Research on calculation method for optical scattering characteristics of space target
-
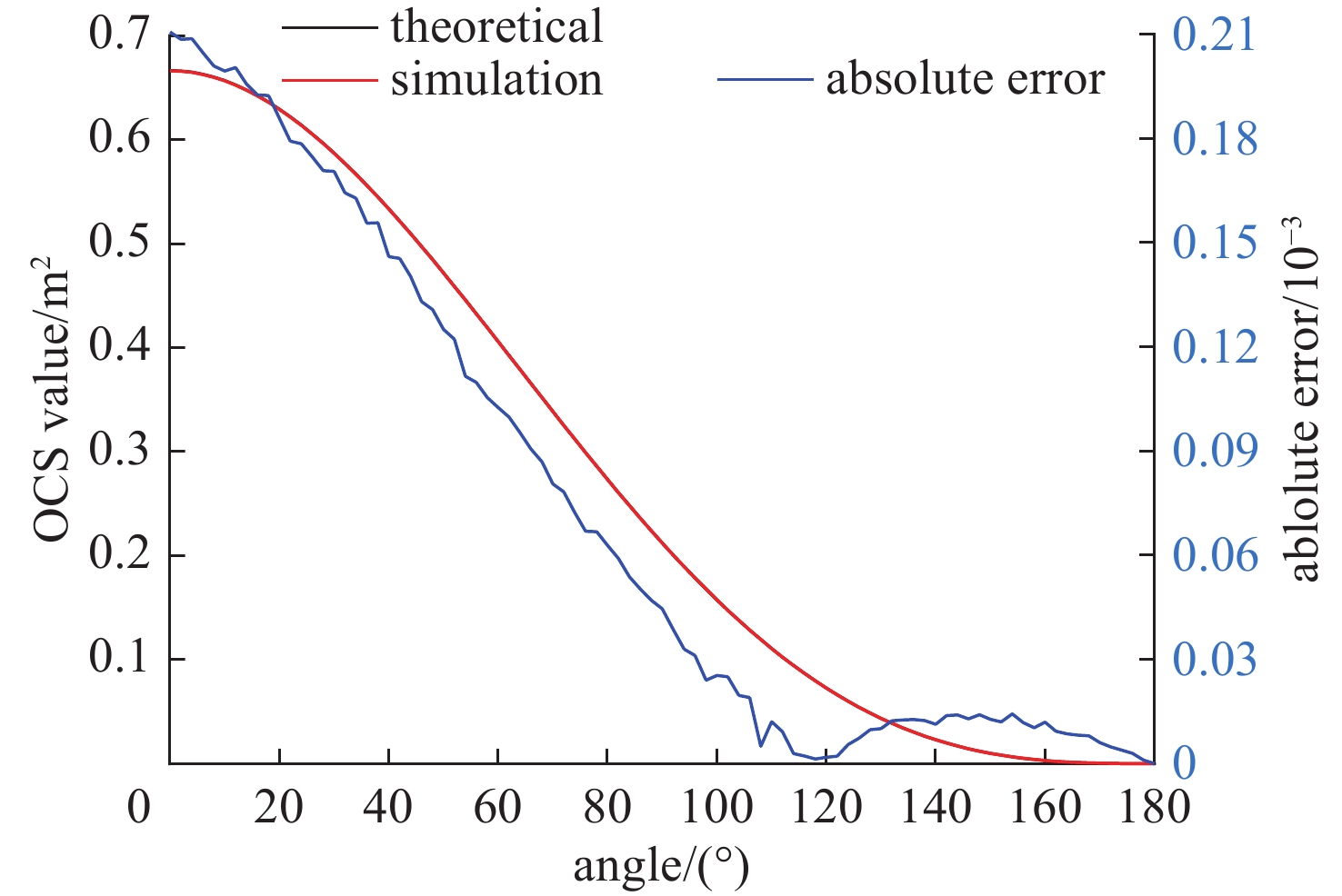
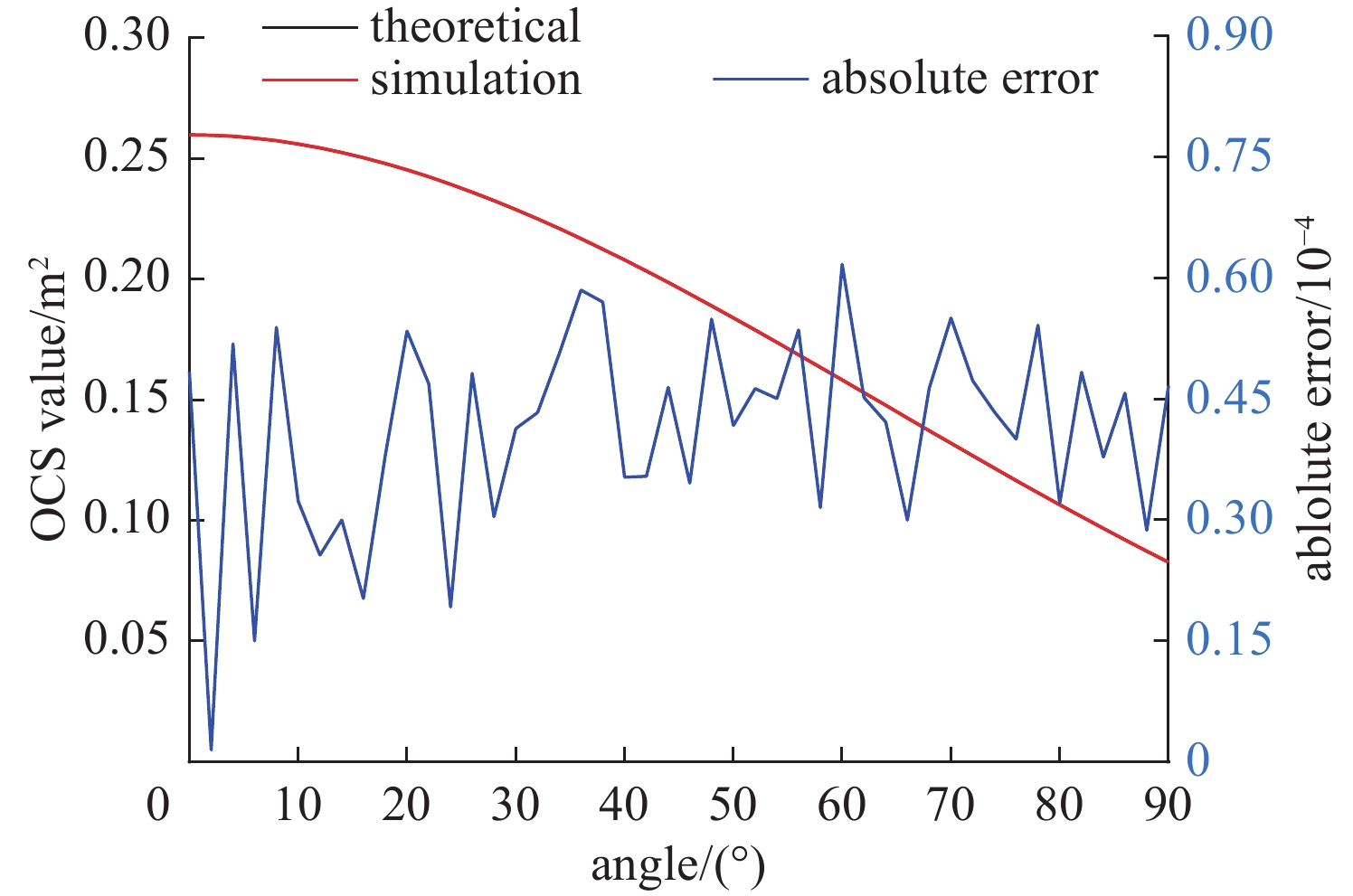
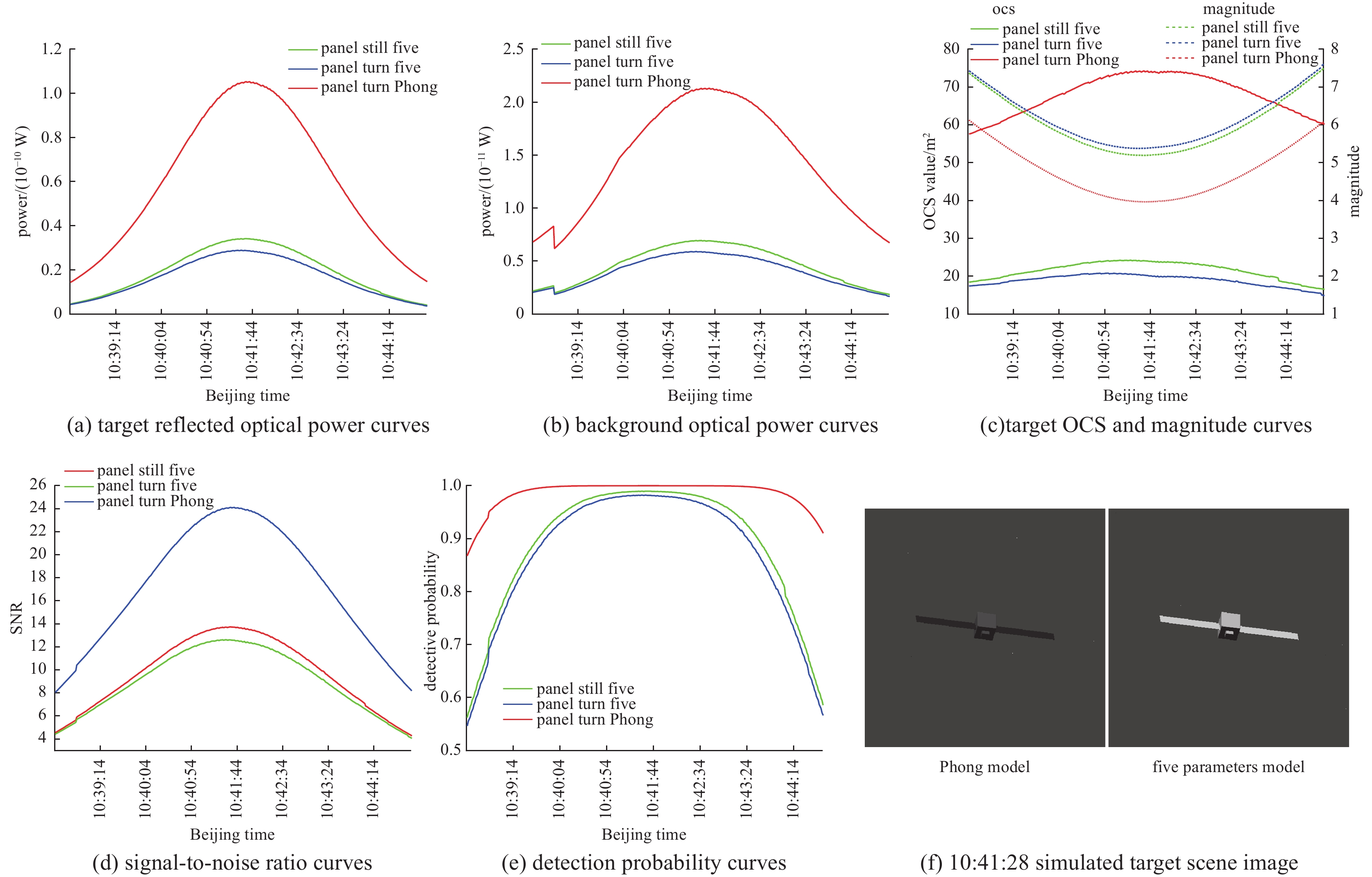
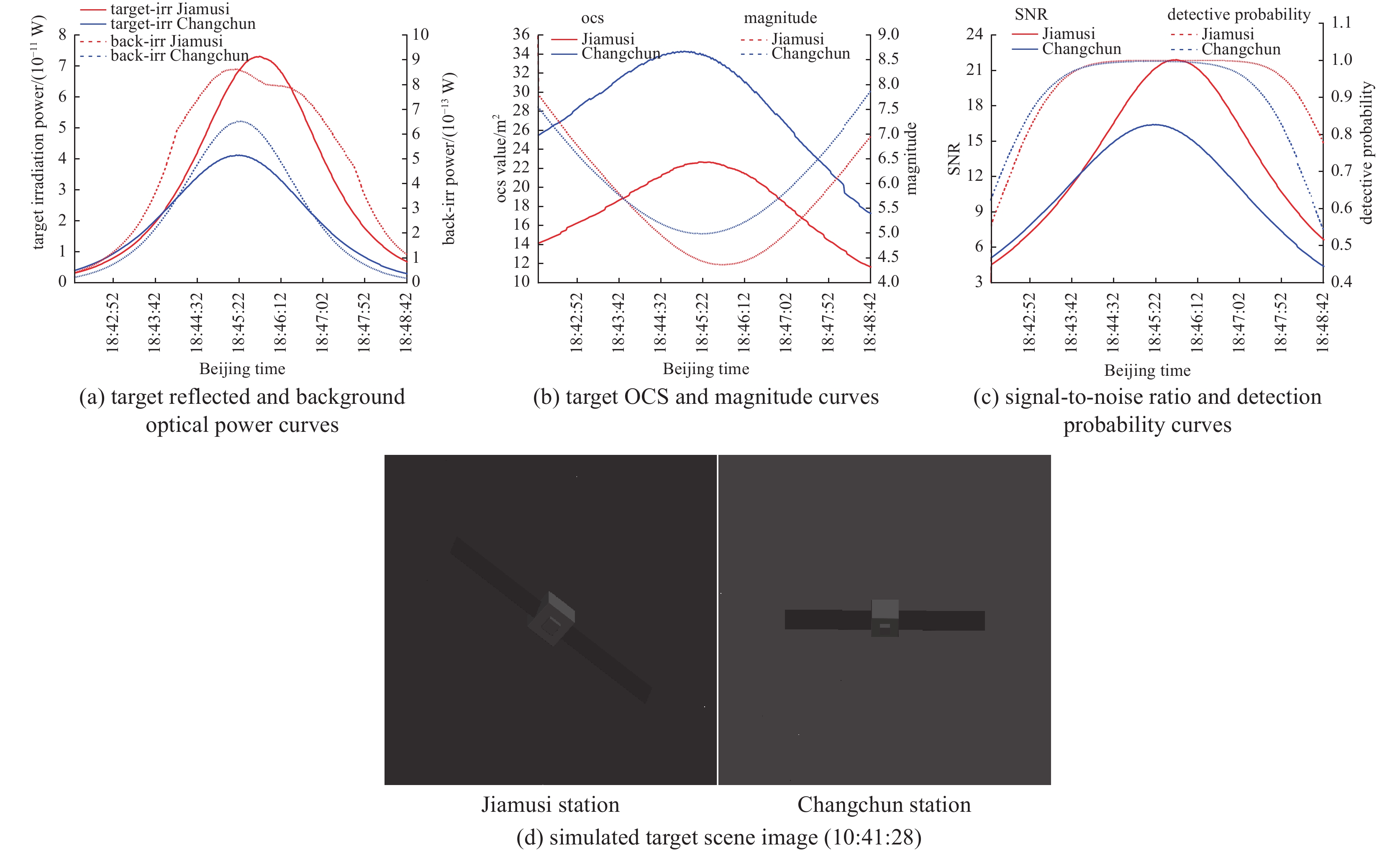
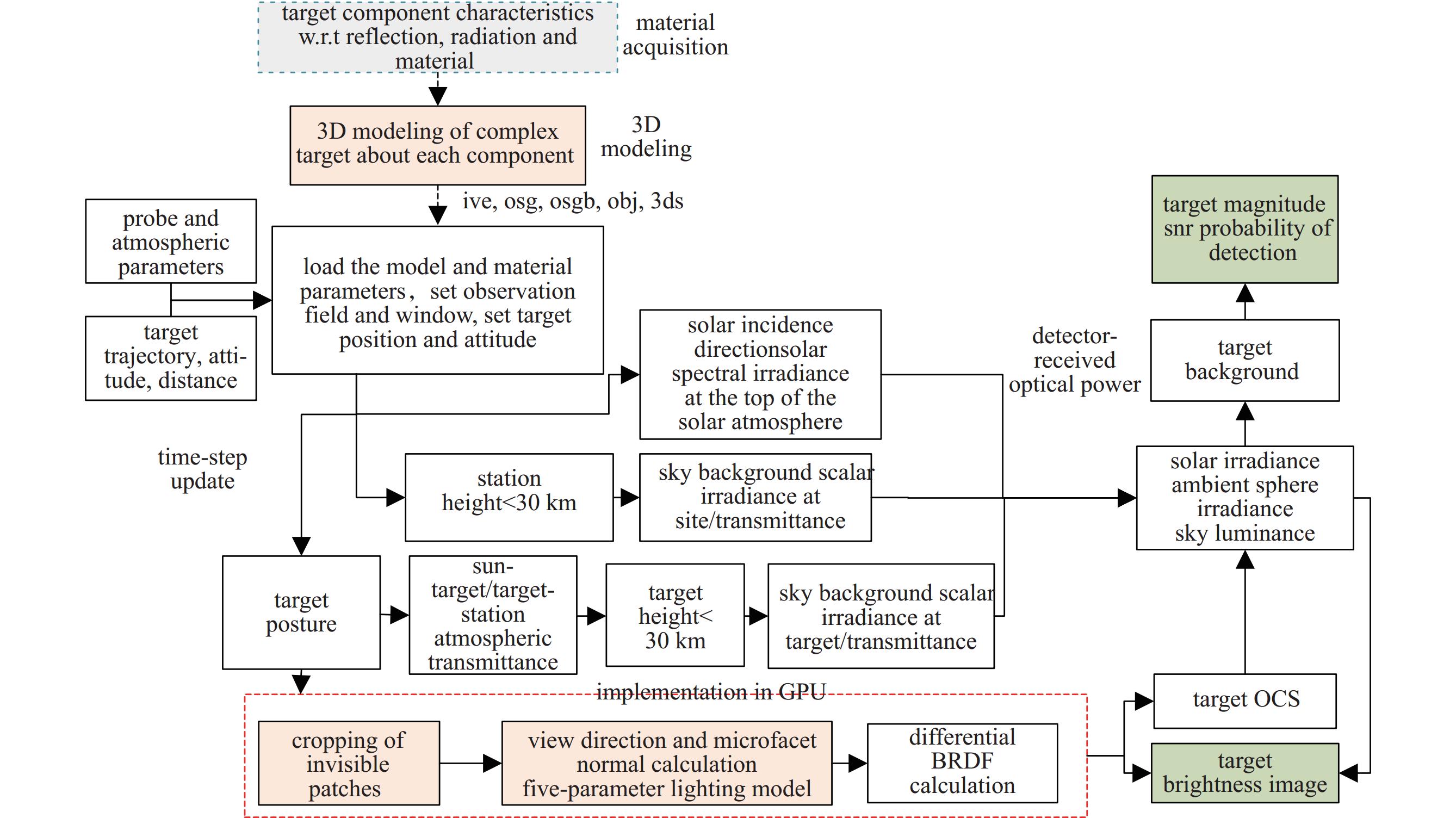
摘要: 光学散射特性是空间目标的重要特征,在目标识别和探测系统中起着非常重要的作用。针对空间目标仿真渲染需求,以及传统目标光学散射特性方法仅给出目标光学散射截面(OCS)、散射特性或模拟目标图像等不足,对空间目标光学散射特性计算进行了较全面研究,给出了空间目标光学散射特性计算流程,给出了目标OCS、目标辐照度、天光背景亮度、目标星等、信噪比和探测概率等计算公式,根据太阳辐射特性、相对于站址位置、天地背景球辐射特性等,利用图形处理单元(GPU)和着色语言实现任意时刻目标光学散射特性计算(目标OCS、探测器接收到的目标反射光功率和背景光功率、目标星等、信噪比和探测概率、模拟目标亮度图像等)。通过球体和圆柱体实验验证了目标OCS计算正确性。通过光学散射特性仿真实验,给出了空间目标在不同站址、不同反射特性和不同探测窗口下目标光学散射特性计算结果,结果表明,目标光学散射特性计算结果合理。给出了全套计算公式、计算参数和计算结果,对空间目标光学散射特性计算、目标图像识别等研究提供了参考。Abstract:
Background Optical scattering characteristics are crucial features of space targets and play a vital role in target recognition and detection systems. Traditional methods are limited in simulating optical scattering properties -which only provide optical cross-section (OCS), scattering characteristics, or synthetic target images.Purpose To address the above limitations and meet requirements of rendering spatial target, this paper conducts a comprehensive study on the computational modeling of optical scattering characteristics for space targets.Methods A systematic workflow is proposed, along with formulas for calculating target OCS, target irradiance, sky background luminance, target magnitude, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and detection probability. By integrating solar radiation properties, observer-site positioning, and celestial-terrestrial background sphere radiation characteristics, a graphics processing unit (GPU) accelerated framework combined with shading languages is implemented to compute time-dependent optical scattering properties, including target OCS, detector-received target/background optical power, target magnitude, SNR, detection probability, and synthetic brightness imagery.Results Experimental validation using spherical and cylindrical objects confirms the accuracy of the OCS calculations. Simulations under varying observer locations, reflective properties, and detection windows demonstrate the rationality of the computed optical scattering characteristics.Conclusions This study provides a complete set of formulas, parameters, and results, offering significant value for research on space target optical scattering modeling and image-based recognition. -
表 2 轨道参数
Table 2. Parameters of satellite orbit
a/km e $ \omega $/(°) I/(°) $ {\mathit{\Omega}} $/(°) M/(°) 7237.394 0.001555 187.7263 98.7169 85.7864 172.364 表 3 探测器参数
Table 3. Parameters of detector
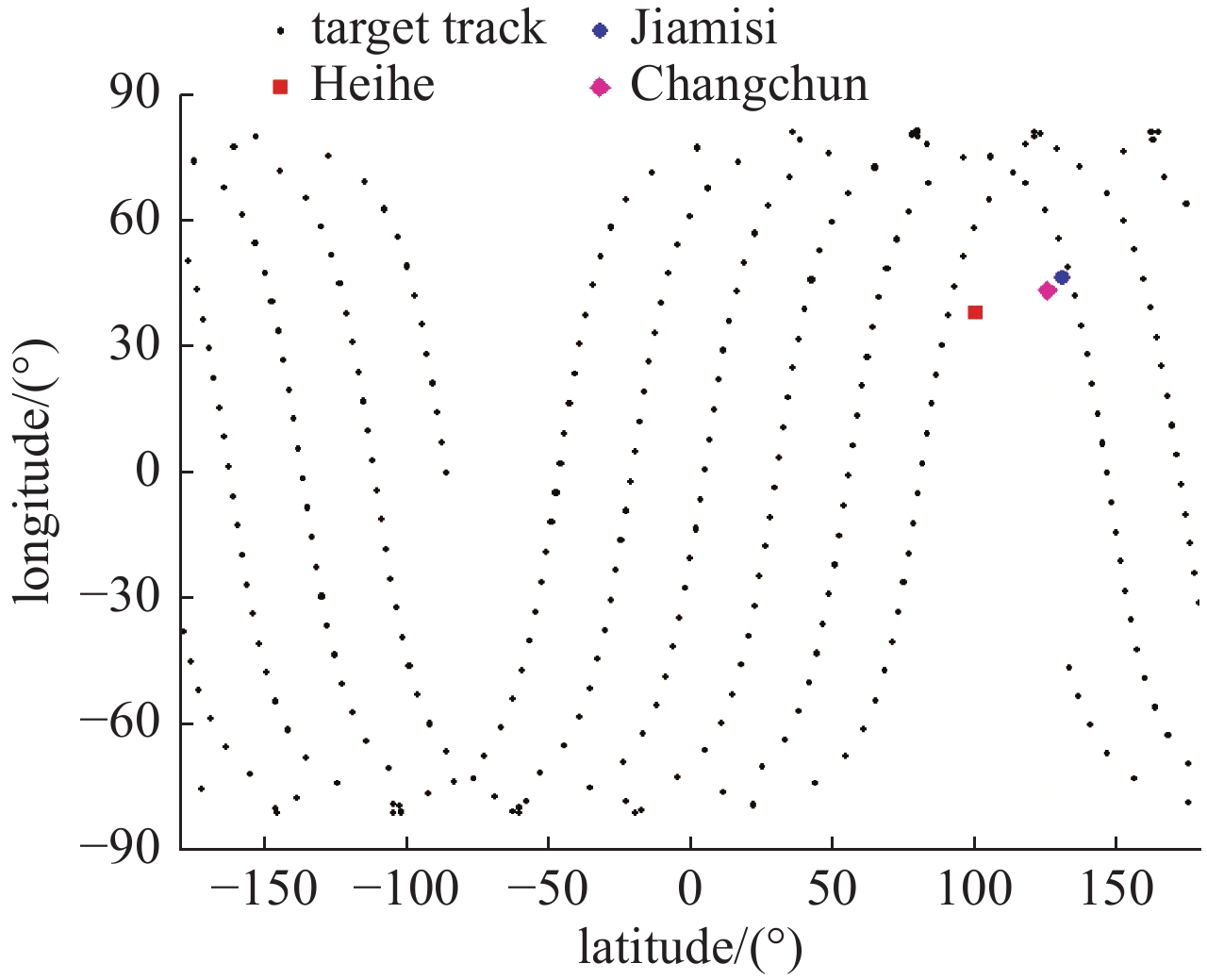
central wavelength/μm spectral width/m QE sampling period/s aperture/m FFOV/(°) PFA 550 20 0.8 0.01 1 0.133 0.01 表 1 站址信息
Table 1. Parameters of station
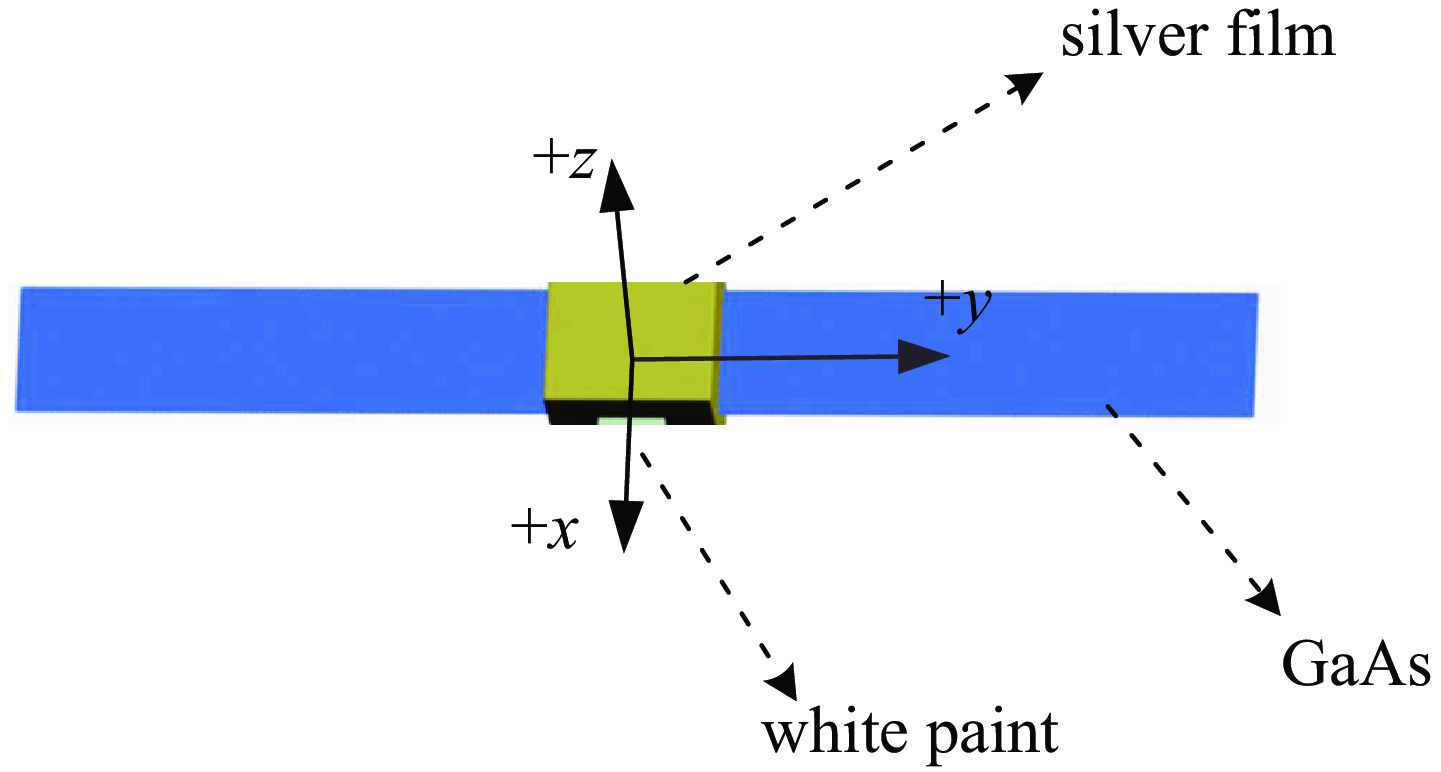
station longitude/(°) latitude/(°) altitude/m Heihe 100.14 38.01 1143.0 Changchun 125.26 43.47 1143.0 Jiamusi 130.78 46.50 1143.0 表 4 目标表面材质BRDF参数
Table 4. BRDF parameters of target surface materials
material $ {K_{\mathrm{d}}} $ $ {K_{\mathrm{s}}} $ $ {A_0} $ $ {A_1} $ B silver film 0.2873 291.8351 4053.5 1.3118 0.7435 white paint 0.2512 2.8358 897.9647 2.7264 2.4693 GaAs 0.0428 23.0067 2122.5 2.1124 4.8569 表 5 窗口信息
Table 5. Window information
station start time end time overhead time maximum elevation/(°) Heihe 10:38:18 10:45:00 10:41:39 41.2860 Changchun 18:41:55 18:48:57 18:45:26 44.9339 Jiamusi 18:41:56 18:45:52 18:49:48 74.7703 -
[1] Yi Han, Sun Huayan, Li Yingchun, et al. Fast calculation method of complex space targets’ optical cross section[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(17): 4013-4019. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.004013 [2] Yi Han, Sun Huayan, Li Yingchun, et al. Fast calculation method of complex space targets’ optical cross section: erratum[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53: 1142. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.001142 [3] Sun Chengming, Yuan Yan, Zhang Xiubao. Application of BRDF for modeling on the optical scattering characteristics of space target[C]//Proceedings of the International Symposium on Photoelectronic Detection and Imaging 2009: Advances in Infrared Imaging and Applications. 2009: 738338. [4] 徐灿, 张雅声, 李鹏, 等. 基于OpenGL拾取技术的空间目标光学横截面积计算[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37: 0720001 doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0720001Xu Can, Zhang Yasheng, Li Peng, et al. Calculation of optical cross section areas of spatial objects based on OpenGL picking technique[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37: 0720001 doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0720001 [5] 李良超, 吴振森, 薛谦忠. 一种计算复杂目标激光雷达散射截面的快速算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 27(5): 577-580Li Liangchao, Wu Zhensen, Xue Qianzhong. A fast algorithm for LRCS of a complex object with a rough surface[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2000, 27(5): 577-580 [6] 鲍文卓, 丛明煜, 张伟, 等. 基于面元网格化的空间目标光学特性计算方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2010, 42(5): 710-750Bao Wenzhuo, Cong Mingyu, Zhang Wei, et al. An optical characteristics calculating method based on surface mesh-creation for space targets[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010, 42(5): 710-715 [7] 杨露, 牛燕雄, 吕建明, 等. 姿态变化对星载光电成像系统探测能力的影响[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34: 1223002 doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.1223002Yang Lu, Niu Yanxiong, Lv Jianming, et al. Influence of attitude variation on the detection ability of satellite photoelectric imaging system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2014, 34: 1223002 doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.1223002 [8] 袁艳, 孙成明, 张修宝, 等. 姿态变化对空间目标可见光特性的影响分析[J]. 光学学报, 2010, 30(9): 2748-2752 doi: 10.3788/AOS20103009.2748Yuan Yan, Sun Chengming, Zhang Xiubao, et al. Analysis of influence of attitude variation on visible characteristics of space target[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2010, 30(9): 2748-2752 doi: 10.3788/AOS20103009.2748 [9] 孙成明, 袁艳, 吕群波. 天基空间目标光学散射特性建模与验证[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39: 1129001 doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.1129001Sun Chengming, Yuan Yan, Lv Qunbo. Modeling and verification of space-based optical scattering characteristics of space objects[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39: 1129001 doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.1129001 [10] Yi Han, Sun Huayan, Guo Huihao. Research on rocket laser scattering characteristic simulation software[J]. Laser Physics, 2013, 23: 056007. doi: 10.1088/1054-660X/23/5/056007 [11] 蓝朝桢. 空间目标天基光学观测系统建模与探测能力分析[D]. 郑州: 解放军信息工程大学, 2009Lan Chaozhen. Modeling and detecting capability analysis of space-based space object optical observation system[D]. Zhengzhou: PLA Information Engineering University, 2009 [12] 田琪琛, 李智, 徐灿, 等. 基于光学散射截面的进动空间目标运动分析[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2017, 46: S113001Tian Qichen, Li Zhi, Xu Can, et al. Motion analysis of precession space target based on optical cross section[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46: S113001 [13] 王锐, 钱学雷. OpenSceneGraph三维渲染引擎设计与实践[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2009: 1-8Wang Rui, Qian Xuelei. OpenSceneGraph 3D rendering engine design and practice[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2009: 1-8 [14] 克赛尼希 J M, 塞勒斯 G, 施莱尔 D. OpenGL编程指南[M]. 王锐, 译. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2017: 1-21Kessenich J M, Sellers G, Shreiner D. OpenGL programming guide: the official guide to learning OpenGl version[M]. Wang Rui, trans. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2017: 1-21 [15] 陈继选, 王毅刚. 基于OSG的GLSL着色器编辑环境[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2011, 20(3): 153-156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3254.2011.03.034Chen Jixuan, Wang Yigang. GLSL shader editing environment based on OSG[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2011, 20(3): 153-156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3254.2011.03.034 [16] 张玉双, 谢晓钢, 苏华, 等. 多光源照射下目标图像实时生成方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36: 061004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.230442Zhang Yushuang, Xie Xiaogang, Su Hua, et al. Method of real-time target image generation under multi-light source illumination[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 061004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.230442 [17] 张玉双, 王锐, 苏华, 等. 一种激光束照射复杂目标图像实时生成新方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35: 101004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230063Zhang Yushuang, Wang Rui, Su Hua, et al. A new approach for real-time imaging from laser beam to complex targets[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 101004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.230063 -




 下载:
下载: