Analysis of reasonable diffraction loss rate in 220 GHz confocal waveguide gyro-TWT amplifier
-
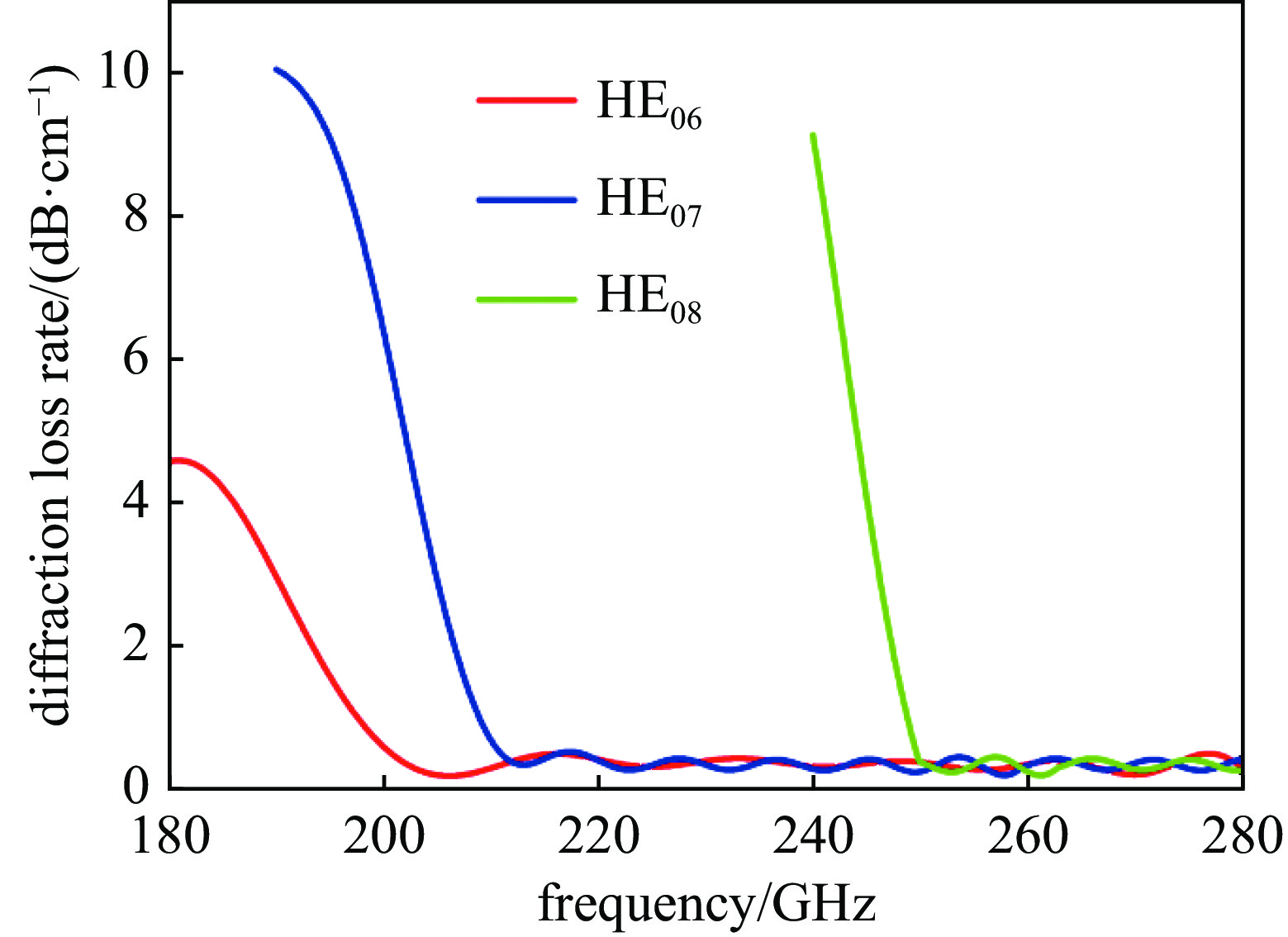
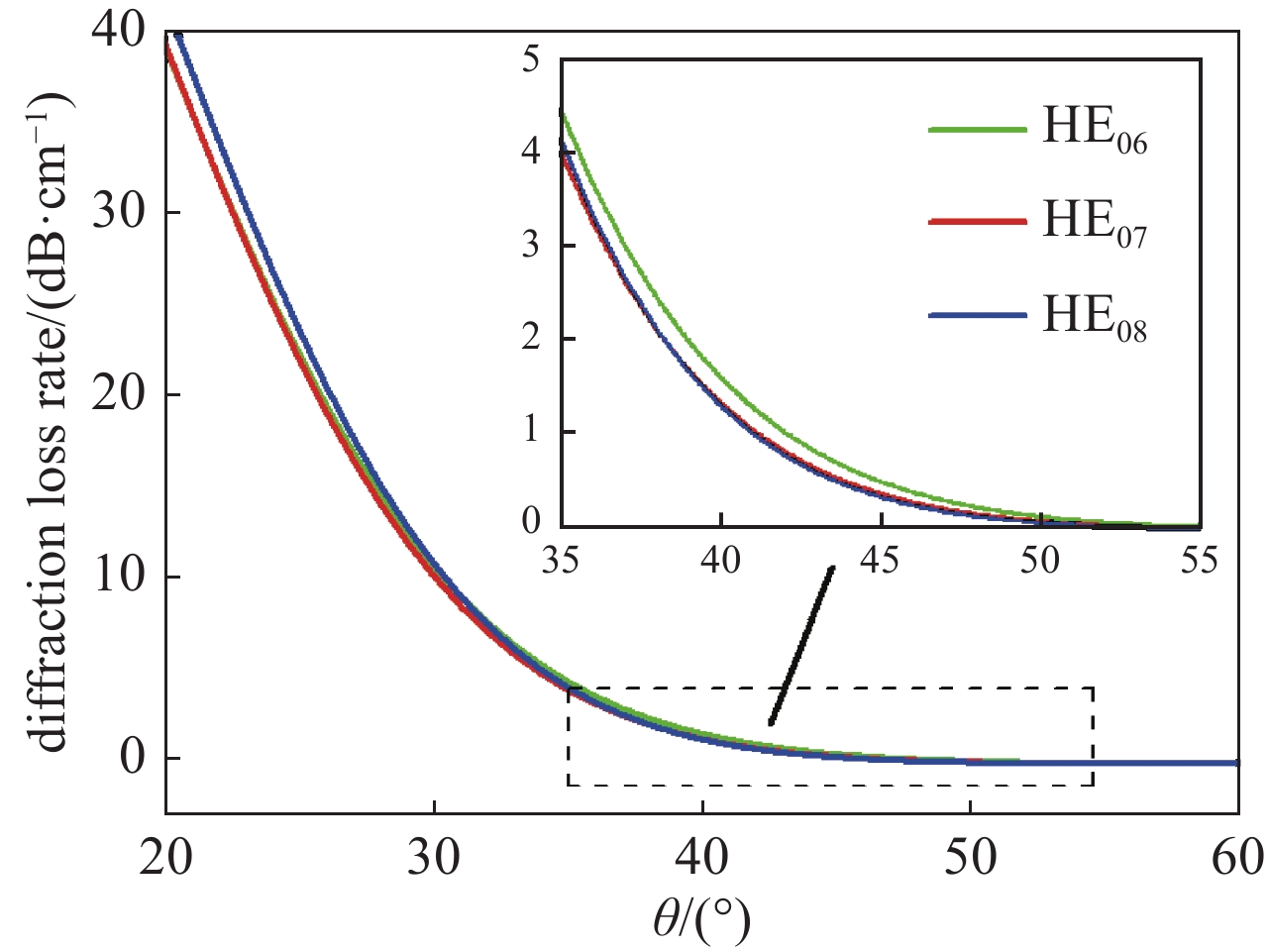
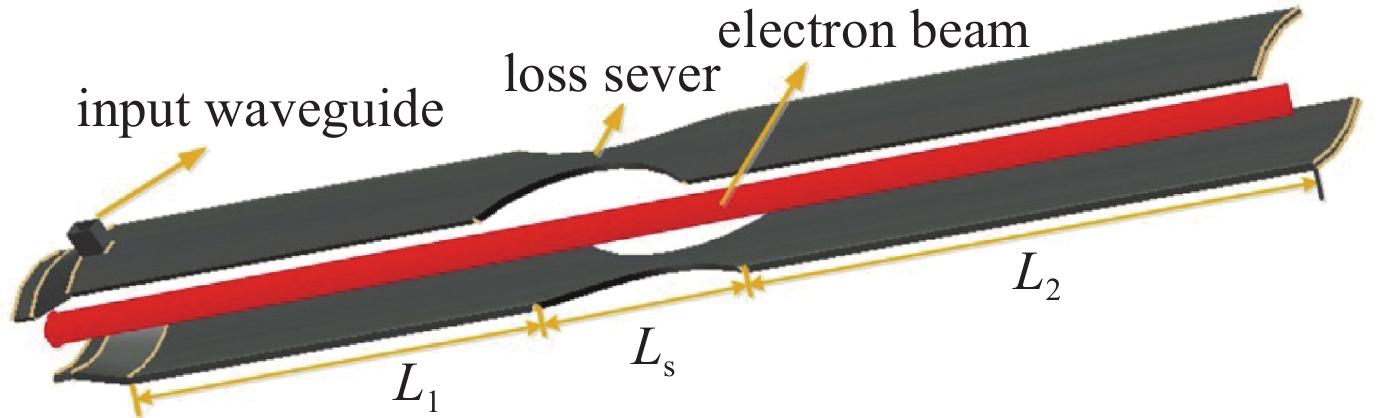
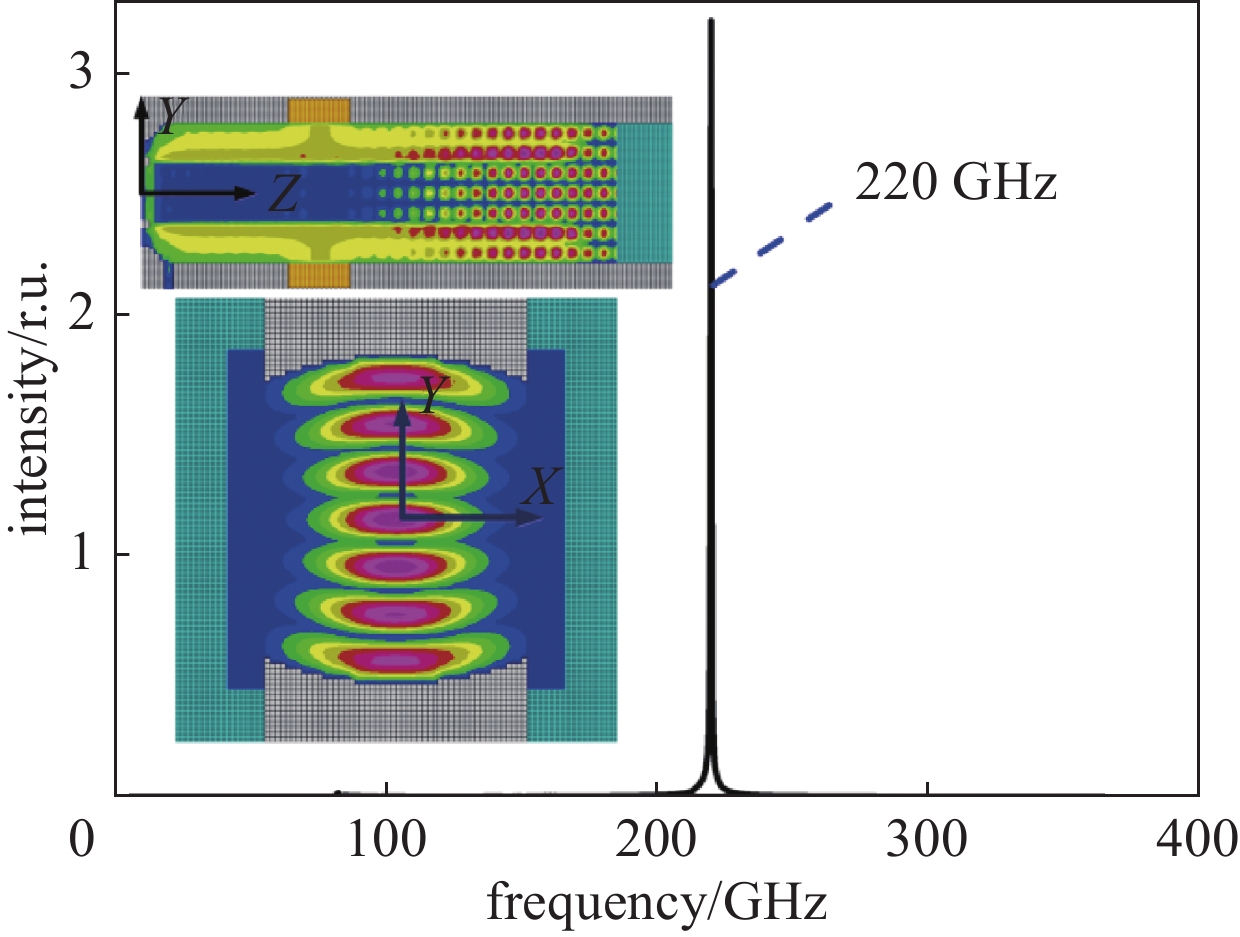
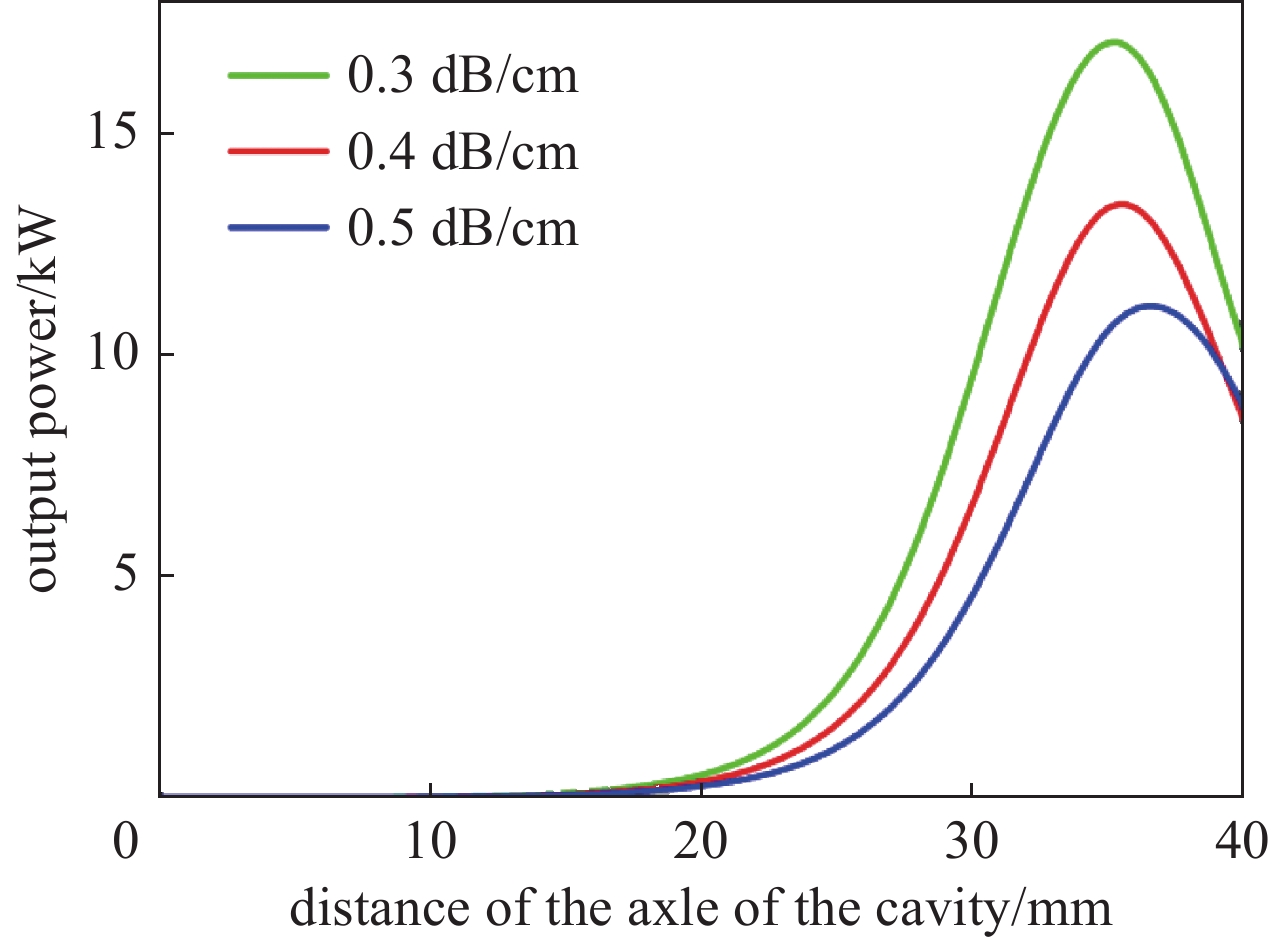
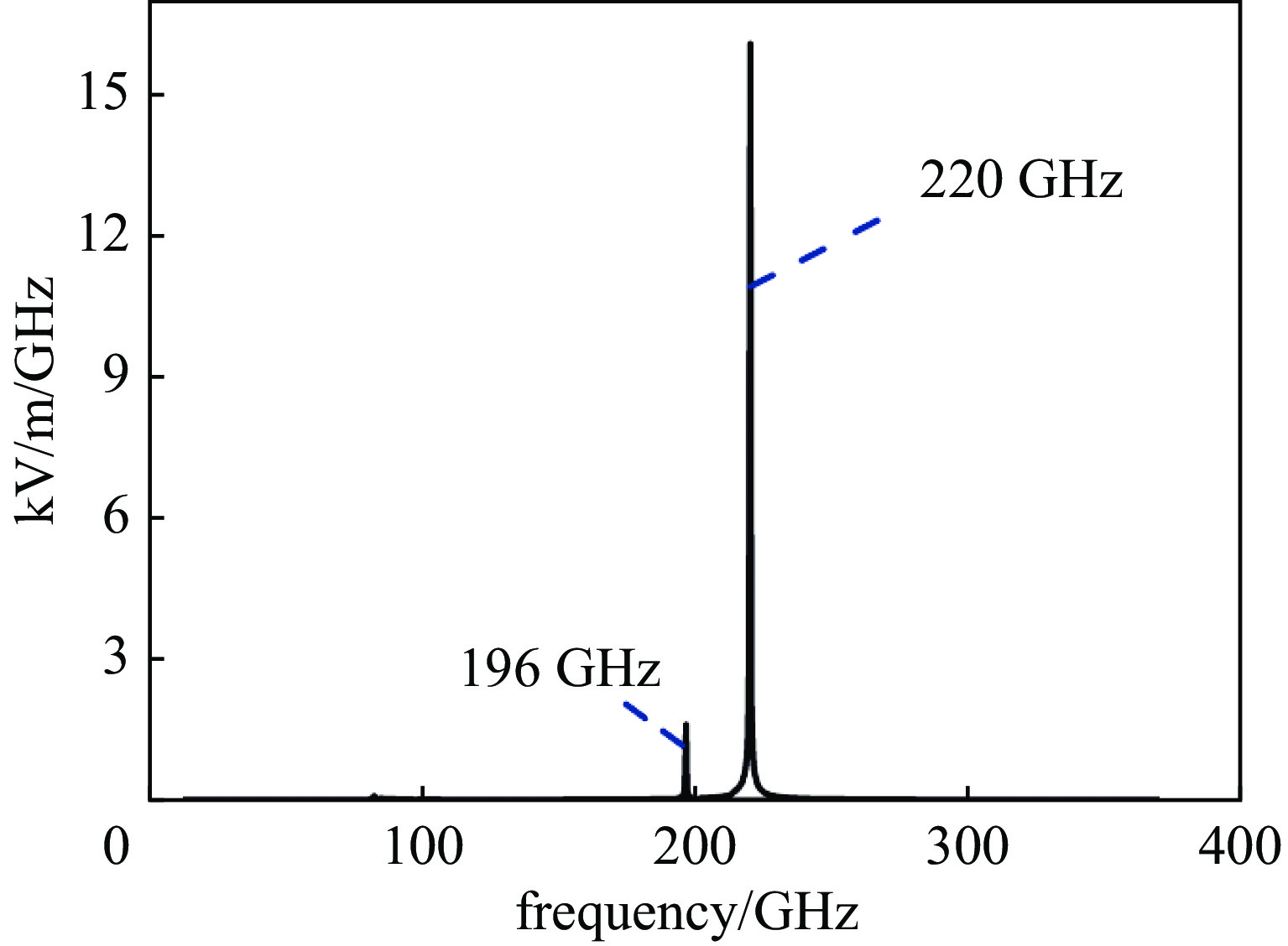
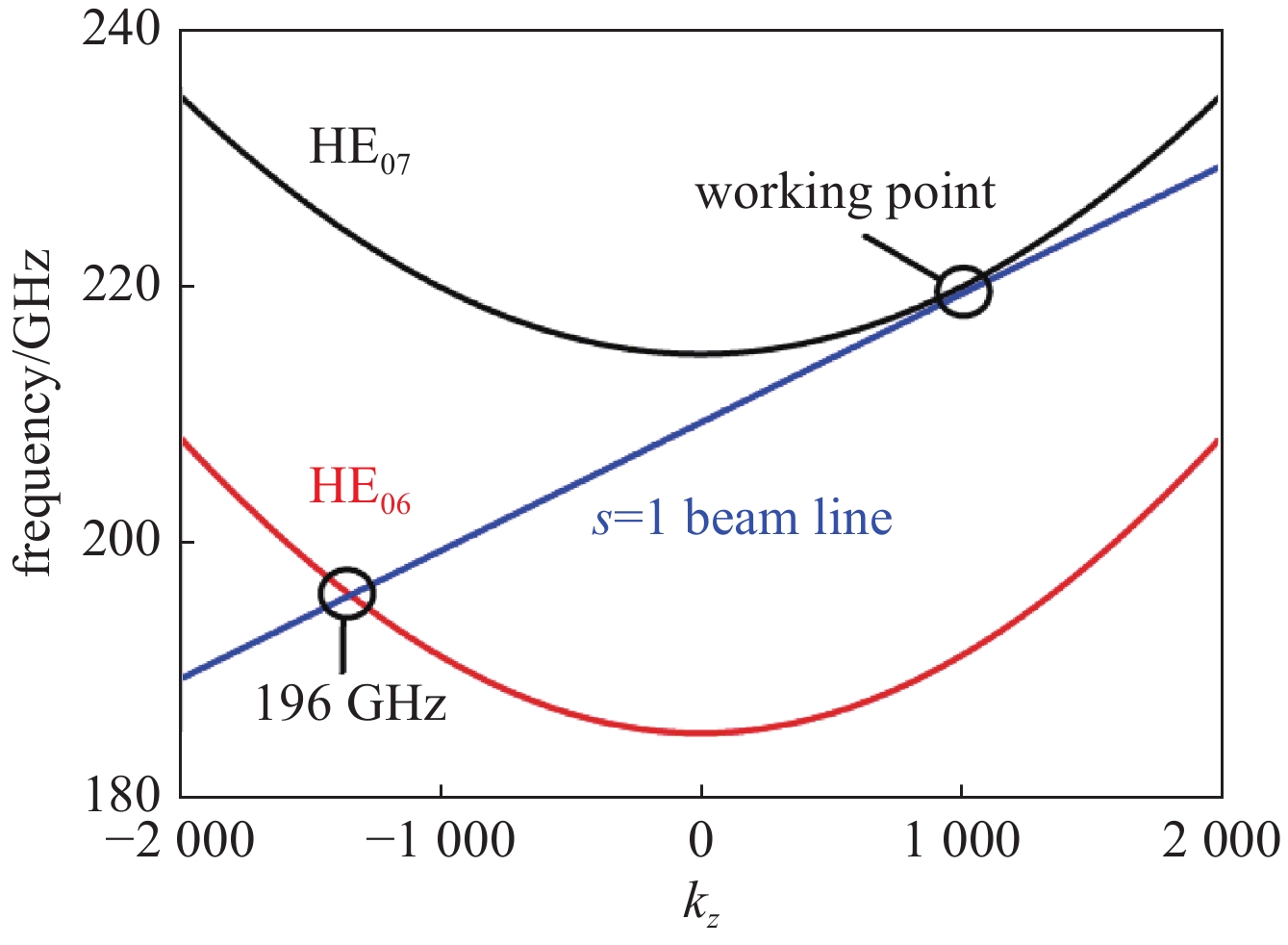
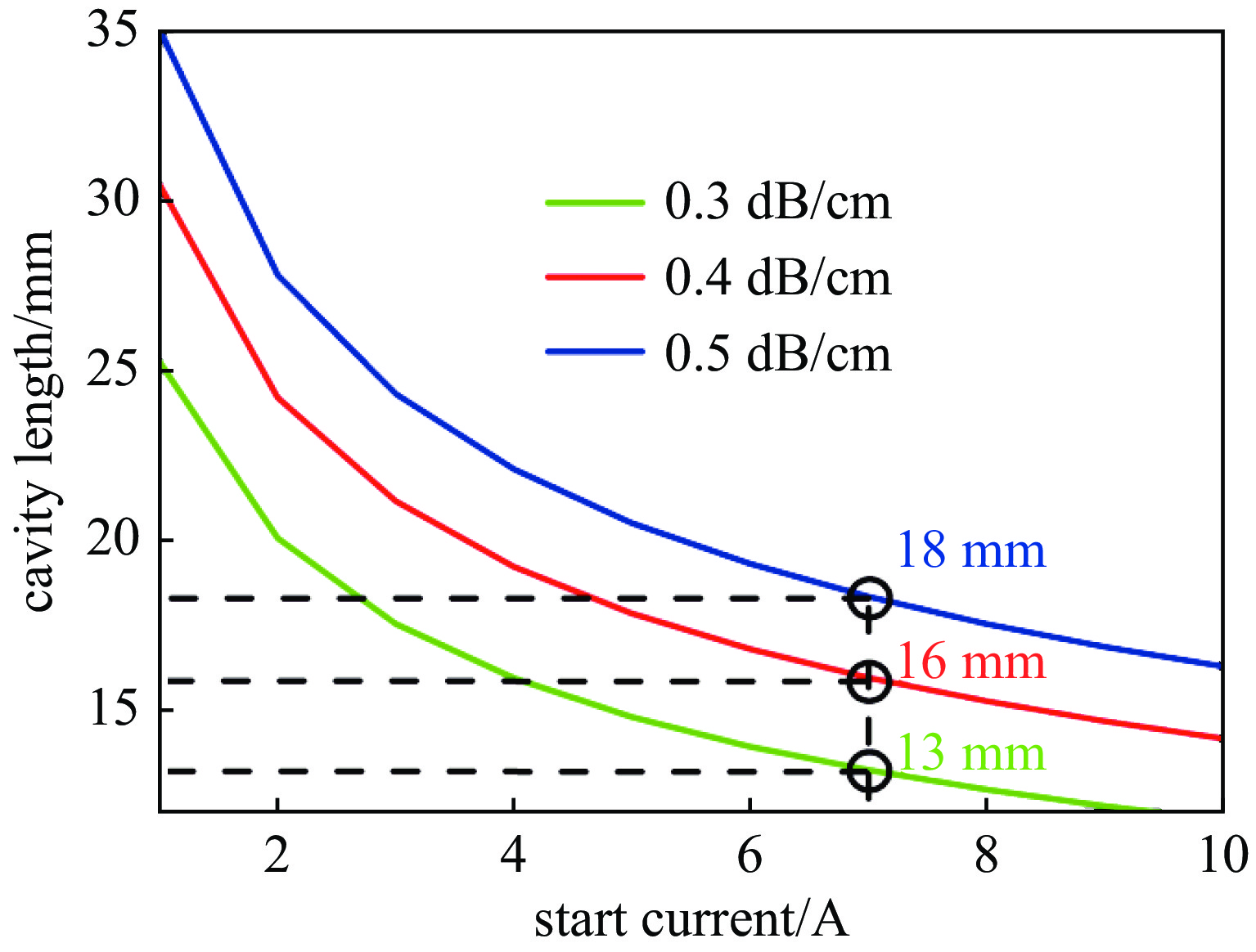
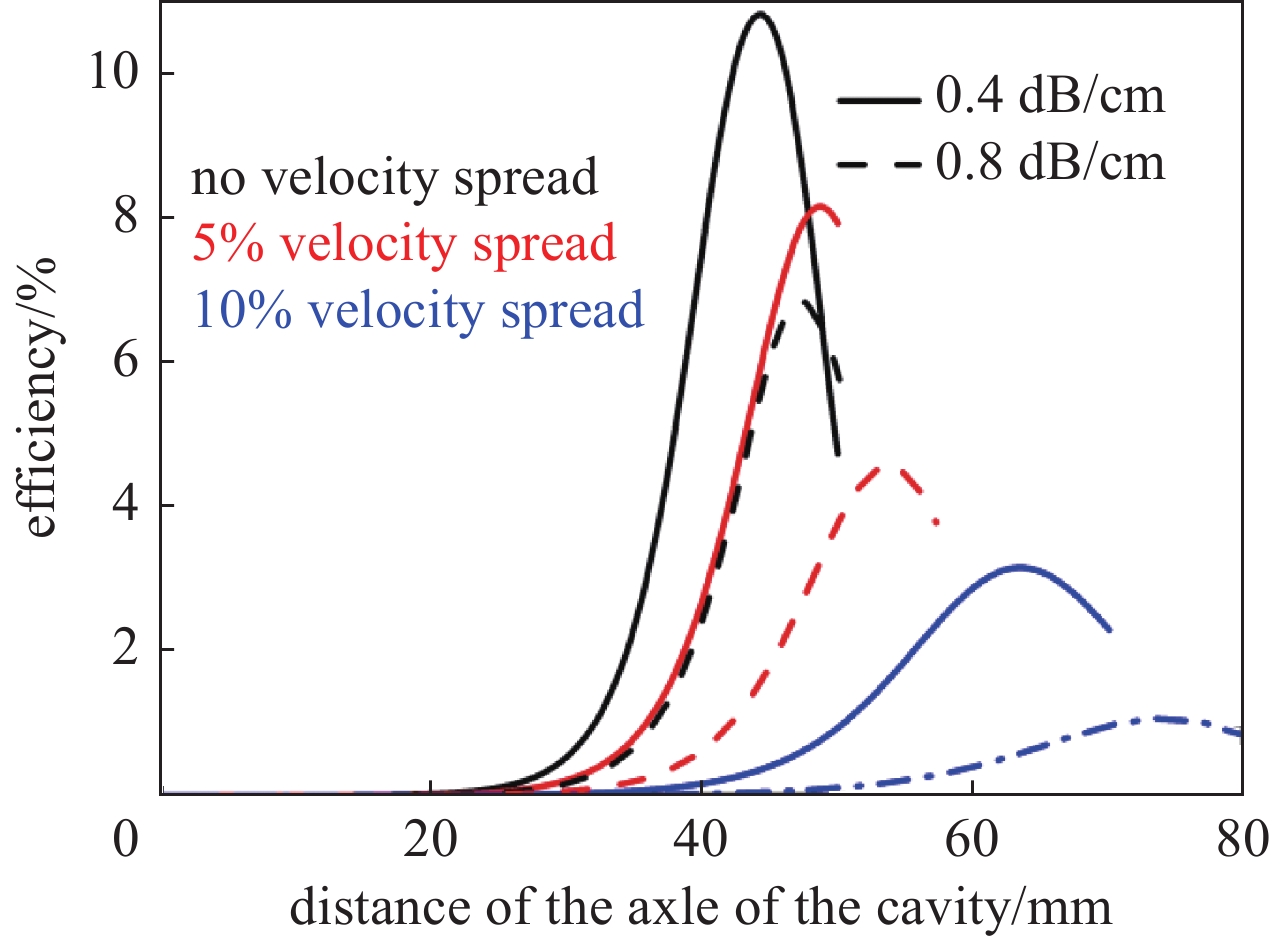
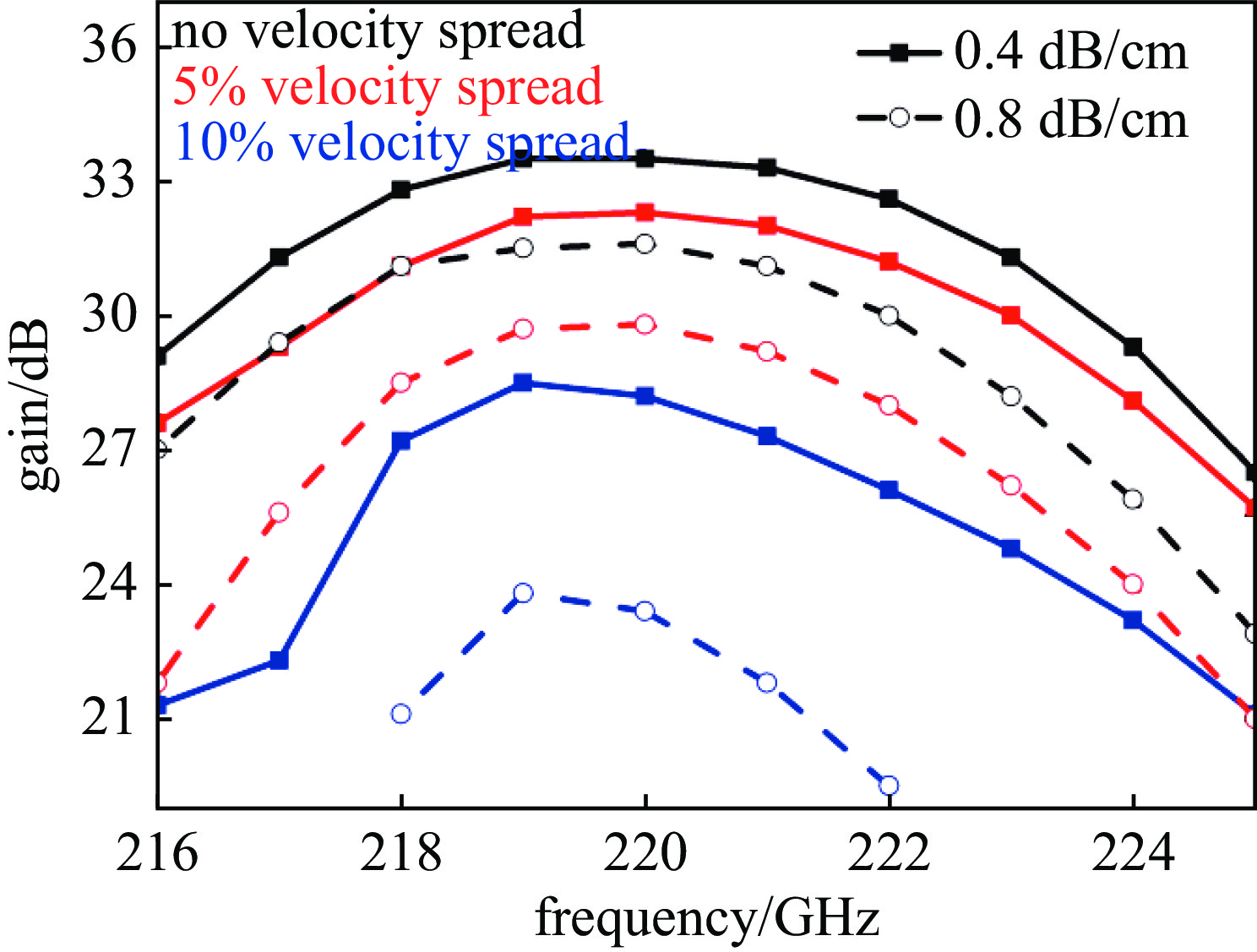
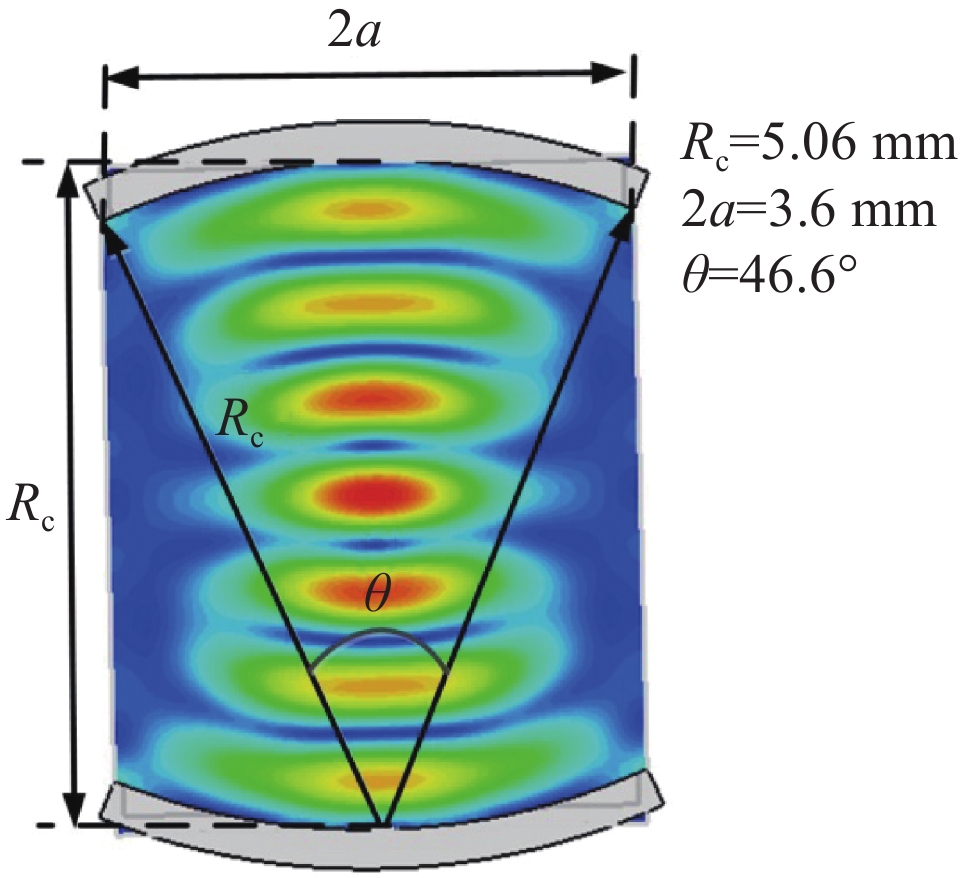
摘要: 共焦波导结构因其衍射损耗可降低模式密度的特性,能够有效抑制模式竞争,进而有助于回旋行波管放大器(gyro-TWT)在太赫兹(>100 GHz)频段实现稳定工作。采用理论分析与三维粒子模拟(3D-PIC)相结合的方法,针对220 GHz共焦波导gyro-TWT的衍射损耗率(DLR)展开综合分析。研究结果表明,DLR的大小对gyro-TWT性能具有显著影响。较小的DLR会激发低阶竞争模式的回旋返波振荡(GBWO);而较大的DLR则会大幅降低共焦波导gyro-TWT的束波互作效率、增益、带宽,同时降低其对电子束速度零散的容忍度,应避免使共焦波导gyro-TWT工作在较大的DLR下。在该设计的共焦波导gyro-TWT中,HE07单模稳定工作的DLR不小于0.38 dB/cm,对应的镜面宽度角θ不大于47°。Abstract:
Background The confocal waveguide structure can effectively suppress mode competition due to its characteristic of reducing mode density through diffraction loss, thereby facilitating stable operation of gyro-traveling-wave-tube (gyro-TWT) amplifiers in the terahertz (>100 GHz) frequency range.Purpose This study aims to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the diffraction loss rate (DLR) in a 220 GHz confocal waveguide gyro-TWT, employing a combination of theoretical analysis and three-dimensional particle-in-cell (3D-PIC) simulations.Methods The research integrates field distribution theory with 3D-PIC simulations to investigate the DLR of the confocal waveguide. A non-ideal waveguide model incorporating the mirror width angle was utilized, and simulations were performed to evaluate beam-wave interaction dynamics under varying DLR conditions.Results The study reveals that a low DLR induces gyro-backward-wave oscillation (GBWO) in low-order competing modes, while a high DLR significantly reduces beam-wave interaction efficiency, gain, and bandwidth, and lowers tolerance to electron beam velocity spread.Conclusions For stable single-mode operation of the HE07 mode in the designed gyro-TWT, the DLR should not be less than 0.38 dB/cm, with the corresponding mirror-surface width angle not exceeding 47°. These findings provide crucial design guidelines for terahertz gyro-TWTs.-
Key words:
- confocal waveguide /
- diffraction loss rate /
- terahertz generation /
- gyro-TWT
-
表 1 共焦波导gyro-TWT电参数
Table 1. Electron parameters of confocal waveguide gyro-TWT
beam voltage
Ub/kVbeam current
Ib/Amagnetic field
B0/Tpitch factor
αguiding center radius
Rb/mminput power
Pin/W30 7 7.91 1.2 0.76 10 -
[1] He Wenlong, Donaldson C R, Zhang Liang, et al. Broadband amplification of low-terahertz signals using axis-encircling electrons in a helically corrugated interaction region[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2017, 119: 184801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.184801 [2] Xiao Renzhen, Chen Kun. Efficiency improvement studies of sub-terahertz multiwave Cherenkov generator with a coaxial coupler[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(8): 4401-4406. doi: 10.1109/TED.2023.3285726 [3] Li Xiaoze, Wang Jianguo, Sun Jun, et al. Experimental study on a high-power subterahertz source generated by an overmoded surface wave oscillator with fast startup[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2013, 60(9): 2931-2935. doi: 10.1109/TED.2013.2273489 [4] 肖仁珍. 相对论返波管研究进展[J]. 现代应用物理, 2022, 13: 020101 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2022.020101Xiao Renzhen. Research progress of relativistic backward wave oscillator[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2022, 13: 020101 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2022.020101 [5] Sirigiri J R, Shapiro M A, Temkin R J. High-power 140-GHz quasioptical gyrotron traveling-wave amplifier[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 90: 258302. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.258302 [6] Joye C D, Shapiro M A, Sirigiri J R, et al. Progress of a 140 GHz, 1 kW confocal Gyro-TWT amplifier[C]//Proceedings of 2007 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference. 2007. [7] 胡鹏, 孙迪敏, 蒋艺, 等. 低速度零散的双阳极磁控注入电子枪设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(3): 671-674 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132503.0671Hu Peng, Sun Dimin, Jiang Yi, et al. Design of double-anode magnetic injection with low velocity spread[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(3): 671-674 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132503.0671 [8] 蒋艺, 陈洪斌, 马国武, 等. 共焦波导结构回旋行波管的设计与仿真[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(2): 403-406 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122402.0403Jiang Yi, Chen Hongbin, Ma Guowu, et al. Design and simulation of confocal gyro-travelling wave tube[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(2): 403-406 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122402.0403 [9] Yang Youwei, Yu Sheng, Liu Yinghui, et al. Efficiency enhancement of a 170 GHz confocal gyrotron traveling wave tube[J]. Journal of Fusion Energy, 2015, 34(4): 721-726. doi: 10.1007/s10894-015-9863-1 [10] Liu Dagang, Tang Xinbing, Yan Yang, et al. Design of confocal waveguide interaction structure for a 220 GHz gyro-TWT[J]. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 2017, 31(6): 650-662. doi: 10.1080/09205071.2017.1306463 [11] An Chenxiang, Zhang Dian, Zhang Jun, et al. Theoretical analysis and PIC simulation of a 220-GHz second-harmonic confocal waveguide gyro-TWT amplifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2019, 66(9): 4016-4021. doi: 10.1109/TED.2019.2925895 [12] Xu Shouxi, Zhang Jian, Geng Zhihui, et al. Investigation of a 0.34-THz quasi-optical gyrotron traveling wave amplifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2024, 52(3): 1033-1038. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2024.3370695 [13] 胡鹏, 蔡金赤, 蒋艺, 等. 共焦波导回旋行波管准光注入结构设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(5): 1337-1340 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132505.1337Hu Peng, Cai Jinchi, Jiang Yi, et al. Design of quasi-optical input structure for confocal gyro-TWT[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(5): 1337-1340 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132505.1337 [14] 胡鹏, 朱辉, 蒋艺, 等. 0.4THz回旋行波管的设计与模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(12): 2865-2868 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122412.2865Hu Peng, Zhu Hui, Jiang Yi, et al. Design and simulation of 0.4 THz gyro-traveling wave tube[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(12): 2865-2868 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122412.2865 [15] Nusinovich G S. To the theory of gyrotrons with confocal resonators[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2019, 26: 053107. doi: 10.1063/1.5099909 [16] Yao Yelei, Sun Yibin, Dai Xinge, et al. Simulation study on a planar quasi-optical waveguide circuit for a W-band gyro-TWT with stability improvement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(6): 3288-3294. doi: 10.1109/TED.2023.3263823 [17] 李志良, 冯进军, 刘本田, 等. 140 GHz共焦波导结构回旋行波管放大器[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2018, 16(5): 767-771,780 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201805.0767Li Zhiliang, Feng Jinjun, Liu Bentian, et al. 140 GHz confocal waveguide Gyrotron-Traveling Wave Tube amplifier[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2018, 16(5): 767-771,780 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201805.0767 [18] Yang Jie, Xu Shouxi, Wang Yong, et al. Theoretical analysis of a 0.22THz multistage confocal waveguide gyro-TWT with circle-sector-shaped electron beam[J]. AIP Advances, 2021, 11: 095217. doi: 10.1063/5.0063867 [19] 夏建波, 王建勋, 付浩, 等. W波段共焦波导回旋行波管色散特性和衍射损耗研究[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2017, 37(1): 28-33Xia Jianbo, Wang Jianxun, Fu Hao, et al. Simulation of dispersion characteristics and diffraction loss of W-band confocal waveguide gyro-TWT[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2017, 37(1): 28-33 [20] Barker R J, Booske J H, Luhmann N C Jr, et al. Modern microwave and millimeter-wave power electronics[M]. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2005: 872. [21] Yao Yelei, Wang Jianxun, Li Hao, et al. Propagation characteristics of confocal waveguides based on spheroidal functions for a W-band gyro-TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2017, 64(4): 1781-1786. doi: 10.1109/TED.2017.2665588 [22] Sun Wei, Yu Sheng, Wang Zhipeng, et al. Linear and nonlinear analyses of a 0.34-thz confocal waveguide gyro-TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2018, 46(3): 511-517. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2018.2794380 [23] Nusinovich G S, Li H. Theory of gyro-travelling-wave tubes at cyclotron harmonics[J]. International Journal of Electronics, 1992, 72(5/6): 895-907. -




 下载:
下载: