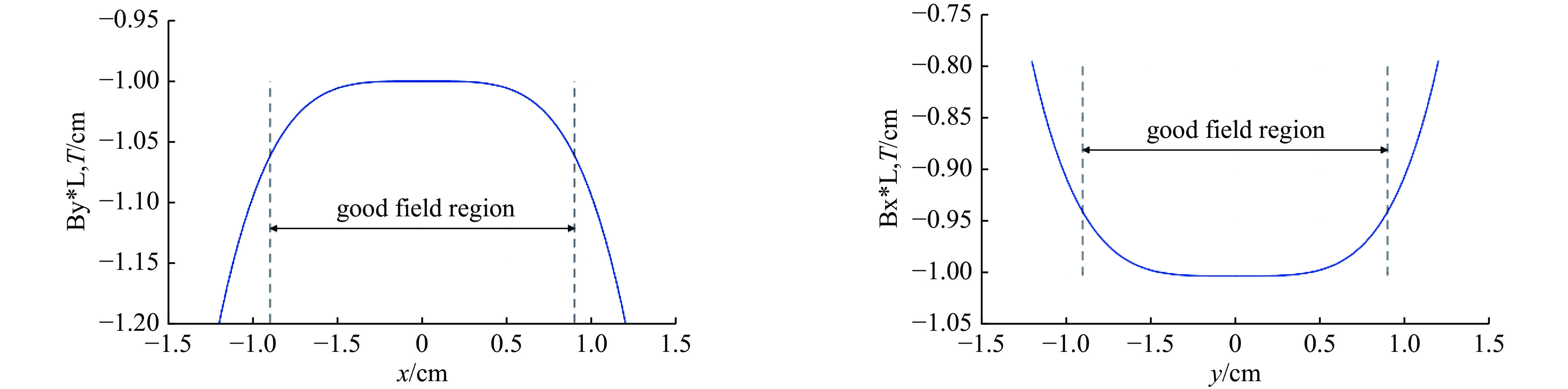
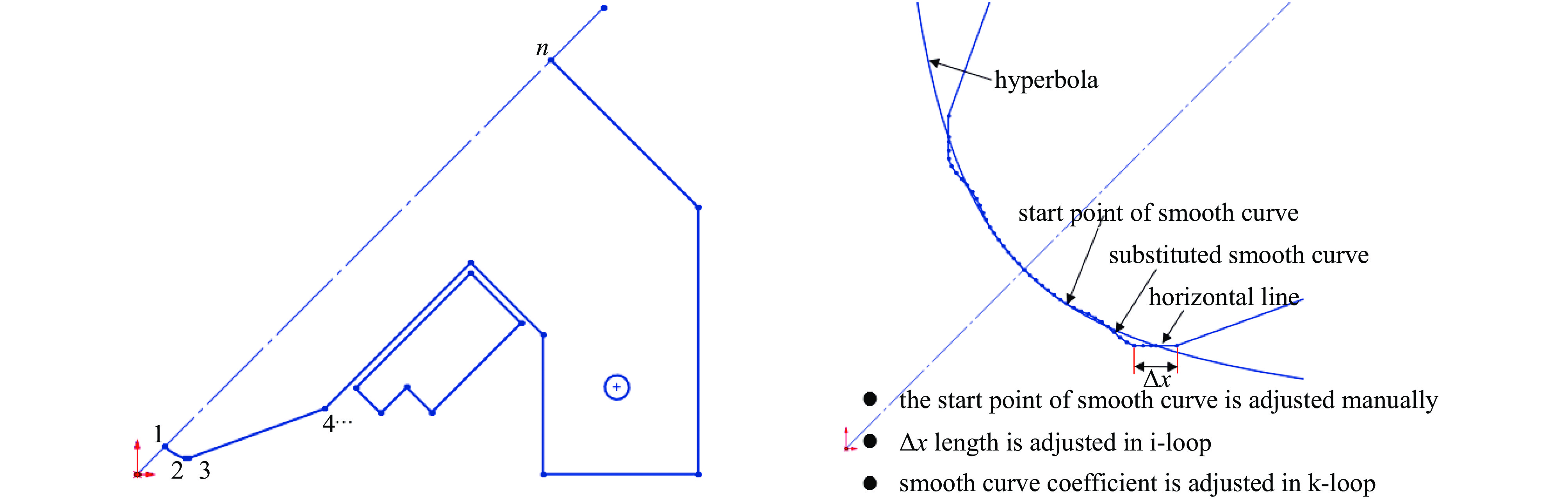
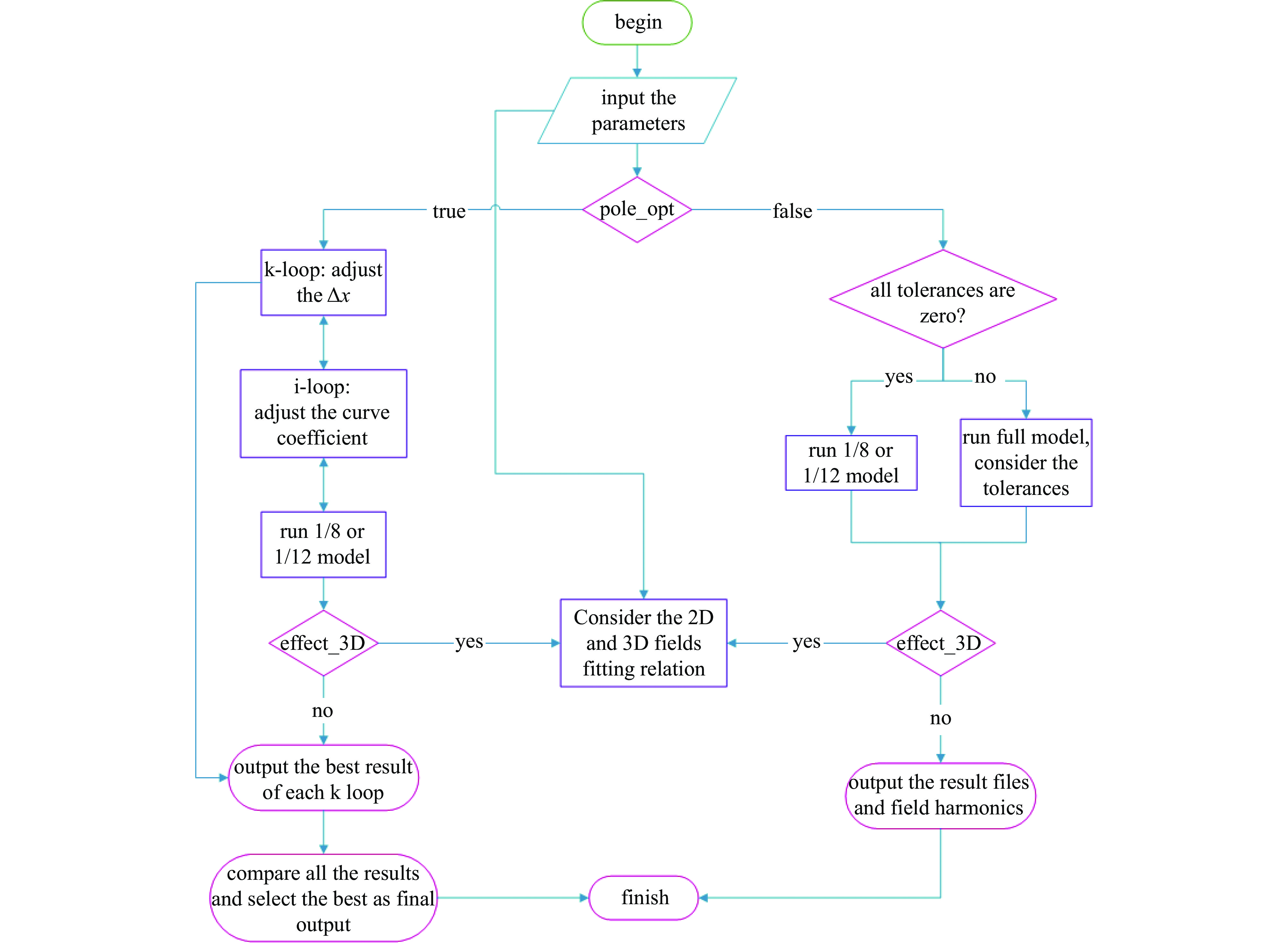
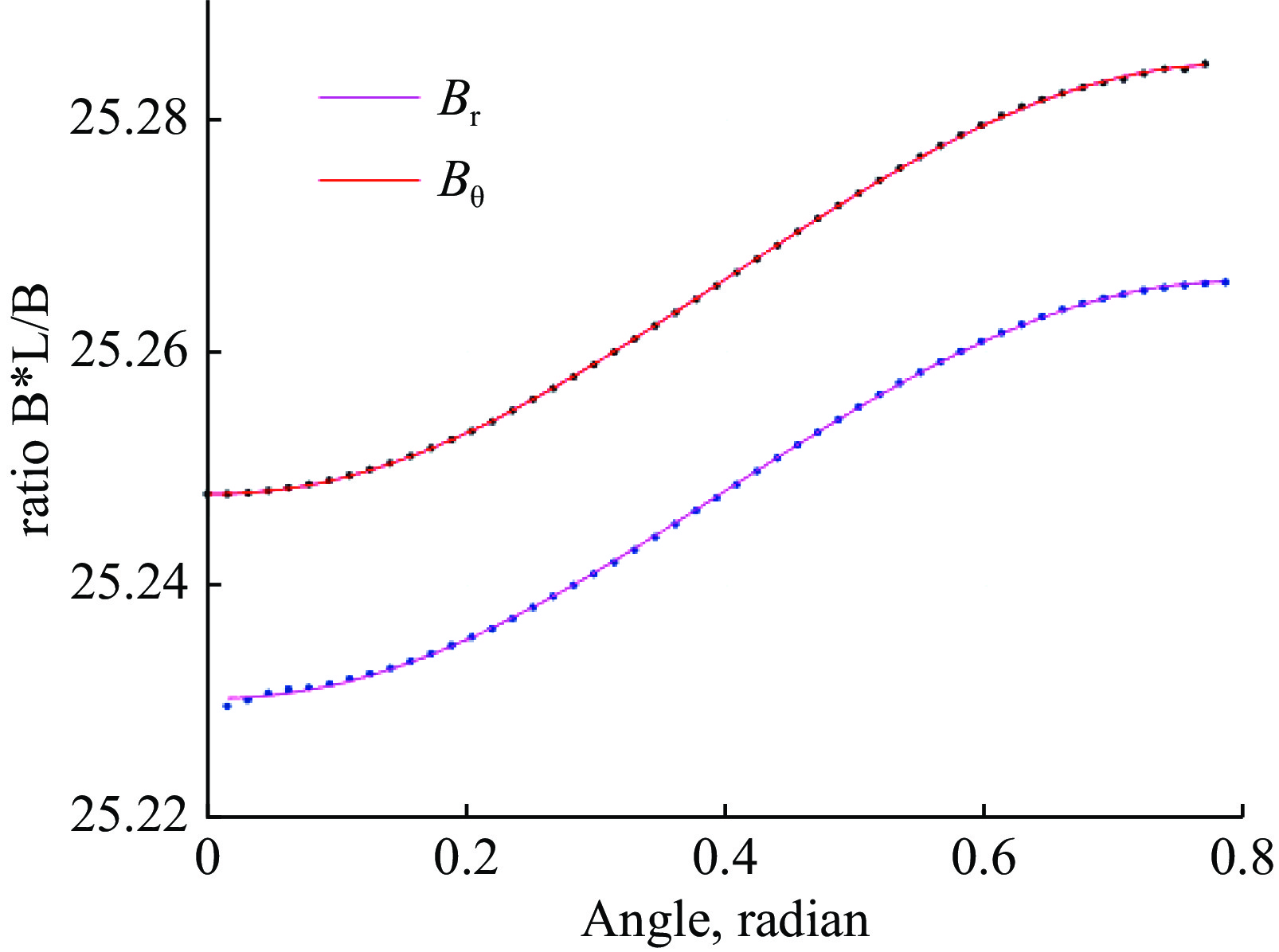
Design and optimization of the quadrupole and sextupole magnets for SILF storage ring
-
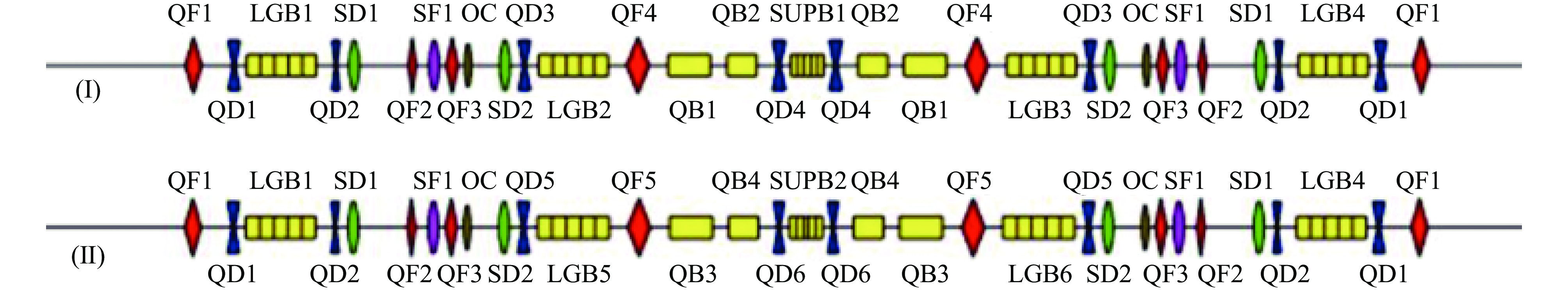
摘要: 相较于第三代同步辐射光源,基于多弯铁消色散(Multi-Bend Achromat, MBA)磁聚焦结构的第四代同步辐射光源可以进一步降低束流发射度达1~2个数量级,从而进一步提升光源亮度和相干性。深圳产业光源(Shenzhen Innovation Light-source Facility, SILF)储存环的周长为696 m,束流设计流强为200~300 mA,发射度约84 pm·rad。根据目前储存环物理设计,共有11种四极磁铁、4种二四极组合功能铁和3种六极磁铁。由于物理设计对磁铁的积分磁场均匀性提出了更高要求,开发了基于Opera-2D®的四六极磁铁磁极面优化程序,该优化程序同时考虑了磁铁的端部磁场效应,从而大大提高了优化效率。首先介绍了深圳产业光源四极磁铁、二四极组合功能铁及六极磁铁的初步设计,然后详细介绍了基于Opera-2D®的四六极磁铁磁极面的优化方法。Abstract: As an advanced 4th generation synchrotron radiation facility, the Shenzhen Innovation Light-source Facility (SILF) storage ring is based on multi-bend achromat (MBA) lattices, which enables an emittance reduction of one to two orders of magnitude pushing beyond the radiation brightness and coherence reached by the 3rd generation storage ring. The multipole magnets of many types for SILF storage ring are under preliminary design, which require high integral field homogeneity. As a result, a dedicated pole tip optimization procedure with high efficiency is developed for quadrupole and sextupole magnets with Opera-2D® python script. The procedure considers also the 3D field effect which makes the optimization more straightforward. In this paper, the design of the quadrupole and sextupole magnets for SILF storage ring is firstly presented, followed by the elaboration of the implemented pole shape optimization method.
-
Table 1. The basic design parameters of the quadrupoles
magnets in
groupsfield gradient/
(T/m)effective magnetic
length/cmcurrent/A turn number
per windingconductor
size/(mm×mm)power/kW water flow
rate/(L/min)QF1 36.23 25.0 115.4 32 7×7 0.69 0.774 QD1/QF3/QD3/QD5 −36.2/34.8/
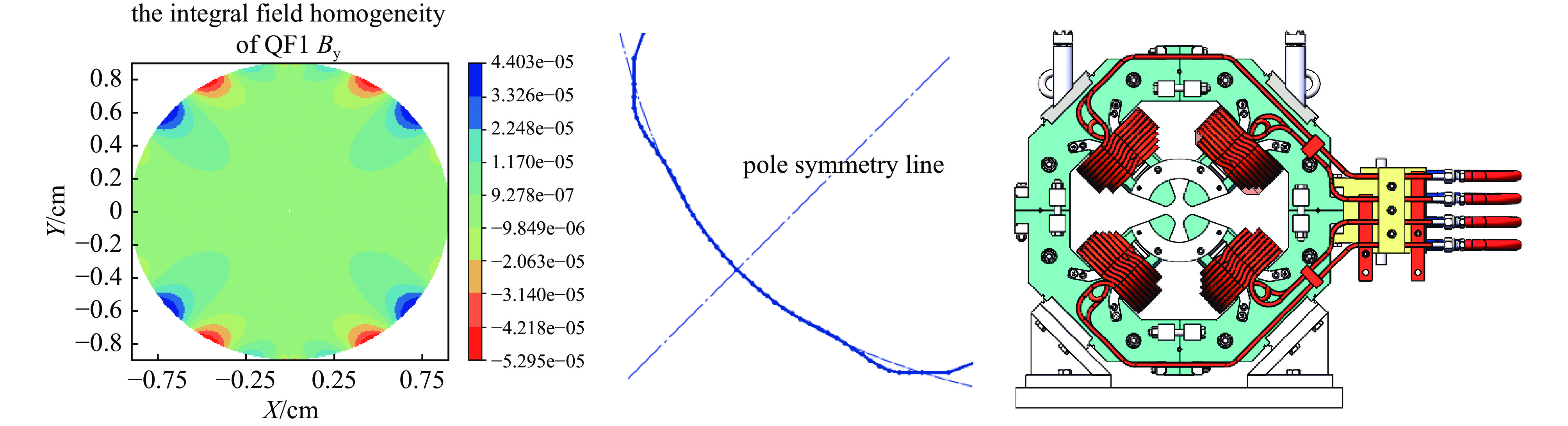
−41.9/−37.018.0 133.4 32 7×7 0.77 0.852 QD2/QF2 −33.1/44.56 12.0 141.9 32 7×7 0.73 0.95 QF4/QF5 51.5/48.0 35.0 163.9 32 8×8 1.39 1.50 QD4 −39.1 20.0 124.5 32 7×7 0.71 0.83 QD6 −28.0 16.0 89.1 32 7×7 0.33 0.88 Table 2. The integrated field harmonics of the quadrupoles
magnets in groups B6/B2 B10/B2 B14/B2 B18/B2 QF1 −9.98E-6 1.68E-5 −8.79E-6 −4.65E-7 QD1/QF3/QD3/QD5 −2.26E-5 2.84E-5 −1.21E-5 −5.09E-7 QD2/QF2 −3.95E-6 1.01E-5 −1.16E-5 −3.20E-7 QF4/QF5 −3.52E-5 2.21E-5 −8.80E-6 −5.10E-7 QD4 −8.69E-6 1.21E-5 −9.44E-6 −2.63E-7 QD6 −3.35E-5 2.68E-5 −1.10E-5 2.07E-7 Table 3. The basic design parameters of Q-bend and sextupole magnets
magnets field
strengthdipole
field/Tmagnetic
length/cmcurrent/A turn number
per windingconductor
size/(mm×mm)power/kW water flow
rate/(L/min)QB1/QB3 −26.87/-29.08 T/m 0.3576 /0.3452 64.5/65.0 265.6/
287.432 8×8 5.78/6.81 2.03/2.02 QB2/QB4 51.43/51.16 T/m − 0.2766 /
-0.2876 45.0 237.2/
236.136 8×8 4.94/4.89 1.95 SF1/SD1/SD2 1900.4 /−1853.1 /
−1532.8 T/m2/ 15.0 88.0 12 6×6 0.2 0.96 Table 4. The integrated field harmonics of Q-bend and sextupole magnets
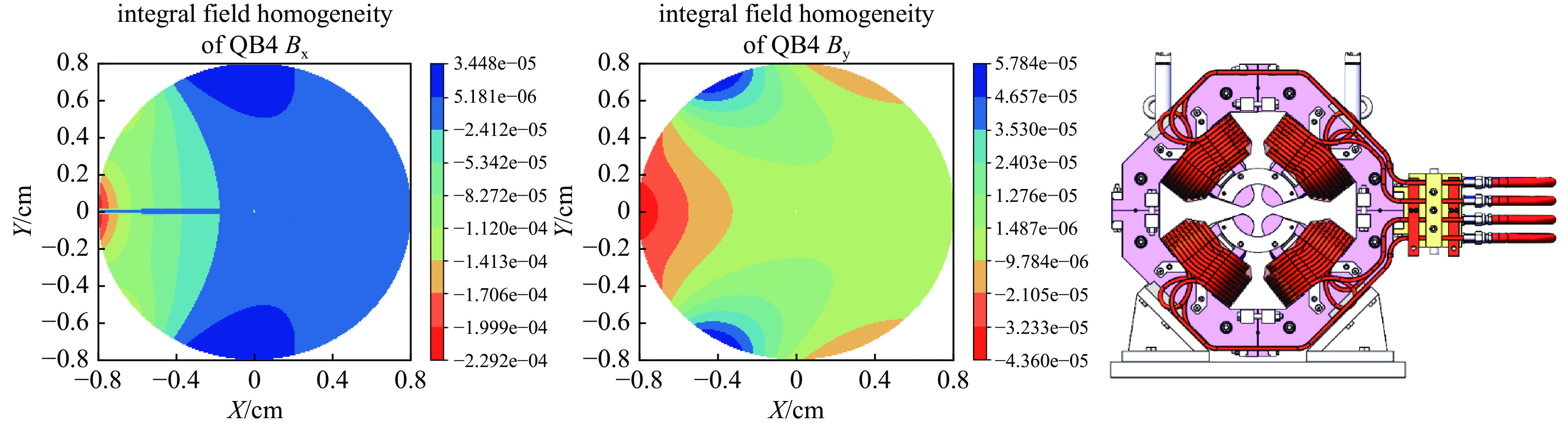
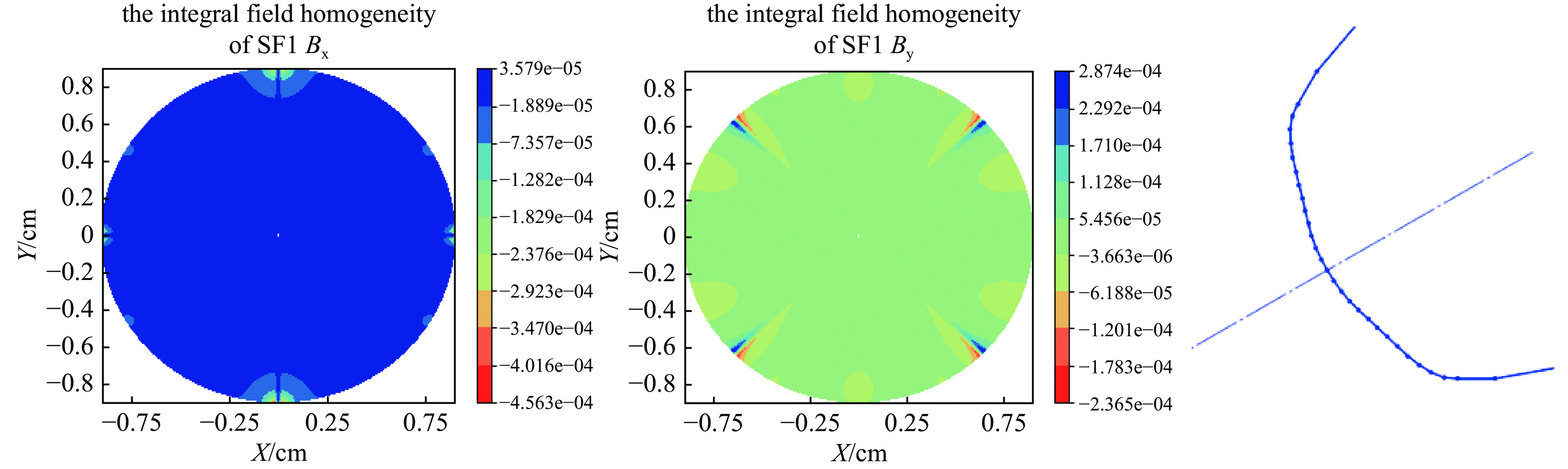
magnets B6/B2, B9/B3 B10/B2, B15/B3 B14/B2, B21/B3 B18/B2, B27/B3 QB1 −2.45E-5 1.32E-4 −7.28E-5 −2.0E-5 QB2 −7.02E-5 4.82E-5 −2.50E-5 −3.89E-5 QB3 −5.14E-5 1.32E-4 −7.26E-5 −1.98E-5 QB4 −6.93E-5 4.82E-5 −2.50E-5 −3.89E-6 SF1/SD1/SD2 1.07E-5 −7.52E-6 1.44E-6 −8.49E-6 -
[1] Shin S. New era of synchrotron radiation: fourth-generation storage ring[J]. AAPPS Bulletin, 2021, 31: 21. doi: 10.1007/s43673-021-00021-4 [2] He Tao, Sun Zhenbiao, Zhang Tong, et al. Physics design of the Shenzhen innovation light source storage ring[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2023, 18: P05037. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/18/05/P05037 [3] Halbach K, Holsinger R. Poisson user manual[R]. Berkeley: Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, 1972. [4] Russenschuck S, Aleksa M, Bazan M, et al. Integrated design of superconducting magnets with the CERN field computation program ROXIE[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Computational Accelerator Physics Conference. 2000. [5] Wang Chunguang, Zhang Miao, Liu Guiming, et al. Magnet designs for the storage ring of the Shenzhen innovation light-source facility[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2024, 34: 4902304. [6] Ying Chuntong. Transport theory and application of gas[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1990. [7] Russenschuck S. Field computation for accelerator magnets: analytical and numerical methods for electromagnetic design and optimization[M]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2010. -




 下载:
下载: