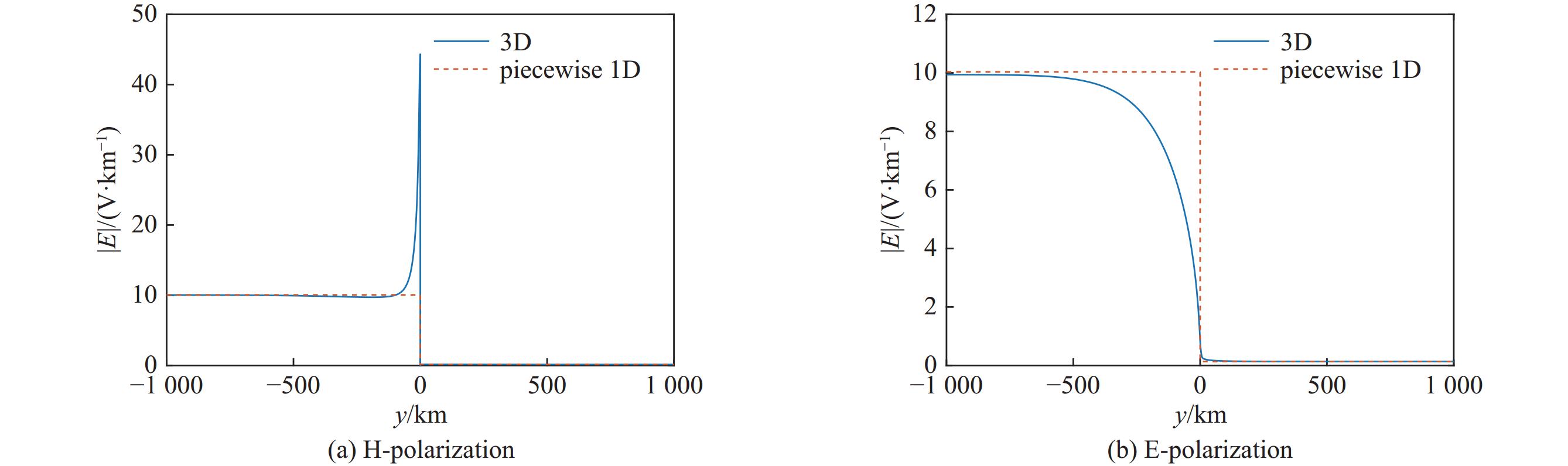
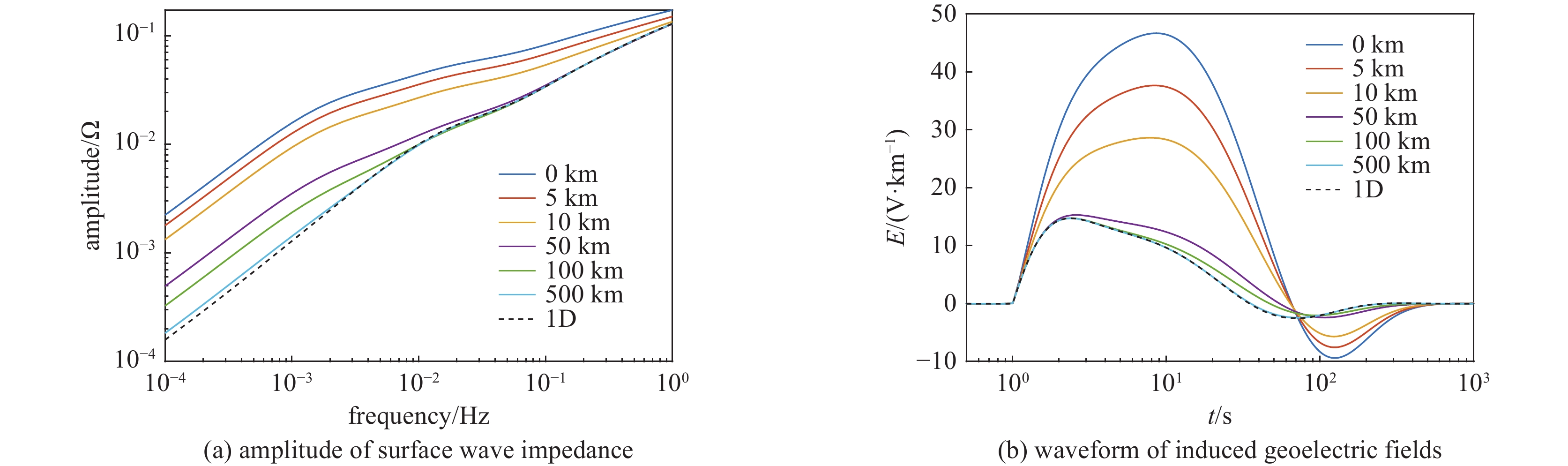
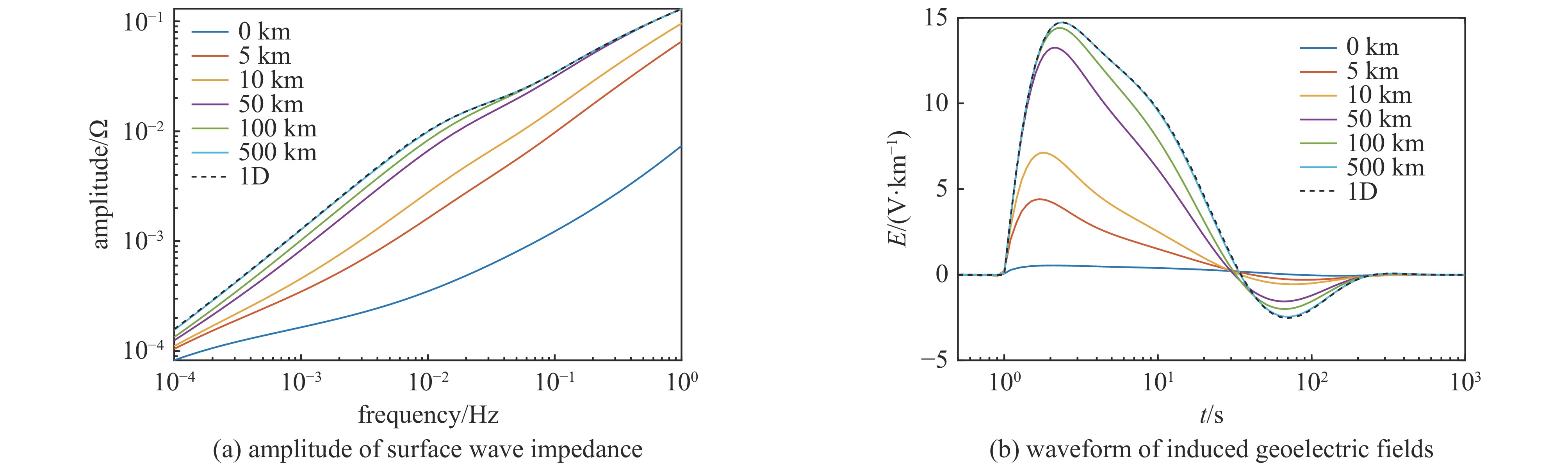
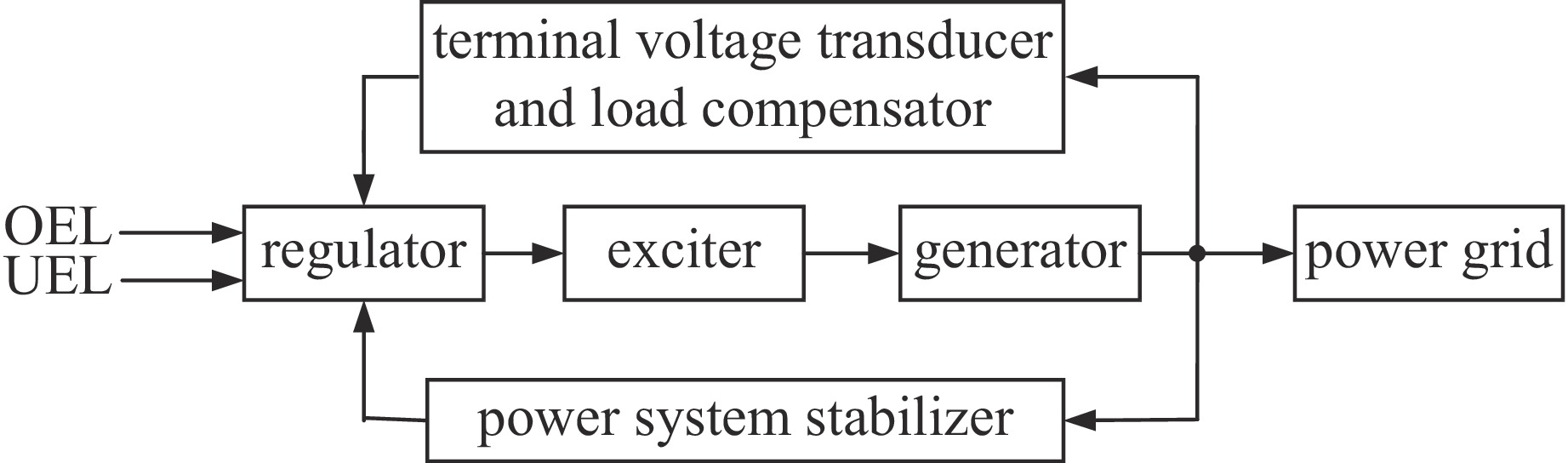
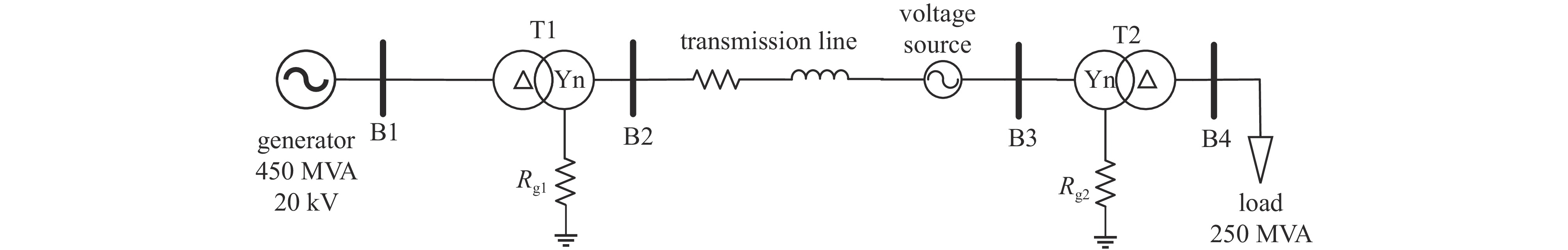
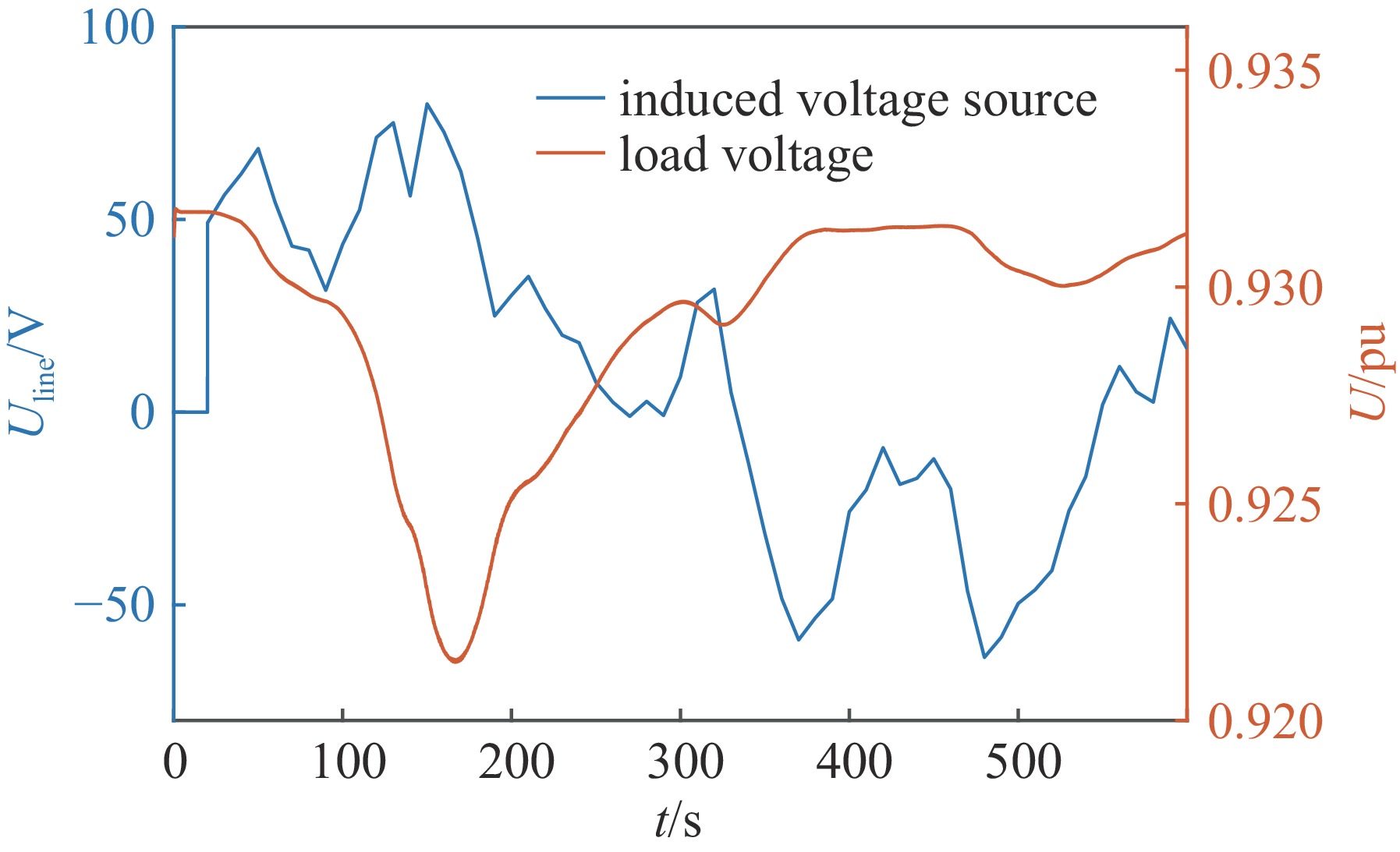
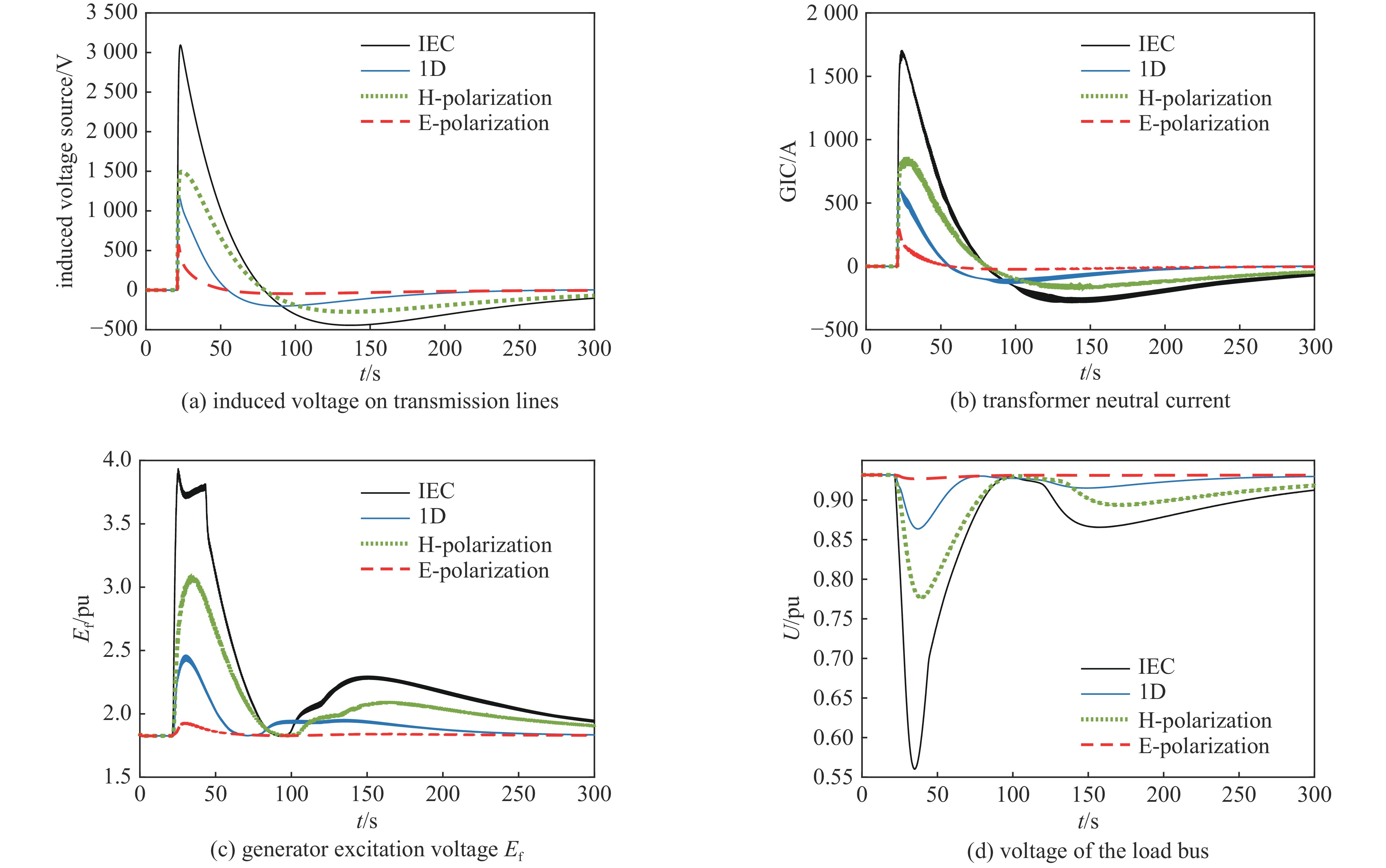
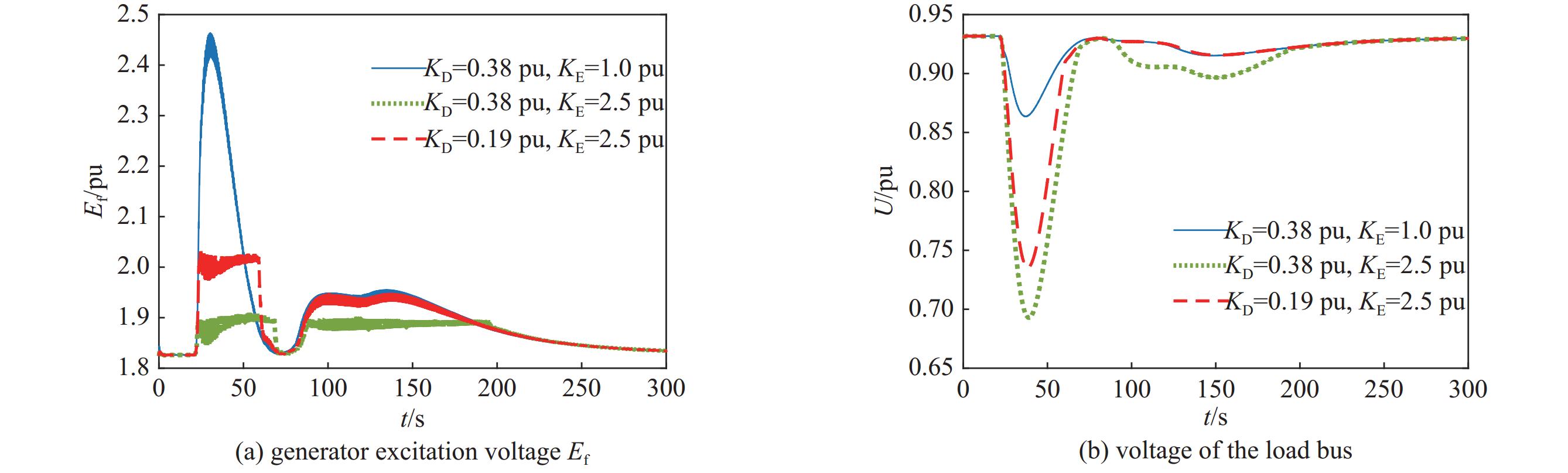
| [1] |
谢彦召, 刘民周, 陈宇浩. 国家关键基础设施电磁恢复力[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:070001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190202Xie Yanzhao, Liu Minzhou, Chen Yuhao. Electromagnetic resilience of critical national infrastructure[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 070001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190202
|
| [2] |
陈宇浩, 谢彦召, 刘民周, 等. 高空电磁脉冲作用下电力系统主要效应模式分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:070007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190184Chen Yuhao, Xie Yanzhao, Liu Minzhou, et al. Analysis of high-altitude electromagnetic effect models on power system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 070007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190184
|
| [3] |
秦锋, 陈伟, 毛从光, 等. 电力系统高空电磁脉冲效应研究综述[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14(3):12-27Qin Feng, Chen Wei, Mao Congguang, et al. Review of high altitude electromagnetic pulse effects on power system[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14(3): 12-27
|
| [4] |
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) —Part 2: environment—section 9: description of HEMP environment—radiated disturbance: IEC61000-2-9[S]. International Electrotechnical Commission, 1996.
|
| [5] |
Kruse V J, Rackliffe G B, Barnes P R. Load flow studies in the presence of magnetohydrodynamic electromagnetic pulse[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1990, 5(2): 1158-1163. doi: 10.1109/61.53135
|
| [6] |
王建国. 高空核爆炸磁流体动力学电磁脉冲[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:073001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240105Wang Jianguo. Magnetohydrodynamic electromagnetic pulse produced by high altitude nuclear explosion[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 073001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240105
|
| [7] |
刘春明, 王红梅, 王璇. 多次磁暴下特高压电网GIC统计规律研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(15):4606-4614Liu Chunming, Wang Hongmei, Wang Xuan. Statistical analysis of geomagnetically induced currents in UHV power grids under multiple geomagnetic storms[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(15): 4606-4614
|
| [8] |
Liu Minzhou, Xie Yanzhao, Chen Yuhao, et al. Modeling the 10, 000-year geomagnetic disturbance scenarios based on extreme value analysis[J]. IEEE Letters on Electromagnetic Compatibility Practice and Applications, 2020, 2(4): 156-160. doi: 10.1109/LEMCPA.2020.3042457
|
| [9] |
Liu Minzhou, Xie Yanzhao, Yang Yifan, et al. Reduced nodal admittance matrix method for probabilistic GIC analysis in power grids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2023, 38(5): 4950-4953. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2023.3280392
|
| [10] |
刘民周. 交流输电网和天然气管网地磁感应建模与高效算法研究[D]. 西安: 西安交通大学, 2024Liu Minzhou. Study on modeling and efficient algorithms for geomagnetic induction in AC transmission grids and gas pipeline networks[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2024
|
| [11] |
余同彬, 周璧华. 近地长电缆对高空电磁脉冲晚期部分的响应[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2003, 15(12):1237-1240Yu Tongbin, Zhou Bihua. Response of long lines to late-time HEMP[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2003, 15(12): 1237-1240
|
| [12] |
高志伟, 周于翔, 朱思熠. 晚期HEMP作用下铁路牵引供电系统GIC算法研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:093001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210061Gao Zhiwei, Zhou Yuxiang, Zhu Siyi. Study on GIC algorithm of railway traction power supply system under action of late time HEMP[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 093001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210061
|
| [13] |
赵志斌, 柯俊吉, 马丽斌. 高空核电磁脉冲晚期效应对电网稳定性影响的研究[J]. 电气技术, 2015(9):16-19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3800.2015.09.004Zhao Zhibin, Ke Junji, Ma Libin. Research on impact of late-time HEMP to stability of power grids[J]. Electrical Engineering, 2015(9): 16-19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3800.2015.09.004
|
| [14] |
杨一帆, 刘民周, 谢彦召, 等. 高空电磁脉冲晚期成分作用下500kV变压器无功损耗仿真研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(1):267-277Yang Yifan, Liu Minzhou, Xie Yanzhao, et al. Simulation research on reactive power loss characteristic of 500 kV transformer under late-time high-altitude electromagnetic pulses[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(1): 267-277
|
| [15] |
刘彤宇, 李丽, 王亚楠, 等. 高空电磁脉冲晚期环境下电力系统效应研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:055020 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240042Liu Tongyu, Li Li, Wang Ya’nan, et al. Research progress on power system effects in late-time high-altitude electromagnetic pulses environment[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 055020 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.240042
|
| [16] |
田君杨, 蒋连钿, 李海勇, 等. 高空核爆电磁脉冲晚期效应对变压器的影响[J]. 电波科学学报, 2024, 39(5):870-877Tian Junyang, Jiang Liandian, Li Haiyong, et al. Effect of strong electromagnetic pulse E3 environment on transformer[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2024, 39(5): 870-877
|
| [17] |
王亚楠, 田逸涵, 马志钦, 等. 模拟极端地磁感应电流注入下缩比变压器电-磁-热效应试验研究[J]. 广东电力, 2024, 37(11):9-17Wang Ya’nan, Tian Yihan, Ma Zhiqin, et al. Experimental study on electro-magnetic-heat effects of scaled-down transformers under simulated extreme geomagnetic induced current injection[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2024, 37(11): 9-17
|
| [18] |
Report of the commission to assess the threat to the United States from electromagnetic pulse (EMP) attack: critical national infrastructures[R]. 2008.
|
| [19] |
Gilbert J, Kappenman J, Radasky W, et al. The late-time (E3) high-altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP) and its impact on the United States power grid[R]. Meta-R-321, 2010.
|
| [20] |
Overbye T J, Hutchins T R, Shetye K, et al. Integration of geomagnetic disturbance modeling into the power flow: A methodology for large-scale system studies[C]//2012 North American Power Symposium (NAPS). 2012: 1-7.
|
| [21] |
Hutchins T R, Overbye T J. Power system dynamic performance during the late-time (E3) high-altitude electromagnetic pulse[C]//2016 Power Systems Computation Conference (PSCC). 2016: 1-6.
|
| [22] |
Lee R H W, Shetye K S, Birchfield A B, et al. Using detailed ground modeling to evaluate electric grid impacts of late-time high-altitude electromagnetic pulses (E3 HEMP)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 34(2): 1549-1557. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2018.2878533
|
| [23] |
Magnetohydrodynamic electromagnetic pulse assessment of the continental United States electric grid: voltage stability analysis[R]. EPRI, Palo Alto, CA: 2017. 3002011969.
|
| [24] |
Kim S, Jeong I. Vulnerability assessment of Korean electric power systems to late-time (E3) high-altitude electromagnetic pulses[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(17): 3335. doi: 10.3390/en12173335
|
| [25] |
王泽忠, 司远, 刘连光. 地磁暴对电力系统稳定性的影响[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(7):1780-1788Wang Zezhong, Si Yuan, Liu Lianguang. Influence of geomagnetic storms on the stability of power system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(7): 1780-1788
|
| [26] |
辛文凯, 王泽忠, 刘春明, 等. 地磁暴影响下特高压交流电网电压稳定性量化评估方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(21):5771-5780Xin Wenkai, Wang Zezhong, Liu Chunming, et al. Quantitative evaluation method of voltage stability of UHV AC power network under geomagnetic storm[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(21): 5771-5780
|
| [27] |
Liu Chunming, Wang Xuan, Zhang Shuming, et al. Effects of lateral conductivity variations on geomagnetically induced currents: H-polarization[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 6310-6318. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2889462
|
| [28] |
Liu Minzhou, Xie Yanzhao, Dong Ning, et al. Numerical analysis of nonuniform geoelectric field impacts on geomagnetic induction in pipeline networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2022, 64(4): 999-1009. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2022.3158885
|
| [29] |
王泽忠, 司远, 刘连光. 考虑地下各向异性介质的磁暴感应地电场研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(5):1070-1077,1114Wang Zezhong, Si Yuan, Liu Lianguang. Study on the induced geoelectric field of geomagnetic storm considering the underground anisotropic medium[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(5): 1070-1077,1114
|
| [30] |
郑宽. 大电网地磁感应电流影响因素及建模方法研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2014Zheng Kuan. Research on influence factors and modelling methods of geomagnetically induced currents in large power grid[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2014
|
| [31] |
Jankee P, Oyedokun D T O, Chisepo H. Synchronous generator modelling and excitation voltage control for GIC studies[C]//2021 13th IEEE PES Asia Pacific Power & Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC). 2021: 1-6.
|
| [32] |
Jankee P, Oyedokun D T O, Chisepo H K. Dynamic response of power systems with real GICs: Impact on generator excitation control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2022, 37(6): 4911-4922. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2022.3162881
|
| [33] |
Kundur P. Power system stability and control[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1994.
|
| [34] |
IEEE Std 421.5-2016, IEEE recommended practice for excitation system models for power system stability studies[S].
|
| [35] |
Haddadi A, Rezaei-Zare A, Gérin-Lajoie L, et al. A modified IEEE 118-bus test case for geomagnetic disturbance studies–Part I: Model data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2020, 62(3): 955-965. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2019.2920271
|
| [36] |
TPL-007-4, Transmission system planned performance for geomagnetic disturbance events[S].
|





 下载:
下载: