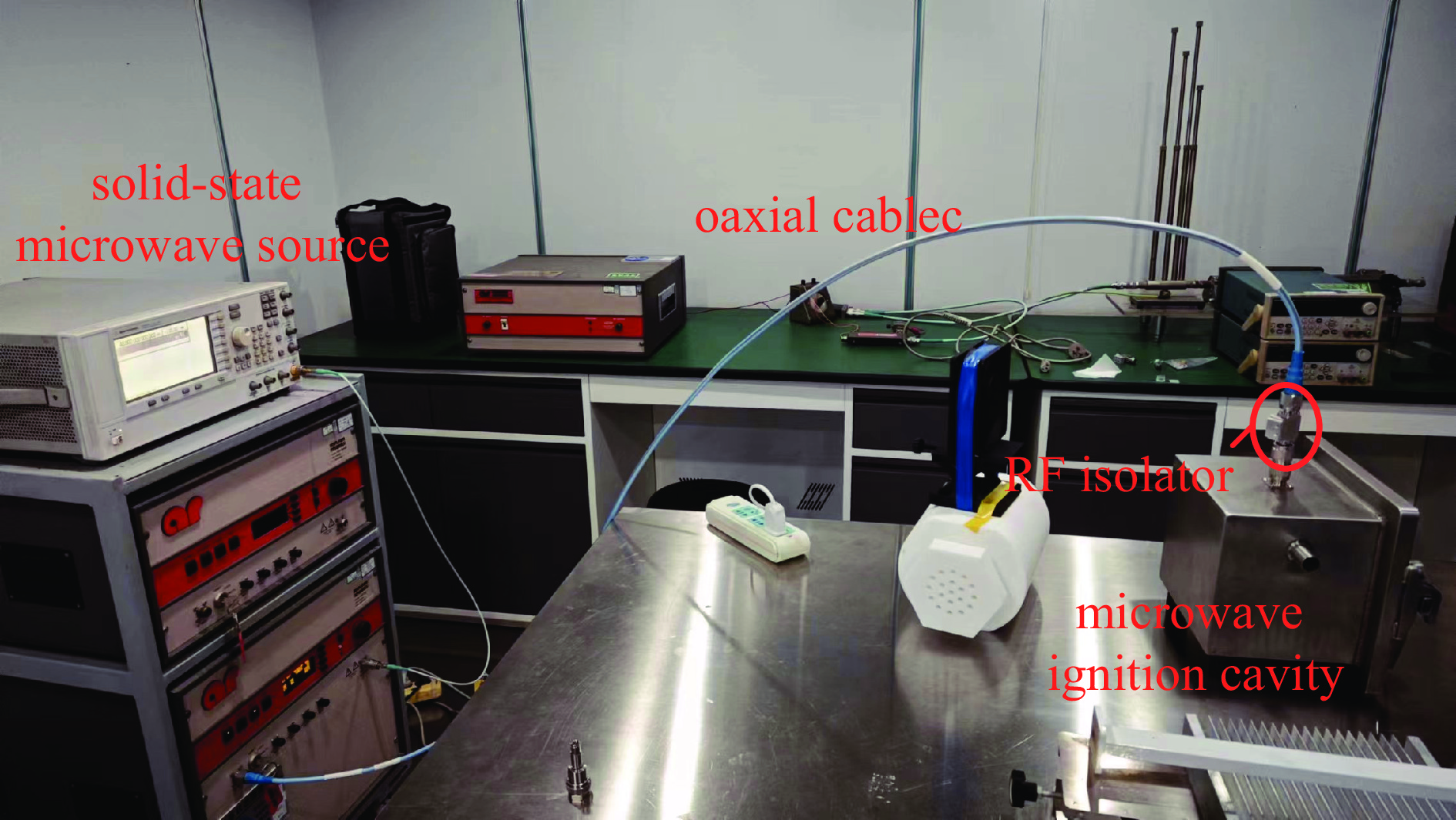
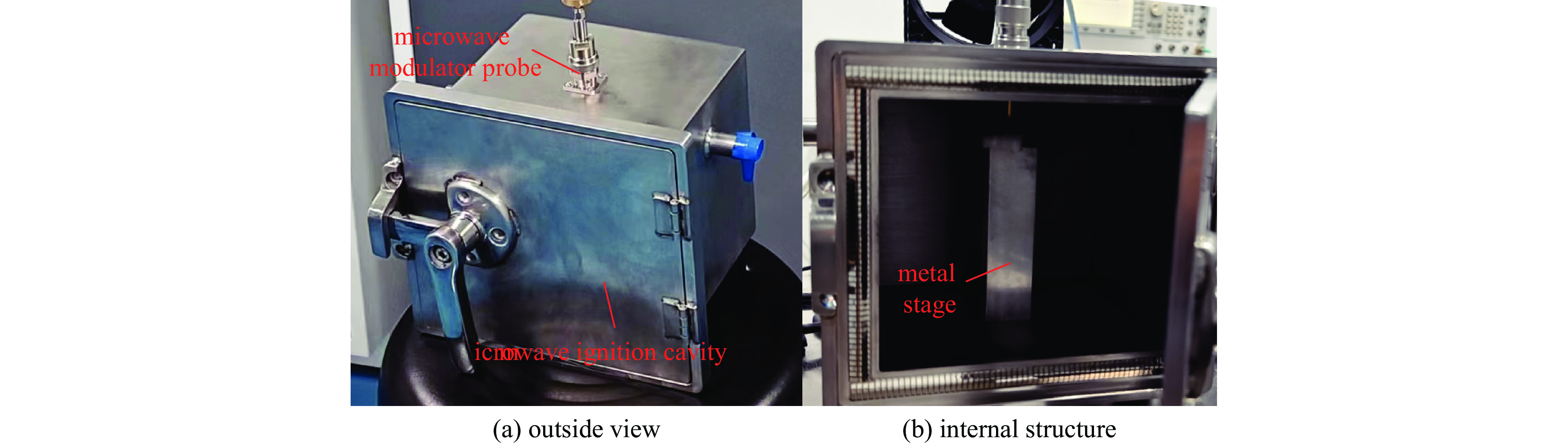
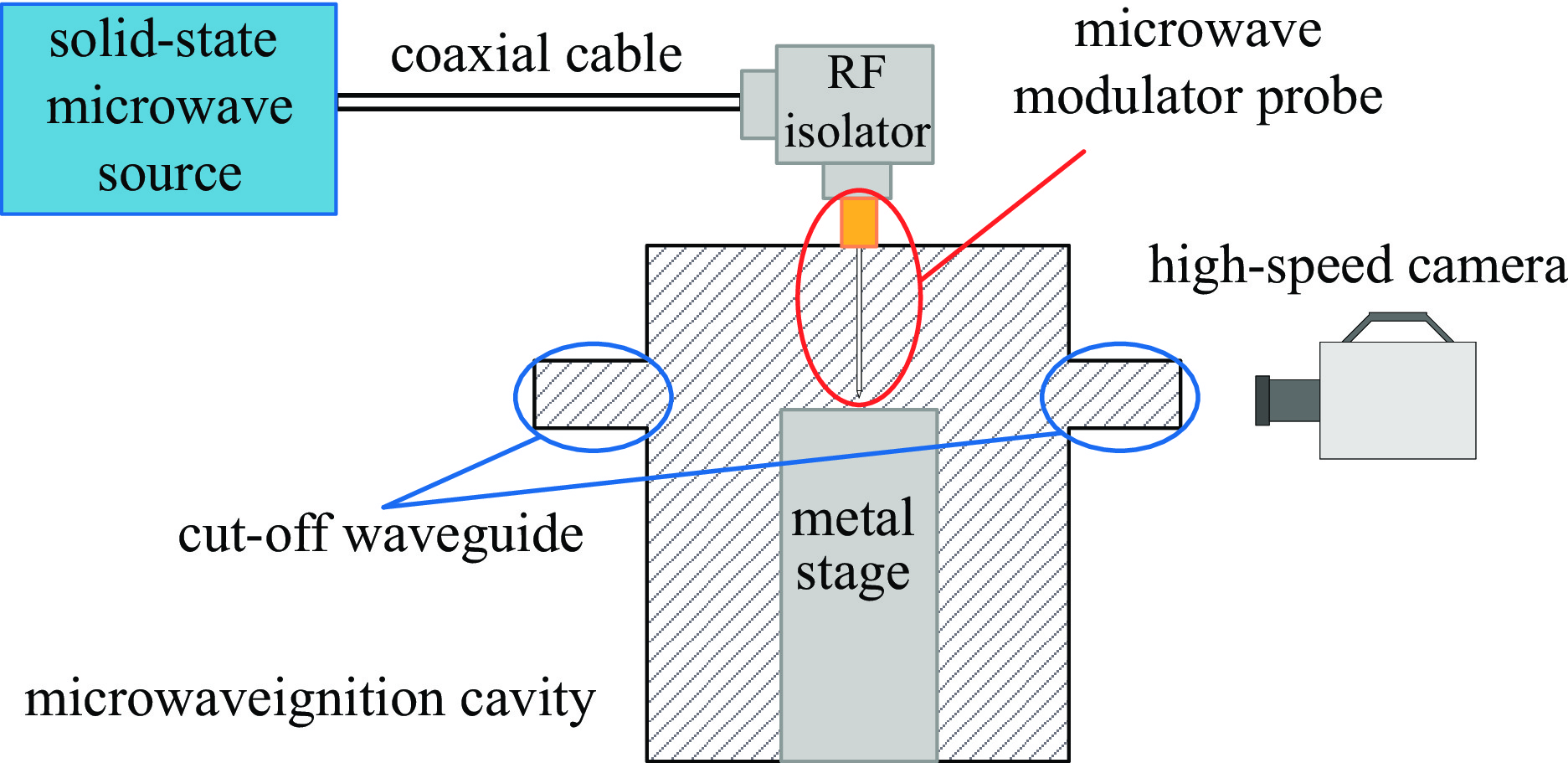
Low power microwave ignition technology of energetic materials based on dual-focusing of rectangular resonant cavity and microwave probe
-
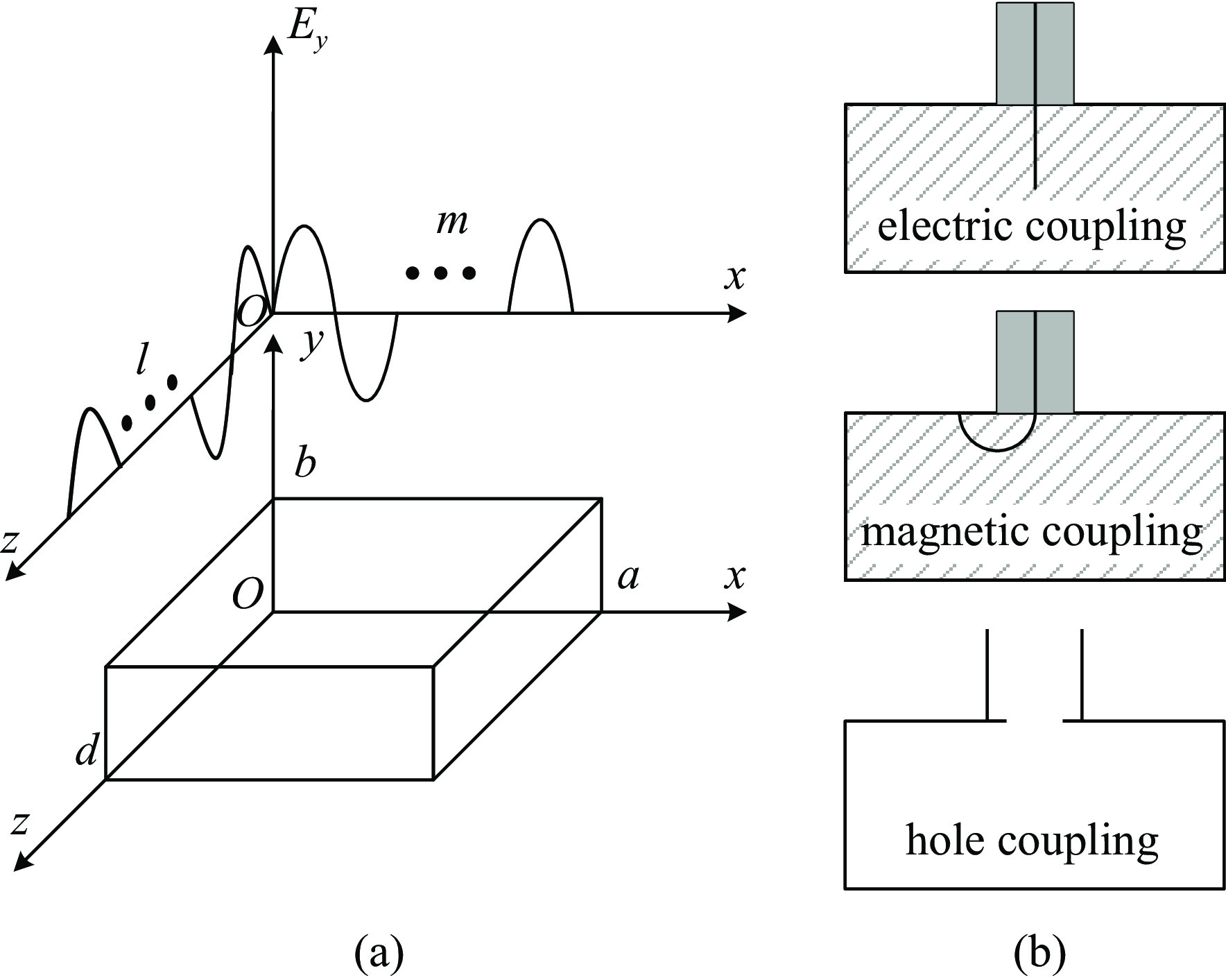
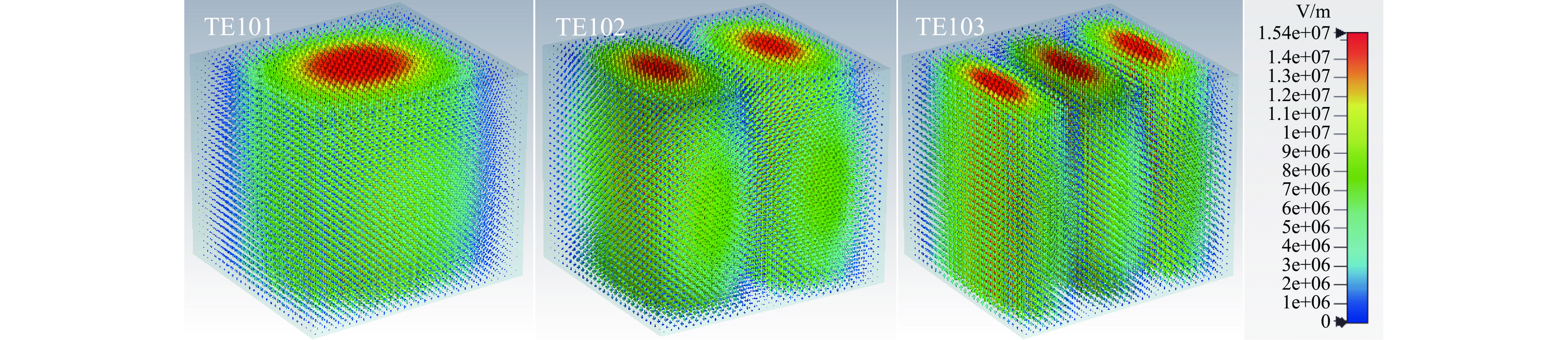
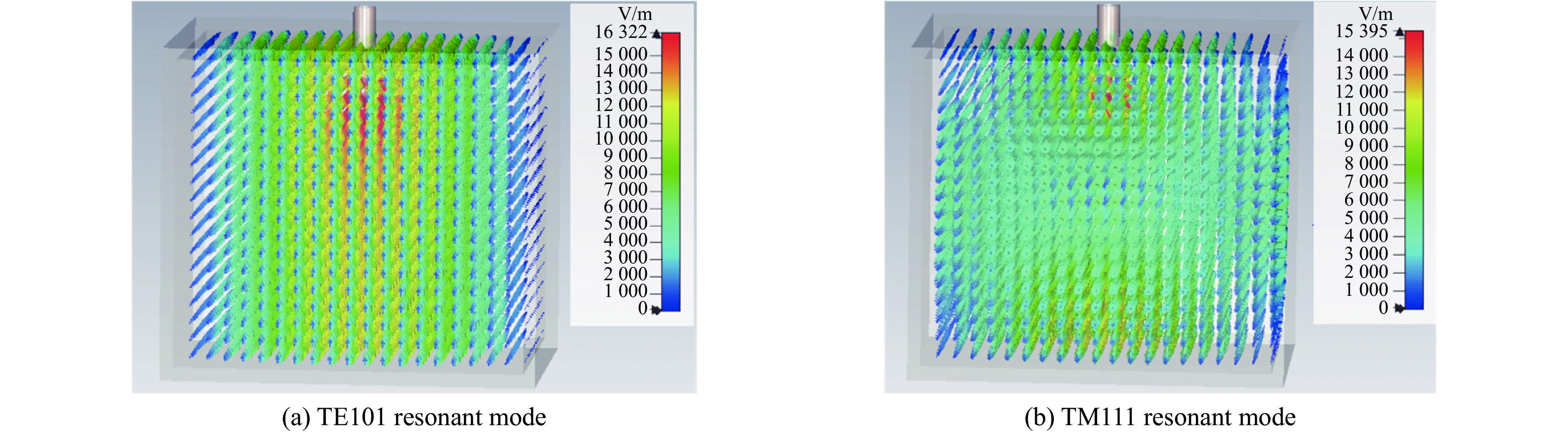
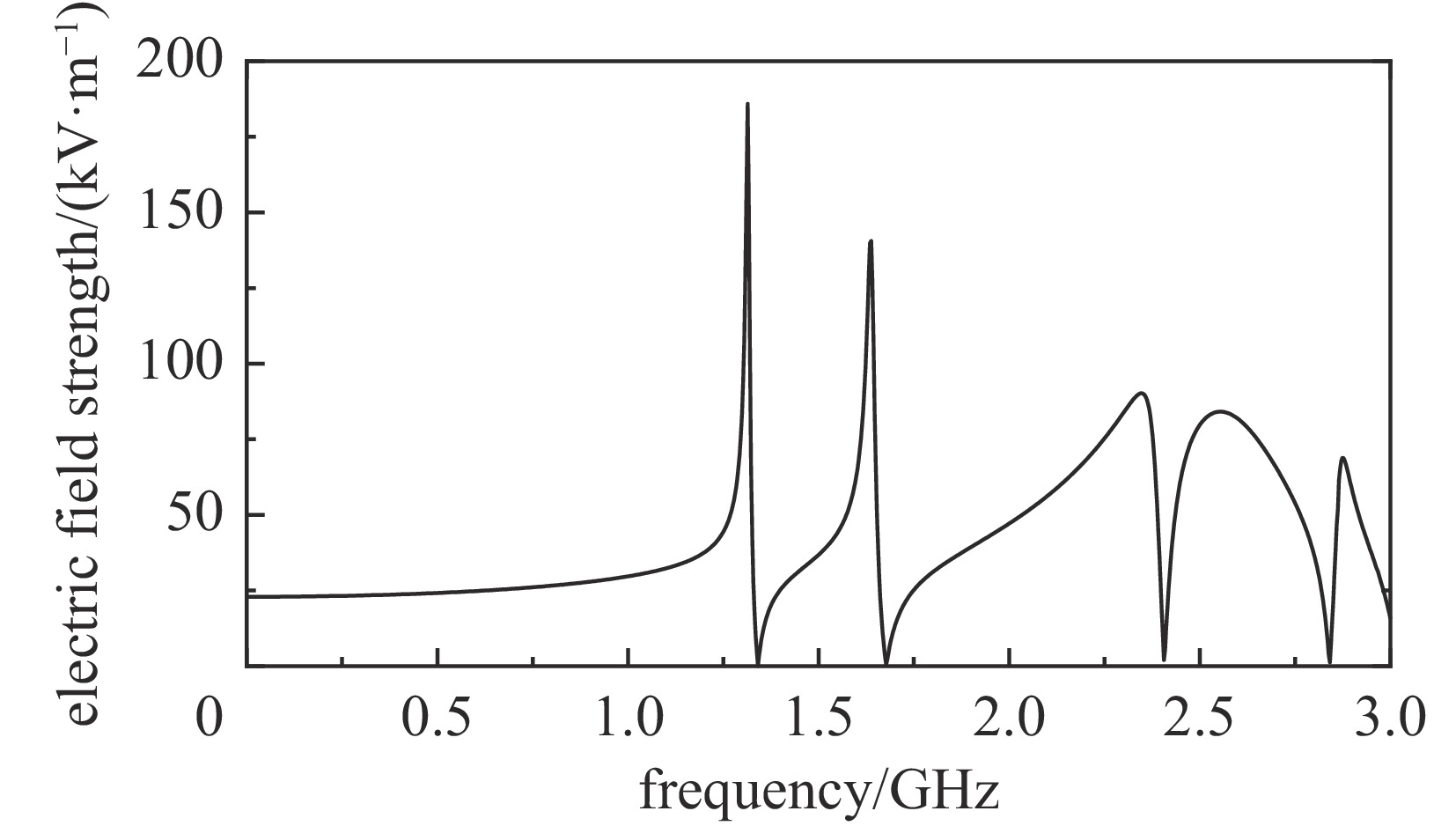
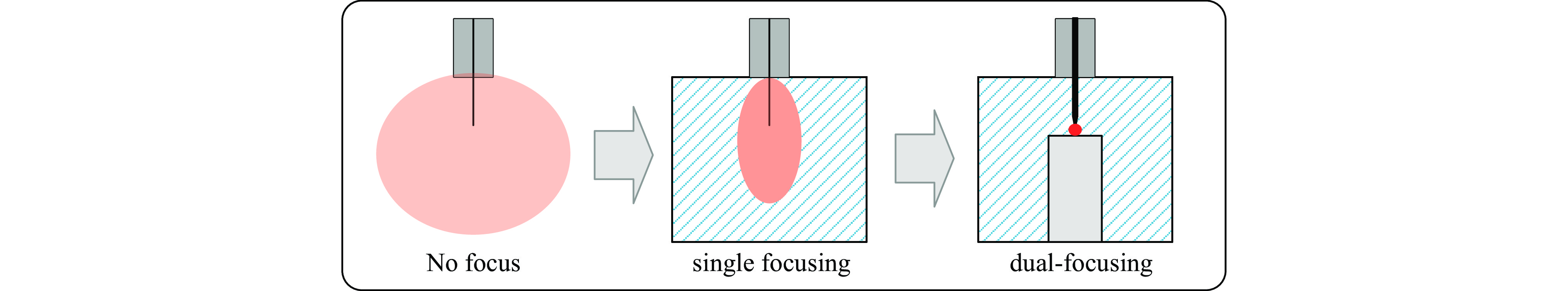
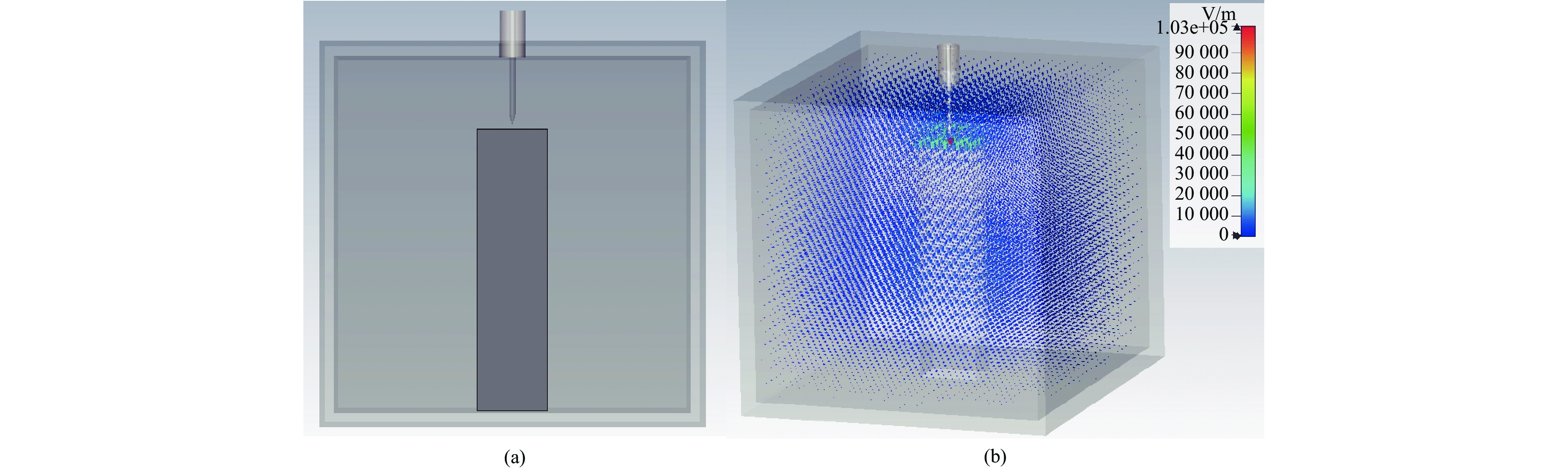
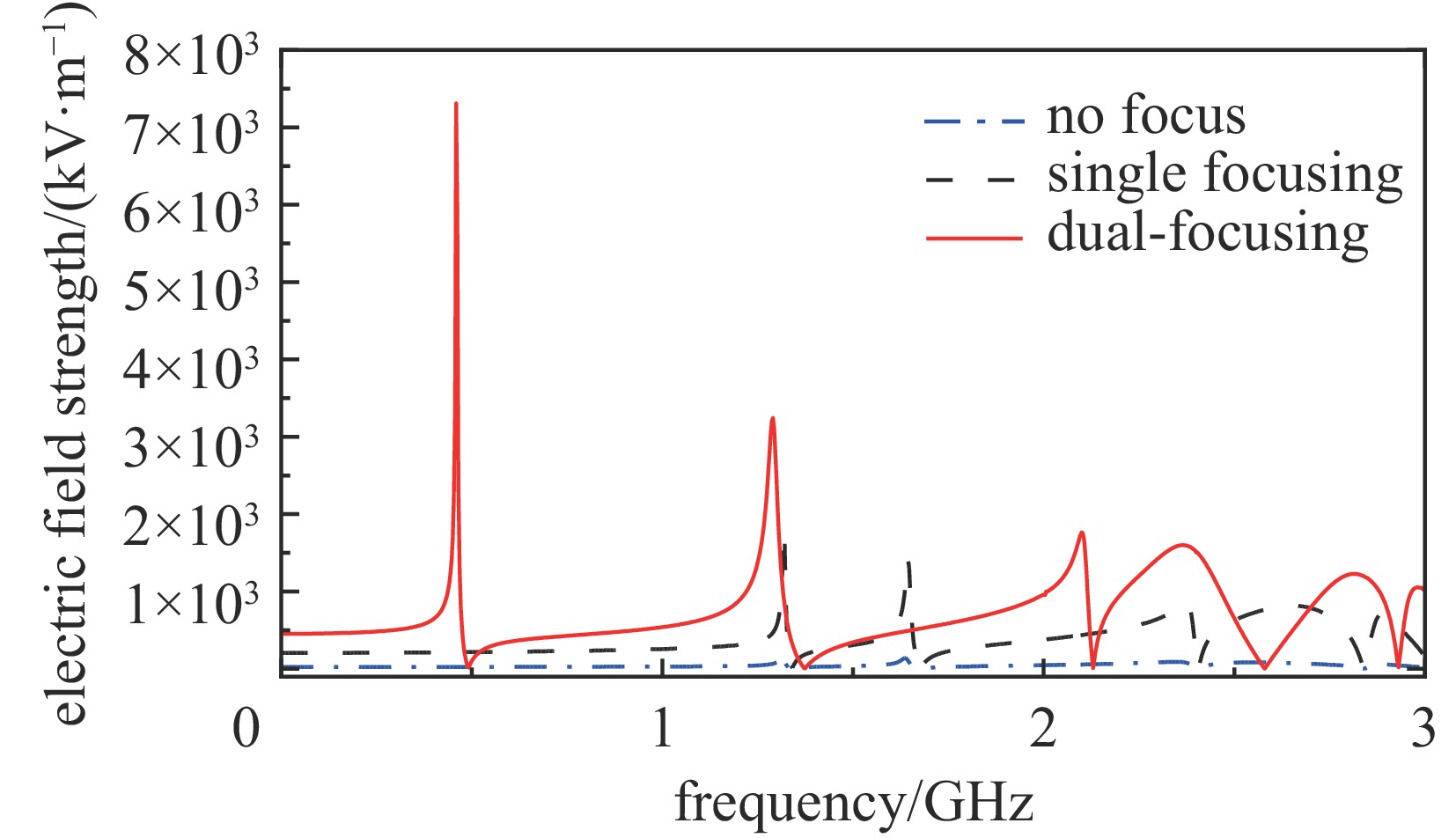
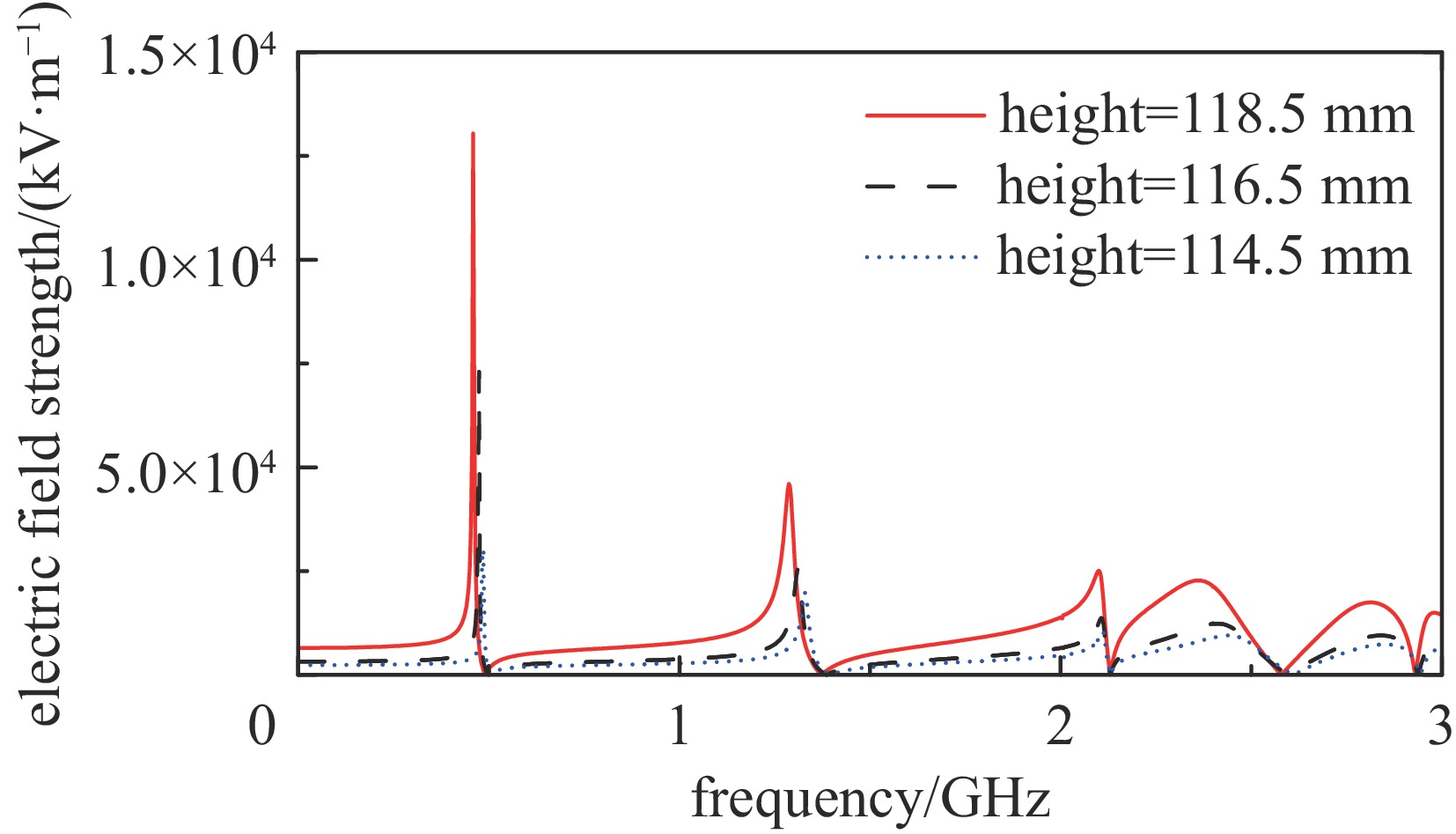
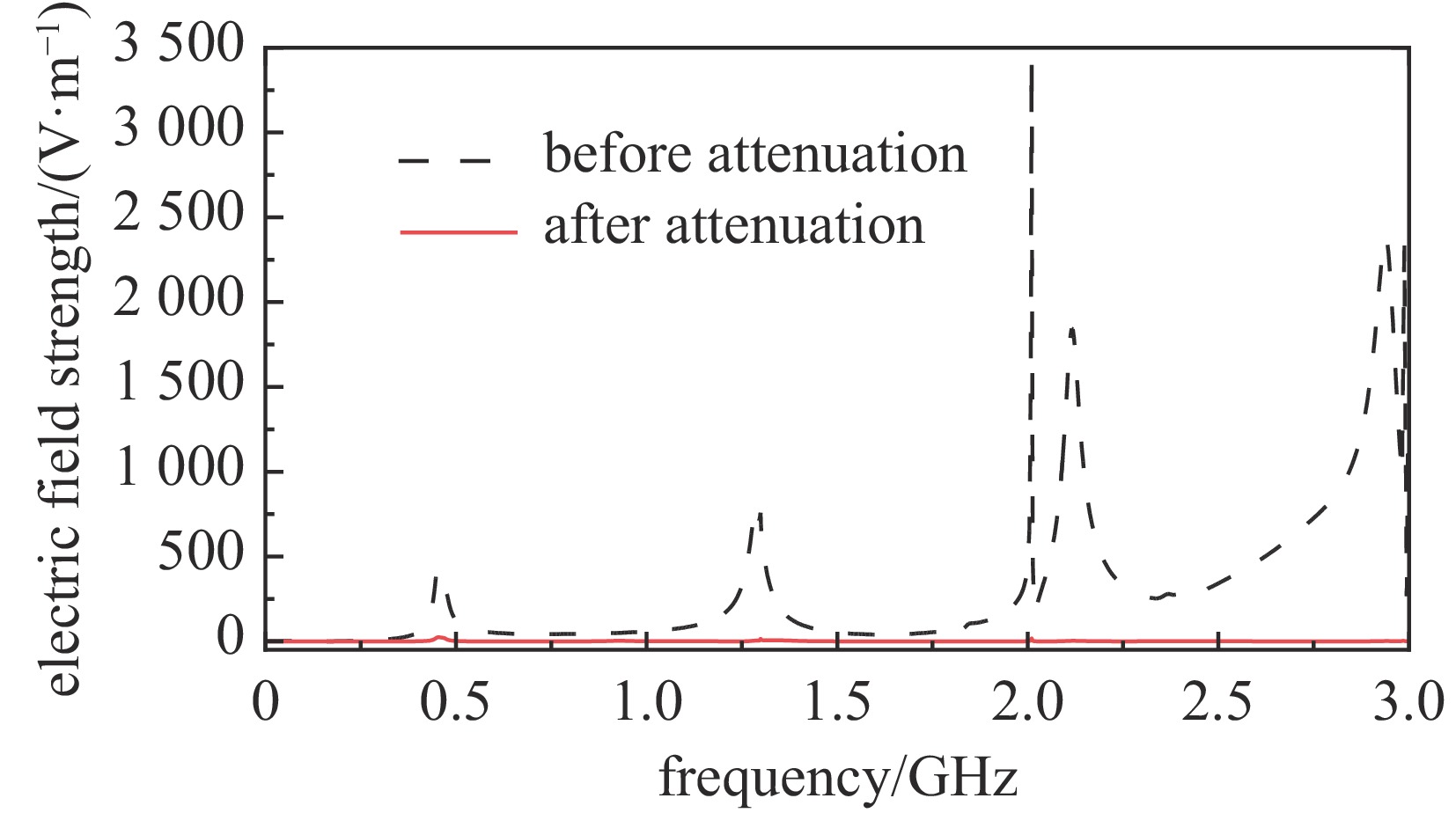
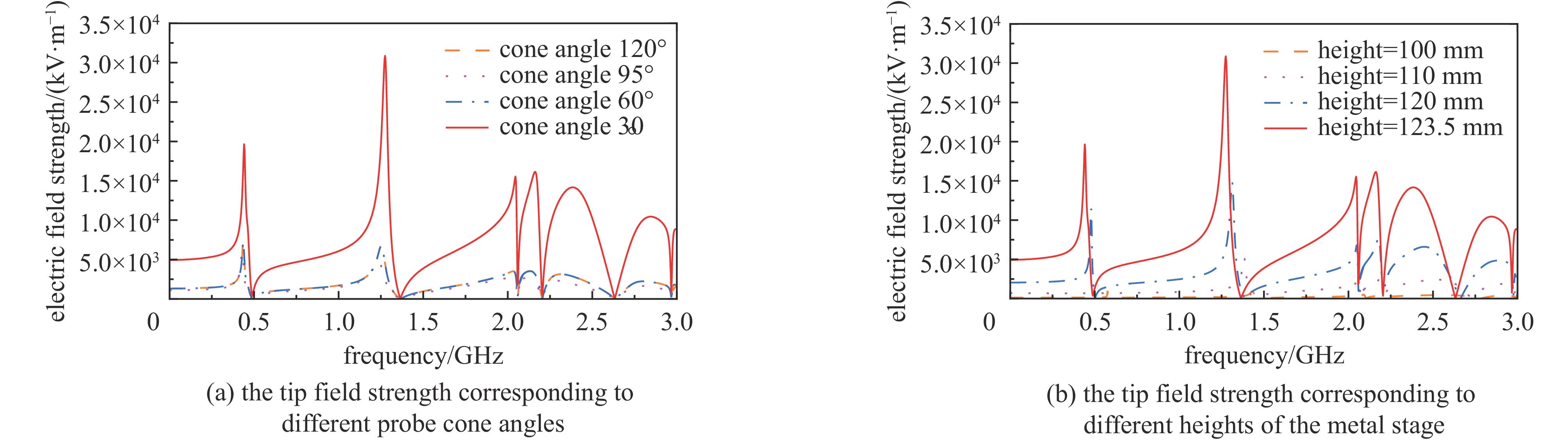
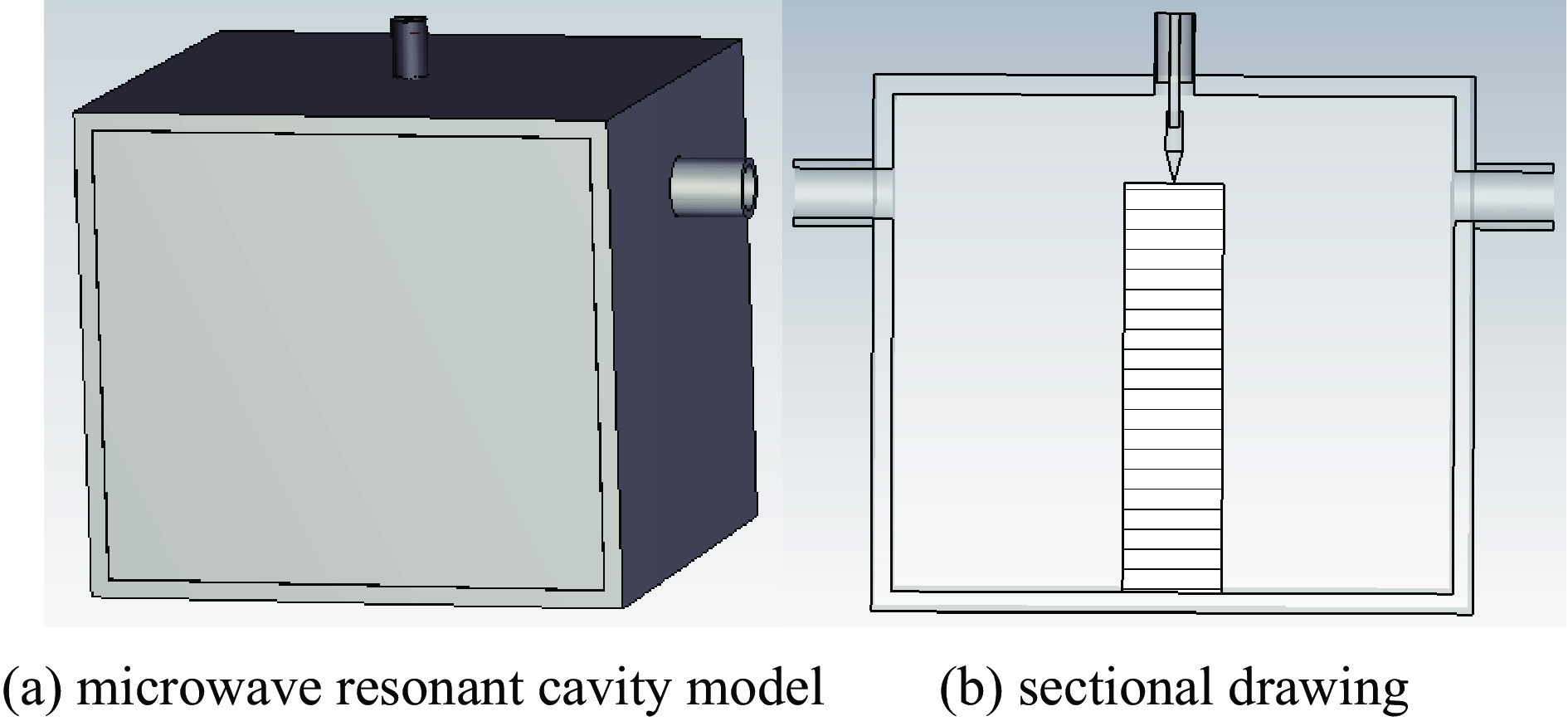
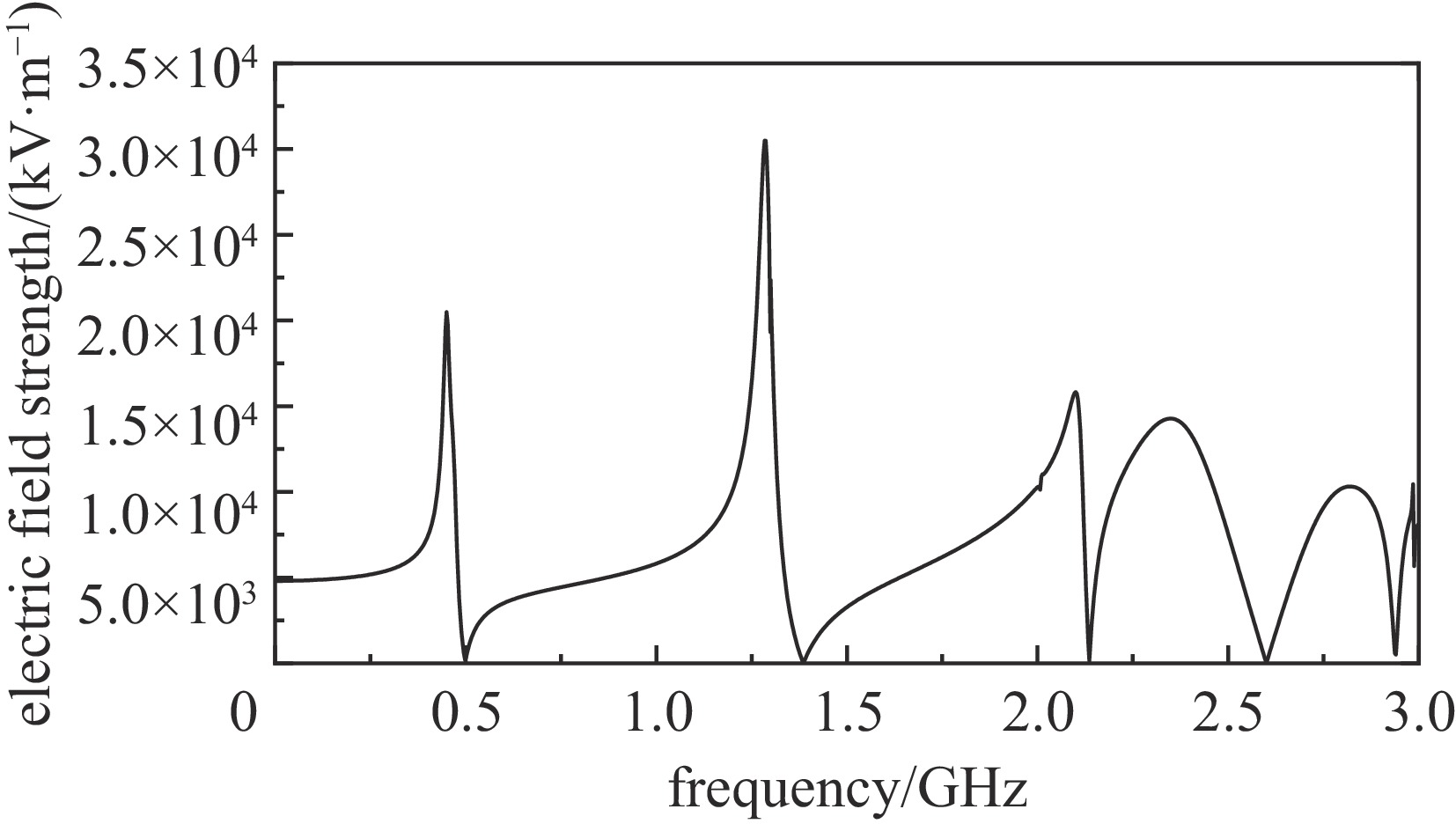
摘要: 为解决小功率条件下固体含能材料微波点火问题,提出了一种基于矩形谐振腔双聚焦优化设计的小功率高场强微波点火技术。研发的微波点火装置由固态微波源、矩形谐振腔、微波探针等部分构成。其中,矩形谐振腔采用探针馈电,通过谐振作用实现能量一次聚焦,结合探针尖端对电场的畸变作用及金属置物台对电场分布空间的压缩效应,实现对谐振时腔内能量二次聚焦,并通过电磁兼容设计防止电磁波泄露。仿真与试验表明:微波点火装置在2~3 GHz范围内具有多个工作频点且频率可调,22 W功率下最大场强可达MV/m级,并能实现对小粒黑火药的有效点火,与现有装置相比,点火功率大幅减小。研发的小功率高场强微波点火技术可为固体含能材料微波点火的研究提供平台。Abstract: In order to solve the problem of microwave ignition of solid energetic materials under low power conditions, this paper proposes a low-power high-field microwave ignition technology based on dual-focusing optimization design of rectangular resonant cavity. The developed microwave ignition device consists of a solid-state microwave source, a rectangular resonant cavity, a microwave probe and other parts. Among them, the rectangular resonant cavity is fed by a probe, and the energy is focused once by resonance. Combined with the distortion effect of the probe tip on the electric field and the compression effect of the metal stage on the electric field distribution space, the secondary focusing of the energy in the cavity during resonance is realized, and the electromagnetic compatibility design is used to prevent electromagnetic wave leakage. The simulation and experiment show that the microwave ignition device has multiple operating frequency points in the range of 2−3 GHz and the frequency is adjustable. The maximum field strength can reach MV/m level at 22 W power, and can realize the effective ignition of small black powder. Compared with the existing device, the ignition power is greatly reduced. The developed low-power and high-field microwave ignition technology can provide a platform for the study of microwave ignition of solid energetic materials.
-
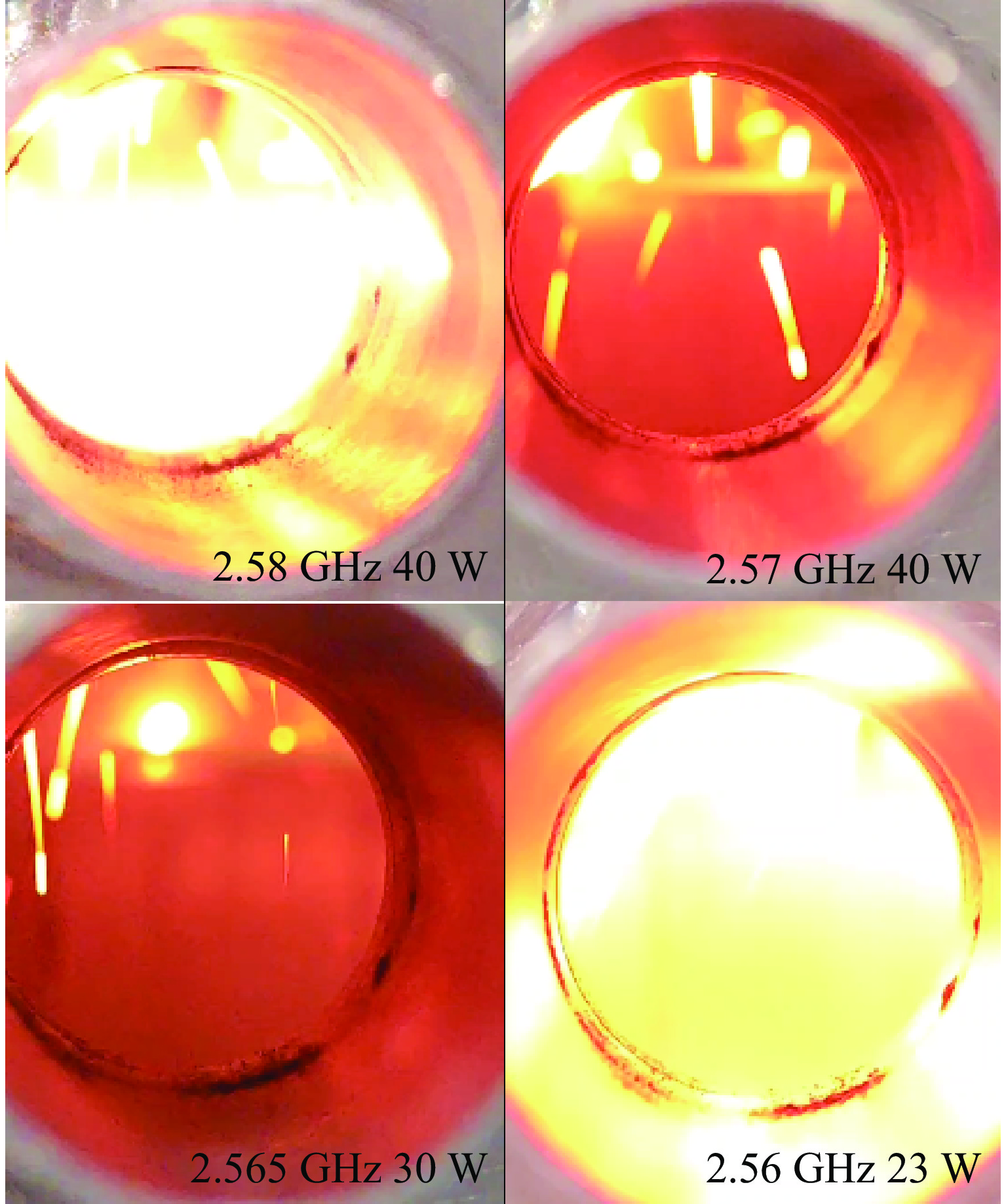
表 1 不同频点下微波点火试验现象
Table 1. Microwave ignition test phenomena at different frequencies
The frequency
of microwave source/
GHzThe power of
microwave
source/WIgnition
situation2.410 40 unignited 2.450 40 unignited 2.490 40 unignited 2.530 40 unignited 2.560 22 ignited 2.565 30 ignited 2.570 40 ignited 2.580 40 ignited -
[1] 严启龙, 刘林林. 含能材料前沿导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022Yan Qilong, Liu Linlin. Frontier introduction of energetic materials[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2022 [2] Daily M E, Glover B B, Son S F, et al. X-band microwave properties and ignition predictions of neat explosives[J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2013, 38(6): 810-817. doi: 10.1002/prep.201300068 [3] Ikuta K. Microwave ignition of wet explosives for hypervelocity[C]//Proceedings of the 2000 13th International Conference on High-Power Particle Beams. 2000: 909-913. [4] 刘鹤欣, 赵凤起, 秦钊, 等. 固体含能材料点火引燃技术研究进展[J]. 火炸药学报, 2023, 46(8):669-687Liu Hexin, Zhao Fengqi, Qin Zhao, et al. Research progress on ignition technologies of solid energetic materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2023, 46(8): 669-687 [5] 高勇. 典型材料高功率下微波介电特性研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2019Gao Yong. Research on microwave dielectric characteristics of typical material under high power level[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019 [6] 廖虹宇. 单质含能材料点火过程温度场与燃烧波测量方法研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2023Liao Hongyu. Research on measurement methods of temperature fields and combustion waves during ignition for single-mass energy-containing materials[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2023 [7] 马晗晔, 王雨时, 王光宇. 国外不敏感炸药综述[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2020, 41(5):166-174 doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2020.05.032Ma Hanye, Wang Yushi, Wang Guangyu. Summary of foreign insensitive explosives[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2020, 41(5): 166-174 doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2020.05.032 [8] 李天宇, 王雨时, 闻泉, 等. 钝感爆炸元件技术发展综述[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2019, 40(7):76-84 doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2019.07.016Li Tianyu, Wang Yushi, Wen Quan, et al. Summary of development of insensitive explosive elements[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2019, 40(7): 76-84 doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2019.07.016 [9] Meir Y, Jerby E. Thermite powder ignition by localized microwaves[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2012, 159(7): 2474-2479. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2012.02.015 [10] Alibay Z, Kline D J, Rehwoldt M C, et al. Mechanism of microwave-initiated ignition of sensitized energetic nanocomposites[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 415: 128657. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128657 [11] Kline D J, Rehwoldt M C, Turner C J, et al. Spatially focused microwave ignition of metallized energetic materials[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 127: 055901. doi: 10.1063/1.5134089 [12] Barkley S J, Lawrence A R, Zohair M, et al. Smart electromagnetic thermites: GO/rGO nanoscale thermite composites with thermally switchable microwave ignitability[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(33): 39678-39688. [13] Cheng Jian, Zhang Zehua, Li Fuwei, et al. Microwave ignition characteristics and distinction of typical nanothermites under different electromagnetic radiation[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2024, 260: 113217. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2023.113217 [14] Tang Kui, Chen Xiaoyuan, Tang Zhenhua, et al. Ignition performance and mechanism of Ti/CuFe2O4 composites with high microwave sensitivity[J]. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(17): 29256-29267. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.05.221 [15] Cheng Jian, Zhang Zehua, Wang Yueting, et al. Doping of Al/CuO with microwave absorbing Ti3C2 MXene for improved ignition and combustion performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 138375. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138375 [16] 岳雅楠. 微波等离子体点火研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020Yue Ya’nan. Research on microwave plasma ignition[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020 [17] 郑良岑. 微波多点点火研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2022Zheng Liangcen. Research on multipoint ignition by microwave[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022 [18] 涂兆正. 基于同轴谐振腔的微波点火技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2022Tu Zhaozheng. Research on microwave ignition technology based on coaxial resonator[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022 [19] Pozar D M. 微波工程[M]. 2版. 谭云华, 译. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2019: 217-249Pozar D M. Microwave engineering[M]. 2nd ed. Tan Yunhua, trans. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2019: 217-249 [20] 吴明英, 毛秀华. 微波技术[M]. 西安: 西北电讯工程学院出版社, 1985: 193-194Wu Mingying, Mao Xiuhua. Microwave technology[M]. Xi’an: Northwest Telecommunication Engineering College Press, 1985: 193-194 [21] 卢言. 小型化铷原子频标中微波谐振腔的研究与设计[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021Lu Yan. Research and design of the microwave cavity in rubidium atomic frequency standard for miniaturization[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021 -




 下载:
下载: