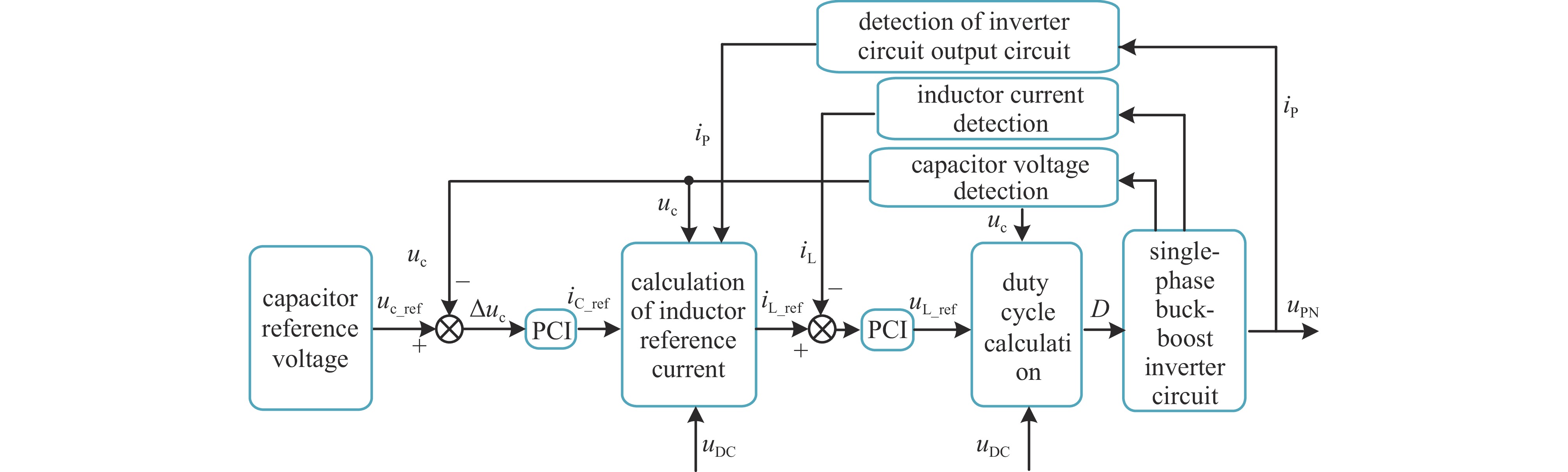
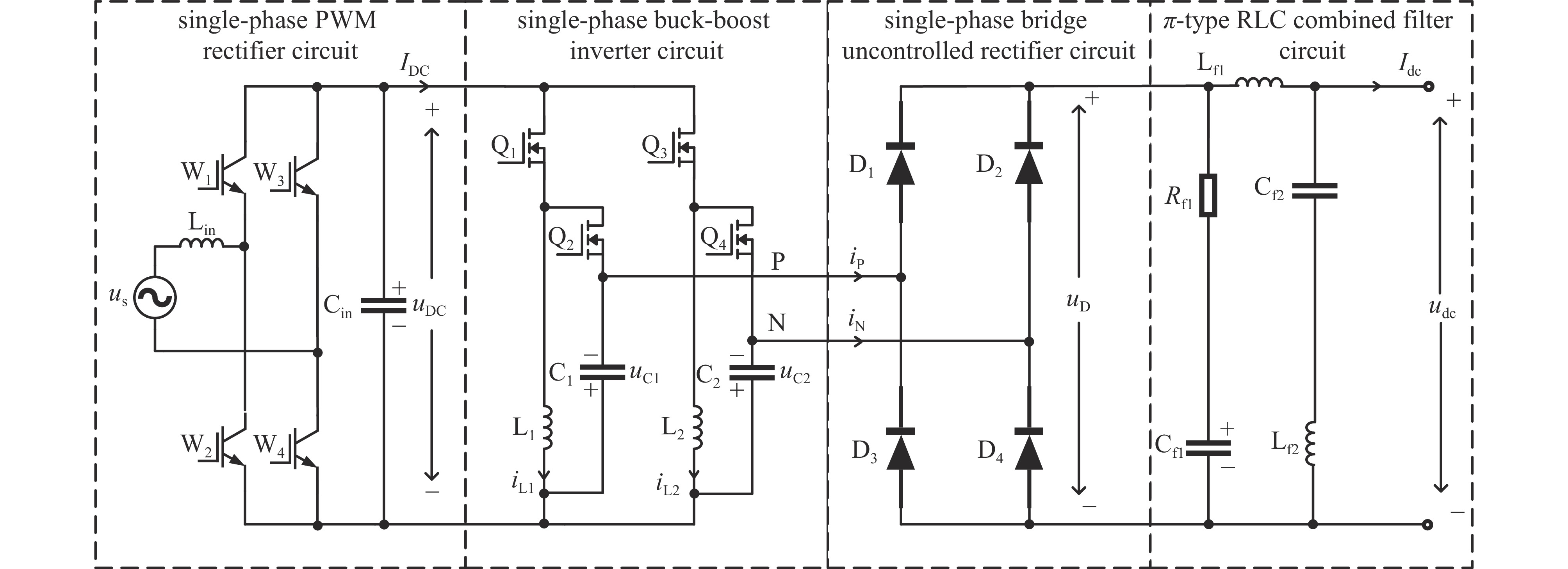
A novel low-ripple adjustable DC regulated power supply with single-phase AC input and control strategy
-
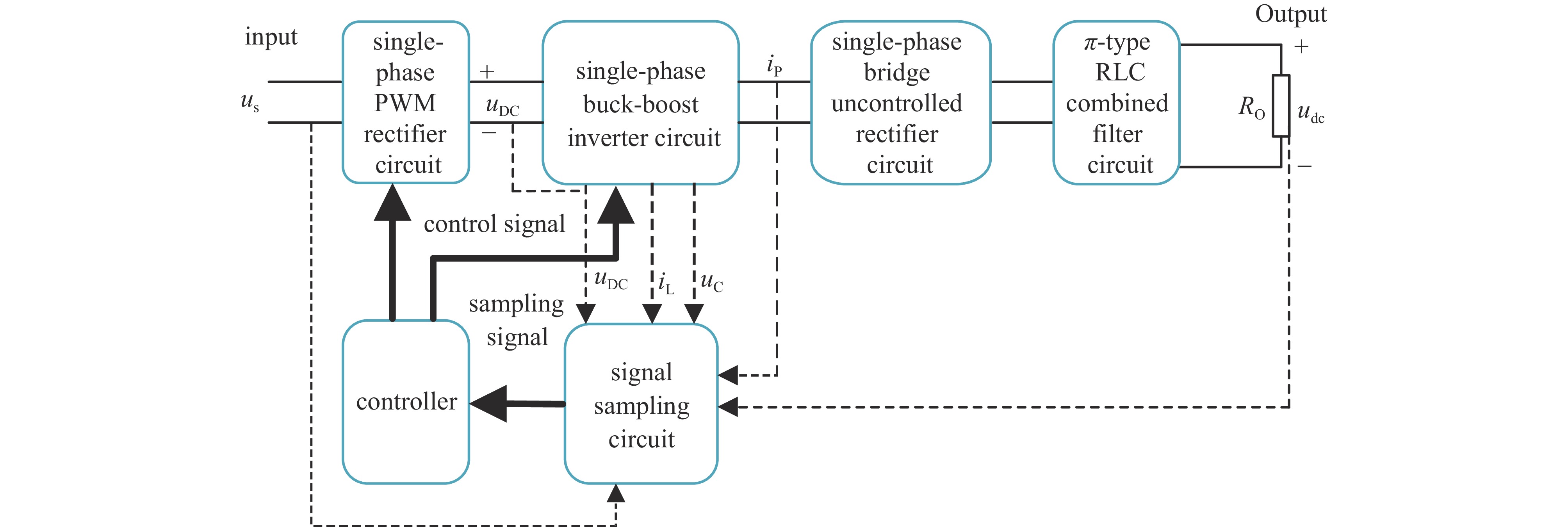
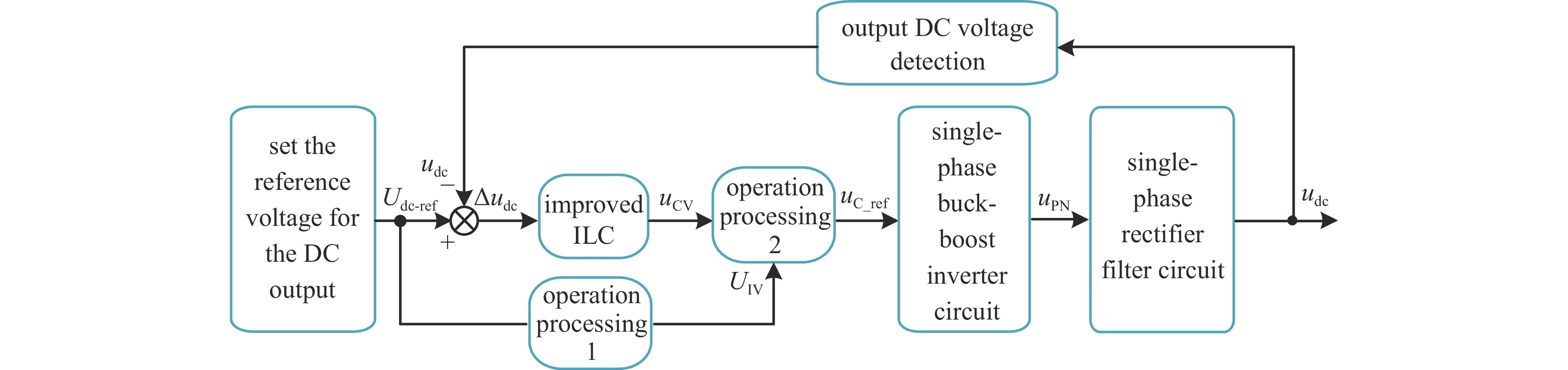
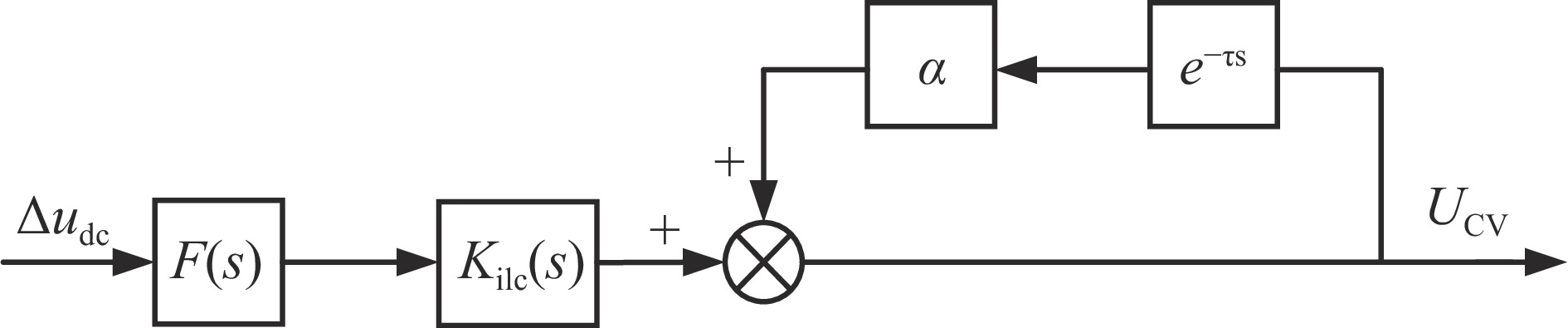
摘要: 针对目前单相交流输入低纹波直流稳压电源存在主电路结构复杂等不足,提出一种新型的单相交流输入低纹波可调直流稳压电源主电路拓扑结构。介绍了该新型拓扑结构的基本工作原理,建立了其数学模型并分析了其电压传输特性,根据其低纹波高稳定度控制要求提出一种基于改进迭代学习控制的参考输出电压幅值自补偿与双闭环比例复数积分(PCI)控制相结合的控制方法,最后对其效果进行了仿真与实验验证,同时与目前常用单相交流输入低纹波直流稳压电源进行了对比分析,结果表明:所提出的单相交流输入低纹波可调直流稳压电源拓扑结构具有电路结构简单、输出电压任意可调、纹波小、稳态精度高等特点,因而具有较好的实际应用价值。
-
关键词:
- 单相交流输入可调直流稳压电源 /
- 新型主电路拓扑结构 /
- 改进迭代学习控制 /
- 双闭环PCI控制
Abstract:Background Single-phase AC-input low-ripple DC regulated power supplies are critical for sensitive applications. However, conventional designs often suffer from complex power circuit configurations, increasing cost and size while potentially compromising reliability. Achieving simultaneously low output voltage ripple, high steady-state accuracy, and wide output voltage adjustability remains a significant challenge in power electronics.Purpose This study aims to overcome the limitations of existing topologies by proposing a novel single-phase AC-input low-ripple adjustable DC regulated power supply circuit. Furthermore, it develops a dedicated advanced control strategy to meet stringent low-ripple and high-stability performance requirements.Methods The fundamental principles of the proposed topology were analyzed, and its mathematical model established to characterize voltage transmission. A composite control scheme integrating reference output voltage amplitude self-compensation using improved Iterative Learning Control (ILC), and a dual-loop Proportional Complex Integral (PCI) control structure, was designed for precise low-ripple regulation and stability. Effectiveness was validated via simulation and experimental testing on a prototype.Results Validation confirmed successful operation. Comparative analysis demonstrated the topology's advantages: simpler/compact structure, wide adjustable output voltage, significantly reduced ripple, and improved steady-state accuracy. The control strategy effectively ensured stability and met performance targets.Conclusions The combined novel topology and advanced control provide a viable solution for high-quality single-phase AC-input adjustable DC supplies. -
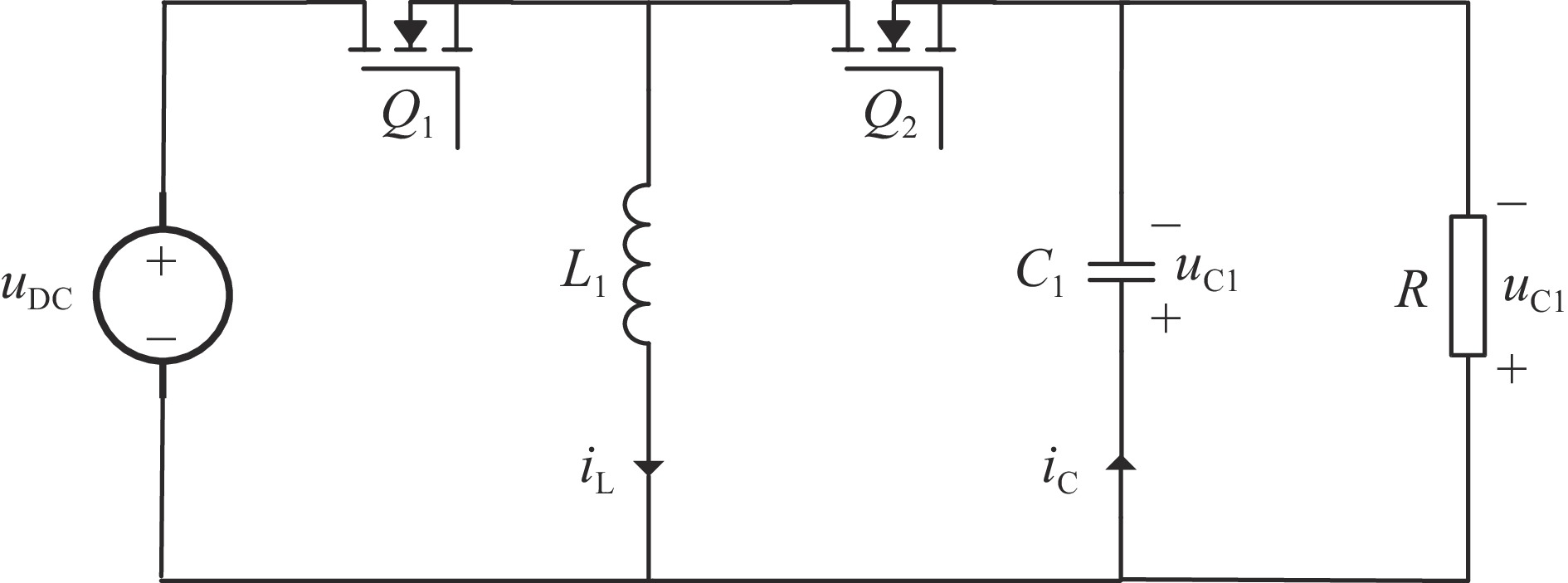
表 1 本结构主电路参数表
Table 1. Main circuit parameter table of this structure
Num. component name parameter value 1 inductor in a Buck-Boost circuit L/μH 10 2 capacitor in a Buck-Boost circuit C/μF 18 3 output filter capacitor Cf1/μF 200 4 output filter capacitorCf2/μF 80 5 output filter inductor Lf1/μH 190 6 output filter inductor Lf2/μH 1.9 7 damping resistor Rf1/Ω 1 8 load resistance RO/Ω 100 表 2 本结构控制参数表
Table 2. Control parameter table of this structure
Num. controller name parameter parameter value 1 capacitor voltage outer loop controller kPC 11.5 kIC 35 2 inductor current inner loop controller kPL 14.15 kIL 4 3 ILC controller kIp 0.144 KIi 35 α 0.55 kF 1.12 表 3 对比结构主电路参数表
Table 3. Main circuit parameter table of comparative structure
Num. component name parameter value 1 resonant capacitor Cr/nF 110 2 resonant inductor Lr/μH 14.5 3 resonant inductor Lm/μH 64.4 4 transformer turns ratio 1:2 5 output filter capacitor Cf/nF 40 6 output filter inductor Lf/μH 200 7 load resistance RO/Ω 100 表 4 对比结构控制参数表
Table 4. Control parameter table of comparative structure
Num. controller name parameter parameter value 1 PI controller proportional gain kp 100 integral gain ki 2.5e+3 2 resonant controller resonant gain kr 1000 quality factor Q 200 resonant frequency wn 1000 表 5 两种结构对应的仿真结果
Table 5. Simulation results of two topologies
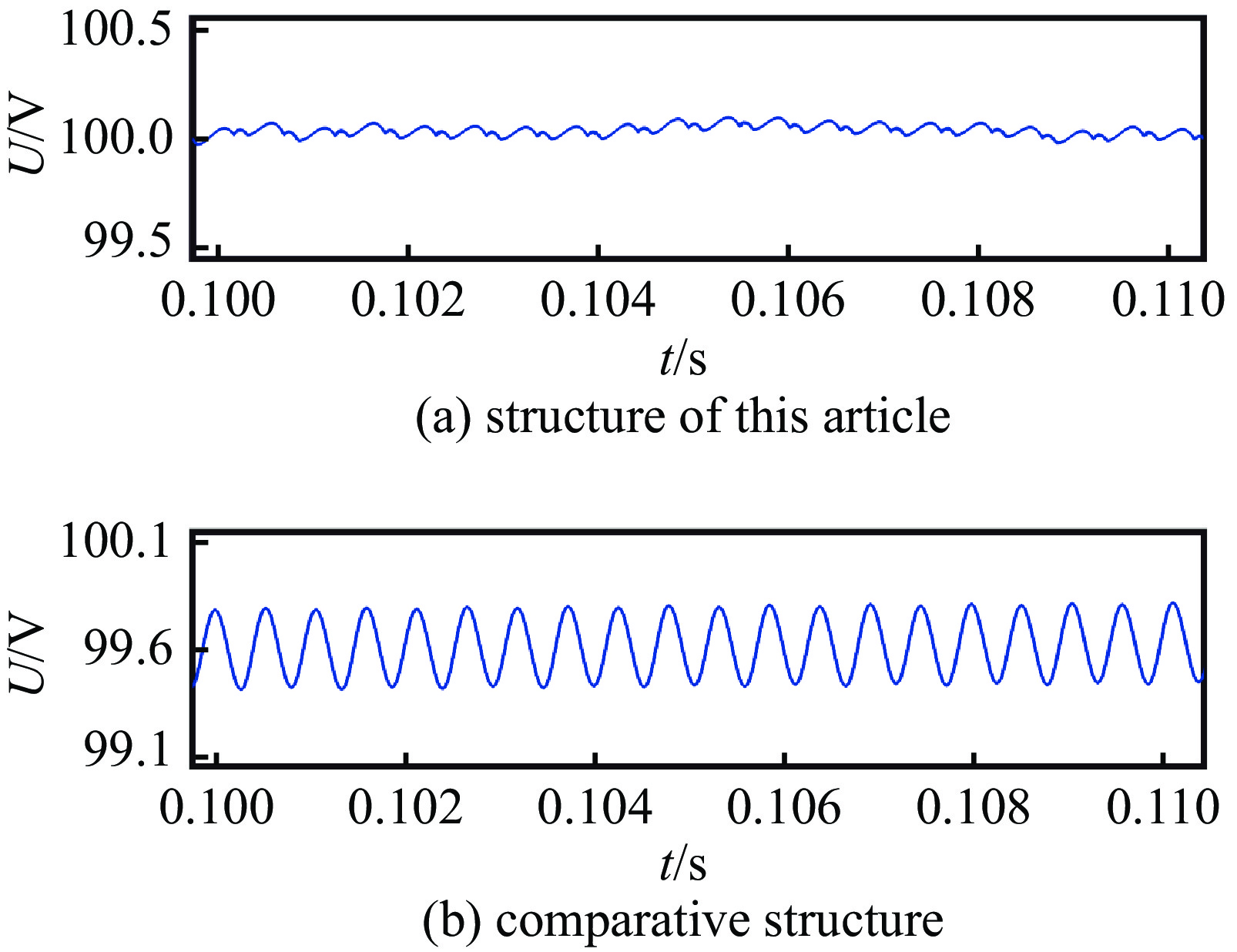
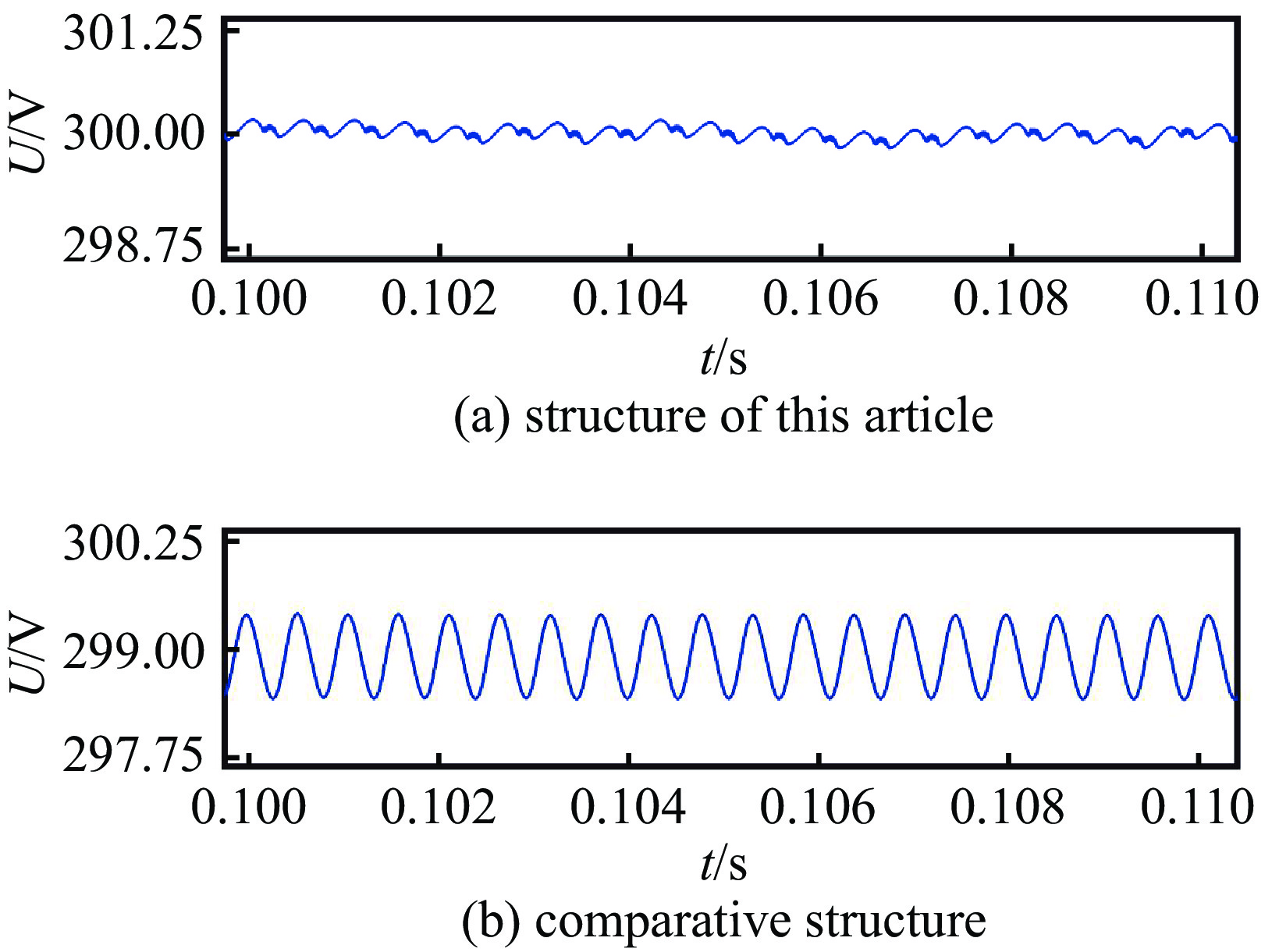
reference output
voltage Udc-ref/Vsteady-state accuracy ripple coefficient this structure comparative structure this structure comparative structure 100 0.11% 0.41% 0.110% 0.47% 300 0.10% 0.37% 0.096% 0.44% 表 7 实验与仿真结果
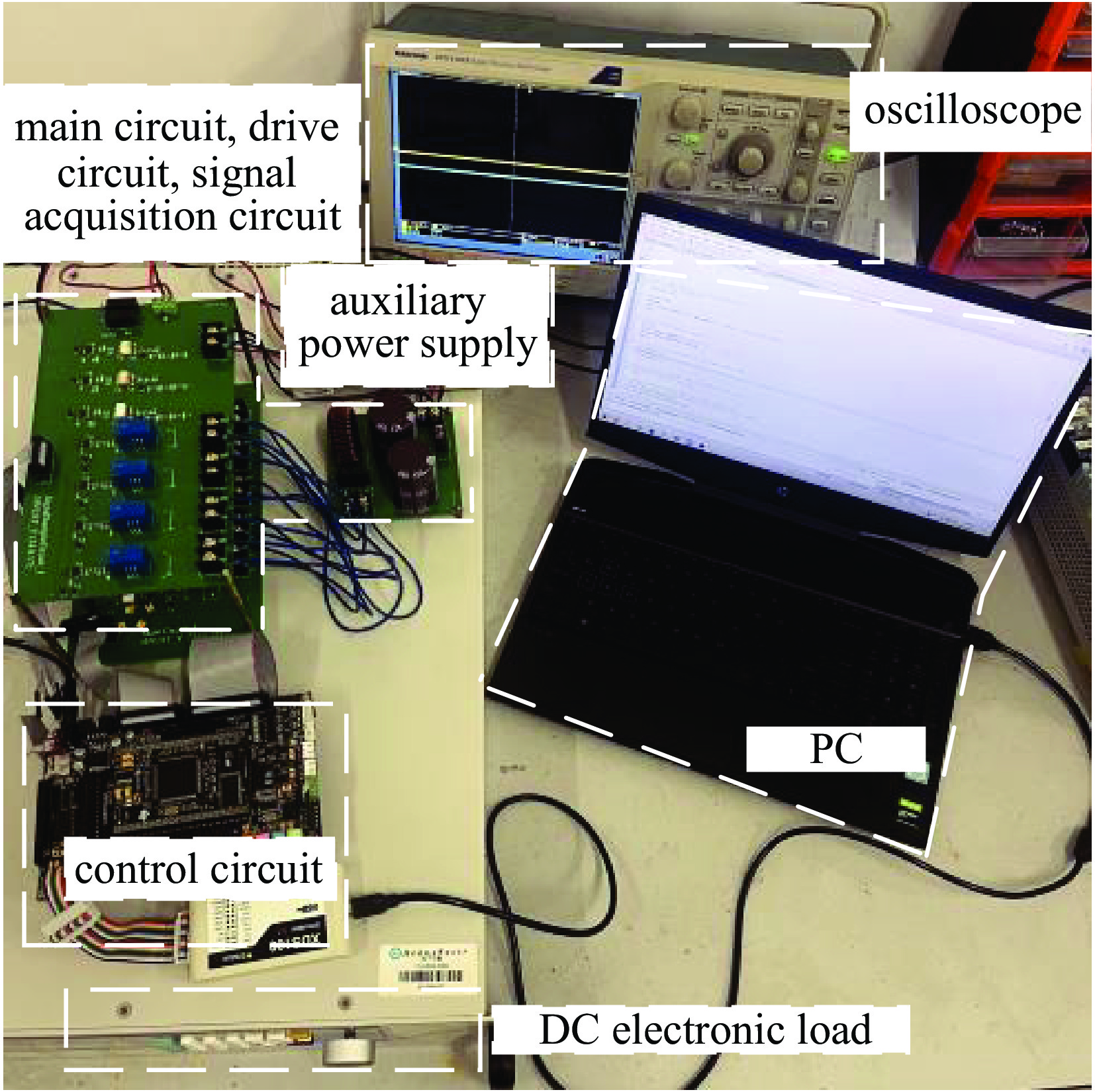
Table 7. Experimental and simulation results
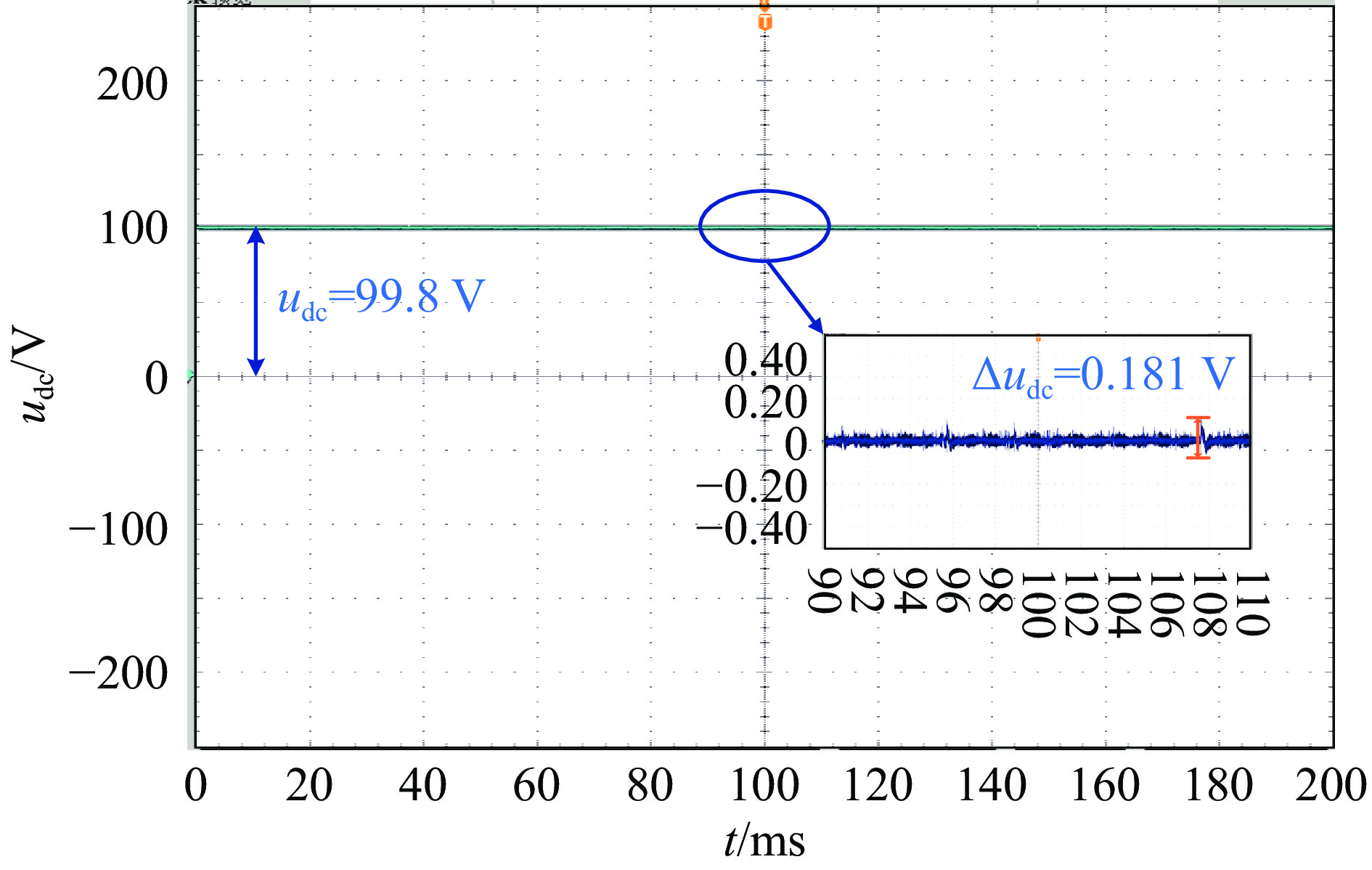
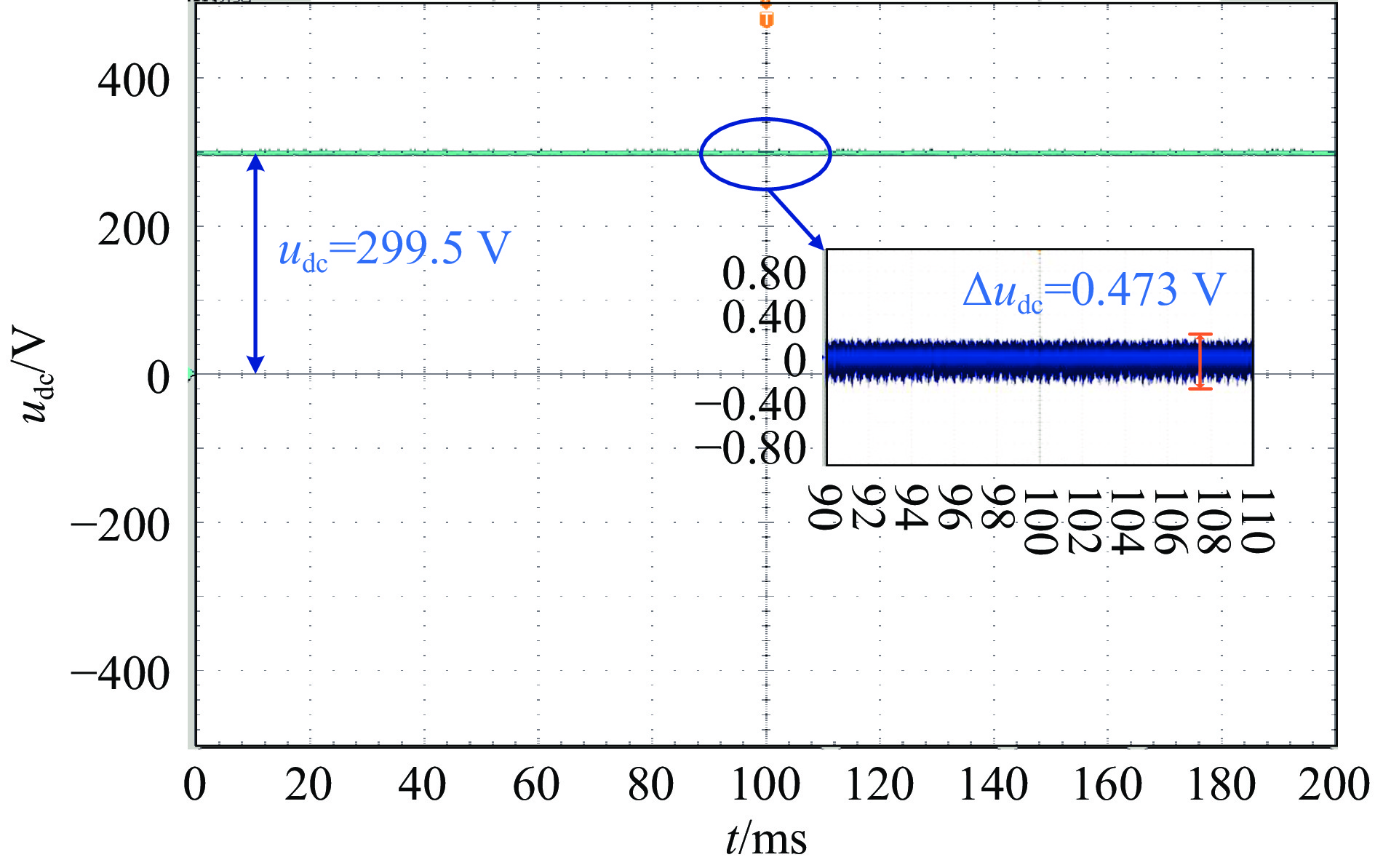
output voltage udc/V steady-state accuracy ripple coefficient experiment simulation experiment simulation 100 0.181% 0.110% 0.20% 0.11% 300 0.157% 0.096% 0.18% 0.10% 表 6 两种结构所采用的元器件数量
Table 6. Number of components of two topologies
Num. name this structure comparative structure 1 power switch 8 8 2 rectifier diode 4 4 3 inductor 5 4 4 capacitor 5 5 5 transformer 0 1 6 damping resistor 1 0 -
[1] 周京华, 孟祥飞, 陈亚爱, 等. 基于新能源发电的电解水制氢直流电源研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43(6):389-397Zhou Jinghua, Meng Xiangfei, Chen Yaai, et al. Research on DC power supply for hydrogen production from electrolytic water based on new energy generation[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43(6): 389-397 [2] 张鑫宇, 樊艳芳, 马健, 等. 适用于光伏直流升压变换器的故障诊断及保护策略[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43(11):68-77Zhang Xinyu, Fan Yanfang, Ma Jian, et al. Fault diagnosis and protection strategy for photovoltaic DC-DC converter[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43(11): 68-77 [3] Han Xiao, Yao Xuliang, Liao Yuefeng. Full operating range optimization design method of LLC resonant converter in marine DC power supply system[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11: 2142. doi: 10.3390/jmse11112142 [4] Zhang Daning, Xu Lulin, Tian Wenrui, et al. A fast dielectric response measurement instrument with dynamic power supply tracking and active suppression of temperature fluctuations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(12): 12839-12850. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3234148 [5] 李亚维, 谢敏, 蓝欣, 等. 200kV低纹波高稳定度直流高压电源[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28:015016Li Yawei, Xie Min, Lan Xin, et al. A 200kV high voltage DC power supply with high stability and low ripple[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 015016 [6] Deblecker O, Moretti A, Vallée F. Comparative study of soft-switched isolated DC-DC converters for auxiliary railway supply[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2008, 23(5): 2218-2229. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2008.2001879 [7] Wang Zhishuang, Wang Ping, Li Bo, et al. A bidirectional DC-DC converter with high voltage conversion ratio and zero ripple current for battery energy storage system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(7): 8012-8027. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.3048043 [8] Bandeira D G, Lazzarin T B, Barbi I. High voltage power supply using a T-type parallel resonant DC-DC converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2018, 54(3): 2459-2470. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2018.2792446 [9] Zhang Yi, Zhang Donglai, Li Jie, et al. Bidirectional LCLL resonant converter with wide output voltage range[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(11): 11813-11826. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.2986505 [10] Jang Y, Jovanovic M M. Interleaved boost converter with intrinsic voltage-doubler characteristic for universal-line PFC front end[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2007, 22(4): 1394-1401. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2007.900502 [11] Kim H S, Baek J W, Ryu M H, et al. The high-efficiency isolated AC-DC converter using the three-phase interleaved LLC resonant converter employing the Y-connected rectifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(8): 4017-4028. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2013.2290999 [12] 阎铁生, 许建平, 高建龙, 等. 低输出电压纹波准单级反激PFC变换器[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2015, 35(9):22-29Yan Tiesheng, Xu Jianping, Gao Jianlong, et al. Quasi single-stage flyback PFC converter with low output voltage ripple[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2015, 35(9): 22-29 [13] Lee S W, Do H L. Boost-integrated two-switch forward AC-DC led driver with high power factor and ripple-free output inductor current[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(7): 5789-5796. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2652407 [14] Kouro S, Cortés P, Vargas R, et al. Model predictive control-A simple and powerful method to control power converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(6): 1826-1838. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.2008349 [15] 张小平, 朱建林, 唐华平, 等. 一种新型Buck-Boost矩阵变换器[J]. 信息与控制, 2008, 37(1):40-45 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0411.2008.01.006Zhang Xiaoping, Zhu Jianlin, Tang Huaping, et al. A novel Buck-Boost matrix converter[J]. Information and Control, 2008, 37(1): 40-45 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0411.2008.01.006 [16] Laird H D, Round S D, Duke R M. A frequency-domain analytical model of an uncontrolled single-phase voltage-source rectifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2000, 47(3): 525-532. doi: 10.1109/41.847892 [17] Hou Z S, Wang Z. From model-based control to data-driven control: survey, classification and perspective[J]. Information Sciences, 2013, 235: 3-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2012.07.014 [18] 孟琦, 侯忠生. 基于周期信号的迭代学习控制在逆变器中的应用[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2016, 33(3):289-294 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2016.50258Meng Qi, Hou Zhongsheng. A novel periodic-signal- based iterative learning control method and its application to inverter system[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2016, 33(3): 289-294 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2016.50258 [19] Bojoi R I, Griva G, Bostan V, et al. Current control strategy for power conditioners using sinusoidal signal integrators in synchronous reference frame[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2005, 20(6): 1402-1412. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2005.857558 [20] 郭小强, 邬伟扬, 赵清林, 等. 三相并网逆变器比例复数积分电流控制技术[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2009, 29(15):8-14 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2009.15.002Guo Xiaoqiang, Wu Weiyang, Zhao Qinglin, et al. Current regulation for three-phase grid-connected inverters based on proportional complex integral control[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2009, 29(15): 8-14 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2009.15.002 [21] 干天助, 梁理程, 陈延礼, 等. 基于改进PCI控制器的光伏并网逆变器的直流分量抑制策略[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43(7):93-100Gan Tianzhu, Liang Licheng, Chen Yanli, et al. DC component suppression of PV grid-connected inverter with improved PCI controller[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43(7): 93-100 [22] 李啸骢, 侯立亮, 罗雪丽, 等. 三相逆变并网系统的分数阶建模与控制器设计研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44(3):415-424Li Xiaocong, Hou Liliang, Luo Xueli, et al. Research on fractional modeling and controller design of three-phase inverter grid-connected system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2023, 44(3): 415-424 [23] 刘世豪, 慕振成, 周文中, 等. 基于Simulink大功率电子管放大器仿真[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:095104 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.095104Liu Shihao, Mu Zhencheng, Zhou Wenzhong, et al. Simulation on high-power tetrode amplifier based on Similink[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 095104 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.095104 [24] 程惠, 任勇峰, 王强. 电源纹波的测量及抑制[J]. 电源技术, 2012, 36(12):1899-1900,1921 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2012.12.040Cheng Hui, Ren Yongfeng, Wang Qiang. Measurement and suppression of power supply ripple[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 36(12): 1899-1900,1921 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2012.12.040 -




 下载:
下载: