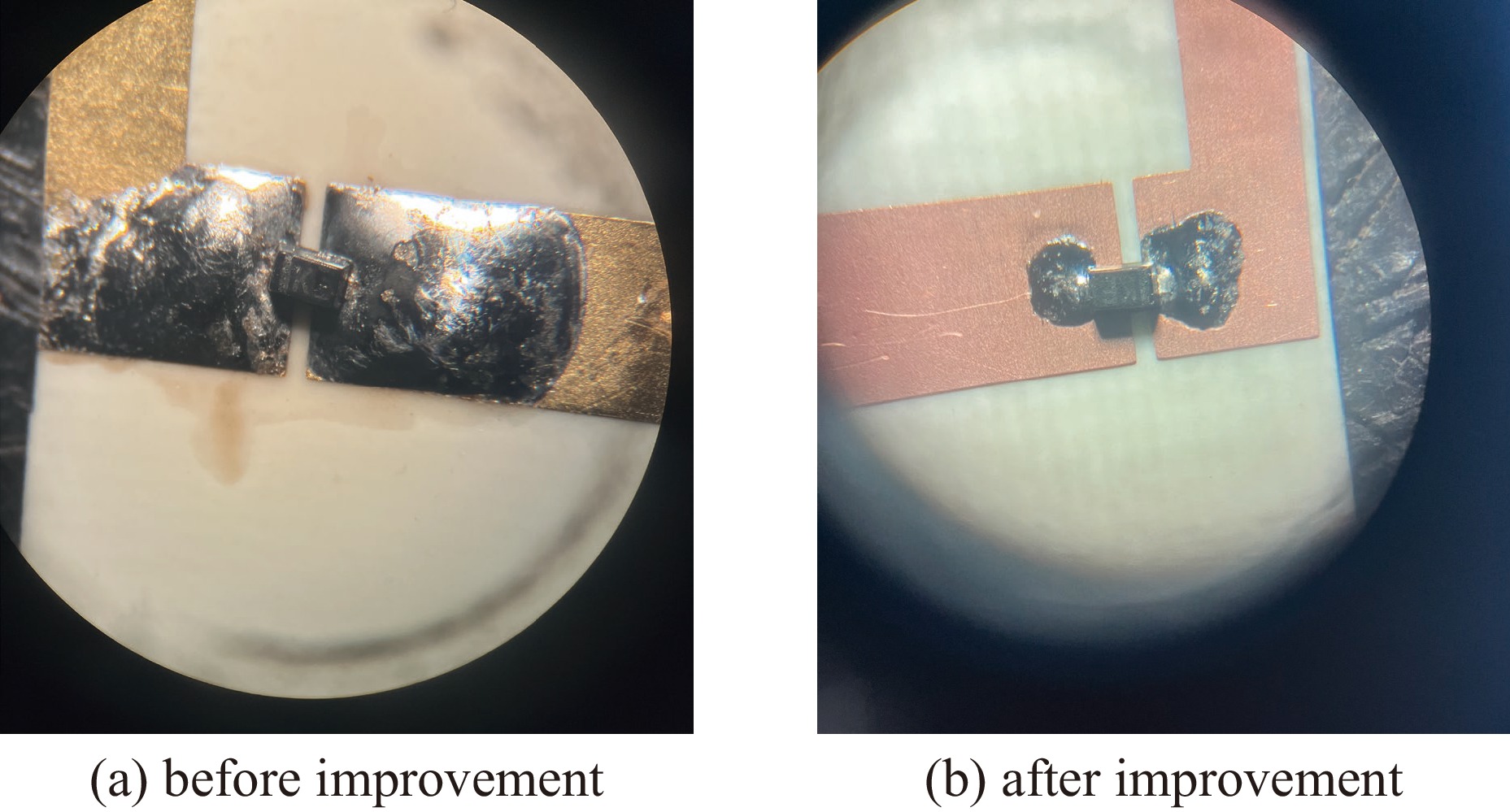
Design of a megawatt-level fast bi-phase modulator based on PIN diodes
-
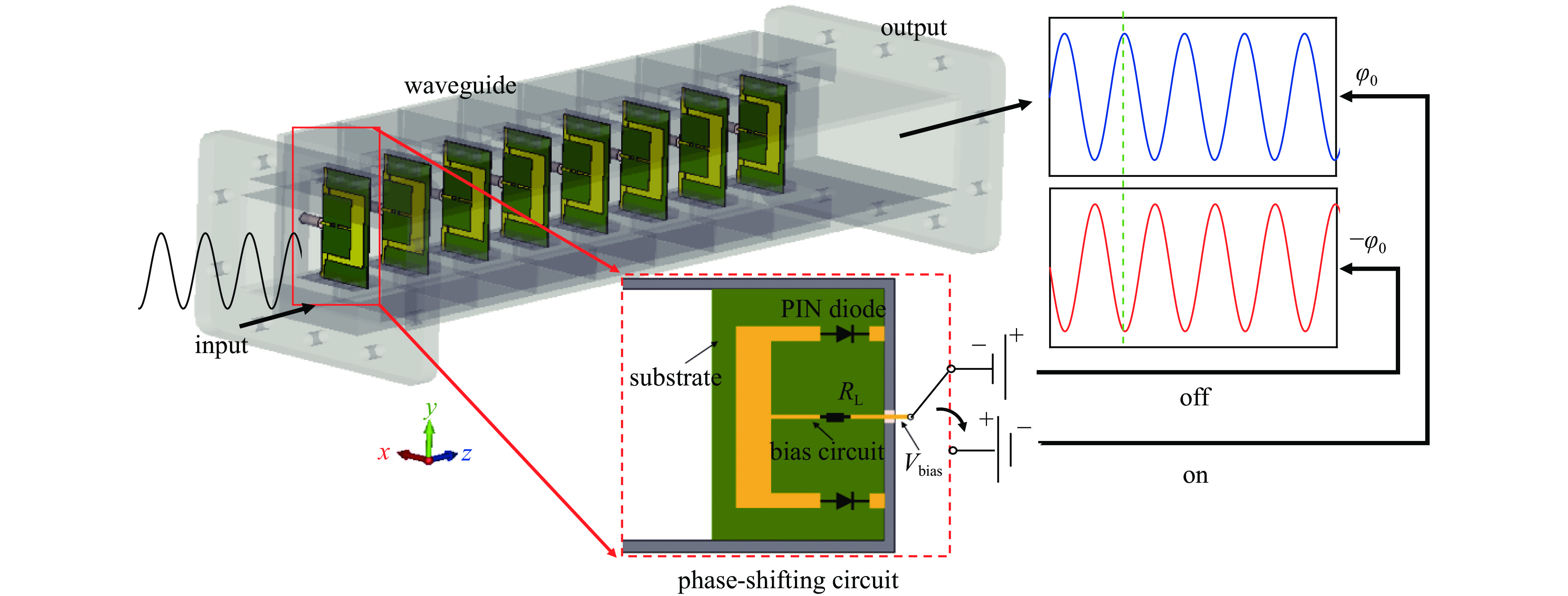
摘要: 为研究基于磁控管等电真空振荡器的低成本、小型化、稳定且可阵列化应用的SLAC能量倍增器(SLED),设计了一种功率容量兆瓦级、响应时间纳秒级的高功率快速倒相开关。在波导结构中插入传统PIN二极管加载线型移相电路单元,通过波导外置偏置电路控制PIN二极管的“开”/“关”状态,改变移相电路的等效阻抗以控制波导传输微波相位。已通过高功率实验验证了此类二极管波导移相器的高功率特性。通过级联8个移相电路单元实现180°相移。对所设计的倒相开关进行了频域与时域参数测试:频域测试结果表明,该倒相开关在工作频率下的插损小于0.7 dB,在中心频率2.458 GHz处相移172°,相移量与仿真设计值相比误差在±4°以内;时域测试结果表明,该倒相开关的倒相时间约为5 ns。Abstract:
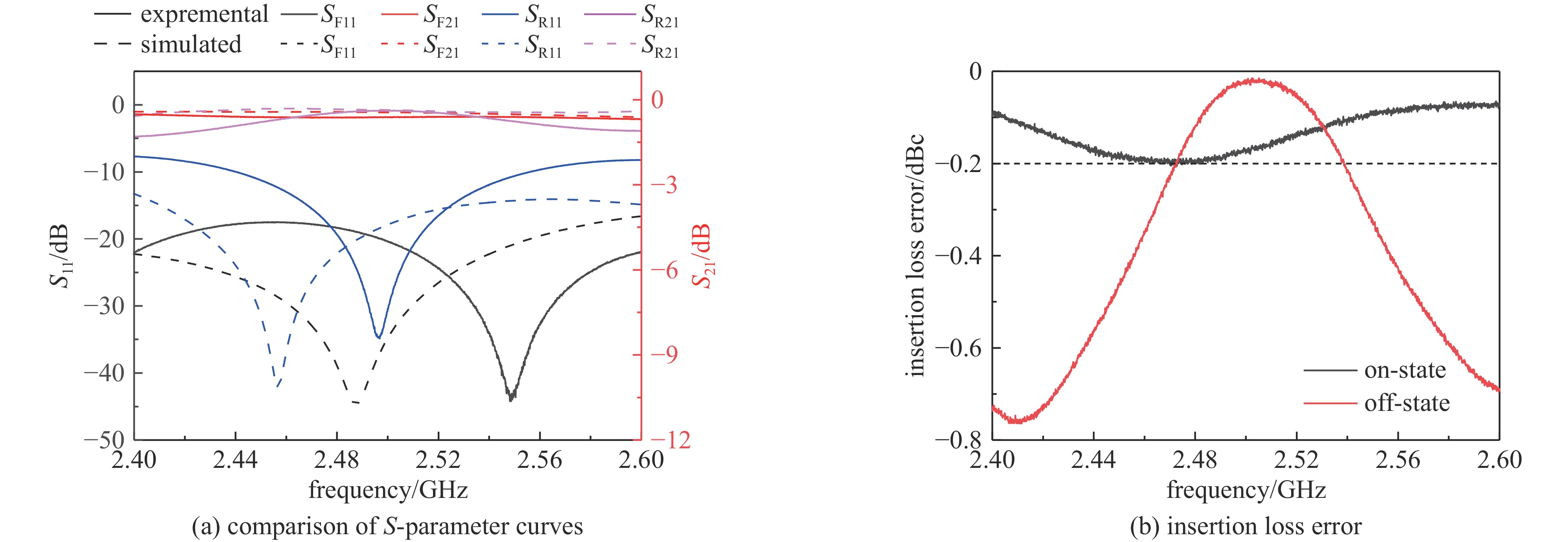
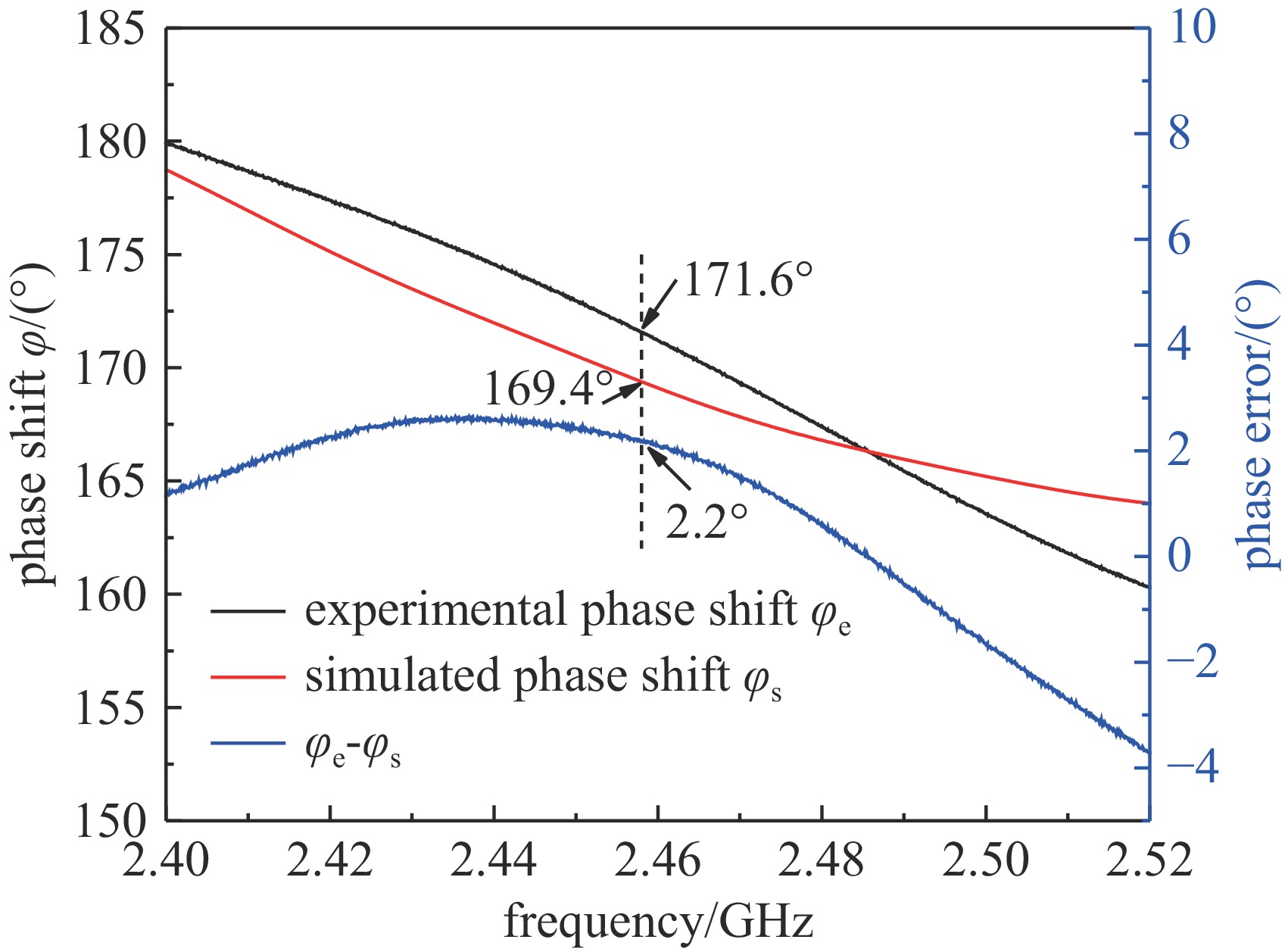
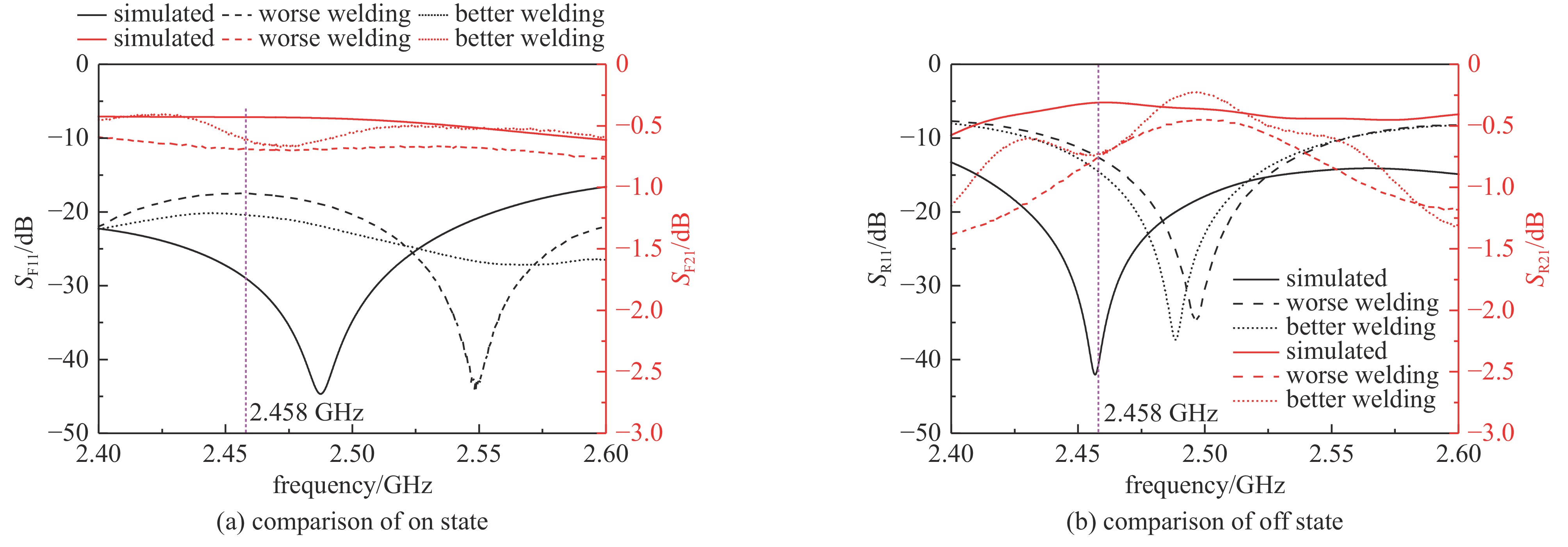
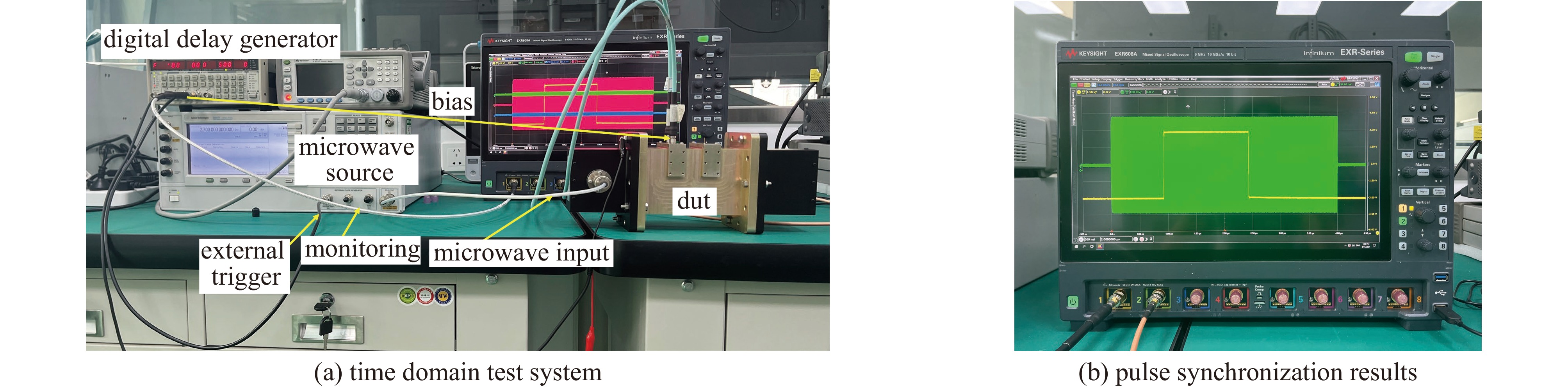
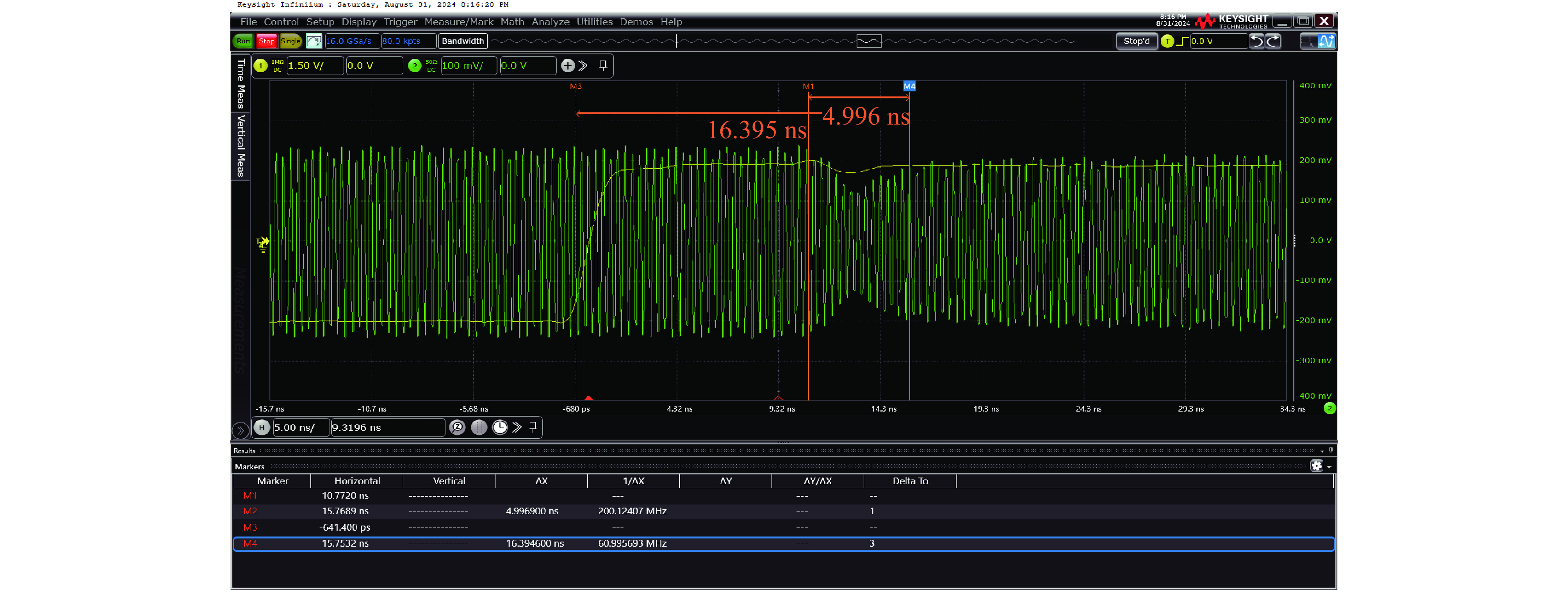
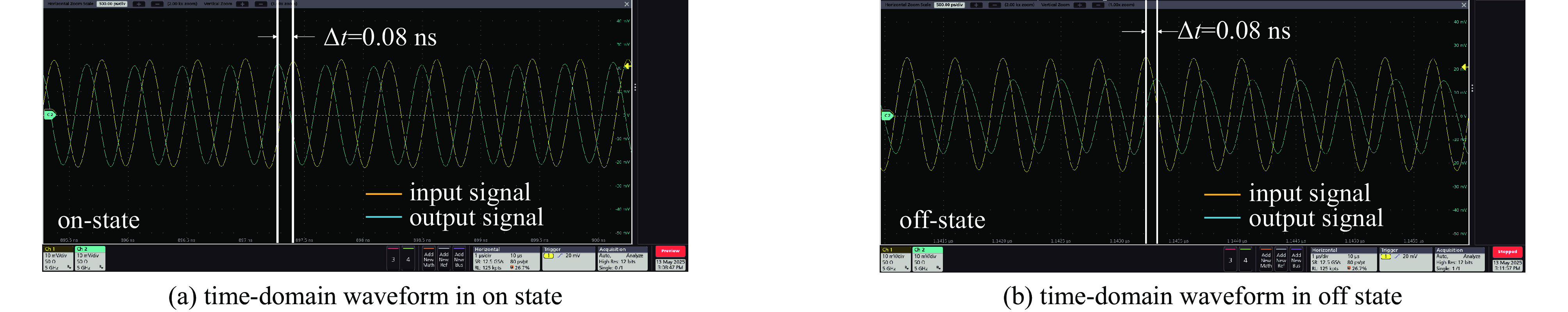
Background High power microwave (HPM) pulse technology has developed rapidly due to its applications in particle accelerators, radar, communications, directed energy, plasma physics, and other fields. Pulse compression technology provides an effective method for enhancing the peak power of microwave pulses.Purpose In order to study a low-cost, miniaturized, stable, and arrayable SLAC Energy Doubler (SLED) based on vacuum electronic oscillators such as magnetrons, a high power fast bi-phase modulator with megawatt-level capacity and nanosecond response time has been designed.Methods Insert a conventional PIN diode loaded-line type phase-shifting circuit into the waveguide structure, and the equivalent impedance of the phase-shifting circuit changes by switching the “on” and “off” states of the PIN diodes through the waveguide external bias circuit, then the waveguide transmission microwave phase changes. The high-power characteristics of such PIN diode waveguide phase shifters have been verified by high-power experiments.Results In this paper, a 180° phase shift is realized by cascading 8 phase-shifting circuit cells. The frequency-domain and time-domain parameters of the designed bi-phase modulator are tested. The frequency-domain test results show that the insertion loss of the bi-phase modulator is less than 0.7 dB, and the phase shift is 172° at the center frequency of 2.458 GHz. The error of the phase shift is within ±4° compared with that of the design value in simulation. The time-domain test results show that the inversion time of the bi-phase modulator is about 5 ns.Conclusions Compared with traditional semiconductor phase shifters, this bi-phase modulator can achieve the same phase-reversal speed while withstanding high power capacities, making it extremely valuable in the HPM field.-
Key words:
- energy doubler /
- pulse compressor /
- bi-phase modulator /
- PIN diode
-
表 1 工作频率2.458 GHz处的实测及仿真参数
Table 1. Measured and simulated parameters at 2.458 GHz operating frequency
SF11/dB SF21/dB SR11/dB SR21/dB φ/(°) simulated −28.98 −0.43 −40.76 −0.31 169.38 experimental −17.53 −0.62 −12.59 −0.68 171.57 error 11.45 0.19 28.17 0.37 2.19 表 2 设计的倒相开关与文献中移相器的性能参数对比
Table 2. Comparison of the performance parameters of the bi-phase modulator designed with the phase shifters (PS) in the literature
-
[1] Woolley B, Syratchev I, Dexter A. Control and performance improvements of a pulse compressor in use for testing accelerating structures at high power[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2017, 20: 101001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.20.101001 [2] 熊正锋. 基于大功率速调管产生高功率微波技术研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2016: 1-13Xiong Zhengfeng. Research on the technology for generating high power microwaves based on high power klystrons[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2016: 1-13 [3] Wang J W, Tantawi S G, Xu Chen, et al. Development for a supercompact X-band pulse compression system and its application at SLAC[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2017, 20: 110401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.20.110401 [4] Wang Ping, Shi Jiaru, Zha Hao, et al. Development of an S-band spherical pulse compressor[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2018, 901: 84-91. [5] Jiang Yuliang, Zha Hao, Wang Ping, et al. Demonstration of a cavity-based pulse compression system for pulse shape correction[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2019, 22: 082001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.22.082001 [6] Jiang Tao, Yang Meng, Xiong Zhengfeng, et al. An X-band switched energy storage microwave pulse compression system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2019, 47(10): 4525-4529. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2019.2920739 [7] Artemenko S N, Igumnov V S, Shlapakovsky A S, et al. Compact active s-band microwave compressors for producing rectangular pulses of up to 100 ns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2019, 67(2): 597-605. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2018.2886850 [8] Ioannidis Z C, Savaidis S P, Mitilineos S A, et al. Design of microwave pulse compressors using small form-factor waveguide cavities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2020, 68(8): 3255-3262. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.2996218 [9] 张治强, 方进勇, 郝文析, 等. X波段脉冲压缩装置的数值模拟及优化设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2006, 18(2): 330-332Zhang Zhiqiang, Fang Jinyong, Hao Wenxi, et al. Numerical simulation and optimization design of X-band pulse compression equipment[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2006, 18(2): 330-332 [10] Vikharev A L, Ivanov O A, Gorbachev A M, et al. Experiments on active RF pulse compressors using plasma switches[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2006, 807(1): 463-473. [11] Artemenko S N, Gorev S A, Igumnov V S, et al. Formation of rectangular pulses in an active microwave compressor with an oversized compact storage cavity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(2): 1255-1264. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.3042509 [12] 陶小魁, 何志文, 邢庆子, 等. SES微波脉冲压缩系统瞬态特性的模拟研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2005, 17(4): 559-563Tao Xiaokui, He Zhiwen, Xing Qingzi, et al. Simulation research on the instantaneous response of HPM pulse compression by SES method[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2005, 17(4): 559-563 [13] Beilin L, Shlapakovski A S, Donskoy M, et al. Fast-framing optical imaging of plasma formation in resonant microwave pulse compressor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2014, 42(5): 1346-1352. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2014.2316204 [14] 宁辉, 方进勇, 李平, 等. 高功率微波脉冲压缩技术实验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2001, 13(4): 471-474Ning Hui, Fang Jinyong, Li Ping, et al. Experimental research on HPM pulse compression[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2001, 13(4): 471-474 [15] Chen Liangping, Yin Yong, Deng Shun, et al. Experimental study on breakdown characteristics of microwave gas discharge tubes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2024, 52(10): 4960-4966. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2024.3376970 [16] Jiang Yuliang, Zha Hao, Shi Jiaru, et al. A compact X-band microwave pulse compressor using a corrugated cylindrical cavity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(3): 1586-1593. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3053913 [17] Jiang Yuliang, Shi Jiaru, Wang Ping, et al. Compact two-stage pulse compression system for producing gigawatt microwave pulses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(10): 4533-4540. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3093554 [18] Wang Ping, Zha Hao, Syratchev I, et al. rf design of a pulse compressor with correction cavity chain for klystron-based compact linear collider[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2017, 20: 112001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.20.112001 [19] 王平. 新型高功率微波脉冲压缩器的研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2018: 79-94Wang Ping. Research on the novel high-power microwave pulse compressors[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2018: 79-94 [20] 王自成, 张志强, 高冬平, 等. 高品质因数谐振腔的储能过程和泄能过程[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33: 103007 doi: :10.11884/HPLPB202133.210132Wang Zicheng, Zhang Zhiqiang, Gao Dongping, et al. Storing and dumping processes of energy in high quality factor resonant cavity[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 103007 doi: :10.11884/HPLPB202133.210132 [21] Xiong Zhengfeng, Cheng Cheng, Yu Jian, et al. Switching speed effect of phase shift keying in SLED for generating high power microwaves[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2016, 40: 017006. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/40/1/017006 [22] 白维达, 江涛, 熊正锋, 等. S波段高精度快速倒相开关设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32(5): 053002 (Bai Weida, Jiang Tao, Xiong Zhengfeng, et al. Design of S-band bi-phase modulator with high speed and accuracy[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32(5): 053002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.190394Bai Weida, Jiang Tao, Xiong Zhengfeng, et al. Design of S-band bi-phase modulator with high speed and accuracy[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32(5): 053002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.190394 [23] 沈旭明, 张鹏, 和天慧. 能量倍增器法微波脉冲压缩[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(4): 849-852 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102204.0849Shen Xuming, Zhang Peng, He Tianhui. High power microwave pulse compression of energy doublers[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(4): 849-852 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102204.0849 [24] Song Minsheng, Bi Liangjie, Meng Lin, et al. High-efficiency phase-locking of millimeter-wave magnetron for high-power array applications[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2021, 42(11): 1658-1661. doi: 10.1109/LED.2021.3112563 [25] Li Wenlong, Li Hailong, Qin Yu, et al. Phase control demonstration of S-band hybrid phase-locking magnetrons for array applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2025.3536474. [26] Qin Yu, Bi Liangjie, Yin Yong, et al. Simulation and experiment study of modular X-band phase-locking magnetron[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2024, 71(7): 4342-4346. doi: 10.1109/TED.2024.3405399 [27] Bi Liangjie, Zheng Qiong, Li Hailong, et al. Multiorder-cascaded matching of coupling structures for high-efficiency phase locking between multiple magnetrons[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2024, 71(6): 3932-3939. doi: 10.1109/TED.2024.3392548 [28] Chen Liangping, Yin Yong, Jiang Tao, et al. A megawatt p-i-n diode waveguide phase shifter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2025.3546193. [29] Li Xin, Wang Bangji, Ding Qiao, et al. High-power mechanical waveguide phase shifter: electromagnetic resonance analysis and protection design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2025, 73(2): 760-769. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2024.3440316 [30] Gurbuz O D, Rebeiz G M. A 1.6–2.3-GHz RF MEMS reconfigurable quadrature coupler and its application to a 360° reflective-type phase shifter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2015, 63(2): 414-421. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2014.2379258 -




 下载:
下载: