Particle simulation and control for beam of ionic liquid ion source
-
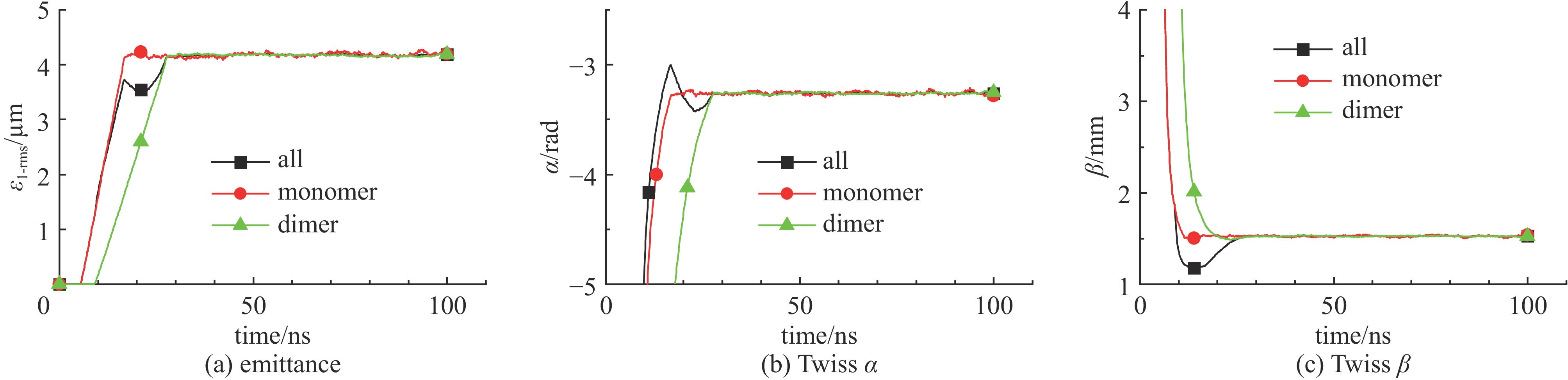
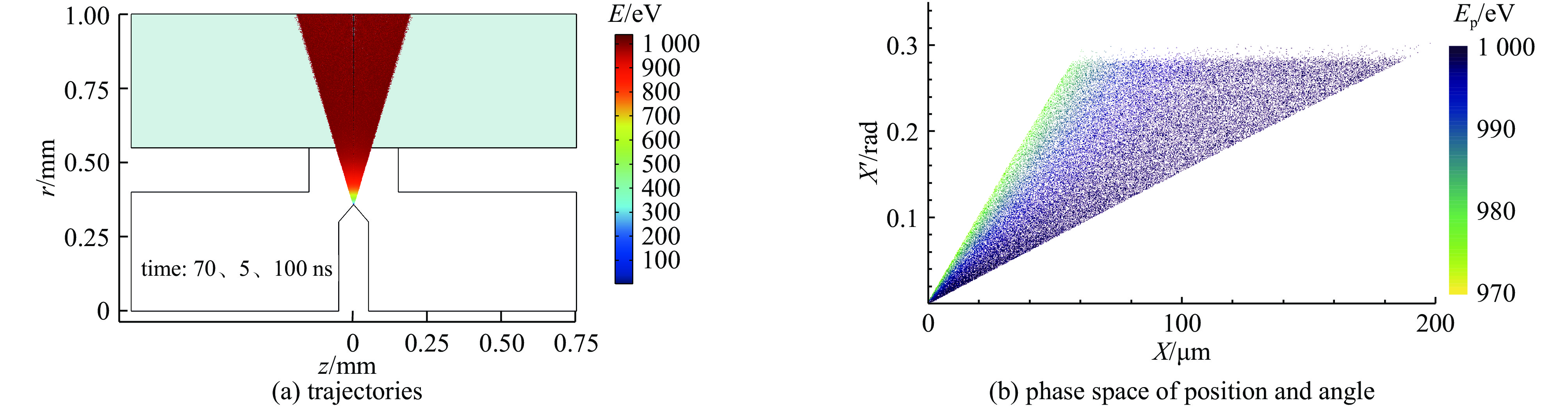
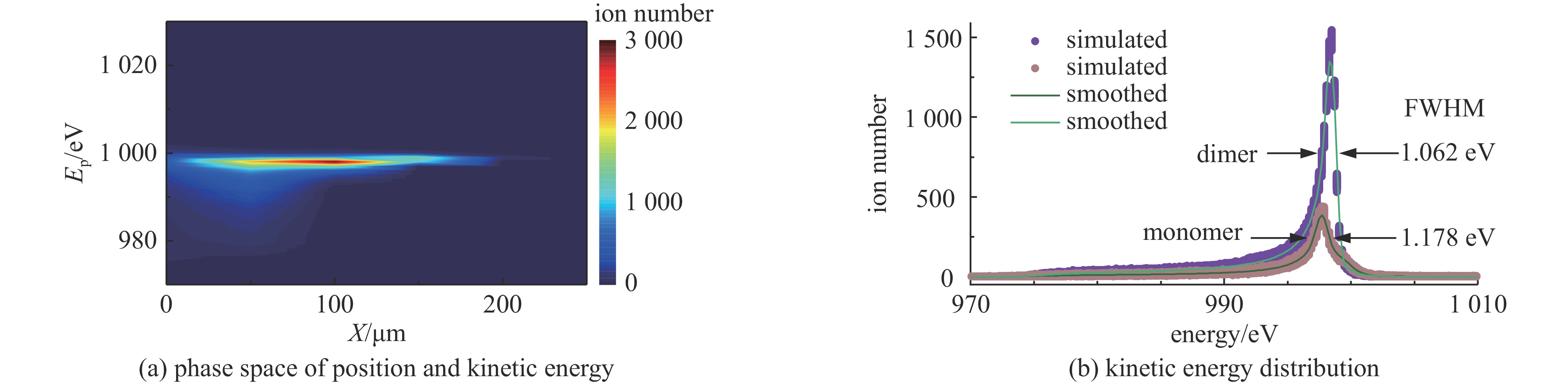
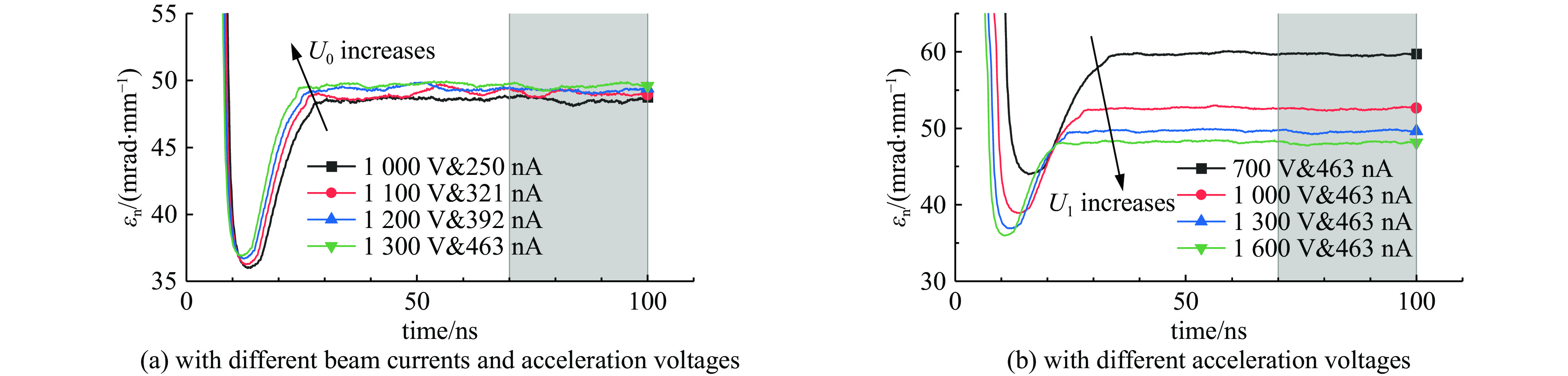
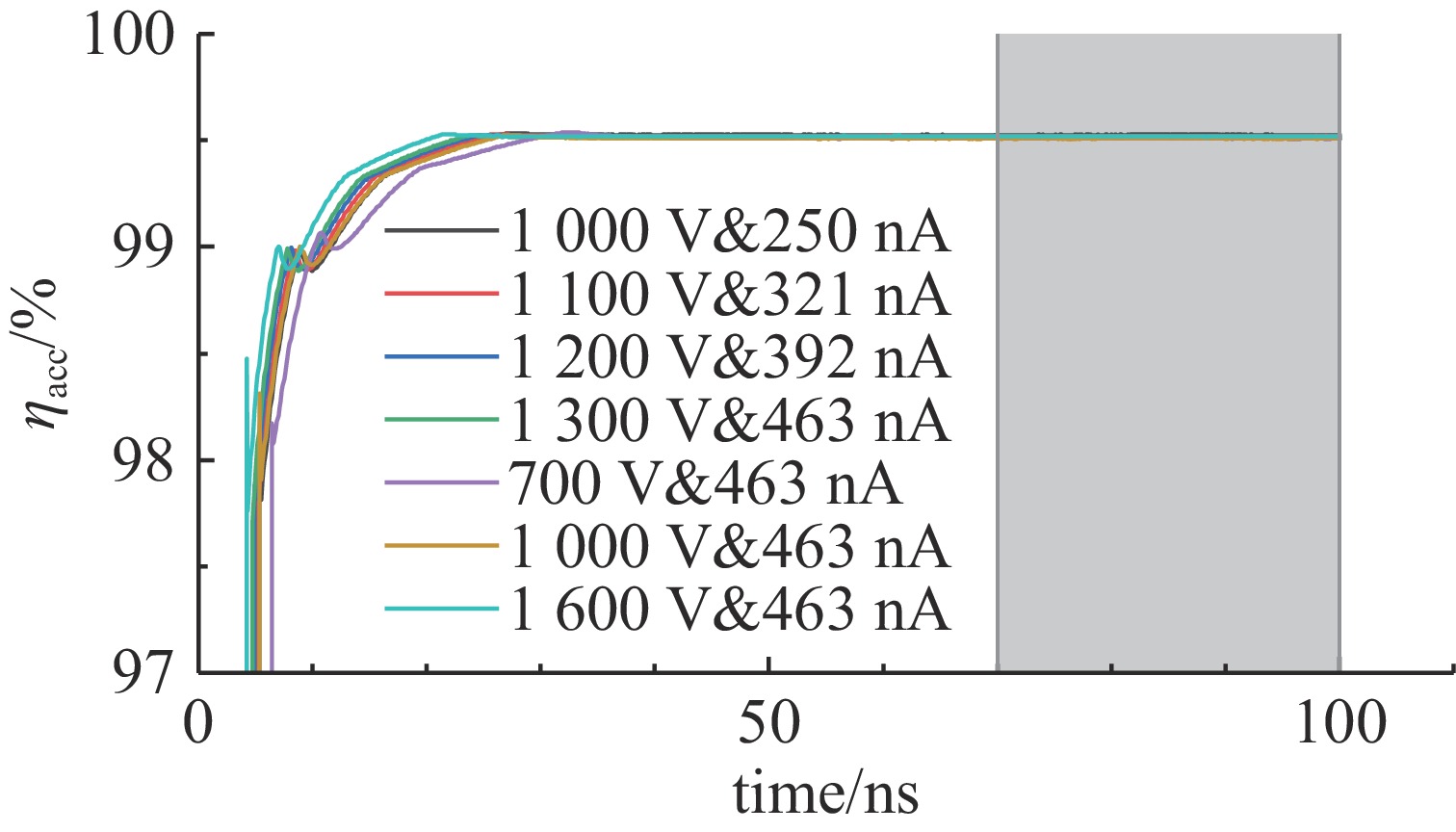
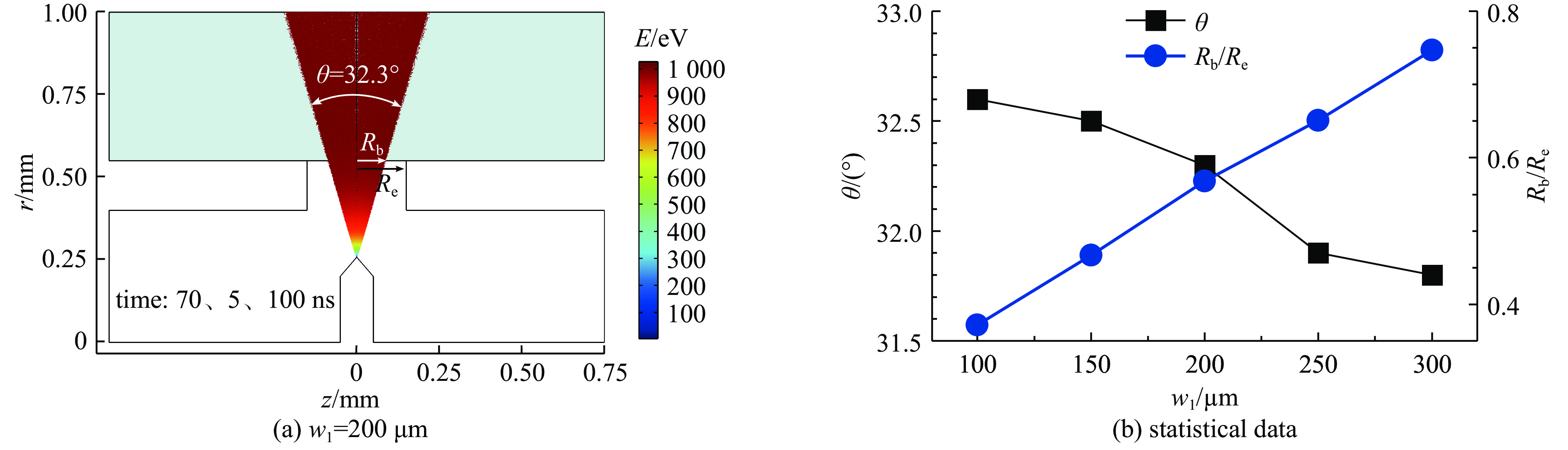
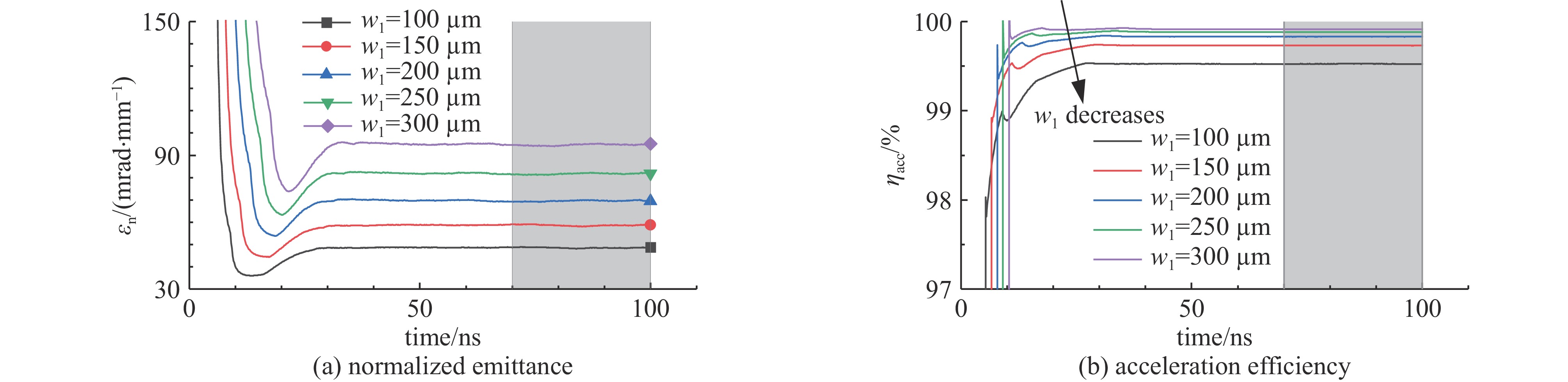
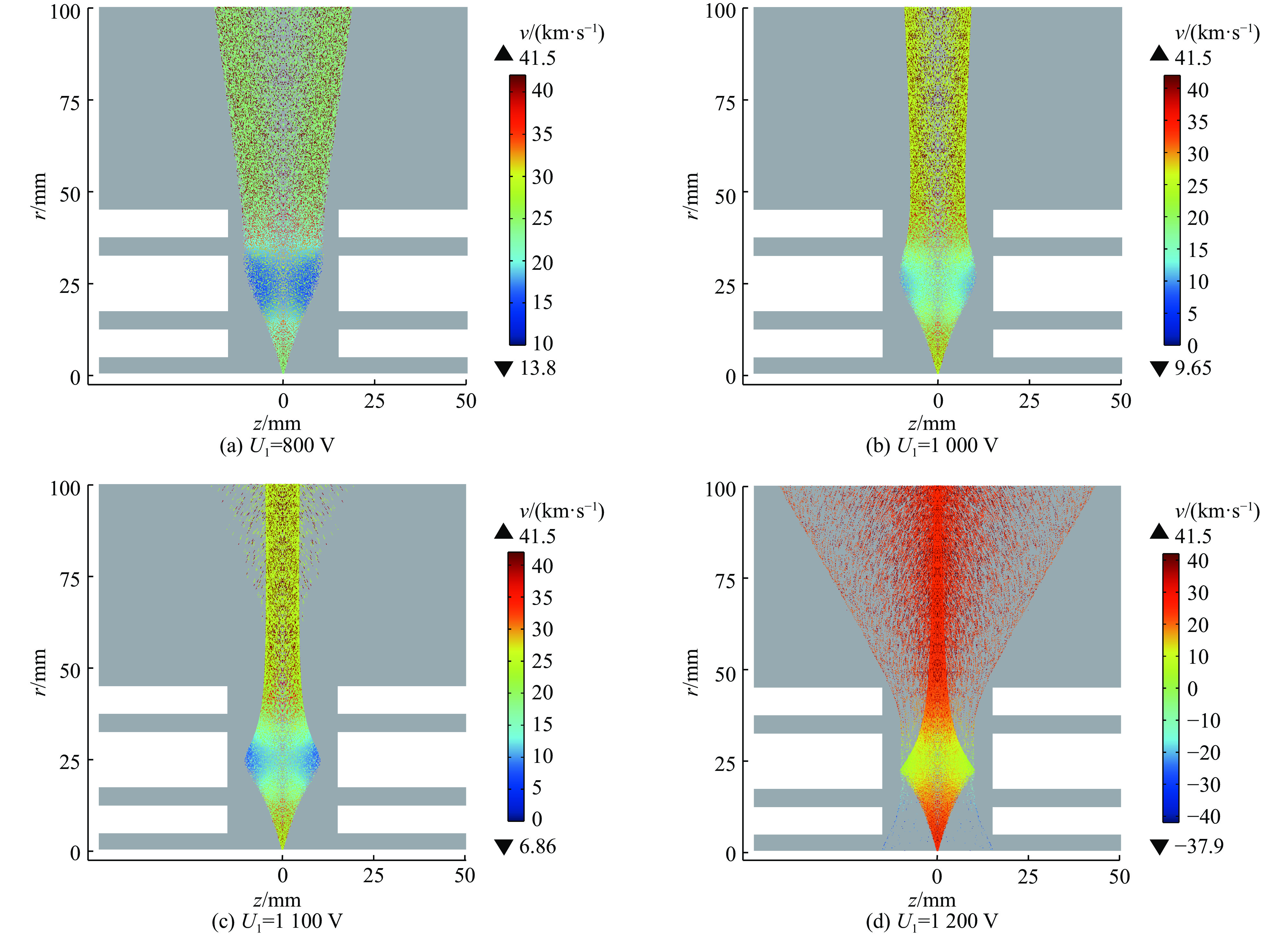
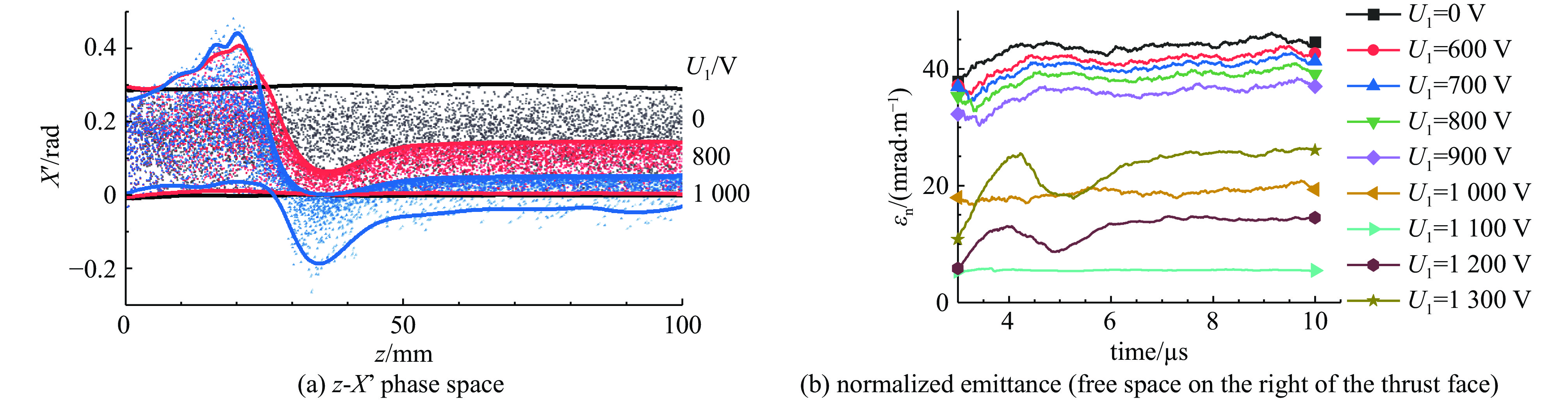
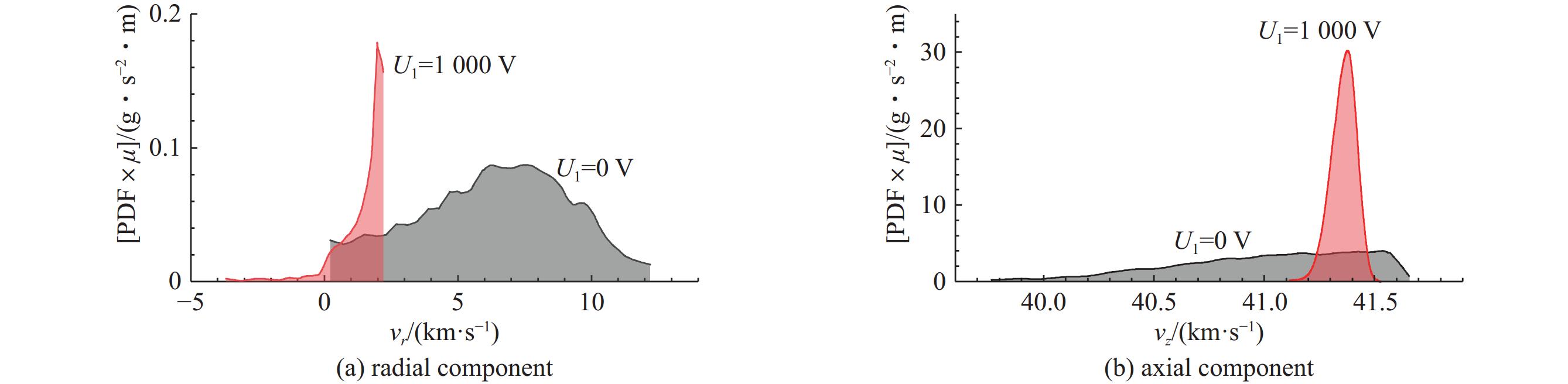
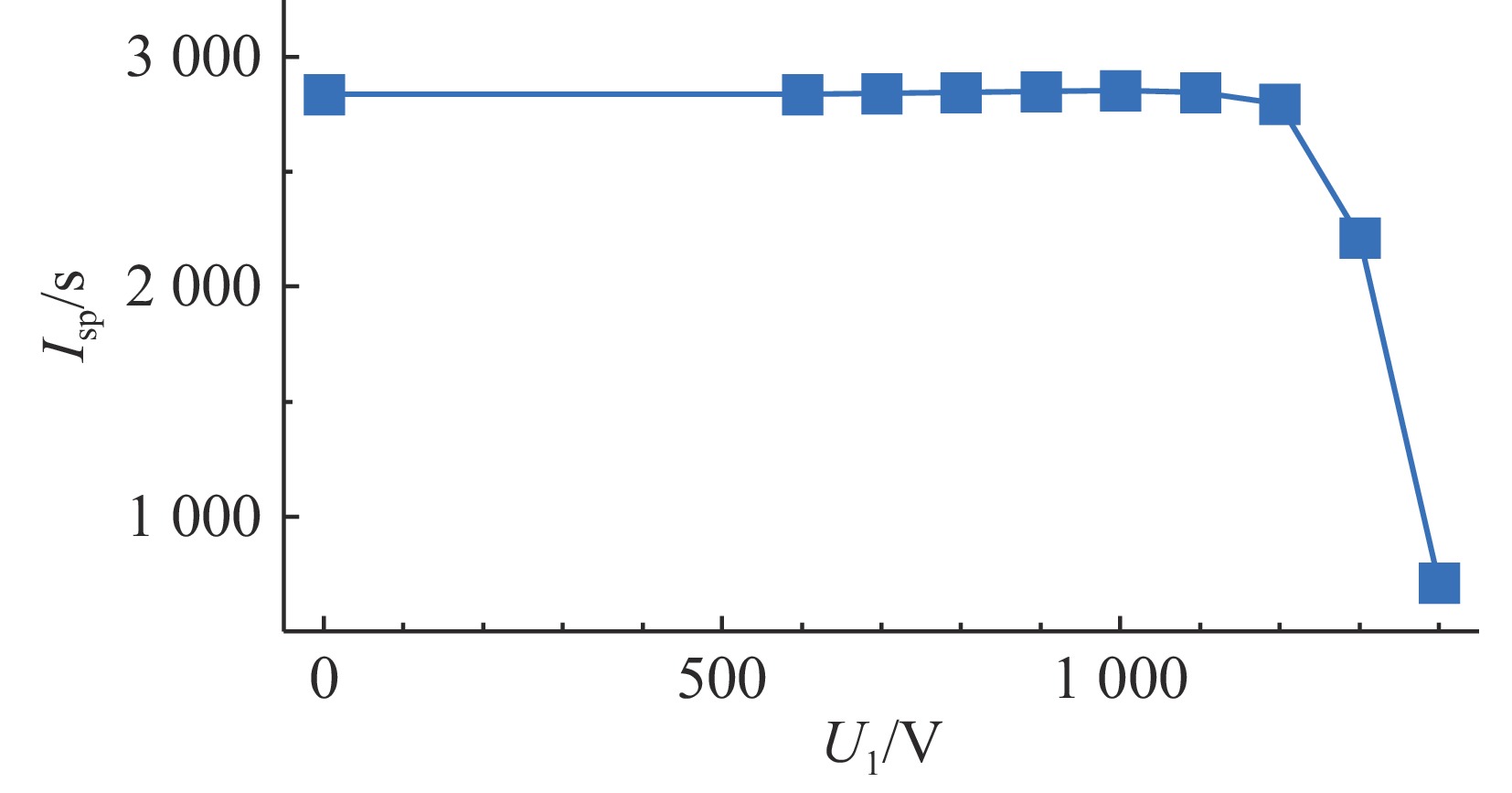
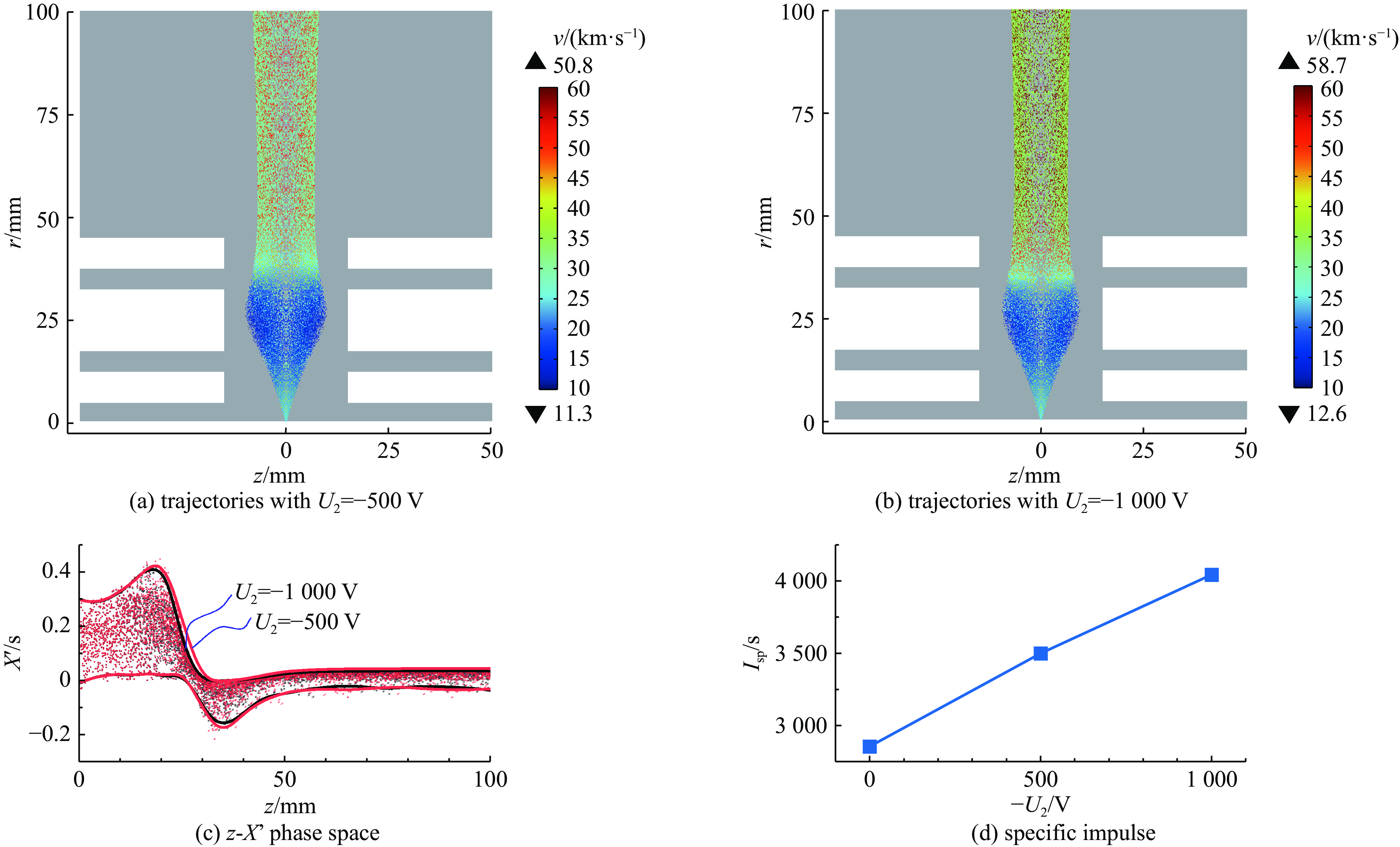
摘要: 离子液体离子源可以提供种类丰富的大质量离子,在离子推力器等方面有重要应用。为了获得离子液体离子源束流品质参数并有效调控束流品质,使用粒子方法模拟了离子液体离子源束流加速过程,研究了束电流、加速电压和发射锥-引出电极轴向间距等三个常用操作条件对束流发射度和Twiss参数的影响。研究表明:束流的归一化发射度随束电流的降低、发射锥-引出电极轴向间距的减小和加速电压的升高而降低。加速过程会造成动能分布展宽,束电流和加速电压对加速效率没有明显影响,而增加发射锥-引出电极轴向间距可以提高加速效率。进一步以加速过程模拟得到的束流参数集为输入,模拟了厘米级空间尺度束流的调控。研究表明通过一组三电极静电透镜,可以有效调控束流的发散、速度分布和比冲性能,而不增加对现有离子液体电推力器电源配置的要求。Abstract: Ionic liquid ion sources have the capability of generating diverse heavy molecular ions, and their applications have been investigated in the field of ion thrusters. This study aims to determine the quality parameters of ionic liquid ion beams and establish methods for their control. Firstly, the beam acceleration process in an ionic liquid ion source was simulated using Particle-in-Cell (PIC) simulation methods, and the effects of the beam current, acceleration voltage, and emitter-extraction gap on the beam emittance and Twiss parameters were investigated. The results indicate that the normalized emittance decreases with a reduction in the beam current and emitter-extraction gap, as well as with an increase in the acceleration voltage. The kinetic energy broadens during the acceleration process. The acceleration efficiency is not obviously affected by the beam current or acceleration voltage. However, it increases with the expansion of the emitter-extraction gap. Secondly, the control of a centimeter-scale beam was simulated by utilizing the beam parameters derived from the simulation of the acceleration process. The results demonstrate that the divergence, velocity distribution, and specific impulse can be controlled by a set of three-electrode electrostatic lenses without imposing additional demands on the power source on the ionic liquid electric thruster.
-
Key words:
- ionic liquid ion source /
- beam control /
- thruster /
- emittance /
- Particle-in-Cell (PIC) simulation
-
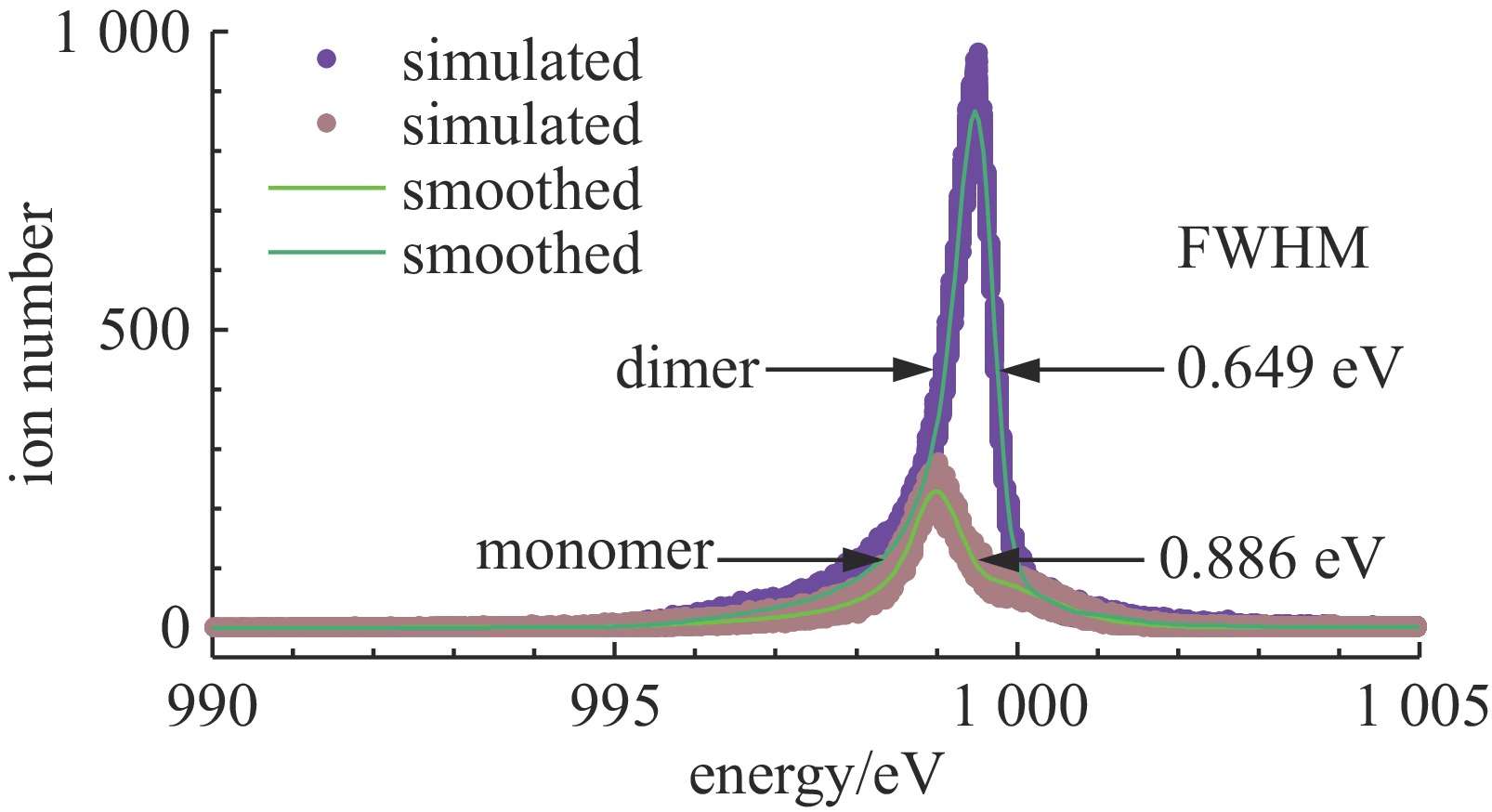
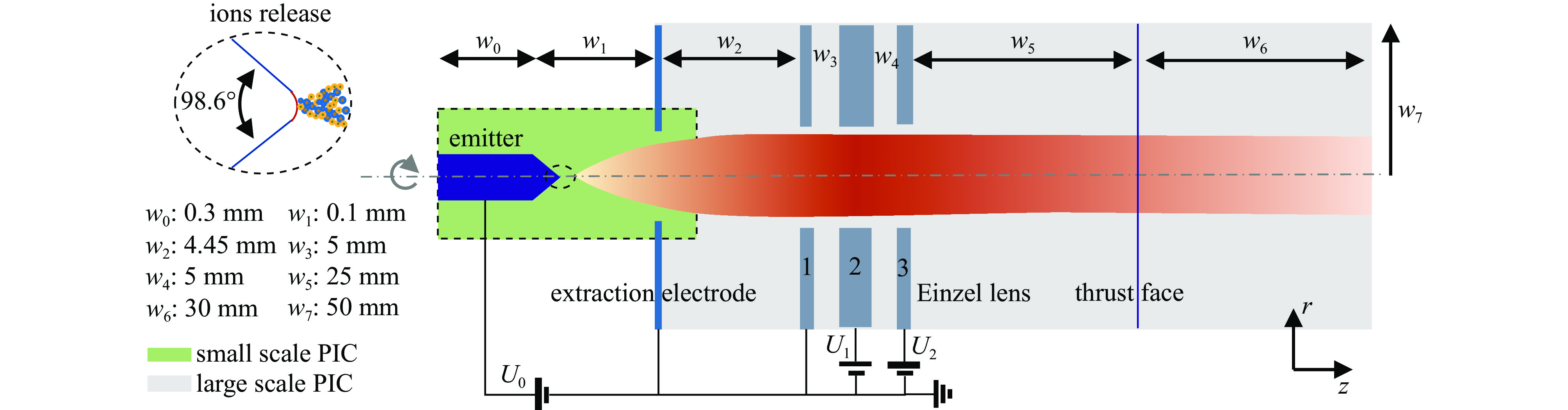
beam current,$ I\mathrm{_b} $/nA acceleration voltage,$ U_0/\mathrm{V} $ composition radius of extraction hole,$ {R_{\text{e}}} $/mm thickness of extraction/mm $ 0.71U_0/\mathrm{V}-460 $ 1000 ~1300 40% monomers+60% dimers 0.15 0.15 表 2 束流参数表
Table 2. Summary of beam parameters
${w_1}{\text{/μm}}$ ${I_{\mathrm{b}}}{\text{/nA}}$ ${U_0}{\text{/V}}$ emittance
${\varepsilon _{1 {\text{-}} {\rm{rms}}}}{\text{/μm}}$Twiss
$ \alpha $/radTwiss
$ \; \beta $/mmnormalized emittance
$ {\varepsilon _{\rm{n}}}/({\rm{mrad}} \cdot {\rm{mm}}) $mean
energy/eVenergy standard
deviation/eV100 250 1000 4.173 −3.260 1.526 48.52 995.3(99.53%U0) 5.14(5.14‰U0) 100 321 1100 4.214 −3.261 1.527 49.03 1094.7 (99.52%U0)5.67(5.15‰U0) 100 392 1200 4.235 −3.261 1.526 49.26 1194.2 (99.52%U0)6.26(5.22‰U0) 100 463 1300 4.262 −3.261 1.526 49.58 1293.7 (99.52%U0)6.78(5.22‰U0) 100 463 700 5.128 −3.260 1.527 59.64 696.56(99.51%U0) 3.53(5.04‰U0) 100 463 1000 4.517 −3.260 1.526 52.53 995.08(99.51%U0) 5.13(5.13‰U0) 100 463 1600 4.133 −3.260 1.526 48.07 1592.3 (99.52%U0)8.55(5.34‰U0) 150 250 1000 4.107 −3.643 1.874 58.61 997.3(99.73%U0) 2.89(2.89‰U0) 200 250 1000 4.042 −4.026 2.261 69.56 998.3(99.83%U0) 1.83(1.83‰U0) 250 250 1000 3.996 −4.409 2.687 81.69 998.8(99.88%U0) 1.31(1.31‰U0) 300 250 1000 3.950 −4.793 3.153 94.68 999.1(99.91%U0) 1.10(1.10‰U0) -
[1] Gamero-Castaño M, Hruby V. Electrospray as a source of nanoparticles for efficient colloid thrusters[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2001, 17(5): 977-987. doi: 10.2514/2.5858 [2] Romero-Sanz I, Bocanegra R, de La Mora J F, et al. Source of heavy molecular ions based on Taylor cones of ionic liquids operating in the pure ion evaporation regime[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 94(5): 3599-3605. doi: 10.1063/1.1598281 [3] Höflich K, Hobler G, Allen F I, et al. Roadmap for focused ion beam technologies[J]. Applied Physics Reviews, 2023, 10: 041311. doi: 10.1063/5.0162597 [4] Lozano P C. Design and microstructuring of materials to boost spacecraft ion propulsion[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2024, 9(11): 757-758. doi: 10.1038/s41578-024-00664-3 [5] Huang Chengjin, Li Jianling, Li Mu. Experimental characterization of the electrospray propulsive performance for ionic liquid propellants [EMIm][DCA] and [BMIm][DCA][J]. Fuel, 2023, 336: 126822. [6] Huang Chengjin, Li Jianling, Li Mu. Performance measurement and evaluation of an ionic liquid electrospray thruster[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2023, 36(3): 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.10.030 [7] Huang Chengjin, Li Jianling, Li Mu, et al. Emission performance of ionic liquid electrospray thruster for micropropulsion[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2022, 38(2): 212-220. doi: 10.2514/1.B37878 [8] Huang Chengjin, Li Jianling, Li Mu, et al. Experimental investigation on current modes of ionic liquid electrospray from a coned porous emitter[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 183: 286-299. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2021.03.014 [9] Chen Chong, Chen Maolin, Fan Wei, et al. Effects of non-uniform operation of emission sites on characteristics of a porous electrospray thruster[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 178: 192-202. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.09.002 [10] Liu Xinyu, Kang Xiaoming, Deng Hanwen, et al. Energy properties and spatial plume profile of ionic liquid ion sources based on an array of porous metal strips[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2021, 23: 125502. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/ac23bd [11] Guo Yuntao, Sun Wei, Sun Zhenning, et al. Direct thrust test and asymmetric performance of porous ionic liquid electrospray thruster[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2023, 36(4): 120-133. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2022.09.007 [12] Yang Cheng, Lu Jiawei, Wu Xiangbei, et al. Axial emission characteristics of an ionic liquid electrospray thruster with a circular emitter[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2025, 38: 103207. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2024.08.038 [13] MacArthur J, Colicci V, Lozano P. Monodisperse porous emitter materials for ion electrospray propulsion[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2024, 40(6): 859-868. doi: 10.2514/1.B39375 [14] 吕建钦. 带电粒子束光学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004Lv Jianqin. Optics of charged particle beams[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2004 [15] Collins A L, Wright P L, Uchizono N M, et al. High angle mass flux of an electrospray plume[J]. Journal of Electric Propulsion, 2022, 1(1): 32. doi: 10.1007/s44205-022-00031-w [16] 孙安邦, 毛根旺, 陈茂林, 等. 离子推力器羽流特性的粒子模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(2):401-405 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102202.0401Sun Anbang, Mao Genwang, Chen Maolin, et al. Particle simulation of ion thruster plume characteristics[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(2): 401-405 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102202.0401 [17] Zhang Baiyi, Cai Guobiao, He Bijiao, et al. Plume neutralization of an ionic liquid electrospray thruster: better insights from particle-in-cell modelling[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2021, 30: 125009. doi: 10.1088/1361-6595/ac3e7f [18] Asher J S, Wang J. Three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations of bipolar ionic electrospray thruster plume[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2022, 38(4): 573-580. doi: 10.2514/1.B38610 [19] Du Zening, Wu Zhiwen, Li Jin, et al. Study on the plume self-neutralization of ionic liquid electrospray thruster based on median potential[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2024, 33: 055016. doi: 10.1088/1361-6595/ad4ac3 [20] Gallud X, Lozano P C. The emission properties, structure and stability of ionic liquid menisci undergoing electrically assisted ion evaporation[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2022, 933: A43. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2021.988 [21] Romero-Sanz I, de La Mora J F. Energy distribution and spatial structure of electrosprays of ionic liquids in vacuo[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2004, 95(4): 2123-2129. doi: 10.1063/1.1639947 [22] Lund S M, Kikuchi T, Davidson R C. Generation of initial kinetic distributions for simulation of long-pulse charged particle beams with high space-charge intensity[J]. Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, 2009, 12: 114801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.12.114801 [23] Humphries S Jr. Charged particle beams[M]. New York: Wiley, 1990. [24] Lozano P, Martínez-Sánchez M. Ionic liquid ion sources: characterization of externally wetted emitters[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2005, 282(2): 415-421. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.132 -




 下载:
下载: