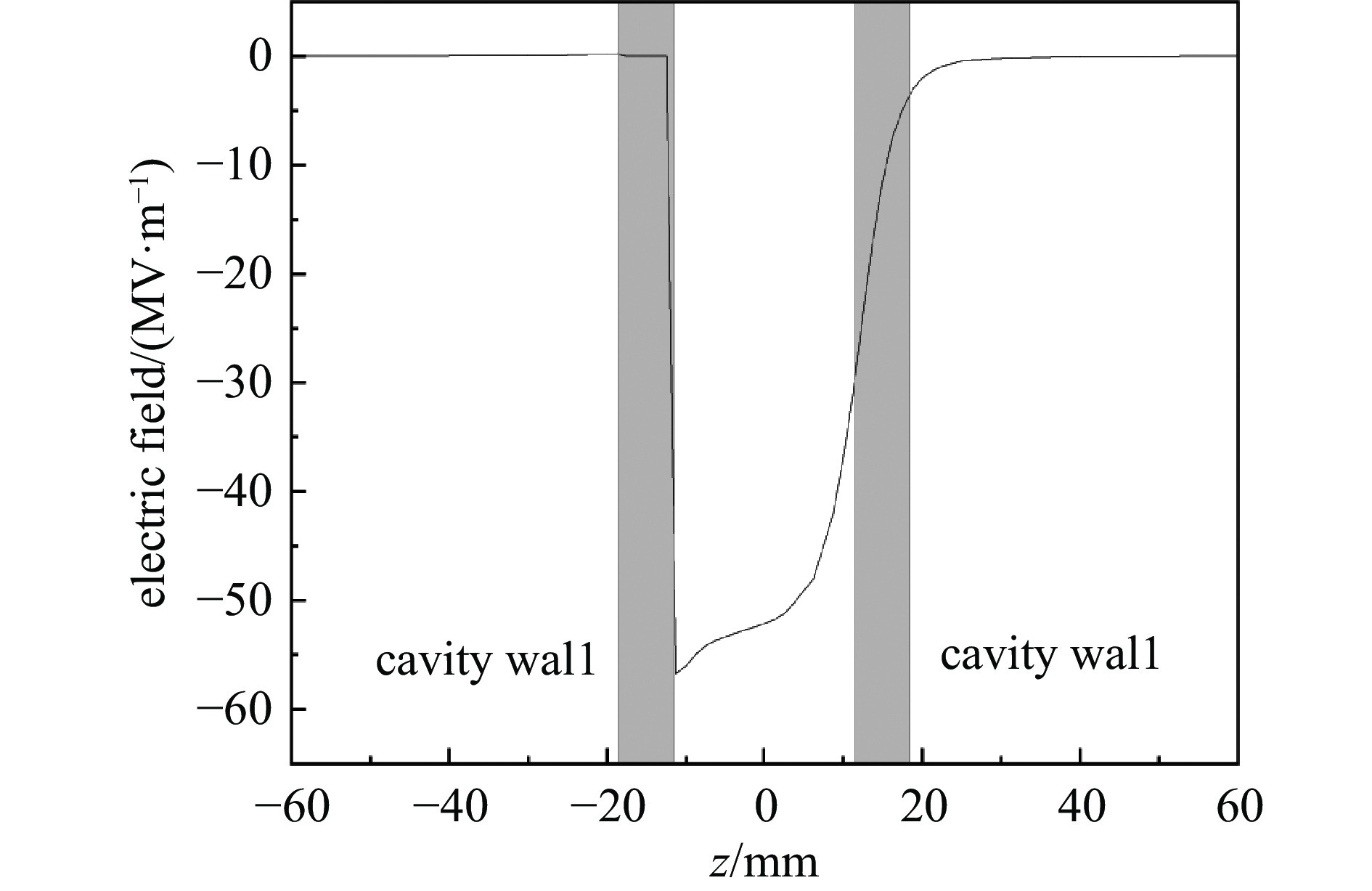
Table 2. Parameters of type-II cavity
material RF frequency/
MHzgap voltage/
MVQ0 shunt impedance/
MΩaverage power loss
(duty factor: 0.1%)/Woxygen free copper 2998.2 1.27 11181 2.68 643 表 3 S波段电子回旋加速器束流参数
Table 3. Beam parameters of the S-band microtron
energy/
MeVcathode current
density/(A·cm−2)peak current/
mAenergy gain
per turn/MeVemittance/
(πmm·mrad)energy
spread/%pulse
frequency/Hzpulse
width/μs6 20 24 0.9 38(H)/3.8(V) 0.64 100 10 -
[1] 陈佳洱. 加速器物理基础[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2012Chen Jiaer. Fundamentals of accelerator physics[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2012 [2] Tsipenyuk Y M. Microtron: development and applications[M]. London: CRC Press, 2001. [3] Borisov M, Ermakov A, Khankin V, et al. Racetrack microtron—pushing the limits[J]. Symmetry, 2021, 13: 2244. doi: 10.3390/sym13122244 [4] Kazakevich G M, Pavlov V M, Kuznetsov G I, et al. Internal injection for a microtron driving a terahertz free electron laser[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102: 034507. [5] Kazakevitch G M, Jeong Y U, Lee B C, et al. Variable-energy microtron-injector for a compact wide-band FIR free electron laser[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2003, 507(1/2): 146-149. [6] Kazakevich G M, Pavlov V M, Kuznetsov G I, et al. Optimization of the injection system for microtron-based terahertz FEL[C]//Proceedings of the 28th International Free Electron Laser Conference (FEL 2006). 2006: 403-406. [7] Abrams R J, Cummings M A C, Johnson R P, et al. Compact, microtron-based gamma source[C]//7th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2016: 3522-3524. [8] Sviatoslavsky I N. The microtron[M]. Kapit︠s︡a S P, Melekhin V N, trans. London: Harwood Academic Publishers, 1978. [9] Lidbjörk P. Microtrons[C]//CAS - CERN accelerator school: 5th General Accelerator Physics Course. 1994: 971-981. [10] Kazakevich G M, Pavlov V M, Jeong Y U, et al. Magnetron-driven microtron injector of a terahertz free electron laser[J]. Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, 2009, 12: 040701. [11] Abrams R J. I. Final report for DOE SBIR phase I project DE-SC0013795 microtron-based compact, portable gamma-ray source[R]. Batavia: Muons Inc. , 2017. [12] Bashmakov Y A, Dyubkov V S, Lozeev Y Y. Numerical simulation of longitudinal and transversal electron dynamics in classical microtron[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2019, 1238: 012071. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1238/1/012071 [13] Bashmakov Y A, Dyubkov V S, Lozeev Y Y. Numerical simulation of electrons dynamics in a microtron on 6–10 MeV[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2017, 941: 012090. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/941/1/012090 [14] Yamada H, Hasegawa D, Yamada T, et al. Tabletop synchrotron light source[J]. Comprehensive Biomedical Physics, 2014, 8: 43-65. [15] Hasegawa D, Yamada H, Kleev A I, et al. The portable synchrotron MIRRORCLE-6X[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2004, 716(1): 116-119. -




 下载:
下载: