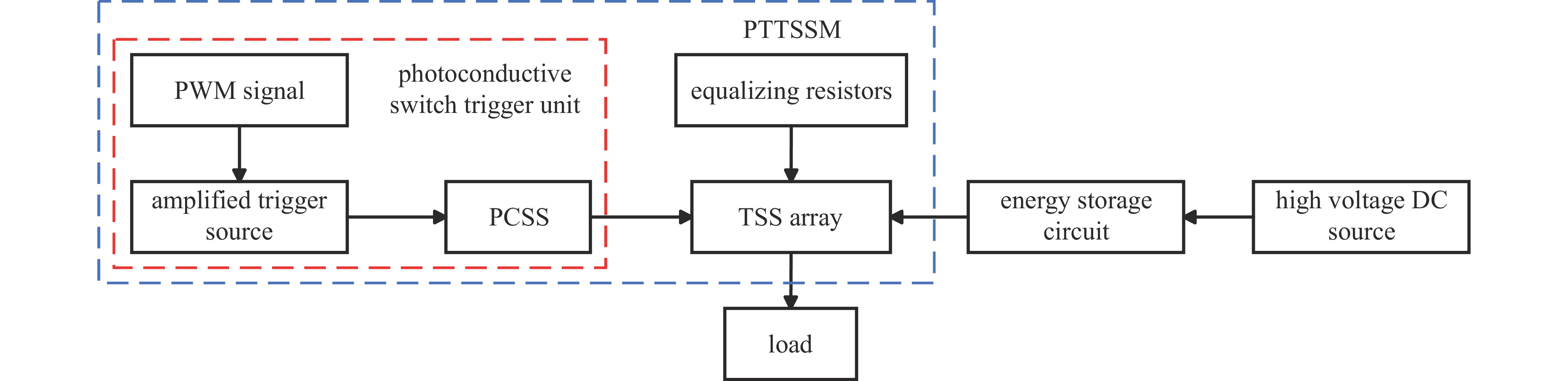
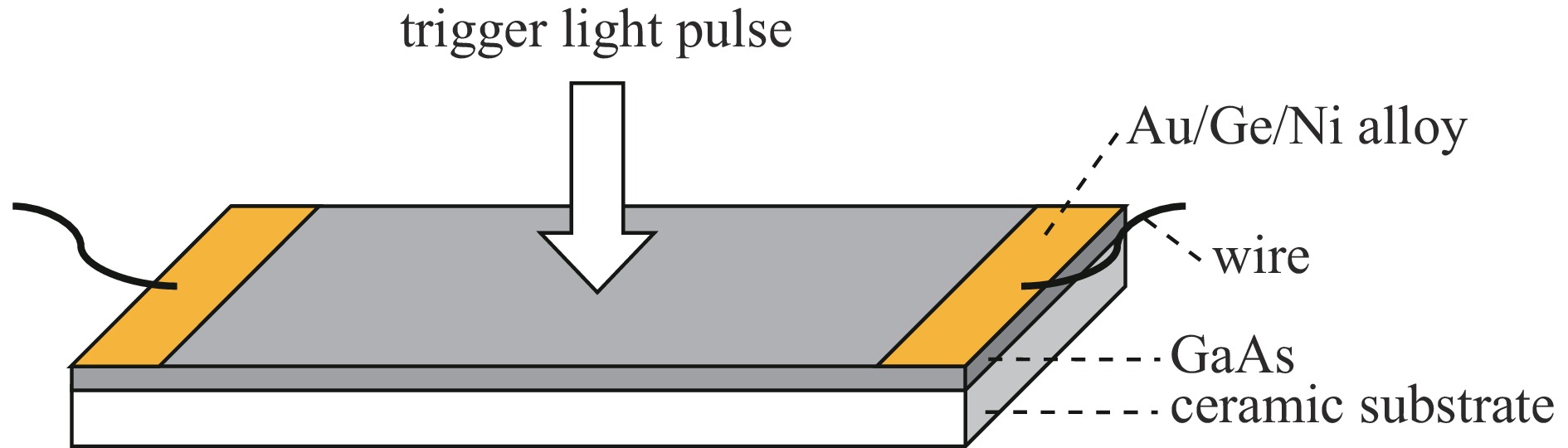
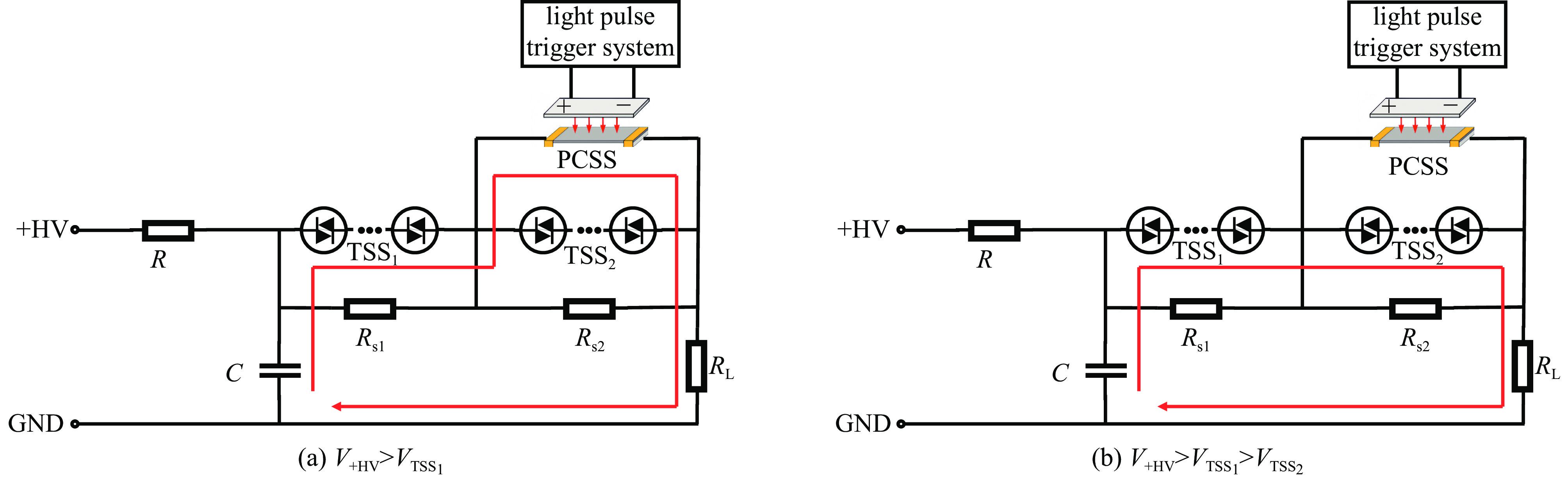
Design and application of high-voltage nanosecond switches based on PCSS triggered thyristor surge suppressor arrays
-
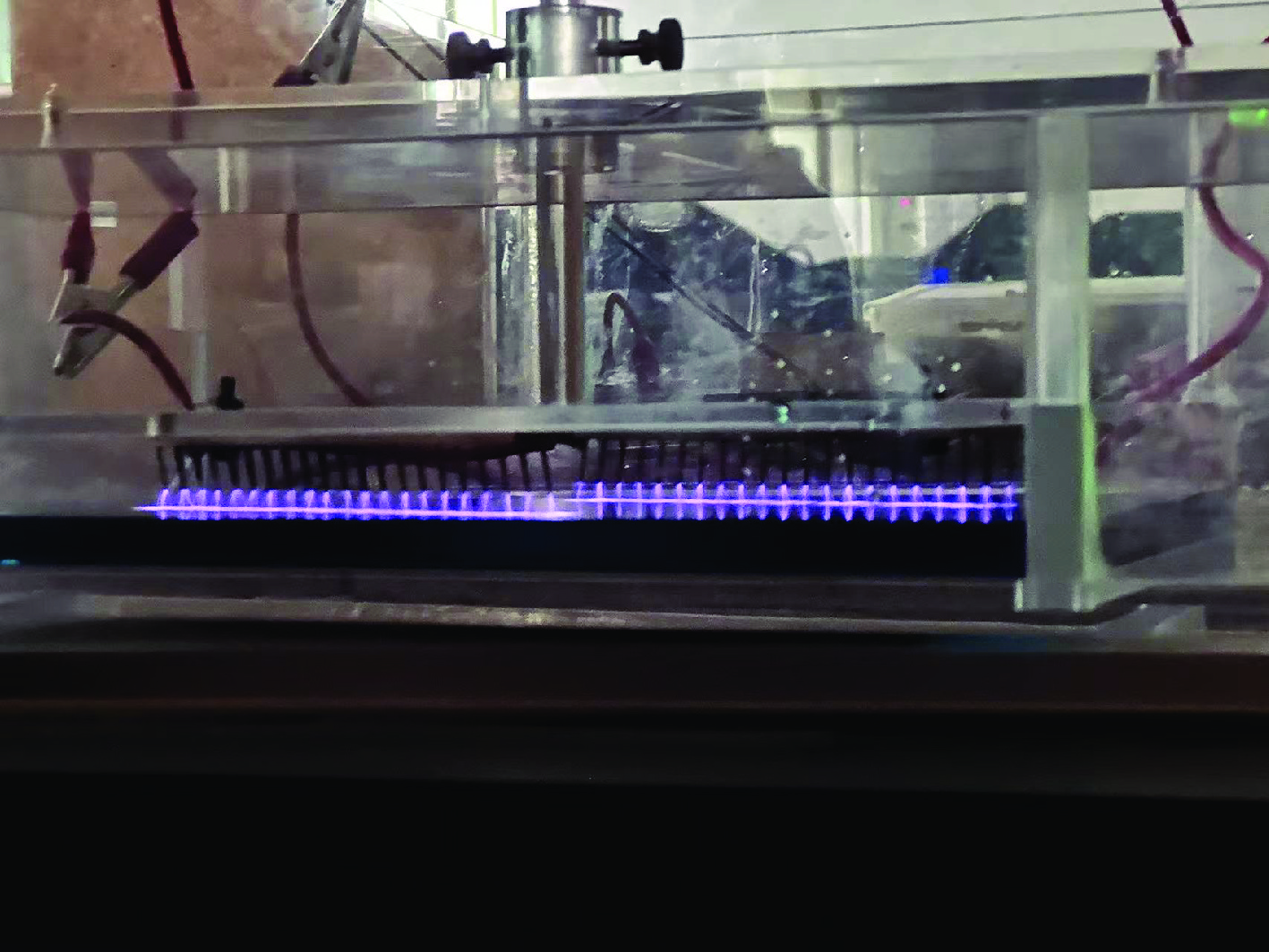
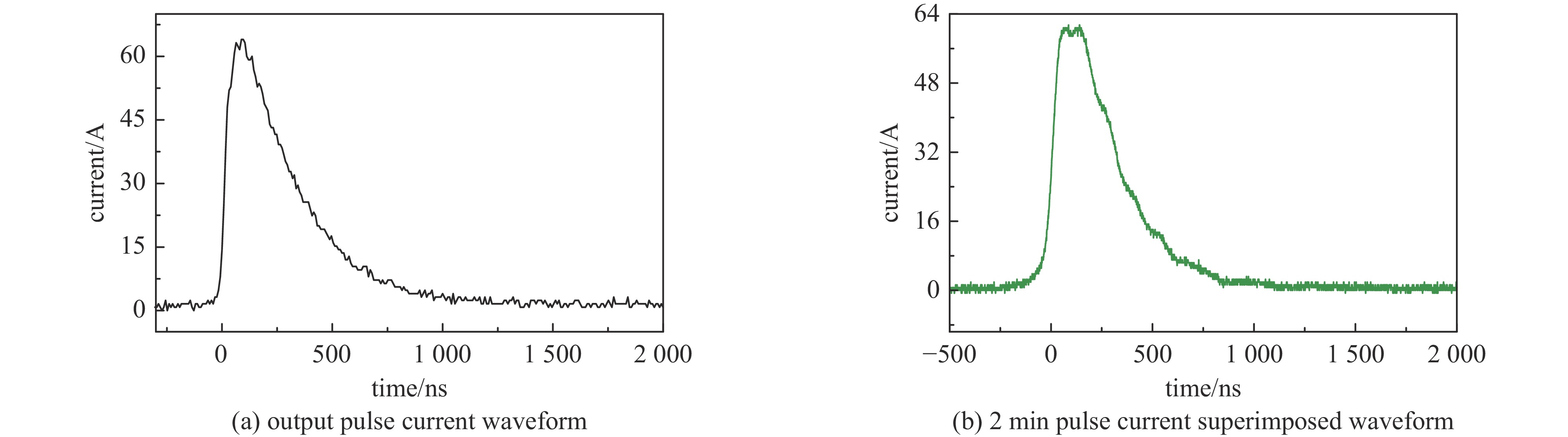
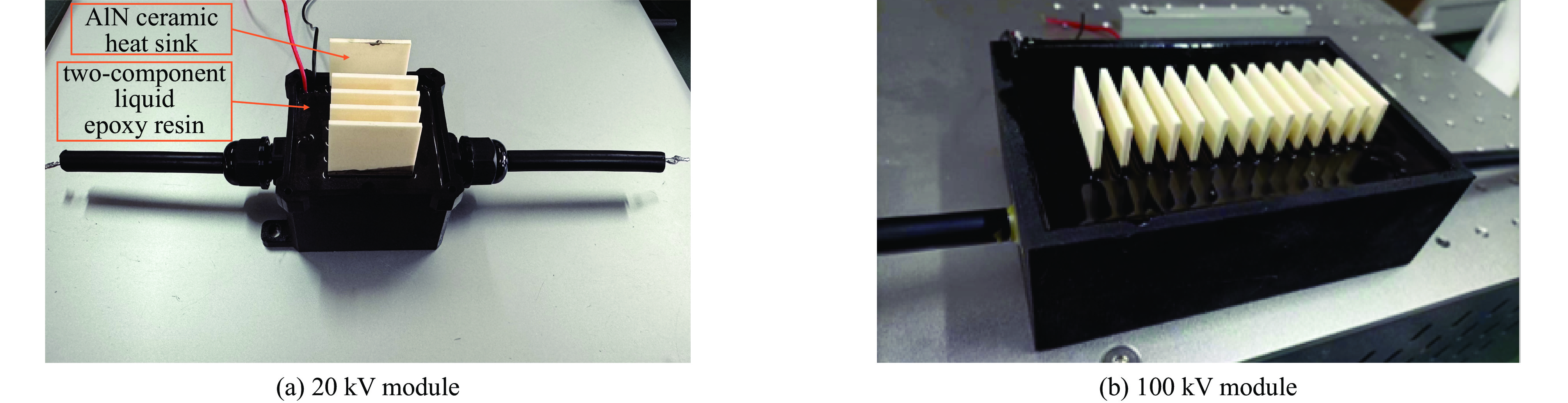
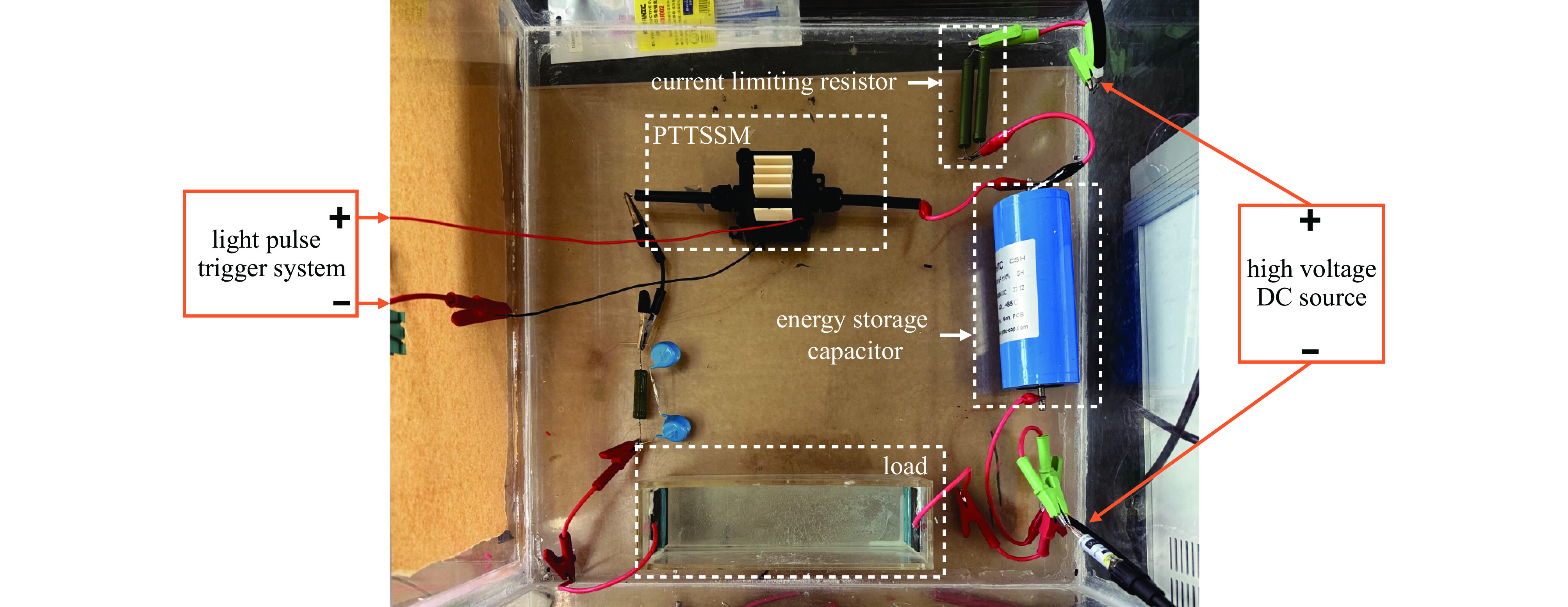
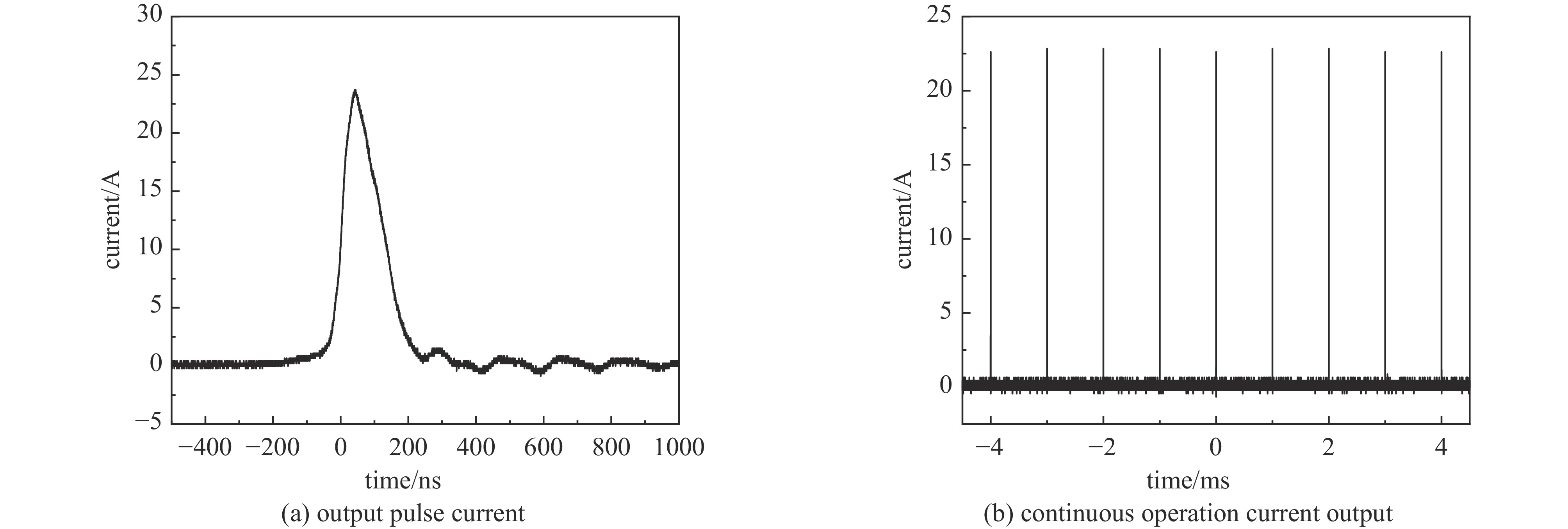
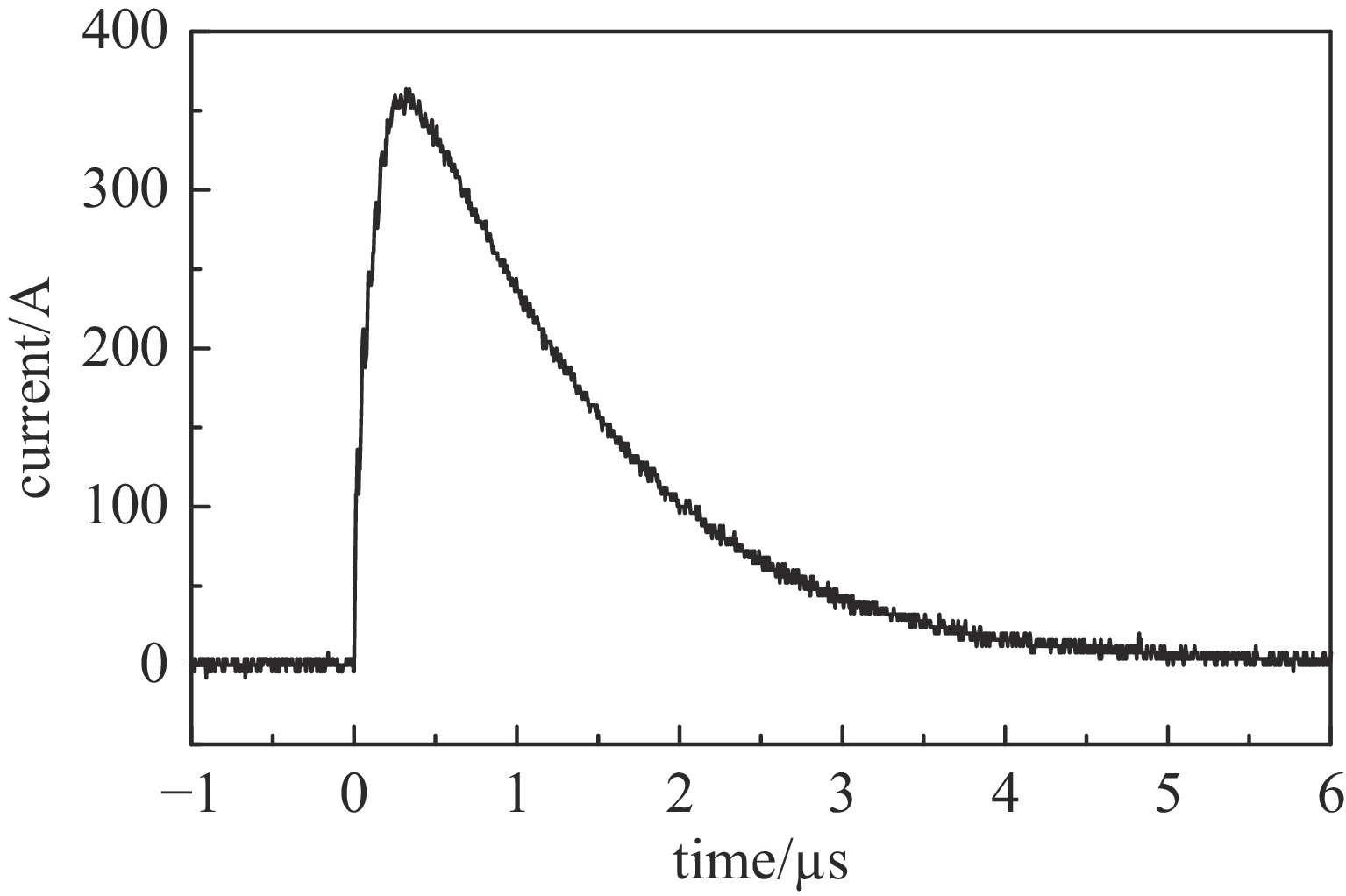
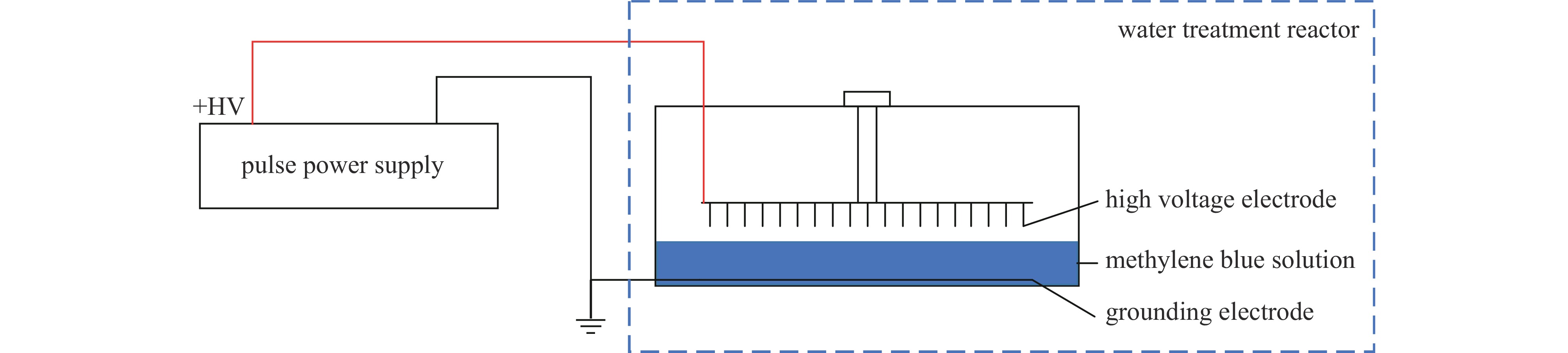
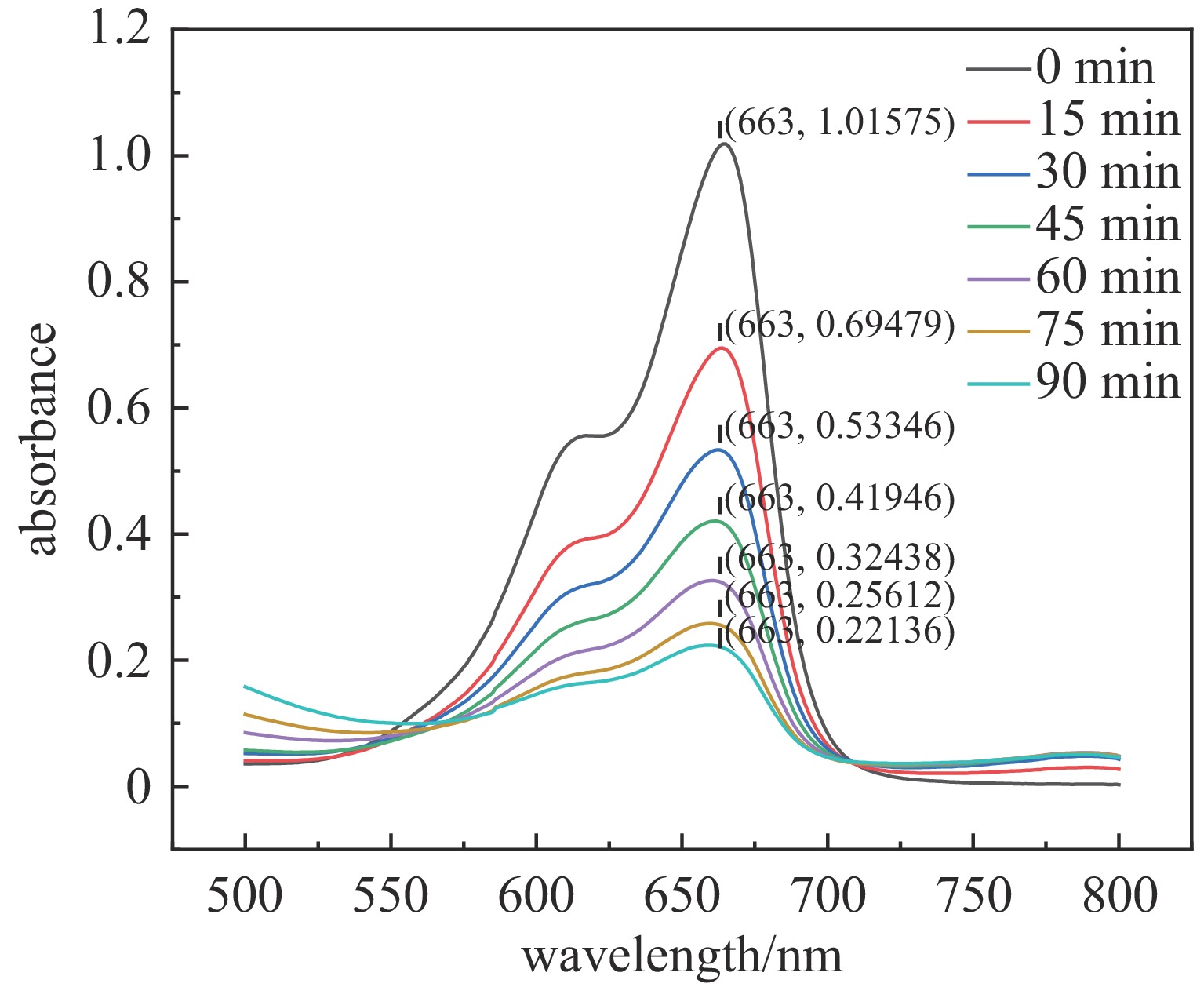
摘要: 指标高、结构紧凑、稳定性好的固态高压脉冲开关对脉冲功率技术的进步具有重要意义。提出基于光电导开关(PCSS)和电涌抑制晶闸管(TSS)阵列的高压纳秒开关技术路线,采用便于实现高压隔离的PCSS作为TSS阵列的触发单元,研制了一种新型高压纳秒开关模块(PTTSSM)。研制的20 kV开关模块输出峰值电流23.7 A,脉冲宽度122.1 ns,上升时间和下降时间分别为55.9 ns和128.3 ns,尺寸为60 mm×60 mm×40 mm;100 kV模块输出峰值电压60~100 kV可调、最大输出峰值电流356 A,脉宽1.308 μs,上升和下降时间分别是160.4 ns和2.454 μs,尺寸为150 mm×100 mm×50 mm,均能够长时间稳定工作。基于新型高压纳秒开关模块的脉冲电源在有机废水处理实验中成功产生大量稳定低温等离子体,有效降解有机物,验证了开关模块驱动产生等离子体的可行性和有效性。Abstract: The solid-state high-voltage pulse switch with high index, compact structure and good stability is of great significance to the progress of pulse power technology. This paper proposes a high-voltage nanosecond switching technology route based on Photoconductive Semiconductor Switches (PCSS) and thyristor surge suppressor (TSS) arrays, and a new type of high voltage switching module (PCSS triggering thyristor surge suppressors module, PTTSSM) is developed by using PCSS, which is convenient for realizing the high-voltage isolation, as the triggering unit of TSS arrays. The 20 kV PTTSSM has a peak output current of 23.7 A, a pulse width of 122.1 ns, a rise time and a fall time of 55.9 ns and 128.3 ns, respectively, and a size of 60 mm×60 mm×40 mm. The 100 kV PTTSSM has an adjustable peak output voltage of 60−100 kV, a maximum peak output current of 356 A, a pulse width of 1.308 µs, rise time and fall time of 160.4 ns and 2.454 µs, respectively, and its size is 150 mm×100 mm×50 mm. All of them can work stably for a long time. Pulse power supply based on a new solid-state switching module successfully generates a large number of stable low-temperature plasmas in organic wastewater treatment experiments, verifying the feasibility and effectiveness of the switching module-driven plasma generation.
-
表 1 P3500SDLRP 参数列表
Table 1. Parameters list of P3500SDLRP
model repetitive peak
off-state voltage/Vbreakover
voltage/Vbreakover
current/mAholding
current/mAcritical rate of decrease of
on-state current/(A·μs−1)P3500SDLRP 320 400 800 50 1000 表 2 光电导开关材料物理特性
Table 2. Physical properties of PCSS materials
parameter band gap/
eVelectron mobility/
(cm2·V−1·s−1)permittivity breakdown electric
field/(MV·cm−1)saturation velocity/
(107cm·V−1·s−1)thermal conductivity/
(W·cm−1·K−1)resistivity/
(Ω·cm)Si 1.12 1350 11.7 0.3 1.0 1.5 2.3×105 GaAs 1.43 8500 12.9 0.4 1.3 0.5 >107 SiC 3.0 800 9.7 3.0 2.0 4.8 105-106 GaN 3.42 440 9.0 3.3 2.5 3.2 108 表 3 各元件参数列表
Table 3. List of parameters for each component
component model power rating/W withstand voltage/kV value current limiting resistor R180-100 100 − 50 MΩ energy storage capacitor CSH50000K0.01-M8-225 − 100 0.01 μF load resistor water resistor − − adjustable 表 4 20 kV PTTSSM、100 kV PTTSSM功率参数
Table 4. Power parameters of 20 kV PTTSSM and 100 kV PTTSSM
peak voltage/kV peak power/MW volume/mm3 peak power
density/(W·cm−3)20 0.31 0.14×106 2.21 100 35 0.75×106 46.7 -
[1] 丛培天. 中国脉冲功率科技进展简述[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32:025002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.200040Cong Peitian. Review of Chinese pulsed power science and technology[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 025002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.200040 [2] Akiyama H, Sakugawa T, Namihira T, et al. Industrial applications of pulsed power technology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2007, 14(5): 1051-1064. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2007.4339465 [3] Kim A A, Kovalchuk B M, Kumpyak E V, et al. Linear transformer driver with a 750-kA current and a 400-ns current risetime[J]. Russian Physics Journal, 1999, 42(12): 985-989. doi: 10.1007/BF02512407 [4] Sugai T, Liu Wei, Tokuchi A, et al. Influence of a circuit parameter for plasma water treatment by an inductive energy storage circuit using semiconductor opening switch[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2013, 41(4): 967-974. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2013.2251359 [5] Jiang Weihua, Yatsui K. Compact pulsed power generators for industrial applications[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Fundamentals and Materials, 2004, 124(6): 451-455. doi: 10.1541/ieejfms.124.451 [6] Renz G, Holzschuh F, Zeyfang E. PFNs switched with stacked SCRs at 20 kV, 500 J, and 100 Hz REP-rate[C]//Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Pulsed Power Conference. 1997: 390-395. [7] 王磊, 章程, 高迎慧, 等. 晶闸管串联开关及同步触发系统研制[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:115001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.115001Wang Lei, Zhang Cheng, Gao Yinghui, et al. Design of series-connected thyristor switch and synchronous triggering circuit[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 115001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.115001 [8] Xu She, Huang A Q, Lucía O, et al. Review of silicon carbide power devices and their applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(10): 8193-8205. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2652401 [9] Okamura K, Naito F, Takayama K, et al. Development of a pulsed power supply utilizing 13 kV class SiC-MOSFETs[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2020, 1004: 1141-1147. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.1004.1141 [10] 李帅康, 黄邦斗, 章程, 等. 用于放电等离子体的重频固态纳秒脉冲电源[J]. 电力电子技术, 2021, 55(10):8-11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-100X.2021.10.004Li Shuaikang, Huang Bangdou, Zhang Cheng, et al. Repetitive solid-state nanosecond pulse power supply for discharge plasma[J]. Power Electronics, 2021, 55(10): 8-11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-100X.2021.10.004 [11] 范华峰, 杨昊, 申巍, 等. 基于级串式MOSFET管的高压重频脉冲电源设计[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2022, 41(8):153-158Fan Huafeng, Yang Hao, Shen Wei, et al. High voltage repetitive pulse power supply based on cascade MOSFET[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2022, 41(8): 153-158 [12] Zorngiebel V, Hecquard M, Spahn E, et al. Modular 50-kV IGBT switch for pulsed-power applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2011, 39(1): 364-367. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2068061 [13] 宋礼伟. 高压大功率脉冲电源关键技术研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019Song Liwei. Research on key technology of high voltage high power pulse power supplyD]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2019 [14] 李祥超, 周中山, 陈则煌, 等. 电涌抑制晶闸管(TSS)冲击性能的分析[J]. 电瓷避雷器, 2015(5):139-144Li Xiangchao, Zhou Zhongshan, Chen Zehuang, et al. Analysis on the impact performance of thyristor surge suppressors[J]. Insulators and Surge Arresters, 2015(5): 139-144 [15] 孙艳玲, 杨萌, 宋朝阳, 等. 低导通电阻4H-SiC光导开关[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:125003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.125003Sun Yanling, Yang Meng, Song Chaoyang, et al. 4H-SiC photoconductive switch with low on-state resistance[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 125003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.125003 [16] 罗燕, 丁蕾, 赵毅, 等. SiC光导开关衬底与电极界面场强仿真与优化设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:063004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210360Luo Yan, Ding Lei, Zhao Yi, et al. Optimization design and simulation of electric field at interface between substrate and electrode of photoconductive switch[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 063004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210360 [17] 杨彪, 孙逊, 李阳凡, 等. 激光能量分布对GaN基光导开关导通特性的影响[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:115005 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240321Yang Biao, Sun Xun, Li Yangfan, et al. Influence of laser spot energy distribution on the on-state performance of GaN-based photoconductive switches[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 115005 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240321 [18] 屈光辉. GaAs光电导开关中载流子输运规律研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2009Qu Guanghui. Study of the tranport of GaAs photoconductive semiconductor switches[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2009 [19] 赵越, 王传伟, 王凌云, 等. 半导体放电管固体场畸变三电极开关[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(4):868-870 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122404.0868Zhao Yue, Wang Chuanwei, Wang Lingyun, et al. Semiconductor arrester solid field distortion three-electrode discharge switch[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(4): 868-870 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122404.0868 [20] Du Zhehua, Lin Xin. Research progress in application of low temperature plasma technology for wastewater treatment[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2020, 512: 012031. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/512/1/012031 [21] 韩家林, 兰青青, 李新月, 等. 低温等离子体协同催化处理有机废水进展[J]. 精细石油化工进展, 2023, 24(6):53-58Han Jialin, Lan Qingqing, Li Xinyue, et al. Progress of low temperature plasma synergistic catalytic treatment of organic wastewater[J]. Advances in Fine Petrochemicals, 2023, 24(6): 53-58 -




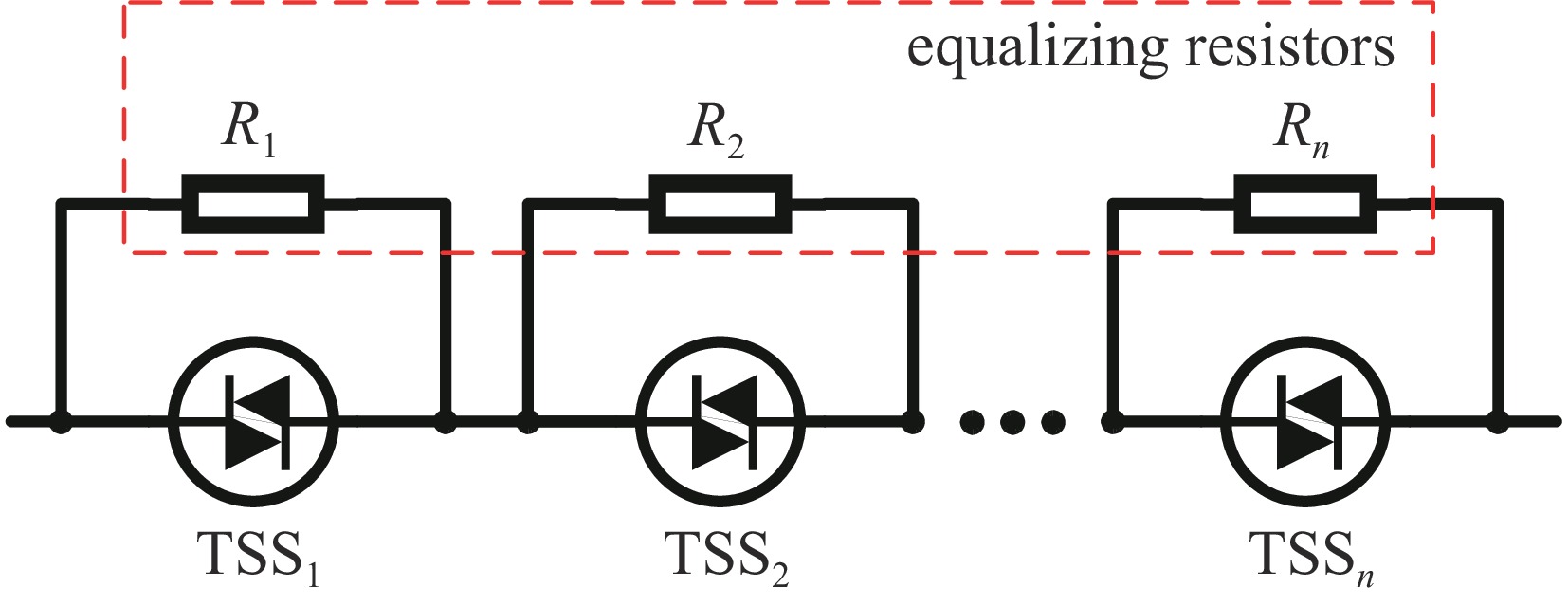
 下载:
下载: