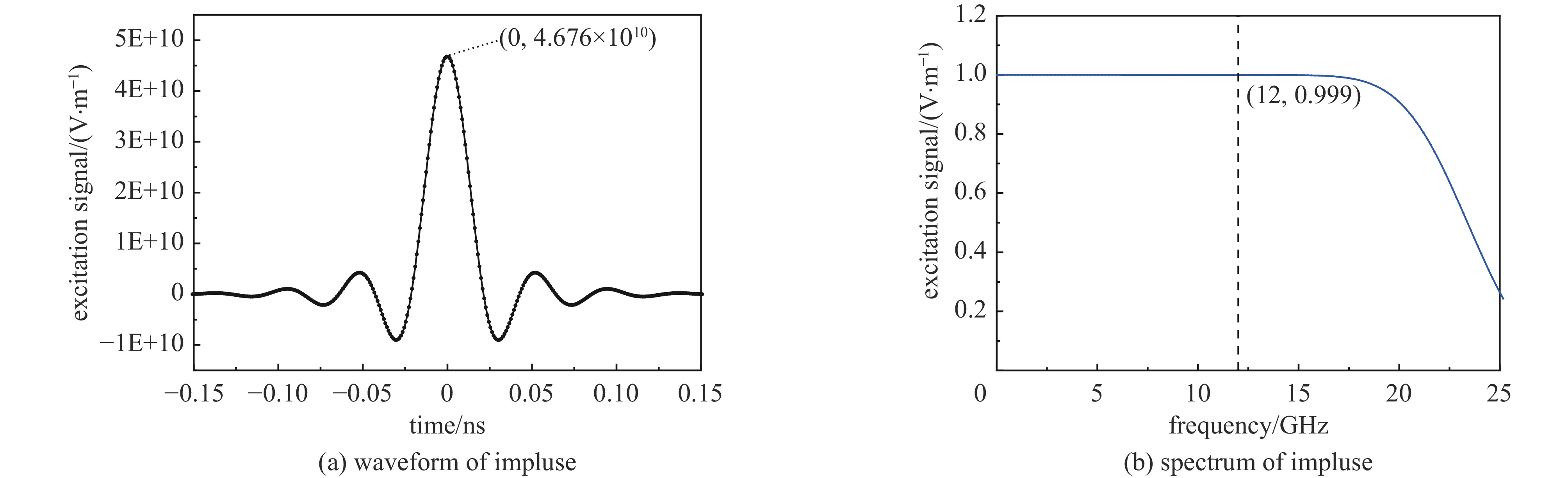
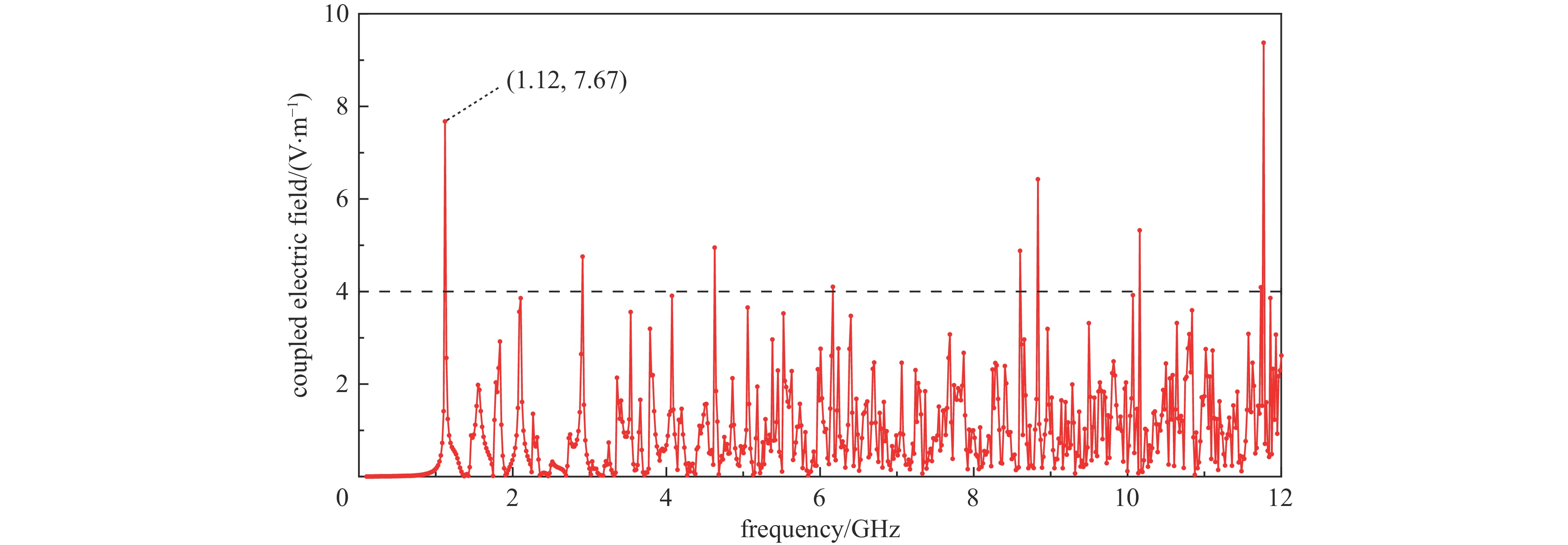
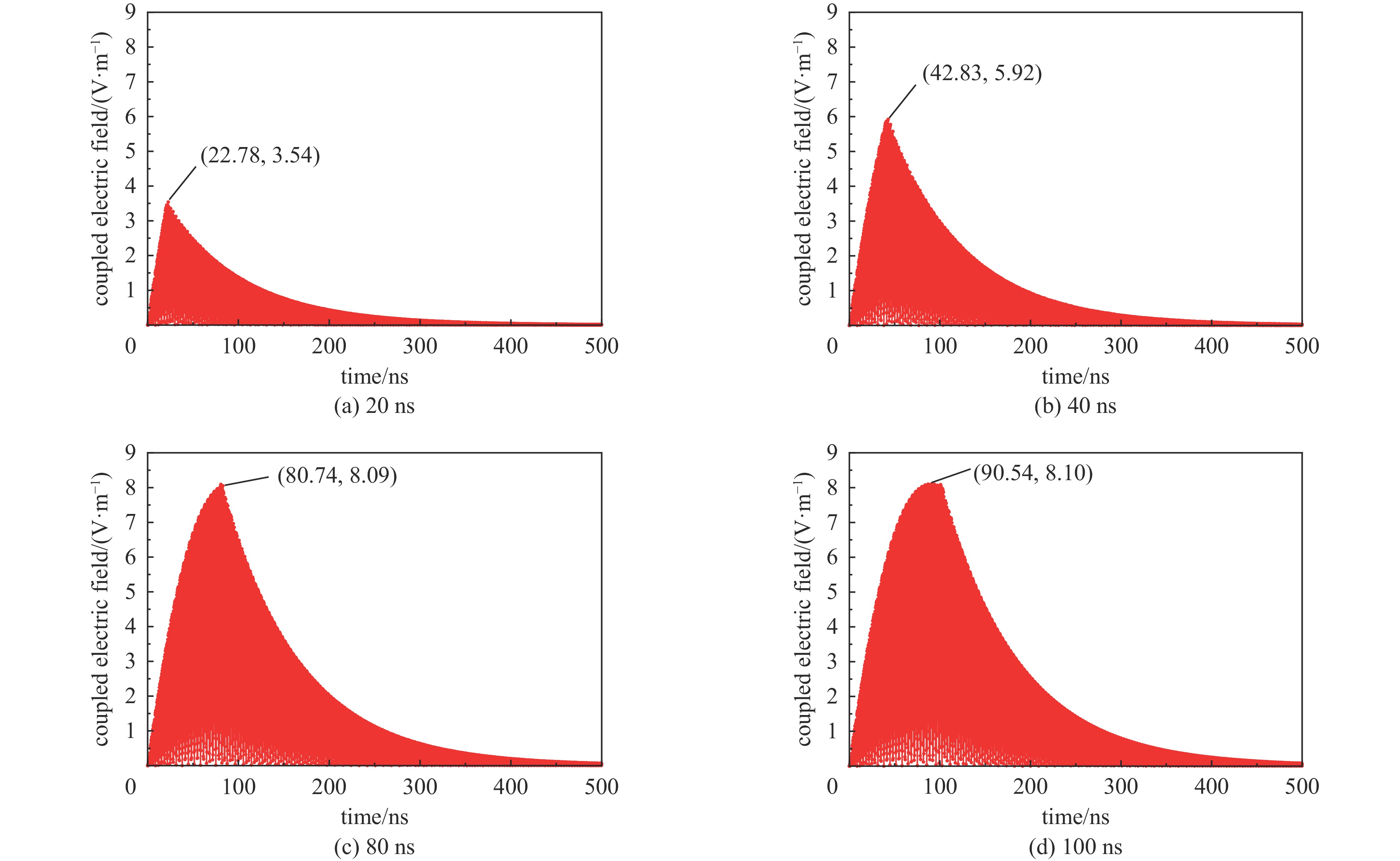
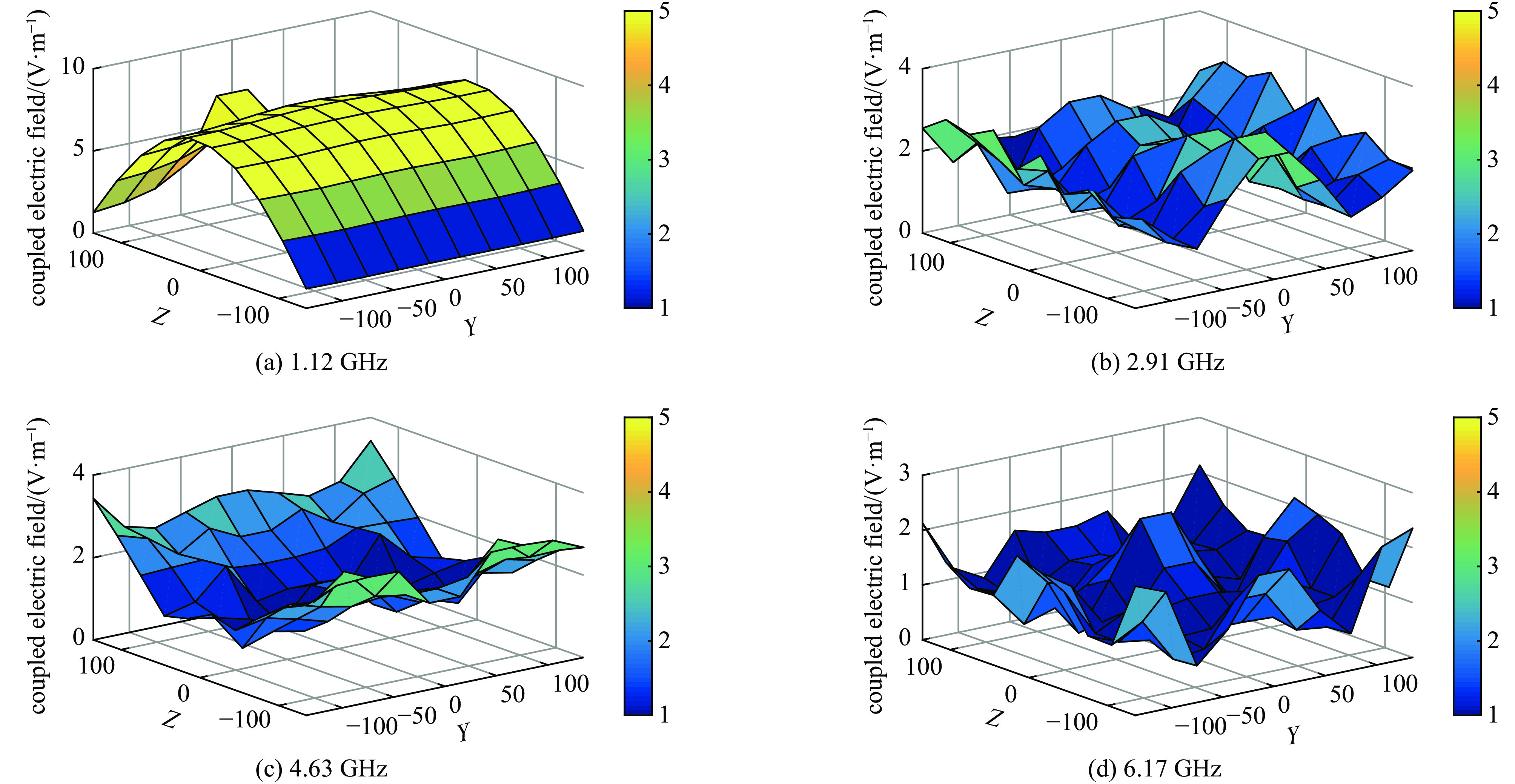
Effect of microwave parameters on the coverage of strong-coupled region of metal cavity
-
摘要: 针对精确评估目标高功率微波后门耦合效应困难的问题,本文以典型金属腔体为对象,提出“强耦合区域覆盖率”指标,采用时域有限差分法(FDTD)建立仿真模型,分析了高功率微波波形参数对后门耦合效应的影响。研究发现:腔体固有谐振频率下强耦合覆盖率显著高于非谐振频率;脉冲宽度增至特定值时,谐振频率下覆盖率趋于稳定;极化角从水平向垂直变化时,覆盖率有显著变化;叠加不同谐振频率可填补非强耦合区域空白,进一步提高覆盖率;脉冲前沿对覆盖率影响较小。该研究可为高功率微波后门耦合效应机理及参数优化提供关键技术支撑。Abstract:
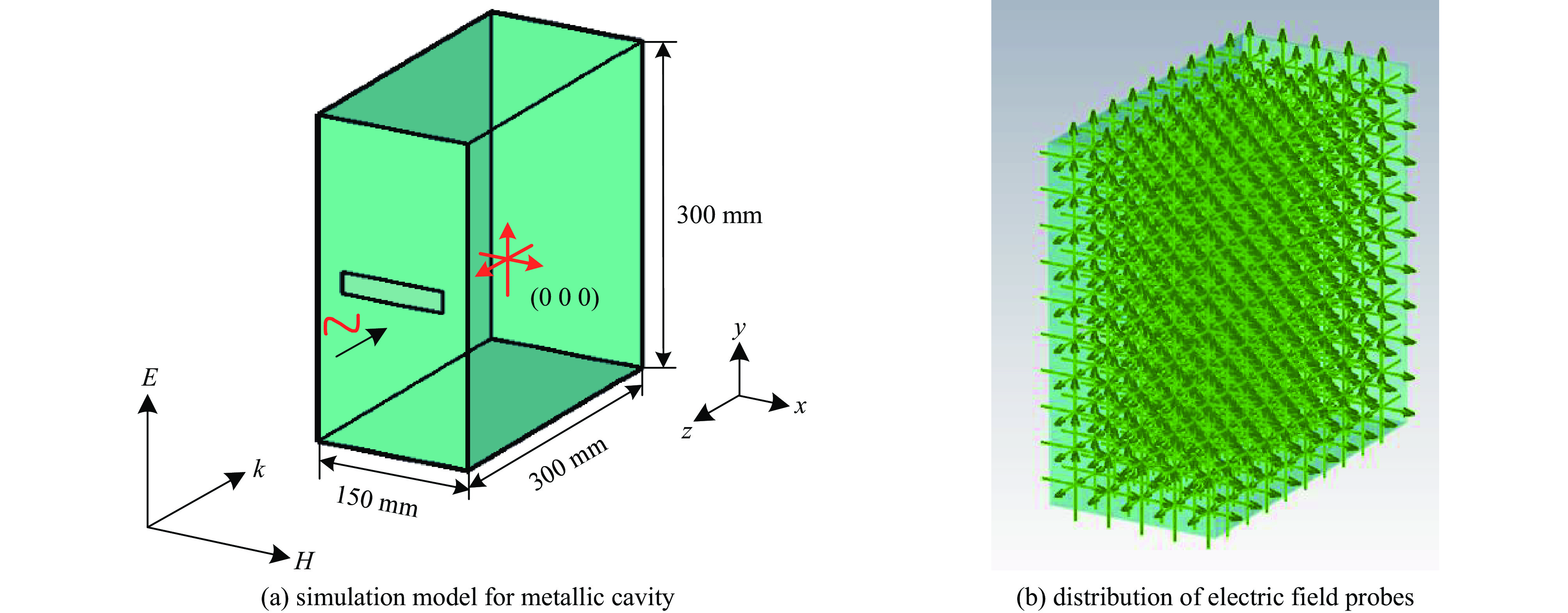
Background High-power microwave (HPM) pulses, which can interfere with or damage electronic components and circuits, have attracted considerable research interest in recent years. Aperture coupling represents a primary mechanism for such pulses to penetrate shielded metallic enclosures, significantly affecting the electromagnetic compatibility and resilience of electronic systems. Although substantial studies have focused on shielding effectiveness and resonant behaviors, the spatial distribution of coupling parameters—particularly the extent of strongly coupled regions within the cavity—remains inadequately investigated. This paper proposes a quantitative metric termed “the coverage rate of strong-coupled region” to better evaluate HPM backdoor coupling effects.Purpose The objective is to systematically examine the influence of key HPM waveform parameters on this coverage rate within a representative metallic cavity.Methods A three-dimensional simulation model of a rectangular metallic cavity with an aperture was developed using the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method. The internal field distribution was monitored via an array of electric field probes. Numerical simulations were performed to assess the effects of various HPM parameters, including frequency, pulse width, the pulse rise time, and polarization angle, on the coverage of strongly coupled regions. The coverage rate was markedly higher at the cavity’s inherent resonant frequencies than at non-resonant frequencies.Results Increasing the pulse width led to a saturation of coverage beyond a specific threshold. Variations in polarization angle from horizontal to vertical considerably enhanced the coverage, with vertical polarization yielding the maximum value. Superimposing multiple resonant frequencies effectively compensated for weakly coupled areas, further increasing the overall coverage. In contrast, the pulse rise time had a negligible effect on the coverage rate. The proposed the coverage rate of strong-coupled region effectively addresses the practical dilemma wherein strong local coupling does not necessarily lead to significant system-level effects.Conclusions This metric provides a quantitative basis for optimizing the alignment between sensitive components and highly coupled zones. Frequency and polarization are identified as decisive parameters for enhancing coupling effectiveness, while pulse width and multi-frequency excitation can be utilized to achieve more uniform and robust coupling coverage. These findings offer valuable guidance for the design and assessment of HPM protection measures and electromagnetic compatibility analysis. -
表 1 腔体内部强耦合区域覆盖率和频率的关系
Table 1. Relationship between coverage rate and frequency of strong coupling region in cavity
frequency/GHz maximum value of coupled electric field/(V/m) 1.12 7.67 2.91 4.75 4.63 4.95 5.74 4.31 6.17 4.10 8.60 4.87 8.84 6.42 10.16 5.32 11.77 9.37 1 1.916 2 1.518 3 1.499 5 1.260 7 1.551 9 2.197 10 2.562 表 2 脉冲宽度与腔体内部强耦合区域覆盖率的关系@1.12 GHz
Table 2. Relationship between pulse width and coverage rate of strong coupling region inside cavity @1.12 GHz
Width of
pulse/(ns)Maximum value of coupled
electric field/(V/m)Number of strong coupling
regions inside the cavityη(f)/% 10 1.99 200 40 20 3.54 384 57.6 40 5.92 384 76.8 60 7.39 420 84 80 8.09 440 88 100 8.10 440 88 120 8.10 440 88 150 8.10 440 88 表 3 脉冲宽度与腔体内部强耦合区域覆盖率的关系@3 GHz
Table 3. Relationship between pulse width and coverage rate of strong coupling region inside cavity @3 GHz
Width of
pulse/(ns)Maximum value of coupled
electric field/(V/m)Number of strong coupling
regions inside the cavityη(f)/% 10 1.36 86 16.8 20 1.53 124 24.8 40 1.53 122 24.4 60 1.53 122 24.4 80 1.53 122 24.4 100 1.53 122 24.4 120 1.53 122 24.4 150 1.53 122 24.4 表 4 激励信号脉冲前沿与腔体内部强耦合区域覆盖率的关系@1.12GHz
Table 4. Relationship between pulse rising edge and coverage rate of strong coupling region inside cavity @1.12GHz
pulse rising
edge /(ns)Maximum value of coupled
electric field/(V/m)Number of strong coupling
regions inside the cavityη(f)/% 0 8.10 440 88.0 2 8.10 440 88.0 5 8.10 436 87.2 8 8.10 436 87.2 10 8.10 432 86.4 15 8.10 428 85.6 20 8.08 428 85.6 25 8.03 416 83.2 30 7.97 416 83.2 表 5 腔体内部强耦合区域覆盖率和频率的关系
Table 5. Relationship between coverage rate and frequency of strong coupling region in cavity
frequency/
(GHz)Maximum value of coupled
electric field/(V/m)Number of strong coupling
regions inside the cavityη(f)/% 1.12 8.10 440 88.0 2.91 3.31 270 54.0 4.63 3.43 252 50.4 5.74 3.11 450 90.0 6.17 2.35 164 32.8 8.60 4.70 296 59.2 8.84 1.59 96 19.2 10.16 1.78 126 25.2 11.77 5.19 340 68.0 1 1.92 6 1.2 2 1.52 16 3.2 3 1.50 122 24.4 5 1.26 18 3.6 7 1.55 44 8.8 9 2.20 184 36.8 10 2.56 198 39.6 表 6 极化方向与腔体内部强耦合区域覆盖率的关系@1.12GHz
Table 6. Relationship between Polarization direction and coverage rate of strong coupling region inside cavity @1.12GHz
Polarization
angle /(°)Maximum value of coupled
electric field/(V/m)Number of strong coupling
regions inside the cavityη(f)/% 0 1.09 20 4.00 10 1.59 186 37.20 20 2.80 276 55.20 30 4.08 360 72.00 40 5.24 382 76.40 50 6.24 392 78.40 60 7.05 410 82.00 70 7.65 424 84.80 80 8.02 436 87.20 90 8.10 440 88.00 左旋圆极化 5.76 384 76.80 右旋圆极化 5.76 384 76.80 -
[1] Benford J, Swegle J A, Schamiloglu E. High power microwaves[M]. 2nd ed. New York: CRC Press, 2007. [2] Tatum J. High-power microwave directed energy weapons: a model and simulation toolbox[J]. DSIAC Journal, 2015, 1(2): 20-22. [3] Wang Jianguo, Yu Hanqing, Liu Guozhi, et al. Numerical studies on resonant and enhancement effects for coupling of microwave pulses into narrow slots[J]. Journal of Electronics (China), 1998, 15(2): 174-181. doi: 10.1007/s11767-998-0053-4 [4] 章勇华, 黄文华, 李平, 等. 集成电路HPM损伤机理分析[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14: 020501 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2023.020501Zhang Yonghua, Huang Wenhua, Li Ping, et al. Analysis of high power microwave damage mechanism in integrated circuits[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 020501 doi: 10.12061/j.issn.2095-6223.2023.020501 [5] Bäckström M G, Lövstrand K G. Susceptibility of electronic systems to high-power microwaves: summary of test experience[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2004, 46(3): 396-403. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2004.831814 [6] 刘顺坤, 傅君眉, 周辉, 等. 电磁脉冲对目标腔体的孔缝耦合效应数值研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 1999, 14(2): 202-206 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.1999.02.014Liu Shunkun, Fu Junmei, Zhou Hui, et al. Numerical studies on coupling effects of EMP into slots[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 1999, 14(2): 202-206 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.1999.02.014 [7] 鲁童童. 基于FDTD的电磁脉冲孔缝耦合效应仿真分析[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2021: 27-36Lu Tongtong. Simulation analysis of electromagnetic pulse slot coupling effect based on FDTD[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021: 27-36 [8] 付继伟, 侯朝桢, 窦丽华. 电磁脉冲斜入射时对孔缝耦合效应的数值分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2003, 15(3): 249-252Fu Jiwei, Hou Chaozhen, Dou Lihua. Numerical analysis on hole coupling effects of an oblique incidence of electromagnetic pulse[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2003, 15(3): 249-252 [9] 曾美玲, 蔡金良, 易早, 等. 孔缝对金属腔体强电磁脉冲耦合特性影响研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33: 043004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200336Zeng Meiling, Cai Jinliang, Yi Zao, et al. Effect of aperture on shielding performance of metal cavity under excitation of high-intensity electromagnetic pulse[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 043004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200336 [10] 周金山, 刘国治, 彭鹏, 等. 不同形状孔缝微波耦合的实验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2004, 16(1): 88-90Zhou Jinshan, Liu Guozhi, Peng Peng, et al. Experimental studies on microwave coupling coefficient for different-shaped apertures[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2004, 16(1): 88-90 [11] 陈修桥, 张建华, 胡以华. 电磁脉冲与窄缝腔体耦合共振特性分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2003, 15(5): 481-484Chen Xiuqiao, Zhang Jianhua, Hu Yihua. Analysis on resonant characteristic of electromagnetic pulse coupling into narrow slot and cavity with slot[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2003, 15(5): 481-484 [12] 王建国, 屈华民, 范如玉, 等. 孔洞厚度对高功率微波脉冲耦合的影响[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 1994, 6(2): 282-286Wang Jianguo, Qu Huamin, Fan Ruyu, et al. Effects of slot depth on couplings of high power microwave pulses[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 1994, 6(2): 282-286 [13] Siah E S, Sertel K, Volakis J L, et al. Coupling studies and shielding techniques for electromagnetic penetration through apertures on complex cavities and vehicular platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2003, 45(2): 245-256. [14] 王建国, 屈华民, 华鸣, 等. 微波脉冲与圆柱腔体耦合的时域有限差分模拟[J]. 计算物理, 1995, 12(4): 10-18Wang Jianguo, Qu Huamin, Hua Ming, et al. FDTD simulations of microwave pulse coupling into cylindrical cavities[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 1995, 12(4): 10-18 [15] 陈伟华, 张厚, 杨宇军. 电磁脉冲对双层屏蔽腔的孔洞耦合特性研究[J]. 辐射防护, 2007, 27(5): 286-290Chen Weihua, Zhang Hou, Yang Yujun. Research on coupling characteristic of electromagnetic pulse into the double layer shielding cavity through aperture[J]. Radiation Protection, 2007, 27(5): 286-290 [16] 田东, 陈少昌. 复杂矩形腔屏蔽效能分析[J]. 电光与控制, 2010, 17(10): 93-96 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2010.10.023Tian Dong, Chen Shaochang. Shielding effectiveness of complex rectangular cavity[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2010, 17(10): 93-96 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2010.10.023 [17] 陈伟华, 张厚, 王剑, 等. 电磁脉冲对计算机机箱的耦合效应[J]. 工程设计学报, 2007, 14(5): 409-413 doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1006-754X.2007.05.014Chen Weihua, Zhang Hou, Wang Jian, et al. Research on coupling effect of electromagnetic pulse and computer box[J]. Journal of Engineering Design, 2007, 14(5): 409-413 doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1006-754X.2007.05.014 [18] 汪柳平, 高攸纲, 沈远茂, 等. 装有PCB有孔矩形腔屏蔽效能的传输线法分析[J]. 电波科学学报, 2008, 23(4): 740-744 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2008.04.029Wang Liuping, Gao Yougang, Shen Yuanmao, et al. Analysis of shielding effectiveness of rectangular cavity of loaded PCB with aperture by transmission line method[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2008, 23(4): 740-744 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2008.04.029 [19] Wallyn W, De Zutter D. Modeling the shielding effectiveness and resonances of metallic shielding enclosures loaded with PCBs[C]//Proceedings of 2021 IEEE EMC International Symposium. Symposium Record. International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility. 2001: 691-696. [20] 王建国, 刘国治, 俞汉清, 等. 微波孔缝耦合函数的研究[J]. 高功率微波技术, 1996(2): 20-31Wang Jianguo, Liu Guozhi, Yu Hanqing, et al. Investigation on coupling function for coupling of microwave into slots[J]. High Power Microwave Technology, 1996(2): 20-31 [21] Pozar D M. Microwave engineering[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: John Wiley & Sons, 2006. -




 下载:
下载: