Analysis of the electromagnetic field effect of proximity lightning strikes by rotary-wing UAV
-
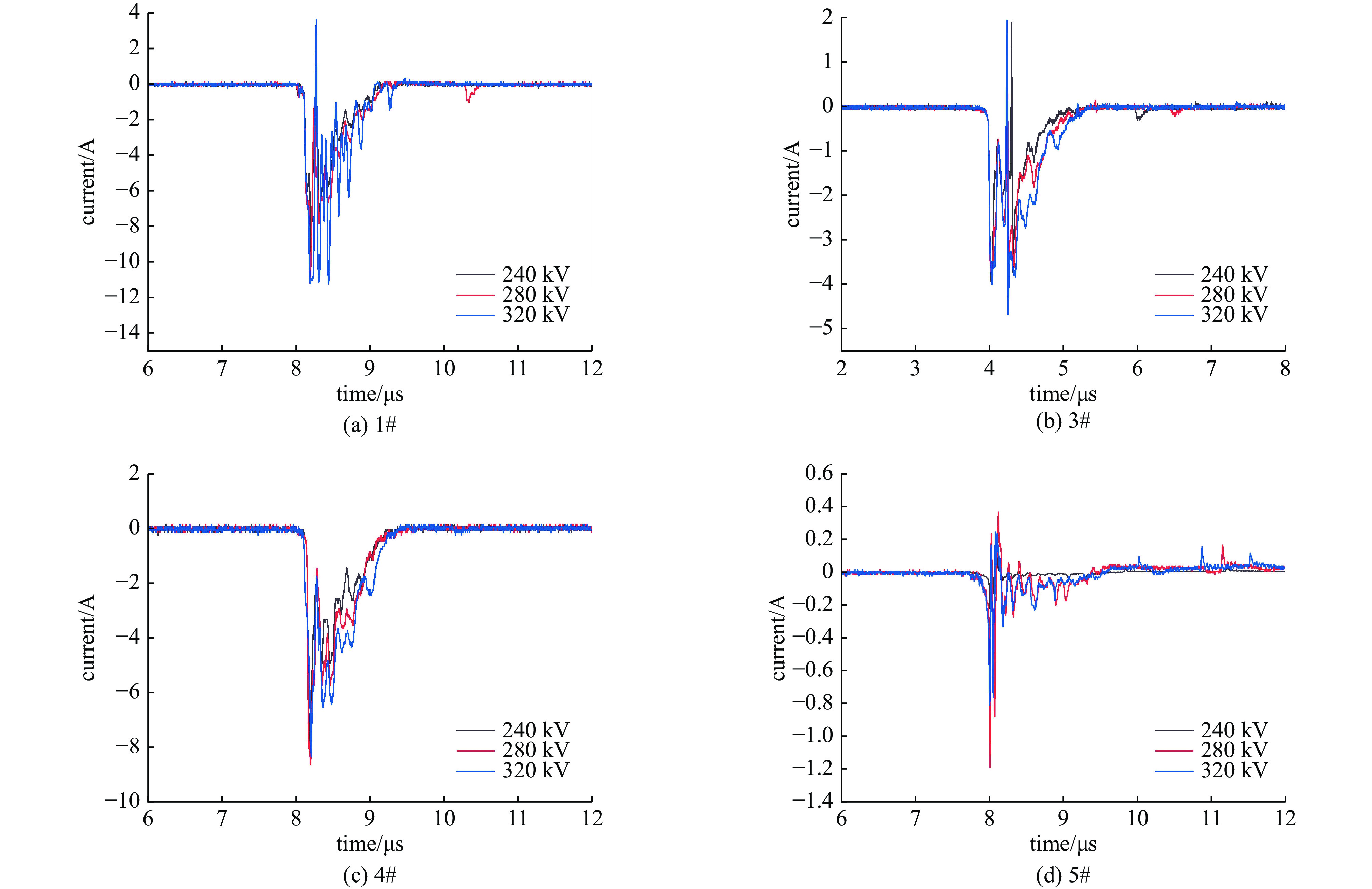
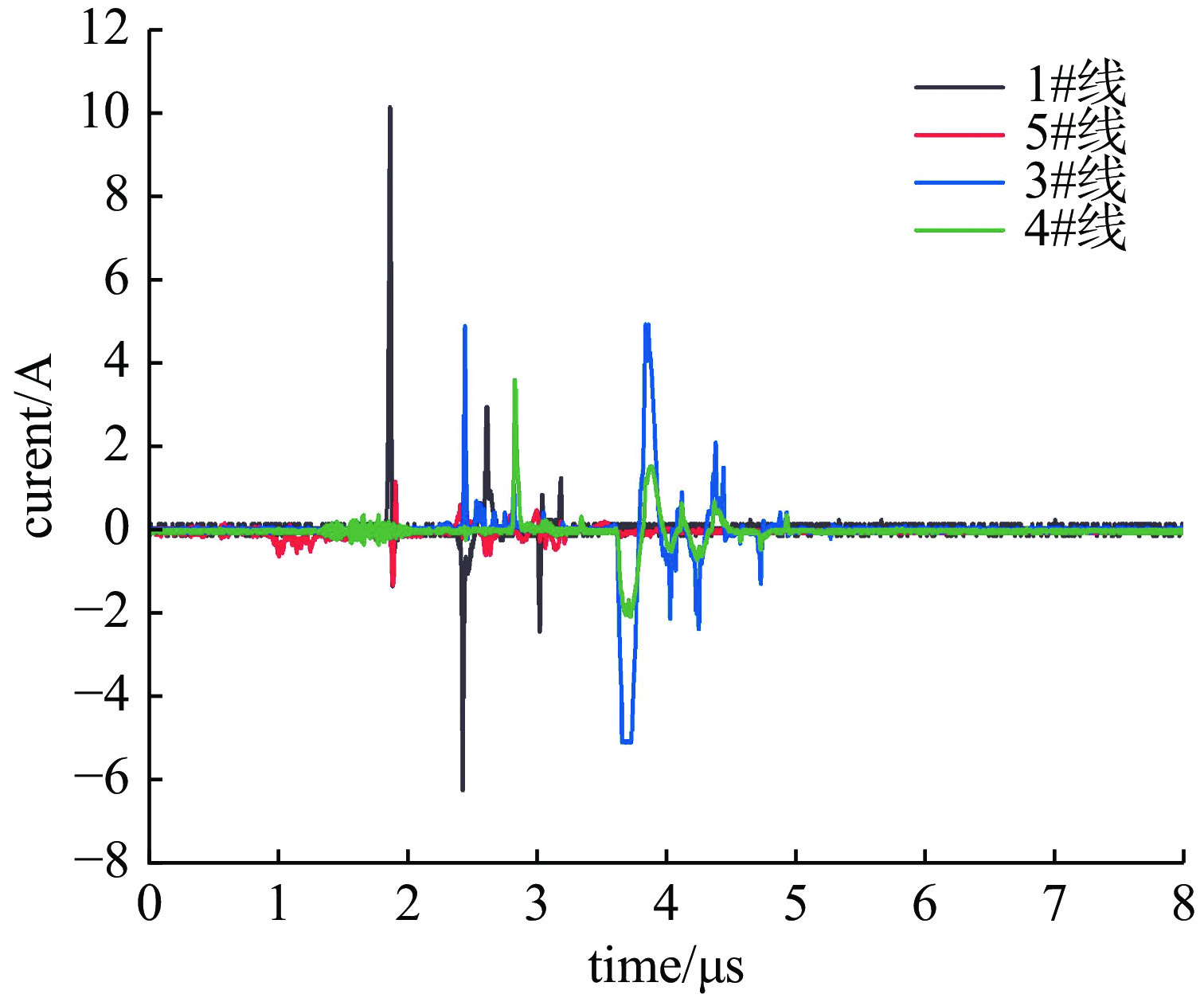
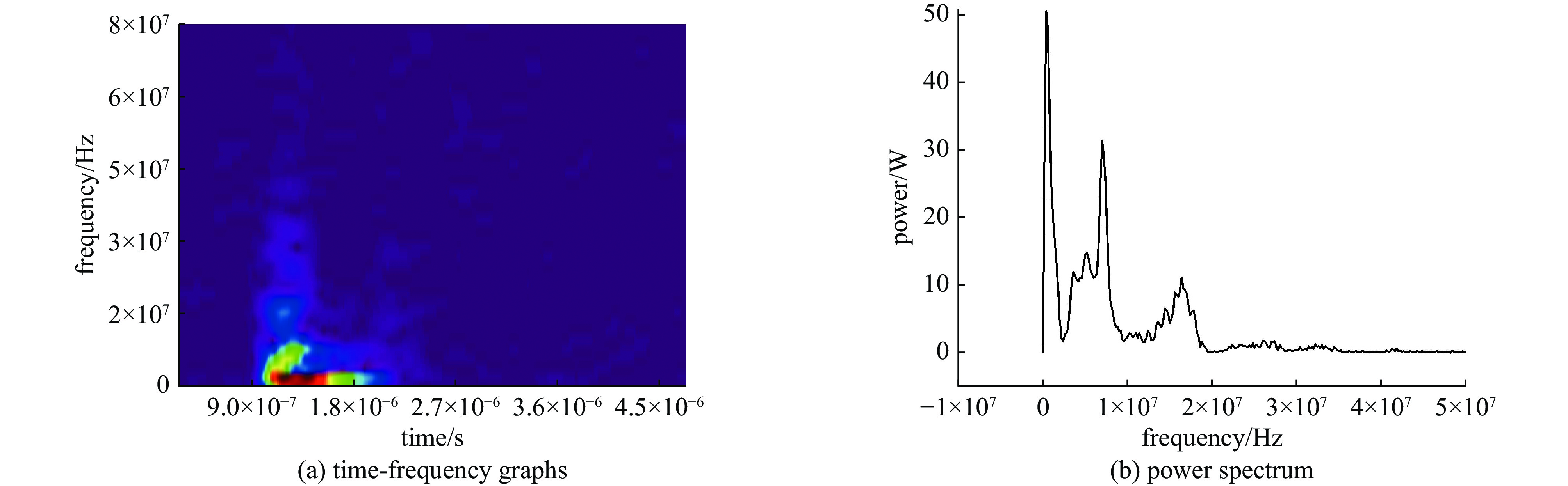
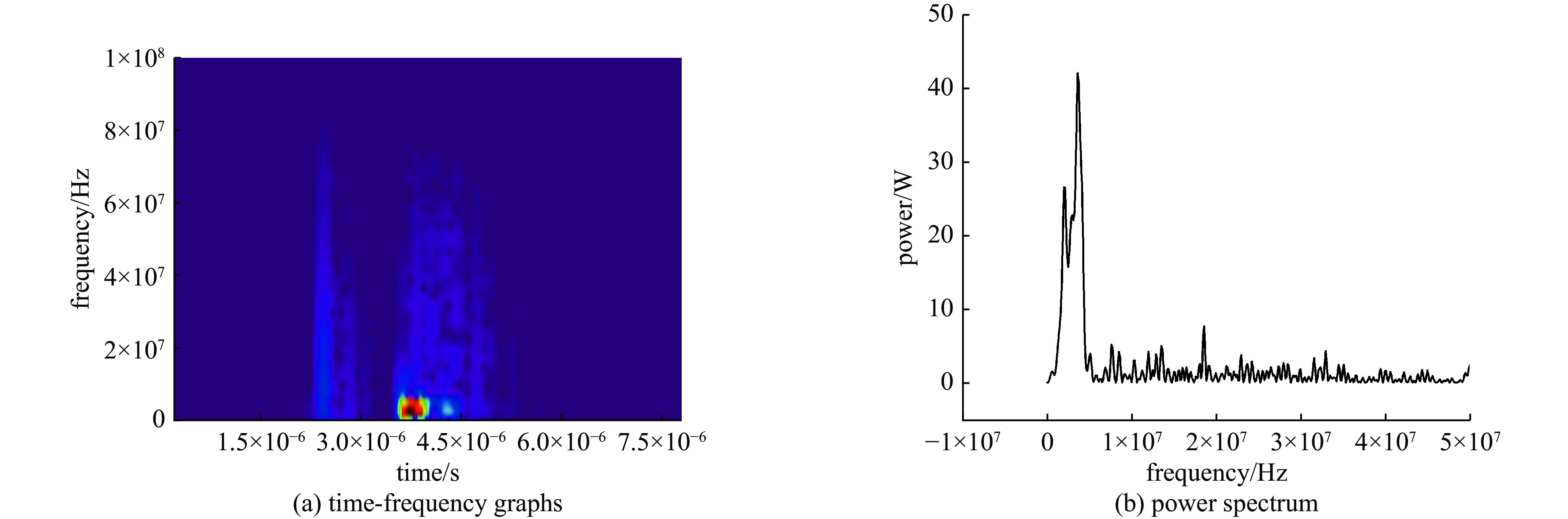
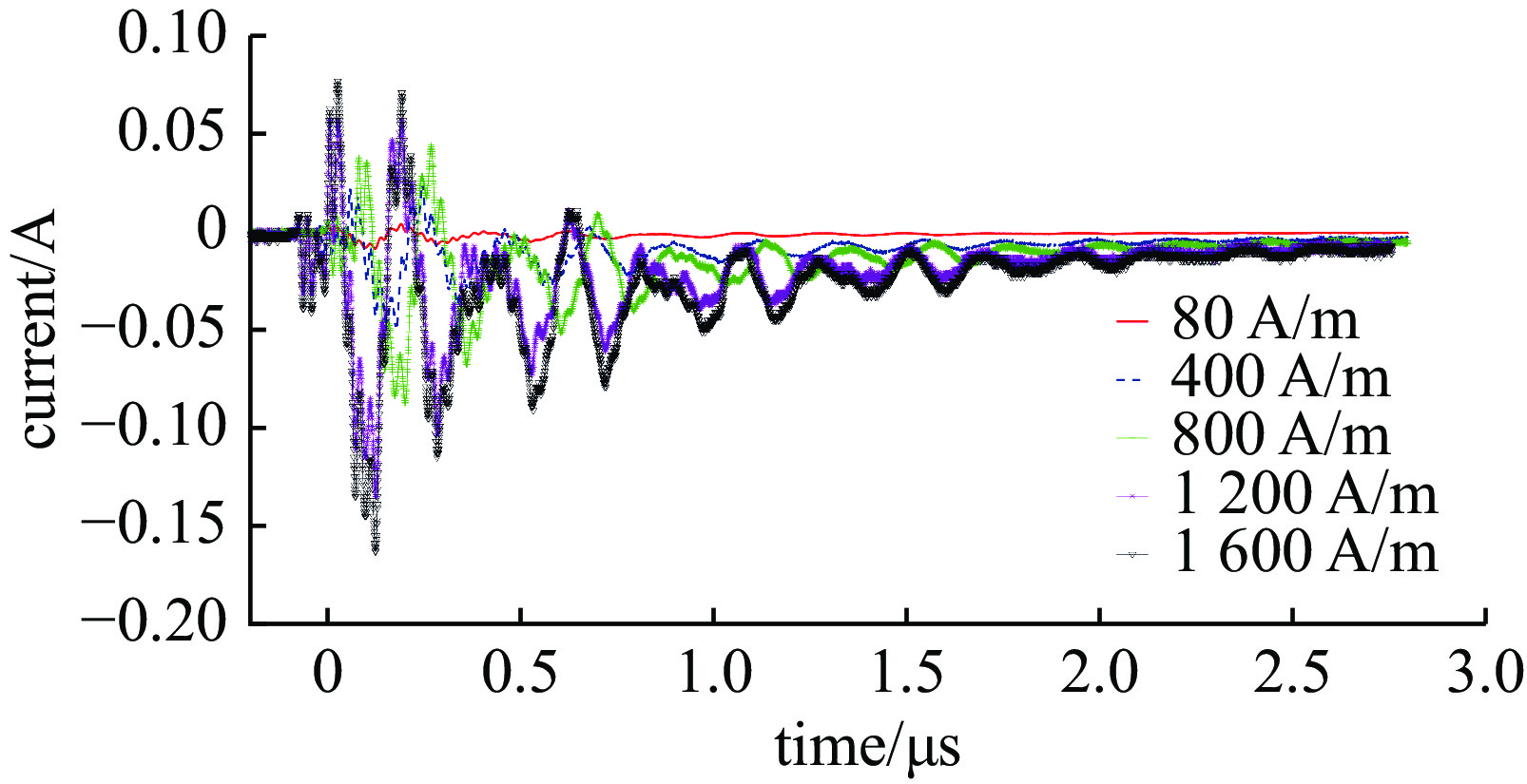
摘要: 随着旋翼无人机在空中雷暴电场探测等领域的应用变得越来越广泛,其在邻近雷击环境下的适应性问题也变得越来越突出。利用邻近雷击脉冲电场和脉冲磁场模拟装置,对无人机内部线缆的耦合效应进行了测试,获取了不同模块的连接线在邻近雷击脉冲电场和磁场作用下的耦合电流波形。结果表明,在邻近雷击脉冲电场作用下,无人机内部各模块之间的连接线都会耦合出较大电流,其中电机与电子调速器之间的电流峰值最高,达到了12 A;脉冲磁场对各连接线缆的耦合效应主要集中在脉冲电压信号上升沿段,电流波形变化更快。研究结果可为无人机的邻近雷击防护设计提供借鉴。Abstract:
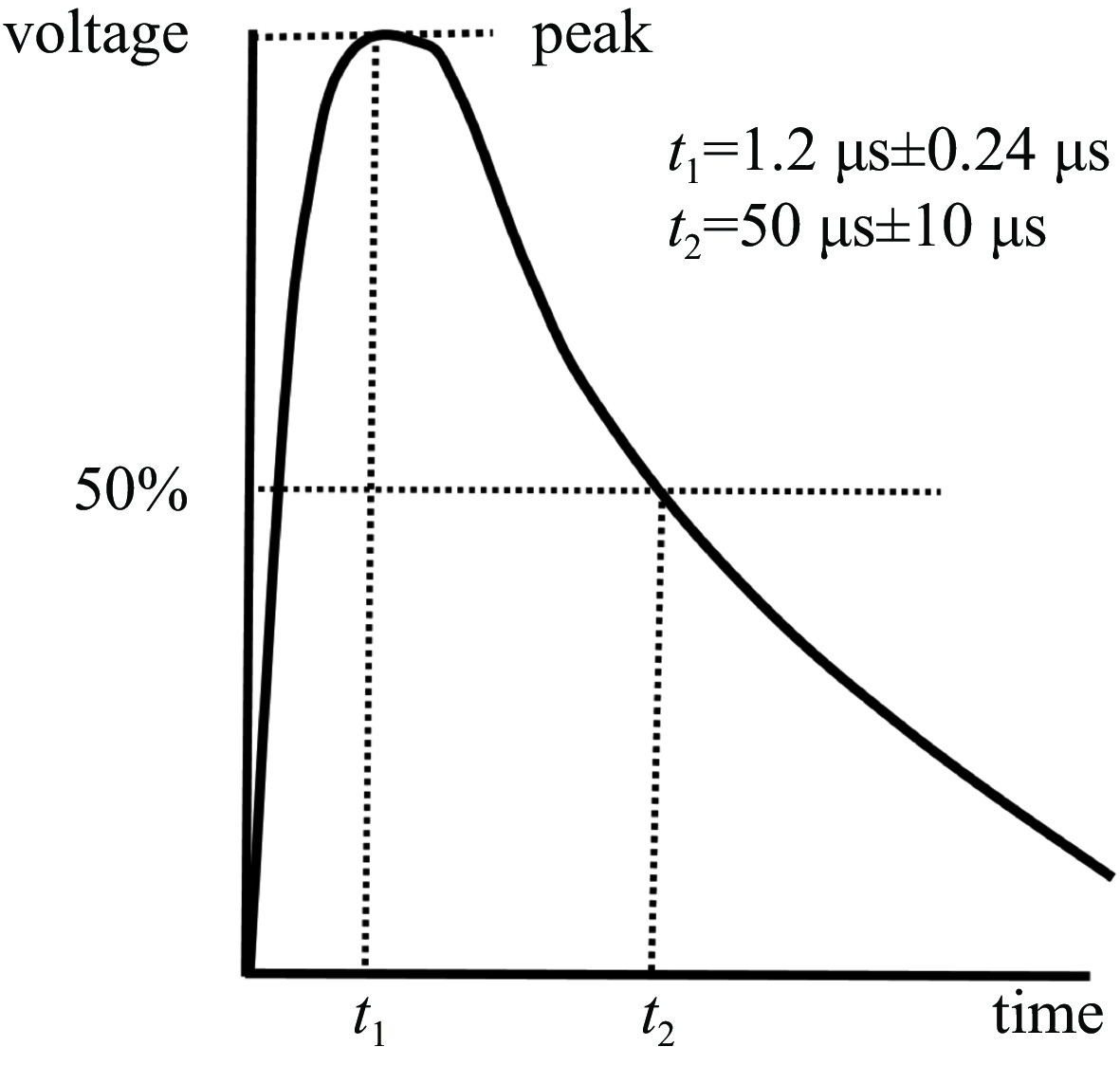
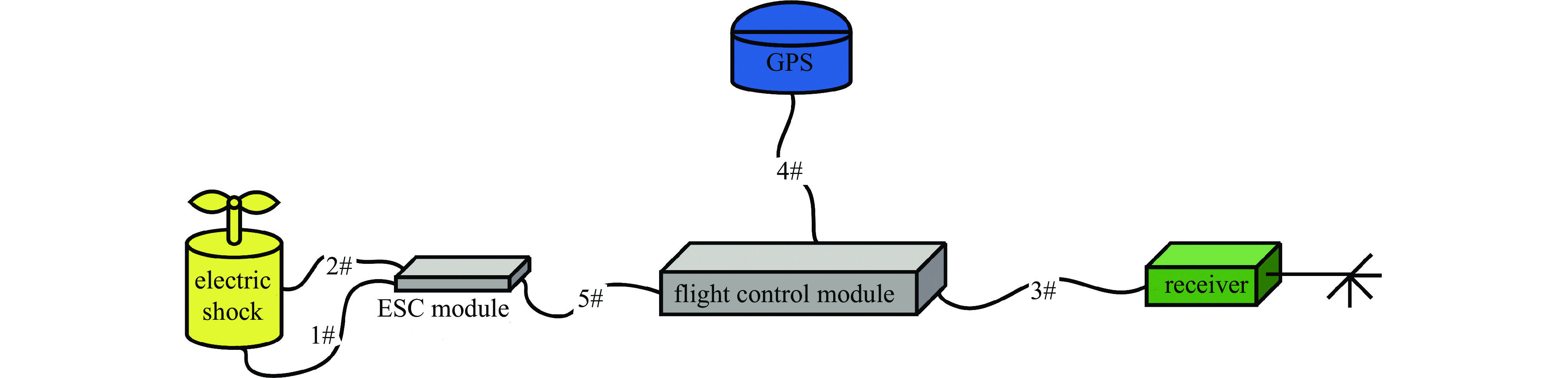
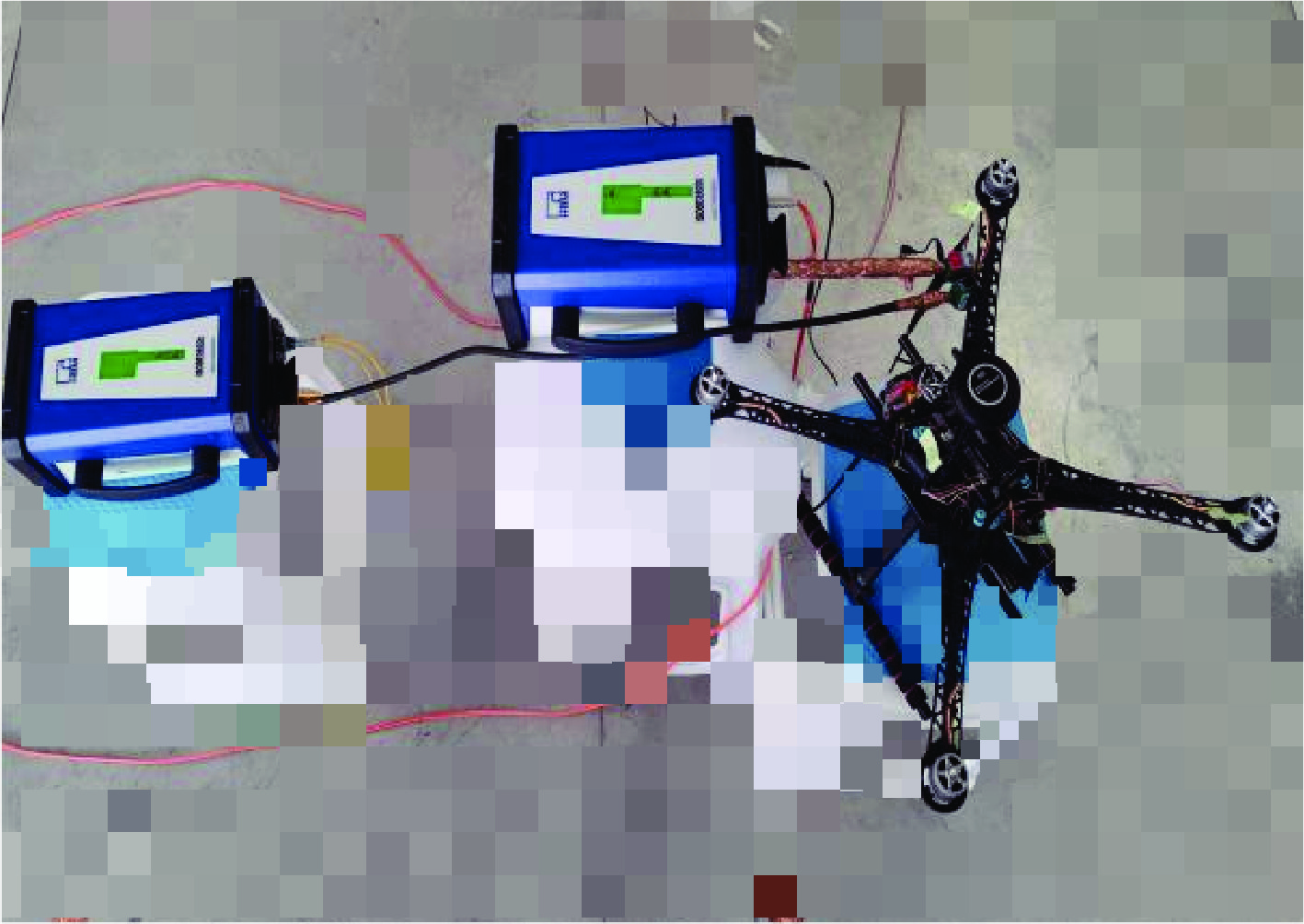
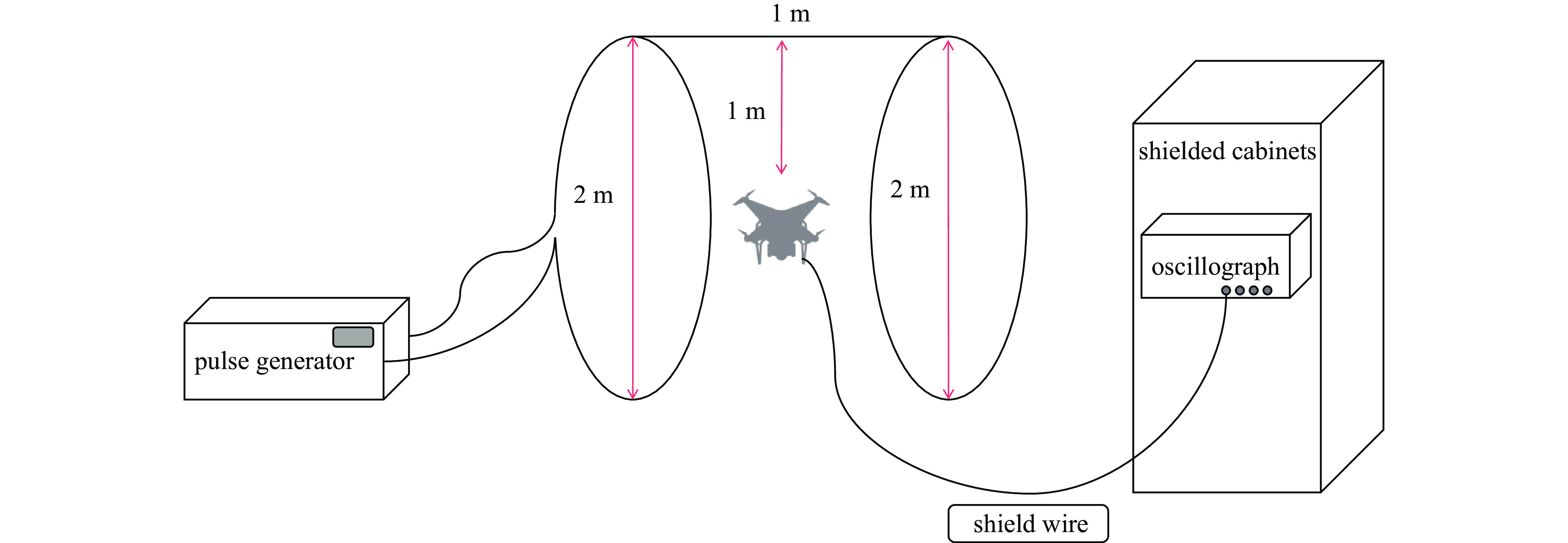
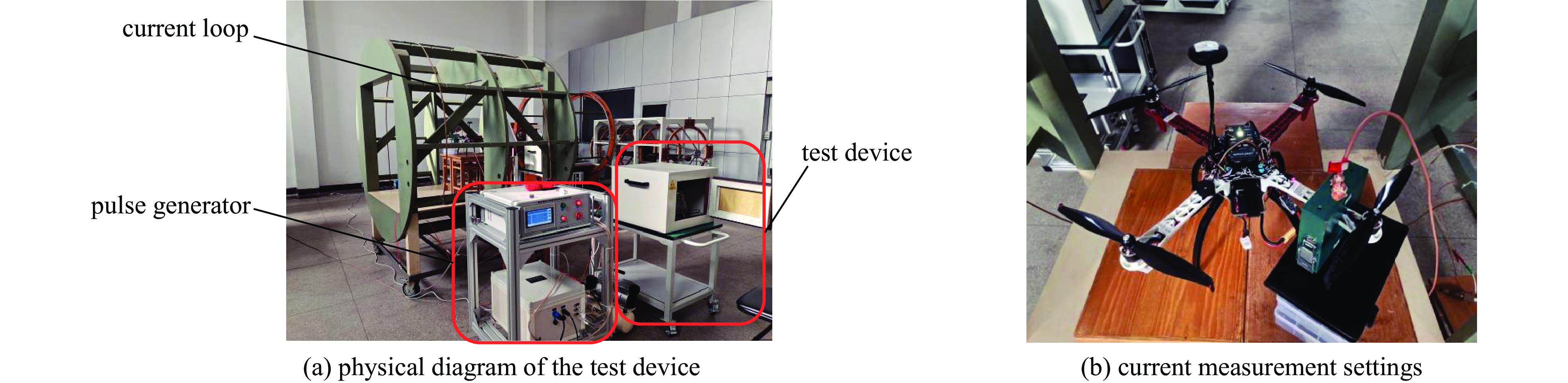
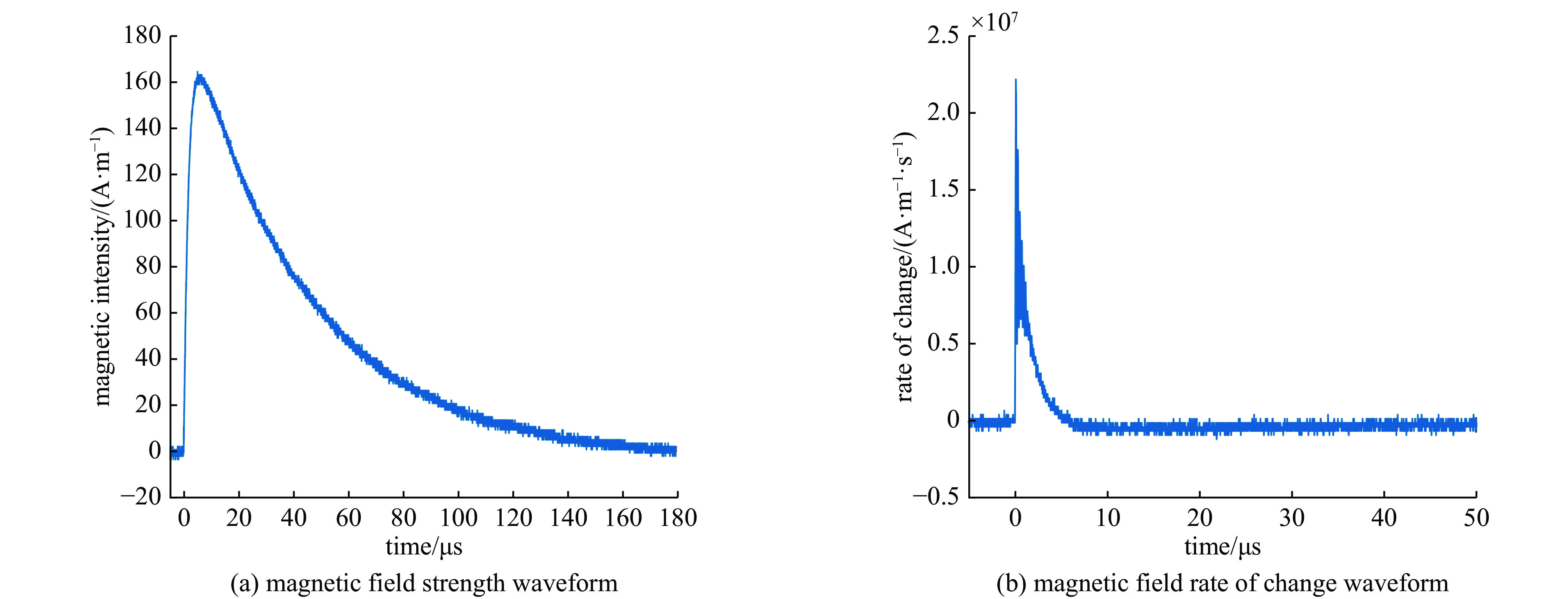
Background With the increasing application of rotorcraft drones in fields such as airborne detection of thunderstorm electromagnetic fields, their operational safety in near-lightning environments has drawn widespread attention. The intense electromagnetic pulses generated by nearby lightning strikes can induce coupled currents in the internal cables of drones, thereby posing a risk of damage to the drone system.Purpose This paper aims to investigate the electromagnetic coupling effects of nearby lightning pulse electromagnetic fields on the internal cables of rotorcraft drones and to evaluate and analyze the induced currents generated on different functional modules.Methods By simulating near-lightning pulse electromagnetic field environments experimentally, under various conditions including electric field strengths of 240 kV, 280 kV, and 320 kV, and magnetic field strengths ranging from 80 to1600 A/m, induced current measurements were conducted on key internal cables connected to the motor, electronic speed controller (ESC), flight control module, GPS, and receiver.Results The experimental results show that under pulsed electric fields, all tested cables exhibited significant induced currents, with the highest peak current of 12 A occurring between the motor and the ESC. Pulsed magnetic fields mainly induced currents during the voltage signal rise phase, reaching a peak value of 0.18 A under the1600 A/m condition.Conclusions When operating in a near-lightning environment, drones generate induced currents, which pose certain risks to their normal operation. Therefore, certain protective measures are necessary for critical modules such as GPS and key cables. Owing to time constraints, this study did not further analyze the impact of near-lightning electromagnetic environments on data links, and the influence of drone cable layout on induced currents warrants further investigation. -
表 1 线型参数
Table 1. Linear parameters
linear inner core
materialouter core
materialcable
diameter/mmsingle Cu PVC 1.5 cable Cu PE 2.5 twisted pair Cu PE 2.0 three twisted
threadsCu PE 2.0 表 2 不同位置耦合电流峰值测量结果
Table 2. Measurement results of coupling current peaks at different locations
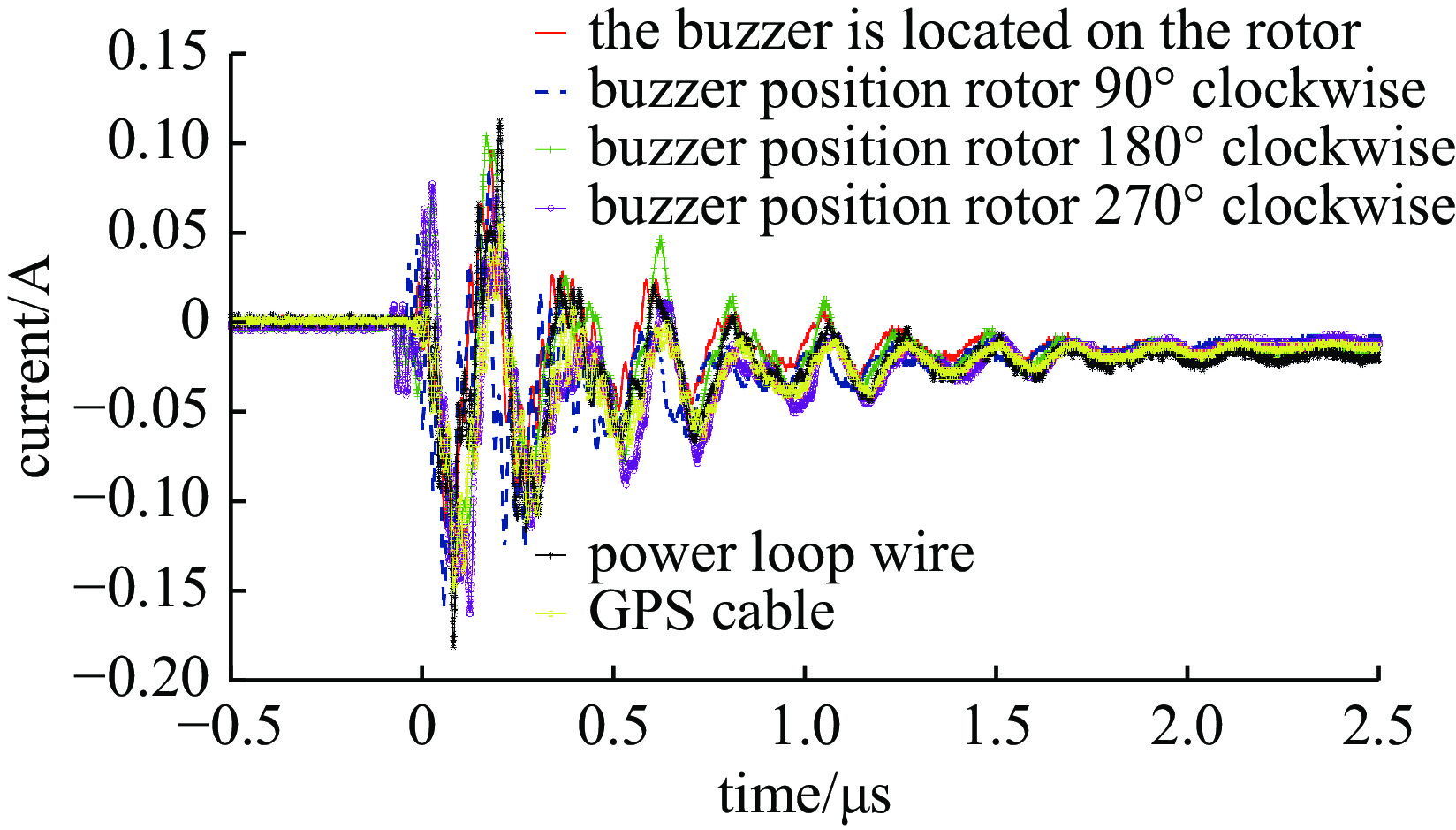
location coupled current peak/A 80 (A∙m−1) 400 (A∙m−1) 800 (A∙m−1) 1200 (A∙m−1)1600 (A∙m−1)the rotor where the buzzer is located 0.007 0.04 0.074 0.11 0.144 buzzer position rotor 90° clockwise 0.008 0.054 0.097 0.139 0.161 buzzer position rotor 180° clockwise 0.006 0.034 0.064 0.09 0.126 buzzer position rotor 270° clockwise 0.009 0.049 0.092 0.135 0.163 power Loop 0.008 0.04 0.092 0.146 0.182 GPS cable 0.007 0.041 0.08 0.114 0.151 -
[1] 虞昊. 现代防雷技术基础[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2005Yu Hao. Fundamentals of modern lightning protection technology[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2005 [2] 杨仲江, 朱浩, 唐宏科, 等. 地面电场仪测量数据的误差来源及分析处理[J]. 大气科学学报, 2010, 33(6): 751-756 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7097.2010.06.015Yang Zhongjiang, Zhu Hao, Tang Hongke, et al. Research on source of error and analytical processing of atmospheric electric field data[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2010, 33(6): 751-756 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7097.2010.06.015 [3] French J R, Helsdon J H, Detwiler A G, et al. Microphysical and electrical evolution of a Florida thunderstorm: 1. observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1996, 101(D14): 18961-18977. doi: 10.1029/96JD01625 [4] 朱男男, 易笑园, 宫全胜, 等. 大气静电场仪组网在天津雷电预警中的初步应用[C]//第七届中国国际防雷论坛论文摘编. 2008Zhu Nannan, Yi Xiaoyuan, Gong Quansheng, et al. Preliminary application of atmospheric electrostatic field instrument networking in lightning early warning in Tianjin[C]//Excerpts from papers of China International Lightning Protection Forum. 2008 [5] 卢新科. 电磁脉冲的耦合及防护[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2009Lu Xinke. EMP coupling and EMP protection[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University, 2009 [6] Rakov V A, Uman M A. Lightning: physics and effects[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003. [7] 王道洪, 郄秀书, 郭昌明. 雷电与人工引雷[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2000Wang Daohong, Xuan Xiushu, Guo Changming. Lightning and artificial lightning guidance[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 2000 [8] Zhang Zhao, Zhou Yang, Zhang Yang, et al. Strong electromagnetic interference and protection in UAVs[J]. Electronics, 2024, 13: 393. doi: 10.3390/electronics13020393 [9] Jiang Wenkai, He Junlin, Zheng Qiwei, et al. Virtual simulation system of broadband electromagnetic pulse damaging UAV[C]//2024 4th International Conference on Energy, Power and Electrical Engineering (EPEE). 2024: 729-735. [10] Gizatullin Z M, Nuriev M G, Shleimovich M P. Physical modeling of electromagnetic interference in unmanned aerial vehicle under action of indirect lightning strike[C]//2017 Dynamics of Systems, Mechanisms and Machines (Dynamics). 2017: 1-4. [11] 陈亚洲, 张冬晓, 田庆民, 等. 某型无人机数据链系统HEMP辐照效应[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(3): 959-965Chen Yazhou, Zhang Dongxiao, Tian Qingmin, et al. HEMP radiation effects on unmanned Aerial Vdehicle data link system[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(3): 959-965 [12] 张冬晓, 陈亚洲, 田庆民, 等. 某型无人机系统雷电脉冲磁场效应[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27: 103236 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.103236Zhang Dongxiao, Chen Yazhou, Tian Qingmin, et al. Lightning pulse magnetic field effects on UAV system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 103236 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.103236 [13] 张万里, 史云雷, 何勇, 等. 雷电电磁脉冲对典型机载GPS模块的损伤效应研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33: 033001Zhang Wanli, Shi Yunlei, He Yong, et al. Study on damage effects of lightning electromagnetic pulse on typical airborne GPS module[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 033001 [14] Kossowski T, Szczupak P. Laboratory tests of the resistance of an unmanned aerial vehicle to the normalized near lightning electrical component[J]. Energies, 2023, 16: 4900. doi: 10.3390/en16134900 [15] 周佳乐, 余道杰, 柴梦娟, 等. 无人机系统级线缆电磁效应与耦合特征分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2025, 37: 023001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202537.240399Zhou Jiale, Yu Daojie, Chai Mengjuan, et al. Analysis of electromagnetic effects and coupling characteristics of UAV system-level cables[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2025, 37: 023001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202537.240399 [16] 杜宝舟, 张冬晓, 程二威. 超宽带电磁脉冲对无人机辐照耦合仿真研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2018, 35(4): 29-32,37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.04.006Du Baozhou, Zhang Dongxiao, Cheng Erwei. Simulation study on irradiation coupling of UWB electromagnetic pulse to UAV[J]. Computer Simulation, 2018, 35(4): 29-32,37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.04.006 [17] Gaynutdinov R R, Chermoshentsev S F. Study of lightning strike impact on unmanned aerial vehicle[C]//2016 17th International Conference of Young Specialists on Micro/Nanotechnologies and Electron Devices (EDM). 2016: 428-432. [18] Kim S, Noh Y H, Lee J, et al. Electromagnetic signature of a quadcopter drone and its relationship with coupling mechanisms[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 174764-174773. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2956499 [19] Gao Shukun, Cheng Erwei, Chen Yazhou, et al. Research on ultra-wideband electromagnetic pulse irradiation effect and protection method of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle[C]//Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 2019: 012165. [20] Qiao Zhijiun, Pan Xuchao, He Yong, et al. A study examining the adverse effects of electromagnetic pulse on system-level unmanned aerial vehicles and their subsequent damage assessment and mitigation strategies[J]. Iranian Journal of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 2024, 43(11): 4185-4199. [21] Ma Zhengyang, He Shaonan, Duan Zhaobin, et al. Analyzing the indirect effects of lightning on unmanned aerial vehicle navigation receivers[J]. Aerospace, 2024, 11: 810. doi: 10.3390/aerospace11100810 [22] 罗成. 基于旋翼无人机平台的雷暴环境大气电场探测研究[D]. 南京: 陆军工程大学, 2025Luo Cheng. Research on atmospheric electric field detection in thunderstorm environment based on rotary-wing UAV platform[D]. Nanjing: Army Engineering University, 2025 [23] Gao Chang, Xue Zhenghui, Li Weiming, et al. The influence of electromagnetic interference of HPM on UAV[C]//2021 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology (ICMMT). 2021: 1-3. -




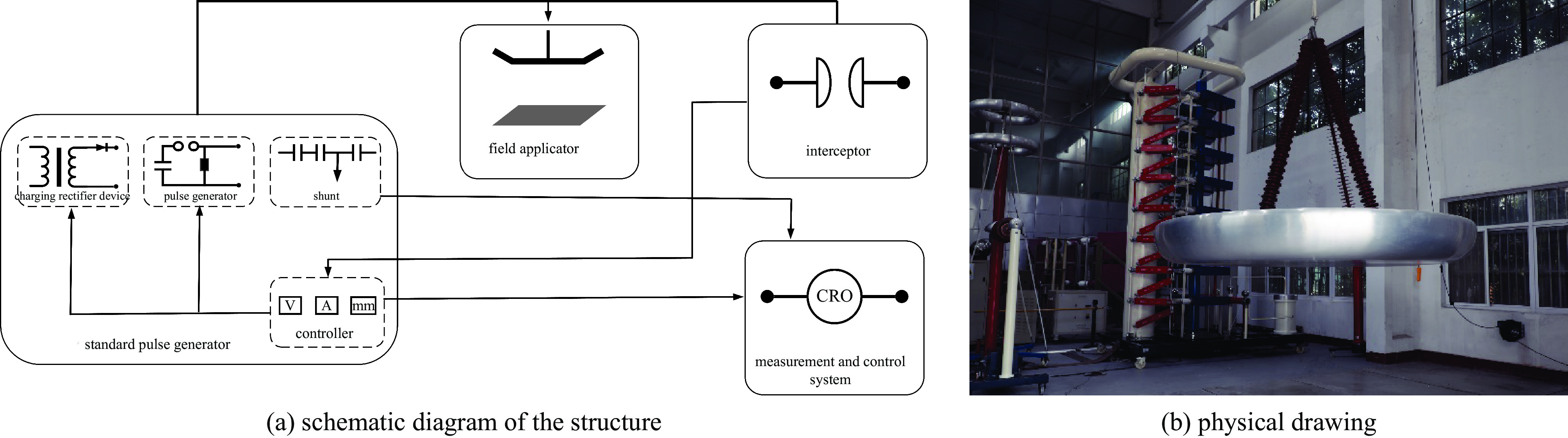
 下载:
下载: