Different voltage limiting methods of pulse power supply based on superconducting pulse transformer
-
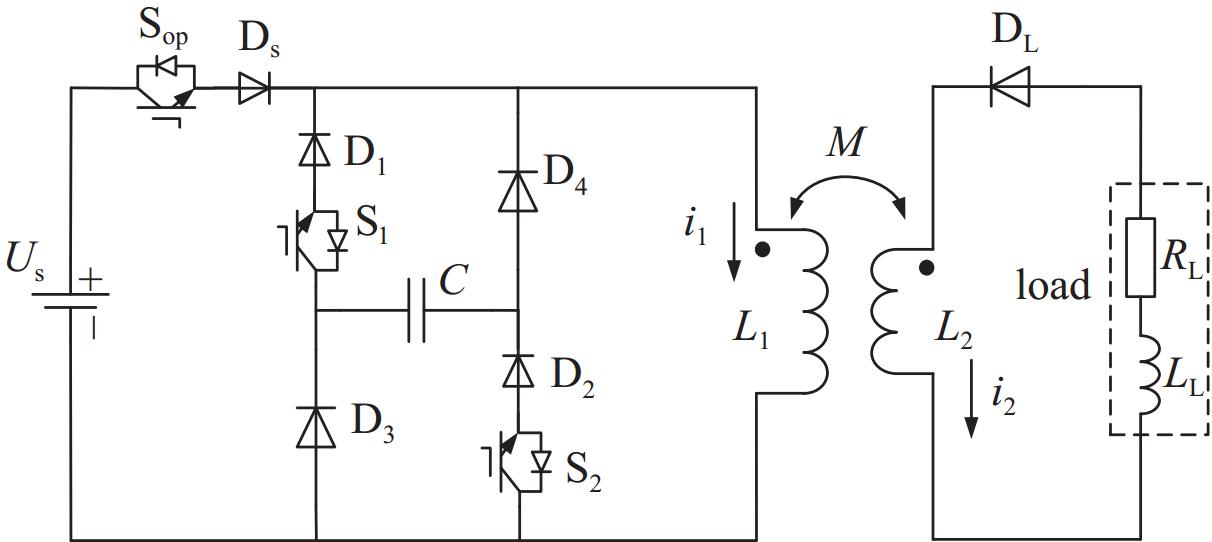
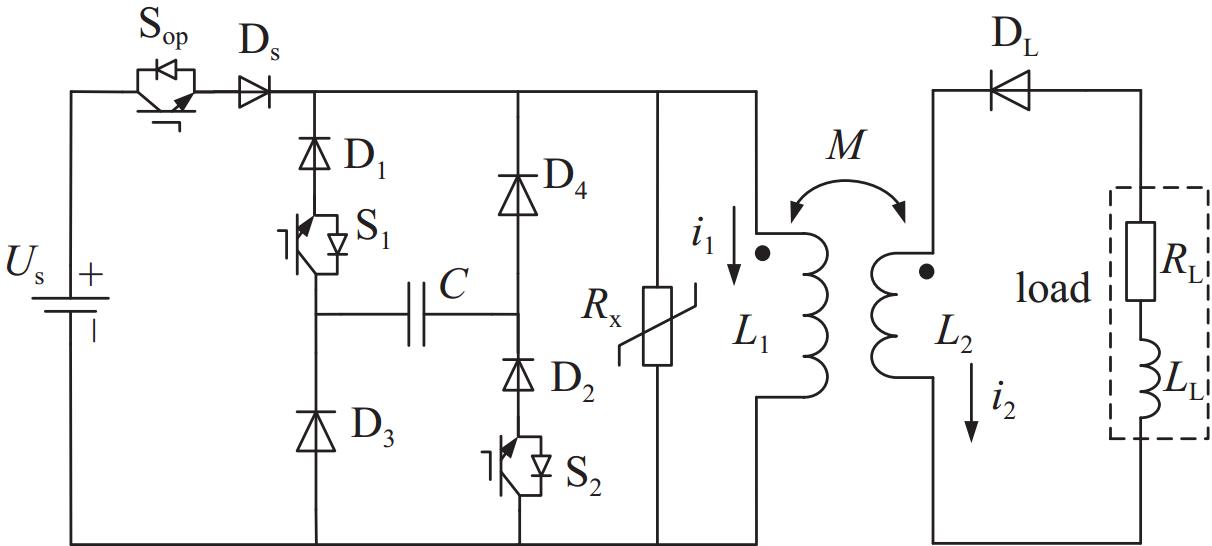
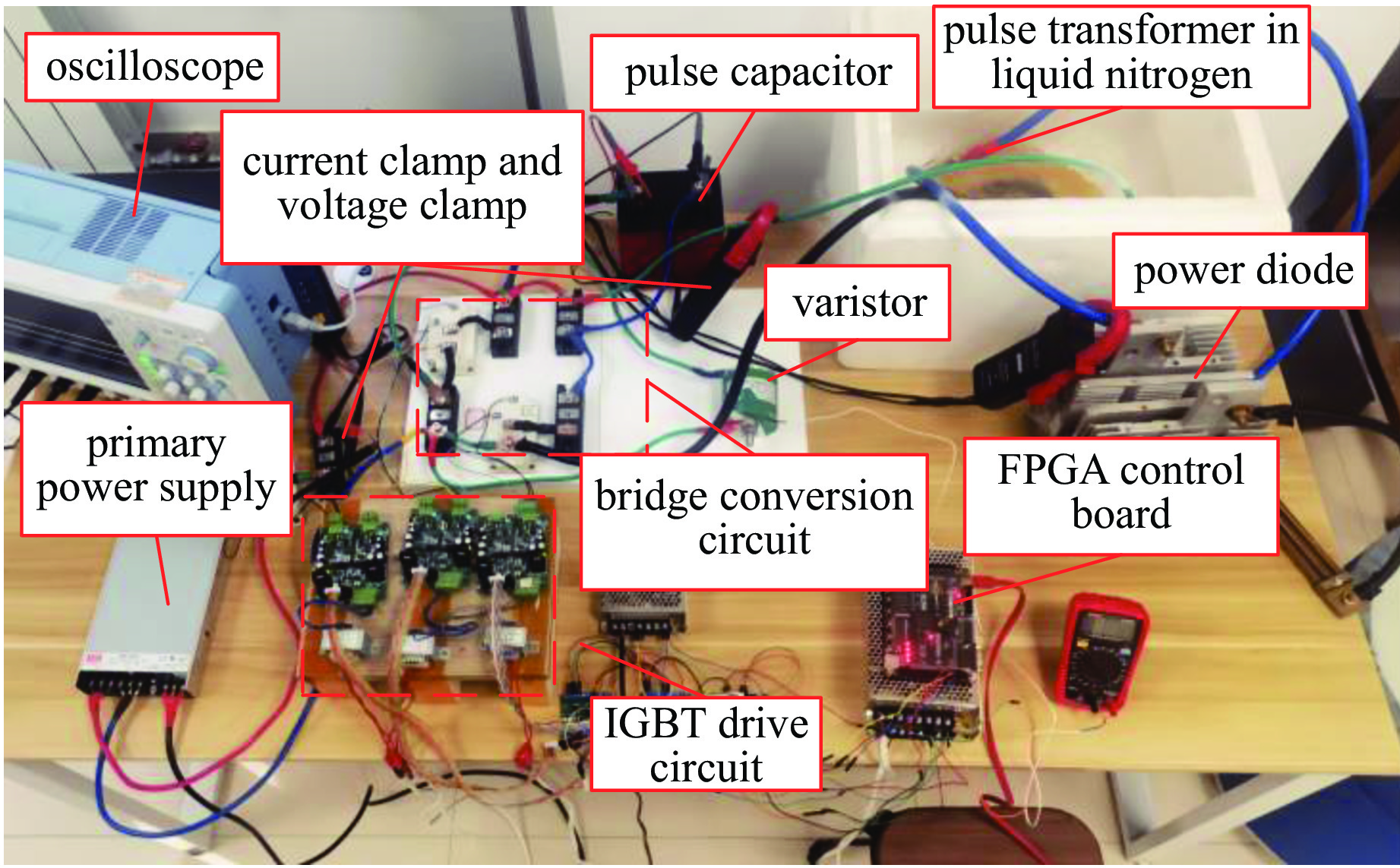
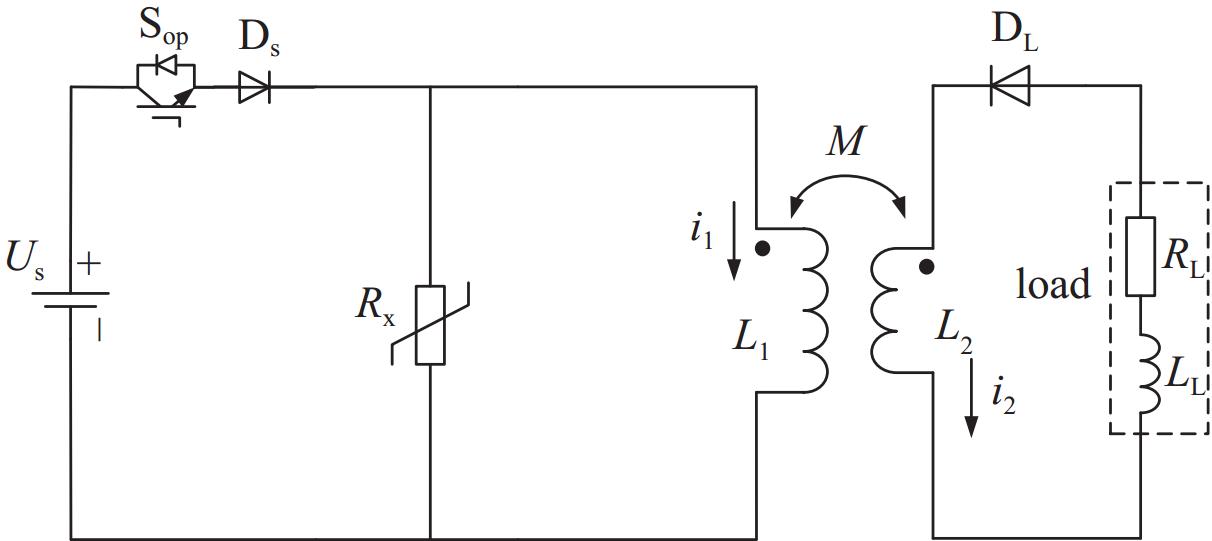
摘要: 电感储能是脉冲功率技术的主要储能方式之一,而断路开关的限压问题是其固有难题。为了探究超导脉冲电源的限压方法,介绍了ZnO压敏电阻限压和脉冲电容器限压两种传统限压方式,提出联合脉冲电容器和压敏电阻以限制断路开关电压。分析了三种限压方式下超导脉冲电源的工作原理,基于同一超导脉冲变压器参数进行仿真,并分别分析了不同限压参数下的输出特性,对比分析了不同限压方法之间的输出特性差异。针对联合限压方式,为验证其限压性能,搭建了小型实验平台进行验证性实验。仿真和实验结果表明,联合限压方式比压敏电阻限压传输效率高,关断性能好;比脉冲电容限压放电速度快,电压幅值低。Abstract: Inductive energy storage is one of the main energy storage methods of pulse power technology, and the problem of limiting voltage of open circuit switch is its inherent problem. To explore the voltage limiting method of superconducting pulse power supply, this paper introduces two traditional voltage limiting methods, namely ZnO varistor voltage limiting and pulse capacitor voltage limiting, and puts forward the combination of pulse capacitor and varistor to limit the open switching voltage. The working principle of superconducting pulse power supply under three voltage limiting modes is analyzed, and the output characteristics under different voltage limiting parameters are simulated based on the same superconducting pulse transformer parameters. Aiming at the combined voltage limiting mode, a small experimental platform was built to verify the voltage limiting performance of the device. Simulation and experimental results show that the combined voltage limiting mode has higher transmission efficiency and better turn-off performance than varistor, and it has faster discharge and lower voltage amplitude than pulse capacitance limiting mode.
-
表 1 超导脉冲变压器参数
Table 1. Parameters of the superconducting pulsed transformer
primary
inductance/mHsecondary
inductance/μHcoupling
coefficientprimary
resistance/mΩsecondary
resistance/mΩcoil critical
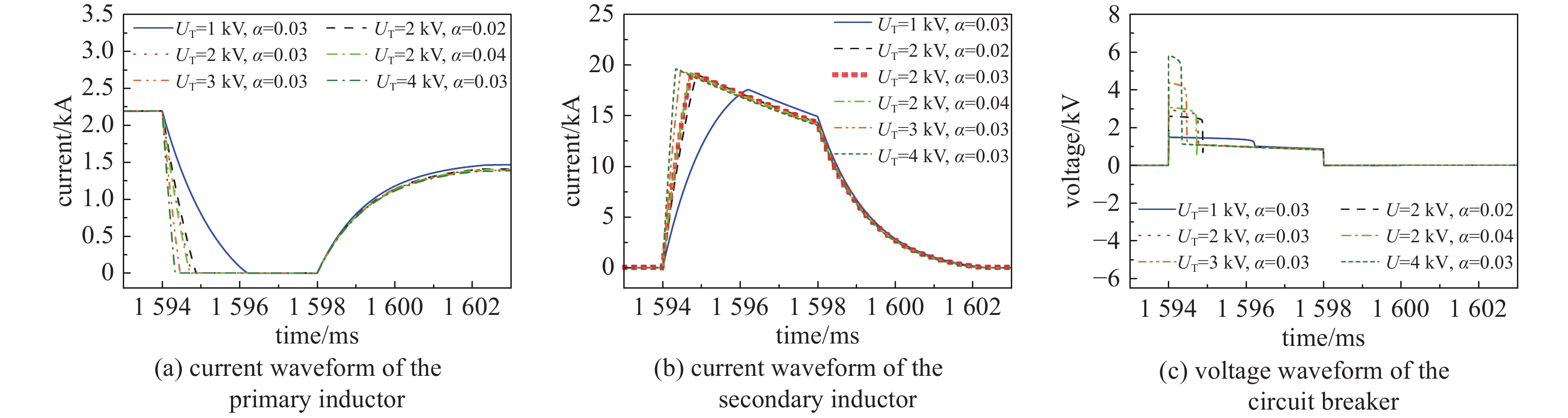
current/kA6.21 60.91 0.974 1 2 2.2 表 2 不同压敏电阻限压的仿真结果比较
Table 2. Comparison of simulation results of voltage limiting by different varistors
UT/kV α I2m/kA T1/ms U1m/kV η/% Ir/kA 1 0.03 17.62 1.21 1.49 54.91 1.45 2 0.02 19.10 0.88 2.61 60.78 1.41 2 0.03 19.19 0.74 2.94 61.30 1.40 2 0.04 19.27 0.72 3.08 61.53 1.39 3 0.03 19.51 0.47 4.39 62.56 1.38 4 0.03 19.64 0.33 5.83 62.92 1.37 表 3 不同电容限压的仿真结果比较
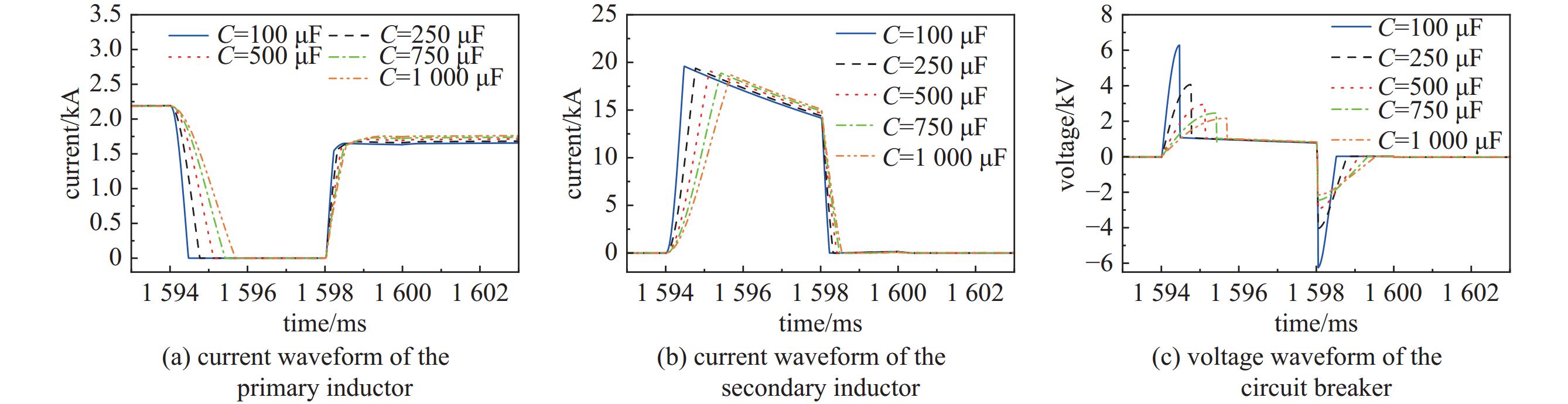
Table 3. Comparison of simulation results of different capacitance limiting voltages
C/μF I2m/kA T1/ms U1m/kV η/% Ir/kA 100 19.67 0.48 6.28 77.11 1.65 250 19.46 0.77 4.07 76.85 1.67 500 19.22 1.15 2.95 76.33 1.71 750 18.97 1.43 2.46 75.77 1.73 1000 18.78 1.69 2.17 75.24 1.75 表 4 不同联合限压的仿真结果比较
Table 4. Comparison of simulation results of different combination limiting voltages
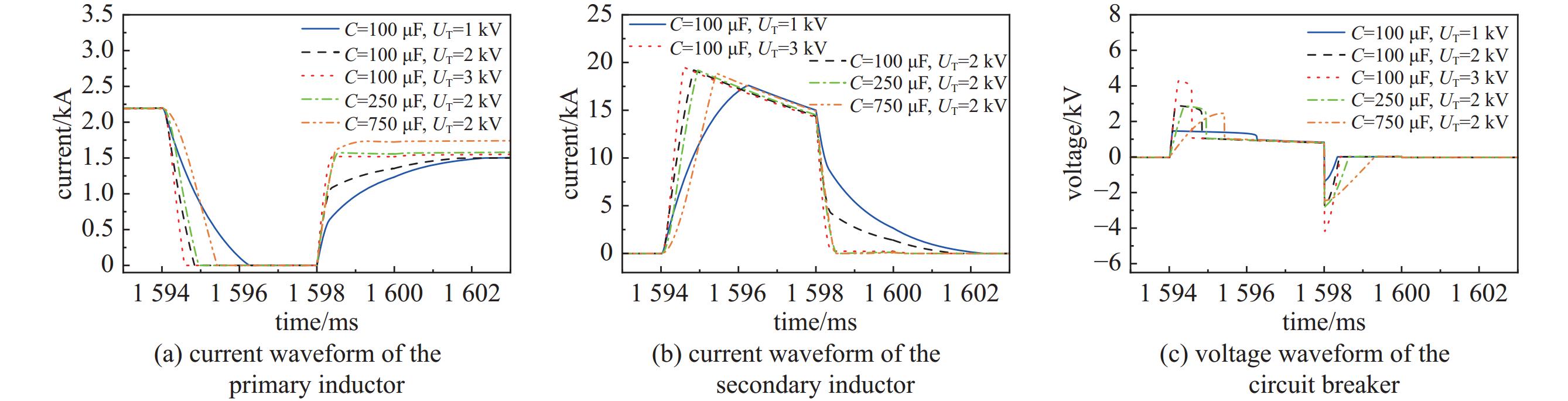
C/μF UT/kV I2m/kA T1/ms U1m/kV η/% Ir/kA 100 1 17.63 1.16 1.41 52.00 1.46 100 2 19.24 0.84 2.84 60.24 1.47 100 3 19.53 0.58 4.25 64.38 1.50 250 2 19.21 0.94 2.83 63.24 1.55 750 2 18.98 1.42 2.46 70.09 1.69 表 5 三种电路限压的仿真结果比较
Table 5. Comparison of simulation results of three voltage limiting circuits
I2m/kA T1/ms U1m/kV η/% Ir/kA varistor voltage limiting 19.19 0.74 2.94 61.30 1.40 capacitance voltage limiting 19.22 1.15 2.95 76.33 1.71 combination voltage limiting 19.21 0.94 2.83 63.24 1.55 表 6 超导脉冲变压器参数
Table 6. Parameters of the superconducting pulsed transformer
primary
inductance/mHsecondary
inductance/μHcoupling
coefficientprimary
resistance/mΩsecondary
resistance/mΩcoil critical
current/A6.45 34.18 0.96 1.4 2.2 110 表 7 不同联合限压电路参数的实验结果比较
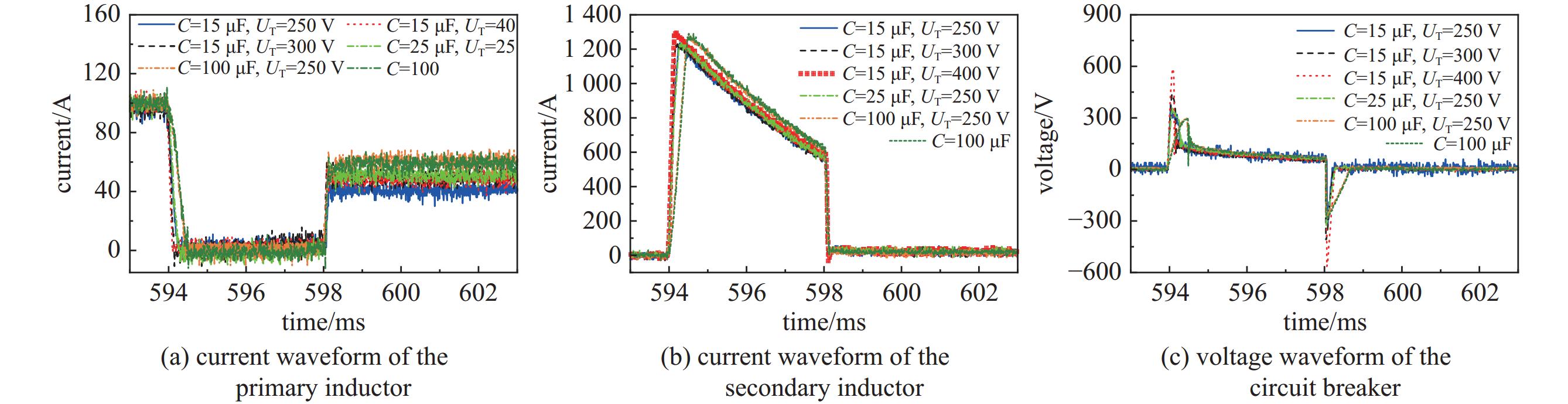
Table 7. Comparison of experimental results of different parameters of combination voltage limiting circuits
C/μF UT/V I2m/A T1/ms U1m/V η/% Ir/A 15 250 1210 0.31 355 58.96 42 15 300 1224 0.23 421 63.00 47 15 400 1280 0.19 479 71.66 51 25 250 1223 0.32 346 70.43 54 100 250 1270 0.51 300 82.53 60 100 / 1275 0.52 300 84.05 60 -
[1] 张玉宸, 戴玲, 樊晟廷, 等. 多级XRAM型脉冲功率电源开关器件简化研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:025002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.230211Zhang Yuchen, Dai Ling, Fan Shengting, et al. Research on switching devices simplification of multistage XRAM pulse power supply[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 025002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.230211 [2] 赵嘉琦, 李海涛, 吴亚楠, 等. 基于桥式驱动电路的磁阻型电磁发射器仿真与实验[J]. 高电压技术, 2024, 50(3):1348-1355Zhao Jiaqi, Li Haitao, Wu Yanan, et al. Simulation and experiment of reluctance electromagnetic launcher based on bridge drive circuit[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2024, 50(3): 1348-1355 [3] Yu Xinjie, Liu Xukun. Overview of circuit topologies for inductive pulsed power supplies[J]. CES Transactions on Electrical Machines and Systems, 2017, 1(3): 265-272. doi: 10.23919/TEMS.2017.8086105 [4] Liebfried O, Hundertmark S, Frings P. Inductive pulsed power supply for a railgun artillery system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2019, 47(5): 2550-2555. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2019.2903725 [5] 张鹏, 李海涛, 胡长勇, 等. 空心脉冲发电机剩磁能量回收方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35:115001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230124Zhang Peng, Li Haitao, Hu Changyong, et al. Remanent magnetic energy recovery method for air-core pulse alternator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 115001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230124 [6] Li Haitao, Zhang Cunshan, Wang Liwei, et al. A repetitive high-current pulse generator circuit based on multistage pulse transformers[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2021, 9(3): 3189-3200. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2020.3010132 [7] Sitzman A, Surls D, Mallick J. Design, construction, and testing of an inductive pulsed-power supply for a small railgun[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2007, 43(1): 270-274. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.887685 [8] Dedie P, Brommer V, Scharnholz S. Experimental realization of an eight-stage XRAM generator based on ICCOS semiconductor opening switches, fed by a magnetodynamic storage system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2009, 45(1): 266-271. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2008.2008418 [9] Yu Xinjie, Ban Rui, Liu Xukun, et al. The meat grinder with SECT circuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2017, 45(7): 1448-1452. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2017.2705663 [10] Sun Hao, Yu Xinjie, Li Bei, et al. Meat grinder with ACC circuit: a novel circuit for inductive pulsed power supplies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2020, 48(2): 566-570. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2020.2966635 [11] 胡长勇, 巴奉丽, 李海涛, 等. 基于改进ICCOS的电感储能脉冲电源电路设计与实验[J]. 低温与超导, 2023, 51(8):5-11Hu Changyong, Ba Fengli, Li Haitao, et al. Design and experiment of inductive pulse power supply circuit based on improved ICCOS[J]. Cryogenics & Superconductivity, 2023, 51(8): 5-11 [12] 赵嘉琦, 李海涛, 王艳萍, 等. 基于ICCOS的超导储能脉冲电源实验研究[J]. 低温与超导, 2022, 50(9):40-45,53Zhao Jiaqi, Li Haitao, Wang Yanping, et al. Experimental study on superconducting energy storage pulse power supply based on ICCOS[J]. Cryogenics & Superconductivity, 2022, 50(9): 40-45,53 [13] Liang Xiaoyu, Li Haitao, Zhang Cunshan, et al. An improved repetitive inductive pulsed power supply circuit with ICCOS technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2020, 48(4): 1082-1087. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2020.2978553 [14] 李海涛, 张涛, 安韵竹, 等. 电感储能连续脉冲电源电路及参数分析[J]. 高电压技术, 2019, 45(3):781-789Li Haitao, Zhang Tao, An Yunzhu, et al. Inductive continuous pulsed power supply circuit and its critical parameters analysis[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2019, 45(3): 781-789 [15] Wu Rui, Wang Yu, Yan Zhongming, et al. Design and testing of a novel inductive pulsed power supply consisting of HTS pulse power transformer and ZnO-based nonlinear resistor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2013, 41(7): 1781-1786. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2013.2263294 [16] 朱海峰, 丁志锋, 黄士君, 等. 两种基于超导脉冲变压器的脉冲电源研究[J]. 低温与超导, 2016, 44(5):36-41Zhu Haifeng, Ding Zhifeng, Huang Shijun, et al. Research of two pulsed power supply modes based on high temperature superconducting pulsed transformers[J]. Cryogenics & Superconductivity, 2016, 44(5): 36-41 [17] 李亚锦, 刘英男, 于大洋. 基于小样本及贝叶斯推理的避雷器缺陷分类技术[J]. 电工电能新技术, 2021, 40(11):56-63 doi: 10.12067/ATEEE2101020Li Yajin, Liu Yingnan, Yu Dayang. Classification of arrester defects based on small sample data and Bayesian inference[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 2021, 40(11): 56-63 doi: 10.12067/ATEEE2101020 [18] Zhang Tao, Li Haitao, Zhang Cunshan, et al. Design and simulation of a multimodule superconducting inductive pulsed-power supply model for a railgun system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2019, 47(2): 1352-1357. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2018.2889872 -




 下载:
下载: