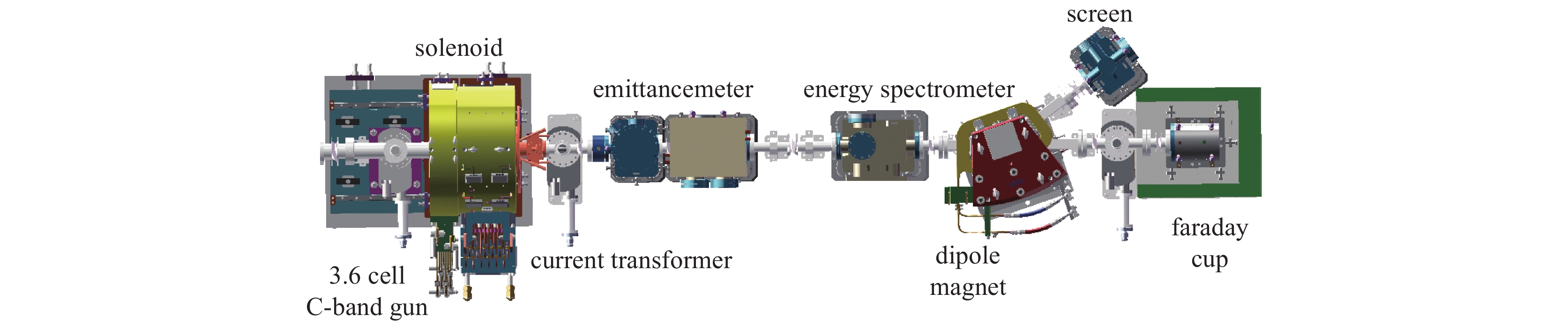
Design of an emittance measurement device for the C-band photocathode RF gun
-
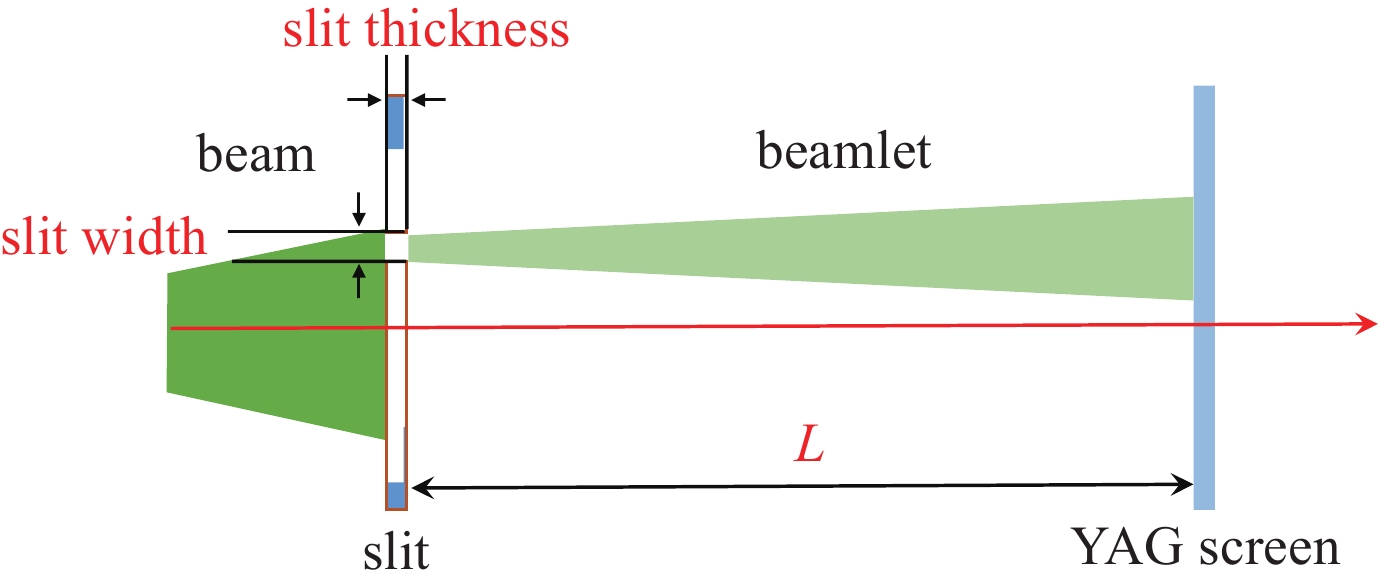
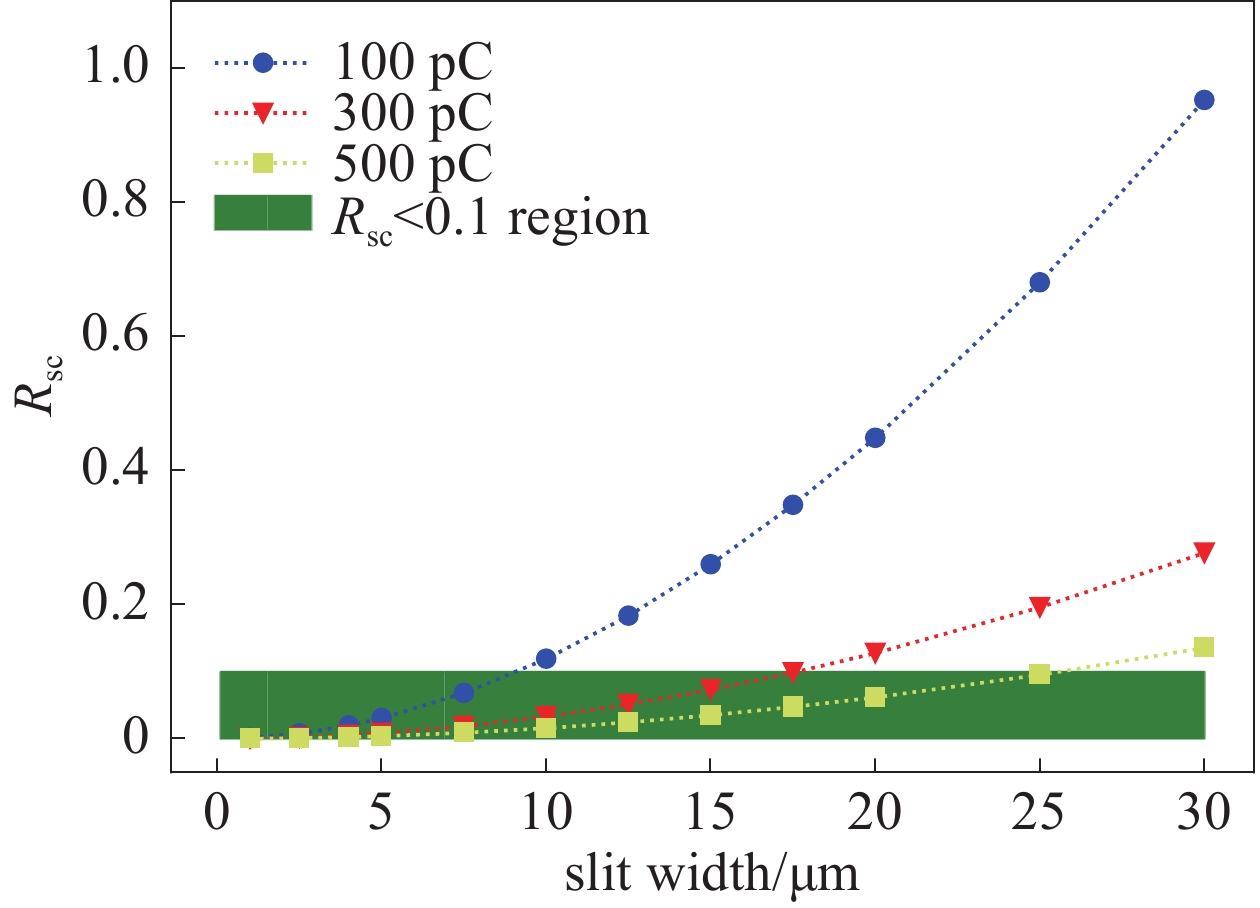
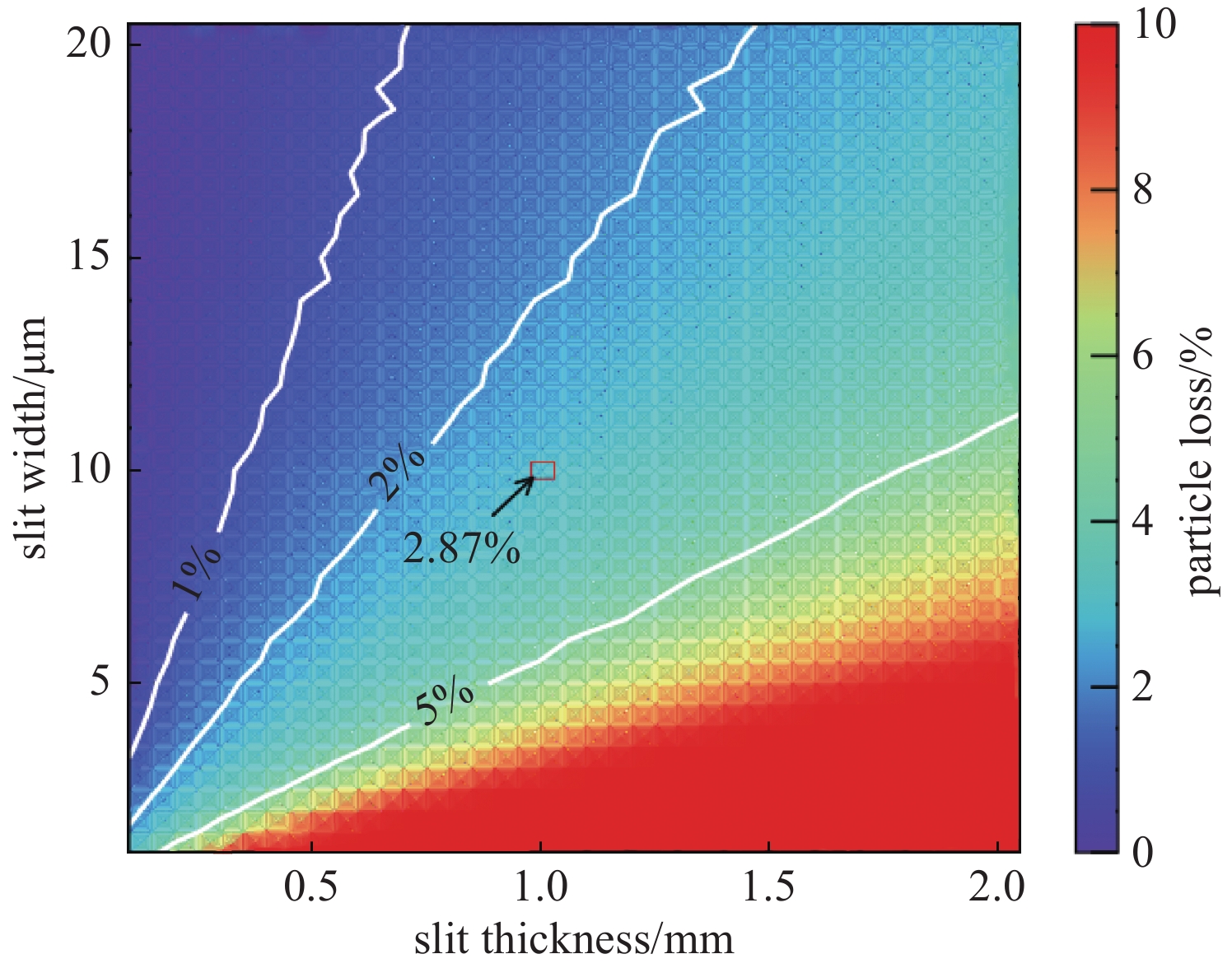
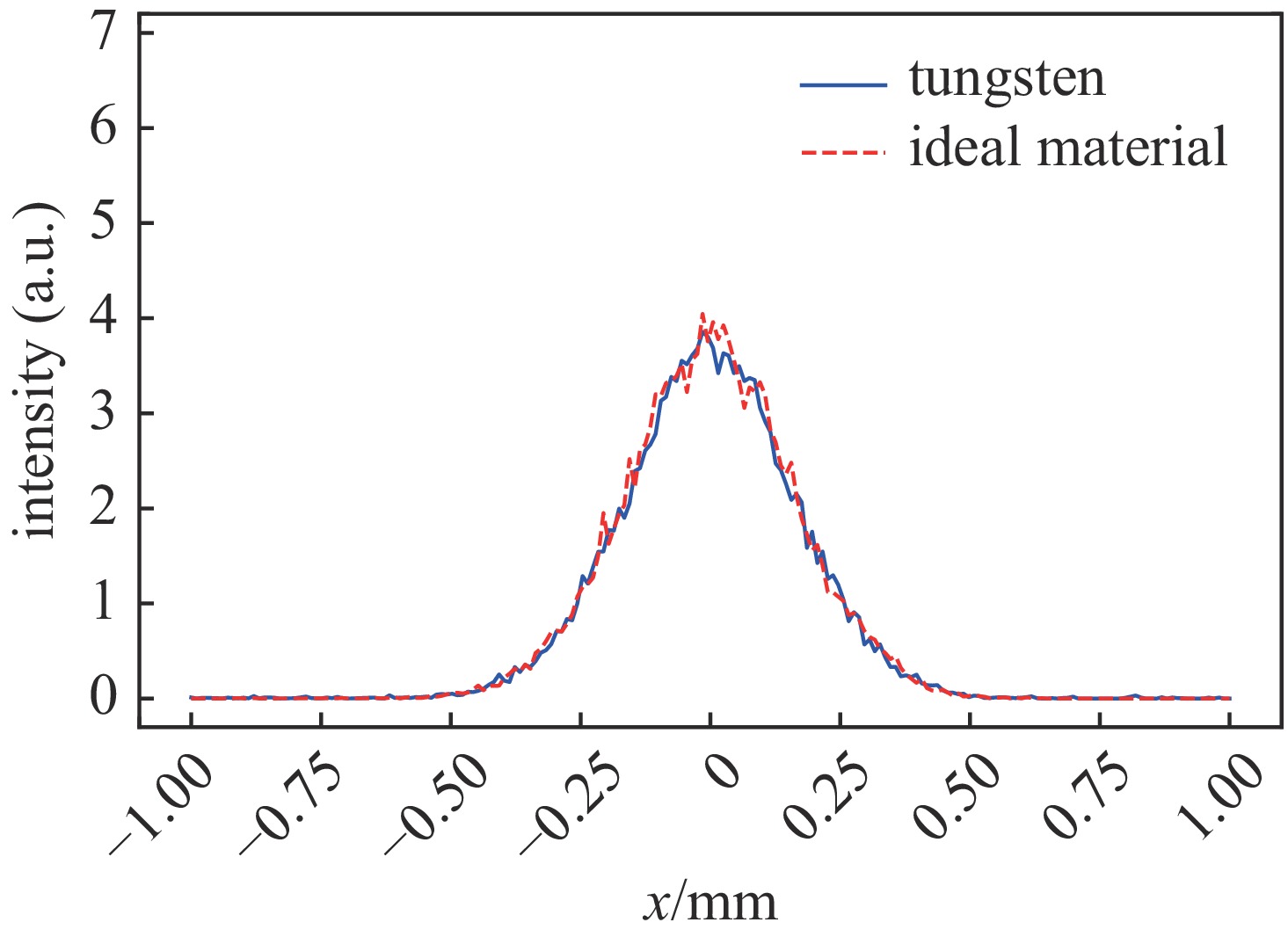
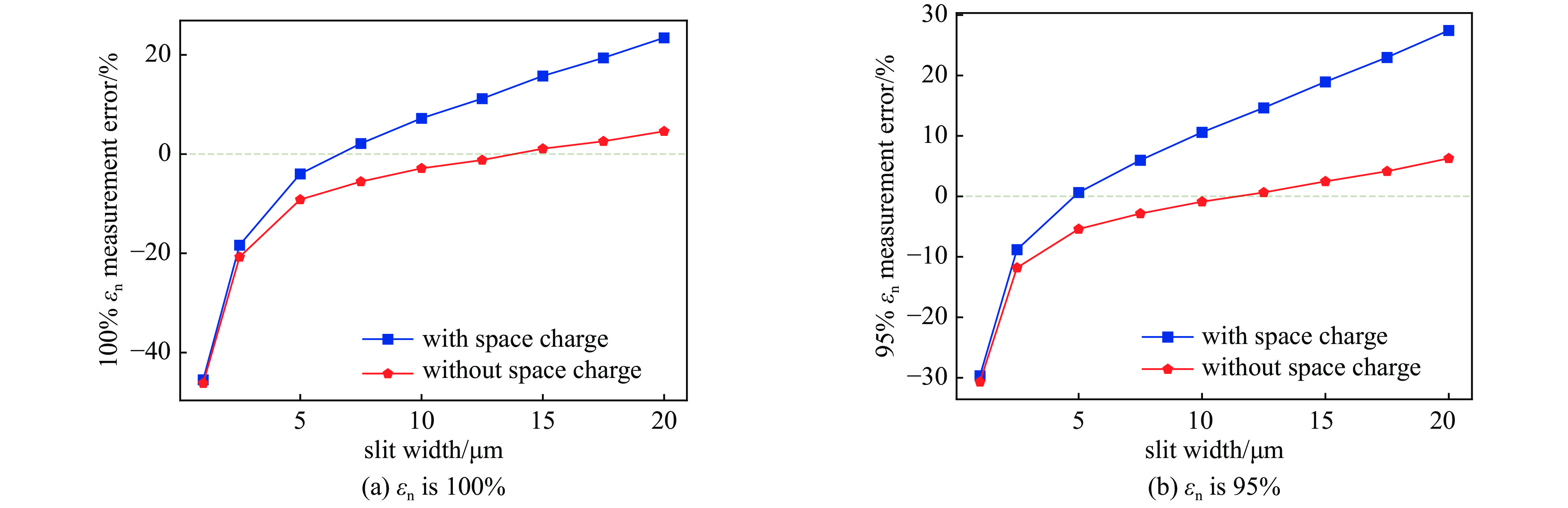
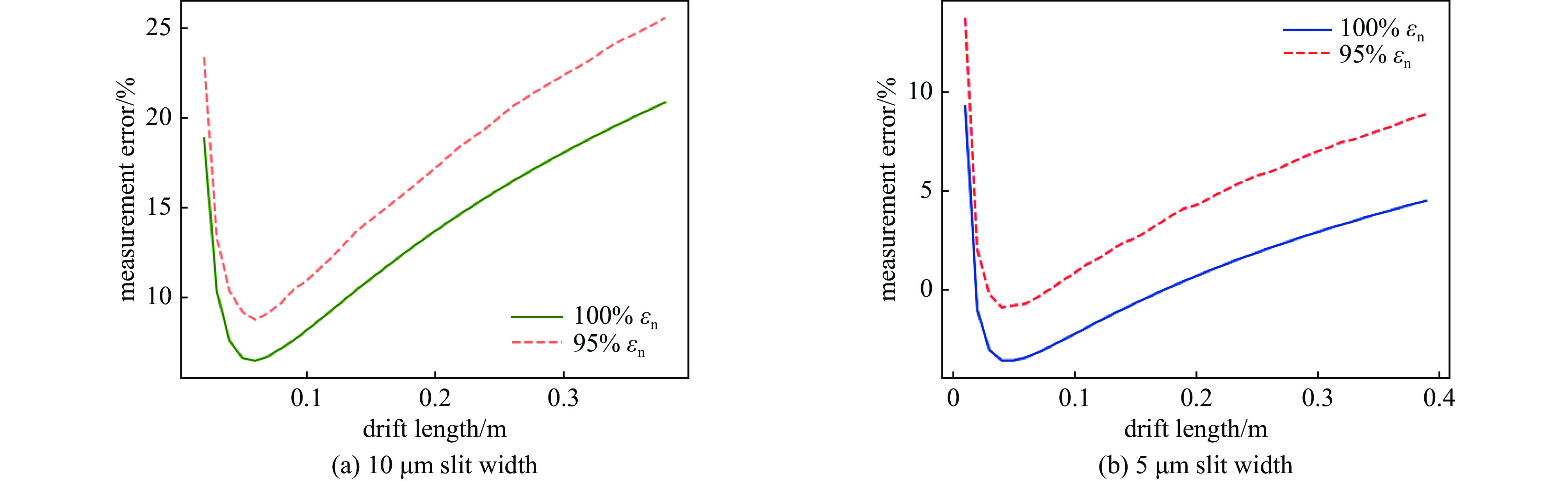
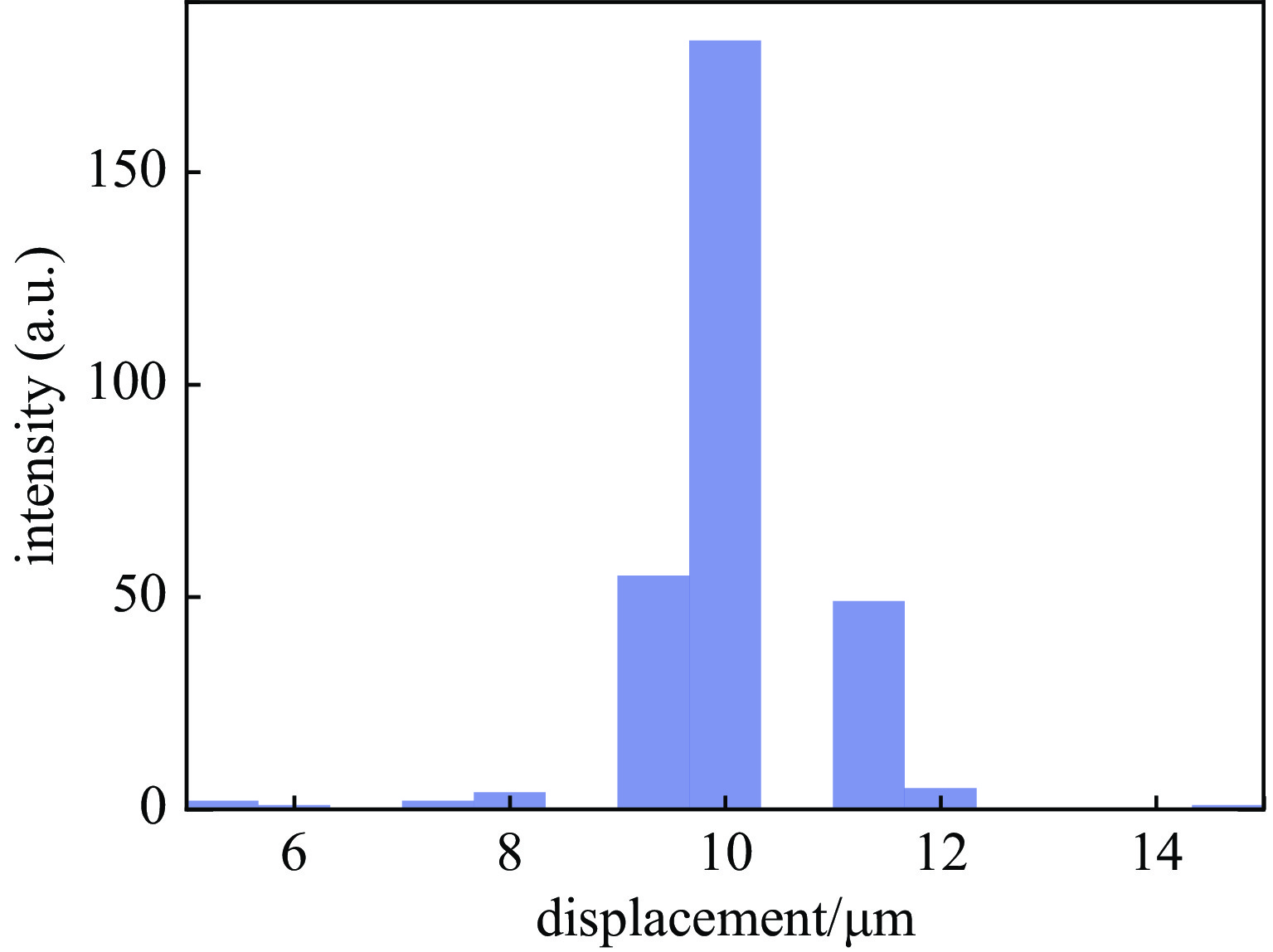
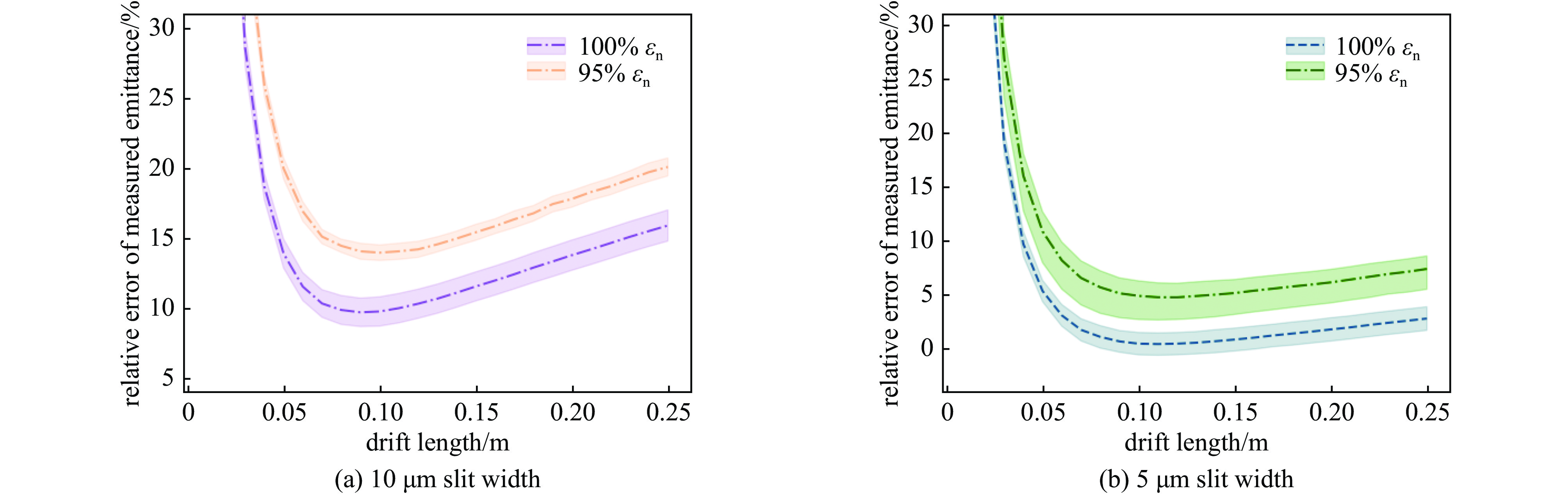
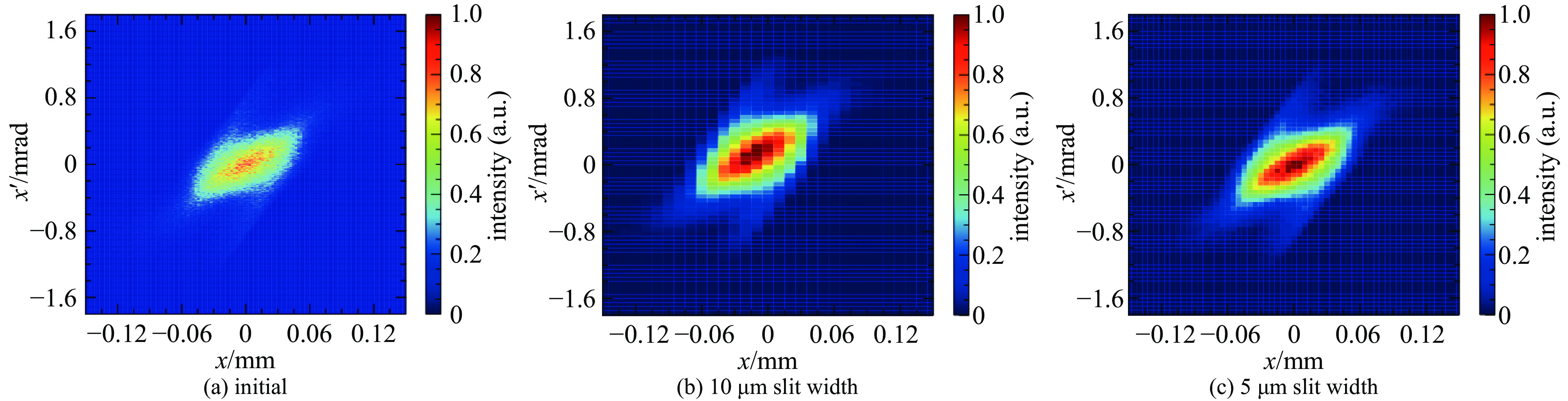
摘要: 束团电荷量100 pC条件下,C波段光阴极微波电子枪出口的束流归一化发射度预计低于0.2 mm.mrad。为实现对极小束流发射度的准确测量,设计了一套基于单狭缝扫描法的发射度测量仪,并利用数值模拟对发射度仪的狭缝结构和子束团漂移距离等核心参数进行了优化。考虑动态误差的数值模拟表明:采用宽度5 μm、厚度1 mm的狭缝和0.11 m的子束团漂移距离时,95%发射度的测量偏差低于5%。
-
关键词:
- C波段光阴极微波电子枪 /
- 高品质束流 /
- 归一化发射度 /
- 发射度测量仪 /
- 单狭缝扫描法
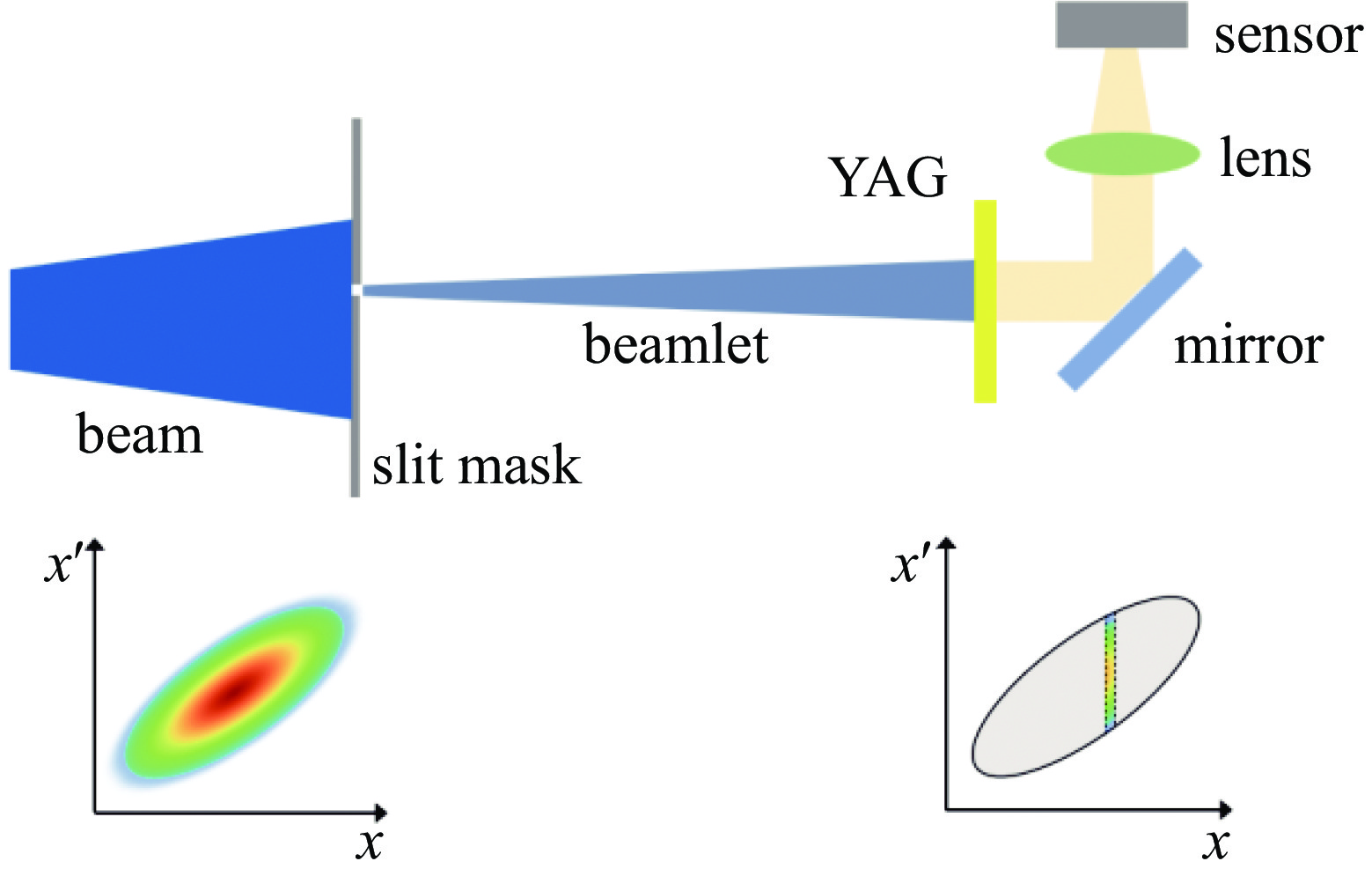
Abstract:Background To enhance the performance of the next-generation X-ray free electron laser (XFEL), a photocathode RF gun capable of providing the required high-quality electron beam with a small emittance has been a significant research objective. In comparison to the conventional L-band or S-band RF gun, the C-band RF gun features a higher acceleration gradient above 150 MV/m and the ability to generate a small-emittance beam. Low-emittance electron beams are critical for enhancing XFEL coherence and brightness, driving demand for advanced RF gun designs. For a bunch charge of 100 pC, a normalized emittance of less than 0.2 mm.mrad has been expected at the gun exit.Purpose This paper presents the design of an emittance measurement device, which can accurately measure such a small emittance at the C-band RF gun exit to ensure beam quality for XFEL applications.Methods To achieve the desired accuracy, the primary parameters —slit width, slit thickness, and beamlet-drift length—have been systematically optimized through numerical simulations using Astra and Python based on the single-slit-scan method. Dynamic errors, including motor displacement and imaging resolution, were quantified to ensure measurement reliability.Results The evaluations indicate that the measurement error of 95% emittance is less than 5%, employing a slit width of 5 μm, a slit thickness of 1 mm, and a beamlet-drift length of 0.11 m under dynamic conditions.Conclusions This optimized emittance measurement device supports precise beam quality characterization for XFELs, offering potential for further advancements in electron beam diagnostics. -
表 1 C波段光阴极微波电子枪的主要束流参数 (设计值)
Table 1. Major beam parameters of the C-band photocathode RF gun (design values)
Charge (pC) Energy (MeV) $100{\text{%}} {\varepsilon _n}$ (mm·mrad) $95{\text{%}} {\varepsilon _n}$ (mm·mrad) 100 7.26 0.175 0.111 300 7.25 0.323 0.215 500 7.24 0.463 0.304 表 2 多缝法和单缝扫描法在光阴极注入器上的应用[27-33]
Table 2. The application of multi-slit and single-slit scan measurement on photoinjectors
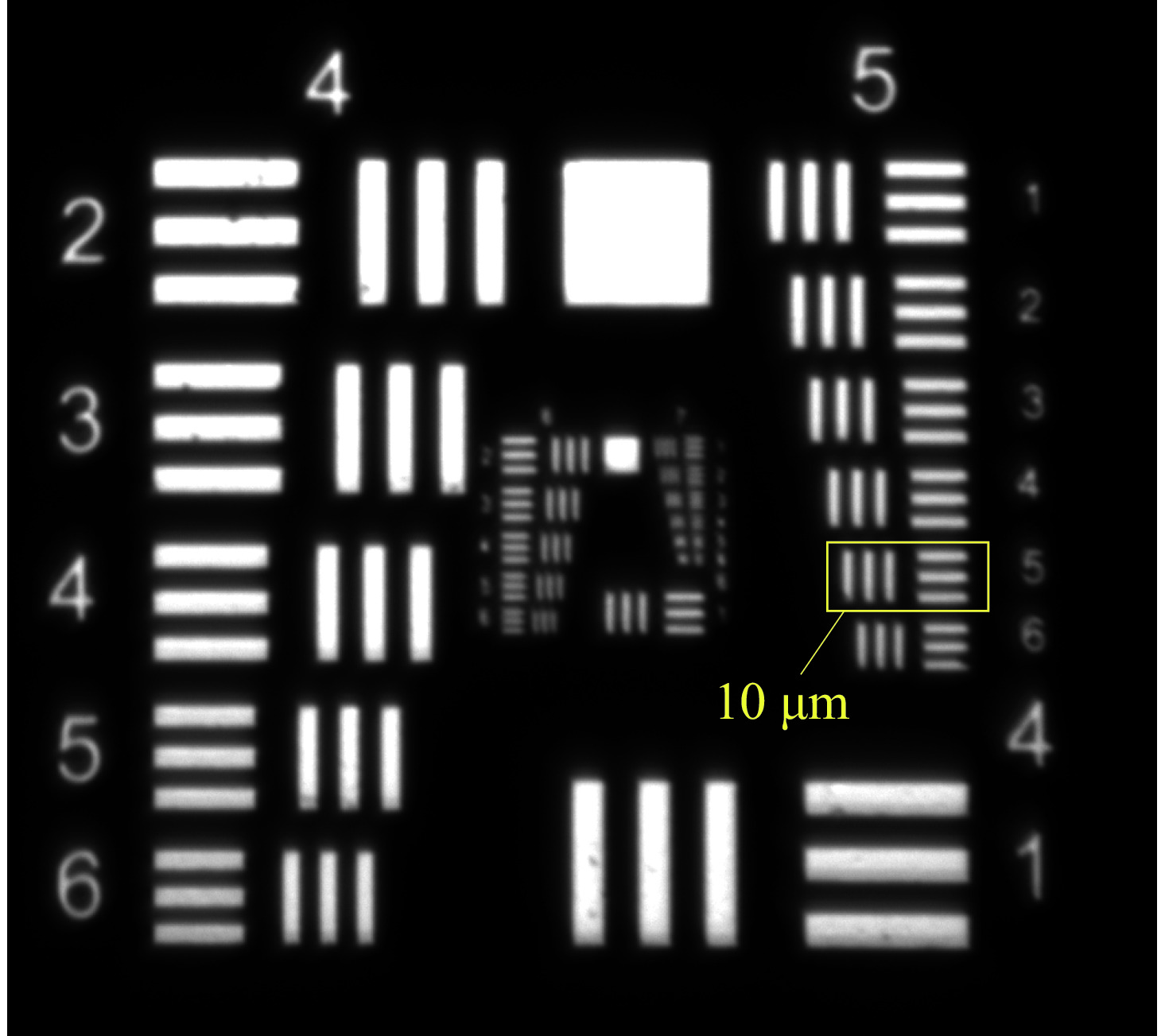
facility name method beam energy /MeV charge/pC slit width/μm Normalize emittance/(mm.mrad) SITF Single-slit-scan 7 100 20 0.46 PITZ Single-slit-scan 4.6 100 10 0.26 ELBE Single-slit-scan 4.45 100 100 2.84 DC-SRF-II Single-slit-scan 2.42 100 30 0.54 ORGAD Multi-slit 6.5 30 40 3 LEReC Multi-slit 2.6 75 150 1.6 -
[1] Emma P, Akre R, Arthur J, et al. First lasing and operation of an ångstrom-wavelength free-electron laser[J]. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4(9): 641-647. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.176 [2] Vinko S M, Ciricosta O, Cho B I, et al. Creation and diagnosis of a solid-density plasma with an X-ray free-electron laser[J]. Nature, 2012, 482(7383): 59-62. doi: 10.1038/nature10746 [3] Takahashi S, Brunel L C, Edwards D T, et al. Pulsed electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy powered by a free-electron laser[J]. Nature, 2012, 489(7416): 409-413. doi: 10.1038/nature11437 [4] McSweeney S, Fromme P. Sources of inspiration[J]. Nature, 2014, 505(7485): 620-621. doi: 10.1038/505620a [5] Duan S F, Cheng Y, Xia W, et al. Optical manipulation of electronic dimensionality in a quantum material[J]. Nature, 2021, 595(7866): 239-244. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03643-8 [6] Rosenzweig J B, Majernik N, Robles R R, et al. An ultra-compact x-ray free-electron laser[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2020, 22: 093067. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/abb16c [7] Palmer D T, Wang X J, Miller R H, et al. Initial commissioning results of the next generation photoinjector[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1997, 398(1): 695-704. [8] Dwersteg B, Flöttmann K, Sekutowicz J, et al. RF gun design for the TESLA VUV free electron laser[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1997, 393(1/3): 93-95. [9] Liu Xingguang, Li Xiao, Jiang Shiming, et al. A C-band test platform for the development of RF photocathode and high gradient accelerating structures[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2023: 1995-1998. [10] Alesini D, Cardelli F, Di Raddo G, et al. Progress on the new high gradient C Band standing wave RF photo-gun[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2023: 1374-1377. [11] Chen H, Huang W H, Liu X H, et al. Development of a compact C-band photocathode RF gun[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2011: 116-118. [12] Taira Y, Kuroda R, Tanaka M, et al. Fabrication and low-power RF test of C-band RF gun[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2014, 331: 27-30. [13] Fang Wencheng, Wang Lin, Zhao Zhentang. Conceptual study and design of A C-band photocathode injector[J]. Radiation Detection Technology and Methods, 2019, 3: 39. doi: 10.1007/s41605-019-0117-z [14] Liu Xingguang, Jiao Yi, Li Biaobin, et al. Preliminary design of the full energy linac injector for the southern advanced photon source[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2021: 1454-1457. [15] Liu X, Li X, Jiang S, et al. A C-band test platform for the development of RF photo cathode and high gradient accelerating structures[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2024, 2687: 042001. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2687/4/042001 [16] Yan M, Beutner B, Ischebeck R, et al. Comparison of quadrupole scan and multi-screen method for the measurement of projected and slice emittance at the SwissFEL injector test facility[C]//Proceedings of FEL2014. 2014: 941-944. [17] Hachmann M, Flöttmann K. Measurement of ultra low transverse emittance at REGAE[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2016, 829: 318-320. [18] Cutler R I, Owen J, Whittaker J. Performance of wire scanner beam profile monitors to determine the emittance and position of high power CW electron beams of the NBS-Los Alamos Racetrack microtron[C]//Proceedings of PAC 1987. 1987: 625-627. [19] Kremers H R, Beijers J P M, Brandenburg S. A pepper-pot emittance meter for low-energy heavy-ion beams[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2013, 84: 025117. doi: 10.1063/1.4793375 [20] Liu C, Gassner D, Minty M, et al. Multi-slit emittance measurement study for BNL ERL[R]. BNL-98657-2012-IR, 2012. [21] Anderson S G, Rosenzweig J B, LeSage G P, et al. Space-charge effects in high brightness electron beam emittance measurements[J]. Physical Review Special Topics-Accelerators and Beams, 2002, 5: 014201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.5.014201 [22] Zhang Min. Emittance formula for slits and pepper-pot measurement[R]. FERMILAB-TM-1988, 1996. [23] Ludwig T, Volk K, Barth W, et al. Quantization error of slit-grid emittance measurement devices[J]. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1 April, 1994, 65(4): 1462-1464. doi: 10.1063/1.1144946 [24] Minty M G, Zimmermann F. Measurement and control of charged particle beams[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2003: 99-111. [25] Forck P. Lecture notes on beam instrumentation and diagnostics[R]. Darmstadt, Germany: Gesellschaft f¨ur Schwerionenforschung (GSI), 2006: 65-77. [26] 赵亚亮, 闫芳, 耿会平, 等. 带空间电荷效应的横向发射度测量[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30: 015101Zhao Yaliang, Yan Fang, Geng Huiping, et al. Transverse Twiss parameter measurement with space charge in CADS Injector[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 30: 015101 [27] Mostacci A, Bacci A, Boscolo M, et al. Analysis methodology of movable emittance-meter measurements for low energy electron beams[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2008, 79: 013303. doi: 10.1063/1.2835715 [28] Liu Chuyu, Fedotov A, Fuchs A, et al. Transverse beam emittance measurements with multi-slit and moving-slit devices for LEReC[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Beam Instrumentation Conference. 2018: 486-489. [29] Miller T, Blaskiewicz M, Drees A, et al. LEReC instrumentation design & construction[C]//Proceedings of IBIC2016. 2016: 417-421. [30] Feigin L, Nause A. Single-shot emittance measurement and optimization of a hybrid photo-cathode gun beam[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2023, 1055: 168539. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2023.168539 [31] Jia H, Li T, Wang T, et al. High-brightness megahertz-rate beam from a direct-current and superconducting radio-frequency combined photocathode gun[J]. Physical Review Research, 2024, 6: 043165. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.6.043165 [32] Feigin L, Weinberg A, Nause A. Algorithm verification of single-shot relativistic emittance proposed measuring method[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11: 2092. doi: 10.3390/electronics11132092 [33] Staykov L. Design optimization of an emittance measurement system at PITZ[C]//Proceedings of DIPAC'05. 2005: 220-222. [34] Tao Tan, Jia Haoyan, Zhao Sheng, et al. Sub-micron normalized emittance measurement for a MeV continuous-wave electron gun[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2023, 1045: 167552. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2022.167552 [35] 向导. 高亮度电子束发射度、束长和束斑的先进测量方法研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2008: 26-27Xiang Dao. Advanced beam measurements of emittance, bunch length and beam size for high-brightness electron beam[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2008: 26-27) [36] DESY. Deutschlands größtes beschleunigerzentrum[EB/OL]. https://www.desy.de/mpyflo/. [37] The FLUKA code[EB/OL]. https://fluka.cern/. [38] Leica absolute tracker[EB/OL]. https://www.pei-france.com/uploads/tx_etim/Hexagon_-_17549.pdf. [39] Crytur. YAP: Ce[EB/OL]. https://www.crytur.com/materials/yap-ce/. -




 下载:
下载: