Effects of parameters on signal compensation performance in signal compensation method based on Wiener filtering
-
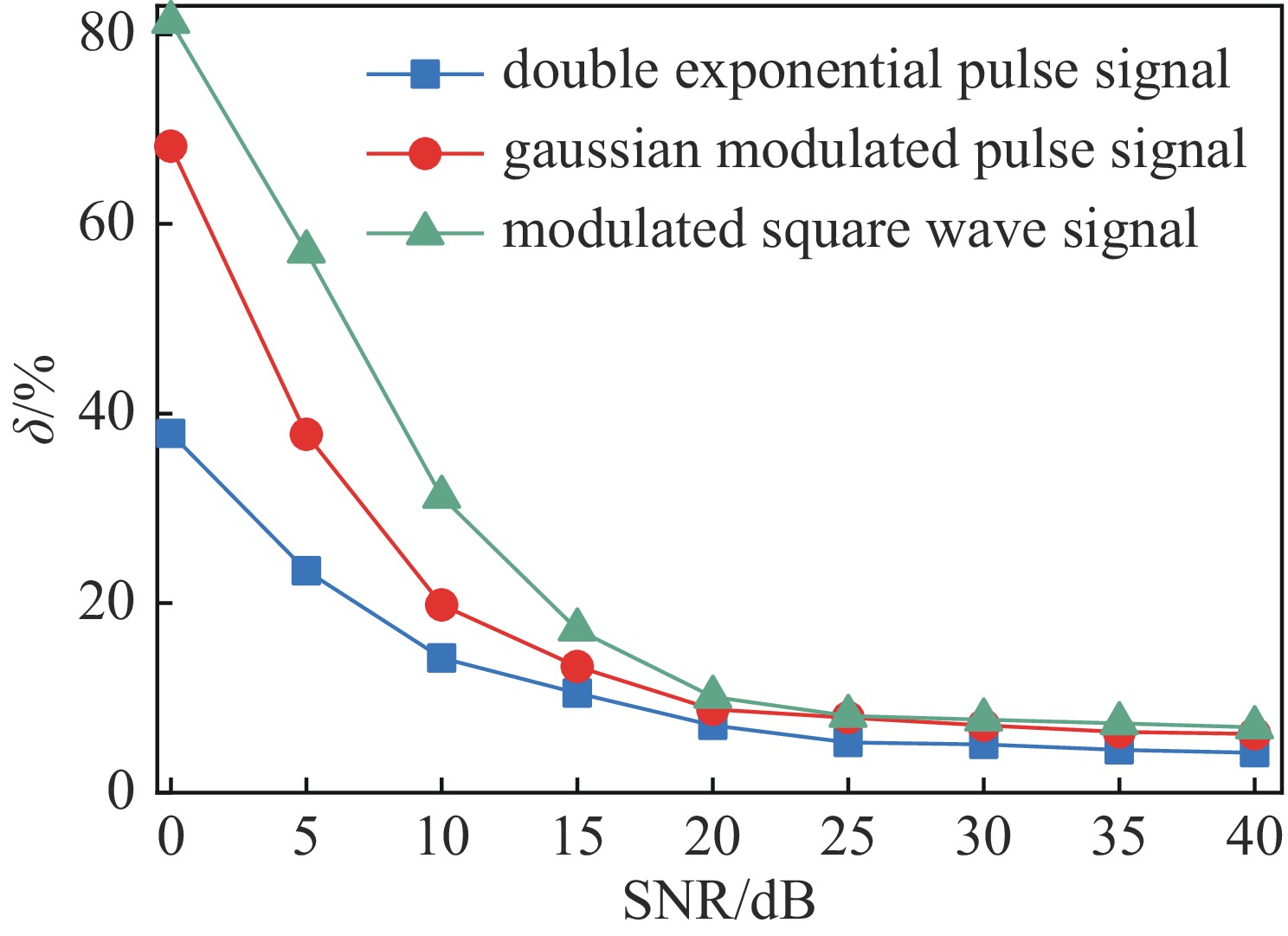
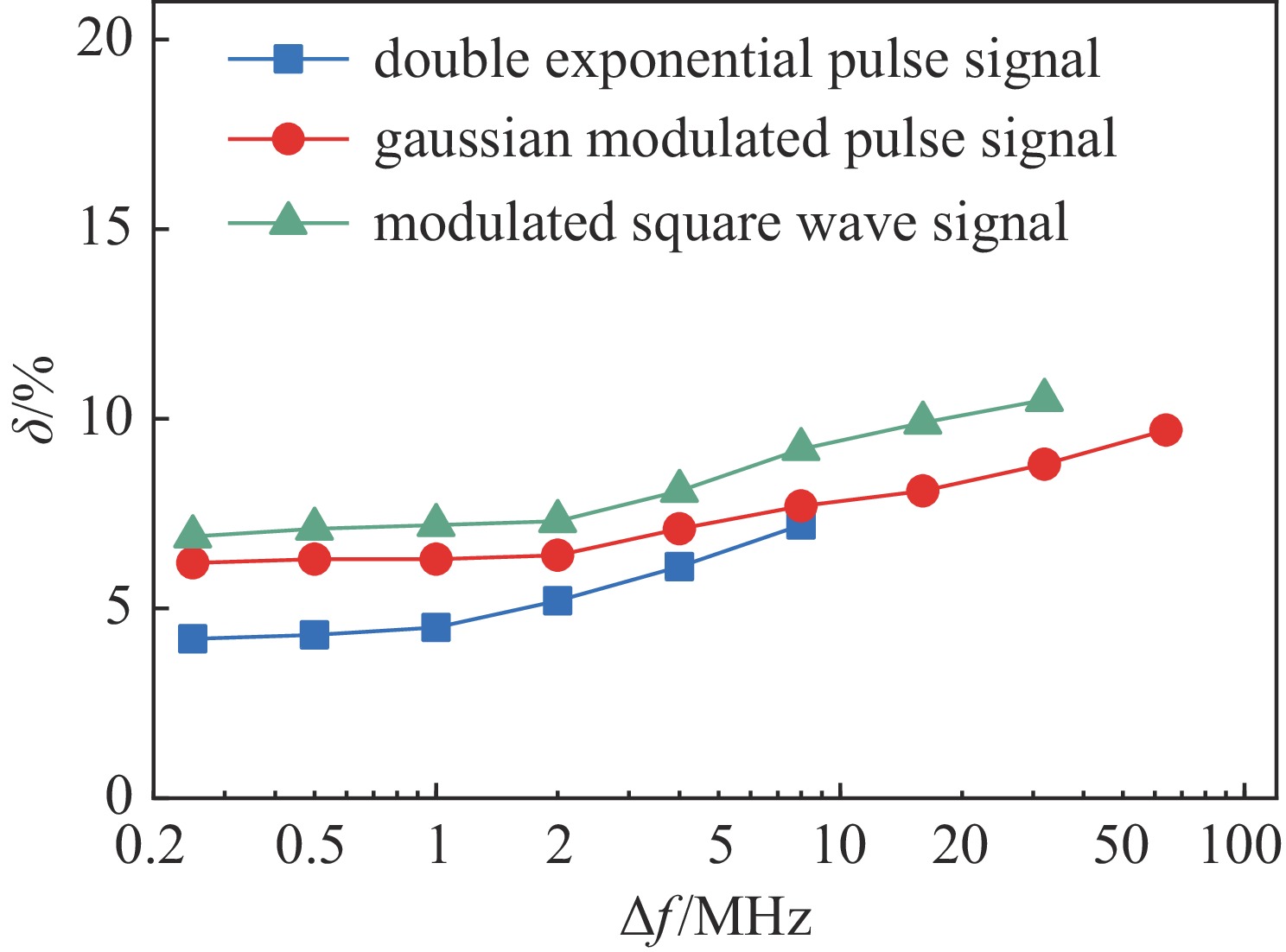
摘要: 研究表明,基于维纳滤波的信号同轴电缆传输畸变补偿方法对于多种不同类型的脉冲信号均表现出优异的补偿性能和补偿效率,可以有效解决脉冲信号同轴电缆传输畸变问题,具有很好的应用价值。但是,目前尚未对影响该方法补偿效果的因素进行分析,也未明确其最佳应用条件或参数设置。本文深入分析了影响基于维纳滤波信号传输畸变补偿方法补偿性能的因素,确定主要影响因素为输出信号信噪比SNR、同轴电缆S21曲线测量步长Δf以及功率谱估计方法。针对上述影响因素开展了同轴电缆信号传输畸变补偿试验,结果表明:当SNR小于25 dB时,SNR越低,补偿方法补偿性能越差,而当SNR大于25 dB时,随着SNR的增大,补偿性能趋于稳定不变;对于S21参数测量频率步长Δf,当Δf较小时,补偿性能几乎保持不变,当Δf较大时,随着Δf的增大时,补偿精度缓慢降低;而对于功率谱估计方法,常用的三种功率谱估计方法(周期图法、Welch法和Burg法)中,Burg法补偿性能最佳。研究结果可为维纳滤波实际应用提供指导。Abstract: The signal compensation method based on Wiener filtering has been demonstrated to have excellent compensation performance towards the signal distortion induced by the long-distance transmission in coaxial cable. However, how the parameters of this compensation method affect the compensation performance has not yet been investigated and analyzed, which may in turn bring some obstacles in the practical utilization of this modified method. Herein, we carried out a systematic study on the effect of the parameters on the signal compensation performance of this modified method. The results show that: for the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), When the SNR is less than 25 dB, the compensation performance is continuously improved as the SNR increases. Once the SNR attains~25 dB, the relative error (δ) in between the compensated signal and input signal nearly keeps unchanged. For the sampling frequency interval Δf in S21 parameter measurement, the compensation performance keeps unchanged when Δf is small, and the compensation performance slowly deteriorates as Δf exceeds a certain value. As for the power estimation method, it is proved that among the traditional power estimation methods, the Burg method can obtain better compensation performance. This study can provide a beneficial reference for the application of the signal compensation method based on Wiener filtering.
-
表 1 三种功率谱估计方法对补偿性能的影响
Table 1. Effect of the of output signal on the compensation performance
method double exponential pulse signal/% rectangular modulated pulse signal/% Gaussian modulated pulse signal/% Periodogram Method 5.5 8.2 9.1 Welch's Method 4.9 7.1 8.4 Burg's Method 4.2 6.2 6.9 -
[1] 陈克难, 刘文红. 信号波形在同轴电缆中的传输[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2004, 25(s1):502-505,515 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3087.2004.z1.217Chen Kenan, Liu Wenhong. Transmission of signal wave through coaxial-cable[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2004, 25(s1): 502-505,515 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-3087.2004.z1.217 [2] 秦风, 高原, 马弘舸. 高置信度强电磁脉冲环境测试技术研究进展与展望[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:123001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210482Qin Feng, Gao Yuan, Ma Hongge. Progress and prospect of high-confidence measurement technology for high-intensity electromagnetic pulse[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 123001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210482 [3] 渠红光, 李宪优, 田耕, 等. 基于衰减特性的电缆传输畸变软件补偿[J]. 装备指挥技术学院学报, 2010, 21(2):87-90Qu Hongguang, Li Xianyou, Tian Geng, et al. Attenuation compensation by software based on the character of transfers of the cable[J]. Journal of the Academy of Equipment Command & Technology, 2010, 21(2): 87-90 [4] 付佳斌, 卿燕玲, 卫兵, 等. 同轴电缆测量纳秒脉冲信号衰减的数字补偿[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(10):2826-2830 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112310.2826Fu Jiabin, Qing Yanling, Wei Bing, et al. Numerical compensation for coaxial cable signal degradation[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(10): 2826-2830 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112310.2826 [5] 黄豹. 新的高频同轴电缆补偿原理[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 1985, 5(4):193-198Huang Bao. New principle of high frequency coaxial cable equalization[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 1985, 5(4): 193-198 [6] 李宪优, 田耕, 蒲明辉, 等. 同轴电缆的远距离传输带宽扩展技术[J]. 宇航计测技术, 2004, 24(3):40-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7202.2004.03.012Li Xianyou, Tian Geng, Pu Minghui, et al. The bandwidth expanding technology of long coax cable[J]. Journal of Astronautic Metrology and Measurement, 2004, 24(3): 40-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7202.2004.03.012 [7] 李宪优, 田耕, 于丽娟, 等. 强光一号加速器测量电缆补偿技术[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2009, 21(3):473-476Li Xianyou, Tian Geng, Yu Lijuan, et al. Bandwidth compensation technology of QG-I accelerator’s cables[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2009, 21(3): 473-476 [8] Sarkar T K, Tseng F I, Rao S M, et al. Deconvolution of impulse response from time-limited input and output: theory and experiment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 1985, IM-34(4): 541-546. doi: 10.1109/TIM.1985.4315400 [9] Boyer W B. Computer compensation for cable signal degradations[R]. SAND-87-3072, 1987. [10] 秦风, 高原, 吴双. 基于改进贝叶斯非负Tikhonov正则化方法的同轴电缆信号传输畸变补偿研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8):2199-2206 doi: 10.11999/JEIT210068Qin Feng, Gao Yuan, Wu Shuang. Signal compensation of coaxial cable based on modified non-negative Tikhonov regularization method within Bayesian inference[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2199-2206 doi: 10.11999/JEIT210068 [11] Gao Yuan, Jiang Yunsheng, Qin Feng, et al. Optimal choice of signal compensation in coaxial cable: modified non-negative Tikhonov regularization method within Bayesian frame[J]. Measurement, 2021, 174: 109072. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109072 [12] 陈广森, 秦风, 高原. 基于维纳滤波的同轴电缆脉冲信号传输畸变补偿研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:123025 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210310Chen Guangsen, Qin Feng, Gao Yuan. Signal compensation of coaxial cable based on wiener filtering method[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 123025 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210310 [13] 冷建华. 傅里叶变换[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004Leng Jianhua. Fourier transform[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004 [14] 杜峰, 唐岚, 丁峻强. PSD和PWELCH函数的分析改进及应用[J]. 中国测试, 2010, 36(1):93-96Du Feng, Tang Lan, Ding Junqiang. Improvement and application of PSD and PWELCH[J]. China Measurement & Test, 2010, 36(1): 93-96 [15] 丁玉美, 阔永红, 高新波. 数字信号处理—时域离散随机信号处理[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2002Ding Yumei, Kuo Yonghong, Gao Xinbo. Digital signal processing—discrete random signal processing in time domain[M]. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2002 [16] 符成山. 一种改进谱减法语音增强算法的研究[J]. 信息通信, 2016(6):21-22Fu Chengshan. Research on an improved spectral subtraction speech enhancement algorithm[J]. Information & Communications, 2016(6): 21-22 -





 下载:
下载: