Ross pair-filters stack mixed spectrometer for hard x-ray detection
-
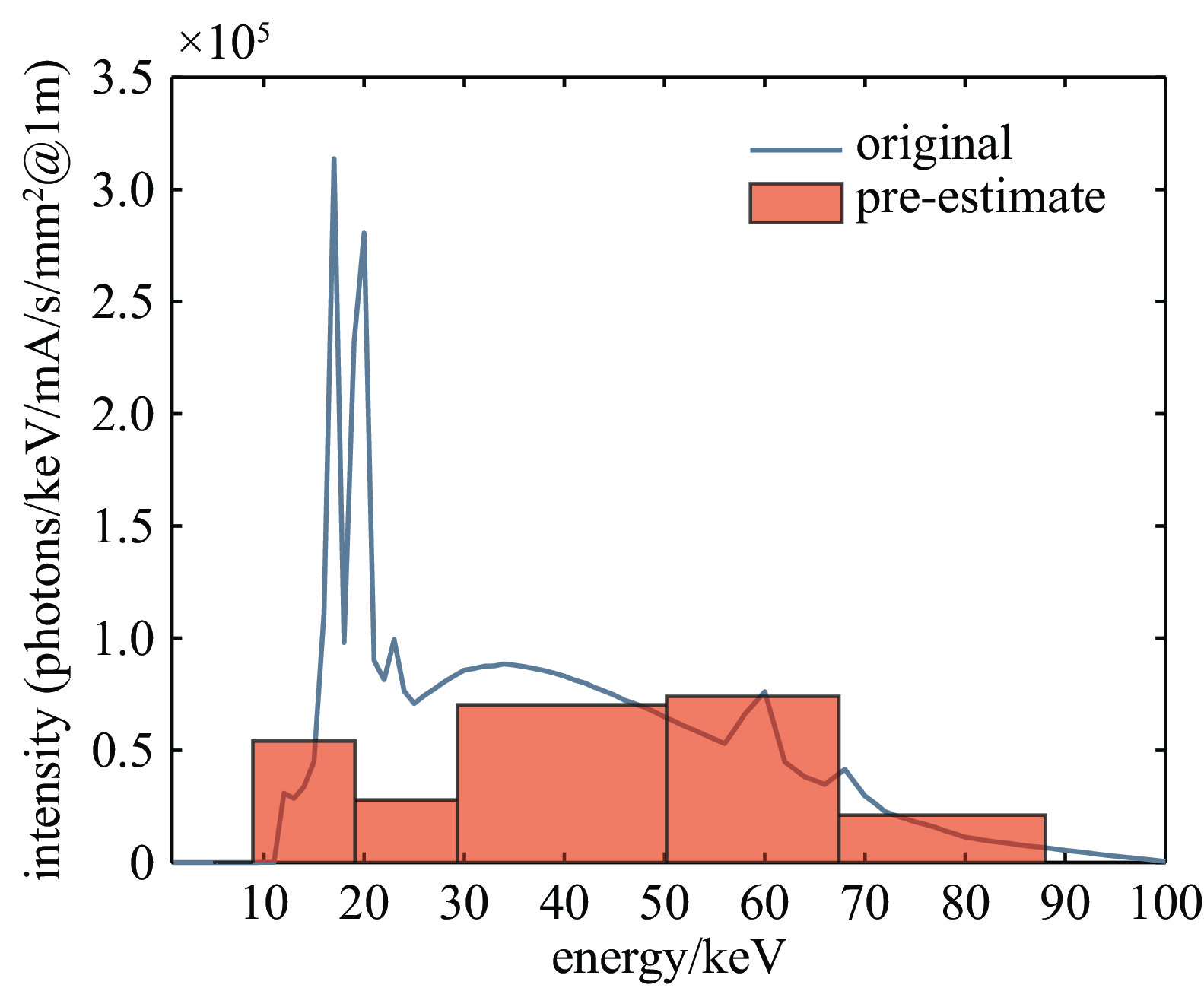
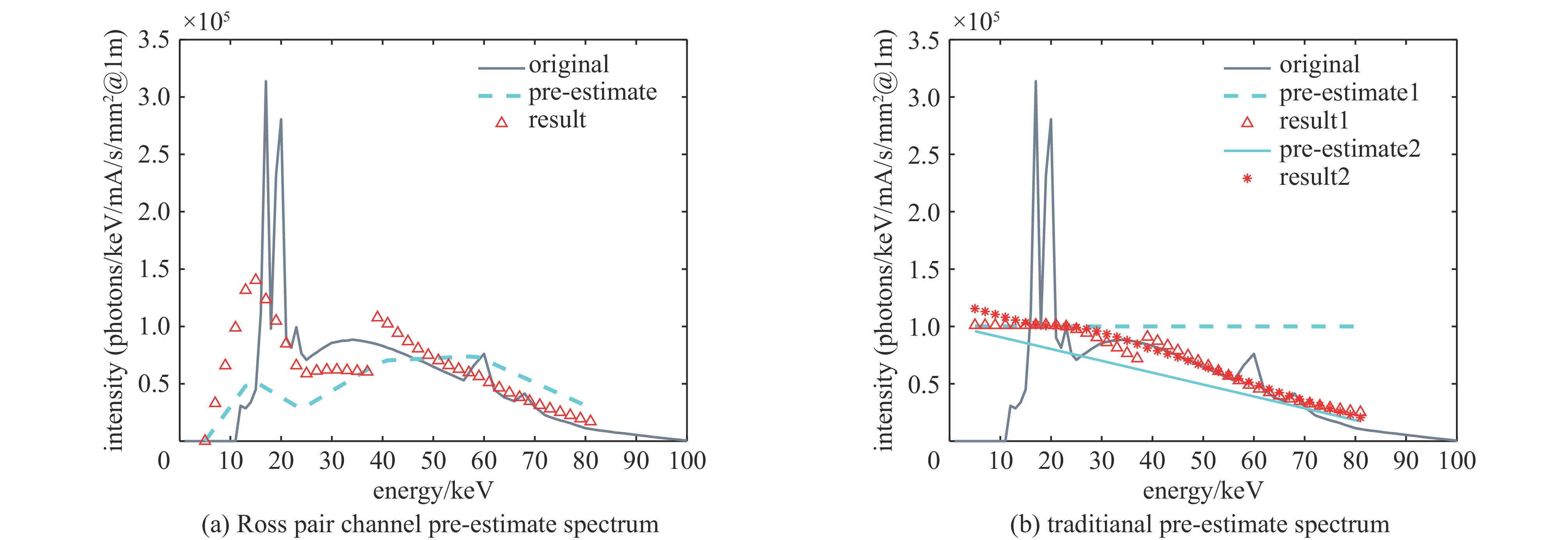
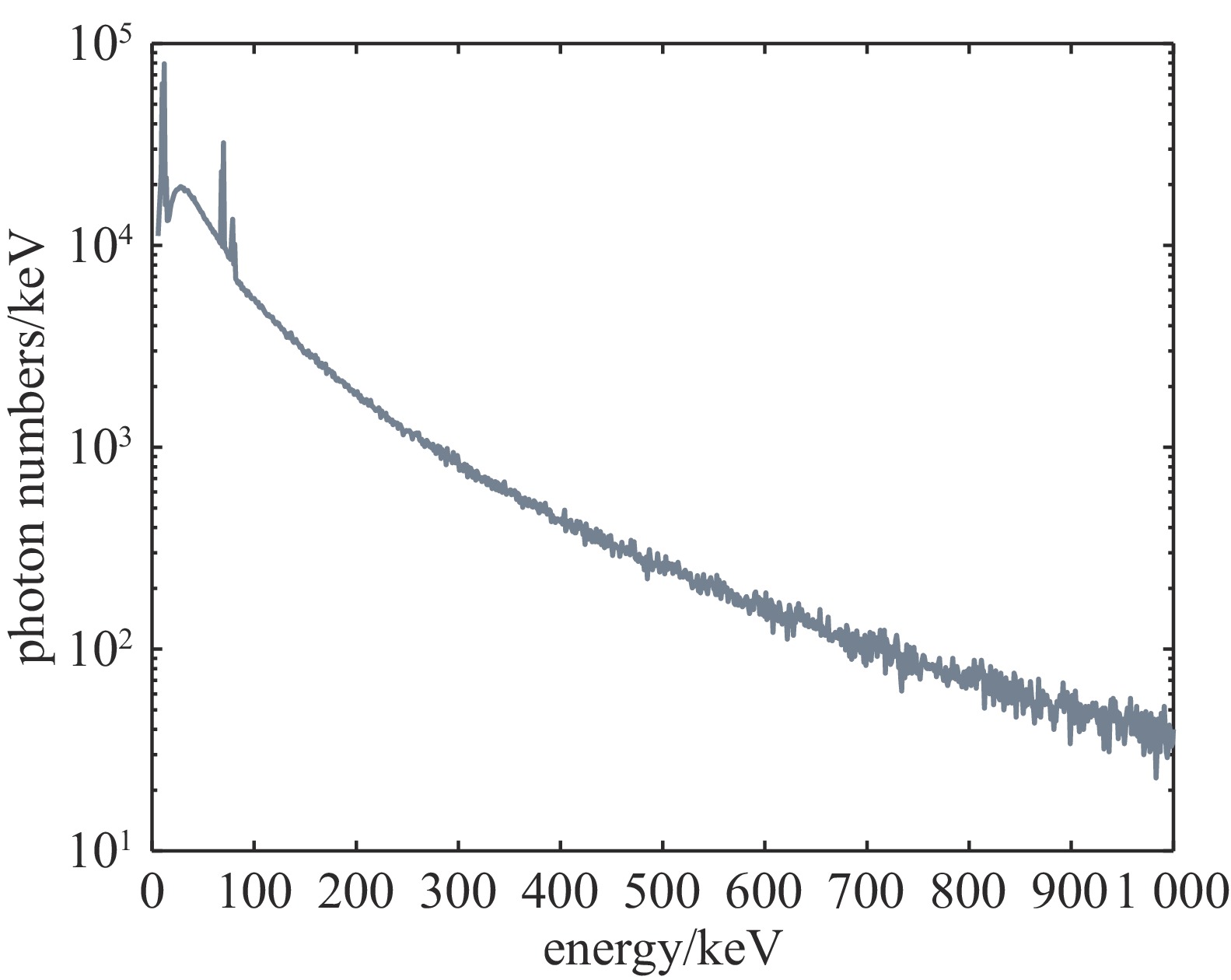
摘要: 罗斯对和滤片堆栈谱仪常被用于探测硬X射线光谱,但滤片堆栈谱仪的结果对预估谱形状十分敏感,而罗斯对只能给出离散的分立谱。发展了一种罗斯对滤片堆栈混合谱仪,结合了传统滤片堆栈谱仪和罗斯对的优点,将传统堆栈谱仪的每一层滤片都换成一对滤片构成的罗斯对,这样可以利用罗斯对测到的离散分立光谱作为预估谱,输入到堆栈通道的解谱程序中求解出整个X射线光谱。数值实验和使用X光机进行的测试都显示,这种罗斯对滤片堆栈混合谱仪相较于传统滤片堆栈谱仪能给出更准确的光谱结构,其紧凑轻便的优势在硬X射线光谱测量中有广泛的应用前景。Abstract: Ross pair and filters stack spectrometers are commonly used to detect hard X-ray spectrum. The results of filters stack spectrometer are highly sensitive to the profile of pre-estimated spectrum, while Ross pair is limited to discrete spectrum. Here we provide a Ross pair- filters stack mixed spectrometer, which combining the advantages of traditional filter stack spectrometers and Ross pairs. Each layer of the filter in the traditional filters stack spectrometer has been replaced with a Ross filters pair. Thus the discrete spectrum given by Ross pair can be used as the pre-estimated spectrum for the filters stack to solve the entire x-ray spectrum. Numerical and physical experiments using x-ray tube confirm that the present mixed spectrometer can provide more accurate spectral structures compared to traditional filter stack spectrometers. The compact and lightweight advantages make it widely applicable in hard x-ray spectral measurements.
-
Key words:
- hard X-ray detect /
- spectral diagnosis /
- filters stack spectrometer /
- Ross pair /
- Monte Carlo simulation
-
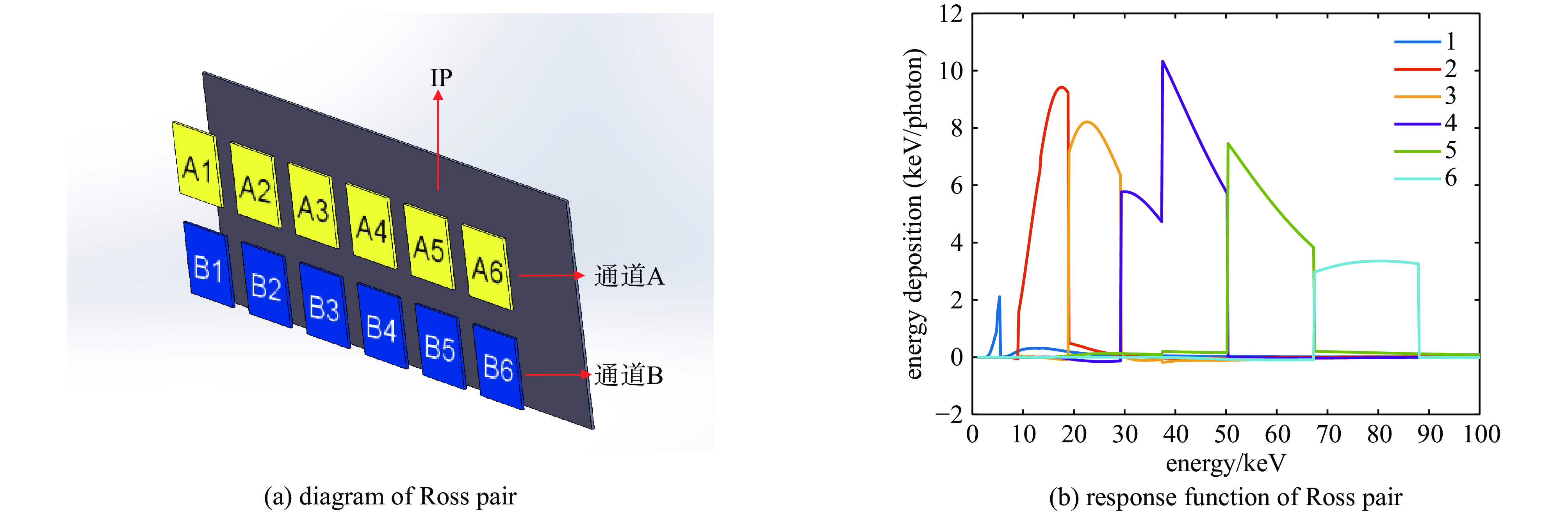
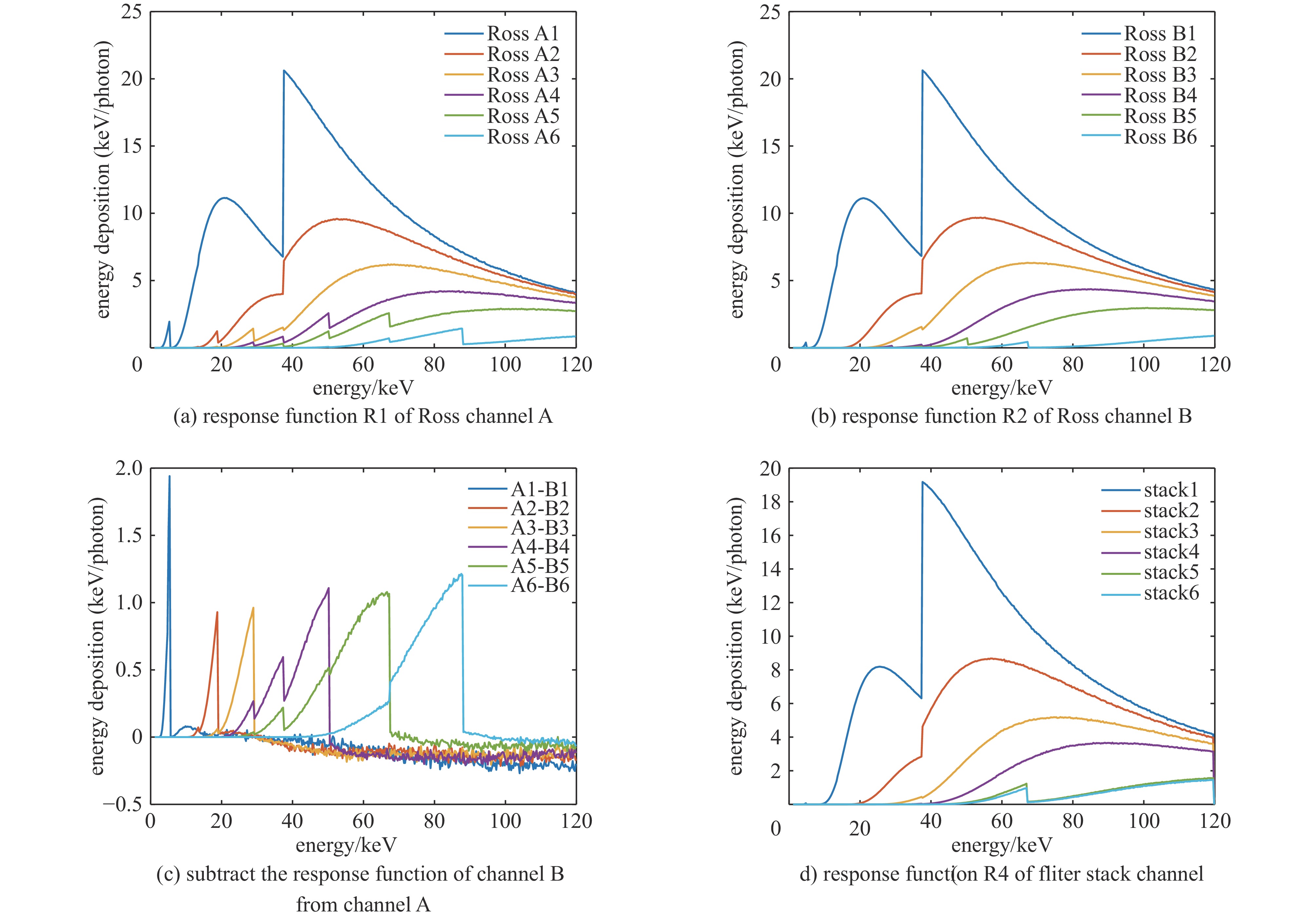
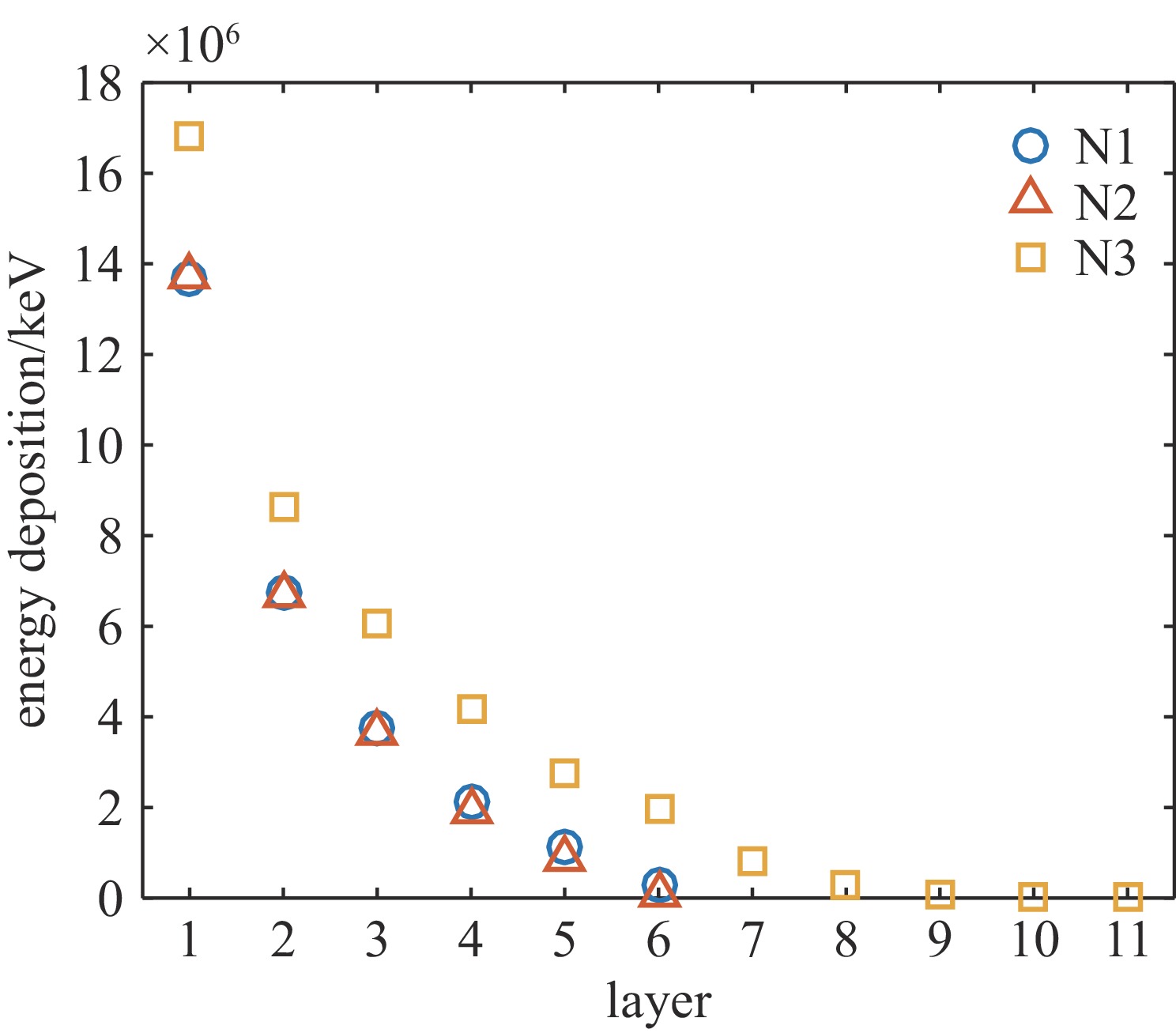
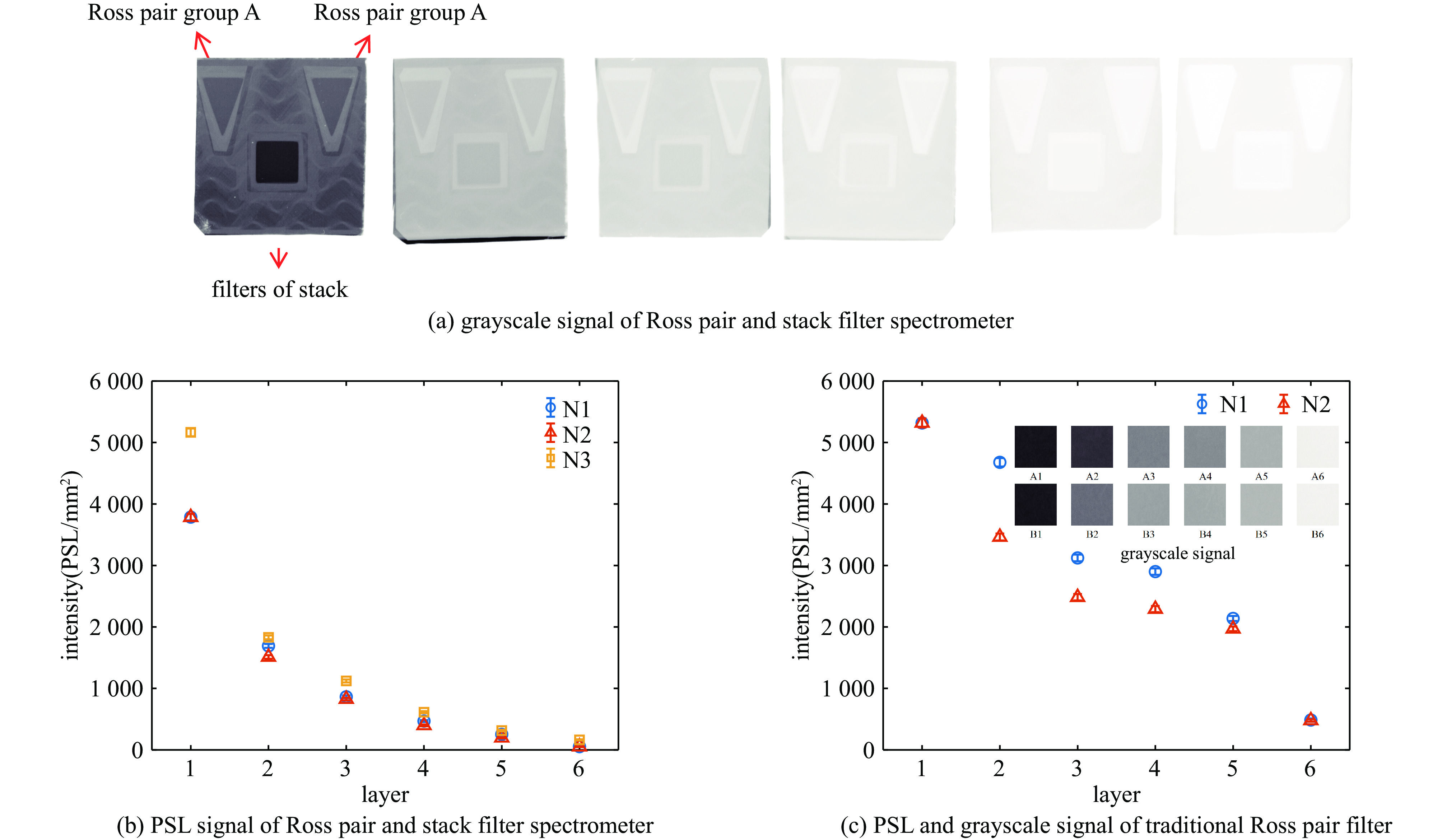
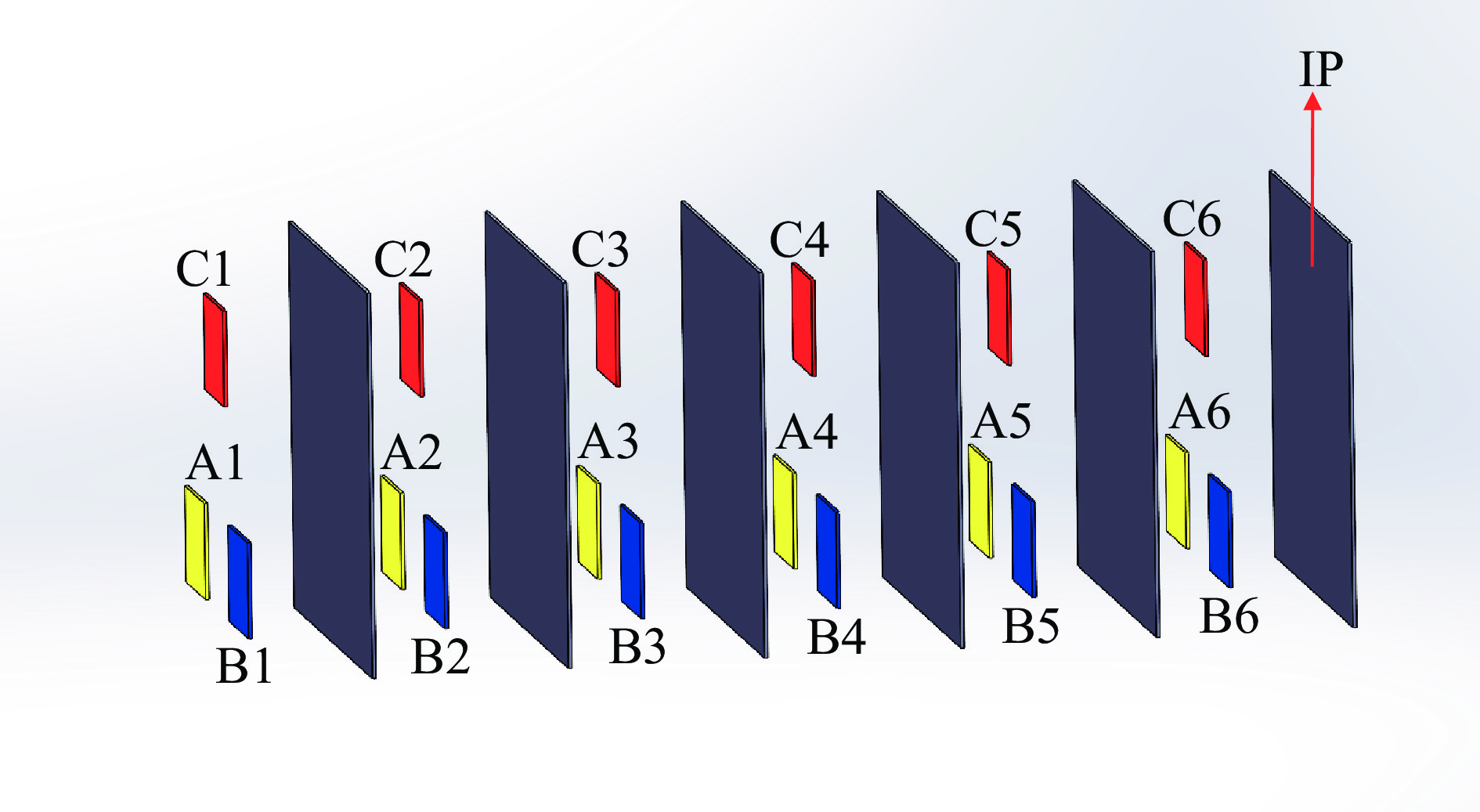
表 1 罗斯对滤片堆栈混合谱仪各通道滤片材料和厚度
Table 1. Filter materials and thickness of Ross pair- filter stack mixed spectrometer
No. material of channel
A filtersthickness of channel
A filters/μmmaterial of channel
B filtersthickness of channel
B filters/μmmaterial of channel
C filtersthickness of channel
C filters/μm1 V 20.99 Ti & Al 29.49 & 20 Al 50 2 Nb 19.93 Cu & Al 46.72 & 20 Ti 100 3 Sn 41 Nb & Al 53.37 & 80 Ti 100 4 Gd 51.20 Sn & Al 94.04 & 276.49 Cu 100 5 Ta 34.96 Gd & Al 102.4 & 355.66 Mo 100 6 Pb 285.52 Ta & Cu 246.48 & 93.44 Ag 100 表 2 低能X光测谱数值实验混合谱仪和传统堆栈谱仪的测谱准确度
Table 2. Spectral accuracy for low energy x-ray spectral detection
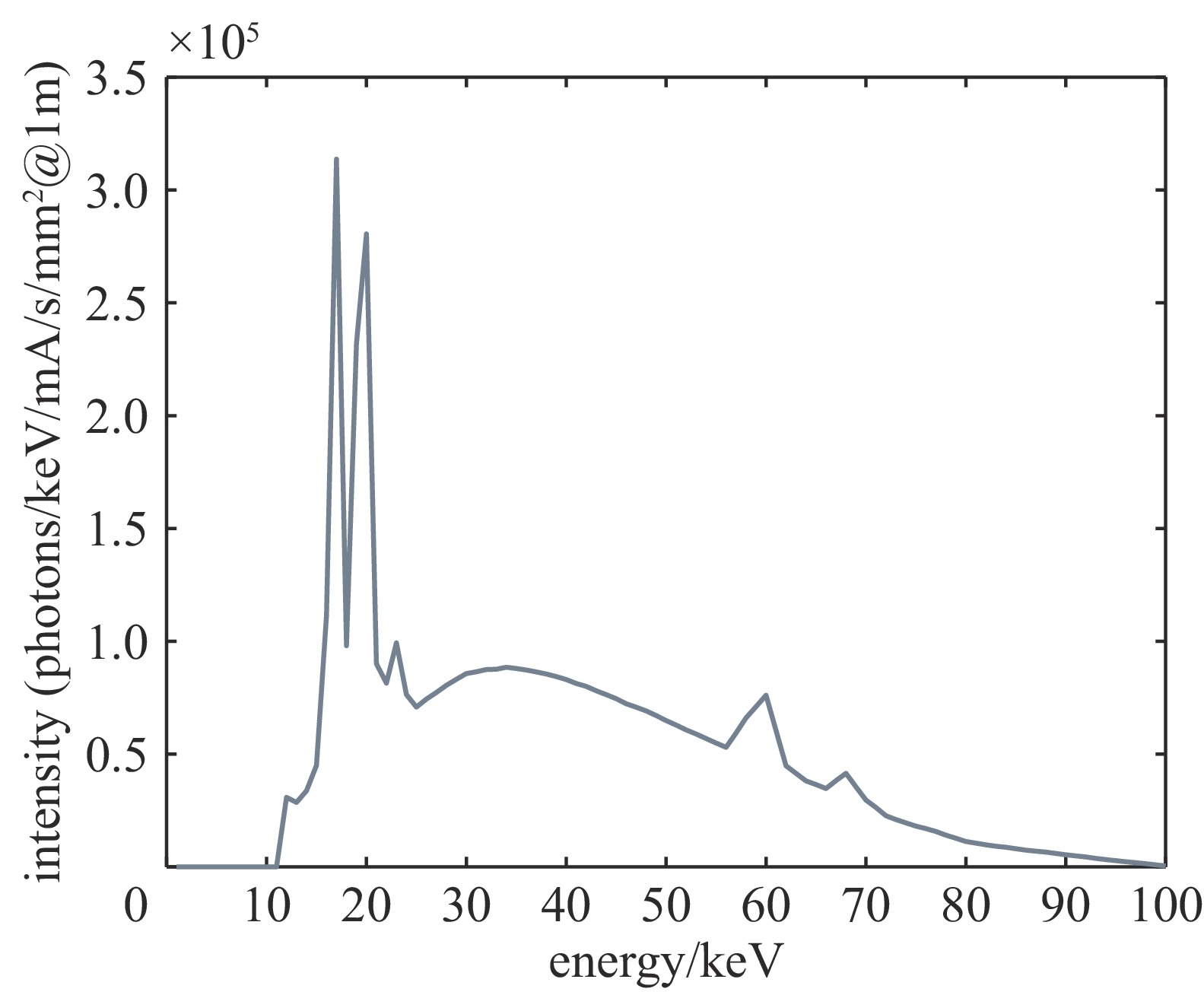
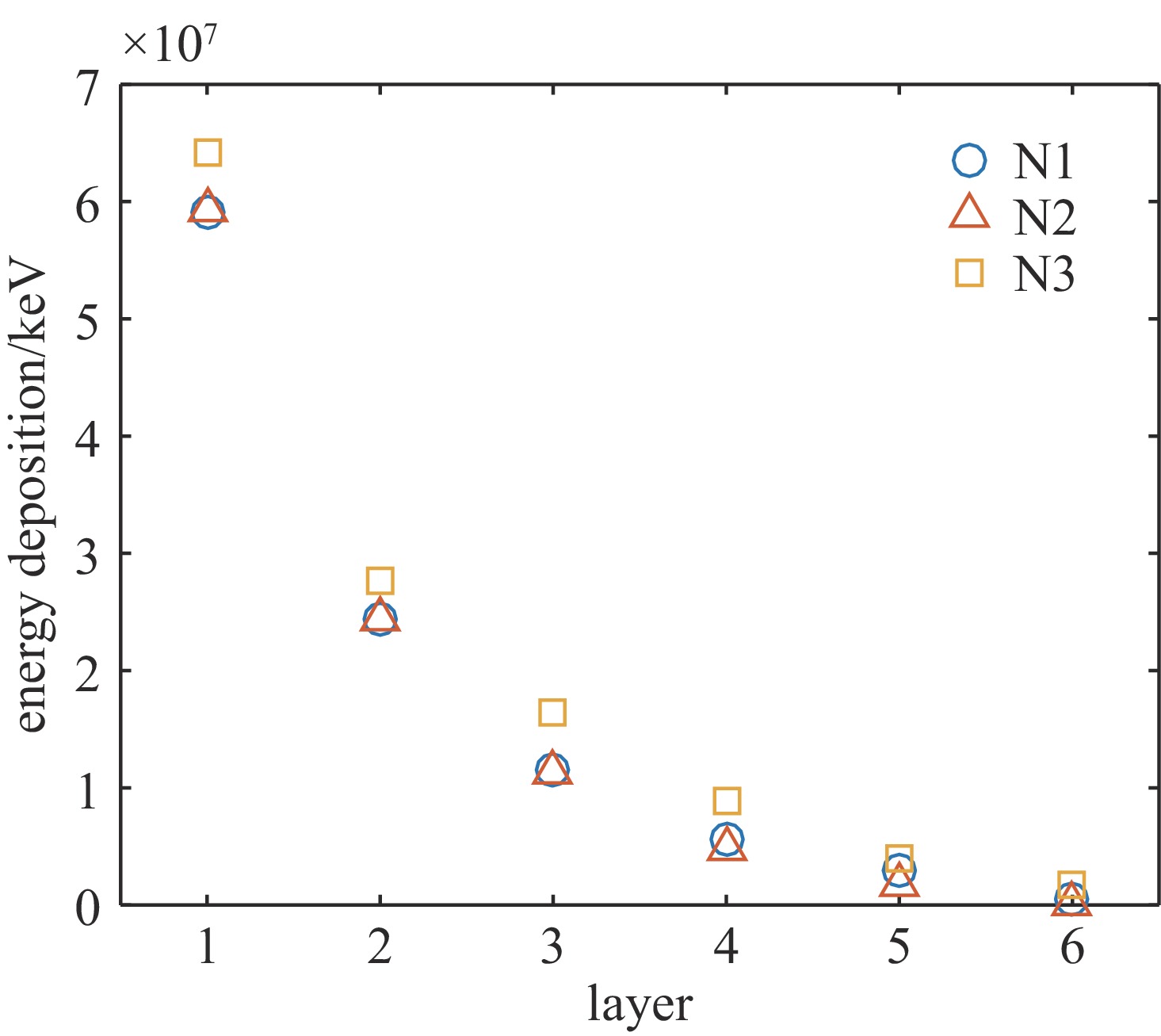
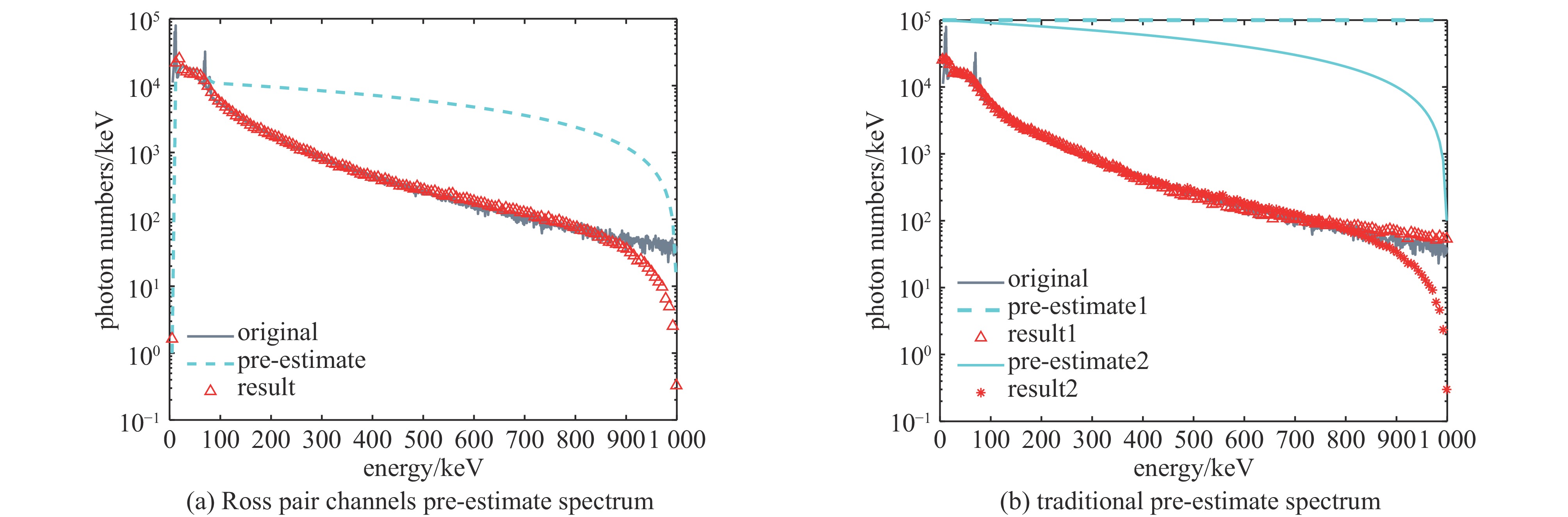
pre-estimate spectrum Ross pair- filters stack mixed spectrometer traditional filters stack 1 traditional filters stack 2 Spectral accuracy
(sum of squared differences)9.0059e+10 1.2749e+11 1.1709e+11 表 3 高能X光测谱数值实验的滤片堆栈通道的滤片材料和厚度
Table 3. Filter material and thickness of filters stacked channel for high energy x-ray spectral detection
No. material of filters thickness of filters /μm 1 Al 50 2 Ti 100 3 Ti 100 4 Cu 100 5 Mo 100 6 Ag 100 7 Sn 1000 8 Sn 3000 9 Ta 2000 10 Ta 4000 11 Ta 6000 表 4 高能X光测谱数值实验中混合谱仪和传统堆栈谱仪的测谱准确度
Table 4. Spectral accuracy for high energy x-ray spectral detection
pre-estimate spectrum Ross pair- filters stack mixed spectrometer traditional filters stack 1 traditional filters stack 2 spectral accuracy
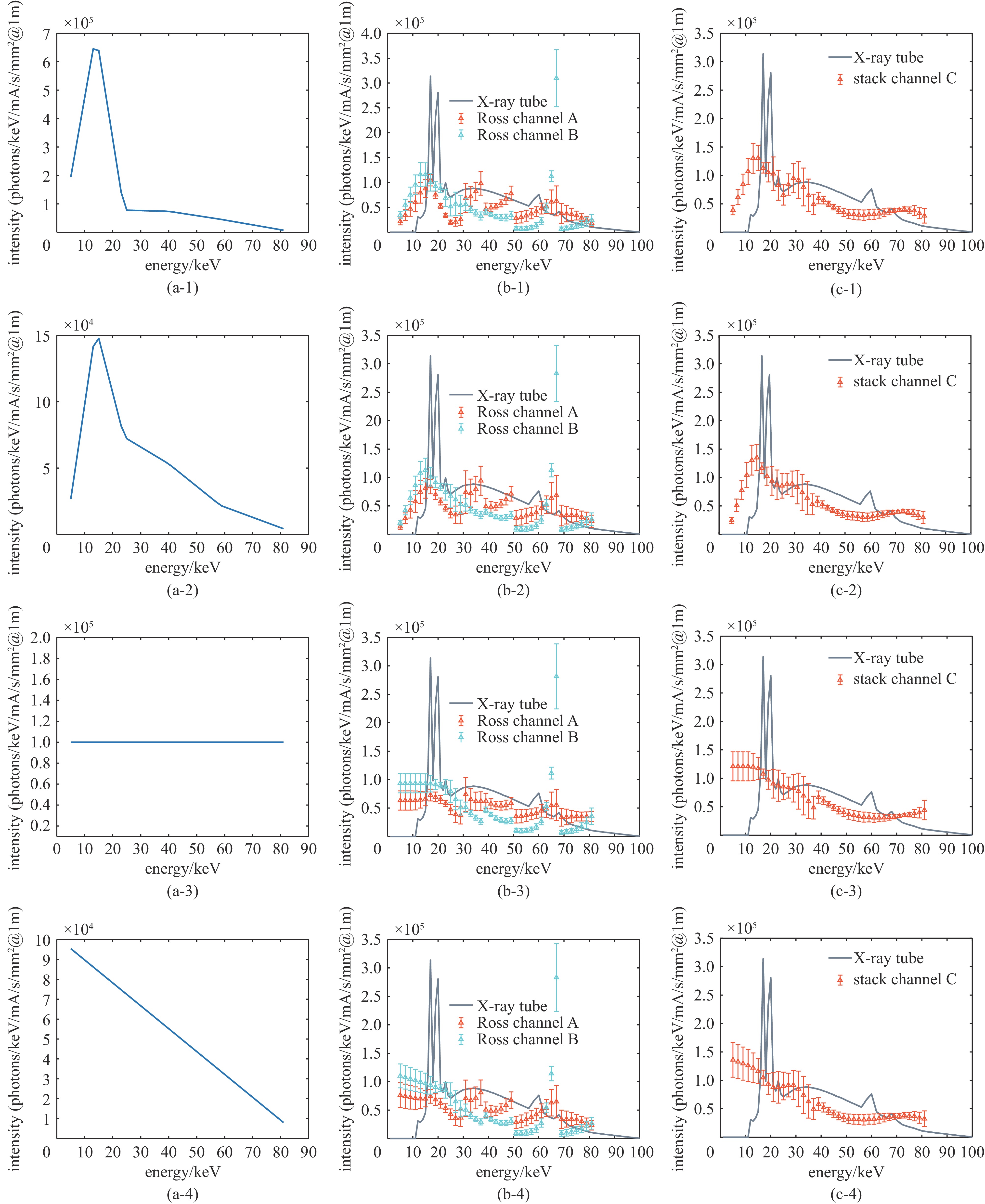
(sum of squared differences)3.5253e+9 3.7512e+9 3.7582e+9 表 5 在钨X光机上的实验中混合谱仪和传统堆栈谱仪的测谱准确度
Table 5. Spectral accuracy for Tungsten X-ray tube spectral detection
pre-estimate
spectrumRoss pair- filters stack
mixed spectrometertraditional Ross
pairtraditional filters
stack 1traditional filters
stack 2spectral accuracy
(sum of squared differences)1.1267e+11 1.0822e+11 1.4294e+11 1.6062e+11 -
[1] Hurricane O A, Patel P K, Betti R, et al. Physics principles of inertial confinement fusion and U. S. program overview[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2023, 95: 025005. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.95.025005 [2] Dimitri B. Inertial confinement fusion: recent results and perspectives[J]. EPJ Web of Conferences, 2024, 310: 00013. doi: 10.1051/epjconf/202431000013 [3] Park H S, Maddox B R, Giraldez E, et al. High-resolution 17-75 keV backlighters for high energy density experiments[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2008, 15: 072705. doi: 10.1063/1.2957918 [4] Yang Tao, Hu Guangyue, Yuan Peng, et al. Abnormal spectral distortion of a silicon sensor-based single photon counting charge coupled device (PIXIS-XB: 1300R) in detecting laser plasma x-ray source of 20-100 keV[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2019, 61: 095008. doi: 10.1088/1361-6587/ab3310 [5] 张双根, 黄文忠, 谷渝秋, 等. 用于激光等离子体中X射线测量的单光子计数型CCD的标定[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2006, 18(1):77-80Zhang Shuanggen, Huang Wenzhong, Gu Yuqiu, et al. Calibration of single-photon counting X-ray CCD[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2006, 18(1): 77-80 [6] 熊勇, 黄文忠, 张双根, 等. 光子计数型CCD测量激光等离子体X射线[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2007, 19(2):271-273Xiong Yong, Huang Wenzhong, Zhang Shuanggen, et al. Measurement of X ray in interaction of laser plasmas by photon counting CCD[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2007, 19(2): 271-273 [7] 闫永宏, 赵宗清, 吴玉迟, 等. 单光子计数型CCD的蒙特卡罗模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(1):211-214 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132501.0211Yan Yonghong, Zhao Zongqing, Wu Yuchi, et al. Monte Carlo simulation on single photon counting charge coupled device[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(1): 211-214 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132501.0211 [8] Yan Yonghong, Wei Lai, Wen Xianlun, et al. Calibration and Monte Carlo simulation of a single-photon counting charge-coupled device for single-shot X-ray spectrum measurements[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2013, 11: 110401. doi: 10.3788/col201311.110401 [9] Hudson L T, Henins A, Deslattes R D, et al. A high-energy x-ray spectrometer diagnostic for the OMEGA laser[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2002, 73(6): 2270-2275. doi: 10.1063/1.1476715 [10] Yu Minghai, Hu Guangyue, An Ning, et al. Hard x-ray transmission curved crystal spectrometers (10-100 keV) for laser fusion experiments at the ShenGuang-III laser facility[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2016, 4: e2. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2015.36 [11] Chen C D, King J A, Key M H, et al. A Bremsstrahlung spectrometer using k-edge and differential filters with image plate dosimeters[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2008, 79: 10E305. doi: 10.1063/1.2964231 [12] 于明海, 谭放, 闫永宏, 等. 用于激光产生的高能X射线源能谱诊断的滤片堆栈谱仪的研制[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2017, 51(6):1090-1095 doi: 10.7538/yzk.2017.51.06.1090Yu Minghai, Tan Fang, Yan YongHong, et al. Development of filter stack spectrometer for spectrum measurement of X ray generated by laser[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2017, 51(6): 1090-1095 doi: 10.7538/yzk.2017.51.06.1090 [13] Maddox B R, Park H S, Remington B A, et al. High-energy x-ray backlighter spectrum measurements using calibrated image plates[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2011, 82: 023111. doi: 10.1063/1.3531979 [14] Wen JiaXing, Ma Ge, Yu Minghai, et al. Optimized online filter stack spectrometer for ultrashort X-ray pulses[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2024, 35: 48. doi: 10.1007/s41365-024-01391-8 [15] Song Honghu, Wu Zhen, Zhang Hui, et al. A simulation optimization design of the filter stack spectrometer for laser-plasma interaction experiment[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2023, 18: P03012. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/18/03/P03012 [16] Meadowcroft A L, Bentley C D, Stott E N. Evaluation of the sensitivity and fading characteristics of an image plate system for x-ray diagnostics[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2008, 79: 113102. doi: 10.1063/1.3013123 [17] Alvarez M A, Wolfe B T, Wong C S, et al. Machine learning based unfolding of x-ray spectra from filter stack spectrometer data[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2024, 95: 085101. doi: 10.1063/5.0216759 [18] 肖庭延, 于慎根, 王彦飞. 反问题的数值解法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003Xiao Tingyan, Yu Shengen, Wang Yanfei, et al. Numerical Methods for Inverse Problems[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003 [19] Matzke M. Unfolding of particle spectra[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 2867, International Conference Neutrons in Research and Industry. 1997: 598-607. [20] Reginatto M. Overview of spectral unfolding techniques and uncertainty estimation[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2010, 45(10): 1323-1329. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2010.06.016 [21] Agostinelli S, Allison J, Amako K, et al. GEANT4—a simulation toolkit[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2003, 506(3): 250-303. [22] Allison J, Amako K, Apostolakis J, et al. Geant4 developments and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2006, 53(1): 270-278. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2006.869826 [23] Allison J, Amako K, Apostolakis J, et al. Recent developments in GEANT4[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2016, 835: 186-225. [24] del Río M S, Dejus R J. Status of XOP: an x-ray optics software toolkit[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5536, Advances in Computational Methods for X-Ray and Neutron Optics. 2004: 171-174. [25] del Río M S, Dejus R J. XOP 2.1—a new version of the x-ray optics software toolkit[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2004, 705(1): 784-787. [26] Boone J M, Seibert J A. Accurate method for computer-generating tungsten anode x-ray spectra from 30 to 140 kV[J]. Medical Physics, 1997, 24(11): 1661-1670. doi: 10.1118/1.597953 [27] Tommasini R, Park H S, Patel P, et al. Development of Compton radiography using high-Z backlighters produced by ultra-intense lasers[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2007, 926(1): 248-258. [28] Malka G, Miquel J L. Experimental confirmation of ponderomotive-force electrons produced by an ultrarelativistic laser pulse on a solid target[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(1): 75-78. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.75 [29] Haines M G, Wei M S, Beg F N, et al. Hot-electron temperature and laser-light absorption in fast ignition[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102: 045008. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.045008 -




 下载:
下载: