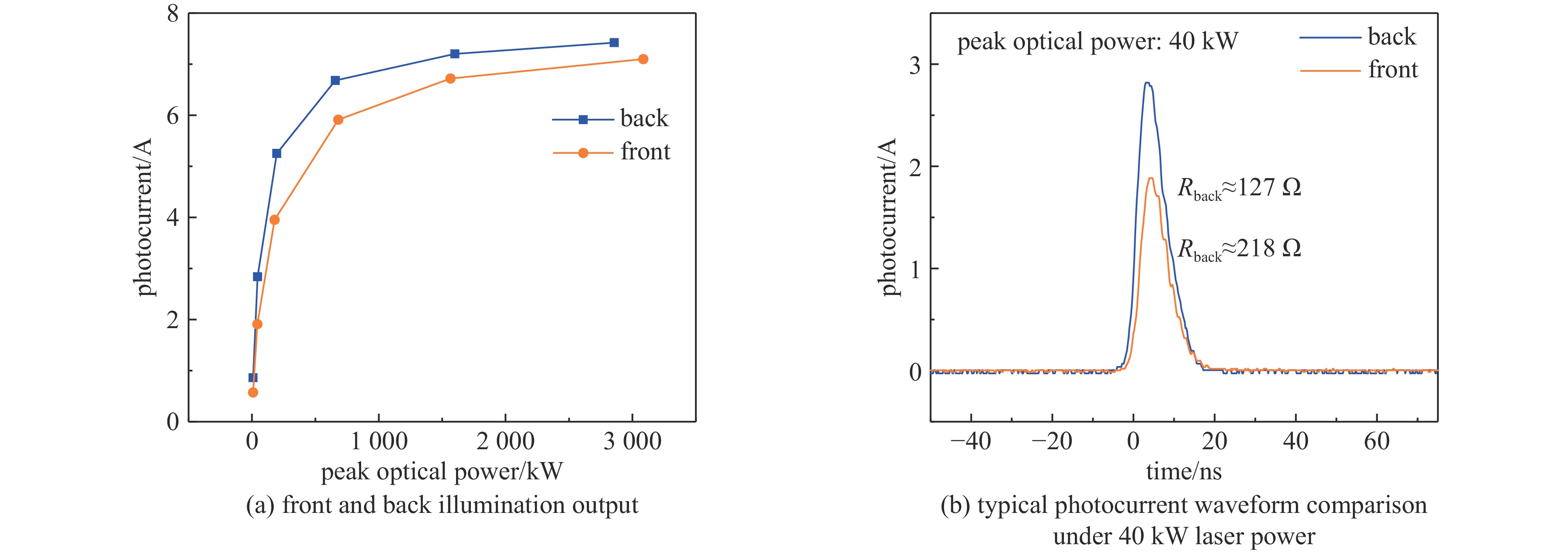
| [1] |
王朗宁. 碳化硅光导开关的初步研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2013Wang Langning. Preliminary study of silicon carbide photoconductive semiconductor switch[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2013
|
| [2] |
朱效庆, 荀涛, 王朗宁, 等. 一种推挽型光导微波放大器的电效率分析[J]. 现代应用物理, 2022, 13:010501 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2022.010501Zhu Xiaoqing, Xun Tao, Wang Langning, et al. Electrical efficiency analysis of a push-pull photoconductive microwave amplifier[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2022, 13: 010501 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2022.010501
|
| [3] |
Cai Ping, Jiang Lijuan, Xu Jiankai, et al. Design of a lateral photoconductive semiconductor switch with a low resistivity region on semi-insulating GaN to enhance breakdown characteristics[J]. Optics Communications, 2024, 555: 130232. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2023.130232
|
| [4] |
Kirawanich P, Yakura S J, Islam N E. Study of high-power wideband terahertz-pulse generation using integrated high-speed photoconductive semiconductor switches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2009, 37(1): 219-228. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2008.2006978
|
| [5] |
Mauch D, Sullivan W, Bullick A, et al. High power lateral silicon carbide photoconductive semiconductor switches and investigation of degradation mechanisms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2015, 43(6): 2021-2031. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2015.2424154
|
| [6] |
Yang Xianghong, Hu Long, Liu Jingliang, et al. Si3N4 passivation and side illumination of high-power photoconductive semiconductor switch based on free-standing SI-GaN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(3): 1128-1133. doi: 10.1109/TED.2023.3238362
|
| [7] |
Xun Tao, Niu Xinyue, Wang Langning, et al. Recent progress of parameter-adjustable high-power photonic microwave generation based on wide-bandgap photoconductive semiconductors[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2024, 22: 012501. doi: 10.3788/COL202422.012501
|
| [8] |
Niu Xinyue, Wu Qilin, Wang Bin, et al. Test of kW class photonic microwave generation using vanadium-compensated 6H-SiC PCSS and burst-mode-operation pulse laser[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2023, 15: 5500407.
|
| [9] |
Zeng Linglong, Niu Xinyue, Liu Fuyin, et al. Dual-stacked SiC vertical photoconductive switch for modulation bandwidth extension of frequency-agile power microwave[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2024, 45(6): 992-995. doi: 10.1109/LED.2024.3386680
|
| [10] |
Chu Xu, Xun Tao, Wang Langning, et al. Wide-range frequency-agile microwave generation up to 10 GHz based on vanadium-compensated 4H-SiC photoconductive semiconductor switch[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2022, 43(7): 1013-1016. doi: 10.1109/LED.2022.3179292
|
| [11] |
Zhu K, Doğan S, Moon Y T, et al. Effect of n+-GaN subcontact layer on 4H–SiC high-power photoconductive switch[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86: 261108. doi: 10.1063/1.1951056
|
| [12] |
Feng Zhuoyun, Luan Chongbiao, Xiao Longfei, et al. Performance of a novel rear-triggered 4H-SiC photoconductive semiconductor switch[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(2): 627-632. doi: 10.1109/TED.2022.3227889
|
| [13] |
Chu Xu, Meng Jin, Wang Haitao, et al. A backward-triggered 4H-SiC photoconductive semiconductor switch with planar electrode structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2024, 71(7): 4253-4258. doi: 10.1109/TED.2024.3405470
|
| [14] |
Hemmat Z, Faez R, Moreno E, et al. Transient and steady state study of a rear-illuminated 6H-SiC photoconductive semiconductor switch[J]. Optik, 2016, 127(11): 4615-4620. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.01.174
|
| [15] |
Rakheja S, Huang L, Hau-Riege S, et al. Performance modeling of silicon carbide photoconductive switches for high-power and high-frequency applications[J]. IEEE Journal of the Electron Devices Society, 2020, 8: 1118-1128. doi: 10.1109/JEDS.2020.3022031
|
| [16] |
伍麒霖. 基于线性光导器件的大功率微波产生技术研究[D]. 长沙. 国防科技大学, 2019Wu Qilin. Research on high power microwave generation technology based on linear photoconductive devices[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2019
|




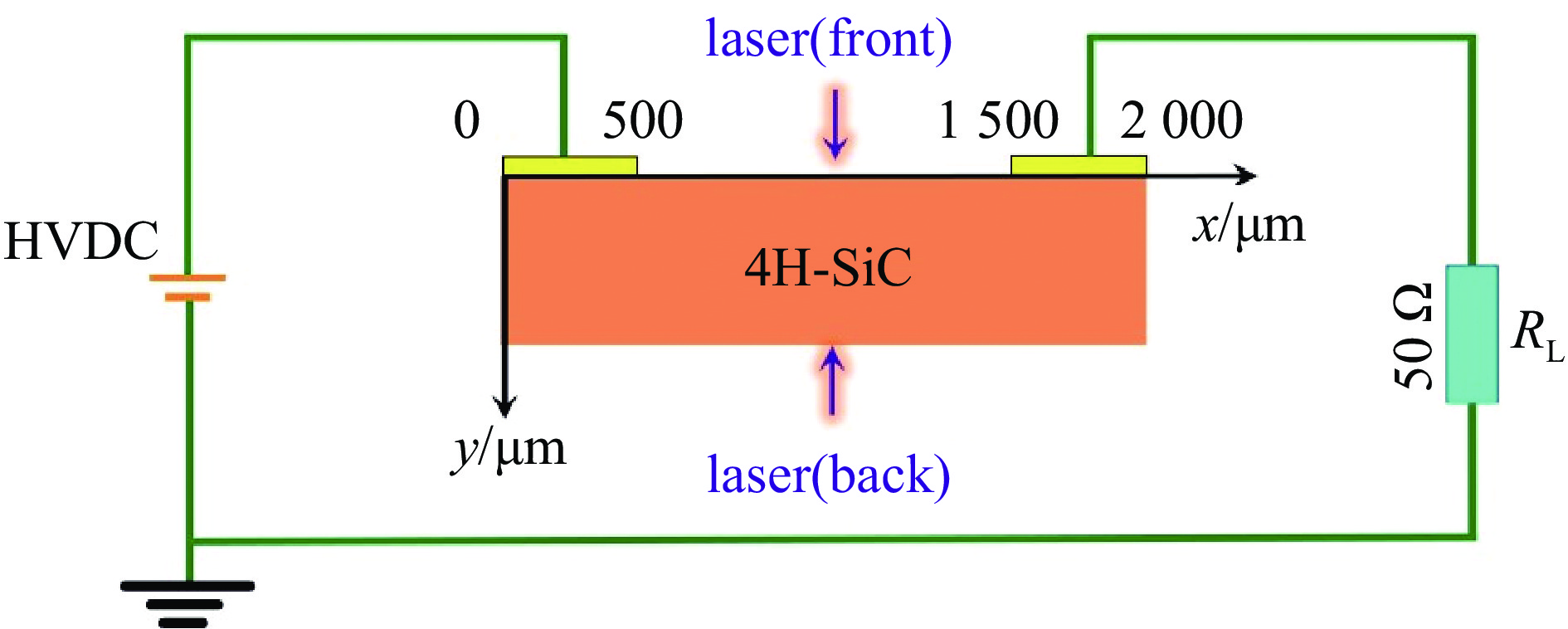
 下载:
下载: