A review of multispectral target detection algorithms and related datasets
-
摘要: 相较于单一波段目标检测技术,多光谱目标检测技术通过捕获物体在多个不同波长的光谱波段下的反射或辐射信息,极大地提高目标检测的准确性和应对复杂环境的鲁棒性。在遥感、农业检测、环境保护、工业生产以及国防安全等领域有着广泛的应用。然而,目前多光谱目标检测领域仍面临着严峻挑战:多样化的高质量数据集以及高效目标检测算法的缺乏,严重制约了该技术的进一步发展和应用。鉴于此,综合阐释了多光谱目标检测数据集的制作方法以及多光谱目标检测算法的重要进展。首先,系统分析了多光谱数据集的构建过程,包括数据采集,预处理和数据标注。其次,全面分析了目标检测算法发展的历史脉络,这些算法涵盖了基于传统特征提取技术的目标检测算法、深度学习方法以及其改进版本。此外,着重强调了算法开发者为提升多光谱目标检测性能在特征融合、模型架构和子网络方面所作的关键改进。最后,探讨了多光谱目标检测技术未来的发展方向,期望为研究人员指明潜在的研究热点和应用领域,促成多光谱目标检测技术在实际场景中更广泛的应用,提升其社会价值。Abstract: Compared with single-band object detection technology, multispectral object detection technology greatly improves the accuracy of object detection and the robustness in dealing with complex environments by capturing the reflection or radiation information of objects in multiple spectral bands of different wavelengths. Therefore, it has extensive applications in fields such as remote sensing, agricultural detection, environmental protection, industrial production, and national defense security. However, the field of multispectral object detection still faces severe challenges at present: the lack of diverse high-quality datasets and efficient object detection algorithms seriously restricts further development and application of this technology. In view of this, this paper comprehensively explains the production method of multispectral object detection datasets and the important progress of multispectral object detection algorithms. First, the article systematically analyzes the construction process of multispectral datasets, including data acquisition, preprocessing, and data annotation, aiming to provide technical support for the subsequent construction of high-quality multispectral object detection datasets. Second, this paper comprehensively analyzes the historical context of the development of object detection algorithms. These algorithms cover object detection algorithms based on traditional feature extraction technologies, deep learning methods, and their improved versions. In addition, this paper summarizes the key improvements made by algorithm developers in terms of feature fusion, model architecture, and sub-networks to improve the performance of multispectral object detection based on deep learning-based object detection algorithms. Finally, this paper discusses future development direction of multispectral object detection technology, hoping to indicate potential research hotspots and application fields for researchers, and promote the wider application of multispectral object detection technology in actual scenarios and enhance its social value.
-
表 1 常用的多光谱目标检测数据集
Table 1. Commonly used multispectral object detection data sets
establishment
timebrief introduction application domain image acquisition
equipmentIndian Pines[18] 1992 Covering 400 - 2500 nm with a total of 224 bands.
The annotations include 16 categories such as Oats and Woods.agricultural detection,
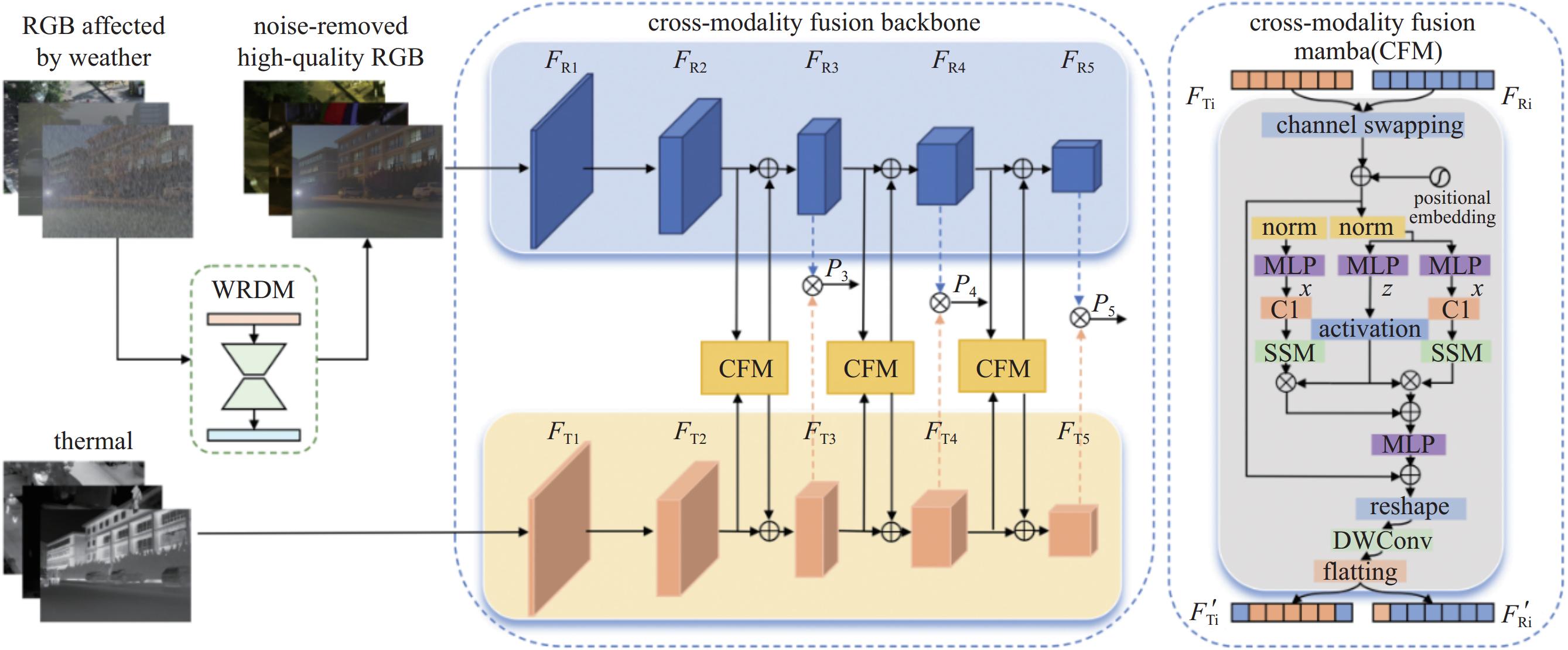
environmental monitoring, etc.Avris (whiskbroom) Salinas[27] 2001 Covering a range of 400 - 2500 nm with a total of 224 bands.
The annotations include 16 categories such as fallow land and celery.Agricultural detection,
environmental monitoring, etc.Avris (whiskbroom) FLIR[15] 2003 9711 thermal imaging pictures and9233 RGB
pictures, covering 15 common object categories.Security monitoring,
autonomous driving.FLIR (filter) Pavia Centre & University[17] 2010 The spectrum covers visible light to near-infrared, with a total of 103 bands. The annotations include 9 categories such as water and trees. Land use and cover detection,
environmental detectionROSIS (pushbroom) VEDAI[20] 2014 A dataset for vehicle detection captured by drones, providing different resolutions for each scene. traffic monitoring,
urban planning/ KAIST[21] 2015 A total of 95 328 pictures, each picture contains two versions of RGBand infrared images, and there are a total of 103 128 densely annotated ones. pedestrian monitoring PointGrey Flea3 and FLIR (filter) EuroSAT[29] 2019 The dataset is based on Sentinel-2 satellite images covering 13 spectral bands and consisting out of 10 classes with in total 27 000 labeled and geo-referenced images. land use and cover
classificationMSI on Sentinel-2 satellite (pushbroom) LLVIP[16] 2021 A pedestrian detection dataset in low-light environments, with 15488 pairs of pixel-aligned RGB-IR images.pedestrian monitoring Hikvision Binocular Photography Platform (filter) MMShip[52] 2023 The dataset encompasses 5 016 sets of ship target images, with each scene consisting of a total of four bands, including the visible light and the near infrared. ship monitoring MSI on Sentinel-2 satellite (pushbroom) SMOD[53] 2024 The dataset comprises 5 378 pairs of daytime scene images captured at 3 p.m. and 3 298 pairs of nighttime ones at 7 p.m. pedestrian monitoring,
traffic monitoringAsens FV6 Binocular Photography Platform (filter) 表 2 多光谱目标检测算法总结
Table 2. A summary of multispectral object detection algorithms
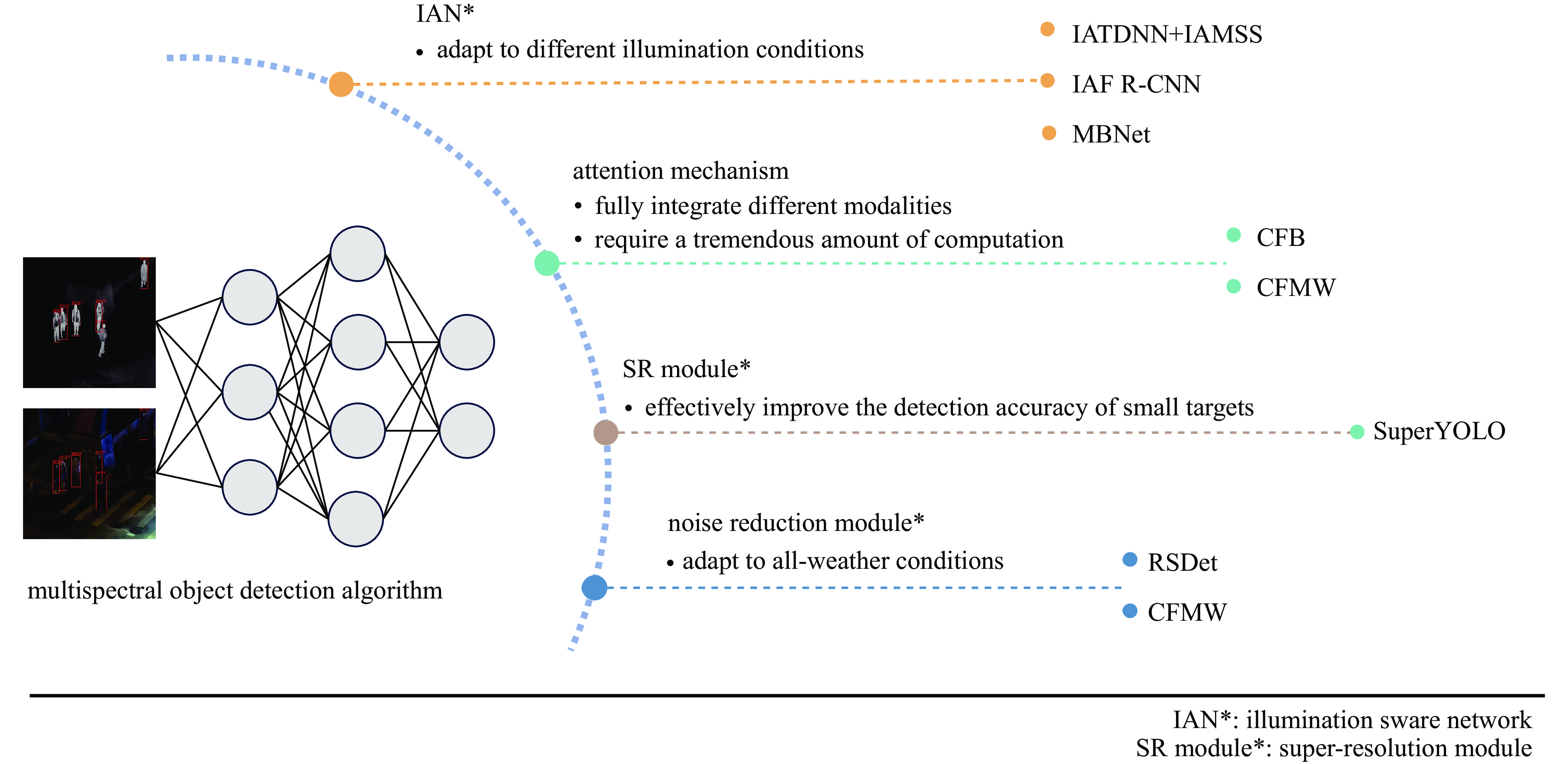
establishment time performance/% KAIST(MR)* LLVIP(mAP) VEDAI(mAP50) IATDNN + IAMSS[11] 2018.2 26.37 \ \ IAF R-CNN[12] 2018.8 15.73 \ \ MBNet[13] 2020.8 8.13 \ \ CFB(CFT)[95] 2022.1 \ 63.6 85.3 SuperYOLO[19] 2023.4 \ \ 75.09 CFMW[10] 2024.4 \ 64.8 \ RSDet[99] 2024.5 26.02 61.3 \ KAIST(MR)*:The data selects the ‘all’ subset under the KAIST dataset. -
[1] Voulodimos A, Doulamis N, Doulamis A, et al. Deep learning for computer vision: a brief review[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2018, 2018: 7068349. [2] Li Ke, Wan Gang, Cheng Gong, et al. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: a survey and a new benchmark[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 159: 296-307. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.11.023 [3] Himeur Y, Rimal B, Tiwary A, et al. Using artificial intelligence and data fusion for environmental monitoring: a review and future perspectives[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 86/87: 44-75. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.06.003 [4] Janakiramaiah B, Kalyani G, Karuna A, et al. Retracted article: military object detection in defense using multi-level capsule networks[J]. Soft Computing, 2023, 27(2): 1045-1059. doi: 10.1007/s00500-021-05912-0 [5] Ren Shaoqing, He Kaiming, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [6] Feng Di, Haase-Schütz C, Rosenbaum L, et al. Deep multi-modal object detection and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving: datasets, methods, and challenges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(3): 1341-1360. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.2972974 [7] Sun Wei, Dai Liang, Zhang Xiaorui, et al. RSOD: real-time small object detection algorithm in UAV-based traffic monitoring[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(8): 8448-8463. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-02893-3 [8] Ghasemi Y, Jeong H, Choi S H, et al. Deep learning-based object detection in augmented reality: a systematic review[J]. Computers in Industry, 2022, 139: 103661. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2022.103661 [9] Li Yongjun, Li Shasha, Du Haohao, et al. YOLO-ACN: focusing on small target and occluded object detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 227288-227303. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3046515 [10] Li Haoyuan, Hu Qi, Yao You, et al. CFMW: cross-modality fusion mamba for multispectral object detection under adverse weather conditions[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2404.16302, 2024. [11] Guan Dayan, Cao Yanpeng, Yang Jiangxin, et al. Fusion of multispectral data through illumination-aware deep neural networks for pedestrian detection[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 50: 148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.11.017 [12] Li Chengyang, Song Dan, Tong Ruofeng, et al. Illumination-aware faster R-CNN for robust multispectral pedestrian detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 85: 161-171. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.08.005 [13] Zhou Kailai, Chen Linsen, Cao Xun. Improving multispectral pedestrian detection by addressing modality imbalance problems[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. 2020: 787-803. [14] Liu Ye, Meng Shiyang, Wang Hongzhang, et al. Deep learning based object detection from multi-modal sensors: an overview[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2024, 83(7): 19841-19870. [15] FLIR Thermal Dataset[DB/OL]. [2023]. https://www.flir.com/oem/adas/adas-dataset-form/. [16] Jia Xinyu, Zhu Chuang, Li Minzhen, et al. LLVIP: a visible-infrared paired dataset for low-light vision[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. 2021: 3489-3497. [17] Paolo Gamba. Pavia Centra[DB/OL]. [2010]. http://tlclab.unipv.it/. [18] Pursue’s university MultiSpecsite[DB/OL]. [1992]. https://engineering.purdue.edu/~biehl/MultiSpec/hyperspectral.html. [19] Zhang Jiaqing, Lei Jie, Xie Weiying, et al. SuperYOLO: super resolution assisted object detection in multimodal remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5605415. [20] Razakarivony S, Jurie F. Vehicle detection in aerial imagery: a small target detection benchmark[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2016, 34: 187-203. [21] Hwang S, Park J, Kim N, et al. Multispectral pedestrian detection: benchmark dataset and baseline[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2015: 1037-1045. [22] Liu Jingjing, Zhang Shaoting, Wang Shu, et al. Multispectral deep neural networks for pedestrian detection[C]//Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference 2016. 2016. [23] Li Chengyang, Song Dan, Tong Ruofeng, et al. Multispectral pedestrian detection via simultaneous detection and segmentation[C]//Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference 2018. 2018. [24] 徐力智. 航空摆扫式成像光谱仪成像质量研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2020: 2Xu Lizhi. Research on imaging quality for airborne sweeping hyperspectral imager[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2020: 2 [25] 于磊. 成像光谱仪的发展与应用(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51:20210940Yu Lei. Development and application of imaging spectrometer (Invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51: 20210940 [26] 李月, 杨灿坤, 周春平, 等. 无人机载高光谱成像设备研究及应用进展[J]. 测绘通报, 2019(9):1-6,17Li Yue, Yang Cankun, Zhou Chunping, et al. Advance and application of UAV hyperspectral imaging equipment[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2019(9): 1-6,17 [27] Saline[DB/OL]. [2001]. https://www.ehu.eus/ccwintco/index.php/Hyperspectral_Remote_Sensing_Scenes. [28] Green R O, Eastwood M L, Sarture C M, et al. Imaging spectroscopy and the airborne visible/infrared imaging spectrometer (AVIRIS)[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1998, 65(3): 227-248. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(98)00064-9 [29] Helber P, Bischke B, Dengel A, et al. EuroSAT: a novel dataset and deep learning benchmark for land use and land cover classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(7): 2217-2226. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2918242 [30] Martimort P, Fernandez V, Kirschner V, et al. Sentinel-2 MultiSpectral imager (MSI) and calibration/validation[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. 2012: 6999-7002. [31] 陈宇鹏. 快照红外傅里叶变换成像光谱仪理论、设计及实验研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2022: 3Chen Yupeng. Theory, design and experiment of snapshot infrared Fourier transform imaging spectrometer[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2022: 3 [32] Lin C H, Huang S H, Lin T H, et al. Metasurface-empowered snapshot hyperspectral imaging with convex/deep (CODE) small-data learning theory[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 6979. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42381-5 [33] Miao Xin, Yuan Xin, Pu Yunchen, et al. Lambda-Net: reconstruct hyperspectral images from a snapshot measurement[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019: 4058-4068. [34] Yorimoto K, Han Xianhua. HyperMixNet: hyperspectral image reconstruction with deep mixed network from a snapshot measurement[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2021: 1184-1193. [35] Cao Xun, Yue Tao, Lin Xing, et al. Computational snapshot multispectral cameras: toward dynamic capture of the spectral world[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2016, 33(5): 95-108. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2016.2582378 [36] Lucieer A, Malenovský Z, Veness T, et al. HyperUAS—imaging spectroscopy from a multirotor unmanned aircraft system[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2014, 31(4): 571-590. doi: 10.1002/rob.21508 [37] Hruska R, Mitchell J, Anderson M, et al. Radiometric and geometric analysis of hyperspectral imagery acquired from an unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Remote Sensing, 2012, 4(9): 2736-2752. doi: 10.3390/rs4092736 [38] Bernath P F. Spectra of atoms and molecules[M]. 4th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2020. [39] Adão T, Hruška J, Pádua L, et al. Hyperspectral imaging: a review on UAV-based sensors, data processing and applications for agriculture and forestry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9: 1110. doi: 10.3390/rs9111110 [40] Yadav A K, Roy R, Kumar R, et al. Algorithm for de-noising of color images based on median filter[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 3rd International Conference on Image Information Processing. 2015: 428-432. [41] Peng Honghong, Rao R, Dianat S A. Multispectral image denoising with optimized vector bilateral filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(1): 264-273. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2287612 [42] Ojha U, Garg A. Denoising high resolution multispectral images using deep learning approach[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 15th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications. 2016: 871-875. [43] Dai Xiaoai, He Xuwei, Guo Shouheng, et al. Research on hyper-spectral remote sensing image classification by applying stacked de-noising auto-encoders neural network[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(14): 21219-21239. doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-10735-0 [44] Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, et al. Microsoft coco: common objects in context[C]//Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. 2014: 740-755. [45] Andriluka M, Pishchulin L, Gehler P, et al. 2D human pose estimation: new benchmark and state of the art analysis[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2014: 3686-3693. [46] Everingham M, Eslami S M A, Van Gool L, et al. The PASCAL visual object classes challenge: a retrospective[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111(1/3): 98-136. [47] Chen Xinlei, Fang Hao, Lin T Y, et al. Microsoft COCO captions: data collection and evaluation server[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1504.00325, 2015. [48] Wu Fan. AutoLabelImg[EB/OL]. [2020]. https://github.com/wufan-tb/AutoLabelImg. [49] Zhou Xingyi, Koltun V, Krähenbühl P. Tracking objects as points[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. 2020: 474-490. [50] Liu Li, Ouyang Wanli, Wang Xiaogang, et al. Deep learning for generic object detection: a survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 261-318. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01247-4 [51] Li Ruihuang, He Chenhang, Zhang Yabin, et al. SIM: semantic-aware instance mask generation for box-supervised instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2023: 7193-7203. [52] 陈丽, 李临寒, 王世勇, 等. MMShip: 中分辨率多光谱卫星图像船舶数据集[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2023, 31(13):1962-1972Chen Li, Li Linhan, Wang Shiyong, et al. MMShip: medium resolution multispectral satellite imagery ship dataset[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2023, 31(13): 1962-1972 [53] Chen Zizhao, Qian Yeqiang, Yang Xiaoxiao, et al. AMFD: distillation via adaptive multimodal fusion for multispectral pedestrian detection[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2405.12944, 2024. [54] Salomonson V V, Barnes W L, Maymon P W, et al. MODIS: advanced facility instrument for studies of the Earth as a system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1989, 27(2): 145-153. doi: 10.1109/36.20292 [55] 闫赟彬, 崔博伦, 杨婷婷, 等. 基于轻型平台的多模态高分辨率高光谱目标检测系统[J]. 红外技术, 2023, 45(6):582-591Yan Yunbin, Cui Bolun, Yang Tingting, et al. Multi-modal high-resolution hyperspectral object detection system based on lightweight platform[J]. Infrared Technology, 2023, 45(6): 582-591 [56] Jia Jianxin, Wang Yueming, Zheng Xiaorou, et al. Design, performance, and applications of AMMIS: a novel airborne multimodular imaging spectrometer for high-resolution earth observations[J]. Engineering, doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2024.11.001. [57] 万源庆, 刘威骏, 林若雨, 等. 基于超构表面的光谱成像及应用研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50:230139Wan Yuanqing, Liu Weijun, Lin Ruoyu, et al. Research progress and applications of spectral imaging based on metasurfaces[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2023, 50: 230139 [58] 薛庆生, 白皓轩, 鲁凤芹, 等. 基于微透镜阵列的快照式高光谱成像仪研制[J]. 光子学报, 2023, 52:0552223 doi: 10.3788/gzxb20235205.0552223Xue Qingsheng, Bai Haoxuan, Lu Fengqin, et al. Development of snapshot hyperspectral imager based on microlens array[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2023, 52: 0552223 doi: 10.3788/gzxb20235205.0552223 [59] 王俊佟, 杨华东. 基于高光谱解混的伪装目标识别技术研究[J]. 半导体光电, 2024, 45(2):261-268Wang Juntong, Yang Huadong. Camouflaged target recognition technology based on hyperspectral unmixing[J]. Semiconductor Optoelectronics, 2024, 45(2): 261-268 [60] Zou Zhengxia, Chen Keyan, Shi Zhenwei, et al. Object detection in 20 years: a survey[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2023, 111(3): 257-276. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2023.3238524 [61] Lowe D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]//Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 1999: 1150-1157. [62] Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [63] Bay H, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L. SURF: speeded up robust features[C]//Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision. 2006: 404-417. [64] Song Yanyan, Lu Ying. Decision tree methods: applications for classification and prediction[J]. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 2015, 27(2): 130-135. [65] Jijo B T, Abdulazeez A M. Classification based on decision tree algorithm for machine learning[J]. Journal of Applied Science and Technology Trends, 2021, 2(1): 20-28. doi: 10.38094/jastt20165 [66] Abdullah D M, Abdulazeez A M. Machine learning applications based on SVM classification: a review[J]. Qubahan Academic Journal, 2021, 1(2): 81-90. doi: 10.48161/qaj.v1n2a50 [67] Viola P, Jones M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features[C]//Proceedings of 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2001: I. [68] Viola P, Jones M J. Robust real-time face detection[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 57(2): 137-154. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000013087.49260.fb [69] Papageorgiou C P, Oren M, Poggio T. A general framework for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision. 1998: 555-562. [70] Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]//Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2005: 886-893. [71] Felzenszwalb P, McAllester D, Ramanan D. A discriminatively trained, multiscale, deformable part model[C]//Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2008: 1-8. [72] Zhang Tianwen, Zhang Xiaoling, Ke Xiao, et al. HOG-ShipCLSNet: a novel deep learning network with hog feature fusion for SAR ship classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210322. [73] Tang Zetian, Zhang Zemin, Chen Wei, et al. An SIFT-based fast image alignment algorithm for high-resolution image[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 42012-42041. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3270911 [74] Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, et al. PyTorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2019: 32. [75] Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P, et al. TensorFlow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1603.04467, 2016. [76] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2012: 1097-1105. [77] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2014: 580-587. [78] Uijlings J R R, Van De Sande K E A, Gevers T, et al. Selective search for object recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 104(2): 154-171. doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0620-5 [79] He Kaiming, Zhang Xiangyu, Ren Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [80] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2015: 1440-1448. [81] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2017: 936-944. [82] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016: 779-788. [83] Liu Wei, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. 2016: 21-37. [84] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2017: 2999-3007. [85] Law H, Deng Jia. CornerNet: detecting objects as paired keypoints[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. 2018: 765-781. [86] Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. 2020: 213-229. [87] Zhu Xizhou, Su Weijie, Lu Lewei, et al. Deformable DETR: deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. 2021. [88] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2017: 6000-6010. [89] Han Dongchen, Pan Xuran, Han Yizeng, et al. Flatten transformer: vision transformer using focused linear attention[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2023: 5938-5948. [90] Yao Ting, Li Yehao, Pan Yingwei, et al. Dual vision transformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(9): 10870-10882. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3268446 [91] Gu A, Dao T. Mamba: linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2312.00752, 2024. [92] Zhu Lianghui, Liao Bencheng, Zhang Qian, et al. Vision mamba: efficient visual representation learning with bidirectional state space model[C]//Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning. 2024. [93] He Kaiming, Zhang Xiangyu, Ren Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016: 770-778. [94] González A, Fang Zhijie, Socarras Y, et al. Pedestrian detection at day/night time with visible and FIR cameras: a comparison[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16: 820. doi: 10.3390/s16060820 [95] Fang Qingyun, Han Dapeng, Wang Zhaokui. Cross-modality fusion transformer for multispectral object detection[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2111.00273, 2022. [96] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: an incremental improvement[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [97] Ho J, Jain A, Abbeel P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2020: 574. [98] Rombach R, Blattmann A, Lorenz D, et al. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models[C]//Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2022: 10674-10685. [99] Zhao Tianyi, Yuan Maoxun, Jiang Feng, et al. Removal and selection: improving RGB-infrared object detection via coarse-to-fine fusion[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2401.10731, 2024. [100] Jacobs R A, Jordan M I, Nowlan S J, et al. Adaptive mixtures of local experts[J]. Neural Computation, 1991, 3(1): 79-87. doi: 10.1162/neco.1991.3.1.79 [101] Shazeer N, Mirhoseini A, Maziarz K, et al. Outrageously large neural networks: the sparsely-gated mixture-of-experts layer[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. 2017. [102] Sohl-Dickstein J, Weiss E A, Maheswaranathan N, et al. Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. 2015: 2256-2265. [103] Ono S. Snapshot multispectral imaging using a pixel-wise polarization color image sensor[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(23): 34536-34573. doi: 10.1364/OE.402947 [104] Hubold M, Montag E, Berlich R, et al. Multi-aperture system approach for snapshot multispectral imaging applications[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(5): 7361-7378. doi: 10.1364/OE.412655 [105] Mengu D, Tabassum A, Jarrahi M, et al. Snapshot multispectral imaging using a diffractive optical network[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2023, 12: 86. [106] Wang Xudong, Girdhar R, Yu S X, et al. Cut and learn for unsupervised object detection and instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2023: 3124-3134. -





 下载:
下载: