Lightweight neural network model for nuclide recognition based on nuclear pulse peak sequence and its FPGA acceleration method
-
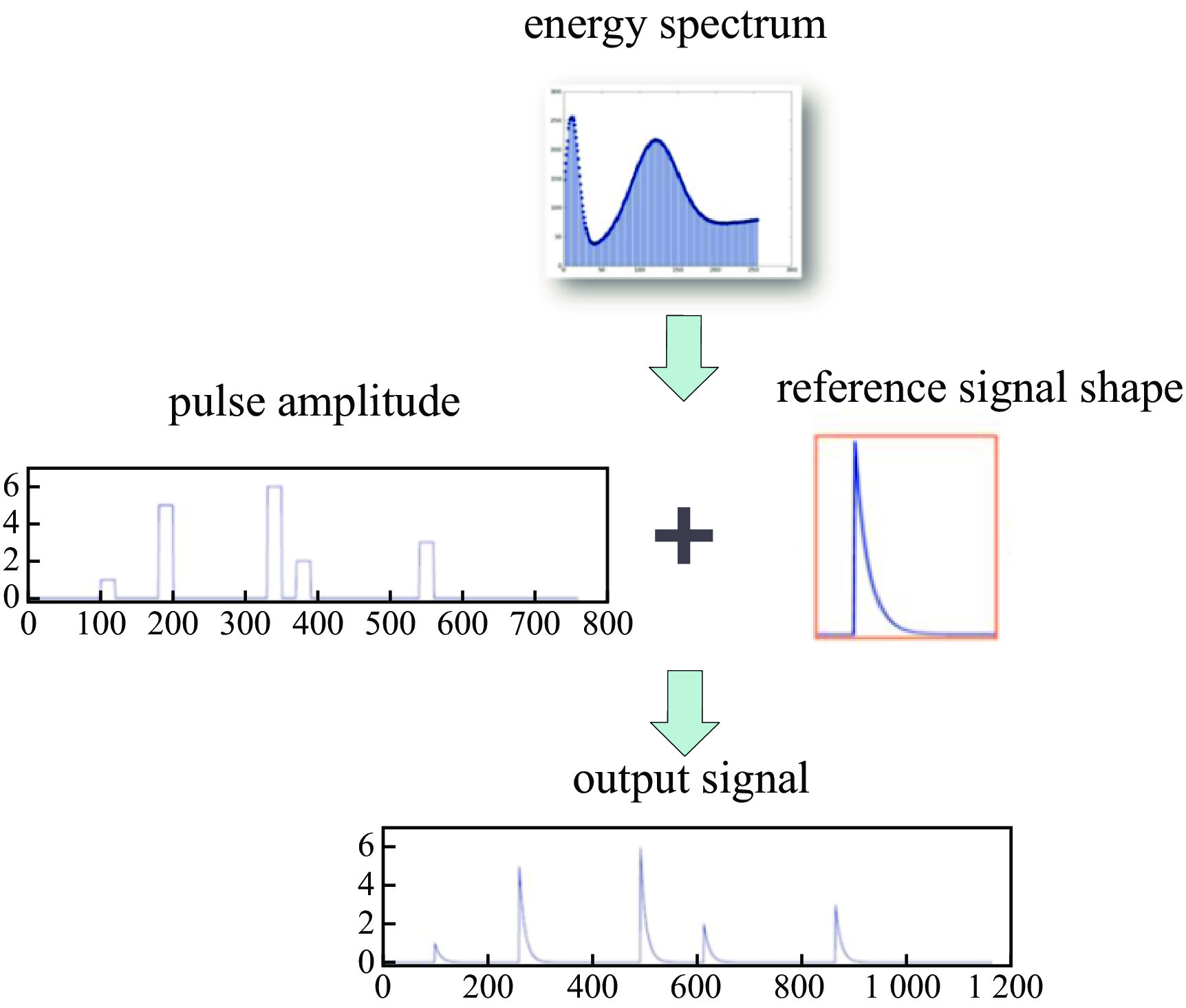
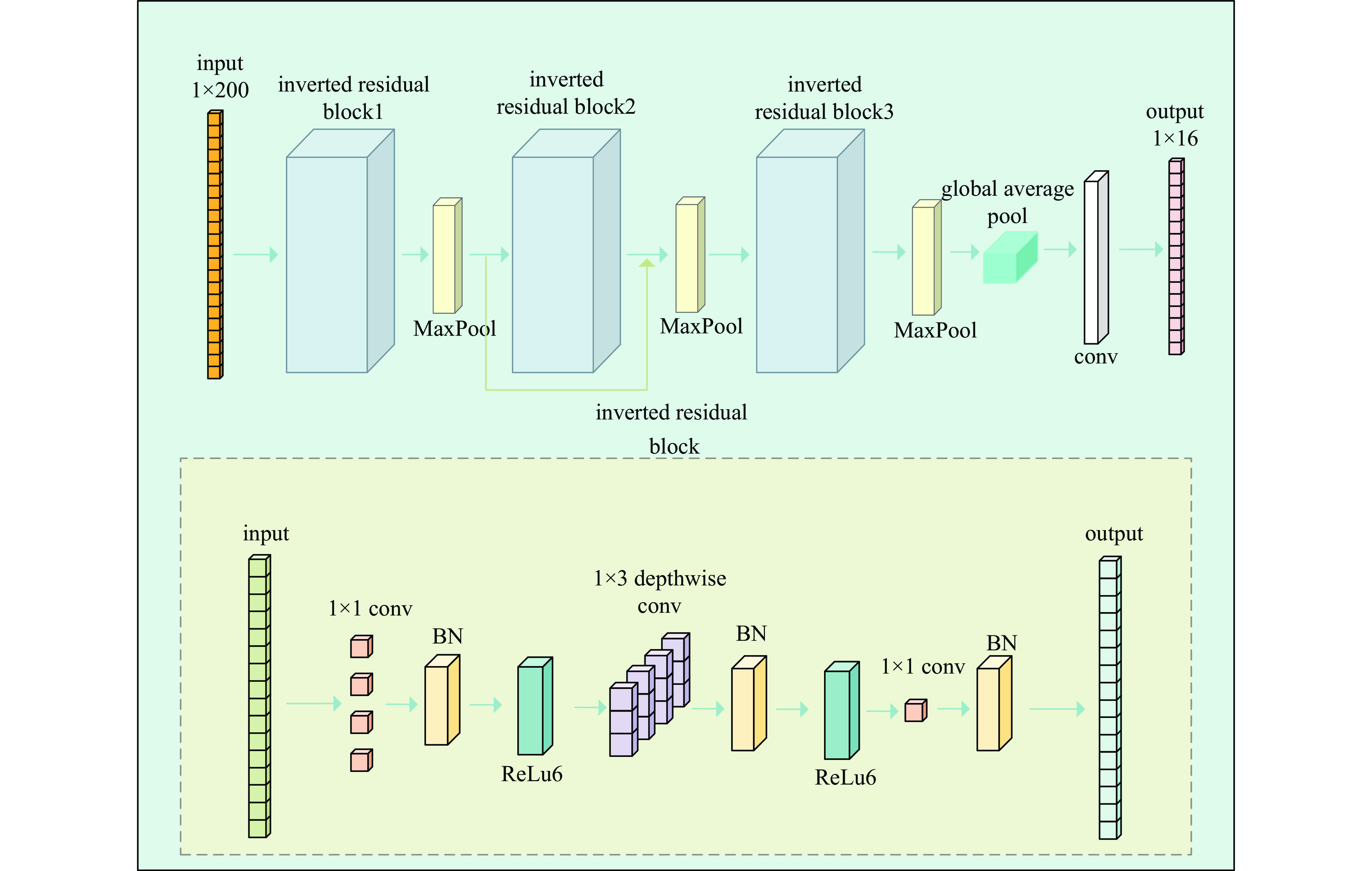
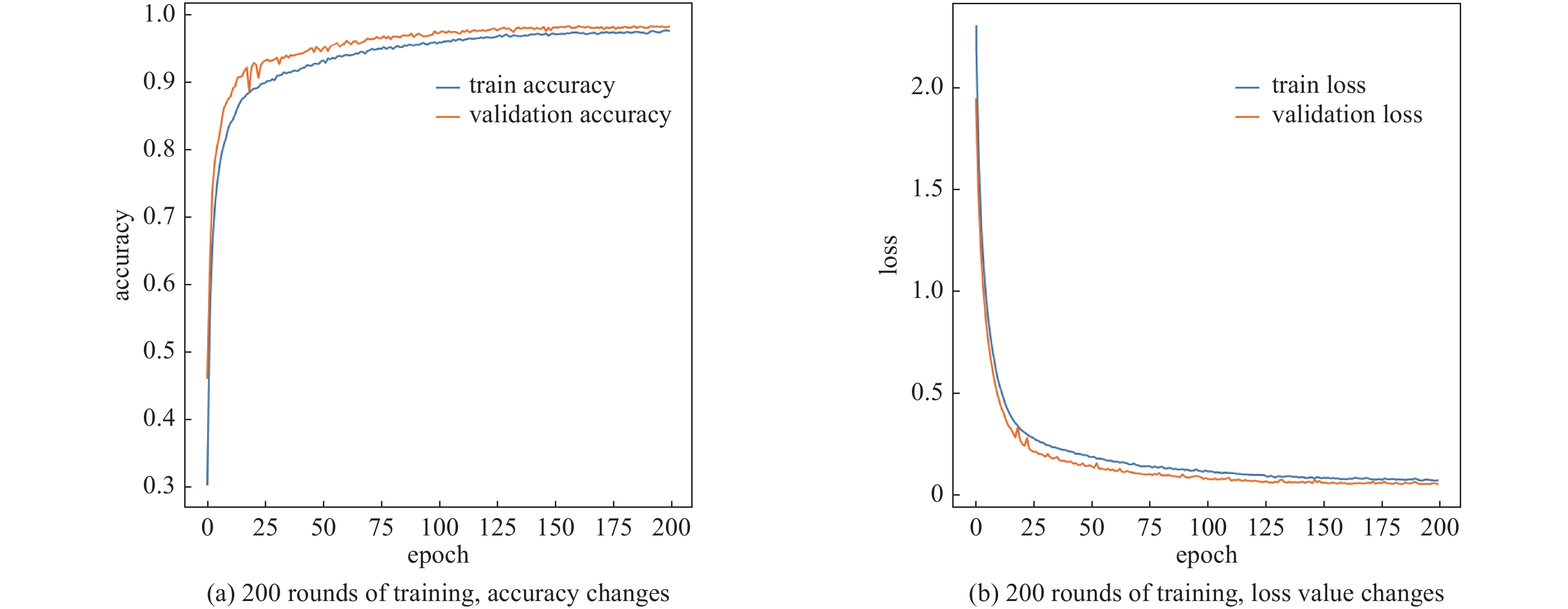
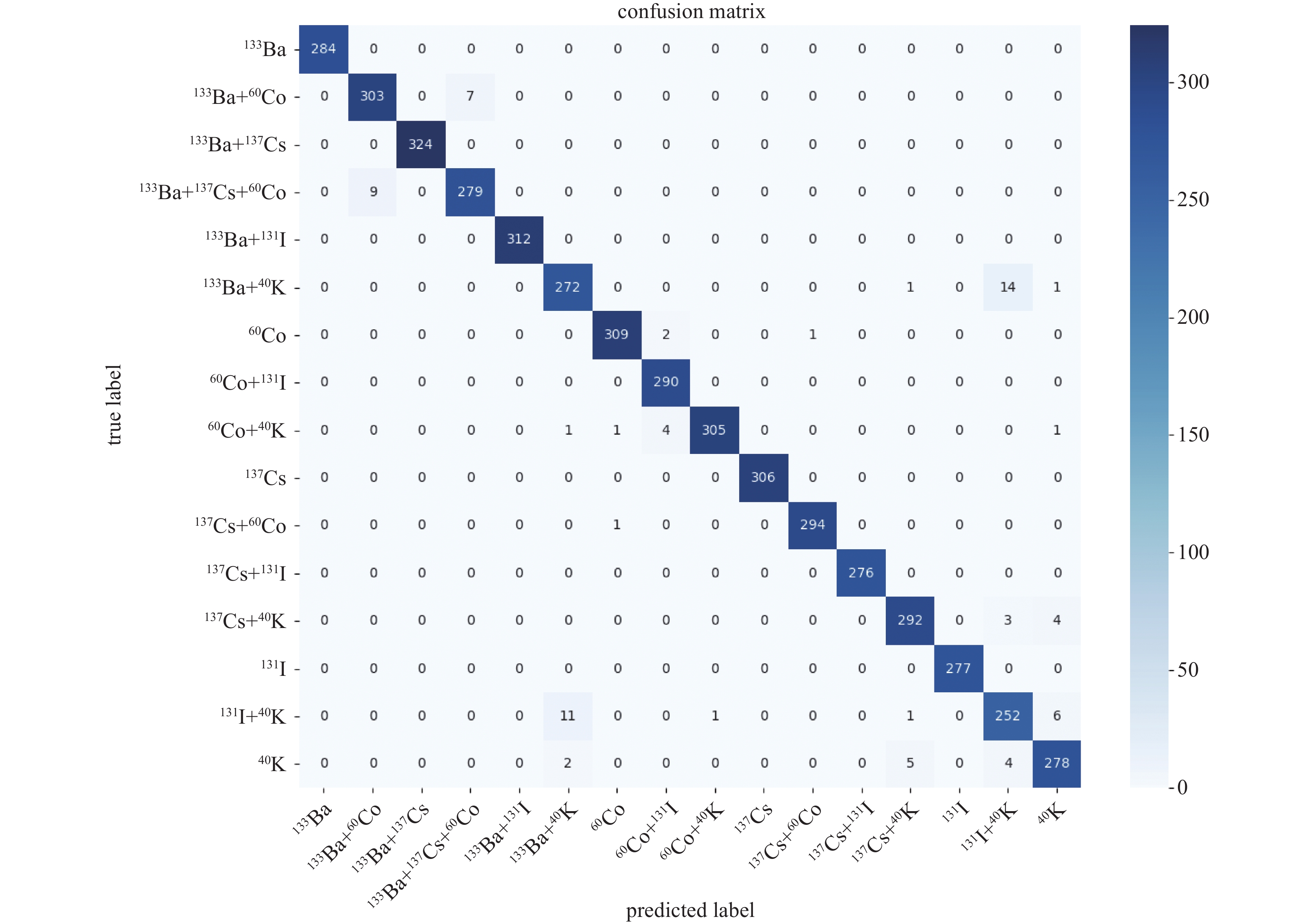
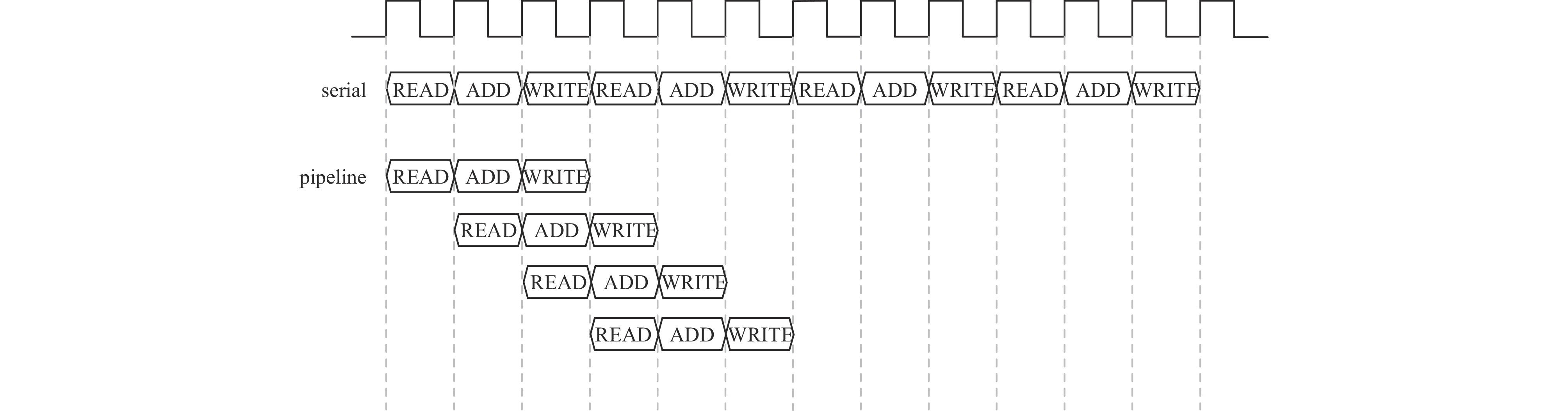
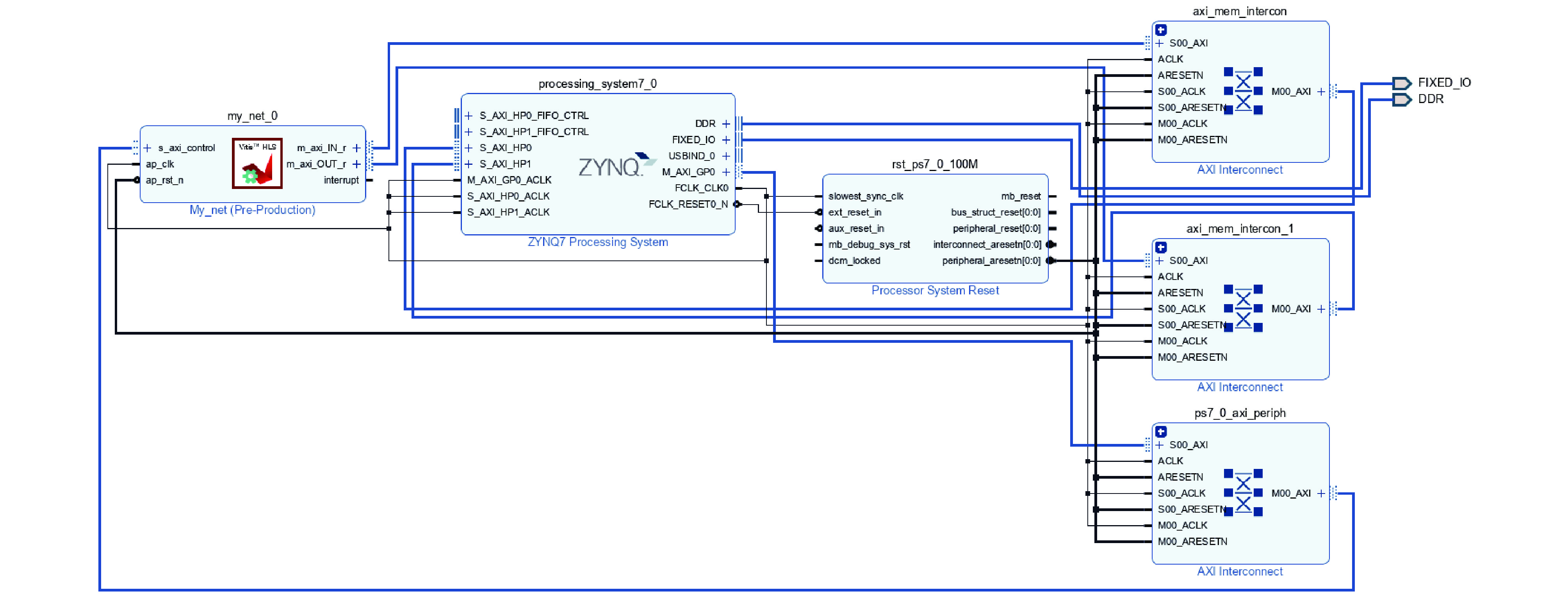
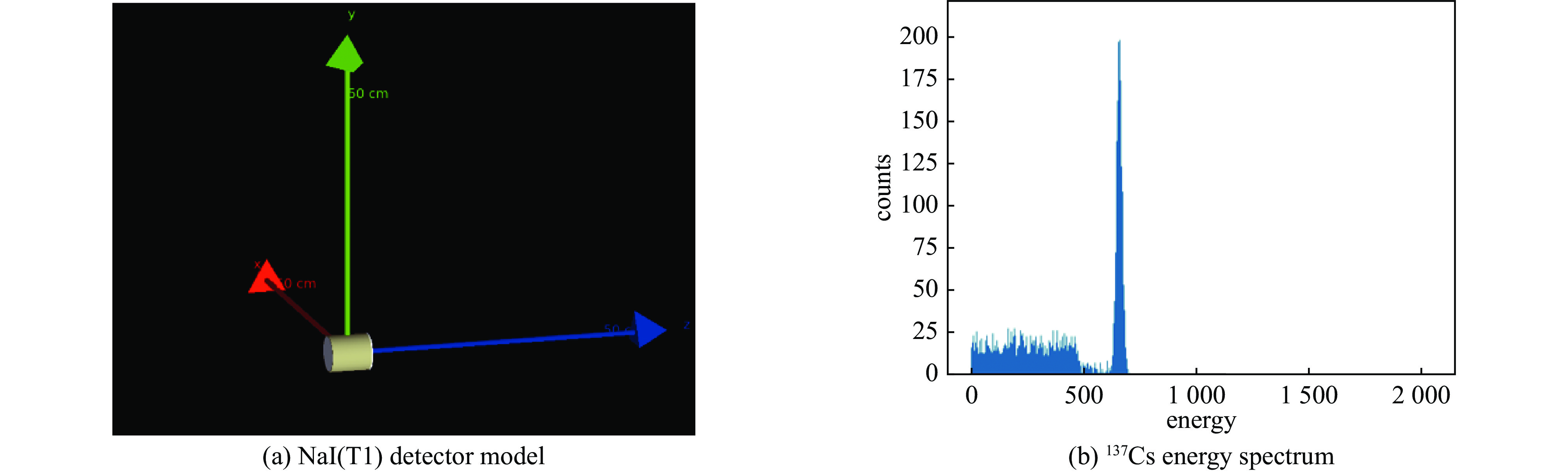
摘要: 放射性核素已在核医疗、核安保及无损检测等领域中广泛应用,而对其准确识别是放射性核素定性检测的基础。在便携式核素识别仪中,基于传统能谱分析方法存在延迟高、识别率低等不足。提出一种基于核脉冲峰值序列的核素识别轻量化神经网络模型及其FPGA硬件加速方法,通过引入深度可分离卷积和倒残差模块,并使用全局平均池化替代传统全连接层,构建了一种轻量化、高效的神经网络模型。针对网络训练数据集,通过蒙特卡罗工具包Geant4构建NaI(Tl)探测器模型,获取模拟能谱,再由核脉冲信号模拟仿真器根据能谱产生核脉冲信号序列,构建了16种核脉冲信号数据。最后,将训练好的模型通过量化、融合与并行计算等优化方法部署到PYNQ-Z2异构芯片,实现加速。实验结果表明,模型识别精度可达98.3%,相较传统卷积神经网络模型提高了13.2%,参数量仅为2 128。FPGA优化加速后单次识别耗时0.273 ms,功耗为1.94 W。Abstract: Radionuclides have been widely used in the fields of nuclear medicine, nuclear security and non-destructive testing, and their accurate identification is the basis of qualitative detection of radionuclides. In the portable nuclide recognition instrument, the traditional energy spectrum analysis method has the shortcomings of high delay and low recognition rate. This paper proposes a lightweight neural network model for nuclide recognition based on kernel pulse peak sequence and its FPGA hardware acceleration method. A lightweight and efficient neural network model is constructed by introducing depth-separable convolution and reciprocal residual modules, and using global average pooling to replace the traditional fully connected layer. For the network training data set, NaI (Tl) detector model was constructed through Monte Carlo toolkit Geant4 to obtain the analog energy spectrum, and then a simulator generated nuclear pulse signal sequences according to the energy spectrum, and 16 kinds of nuclear pulse signal data were constructed. Finally, the trained model is deployed to PYNQ-Z2 heterogeneous chip through optimization methods such as quantization, fusion and parallel computing to achieve acceleration. Experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of the proposed model can reach 98.3%, which is 13.2% higher than that of the traditional convolutional neural network model, and the number of parameters is only 2 128. After FPGA optimization and acceleration, the single recognition time is 0.273 ms, and the power consumption is 1.94 W.
-
Key words:
- nuclide identification /
- nuclear signal /
- neural network /
- FPGA /
- hardware acceleration
-
表 1 模型对比
Table 1. Model comparison
model recognition accuracy/% model parameter model size/kbit my model 98.3 2128 25.9 LSTM 85.3 27536 111 GhostNet 96.9 1710096 6711 MobileNet-V1 94.1 2396688 9430 ResNet-18 93.8 3856912 15151 VGGNet-16 93.0 34341200 134156 表 2 量化资源消耗与时延
Table 2. Quantifying resource consumption and delay
resource 32 bit float (utilization rate) 16 bit fixed-point number (utilization rate) BRAM_18K 240(85%) 79(28%) DSP 162(73%) 114(51%) FF 46 657(43%) 12 968(12%) LUT 51 846(97%) 21 483(40%) latency(cycles) 38 101 34 792 表 3 融合前后资源消耗与时延
Table 3. Resource consumption and latency before and after fusion
resource before fusion(utilization rate) after fusion(utilization rate) BRAM_18K 252(90%) 240(85%) DSP 169(76%) 162(73%) FF 51006 (47%)46657 (43%)LUT 54753 (102%)51846 (97%)latency(cycles) 47013 38101 表 4 部分优化前后资源消耗与时延
Table 4. Resource consumption and delay before and after partial optimization
resource before optimization (utilization rate) after optimization (utilization rate) BRAM_18K 0(0%) 0(0%) DSP 4(1%) 32(14%) FF 328(~0%) 1 808(1%) LUT 427(~0%) 802(1%) latency(cycles) 3 208 811 表 5 优化前后资源消耗与时延
Table 5. Resource consumption and delay before and after optimization
resource 16 bit fixed-point number (utilization rate) after-optimization (utilization rate) VIVADO (utilization rate) BRAM_18K 79(28%) 109(38%) 95(68%) DSP 114(51%) 136(61%) 154(70%) FF 12968 (12%)21099 (19%)15372 (14%)LUT 21483 (40%)39204 (73%)12452 (23%)latency(cycles) 34792 27334 \ -
[1] Likar A, Vidmar T. A peak-search method based on spectrum convolution[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2003, 36(15): 1903-1909. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/36/15/323 [2] Li Xiaozhe, Zhang Qingxian, Tan Heyi, et al. Fast nuclide identification based on a sequential Bayesian method[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2021, 32: 143. doi: 10.1007/s41365-021-00982-z [3] Ling Yongsheng, Huang Tian, Yue Qi, et al. Improving the estimation accuracy of multi-nuclide source term estimation method for severe nuclear accidents using temporal convolutional network optimized by Bayesian optimization and hyperband[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2022, 242: 106787. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2021.106787 [4] 张江梅, 任俊松, 李培培, 等. 基于支持向量机的复杂核素能谱识别[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2016, 36(8):856-861 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2016.08.019Zhang Jiangmei, Ren Junsong, Li Peipei, et al. Complex radioactive nuclide identification method based on support vector machine[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2016, 36(8): 856-861 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2016.08.019 [5] El_Tokhy M S. Rapid and robust radioisotopes identification algorithms of X-Ray and gamma spectra[J]. Measurement, 2021, 168: 108456. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108456 [6] 问斯莹, 王百荣, 肖刚, 等. 基于序贯贝叶斯方法的核素识别算法研究[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2016, 36(2):179-183 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2016.02.015Wen Siying, Wang Bairong, Xiao Gang, et al. The study on nuclide identification algorithm based on sequential Bayesian analysis[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2016, 36(2): 179-183 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2016.02.015 [7] Qi Sheng, Zhao Wei, Chen Ye, et al. Comparison of machine learning approaches for radioisotope identification using NaI (TI) gamma-ray spectrum[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2022, 186: 110212. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2022.110212 [8] 胡浩行, 张江梅, 王坤朋, 等. 卷积神经网络在复杂核素识别中的应用[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2019, 38(10):154-156,160Hu Haohang, Zhang Jiangmei, Wang Kunpeng, et al. Application of convolutional neural networks in identification of complex nuclides[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2019, 38(10): 154-156,160 [9] 王瑶, 刘志明, 万亚平, 等. 基于长短时记忆神经网络的能谱核素识别方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32:106001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.200118Wang Yao, Liu Zhiming, Wan Yaping, et al. Energy spectrum nuclide recognition method based on long short-term memory neural network[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 106001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.200118 [10] Turner A N, Wheldon C, Wheldon T K, et al. Convolutional neural networks for challenges in automated nuclide identification[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21: 5238. doi: 10.3390/s21155238 [11] Zhao Wei, Shi Rui, Tuo Xianguo, et al. Novel radionuclides identification method based on Hilbert–Huang Transform and Convolutional Neural Network with gamma-ray pulse signal[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2023, 1051: 168232. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2023.168232 [12] 张军阳, 王慧丽, 郭阳, 等. 深度学习相关研究综述[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2018, 35(7):1921-1928,1936Zhang Junyang, Wang Huili, Guo Yang, et al. Review of deep learning[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2018, 35(7): 1921-1928,1936 [13] 陈辰, 柴志雷, 夏珺. 基于Zynq7000 FPGA异构平台的YOLOv2加速器设计与实现[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2019, 13(10):1677-1693Chen Chen, Chai Zhilei, Xia Jun. Design and implementation of YOLOv2 accelerator based on Zynq7000 FPGA heterogeneous platform[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2019, 13(10): 1677-1693 [14] He Dazhong, He Junhua, Liu Jun, et al. An FPGA-based LSTM acceleration engine for deep learning frameworks[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10: 681. doi: 10.3390/electronics10060681 [15] Pacini T, Rapuano E, Fanucci L. FPG-AI: a technology-independent framework for the automation of CNN deployment on FPGAs[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 32759-32775. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3263392 [16] 王博, 石睿, 刘敏俊, 等. 基于FPGA的卷积神经网络核素识别硬件加速方法研究[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2024, 44(2):334-343Wang Bo, Shi Rui, Liu Minjun, et al. Hardware acceleration method of convolutional neural network nuclide identification algorithm based on FPGA[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2024, 44(2): 334-343 [17] 陈亮. 核素识别算法及数字化能谱采集系统研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2009Chen Liang. Research on the nuclide identification algorithm and digital spectra acquisition system[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2009 [18] 王军, 冯孙铖, 程勇. 深度学习的轻量化神经网络结构研究综述[J]. 计算机工程, 2021, 47(8):1-13Wang Jun, Feng Suncheng, Cheng Yong. Survey of research on lightweight neural network structures for deep learning[J]. Computer Engineering, 2021, 47(8): 1-13 [19] Howard A G, Zhu Menglong, Chen Bo, et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1704.04861, 2017. [20] Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu Menglong, et al. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 4510-4520. -




 下载:
下载: