Engineering computational model for high-altitude atmospheric X-ray ionization
-
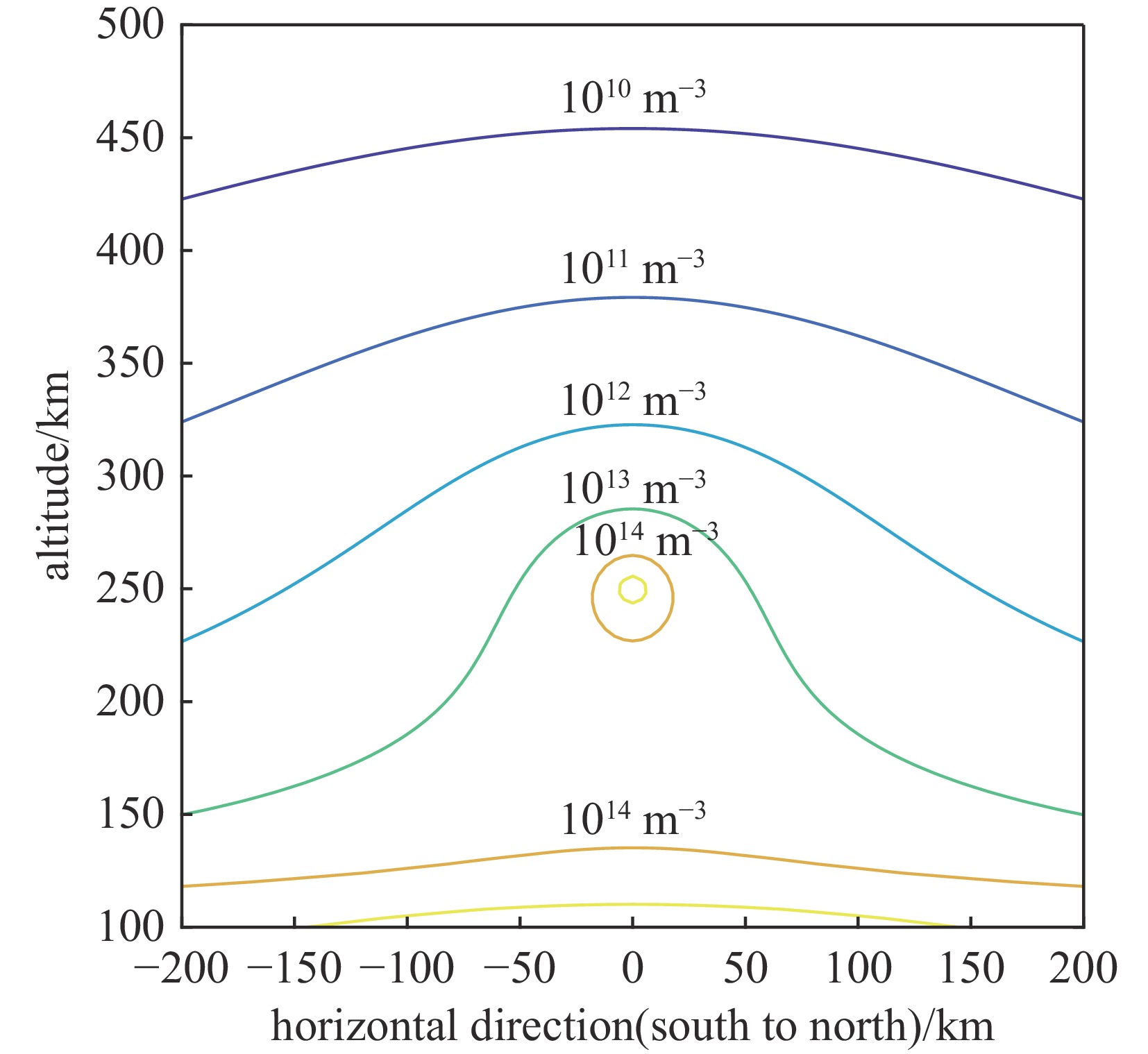
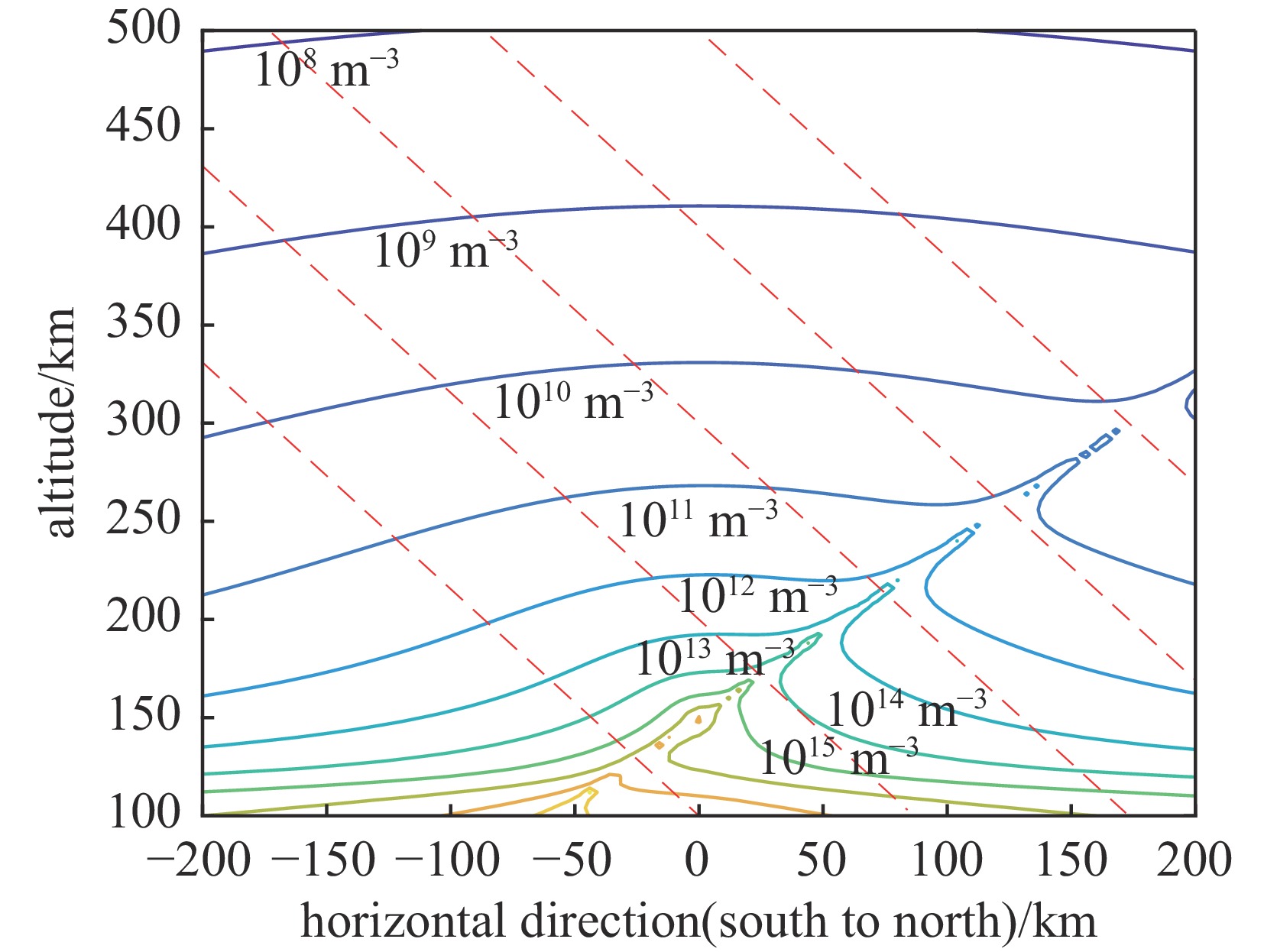
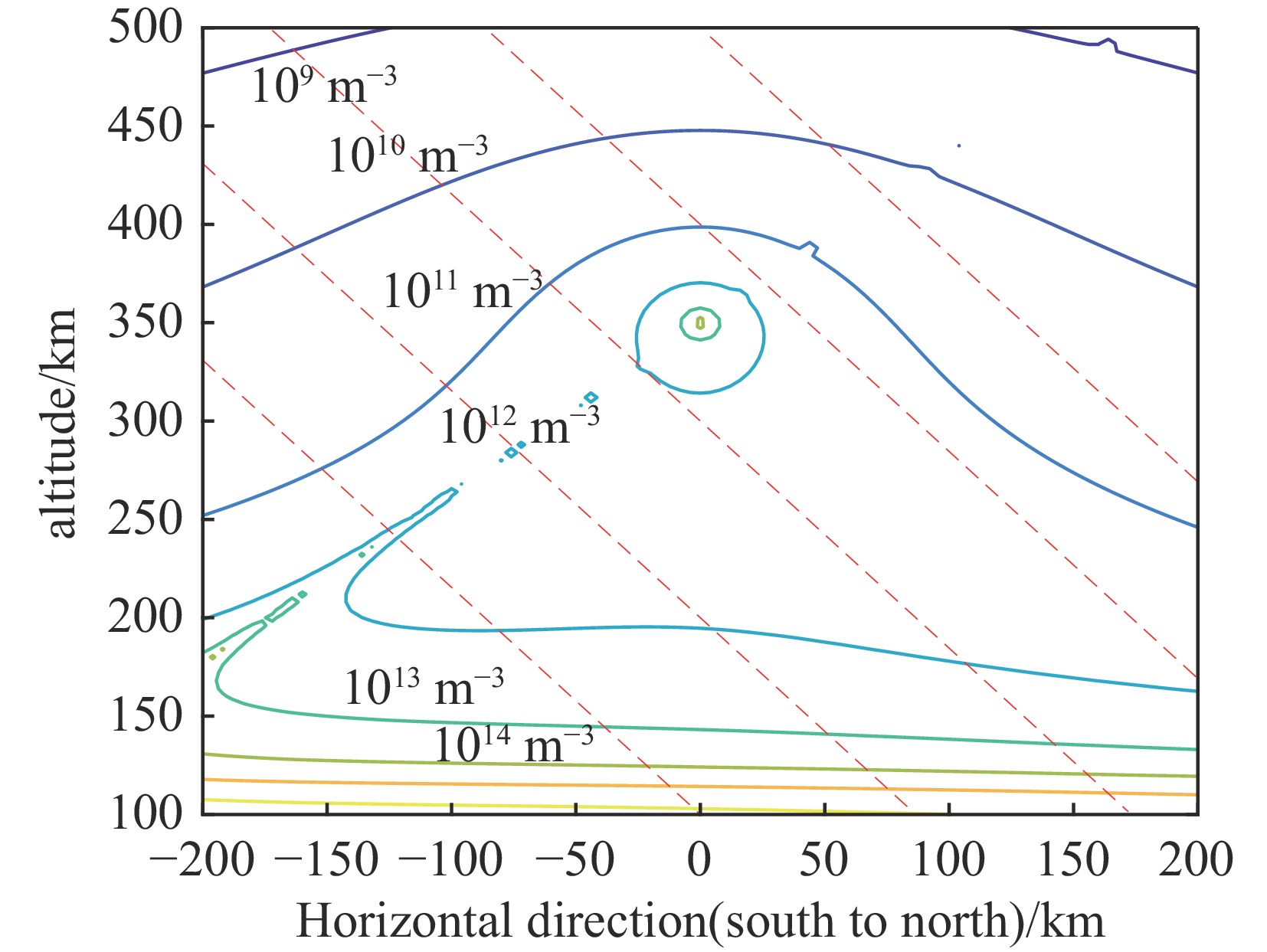
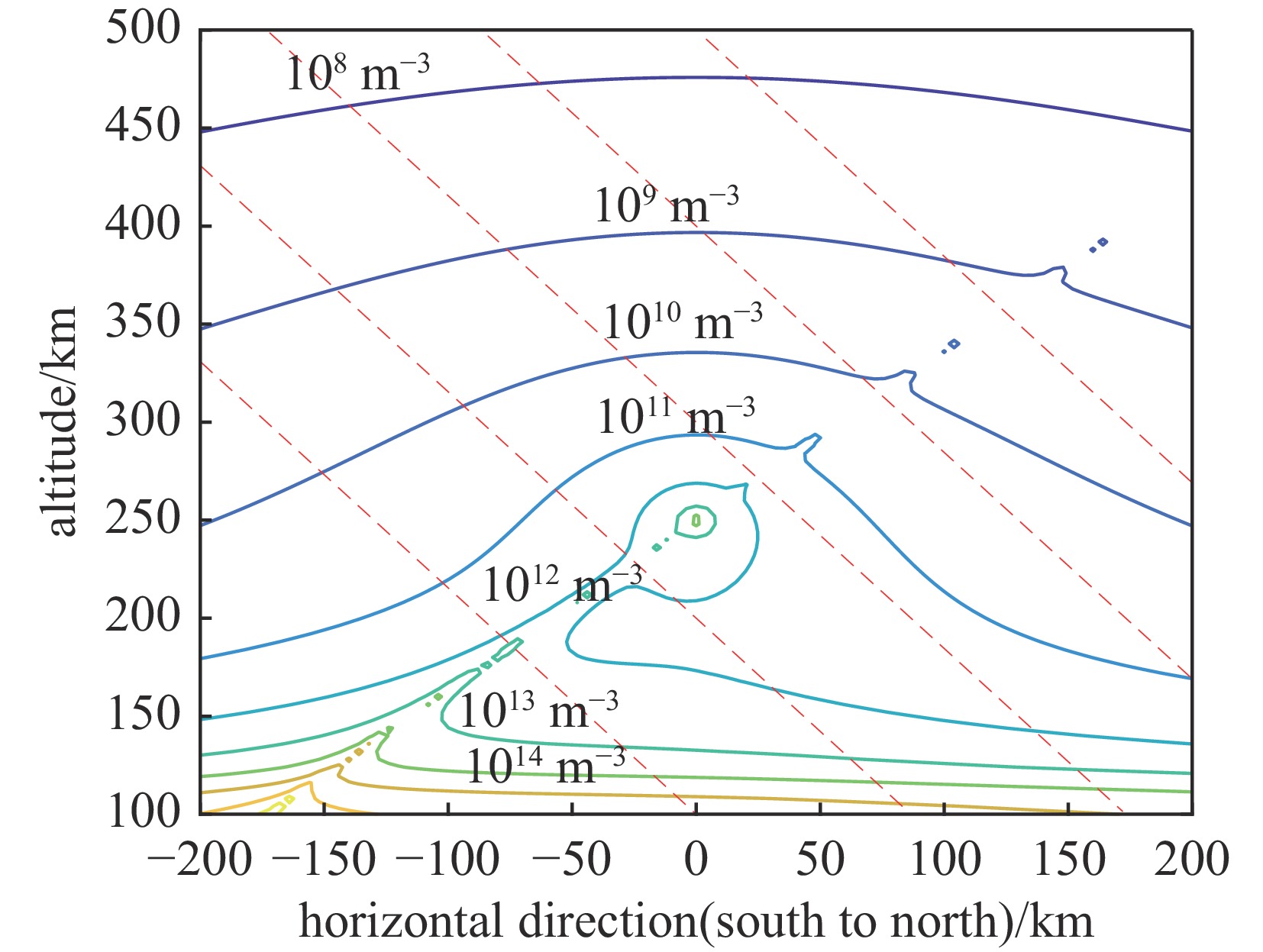
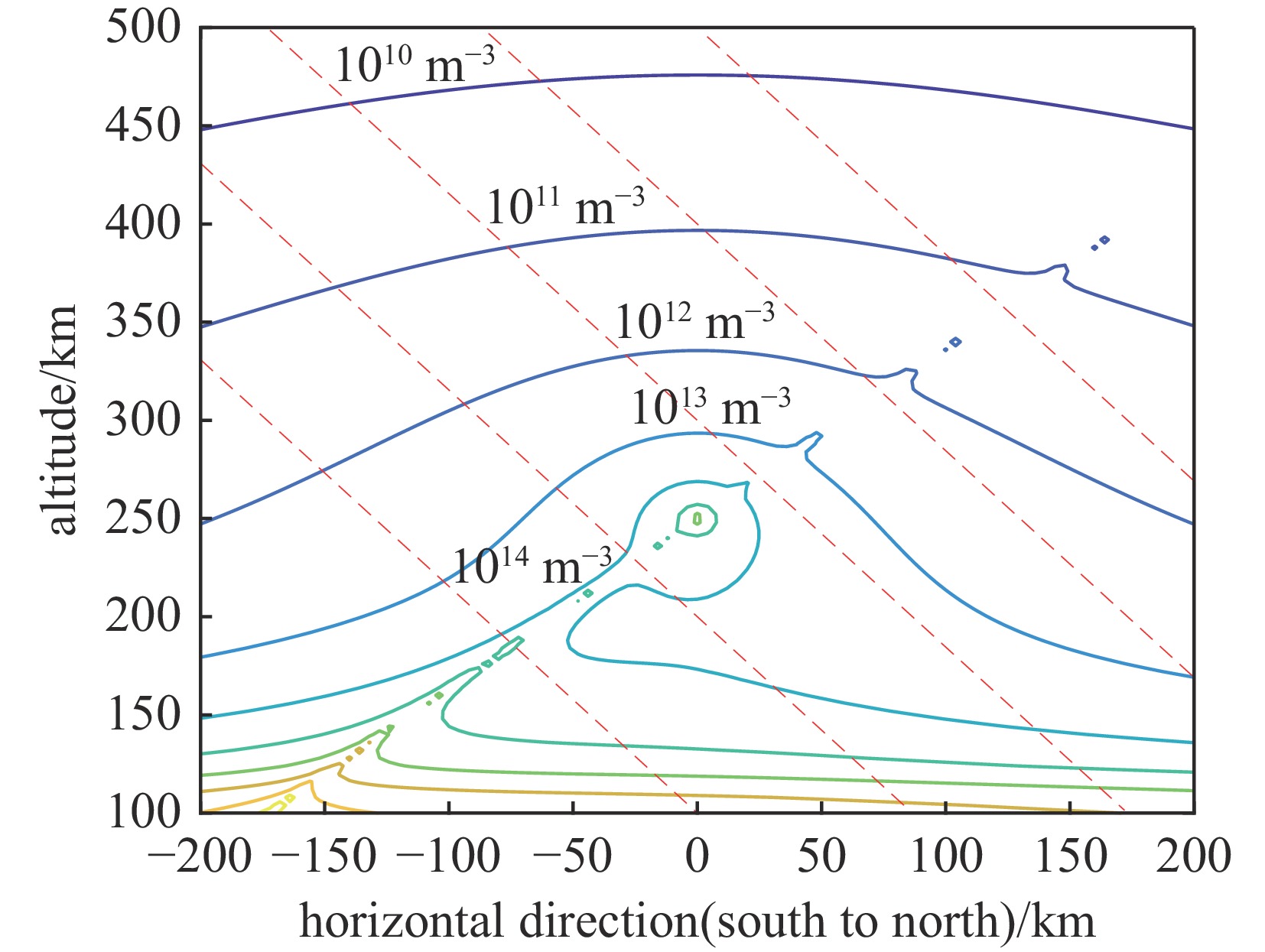
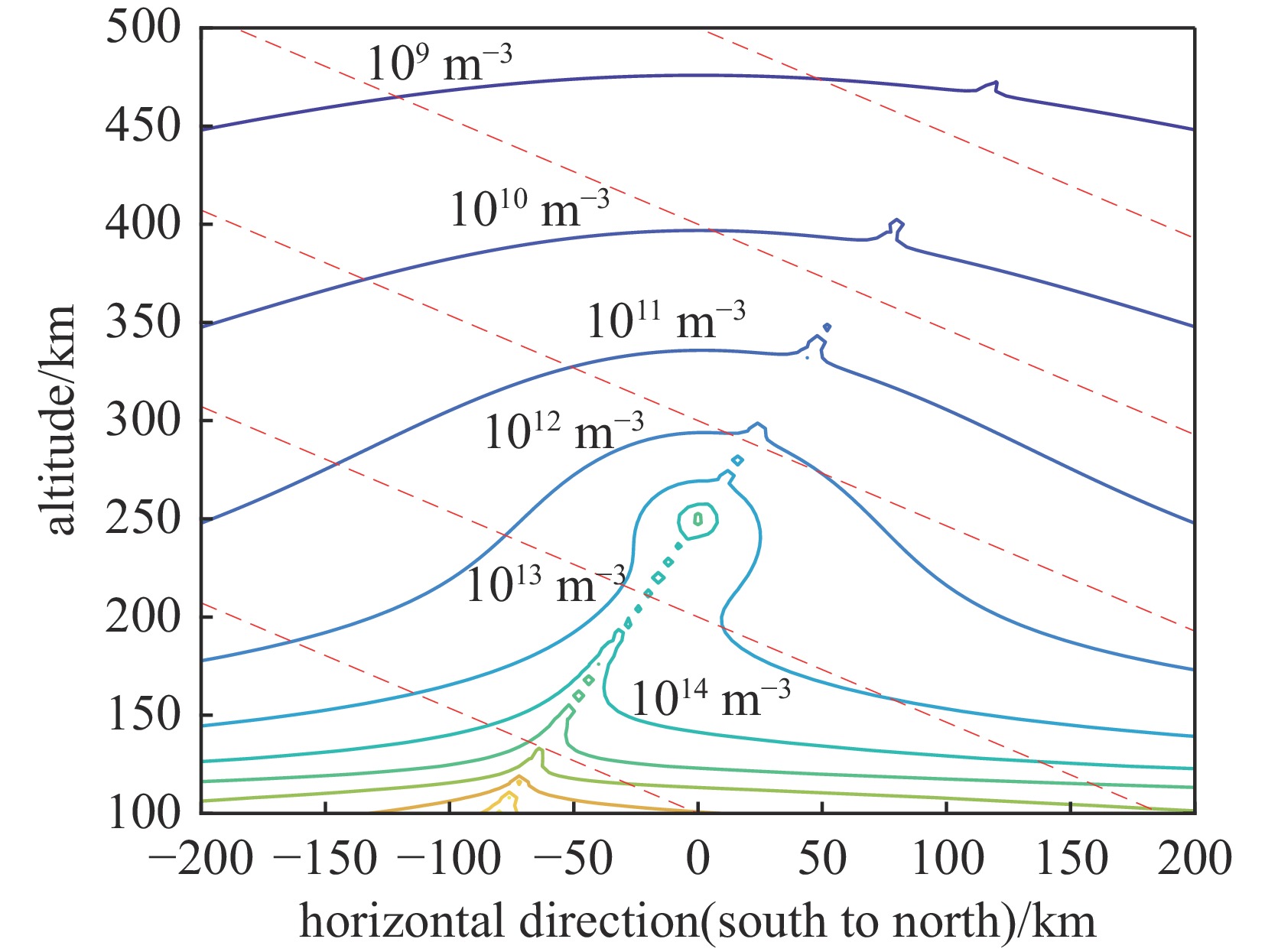
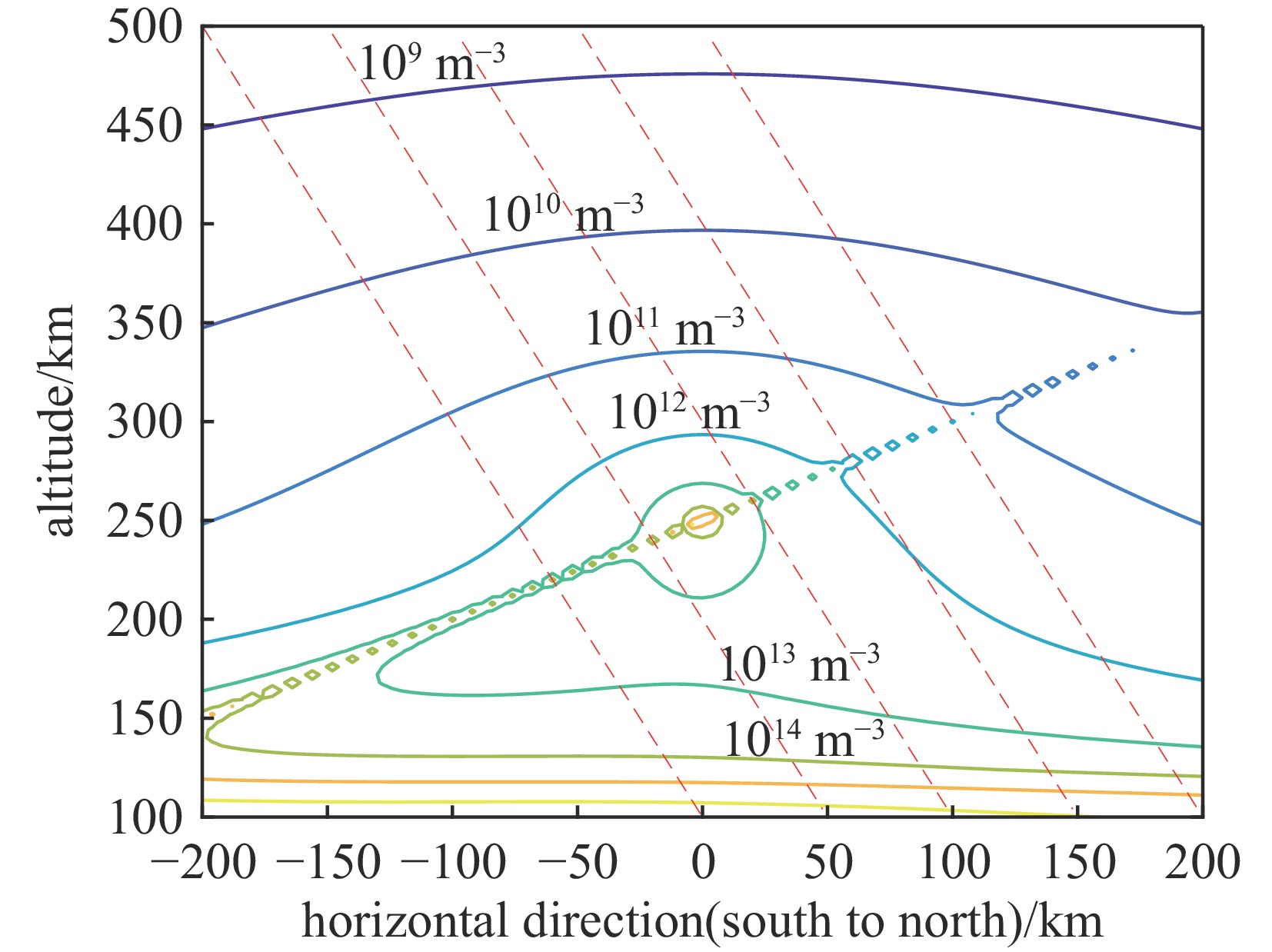
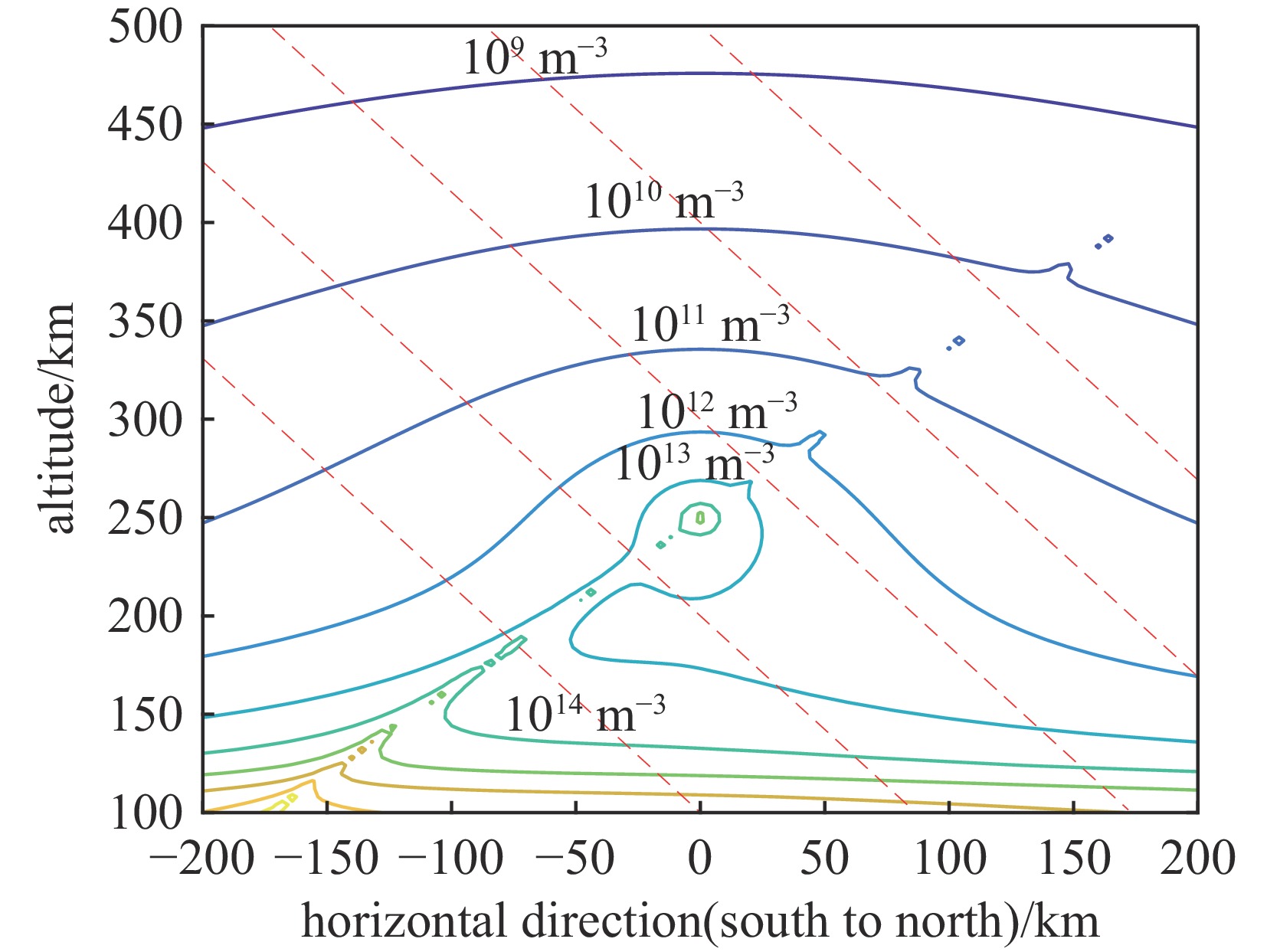
摘要: 建立了高空大气X射线辐射电离的工程计算模型,模型考虑了X射线与大气作用产生的高能电子在地磁场中的输运及电离大气问题,相较传统的射线能量沉积模型提高了计算精度。利用该模型分析了爆炸高度、纬度和当量对电离密度分布的影响规律,结果表明:由于高能电子输运的影响,电离密度分布丧失了对称性;电离密度分布在经过爆心垂直于磁力线方向有明显增强;爆高越大,高海拔位置电离密度变大,高能电子输运带来的影响在高海拔区域变小,低海拔位置电离密度变小;当量对电离密度的数值有较大影响,但对电离密度的相对分布影响较小。Abstract:
Background More than 70% of the energy from a high-altitude nuclear explosion is transmitted via X-ray radiation, which serves as the primary source of atmospheric ionization. When the detonation altitude of a high-altitude nuclear explosion exceeds 80 kilometers, the absorption of X-rays by air weakens. Consequently, X-rays can propagate over a wide range and gradually dissipate their energy through the ionization of the atmosphere. The atmospheric ionization effect of X-rays causes drastic fluctuations in the electron density within the Earth's ionosphere. This, in turn, leads to significant changes in the signals of electromagnetic waves as they pass through the ionosphere, thereby exerting adverse impacts on systems such as satellites, radars, and communications. However, there are currently still problems such as slow calculation speed and incomplete model considerations in the calculation of the atmospheric ionization effect caused by high-altitude X-rays.Purpose The purpose of this paper is to propose a new engineering method for calculating the X-ray atmospheric ionization process in the high-altitude rarefied atmosphere.Methods The model accounts for the transport of high-energy electrons (generated by the interaction between X-rays and the atmosphere) in the geomagnetic field as well as the atmospheric ionization issue, and performs an averaging process on the microscopic interaction processes.Results Compared with traditional ray energy deposition models, it improves the calculation accuracy.Conclusions This model was used to analyze the influence laws of explosion altitude, latitude, and yield on the ionization density distribution. The results show that: Due to the influence of high-energy electron transport, the symmetry of the ionization density distribution is lost; The ionization density distribution is significantly enhanced in the direction passing through the explosion center and perpendicular to the magnetic field lines;The higher the explosion altitude, the greater the ionization density at high-altitude positions, while the influence caused by high-energy electron transport becomes smaller in high-altitude regions, and the ionization density at low-altitude positions decreases;The yield has a significant impact on the numerical value of the ionization density, but has a relatively small impact on the relative distribution of the ionization density. -
表 1 计算条件
Table 1. Computational conditions
case id detonation
altitude/kmdetonation
yield/ktdetonation
latitude1 150 100 N30° 2 250 100 N30° 3 350 100 N30° 4 250 10 N30° 5 250 1000 N30° 6 250 100 N15° 7 250 100 N45° 8 250 100 N30° -
[1] 王建国, 刘利, 牛胜利, 等. 高空核爆炸环境数值模拟[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14: 010101Wang Jianguo, Liu Li, Niu Shengli, et al. Numerical simulations of environmental parameters of high-altitude nuclear explosion[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 010101 [2] 彭国良, 王仲琦, 张俊杰, 等. 高空核爆炸晚期核电磁脉冲的数值模拟研究[J]. 现代应用物理, 2024, 15: 050501Peng Guoliang, Wang Zhongqi, Zhang Junjie, et al. Numerical simulation of late electromagnetic pulse in high-altitude nuclear explosion[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2024, 15: 050501 [3] Crain C M, Tamarkin P. A note on the cause of sudden ionization anomalies in regions remote from high-altitude nuclear bursts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1961, 66(1): 35-39. doi: 10.1029/JZ066i001p00035 [4] Willard H R, Kenney J F. Ionospheric effects of high-altitude nuclear tests[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1963, 68(7): 2053-2056. doi: 10.1029/JZ068i007p02053 [5] Latter R, LeLevier R E. Detection of ionization effects from nuclear explosions in space[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1963, 68(6): 1643-1666. doi: 10.1029/JZ068i006p01643 [6] 赵正予, 王翔. 空中核爆炸电离效应的数值模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2007, 56(7): 4297-4304 doi: 10.7498/aps.56.4297Zhao Zhengyu, Wang Xiang. Numerical simulation of the ionization effects of low-and high-altitude nuclear explosions[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2007, 56(7): 4297-4304 doi: 10.7498/aps.56.4297 [7] 陶应龙. 高空核爆炸对电离层影响的数值模拟研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2010: 41-64Tao Yinglong. Numerical simulation of the influence on ionosphere by high-altitude nuclear explosion[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2010: 41-64 [8] 朱金辉, 左应红, 刘利, 等. 蒙特卡罗方法在核爆辐射环境模拟中的应用与发展[J]. 现代应用物理, 2023, 14: 030104Zhu Jinhui, Zuo Yinghong, Liu Li, et al. Application and development of Monte Carlo method in simulation of nuclear explosion radiation environments[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2023, 14: 030104 [9] 欧阳建明. 高空核爆炸背景下大气的电离过程及其影响研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2014: 20-36Ouyang Jianming. The research on ionization processes and ionization effects of atmosphere by high-altitude nuclear explosions[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2014: 20-36 [10] 欧阳建明, 马燕云, 邵福球, 等. 高空核爆炸X射线电离的时空分布数值模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61: 242801 doi: 10.7498/aps.61.242801Ouyang Jianming, Ma Yanyun, Shao Fuqiu, et al. Numerical simulation of temporal and spatial distribution of X-ray ionization with high-altitude nuclear explosion[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61: 242801 doi: 10.7498/aps.61.242801 [11] Zinn J, Hoerlin H, Petschek A G. The motion of bomb debris following the starfish test[C]//Proceedings of the Advanced Study Institute on Radiation Trapped in the Earth’s Magnetic Field. 1967: 671-692. [12] 王建国, 牛胜利, 张殿辉, 等. 高空核爆炸效应参数手册[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2010: 4-38Wang Jianguo, Niu Shengli, Zhang Dianhui, et al. Manual of high-altitude nuclear explosion effects[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2010: 4-38 [13] Picone J M, Hedin A E, Drob D P, et al. NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: statistical comparisons and scientific issues[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(A12): 1468. [14] Li Xiazhi, Niu Shengli, Zhu Jinhui. X-ray induced total ionization of air[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2022, 50(6): 1749-1753. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2022.3168145 [15] 徐荣栏, 李磊. 磁层粒子动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 16Xu Ronglan, Li Lei. Magnetospheric particle dynamics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 16 [16] Holland D H, Kaufman A M, O’Dell A A. Physics of high-altitude nuclear burst effects[R]. DNA-4501F, 1977: 202. -




 下载:
下载: