Design of detector for measuring beam profile of high-intensity proton accelerator
-
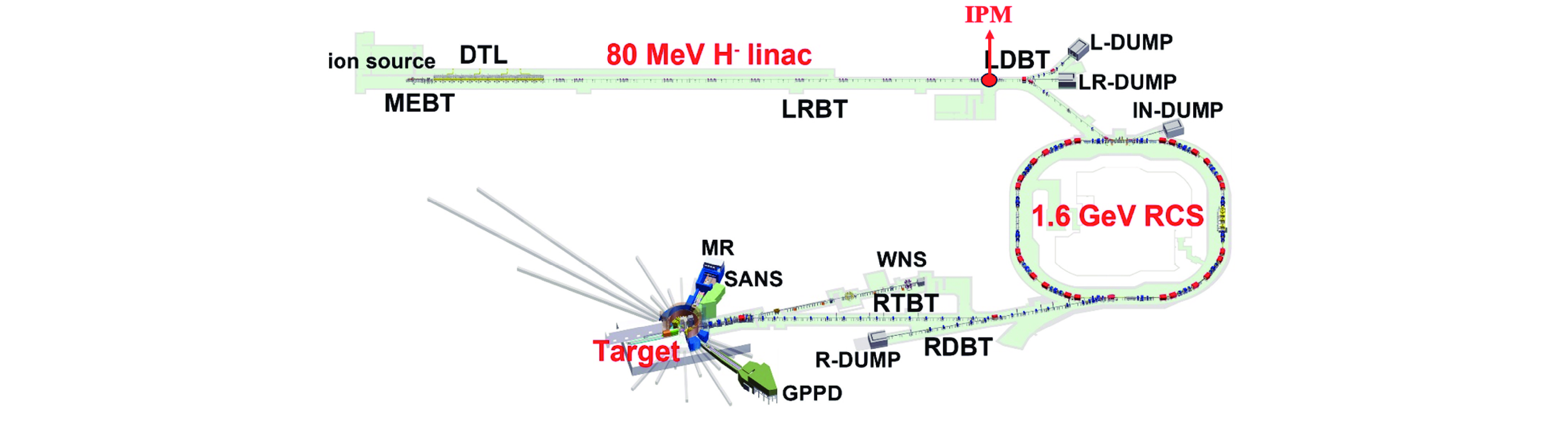
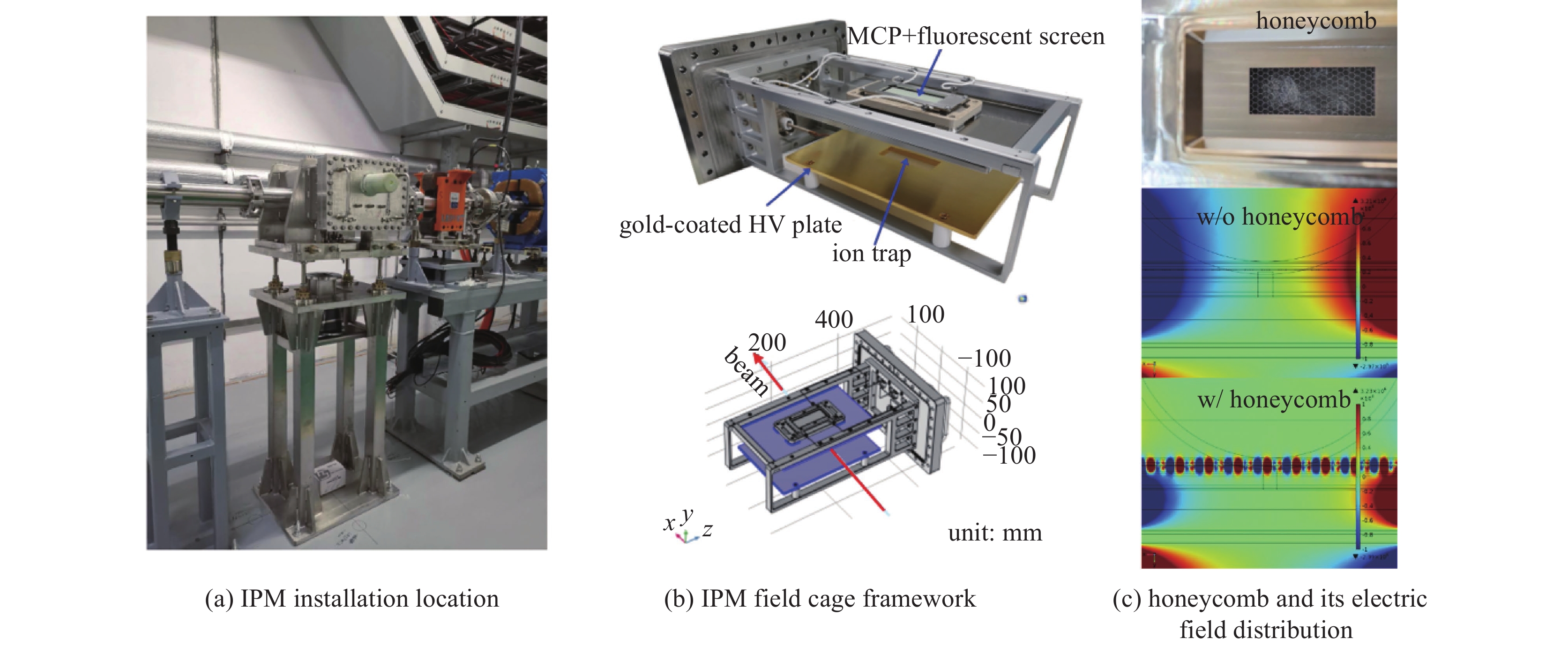
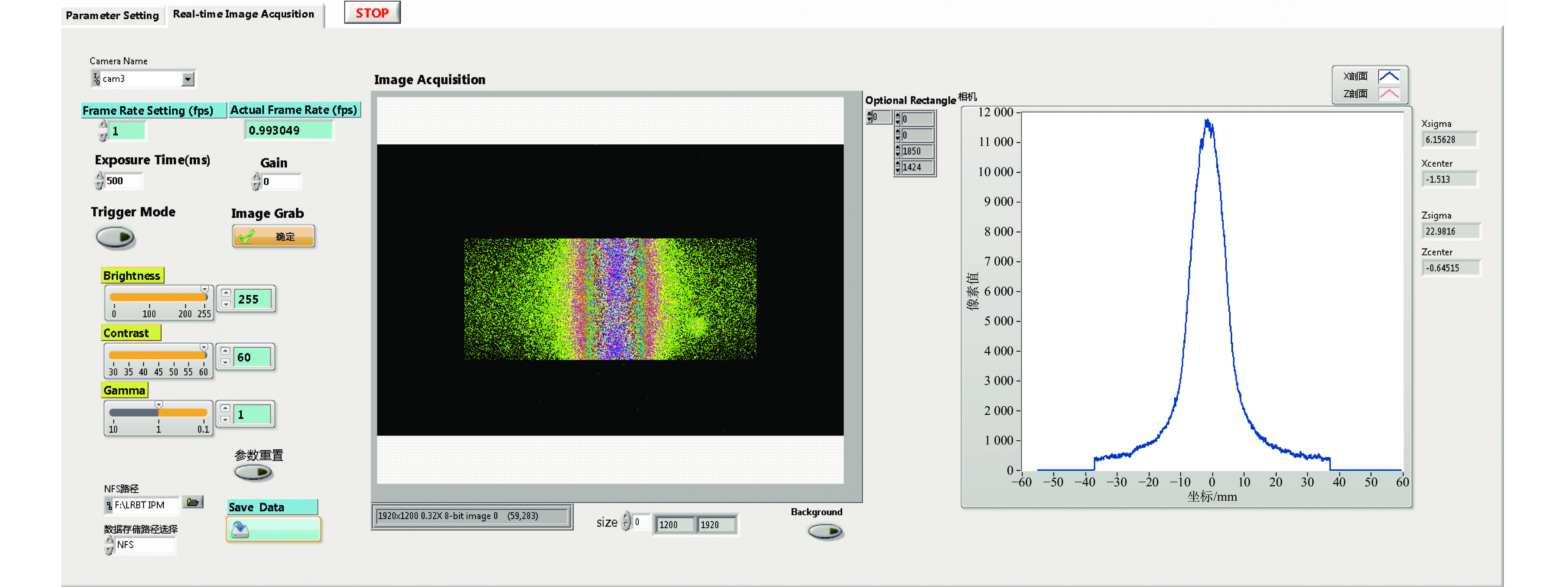
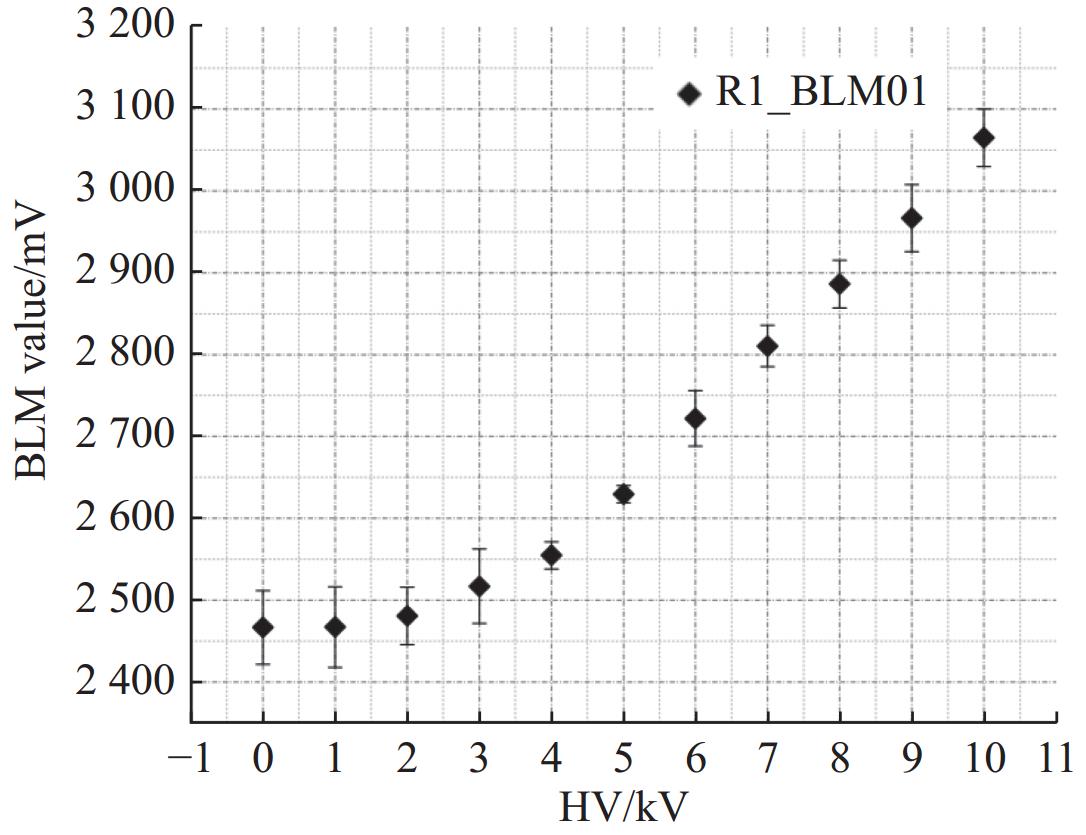
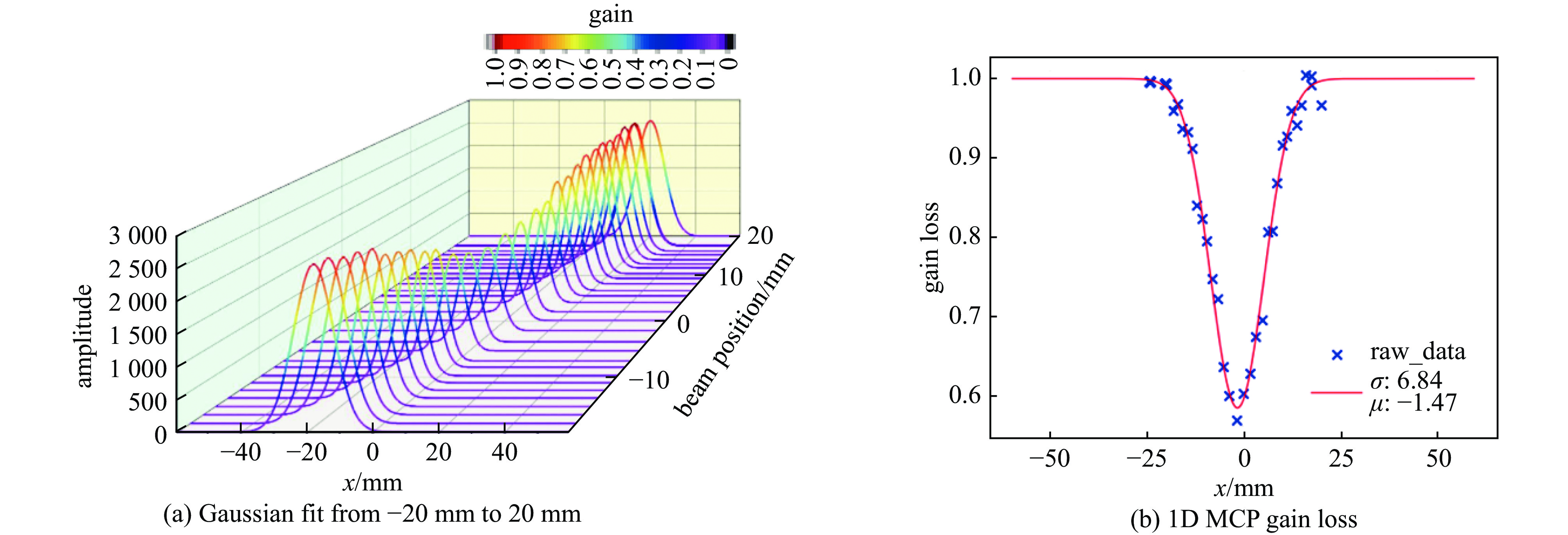
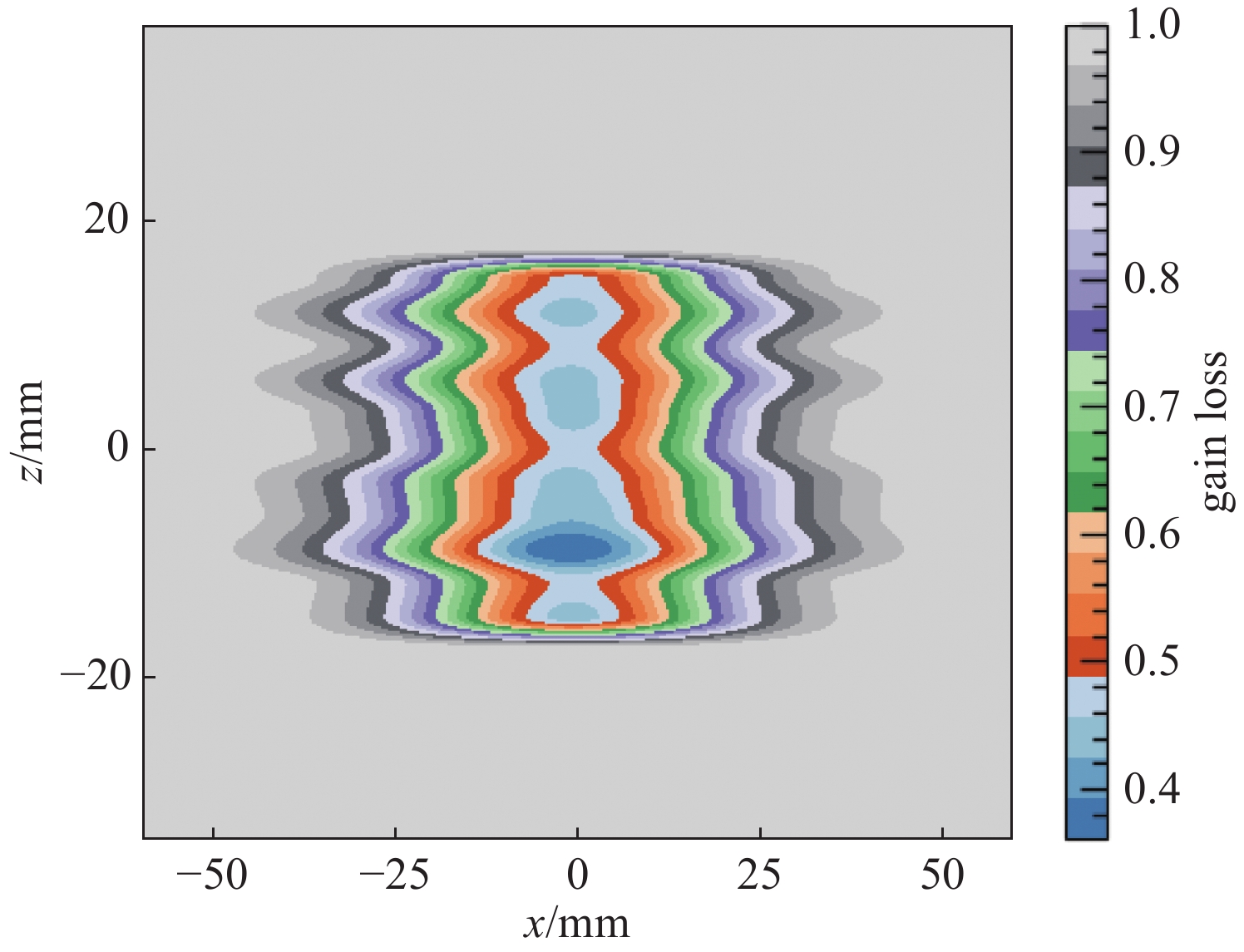
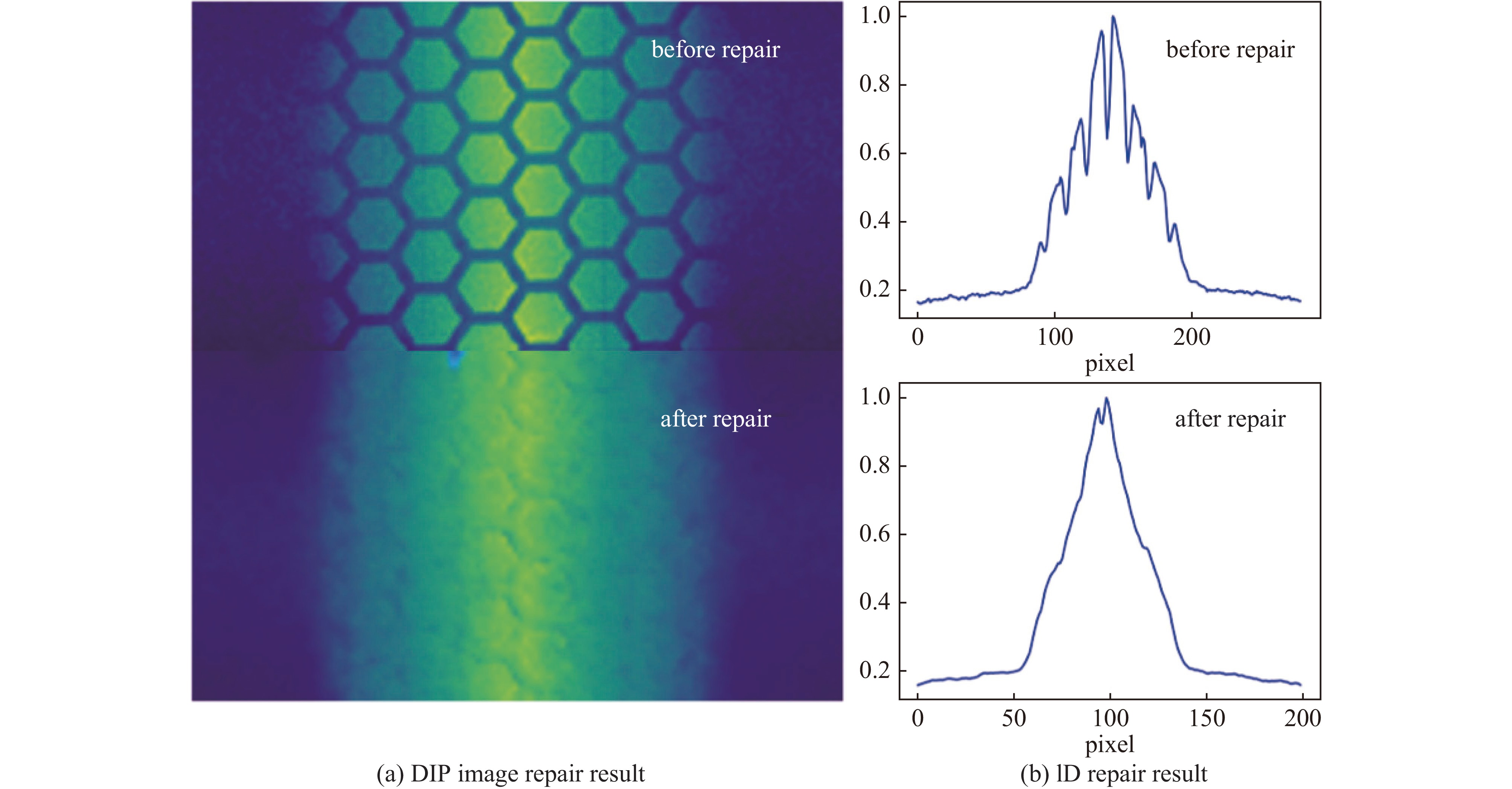
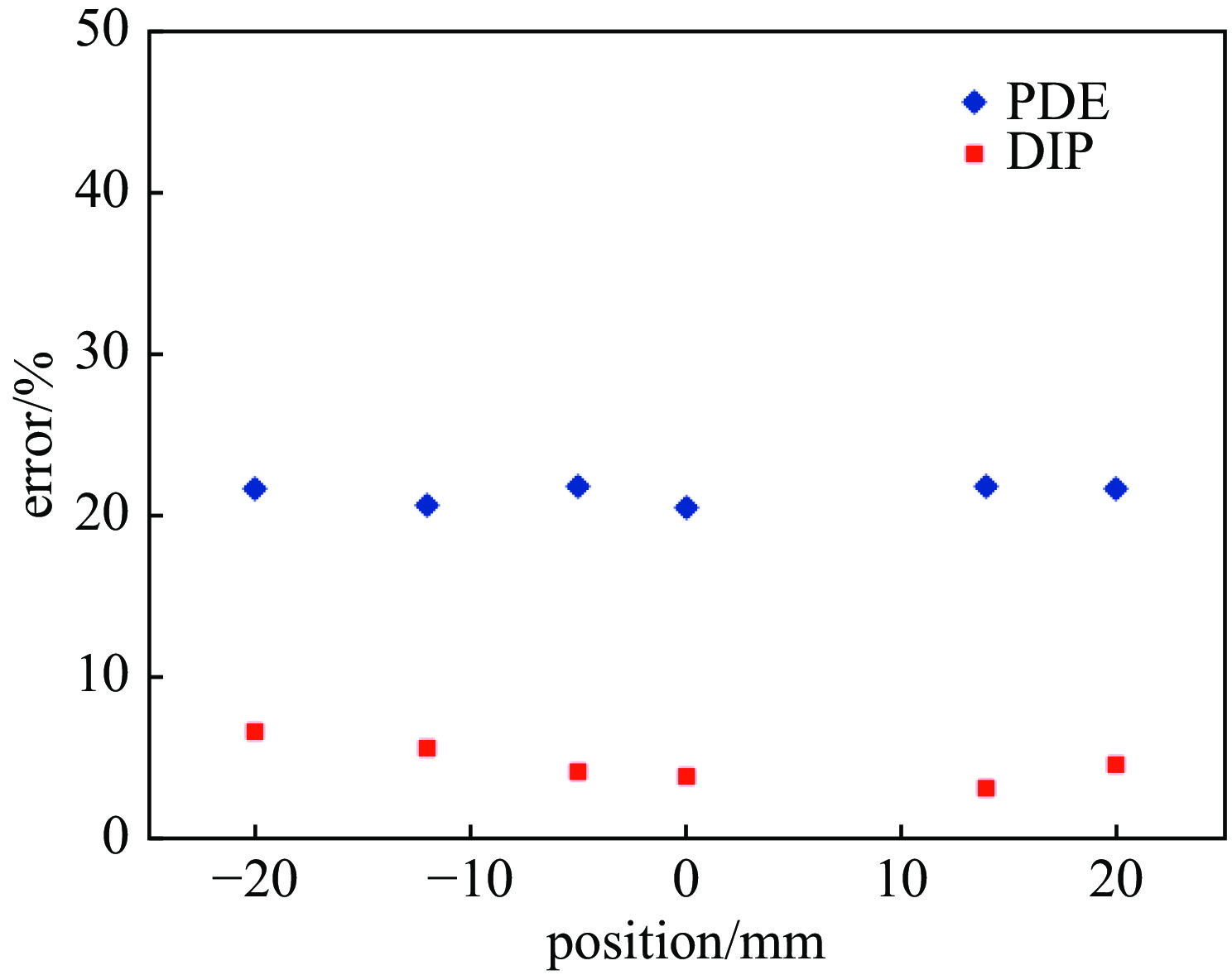
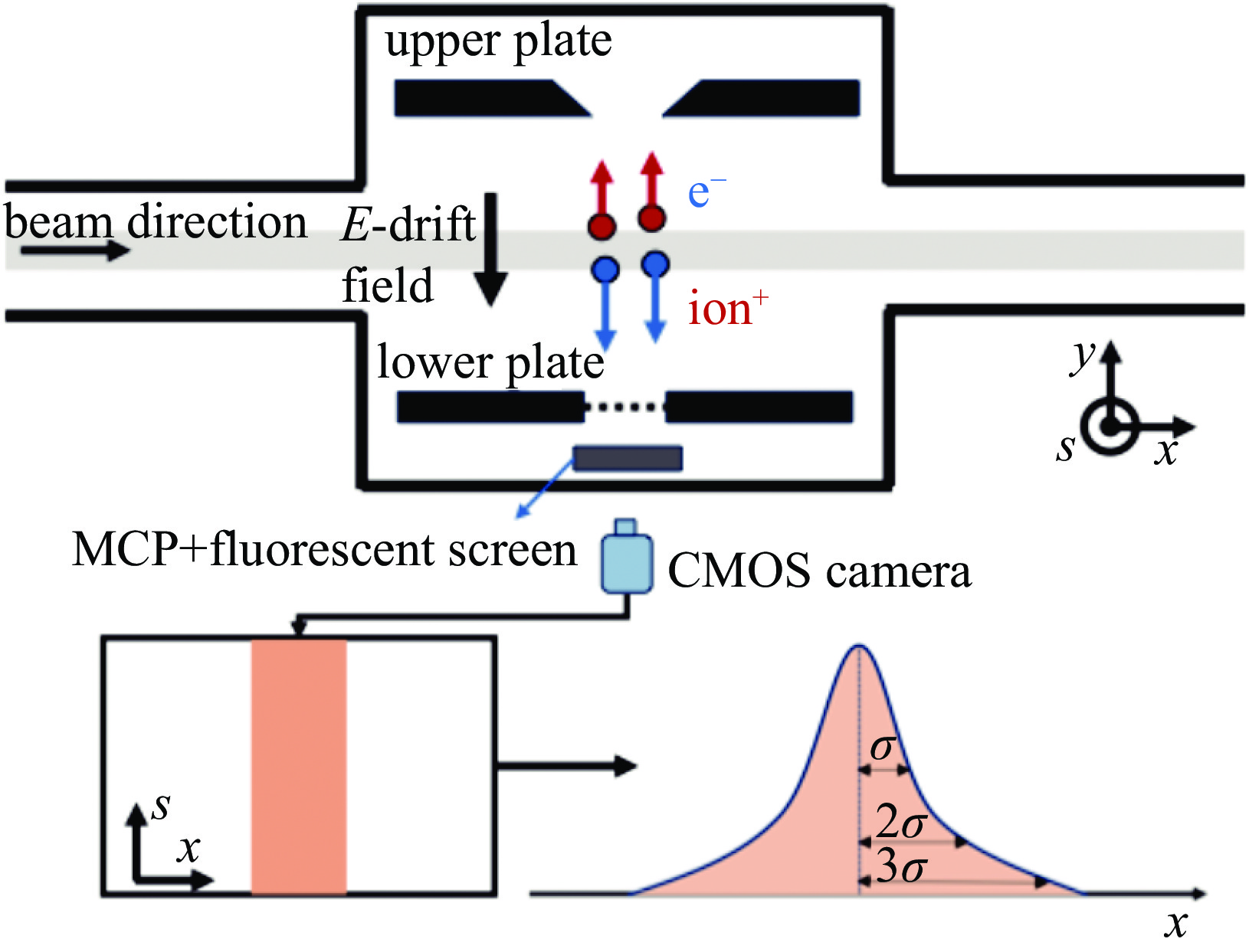
摘要: 束流的横向剖面分布是强流质子加速器的关键性能指标之一。中国散裂中子源直线加速器新安装一台残余气体电离型束流剖面探测器(IPM),用于关键位置束流横向剖面等参数的非拦截式实时测量。介绍了该剖面探测器的选型、结构设计思路及束流实验结果。探测器采用紧凑型结构,提供了一种较小空间占用下较高分辨率的设计思路。紧凑型IPM在低压板通孔处采用匀场栅网的结构形式改善电场均匀度,减小横向电场分量及剖面测量畸变。探测器带束实验测试了其在轨道和剖面等参数测量任务中引导电场、MCP、相机等关键影响因素的性能,并与探测器位置附近的BPM所测得的束流轨道进行比对和校准。该IPM的横向剖面测量值与理论计算值对比最终误差小于8.3%,满足束流剖面的测量需求。Abstract: Beam profile is one of the key performance indicators for high-intensity proton accelerators. A new residual gas ionization profile monitor has been installed at the Linac of the China Spallation Neutron Source for non-destructive, real-time measurement of parameters such as the transverse beam profile at critical locations. This paper presents the selection, structural design rationale, and beam test results of this profile monitor. The detector adopts a compact structure, offering a high-resolution design within a limited space. The compact design eliminates the equipotential strips that uniformly act on the electric field and adds a field grid at the lower plate apertures to improve the uniformity of the electric field and reduce the electric field components. Beam tests evaluated the performance of the new detector in measuring orbit and profile parameters, with calibration performed in comparison to the BPM near the detector’s location. The error between the transverse profile measurement and theoretical calculation was less than 8.3%, meeting the beam measurement requirements.
-
Key words:
- high-intensity proton accelerator /
- transverse profile /
- residual gas /
- beam profile /
- detector /
- non-destructive
-
表 1 CSNS直线加速器IPM处束流参数
Table 1. Beam parameters at the IPM of CSNS linac
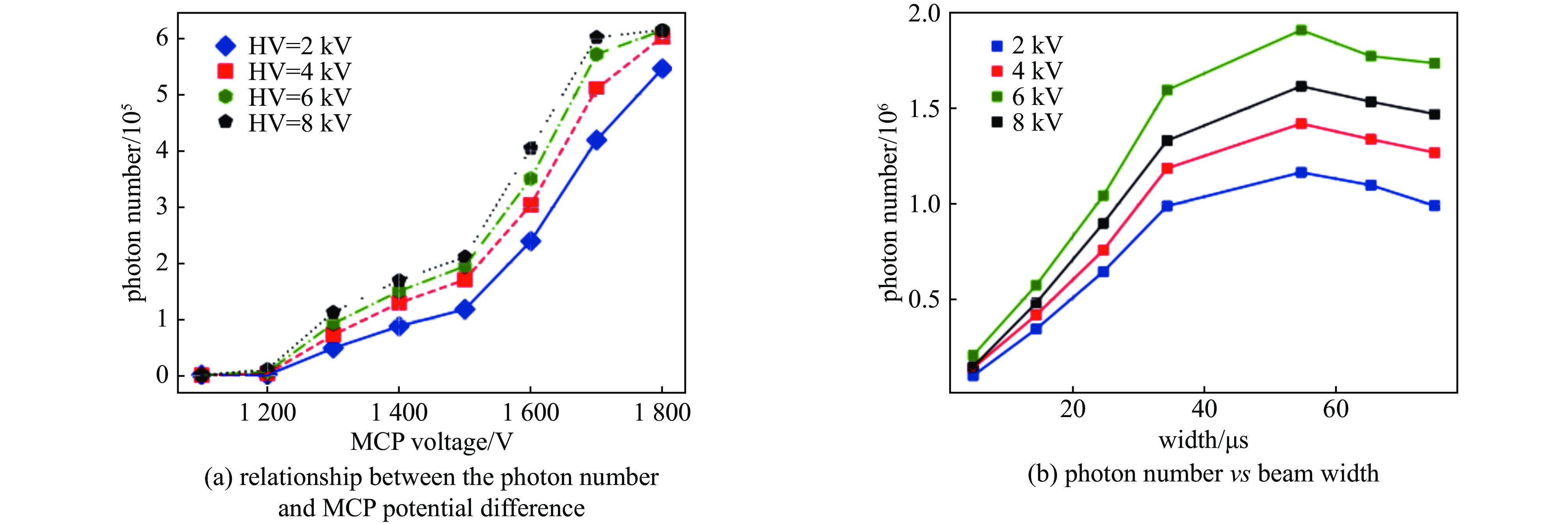
energy/MeV repetition rate/Hz vacuum/Pa gas type beam width/µs N 80 25 10−6~10−7 H2, He, etc. 20~415 1.56×1013 -
[1] Wang Sheng, Fang Shouxian, Fu Shinian, et al. Introduction to the overall physics design of CSNS accelerators[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2009, 33(s2): 1-3. [2] 陈和生, 马力, 陈元柏, 等. 散裂中子源初步设计报告[R]. 北京: 中国科学院, 2016Chen Hesheng, Ma Li, Chen Yuanbai, et al. Preliminary design report for the China Spallation Neutron Source[R]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016 [3] 孙纪磊, 阮玉芳, 肖帅, 等. 强流质子加速器束流剖面分布及束晕测量系统设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(1):190-194 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112301.0190Sun Jilei, Ruan Yufang, Xiao Shuai, et al. Design of beam profile and halo measurement system for high-intensity RFQ accelerator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(1): 190-194 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112301.0190 [4] Hornstra Jr F, DeLuca W H. Nondestructive beam profile detection systems for the zero gradient synchrotron[R]. Du Page County: Argonne National Lab, 1968: 374-377. [5] DeLuca W H. Beam detection using residual gas ionization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear science, 1969, 16(3): 813-822. [6] Hardek T, Kells W, Lai H. Very low intensity storage-ring profile monitor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1981, 28(3): 2219-2221. [7] Weisberg H, Gill E, Ingrassia P, et al. An ionization profile monitor for the Brookhaven AGS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1983, 30(4): 2179-2181. [8] Sandberg H, Bertsche W, Bodart D, et al. Measuring the beam profile by counting ionization electrons[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Beam Instrumentation Conference. 2019: 257-260. [9] Bethe H. Zur Theorie des Durchgangs schneller Korpuskularstrahlen durch Materie[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1930, 397(3): 325-400. [10] 王生, 傅世年, 屈化民, 等. 中国散裂中子源强流质子加速器设计、研制及调试运行[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2022, 56(9):1747-1759 doi: 10.7538/yzk.2022.youxian.0591Wang Sheng, Fu Shinian, Qu Huamin, et al. Design, development and commissioning for high-intensity proton accelerator of China Spallation Neutron Source[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2022, 56(9): 1747-1759 doi: 10.7538/yzk.2022.youxian.0591 [11] Yang Tao, Tian Jianmin, Zeng Lei, et al. Experimental studies and Monte Carlo simulations for beam loss monitors[J]. Physical Review-Accelerators and Beams, 2021, 24: 032804. [12] Lempitsky V, Vedaldi A, Ulyanov D. Deep image prior[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 9446-9454. -




 下载:
下载: