Design of injector dump beam window for the electron beam test platform of S3FEL
-
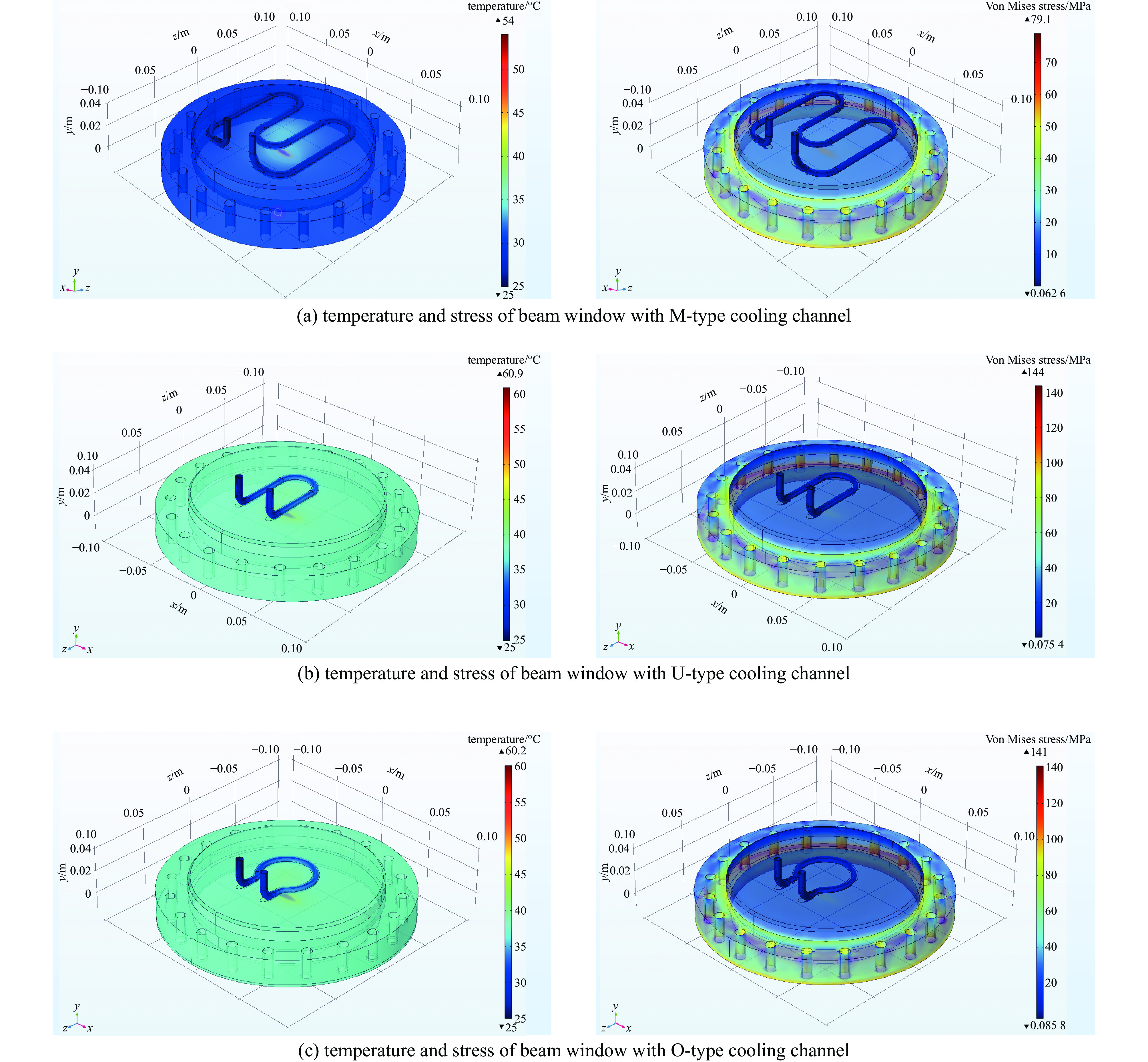
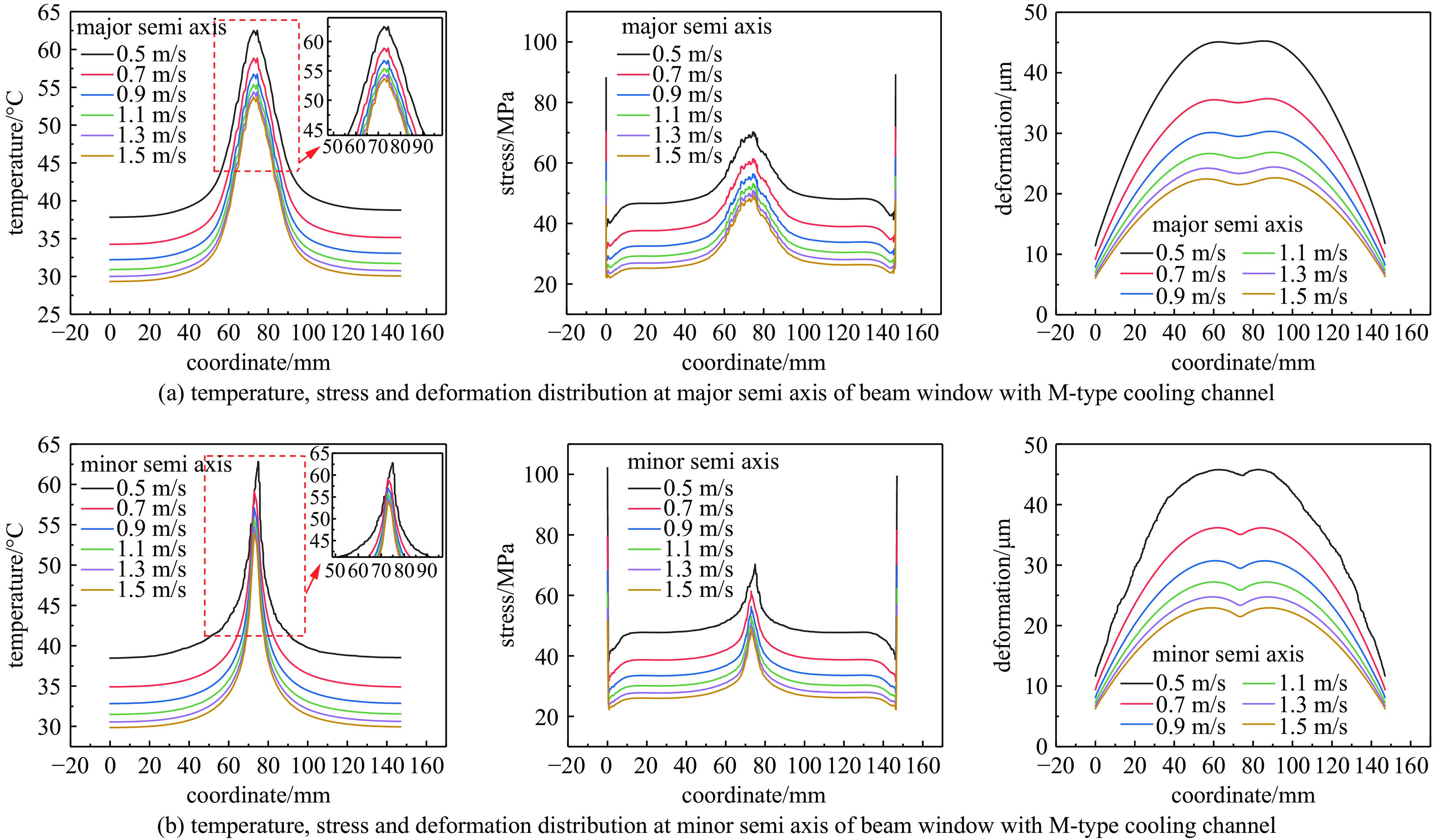
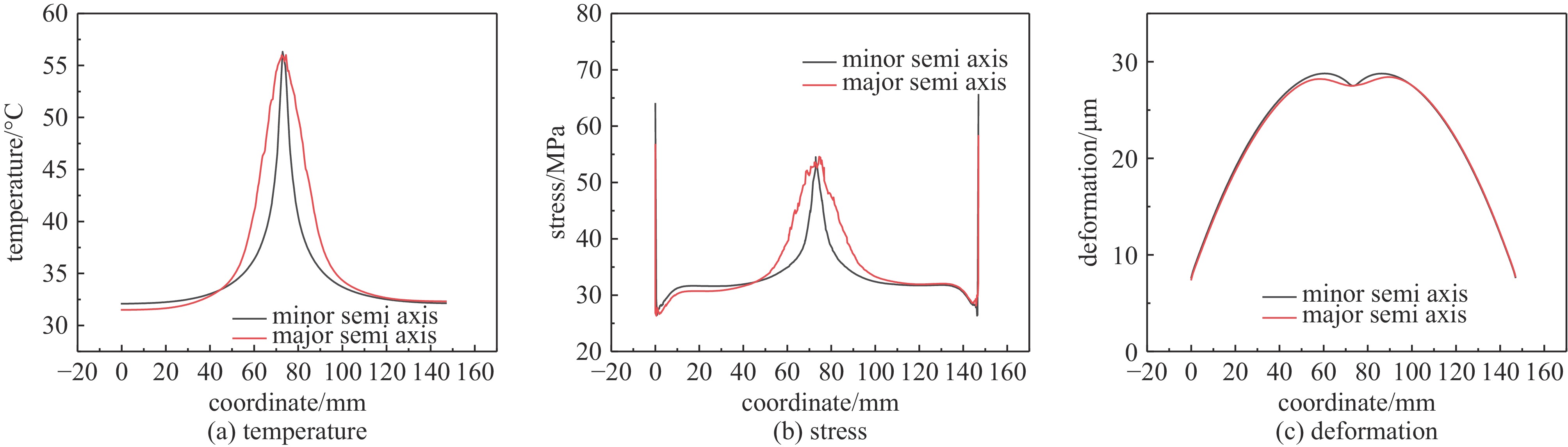
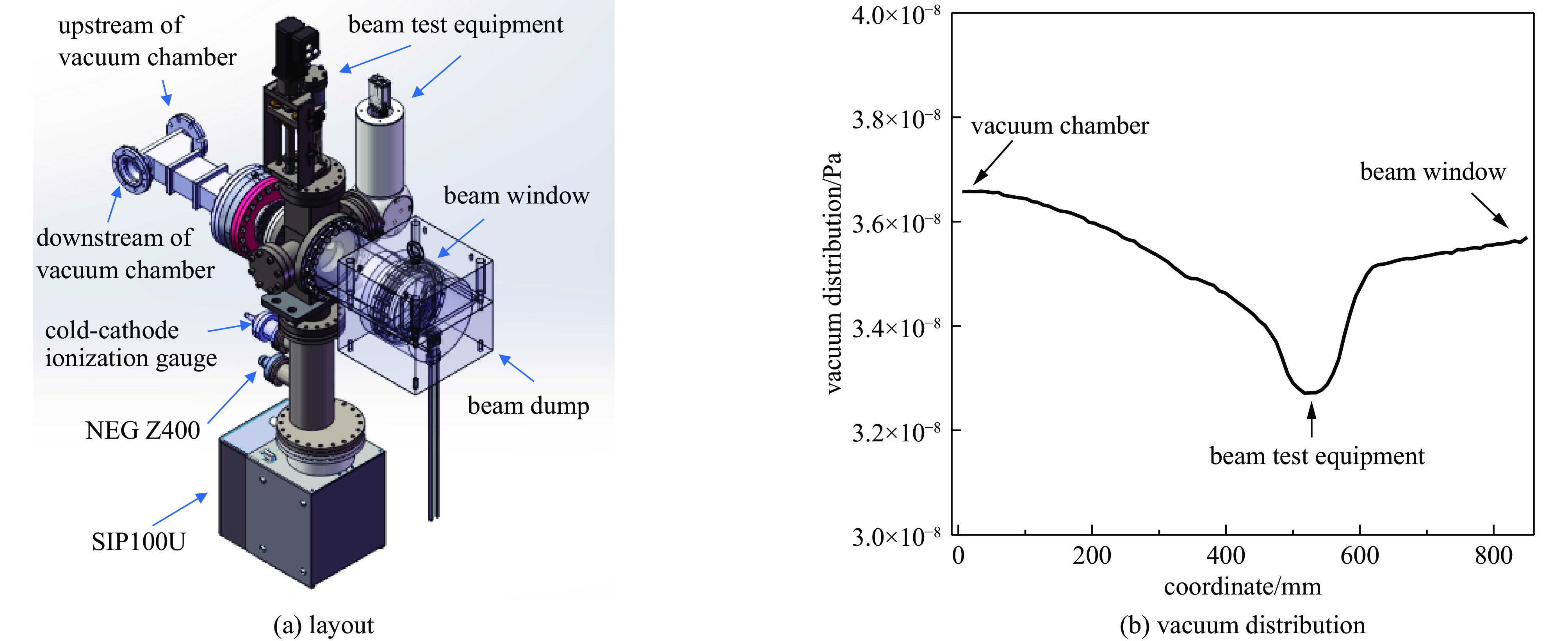
摘要: 深圳中能高重复频率X射线自由电子激光(S3FEL)的预研项目中的束流测试平台,将用于攻克高重复频率自由电子激光中的多项重大关键技术。对S3FEL束流测试平台中注入段废束桶束窗进行结构设计,结合电子束流参数设计了一种钎焊水冷铜窗。通过有限元分析方法对束窗进行热结构计算,分析了不同冷却通道和冷却流速下的温度、应力和变形。综合考虑冷却效果、流致振动和经济效益因素,最终选取了M型水冷通道和流速为1 m/s的束窗设计。并对该束窗处的真空分布进行计算,结果满足了设计要求,验证了设计的合理性,能够确保装置稳定可靠运行。Abstract: The electron beam test platform, as a pre-research project for Shenzhen Superconducting Soft X-ray Free Electron Laser (S3FEL), will be used to overcome several major key technology challenges in high repetition frequency free electron laser. In this paper, the structural design of the injector dump beam window for the Electron Beam Test Platform of S3FEL is carried out, and a brazing water-cooled copper window is designed based on the electron beam parameters. The thermal structural calculation of the beam window is carried out using finite element analysis method, and the temperature, stress and deformation under different cooling channels and cooling water flow rates are analyzed. Considering the cooling effect, economic efficiency and flow vibration factors, the M-type cooling channel with the flow rate of 1 m/s is finally selected for the beam window. In addition, the vacuum distribution at the beam window is calculated, and all the results meet the design requirements, verifying the rationality of the design and ensuring the stable and reliable operation of the facility.
-
Key words:
- free electron laser /
- high repetition frequency /
- beam window /
- vacuum
-
表 1 材料物性参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of materials
material density/
(kg·m−3)elastic modulus/
GPaPoisson’s
ratioyield stress/
MPathermal conductivity/
(W·m−1·K−1)thermal expansion
coefficient/℃−1316L 7980 193.0 0.300 290 15 12.0×10−6 A5083 2660 71.0 0.330 145 117 23.0×10−6 Ti-6Al-4V 4430 113.8 0.360 880 6.7 8.6×10−6 Be 1844 303.0 0.100 240 216 12.0×10−6 OFHC 8940 115.0 0.343 340 391 17.7×10−6 表 2 束窗材料物性参数
Table 2. Material physical parameters of beam window
material density/
(kg·m−3)melting
point/℃elastic modulus/
GPaPoisson’s
ratioyield stress/
MPathermal conductivity/
(W·m−1·K−1)thermal expansion
coefficient/℃−1316L 7980 1375 193 0.300 290 15 12.0×10−6 OFHC 8940 1083 115 0.343 340 391 17.7×10−6 表 3 材料放气率
Table 3. Material outgassing rates
material conditions outgassing rate[19] /(Pa·L·s−1·cm−2) calculation outgassing rate/(Pa·L·s−1·cm−2) 316L 20 h at 100 ℃ 10−11 1×10−9 copper 20 h at 100 ℃ 10−10 1×10−8 copper (with Gaussian heat source ) 20 h at 100 ℃ 10−10 5×10−8 -
[1] Decking W, Abeghyan S, Abramian P, et al. A MHz-repetition-rate hard X-ray free-electron laser driven by a superconducting linear accelerator[J]. Nature Photonics, 2020, 14(6): 391-397. doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-0607-z [2] Pandey S, Bean R, Sato T, et al. Time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography at the European XFEL[J]. Nature Methods, 2020, 17(1): 73-78. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0628-z [3] Halavanau A, Decker F J, Emma C, et al. Very high brightness and power LCLS-II hard X-ray pulses[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2019, 26(3): 635-646. doi: 10.1107/S1600577519002492 [4] Zhang Baichao, Li Xiaoshen, Liu Qi, et al. High repetition-rate photoinjector laser system for S3FEL[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2023, 11: 1181862. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2023.1181862 [5] Xu Zhongmin, Zhang Weiqing, Yang Chuan, et al. Shape optimization design of the offset mirror in FEL-1 beamline at S3FEL[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13: 9653. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36645-9 [6] Huang Liming, E Dejun, Tao Kai, et al. Simulation study of coupled particle cascade and finite element analysis for beam dump of DALS[J]. Radiation Detection Technology and Methods, 2024, 8(2): 1254-1263. doi: 10.1007/s41605-023-00444-7 [7] 张浩, 黄礼明, 赵峰, 等. 一种高重频废束桶束窗的设计及热结构分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35:034001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220350Zhang Hao, Huang Liming, Zhao Feng, et al. Design and thermal structure analysis of a dump beam window for high repetition frequency[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 034001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220350 [8] 马文静, 赵壮, 王思慧, 等. 合肥先进光源前端光子吸收器的设计及热分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:104007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220057Ma Wenjing, Zhao Zhuang, Wang Sihui, et al. Design and thermal analysis of front-end photon absorber at HALF[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 104007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220057 [9] 李勇军. 上海光源高热负载前端区的系统设计与研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所, 2016Li Yongjun. Design and study of high heat load front-end at SSRF[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016 [10] 陈丽萍. 上海光源储存环光子吸收器结构设计与研制[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2009, 29(5):546-551 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7126.2009.05.18Chen Liping. Photon absorber development for storage ring of Shanghai synchrotron radiation facility[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2009, 29(5): 546-551 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7126.2009.05.18 [11] 聂小军, 刘磊, 康玲, 等. 一种废束站束窗结构设计与优化[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30:105105 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.180057Nie Xiaojun, Liu Lei, Kang Ling, et al. Structure design and optimization of a dump beam window[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 30: 105105 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.180057 [12] Poo-arporn Y, Duangnil S, Bamrungkoh D, et al. Gas tungsten arc welding of copper to stainless steel for ultra-high vacuum applications[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 277: 116490. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116490 [13] Böhlen T T, Cerutti F, Chin M P W, et al. The FLUKA code: developments and challenges for high energy and medical applications[J]. Nuclear Data Sheets, 2014, 120: 211-214. doi: 10.1016/j.nds.2014.07.049 [14] 马忠剑, 随艳峰, 王庆斌, 等. FLUKA程序在法拉第杯设计中的应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(1):207-210 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132501.0207Ma Zhongjian, Sui Yanfeng, Wang Qingbin, et al. Application of Monte Carlo code FLUKA to design of Faraday cup[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(1): 207-210 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132501.0207 [15] 翟红雨, 程健, 陈银华, 等. 离子能量分析器测量特性的仿真研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32:084002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.190459Zhai Hongyu, Cheng Jian, Chen Yinhua, et al. Simulation study on measurement characteristics of ion energy analyzer[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 084002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.190459 [16] 卢鹏, 潘艳秋, 俞路, 等. 固体激光微通道冷却器内流动特性的数值模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:051008 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.051008Lu Peng, Pan Yanqiu, Yu Lu, et al. Numerical simulation of flow characteristic in solid-state laser microchannel cooler[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 051008 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.051008 [17] Chai Shuo, Zhu Wanqian, Zhang Zhanfei, et al. Research and optimization of flow-induced vibrations in a water-cooled monochromator[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2024, 95: 035124. doi: 10.1063/5.0191196 [18] Notari L, Pasquali M, Carra F, et al. Materials adopted for particle beam windows in relevant experimental facilities[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2024, 27: 024801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.27.024801 [19] Malyshev O B. Vacuum in particle accelerators: modelling, design and operation of beam vacuum systems[M]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2019. [20] 王姣龙, 王国栋, 刘霄, 等. NEG泵抽气性能仿真模拟与测试系统设计[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2024, 44(2):139-145Wang Jiaolong, Wang Guodong, Liu Xiao, et al. Simulation and design of test system for the pumping performance of NEG pump[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2024, 44(2): 139-145 -




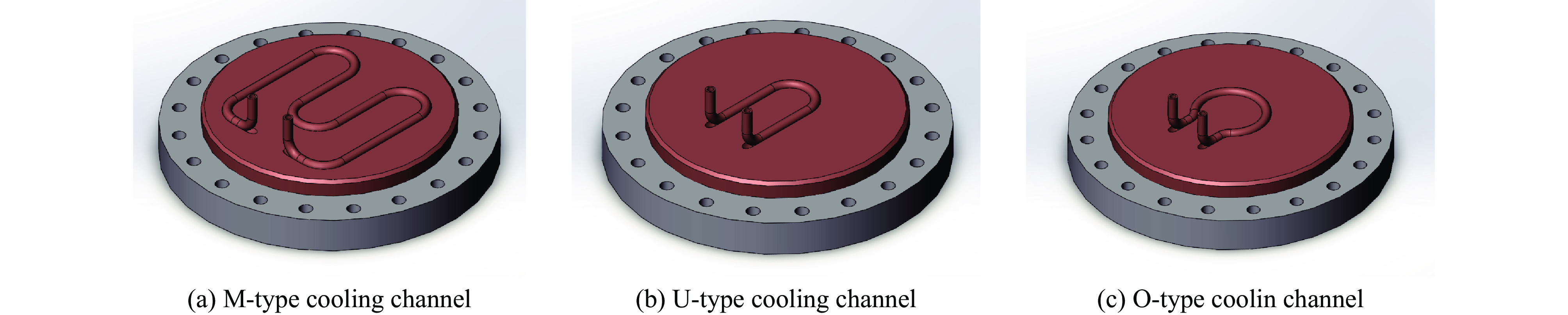
 下载:
下载: