Research progress of microwave kinetic inductance detector applied to terahertz astronomical detection
-
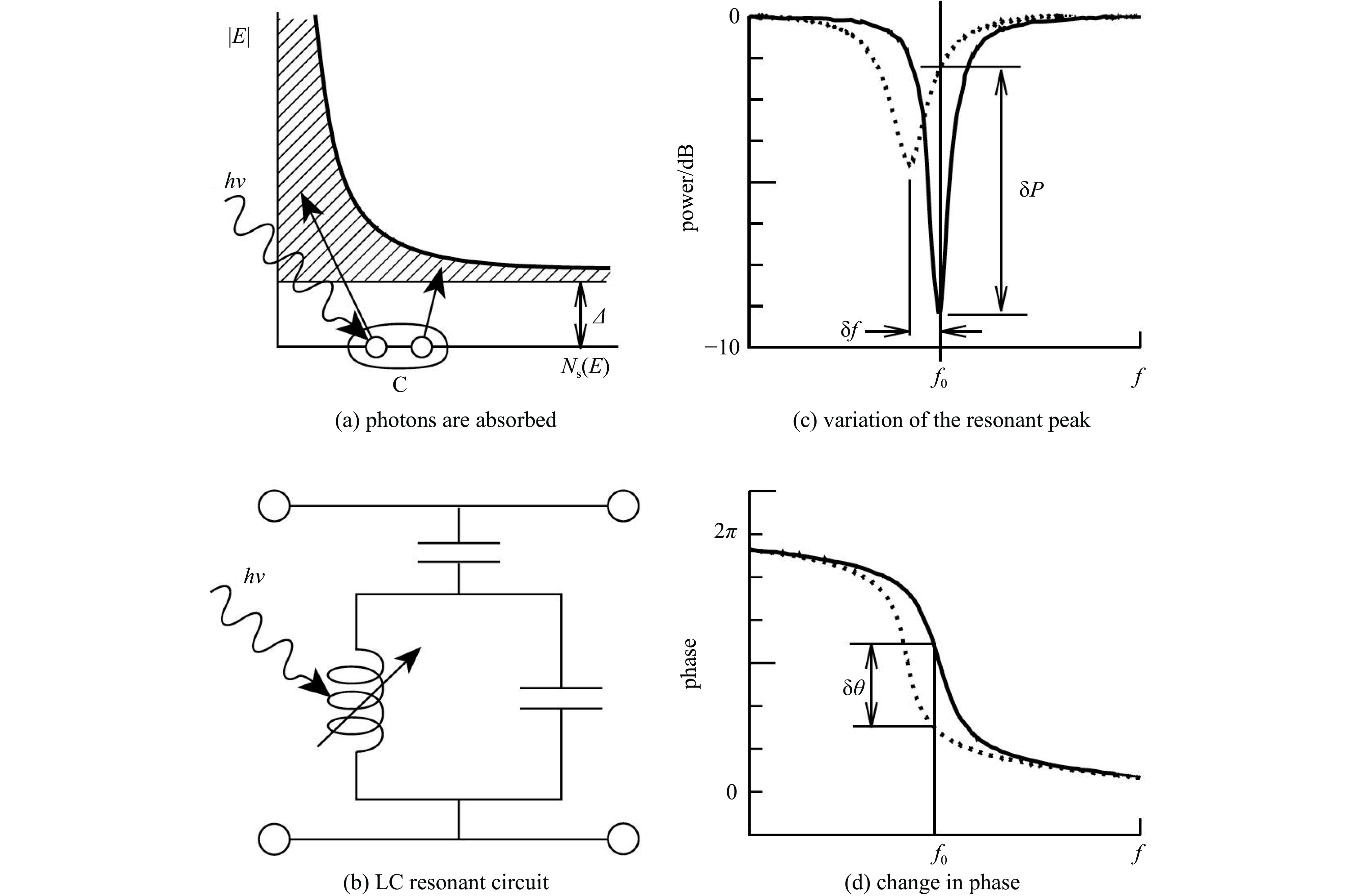
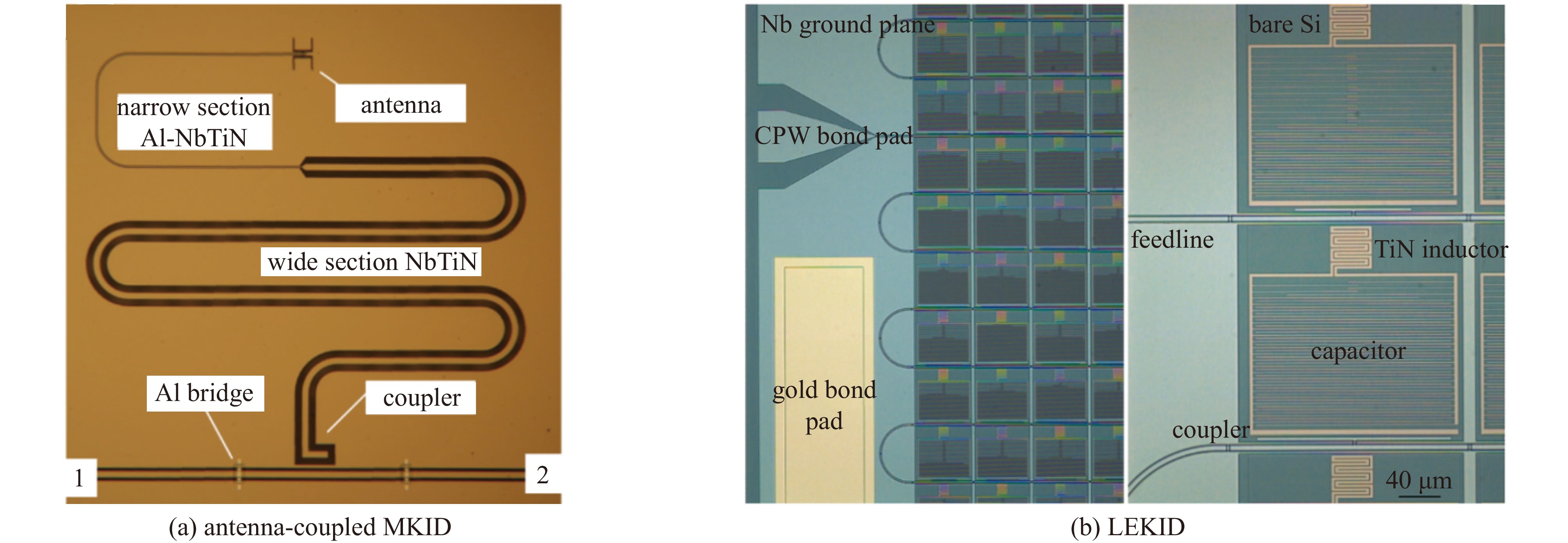
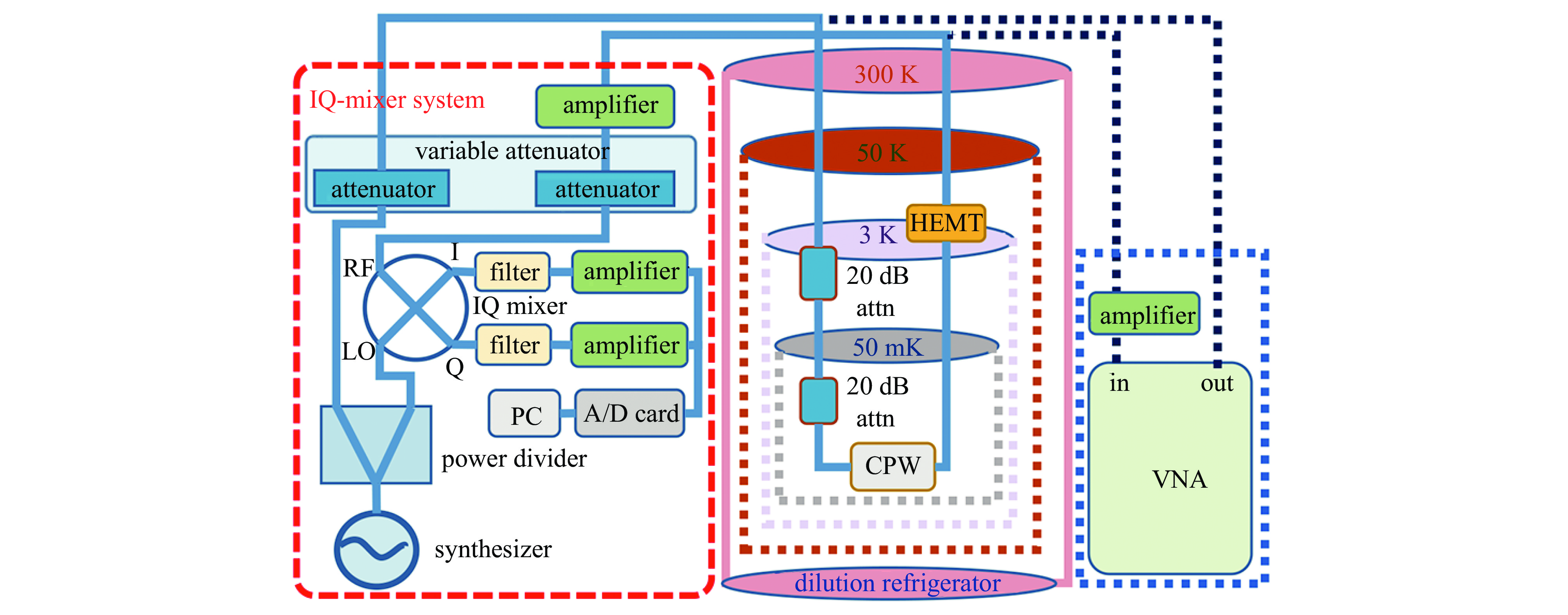
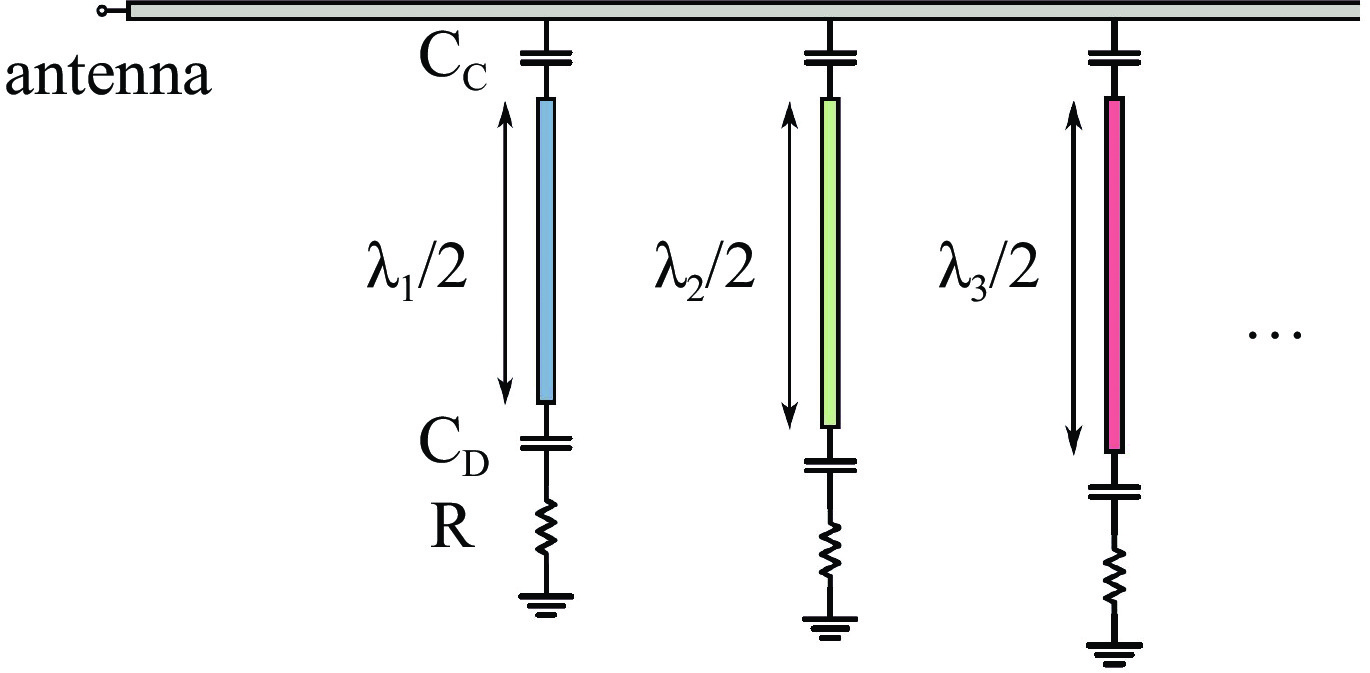
摘要: 太赫兹波是介于微波和远红外区域之间的毫米/亚毫米波,波长从3 mm到30 μm。自宇宙开始以来发射的所有可探测光子中,98%落在太赫兹和远红外区域,其中许多光子来自宇宙微波背景辐射,其他重要的发射来自大量的受激分子,这些分子在太赫兹范围内具有明亮的光谱发射特征。基于太赫兹的天文观测技术在天体物理和宇宙学的研究中扮演着愈加重要的作用,对星际原子、分子和尘埃的太赫兹观测可以洞察宇宙星际介质的内部条件,并提供对恒星、行星、星系和宇宙本身起源和演化的独特观察窗口。近年来,许多大型天文望远镜不断部署基于微波动态电感探测器(MKID)的太赫兹探测器,MKID成为了太赫兹天文探测领域重要的技术手段。本文主要阐述MKID的基础原理和应用在太赫兹探测领域的研究进展,通过MKID在多个太赫兹天文探测项目的应用总结,厘清MKID 探测器的工作原理和架构,梳理MKID取得的突破,并对其发展进行展望。Abstract: Terahertz waves, spanning the millimeter and submillimeter wavelength ranges between the microwave and far-infrared regions (approximately 3 mm to 30 μm), represent a critical spectral range in astrophysical and cosmological research. Of the photons detectable since the beginning of the universe, approximately 98% fall within the terahertz and far-infrared bands. A significant proportion of these photons originate from the cosmic microwave background radiation, while others arise from excited molecules that exhibit bright spectral emissions in the terahertz range. As a result, terahertz-based astronomical observation techniques are becoming increasingly essential for investigating the universe’s fundamental properties. Through the observation of interstellar atoms, molecules, and dust, terahertz astronomy provides valuable insights into the internal conditions of the interstellar medium and offers a unique observational window into the formation and evolution of stars, planets, galaxies, and the universe itself. In recent years, many large astronomical telescopes have begun incorporating terahertz detectors based on microwave kinetic inductance detector (MKID), positioning MKID as a pivotal technology in the field of terahertz astronomical detection. This paper outlines the fundamental principles of MKID, reviews recent advancements in their application to terahertz detection, and discusses future developments in this promising area of research.
-
Key words:
- terahertz /
- inductance detectors /
- astronomical detection /
- superconducting resonator
-
表 1 基于MKID的片上光谱仪
Table 1. On-chip spectrometers based on MKID
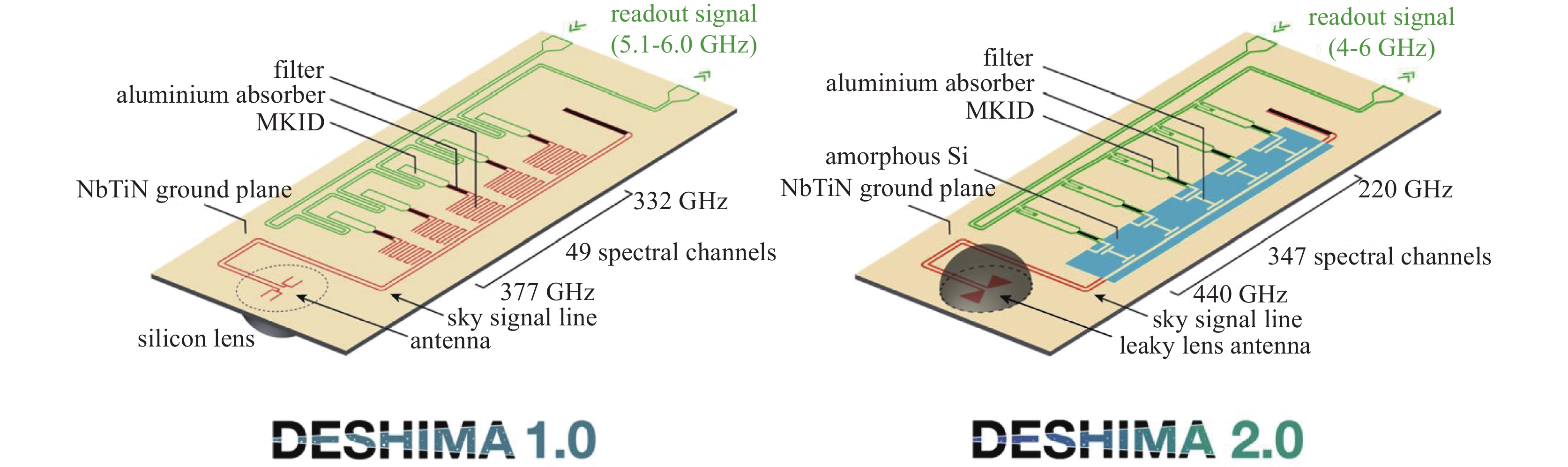
spectrometers scale (channels/pixels) frequency/GHz wavelength/mm materials installation SuperSpec 500 195-310 1.54-0.97 Nb、TiN LMT DESHIMA 49 332-377 0.903-0.795 NbTiN、Al ASTE DESHIMA2.0 347 220-440 1.36-0.682 NbTiN、A1 ASTE CAMELS 500 103-114.7 2.9-2.6 NbN、Ta Greenland
TelescopeMicro-Spec 355 540-420 0.555-0.714 Nb、Al EXCLAIM WSPEC 54 135-175 2.2-1.7 A1 − 190-250 1.6-1.2 表 2 基于MKID的偏振计
Table 2. Polarimeters based on MKID
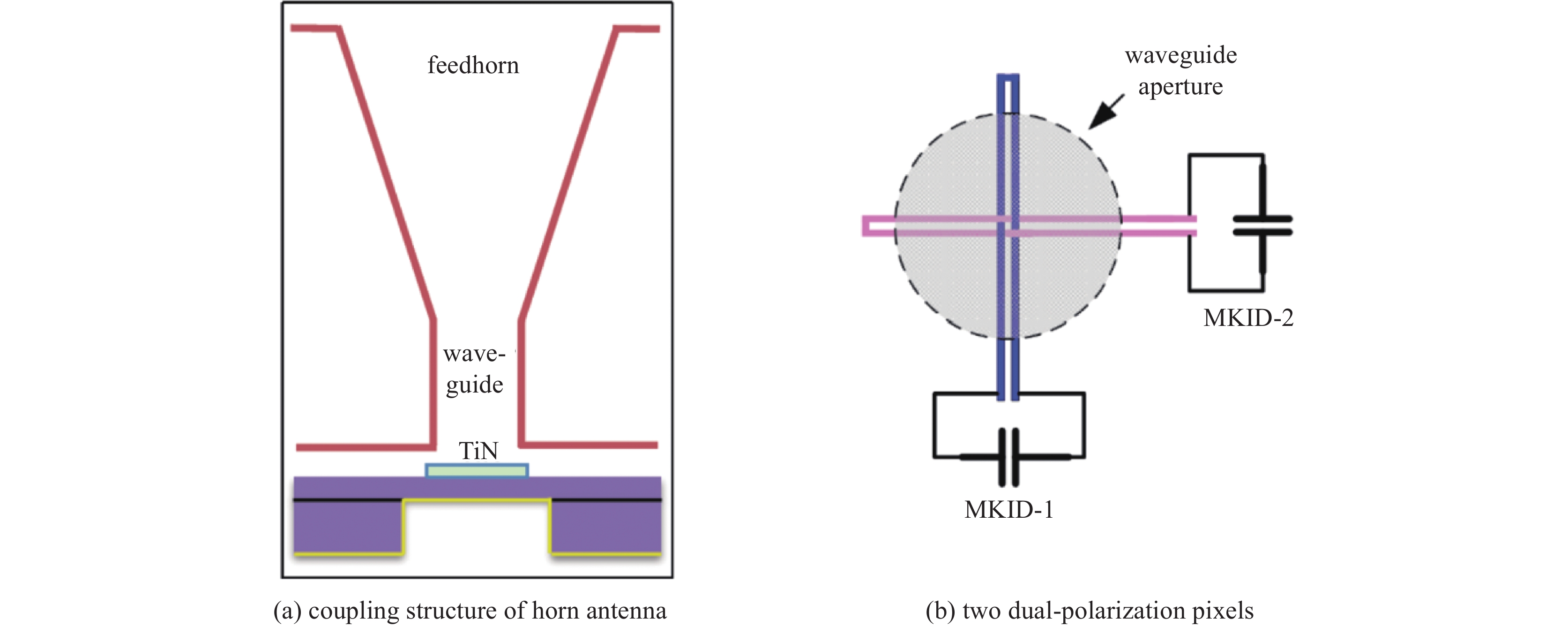
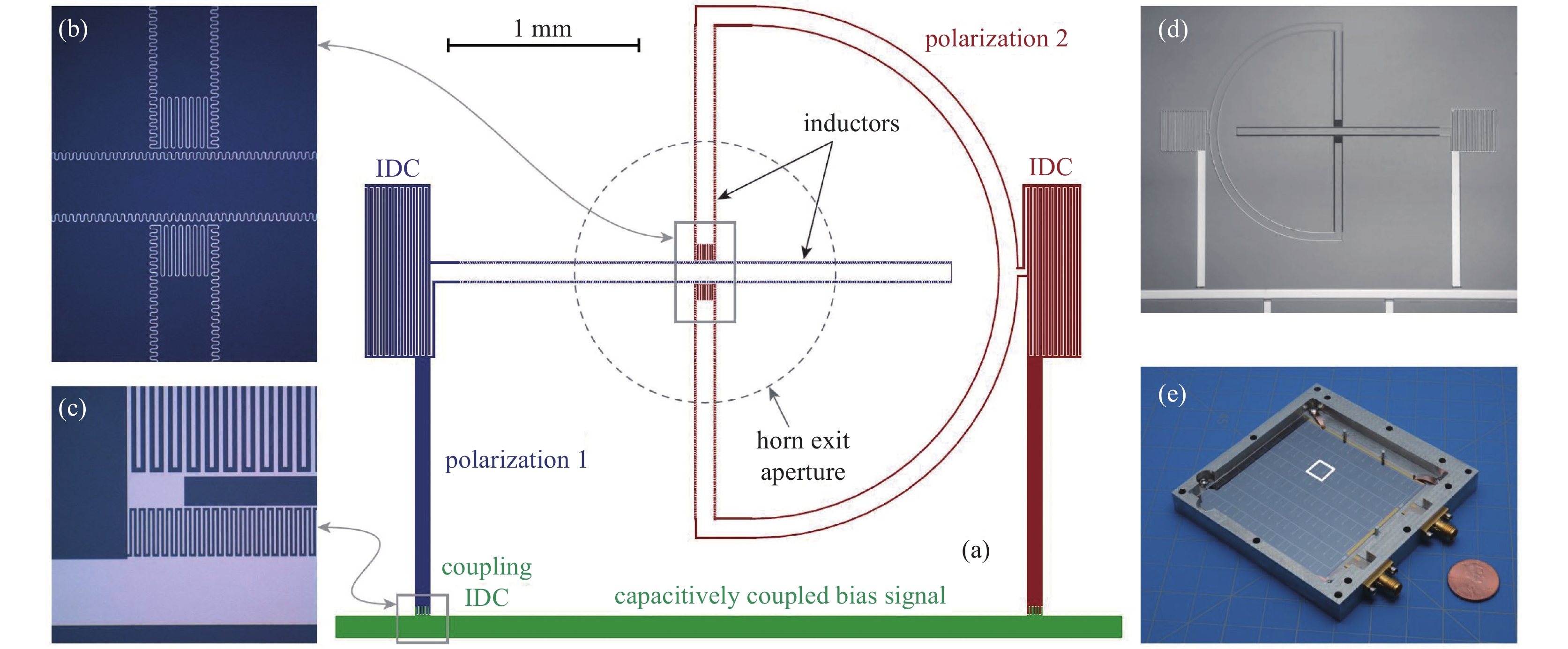
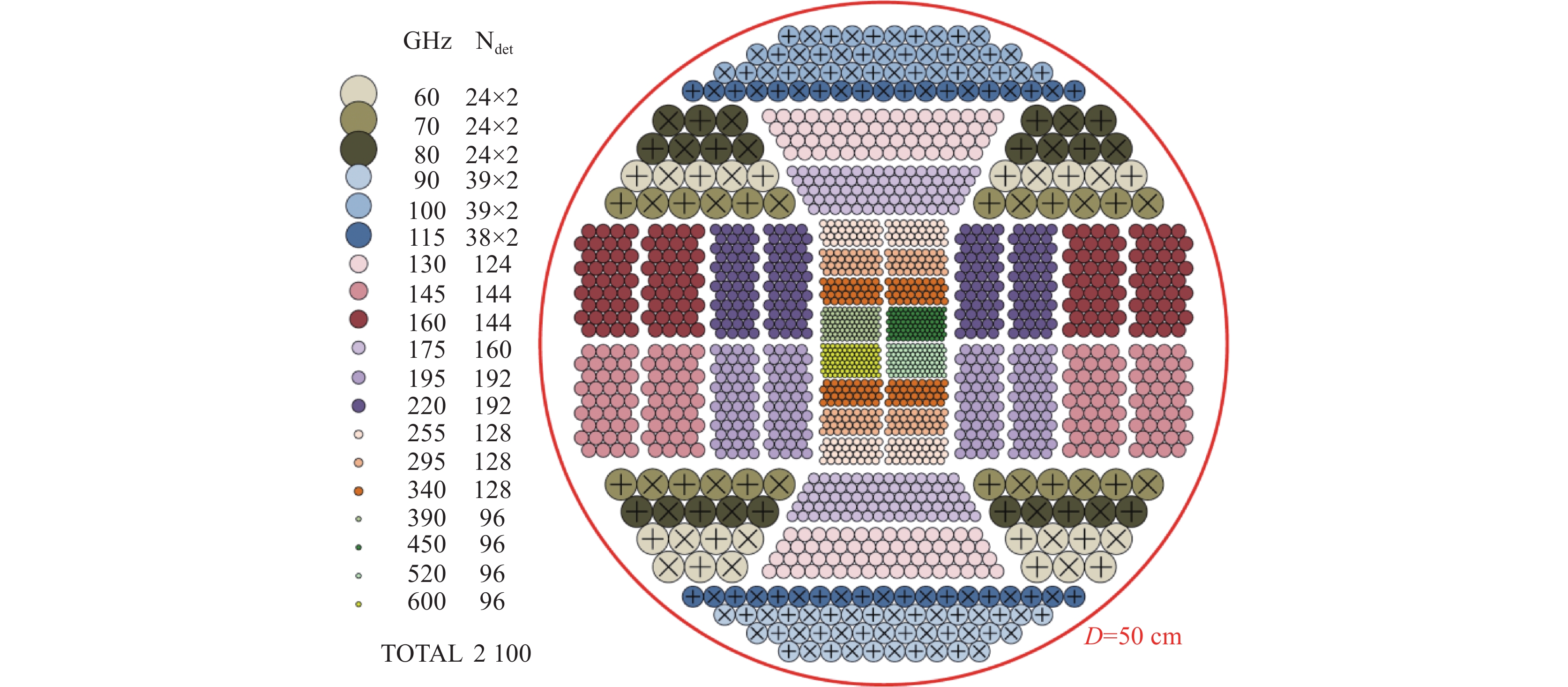
polarimeters pixels frequency/GHz wavelength/mm materials installation(loading mode) BLAST-TNG 1836/938/544 1200 、857、6000.25、0.35、0.5 TiN BLAST-TNG MUSCAT 1600 273 1.1 A1 LMT ToITEC 1900/950/475 270、214、150 1.1、1.4、2 TiN/Ti/TiN LMT CORE 2100 60-600 5-0.5 NbTiN, A1 LiteBIRD SKIP 2317 150、260-350 2、1.2-0.9 A1 Balloon-borne B-SIDE 980- 1800 400-700 0.75-0.43 Ti、Al Balloon-borne GroundBIRD 161(138/23) 145、220 2.1、1.4 Nb、A1 GroundBIRD BICEP-Array > 30000 30/40、95、150 、220/270 10/6.5、3.16、2 、1.36/1.1 Nb、A1 South Pole Telescope 表 3 基于MKID的天文相机
Table 3. Astronomical cameras based on MKID
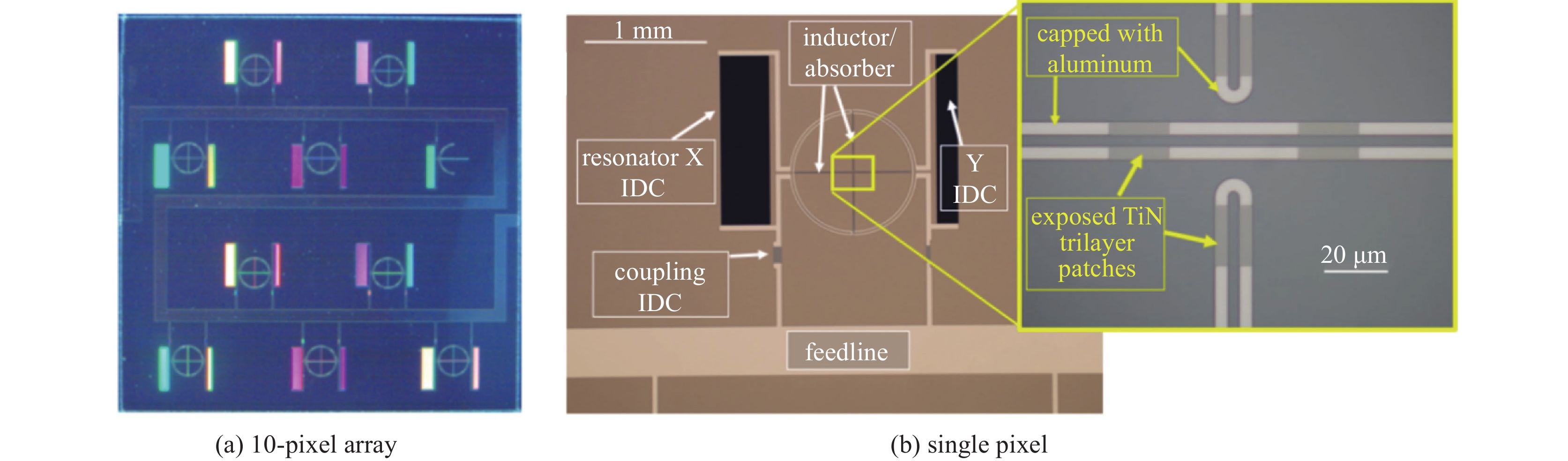
cameras pixels frequency/GHz wavelength/mm materials installation DemoCam 32 240、350 1.25、0.86 A1、Nb CSO MUSIC 2304 150、230、290、350 2、1.3、1.03、0.86 TiN CSO NIKA(2009) 72 150 2 A1 IRAM NIKA(2010) 144 150 2 NbTiN、Al IRAM 256 220 1.36 NIKA2 2280 260 1.15 A1 IRAM 616 150 2 MUSCAT 1600 270 1.1 A1 LMT A-MKID ~ 1000 350 0.85 NbTiN、Al APEX ~ 5000 850 0.35 MUSICAM ~100 150、225、 288、350 2、1.33、1.04、0.86 A1 ESMT KISS 316 80-300 3.75-1 Ti、Al QUIJOTE CONCERTO 2152 130-310 2.3-0.97 Al APEX Prime-Cam 60000 220、280、350、410 1.36、1.07、0.86、0.73 TiN、Al CCAT-prim 21000 850 0.353 31000 250、360 1.2、0.833 MISTRAL 415 77-103 3.896-2.913 Ti、Al SRT -
[1] Hey J S. The evolution of radio astronomy[M]. New York: Science History Publications, 1973. [2] Fleming J W. High-resolution submillimeter-wave Fourier-transform spectrometry of gases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1974, 22(12): 1023-1025. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.1974.1128419 [3] Huang Yi, Shen Yaochun, Wang Jiayou. From terahertz imaging to terahertz wireless communications[J]. Engineering, 2023, 22: 106-124. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2022.06.023 [4] Sizov F. Terahertz radiation detectors: the state-of-the-art[J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2018, 33: 123001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/aae473 [5] Rogalski A, Sizov F. Terahertz detectors and focal plane arrays[J]. Opto-Electronics Review, 2011, 19(3): 346-404. [6] 潘晓凯, 姜梦杰, 王东, 等. 红外-太赫兹光电探测器应用及前沿变革趋势[J]. 量子电子学报, 2023, 40(2):217-237 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2023.02.005Pan Xiaokai, Jiang Mengjie, Wang Dong, et al. Application and frontier trend of infrared-terahertz photoelectric detector[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2023, 40(2): 217-237 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2023.02.005 [7] Widicus Weaver S L. Millimeterwave and submillimeterwave laboratory spectroscopy in support of observational astronomy[J]. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2019, 57(1): 79-112. doi: 10.1146/annurev-astro-091918-104438 [8] Horowitz G. Organic field-effect transistors[J]. Advanced Materials, 1998, 10(5): 365-377. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4095(199803)10:5<365::AID-ADMA365>3.0.CO;2-U [9] Jansen C, Wietzke S, Peters O, et al. Terahertz imaging: applications and perspectives[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(19): E48-E57. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.000E48 [10] Jepsen P U, Cooke D G, Koch M. Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging–modern techniques and applications[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2011, 5(1): 124-166. [11] Stacey G J. THz low resolution spectroscopy for astronomy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2011, 1(1): 241-255. doi: 10.1109/TTHZ.2011.2159649 [12] 贺青, 李栋, 谷立, 等. 基于里德堡原子的无线电技术研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:079001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240061He Qing, Li Dong, Gu Li, et al. Research progress in radio technology based on Rydberg atoms[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 079001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240061 [13] 贺青, 李栋, 罗思源, 等. 超宽带里德堡原子天线技术研究进展[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 43(2):1-19He Qing, Li Dong, Luo Siyuan, et a1. Research progress in ultra-wideband Rydberg atomic antenna technology[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2025, 43(2): 1-19 [14] Walker C K. Terahertz astronomy[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2015. [15] 任远, 缪巍, 史生才. 超导探测器与太赫兹天文应用[J]. 物理, 2023, 52(4):255-265 doi: 10.7693/wl20230405Ren Yuan, Miao Wei, Shi Shengcai. Superconducting detectors and their applications in terahertz astronomy[J]. Physics, 2023, 52(4): 255-265 doi: 10.7693/wl20230405 [16] Hughes D H, Serjeant S, Dunlop J, et al. High-redshift star formation in the Hubble Deep Field revealed by a submillimetre-wavelength survey[J]. Nature, 1998, 394(6690): 241-247. doi: 10.1038/28328 [17] Brogan C L, Pérez L M, Hunter T R, et al. The 2014 ALMA long baseline campaign: first results from high angular resolution observations toward the HL Tau region[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2015, 808: L3. doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/808/1/L3 [18] Hashimoto T, Laporte N, Mawatari K, et al. The onset of star formation 250 million years after the Big Bang[J]. Nature, 2018, 557(7705): 392-395. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0117-z [19] Akiyama K, Alberdi A, Alef W, et al. First M87 event horizon telescope results. IV. Imaging the central supermassive black hole[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2019, 875: L4. doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ab0e85 [20] Day P K, Leduc H G, Mazin B A, et al. A broadband superconducting detector suitable for use in large arrays[J]. Nature, 2003, 425(6960): 817-821. doi: 10.1038/nature02037 [21] Brien T L R, Ade P A R, Barry P S, et al. MUSCAT: the Mexico-UK sub-millimetre camera for AsTronomy[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy IX. 2018: 173-181. [22] Austermann J E, Beall J A, Bryan S A, et al. Millimeter-wave polarimeters using kinetic inductance detectors for TolTEC and beyond[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2018, 193(3/4): 120-127. [23] Takekoshi T, Karatsu K, Suzuki J, et al. DESHIMA on ASTE: on-sky responsivity calibration of the integrated superconducting spectrometer[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2020, 199(1/2): 231-239. [24] Baryshev A M, Baselmans J J A, Yates S J C, et al. Large format antenna coupled micorwave kinetic iinductance detector arrays for radioastronomy[C]//2014 39th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz waves (IRMMW-THz). 2014: 1. [25] Duan Ran, Khaikin V, Lebedev M, et al. Toward Eurasian SubMillimeter Telescopes: the concept of multicolor subTHz MKID-array demo camera MUSICAM and its instrumental testing[C]//2020 7th All-Russian Microwave Conference (RMC). 2020: 41-46. [26] Isopi G, Cacciotti F, Paiella A, et al. MISTRAL: technical commissioning and first W-band photons from the Sardinia Radio Telescope[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy XII. 2024: 116-125. [27] Vicarelli L, Vitiello M S, Coquillat D, et al. Graphene field-effect transistors as room-temperature terahertz detectors[J]. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(10): 865-871. doi: 10.1038/nmat3417 [28] Chen S L, Chang Y C, Zhang Cheng, et al. Efficient real-time detection of terahertz pulse radiation based on photoacoustic conversion by carbon nanotube nanocomposite[J]. Nature Photonics, 2014, 8(7): 537-542. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.96 [29] Coppinger M, Sustersic N A, Kolodzey J, et al. Sensitivity of a vanadium oxide uncooled microbolometer array for terahertz imaging[J]. Optical Engineering, 2011, 50: 053206. doi: 10.1117/1.3574066 [30] Lee A W, Hu Qing. Real-time, continuous-wave terahertz imaging by use of a microbolometer focal-plane array[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30(19): 2563-2565. doi: 10.1364/OL.30.002563 [31] Han Ruonan, Zhang Yaming, Kim Y, et al. 280GHz and 860GHz image sensors using Schottky-barrier diodes in 0.13 μm digital CMOS[C]//2012 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. 2012: 254-256. [32] Otsuji T. Trends in the research of modern terahertz detectors: plasmon detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2015, 5(6): 1110-1120. [33] Huhn A K, Spickermann G, Ihring A, et al. Uncooled antenna-coupled terahertz detectors with 22 μs response time based on BiSb/Sb thermocouples[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102: 121102. doi: 10.1063/1.4798369 [34] 张鹏, 曹乾涛, 董航荣, 等. 大面元太赫兹热释电探测器[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49:20190338 doi: 10.3788/irla.30_2019-0338Zhang Peng, Cao Qiantao, Dong Hangrong, et al. Large area terahertz pyroelectric detector[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49: 20190338 doi: 10.3788/irla.30_2019-0338 [35] 梁志清, 刘子骥, 蒋亚东, 等. 基于超薄钽酸锂晶体材料高响应太赫兹探测器[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2016, 35(5):520-524,616 doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2016.05.002Liang Zhiqing, Liu Ziji, Jiang Yadong, et al. High responsivity of terahertz detector based on ultra-thin LiTaO3 crystal material[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2016, 35(5): 520-524,616 doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2016.05.002 [36] 王军, 蒋亚东. 室温微测辐射热计太赫兹探测阵列技术研究进展(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48:0102001 doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0102001Wang Jun, Jiang Yadong. Research development about room temperature terahertz detector array technology with microbolometer structure (invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48: 0102001 doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0102001 [37] Tucker J R, Feldman M J. Quantum detection at millimeter wavelengths[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1985, 57(4): 1055-1113. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.57.1055 [38] Miao W, Zhang W, Zhong J Q, et al. Non-uniform absorption of terahertz radiation on superconducting hot electron bolometer microbridges[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104: 052605. doi: 10.1063/1.4864763 [39] Miao W, Zhang W, Zhou K M, et al. Investigation of the performance of NbN superconducting HEB mixers of different critical temperatures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2017, 27: 2200304. [40] Hijmering R A, Khosropanah P, Ridder M, et al. Effect of magnetic fields on TiAu TES bolometers for the SAFARI instrument on the SPICA FIR telescope[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2012, 167(3/4): 242-247. [41] Rosenberg D, Lita A E, Miller A J, et al. Noise-free high-efficiency photon-number-resolving detectors[J]. Physical Review A, 2005, 71: 061803. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.71.061803 [42] 史生才, 李婧, 张文, 等. 超高灵敏度太赫兹超导探测器[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64:228501 doi: 10.7498/aps.64.228501Shi Shengcai, Li Jing, Zhang Wen, et al. Terahertz high-sensitivity superconducting detectors[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64: 228501 doi: 10.7498/aps.64.228501 [43] Zmuidzinas J. Superconducting microresonators: physics and applications[J]. Annual Review of Condensed Matter Physics, 2012, 3(1): 169-214. doi: 10.1146/annurev-conmatphys-020911-125022 [44] Gao Jiansong. The physics of superconducting microwave resonators[D]. Pasadena: California Institute of Technology, 2008. [45] He Q, Ouyang P, Gao H, et al. Low-loss superconducting aluminum microwave coplanar waveguide resonators on sapphires for the qubit readouts[J]. Superconductor Science and Technology, 2022, 35: 065017. doi: 10.1088/1361-6668/ac6a1d [46] Shi Qing, Li Jing, Zhi Qiang, et al. Terahertz superconducting kinetic inductance detectors demonstrating photon-noise-limited performance and intrinsic generation-recombination noise[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2022, 65: 239511. [47] Baselmans J J A, Bueno J, Yates S J C, et al. A kilo-pixel imaging system for future space based far-infrared observatories using microwave kinetic inductance detectors[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2017, 601: A89. [48] Mazin B A, Meeker S R, Strader M J, et al. ARCONS: a 2024 pixel optical through near-IR cryogenic imaging spectrophotometer[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2013, 125(933): 1348-1361. doi: 10.1086/674013 [49] Barry P S, Shirokoff E, Kovács A, et al. Electromagnetic design for SuperSpec: a lithographically-patterned millimetre-wave spectrograph[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy VI. 2012. [50] Karkare K S, Barry P S, Bradford C M, et al. Full-array noise performance of deployment-grade SuperSpec mm-wave on-chip spectrometers[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2020, 199(3/4): 849-857. [51] Endo A, Karatsu K, Tamura Y, et al. First light demonstration of the integrated superconducting spectrometer[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2019, 3(11): 989-996. doi: 10.1038/s41550-019-0850-8 [52] Taniguchi A, Bakx T J L C, Baselmans J J A, et al. DESHIMA 2.0: development of an integrated superconducting spectrometer for science-grade astronomical observations[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2022, 209(3/4): 278-286. [53] Thomas C N, Blundell R, Glowacka D, et al. Progress on the Cambridge emission line surveyor (CAMELS)[C]//26th International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology. 2015: M4. [54] Grimes P K, Asada K, Blundell R, et al. Instrumentation for single-dish observations with The Greenland Telescope[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy VII. 2014: 602-612. [55] Cataldo G, Barrentine E M, Bulcha B T, et al. Second-generation design of micro-spec: a medium-resolution, submillimeter-wavelength spectrometer-on-a-chip[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2018, 193(5/6): 923-930. [56] Cataldo G, Barrentine E M, Bulcha B T, et al. Second-generation Micro-Spec: a compact spectrometer for far-infrared and submillimeter space missions[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2019, 162: 155-159. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2019.06.012 [57] Ade P A R, Anderson C J, Barrentine E M, et al. The experiment for cryogenic large-aperture intensity mapping (EXCLAIM)[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2020, 199(3/4): 1027-1037. [58] Switzer E R, Barrentine E M, Cataldo G, et al. Experiment for cryogenic large-aperture intensity mapping: instrument design[J]. Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems, 2021, 7: 044004. [59] Pullen A R, Breysse P C, Oxholm T, et al. Extragalactic science with the experiment for cryogenic large-aperture intensity mapping[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023, 521(4): 6124-6142. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stad916 [60] Bryan S, Aguirre J, Che G, et al. WSPEC: a waveguide filter-bank focal plane array spectrometer for millimeter wave astronomy and cosmology[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2016, 184(1/2): 114-122. [61] Hubmayr J, Beall J A, Becker D, et al. Dual-polarization-sensitive kinetic inductance detectors for balloon-borne sub-millimeter polarimetry[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2014, 176(3/4): 490-496. [62] Moncelsi L, Ade P A R, Angilè F E, et al. Empirical modelling of the BLASTPol achromatic half-wave plate for precision submillimetre polarimetry[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2014, 437(3): 2772-2789. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stt2090 [63] Galitzki N, Ade P A R, Angilè F E, et al. The balloon-borne large aperture submillimeter telescope for polarimetry-BLASTPol: performance and results from the 2012 Antarctic flight[C]//Ground-based and Airborne Telescopes V. 2014: 257-267. [64] Gandilo N. The balloon-borne large aperture submillimeter telescope for Polarimetry (BLAST-Pol): instrument and 2010 Science Campaign[D]. University of Pennsylvania, 2013. [65] Galitzki N, Ade P, Angilè F E, et al. Instrumental performance and results from testing of the BLAST-TNG receiver, submillimeter optics, and MKID detector arrays[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy VIII. 2016: 108-118. [66] Galitzki N, Ade P A R, Angilè F E, et al. The next generation BLAST experiment[J]. Journal of Astronomical Instrumentation, 2014, 3: 1440001. doi: 10.1142/S2251171714400017 [67] Brien T L R, Ade P, Barry P S, et al. Performance and deployment status of MUSCAT: a 1500-pixel LEKID-based mm-wave camera for the large millimeter telescope[C]//2020 45th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz). 2020: 1. [68] Rowe S, Tapia M, Barry P S, et al. The MUSCAT readout electronics backend: design and pre-deployment performance[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2023, 211(5/6): 289-301. [69] Ade P A R, Aghanim N, Arnaud M, et al. Planck intermediate results: XVI. Profile likelihoods for cosmological parameters[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2014, 566: A54. [70] Ade P A R, Aghanim N, Arnaud M, et al. Planck 2015 results: XIII. Cosmological parameters[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2016, 594: A13. [71] Mccarrick H, Jones G, Johnson B R, et al. Design and performance of dual-polarization lumped-element kinetic inductance detectors for millimeter-wave polarimetry[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2018, 610: A45. [72] de Bernardis P, Ade P A R, Baselmans J J A, et al. Exploring cosmic origins with CORE: the instrument[J]. Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, 2018, 2018: 015. [73] Johnson B R, Ade P A R, Araujo D, et al. The detector system for the stratospheric kinetic inductance polarimeter (SKIP)[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2014, 176(5/6): 741-748. [74] Monfardini A, Baselmans J, Benoit A, et al. Lumped element kinetic inductance detectors for space applications[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy VIII. 2016: 142-149. [75] Lee K, Choi J, Génova-Santos R T, et al. GroundBIRD: a CMB polarization experiment with MKID arrays[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2020, 200(5/6): 384-391. [76] Nagasaki T, Choi J, Génova-Santos R T, et al. GroundBIRD: observation of CMB polarization with a rapid scanning and MKIDs[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2018, 193(5/6): 1066-1074. [77] Hui H, Ade P A R, Ahmed Z, et al. BICEP Array: a multi-frequency degree-scale CMB polarimeter[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy IX. 2018: 75-89. [78] Gao Jiansong, Daal M, Vayonakis A, et al. Experimental evidence for a surface distribution of two-level systems in superconducting lithographed microwave resonators[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92: 152505. doi: 10.1063/1.2906373 [79] Vissers M R, Austermann J E, Malnou M, et al. Ultrastable millimeter-wave kinetic inductance detectors[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2020, 116: 032601. doi: 10.1063/1.5138122 [80] Schlaerth J A, Czakon N G, Day P K, et al. MKID multicolor array status and results from DemoCam[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy V. 2010: 59-69. [81] Schlaerth J, Vayonakis A, Day P, et al. A millimeter and submillimeter kinetic inductance detector camera[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2008, 151(3/4): 684-689. [82] Glenn J, Day P K, Ferry M, et al. A microwave kinetic inductance camera for sub/millimeter astrophysics[C]//Millimeter and Submillimeter Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy IV. 2008: 117-126. [83] Golwala S R, Bockstiegel C, Brugger S, et al. Status of MUSIC, the MUltiwavelength sub/millimeter inductance camera[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy VI. 2012: 33-53. [84] Maloney P R, Czakon N G, Day P K, et al. MUSIC for sub/millimeter astrophysics[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy V. 2010: 124-134. [85] Schlaerth J A, Czakon N G, Day P K, et al. The status of music: a multicolor sub/millimeter MKID instrument[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2012, 167(3/4): 347-353. [86] Monfardini A, Benoit A, Bideaud A, et al. The Néel IRAM KID Arrays (NIKA)[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2012, 167(5/6): 834-839. [87] Monfardini A, Adam R, Adane A, et al. Latest NIKA results and the NIKA-2 project[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2014, 176(5/6): 787-795. [88] Ritacco A, Macías-Pérez J F, Ponthieu N, et al. NIKA 150 GHz polarization observations of the Crab nebula and its spectral energy distribution[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2018, 616: A35. [89] Adam R, Hahn O, Ruppin F, et al. Substructure and merger detection in resolved NIKA Sunyaev-Zel’dovich images of distant clusters[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2018, 614: A118. [90] Adam R, Bartalucci I, Pratt G W, et al. Mapping the kinetic Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect toward MACS J0717.5+3745 with NIKA[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2017, 598: A115. [91] Adam R, Comis B, Bartalucci I, et al. High angular resolution Sunyaev-Zel’dovich observations of MACS J1423.8+2404 with NIKA: multiwavelength analysis[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2016, 586: A122. [92] Calvo M, Benoît A, Catalano A, et al. The NIKA2 instrument, a dual-band kilopixel KID array for millimetric astronomy[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2016, 184(3/4): 816-823. [93] Adam R, Adane A, Ade P A R, et al. The NIKA2 large-field-of-view millimetre continuum camera for the 30 m IRAM telescope[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2018, 609: A115. [94] Catalano A, Adam R, Ade P A R, et al. The NIKA2 instrument at 30-m IRAM telescope: performance and results[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2018, 193(5/6): 916-922. [95] Katsioli S, Xilouris E M, Kramer C, et al. The stratification of ISM properties in the edge-on galaxy NGC 891 revealed by NIKA2[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2023, 679: A7. [96] Reyes N, Mayorga I C, Grutzeck G, et al. Characterization of widefield THz optics using phase shifting interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2023, 13(6): 614-621. doi: 10.1109/TTHZ.2023.3320554 [97] Davis K. Instrument design and radiation pattern testing for terahertz astronomical instruments[D]. Tempe: Arizona State University, 2018. [98] Fasano A, Aguiar M, Benoit A, et al. The KISS experiment[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2020, 199(1/2): 529-536. [99] Fasano A, Aguiar M, Benoit A, et al. KISS: a spectrometric imager for millimetre cosmology[C]//EPJ Web of Conferences. 2020: 00010. [100] Ade P, Aravena M, Barria E, et al. A wide field-of-view low-resolution spectrometer at APEX: instrument design and scientific forecast[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2020, 642: A60. [101] Fasano A, Ade P, Aravena M, et al. CONCERTO: instrument and status[C]//EPJ Web of Conferences. 2024: 00018. [102] Hu W, Beelen A, Lagache G, et al. CONCERTO at APEX on-sky performance in continuum[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2024, 689: A20. [103] Choi S K, Austermann J, Basu K, et al. Sensitivity of the Prime-Cam instrument on the CCAT-prime telescope[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2020, 199(3/4): 1089-1097. [104] Huber Z B, Lin L T, Vavagiakis E M, et al. CCAT: Prime-Cam optics overview and status update[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy XII. 2024: 784-793. [105] Vavagiakis E M, Ahmed Z, Ali A, et al. Prime-Cam: a first-light instrument for the CCAT-prime telescope[C]//Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy IX. 2018: 375-390. [106] Yang H, Kulesa C A, Walker C K, et al. Exceptional terahertz transparency and stability above Dome A, Antarctica[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2010, 122: 490. doi: 10.1086/652276 [107] Shi Shengcai, Li Jing, Lin Zhenhui, et al. Development of an MKIDs-based THz superconducting imaging array (TeSIA) at 0.85 THz[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2018, 193(3/4): 128-133. [108] Liu X, Guo W, Wang Y, et al. Cryogenic LED pixel-to-frequency mapper for kinetic inductance detector arrays[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 122: 034502. doi: 10.1063/1.4994170 [109] Liu X, Guo W, Wang Y, et al. Superconducting micro-resonator arrays with ideal frequency spacing[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111: 252601. doi: 10.1063/1.5016190 [110] Guo W, Liu X, Wang Y, et al. Counting near infrared photons with microwave kinetic inductance detectors[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110: 212601. doi: 10.1063/1.4984134 [111] Dai X, Wang H, Wang Y, et al. Photon number-resolving aluminum kinetic inductance detectors[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2025, 126: 012602. doi: 10.1063/5.0234649 [112] Morozov D, Doyle S M, Banerjee A, et al. Design and characterisation of titanium nitride subarrays of kinetic inductance detectors for passive terahertz imaging[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2018, 193(3/4): 196-202. [113] Rowe S, Pascale E, Doyle S, et al. A passive terahertz video camera based on lumped element kinetic inductance detectors[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87: 033105. doi: 10.1063/1.4941661 [114] O'brien K, Mazin B, Mchugh S, et al. ARCONS: a highly multiplexed superconducting UV-to-near-IR camera[J]. Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union, 2011, 7(S285): 385-388. doi: 10.1017/S1743921312001159 [115] Meeker S R, Mazin B A, Walter A B, et al. DARKNESS: a microwave kinetic inductance detector integral field spectrograph for high-contrast astronomy[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2018, 130: 065001. doi: 10.1088/1538-3873/aab5e7 [116] Walter A B, Fruitwala N, Steiger S, et al. The MKID Exoplanet Camera for Subaru SCExAO[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2020, 132: 125005. doi: 10.1088/1538-3873/abc60f -




 下载:
下载: